AP Bio. Unit 3 College board questions
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Alcohol dehydrogenase (ADHADH) is an enzyme that aids in the decomposition of ethyl alcohol (C2H5OH)(C2H5OH) into nontoxic substances. Methyl alcohol acts as a competitive inhibitor of ethyl alcohol by competing for the same active site on ADHADH. When attached to ADHADH, methyl alcohol is converted to formaldehyde, which is toxic in the body.
Which of the following statements best predicts the effect of increasing the concentration of substrate (ethyl alcohol), while keeping the concentration of the inhibitor (methyl alcohol) constant?
Competitive inhibition will decrease because the proportion of the active sites occupied by substrate will increase.
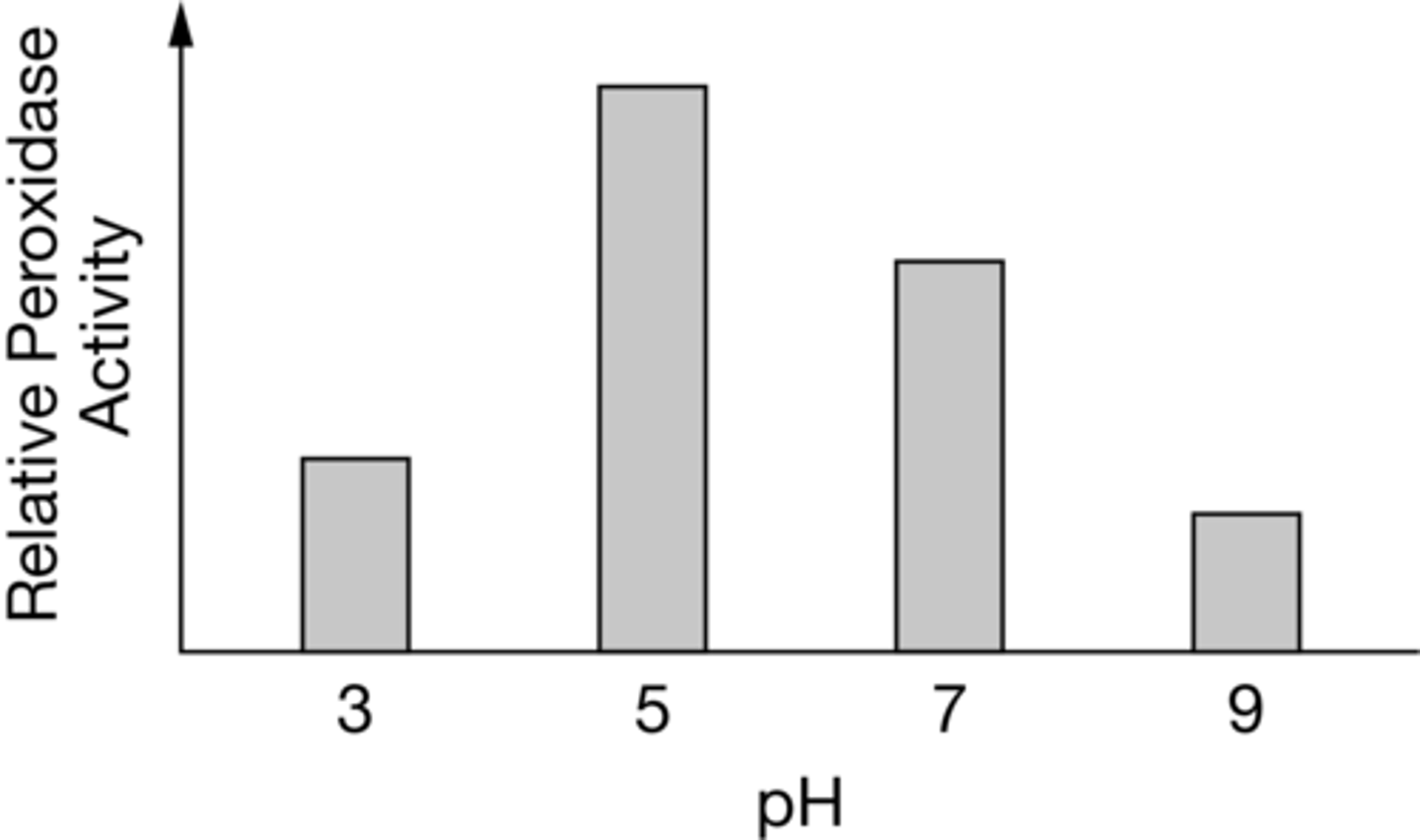
The enzyme peroxidase is found in many organisms. It catalyzes the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen gas. The rate of peroxidase activity at different pH values was assessed by students in the lab. The students' results are shown in graph 1.
If the experiment is repeated at pH 11, the observed activity level of the enzyme will most likely be
lower than the level at pH 9
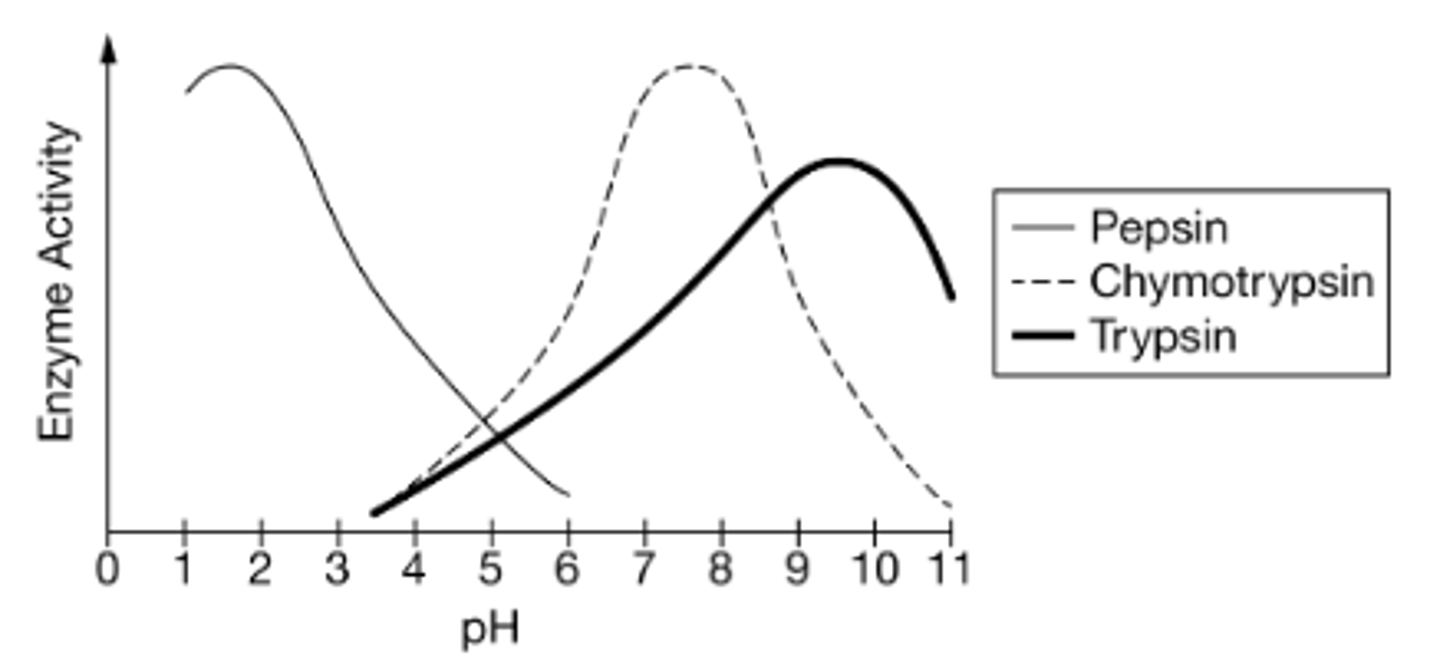
Protein digestion in humans is primarily carried out by three enzymes. Pepsin is found in the stomach (pH2), where it aids in the breakdown of large proteins into smaller peptides, while trypsin and chymotrypsin are found in the small intestine (pH8), where they aid in the further breakdown of the proteins into amino acids and dipeptides that can be absorbed into the bloodstream. Graph 1 shows the effect of pH on the activity levels of the three enzymes.
Graph 1. Relative activity of pepsin, trypsin, and chymotrypsin at pH 0 through 11
Which of the following best predicts how the structure and function of pepsin will change as it enters the small intestine?
Pepsin will change in shape because of the basic environment of the small intestine; therefore, its enzymatic activity will decrease.
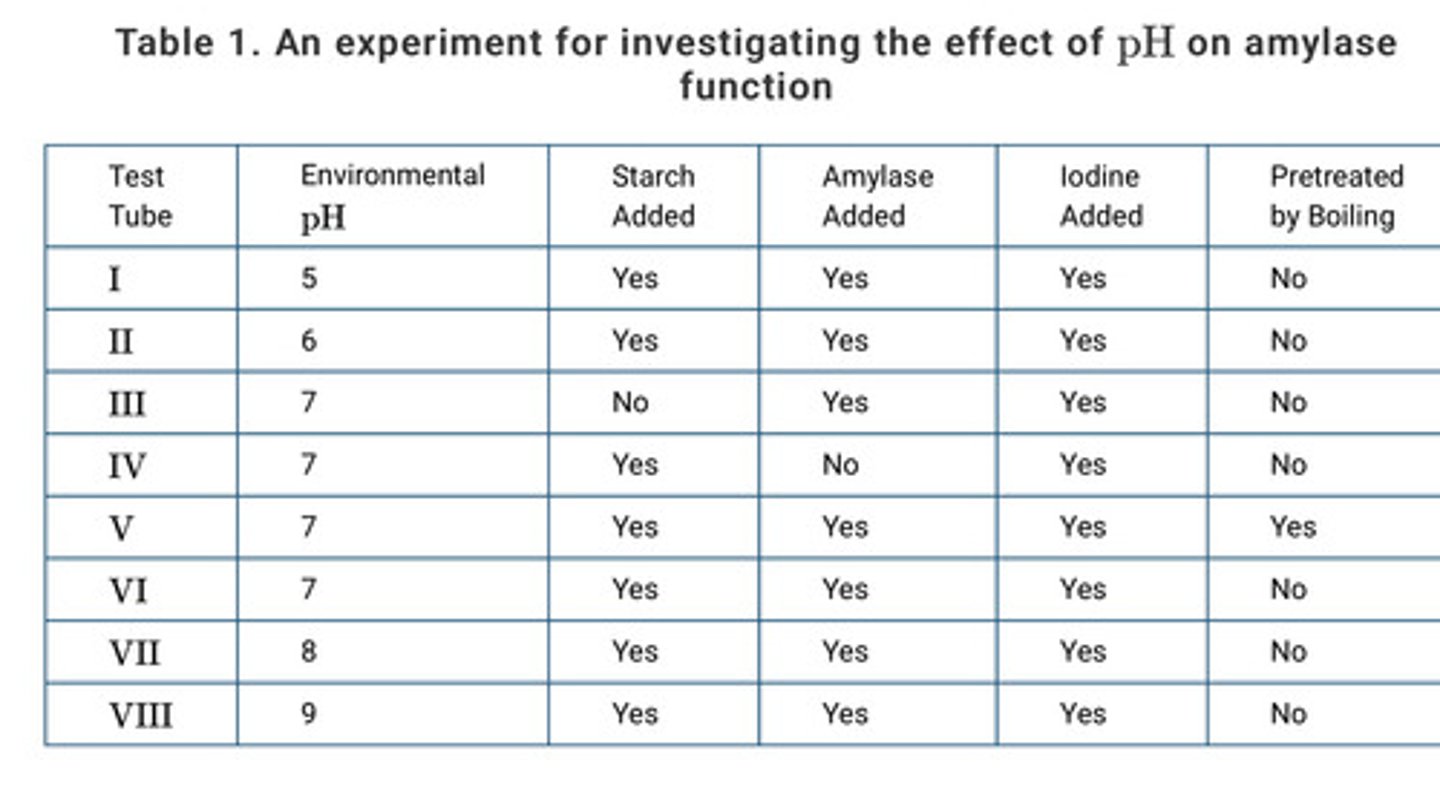
Amylase is a protein that catalyzes the conversion of starch to simple sugars. Amylase activity in an aqueous solution can be measured by using iodine as a starch indicator. A solution containing iodine and starch will have a dark-blue color, whereas a solution containing iodine but no starch will have a light-brown color. The color change of an iodine solution from dark blue to light brown can be used to measure the rate at which starch is converted to simple sugars.
A student designs an experiment to investigate the effect of environmental pH on amylase function. The design of the experiment is presented in Table 1.
Which of the following statements best justifies the inclusion of test tube VV as a control in the experiment?
It will show the color change that occurs in the absence of enzyme activity.
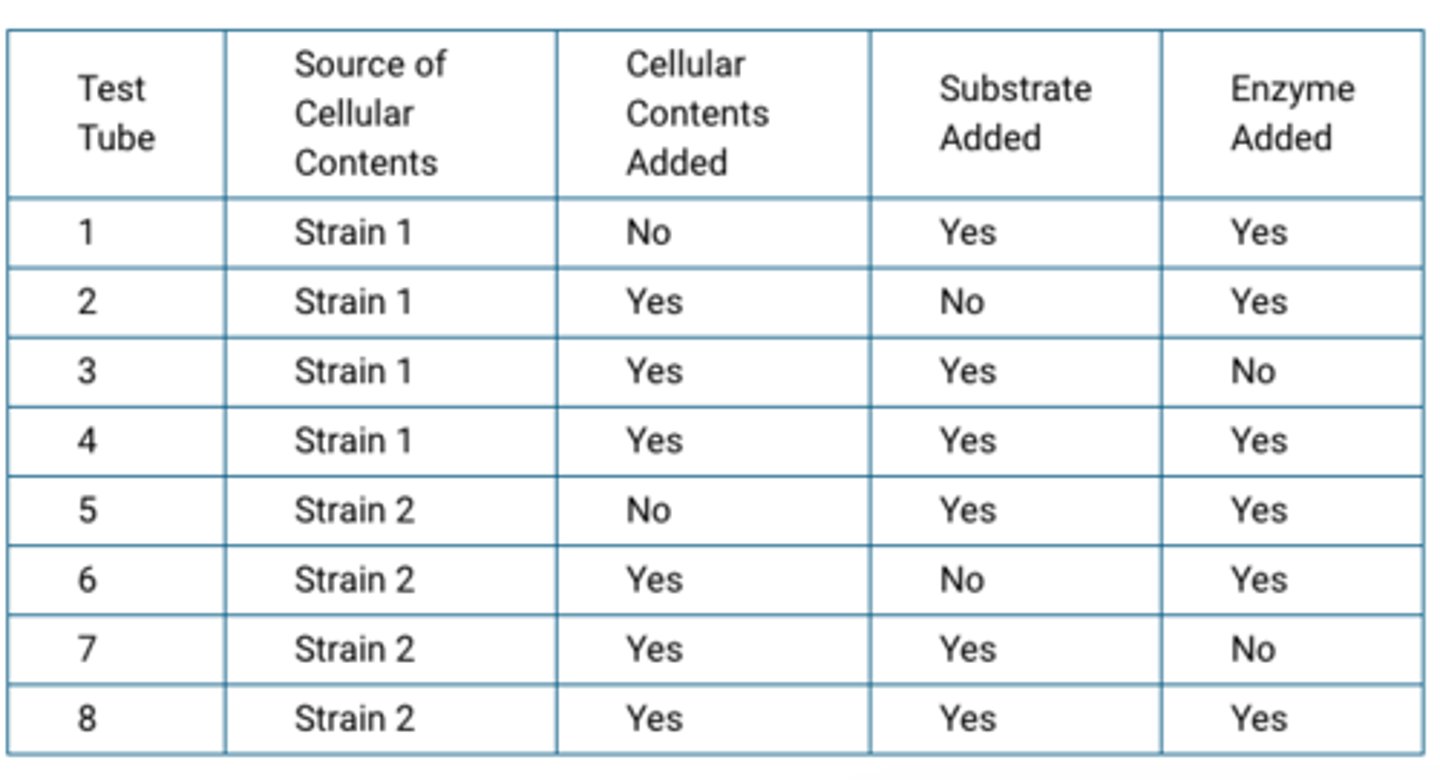
A researcher claims that some bacteria contain factors that influence the function of a particular enzyme but other bacteria do not. To test the claim experimentally, the researcher will grow two different bacterial strains in separate liquid cultures and isolate the contents of the cells in each culture. The researcher will add different combinations of cellular contents, substrate, and enzyme to test tubes containing a buffer solution adjusted to the optimal pH of the enzyme and then measure the rate of product formation. The design of the researcher's experiment is presented in Table 1.
They will show whether the isolated cellular contents have enzymatic activity.
A researcher designs an experiment to investigate the effect of environmental temperature on the function of an enzyme. For each trial included in the experiment, the researcher will add the enzyme and its substrate to an aqueous buffer solution and then measure the amount of product formed over 20 minutes.
Which of the following must remain the same for all trials of this experiment?
The initial concentration of the substrate
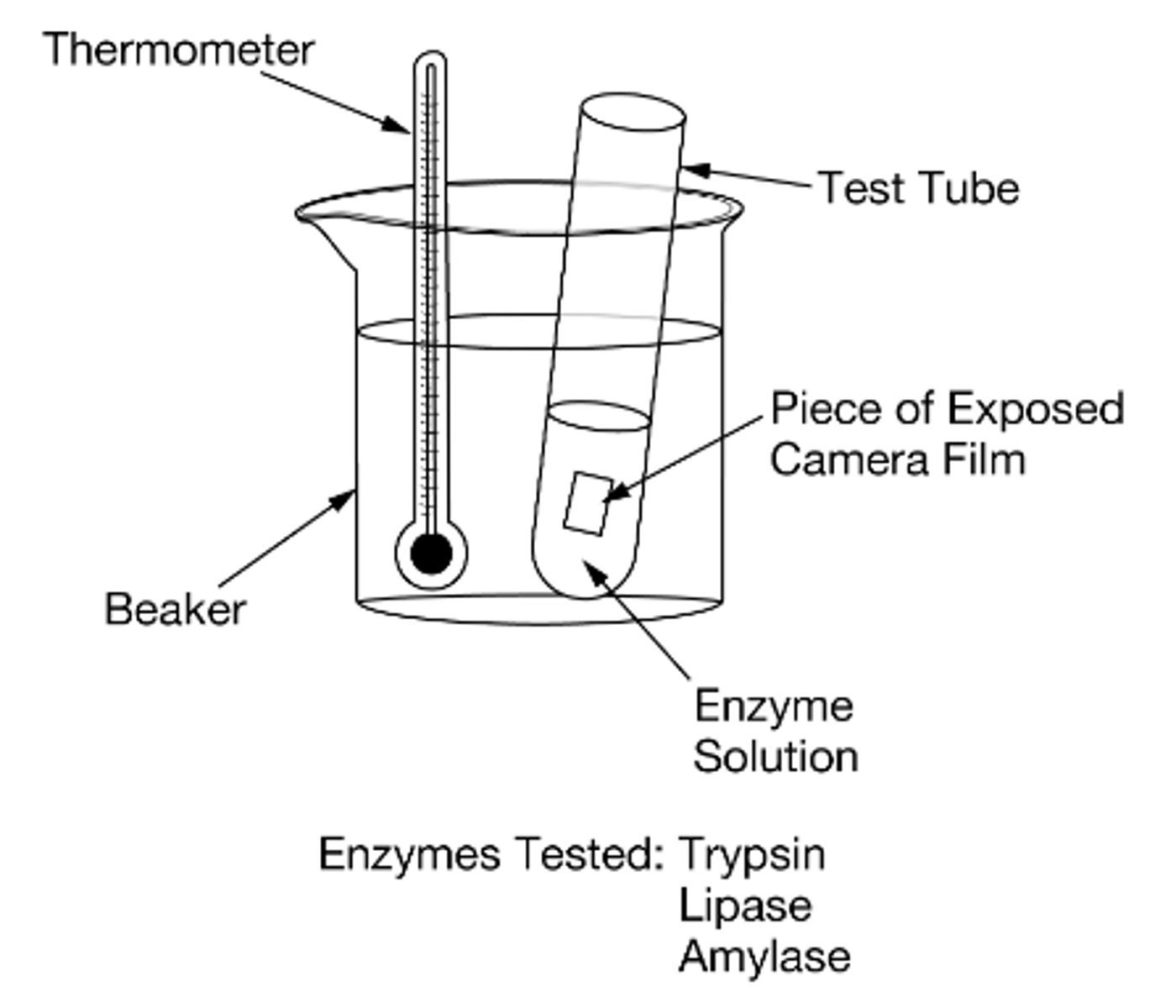
Gelatin is a protein that is derived from collagen which is found in the bones, skin, and connective tissue of animals. To investigate the ability of various enzymes to digest gelatin, a group of students set up an assay involving camera film. Camera film contains gelatin and appears black when exposed to light but turns clear as the gelatin gets broken down. The students incubated pieces of exposed camera film in test tubes, each containing one of three different enzyme solutions (trypsin, lipase, or amylase) as indicated in Figure 1. The students recorded the time it took for the enzymes to digest the gelatin in each test tube, turning the film from black to clear.
Figure 1. Diagram of experimental setup.
Which of the following would be the most appropriate control for this experiment?
A test tube containing a piece of exposed camera film submerged in water
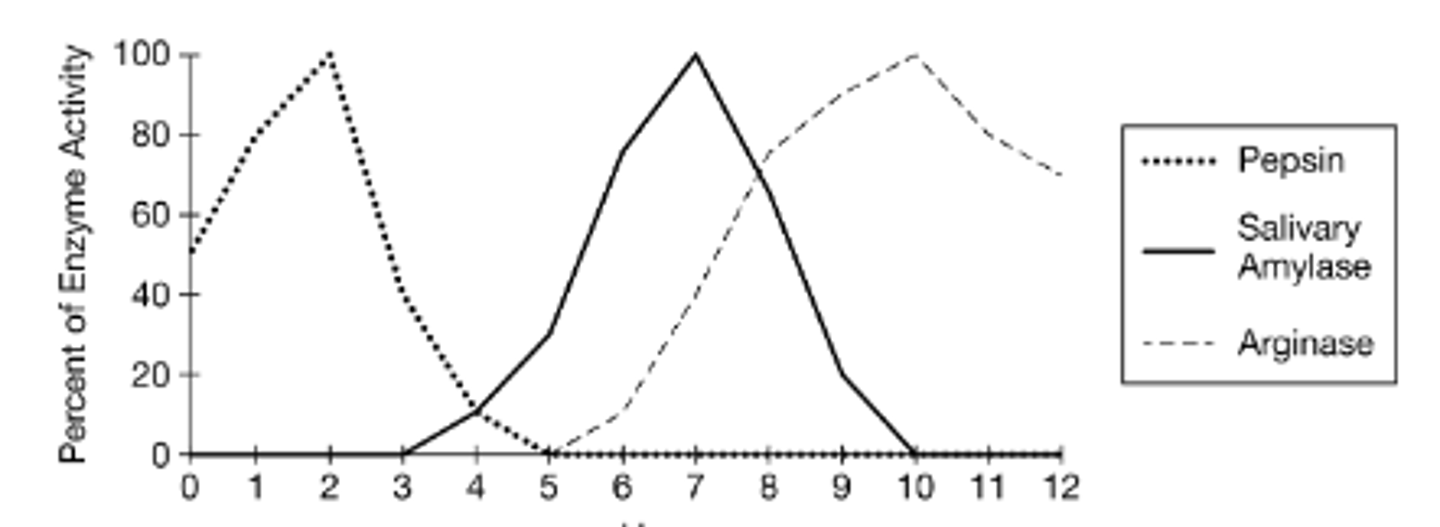
A researcher claims that different enzymes exhibit maximal function over different pH ranges. To test the claim, the researcher carries out an experiment that includes three different enzymes: pepsin, salivary amylase, and arginase. The results of the experiment are represented in Figure 1.
Which of the following actions will provide the most appropriate negative control for the experiment?
Repeating the experiment with denatured enzymes
A researcher claims that increasing the environmental temperature by 10°C will double the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction. To test the claim, the researcher designs an experiment that uses a particular enzyme isolated from plants. The design of the experiment is presented in Table 1. For each test tube in the experiment, the researcher will measure the rate of product formation.
Which of the following statements best helps justify the inclusion of test tube 5 as a control in the experiment?
It will provide a measurement of product formation in the presence of a denatured enzyme.
A researcher proposes a model of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction in which a reactant is converted to a product. The model is based on the idea that the reactant passes through a transition state within the enzyme-substrate complex before the reactant is converted to the product.
Which of the following statements best helps explain how the enzyme speeds up the reaction?
The enzyme's active site binds to and stabilizes the transition state, which decreases the activation energy of the reaction.
Which of the following statements best helps explain the reaction specificity of an enzyme?
The shape and charge of the substrates are compatible with the active site of the enzyme.
The enzyme hexokinase catalyzes the conversion of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate, which is an important step in glycolysis. The reaction involves the transfer of a phosphate group from ATP to glucose.
Either a glucose molecule or a water molecule can fit in the active site of hexokinase. The presence of a water molecule in hexokinase's active site would result in the hydrolysis of ATP to ADP instead of the conversion of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate.
Which of the following statements best helps explain the reaction specificity of hexokinase?
Glucose has the right shape and charge to cause hexokinase to undergo a structural change needed for catalysis, whereas water does not.
Researchers investigated the influence of environmental pH on the activity of peroxidase, an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen gas. In an experiment, the researchers added a hydrogen peroxide solution containing guaiacol to several identical test tubes and adjusted the solution in each test tube to a different pH . The researchers included the guaiacol because it caused the solutions to change color as the reactions proceeded, which the researchers relied on for measuring reaction rates. Finally, the researchers added the same amount of peroxidase to each test tube and measured the rate of each reaction at 23°C . The results of the experiment are represented in Figure 1.
Based on Figure 1, which of the following statements best predicts the effect that a change from a moderately acidic environment (pH near 6) to a basic environment will have on peroxidase activity?
Peroxidase activity will decrease.
Researchers investigated the influence of environmental pH on the activity of peroxidase, an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen gas. In an experiment, the researchers added a hydrogen peroxide solution containing guaiacol to several identical test tubes and adjusted the solution in each test tube to a different pH. The researchers included the guaiacol because it caused the solutions to change color as the reactions proceeded, which the researchers relied on for measuring reaction rates. Finally, the researchers added the same amount of peroxidase to each test tube and measured the rate of each reaction at 23°C. The results of the experiment are represented in Figure 1.
Which of the following actions will provide a negative control for the investigation?
Repeating the experiment using heat-denatured peroxidase
Researchers investigated the influence of environmental pH on the activity of peroxidase, an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen gas. In an experiment, the researchers added a hydrogen peroxide solution containing guaiacol to several identical test tubes and adjusted the solution in each test tube to a different pH. The researchers included the guaiacol because it caused the solutions to change color as the reactions proceeded, which the researchers relied on for measuring reaction rates. Finally, the researchers added the same amount of peroxidase to each test tube and measured the rate of each reaction at 23°C. The results of the experiment are represented in Figure 1.
One of the researchers proposes using oxygen gas production to measure reaction rates. Which of the following statements best justifies the use of the proposed modification as a way of creating an appropriate control for the investigation?
The experiment can be repeated without guaiacol, which will reveal the effect of guaiacol on the reaction rates.
Aminolevulinate dehydratase (ALAD) is an enzyme that relies on zinc as a coenzyme. A zinc ion binds to the ALAD active site, where it forms favorable interactions with the side chains of three amino acids. Researchers have found that substituting a lead ion for a zinc ion in the ALAD active site causes inhibition of ALAD.
Which of the following statements best helps explain how the lead ion causes inhibition of ALAD?
It changes the three-dimensional structure of the active site so that ALAD is no longer compatible with its substrate.
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) is a protein that catalyzes the conversion of acetylcholine to acetate and choline. When the concentration of AChE in an aqueous solution is held constant, the rate of the reaction catalyzed by AChE increases with increasing concentrations of substrate. At low concentrations of acetylcholine, a small increase in the substrate concentration results in a large increase in the reaction rate. At high concentrations of acetylcholine, however, a large increase in the substrate concentration results in only a small increase in the reaction rate.
Which of the following statements correctly explains the observed effect of the acetylcholine concentration on the rate of the enzyme-catalyzed reaction?
The active site of AChE is specific for acetylcholine, and only one substrate molecule can occupy the active site at a time.
A researcher proposes a model to explain how enzyme-substrate interactions determine enzyme specificity. The model is based on the idea that substrate molecules form favorable interactions with the amino acid side chains in an enzyme's active site.
Based on the model, which of the following statements best explains an enzyme's specificity for a particular substrate molecule?
A molecule with negative charges interacts with positively charged side chains in the enzyme's active site.
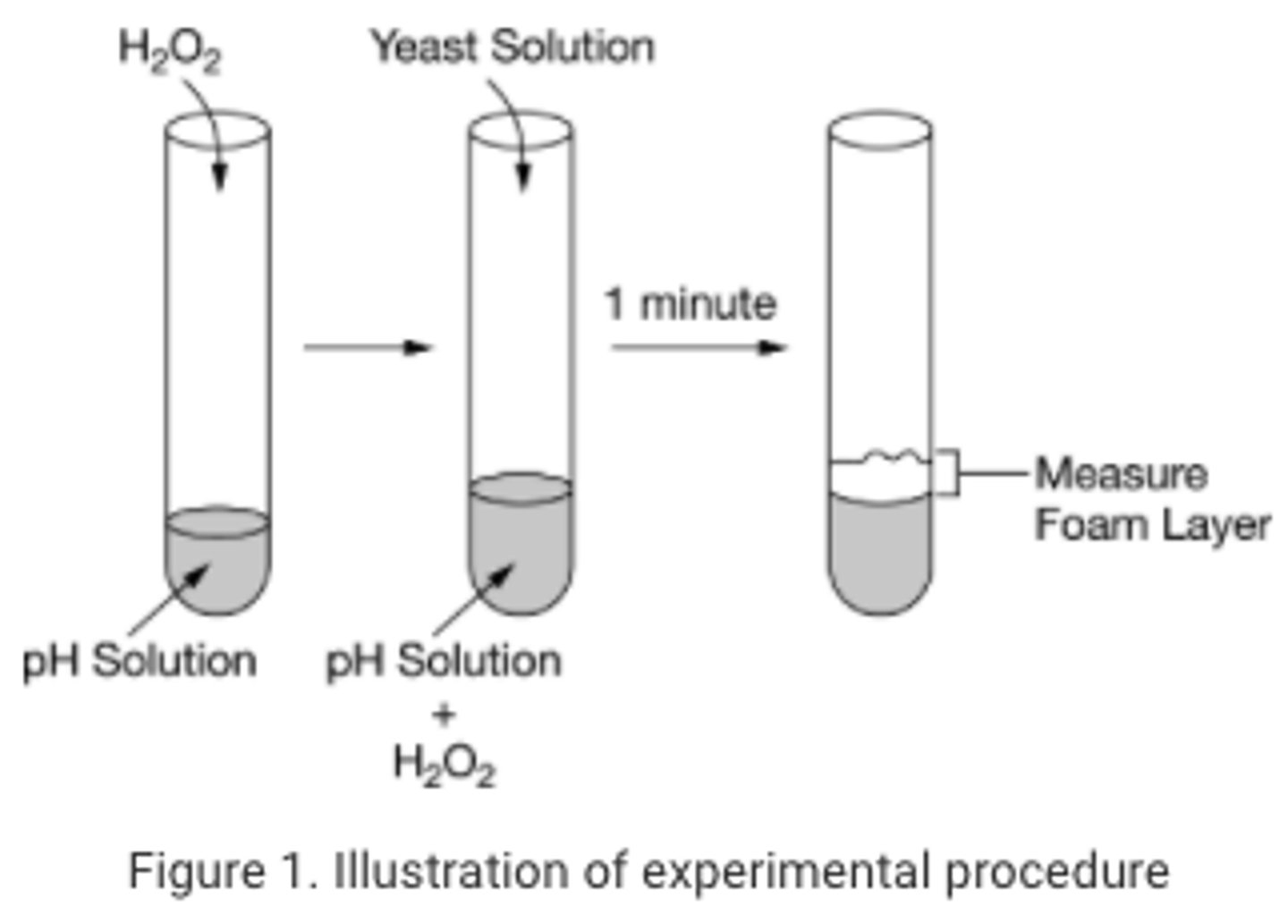
Catalase is an enzyme found in yeast cells that facilitates the chemical breakdown of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen gas. An experiment was conducted to determine the effect of pH on catalase function. Five buffer solutions of varying pH (2, 4, 6, 8, and 10) were prepared and added to separate test tubes. Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) was added to each test tube. Yeast was added, and the reactions were timed. After 1 minute the amount of oxygen gas released was determined by measuring the foam layer produced in each test tube. Figure 1 illustrates the experimental setup.
A set of five additional test tubes were prepared and used as controls. Which of the following best describes the contents expected to be contained in one of the five control test tubes?
pH 4 buffer solution and hydrogen peroxide only
A student designs an experiment to investigate the influence of temperature on enzyme function. The student's plan is presented in Table 1. Which test tubes are controls in the experiment?
Test Tube Substrate Added Enzyme Added Temperature (°C)
1 Yes No 10
2 Yes Yes 10
3 Yes No 20
4 Yes Yes 20
5 Yes No 30
6 Yes Yes 30
7 Yes No 40
8 Yes Yes 40
Test tubes 1, 3, 5, and 7
A researcher designs an experiment to investigate whether soil bacteria trigger the synthesis of defense enzymes in plant roots. The design of the experiment is presented in Table 1. For each group in the experiment, the researcher will determine the average rate of change in the amount of defense enzymes in the roots of the seedlings.
Group Number of Seedlings Type of Soil Treatment Solution
1 10 Sterile potting soil Contains actively reproducing soil bacteria
2 10 Sterile potting soil Contains heat-killed soil bacteria
3 10 Sterile potting soil Contains no soil bacteria
Which of the following statements best helps justify the inclusion of group 2 as one of the controls in the experiment?
It will show whether the changes observed in group 1 depend on the metabolic activity of soil bacteria.
Pectinase is a protein that catalyzes the breakdown of pectic polysaccharides in plant cell walls. A researcher designs an experiment to investigate the effect of salinity on the ability of pectinase to lower the activation energy of the reaction involved. The design of the experiment is presented in Table 1. For each test tube, the researcher will measure the amount of product formed over 20 minutes.
Test Tube Sodium Chloride Concentration (molar) Temperature (degrees C) Substrate Added Pectinase Added
1 0 23 Yes No
2 0 23 Yes Yes
3 0.5 23 Yes No
4 0.5 23 Yes Yes
5 1.0 23 Yes No
6 1.0 23 Yes Yes
7 1.5 23 Yes No
8 1.5 23 Yes Yes
Which of the following statements best helps justify the inclusion of test tube 5 in the experiment?
It will act as a control for test tube 6 by showing the effect of the presence or absence of the enzyme.
Researchers investigated the effect of urea on the three-dimensional structure of a certain enzyme. The researchers dissolved the enzyme in an aqueous buffer solution and added urea to the solution. The enzyme did not appear to have a secondary or tertiary structure. The researchers carefully removed the urea from the solution and determined that the enzyme had the original secondary and tertiary structure again.
Based on the results of the experiment, which of the following statements best predicts the effect of urea on the enzyme's function?
Function will be disrupted by adding the urea and regained by removing the urea.
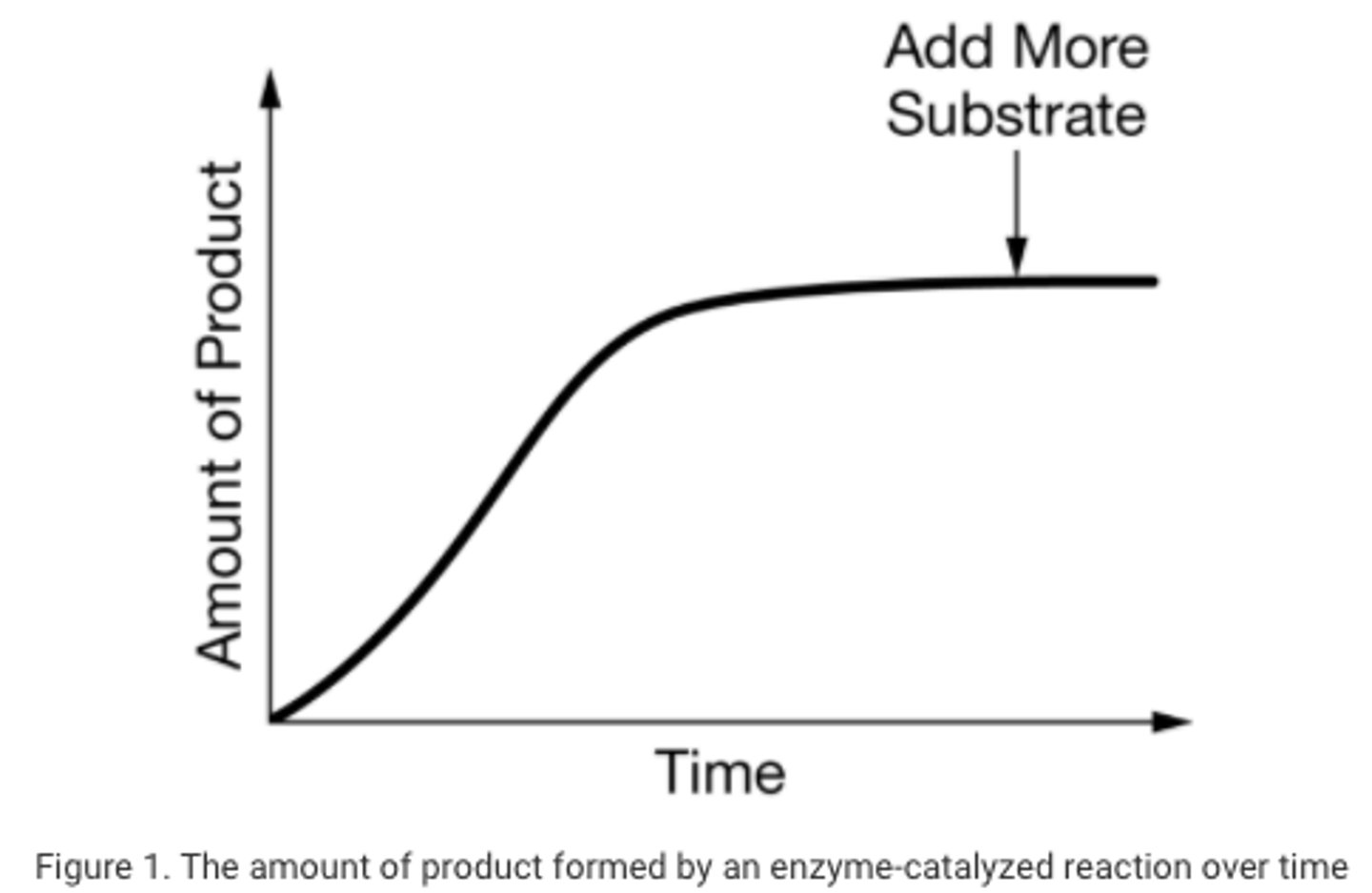
In an experiment, a researcher prepares a reaction mixture by dissolving a substance in a buffered solution. The substance is the substrate of a certain enzyme. The researcher adds a small amount of the enzyme to the reaction mixture and measures the amount of product that is formed over time. The data are represented in Figure 1.
Which of the following best predicts the immediate result of adding more substrate to the reaction mixture at the point indicated by the arrow in Figure 1?
The amount of product will increase until the reaction reaches its equilibrium point or until the substrate is used up by the reaction.
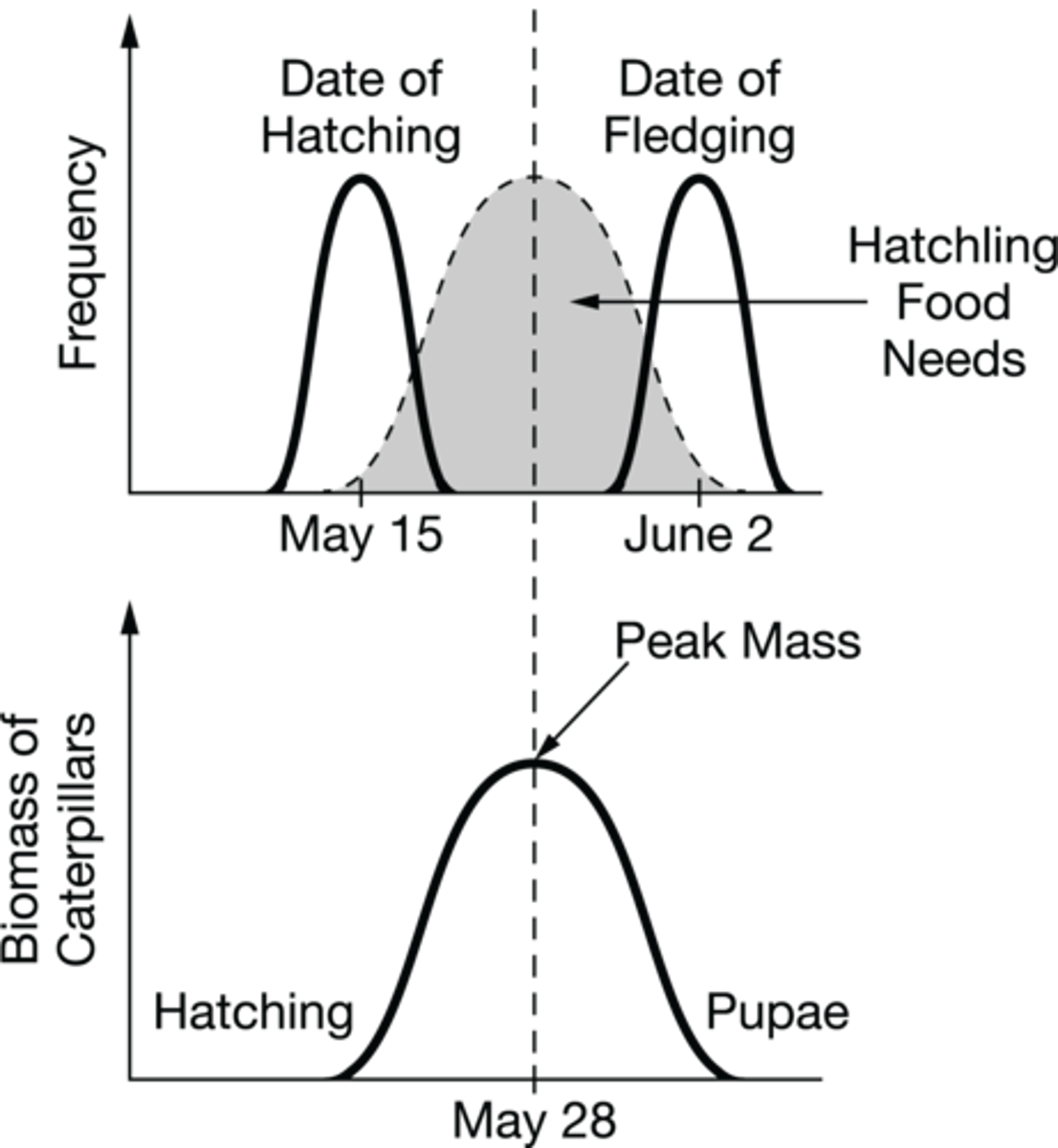
European flycatchers feed caterpillars to their hatchlings. Graph 1 shows the average dates of hatching and fledging (leaving the nest), and the biomass of the caterpillars between early May (when flycatcher young hatch) and June (when fledging of young occurs).
Based on the data, scientists claim that the reproductive behavior of European flycatchers is influenced by the availability of energy sources. Which of the following statements best justifies this claim?
Young European flycatchers hatch from eggs when caterpillar biomass is available for the young birds to consume and convert into energy for growth.
A researcher claims that the incorporation of carbon dioxide into organic molecules during photosynthesis does not violate the second law of thermodynamics.
Which of the following statements best helps justify the researcher's claim?
The total system that includes photosynthetic organisms and the Sun becomes less ordered over time.
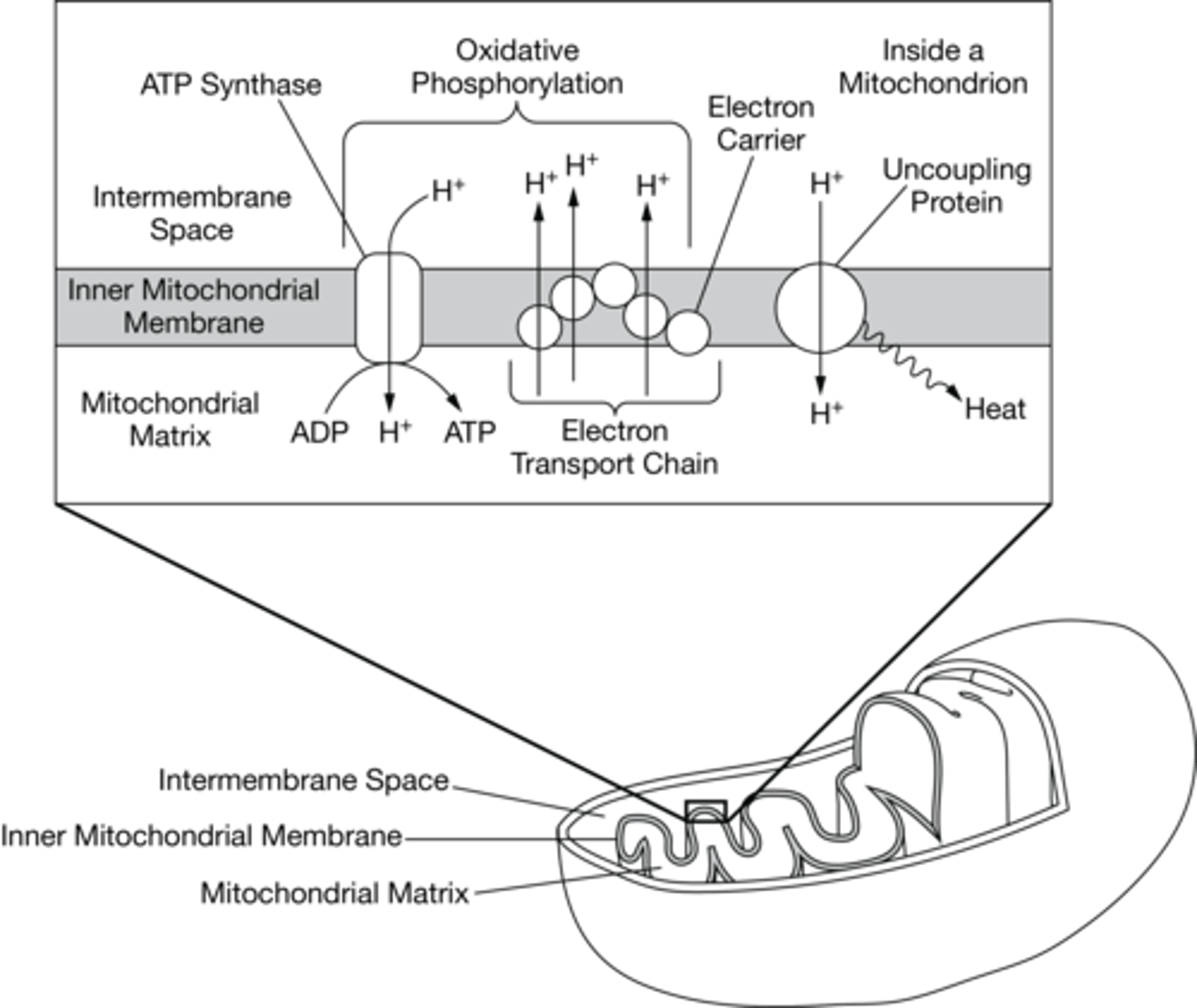
Brown fat is a type of fat tissue found in hibernating mammals. Inside the mitochondria of these fat tissue cells, these mammals have an uncoupling protein embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane. This uncoupling protein allows hydrogen ions to leak from the intermembrane space back into the mitochondrial matrix. Figure 1 shows details of the processes in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
Which of the following statements provides reasoning that supports the claim that brown fatty tissue keeps an animal warm?
The uncoupling protein in this tissue reduces the proton gradient across the membrane and thus produces heat to warm the animal without ATP production.
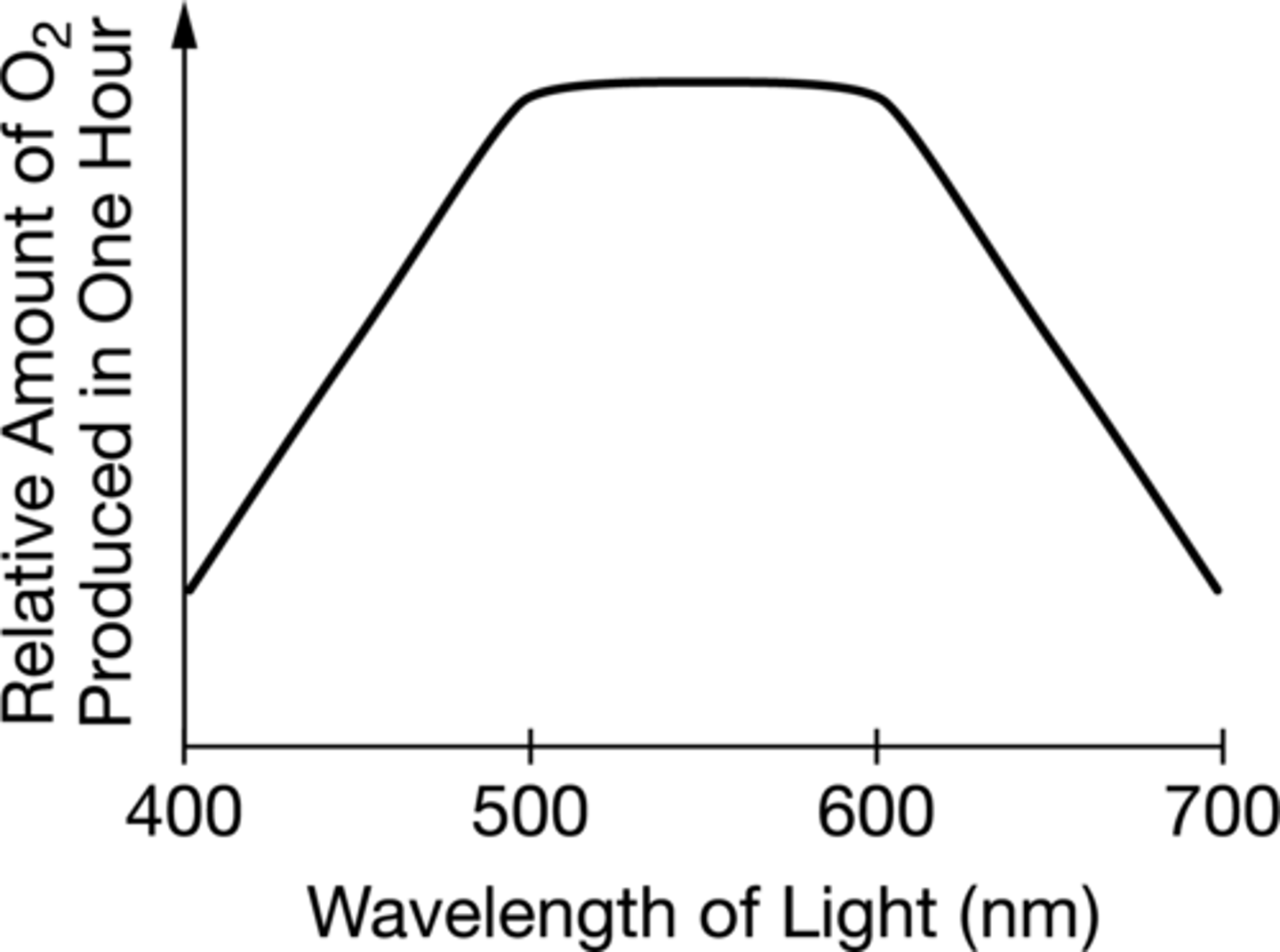
A researcher claims that spinach leaves capture the most energy from light waves in the range of 500 nm to 600 nm. To test the claim, the researcher will place spinach leaves in separate chambers and expose the leaves to different wavelengths of light. For each chamber, the researcher will measure the amount of oxygen gas (O2) that is produced in one hour.
Which of the following graphs best represents data from the experiment that will support the researcher's claim?
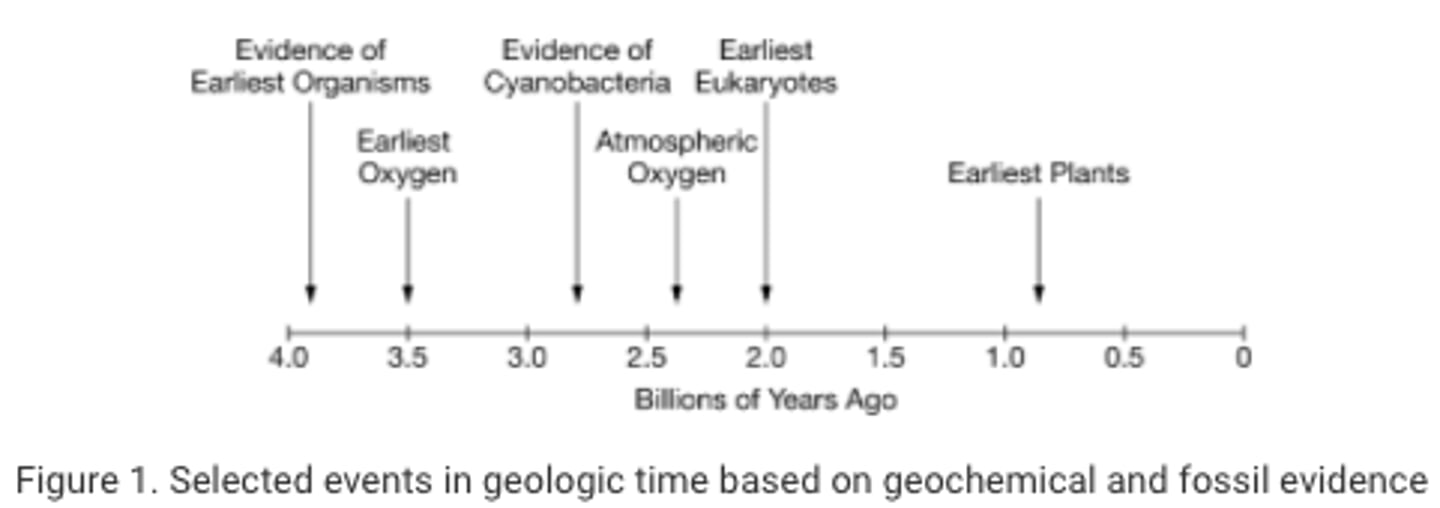
A researcher claims that the initial rise of oxygen in Earth's early atmosphere, which occurred approximately 2.3 billion years ago, resulted from the metabolic activity of prokaryotic organisms. The claim is based on an interpretation of the geochemical and fossil evidence represented in Figure 1.
Which of the following types of evidence will best support the researcher's claim?
Evidence that the cyanobacteria produced oxygen as a by-product of photosynthesis

A researcher claims that a certain herbicide suppresses plant growth by inhibiting chloroplast function. To test the claim, the researcher treats isolated chloroplasts with increasing concentrations of the herbicide. The data from the experiment are presented in Table 1.
Herbicide Concentration (μg/L) pH Difference across Thylakoid Membrane ATP Production
0 3.5 Very high
2 2.5 Moderate
8 0.5 Very low
32 0 Very low
Which of the following statements best clarifies how the data support the researcher's claim?
ATP synthase activity depends on a proton gradient across the thylakoid membrane.
A researcher claims that genetic variation provides organisms with the ability to survive and reproduce in different environments. To support the claim, the researcher makes the following observation: bacteria that contain plasmids (small DNA molecules) are resistant to a wider range of antibiotics than are bacteria that contain no plasmids.
Which of the following statements best establishes a connection between the observation and the researcher's claim?
Some plasmids contain antibiotic resistance genes
Phycobiliproteins are a complex of accessory pigments and proteins found in cyanobacteria but not in green algae. A researcher claims that the phycobiliprotein pigments in cyanobacteria allow the cyanobacteria to survive in certain aquatic niches better than green algae can.
Which of the following statements best justifies the researcher's claim?
The additional pigments absorb light at wavelengths that green algae cannot absorb; this may allow cyanobacteria to capture more light energy for photosynthesis than green algae can in certain areas.
A researcher claims that budding yeast are able to survive in different environments because they produce enzymes that allow them to use different molecules as sources of matter and energy.
Which of the following statements best helps justify the researcher's claim by providing a relevant example?
Yeast cells produce invertase, which is an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of the disaccharide sucrose into glucose and fructose.