Unit 5: Chapter 14 - Agricultural Sustainability in a Global Market
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Agricultural landscapes
result from the interactions between farming activities and a location's natural environment.
Agroecosystems
ecosystems that are modified for agricultural use.
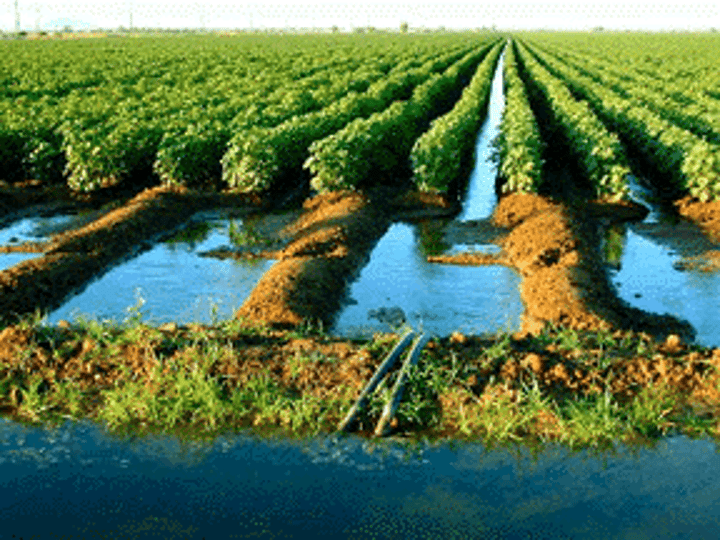
Irrigation
to water crops by bringing in water from pipes, canals, sprinklers, or other man-made means, rather than relying on rainfall alone

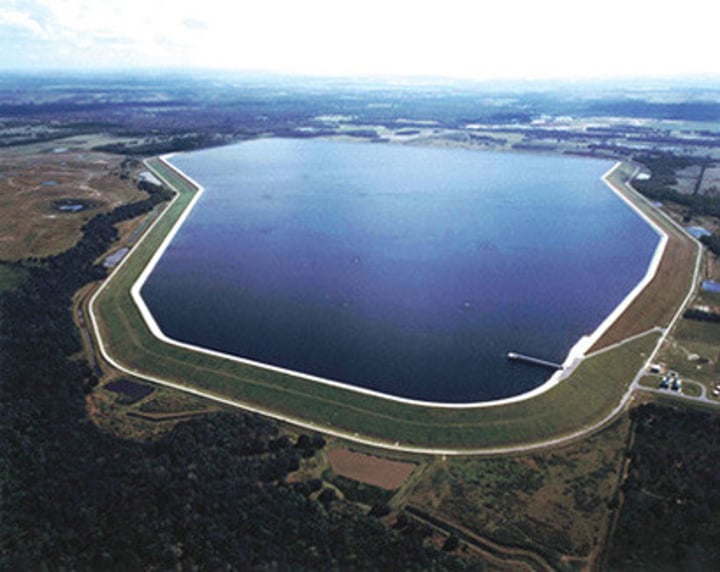
Reservoirs
artificial lakes created by building dams across streams and rivers.

Aquifers
water sources below the land's surface and sometimes tapped for irrigation.
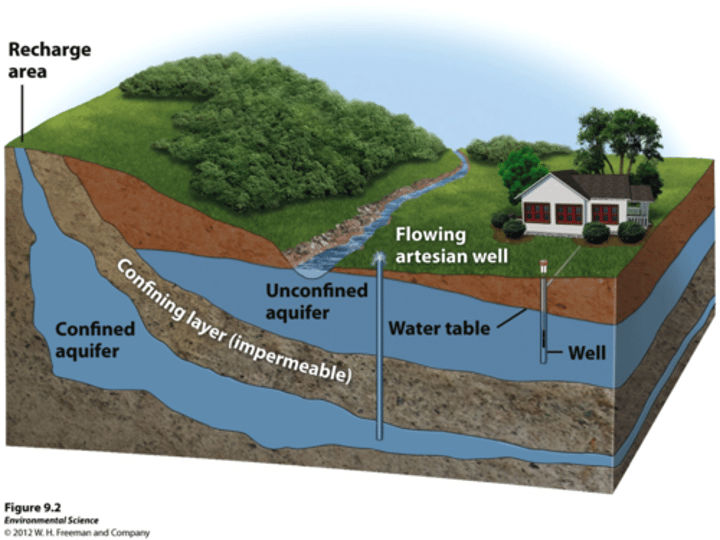
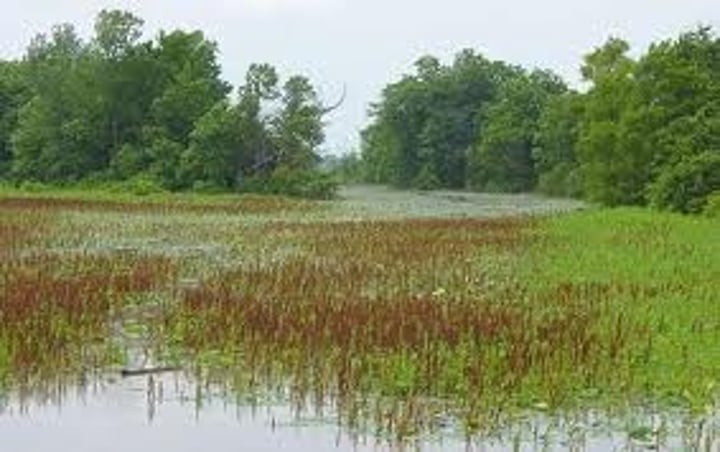
Wetlands
areas of land that are covered by or saturated with water
Ex:
swamps, marshes, and bogs.

Water Pollution
water runoff from irrigated farms may contain chemicals and nutrients from pesticides and fertilizers, as well as bacteria and disease-carrying organisms.
Soil salinization
the process of water-soluble salts building up in the soil
Where does soil salinization happen?
It happens in arid and semi-arid regions when water evaporates from the ground more rapidly than it is replenished by rain or irrigation.
Why is soil salinization bad for plants?
When salts accumulate in the root of the crop, the plant can no longer extract adequate water to grow.
How have governments and organizations worldwide addressed the negative environmental effects of agriculture?
through a variety of policies and sustainability efforts.
Debt-for-Nature swaps with peripheral countries
In exchange for local investment in conservation measures, the banks agree to forgive a portion of a country's debt.
Commercial Agriculture Conservation Efforts
offer farmers financial incentives to use more sustainable practices.
Ex:
-reducing air pollution from heavy machinery
-better stewardship of water resources
-seeking to minimize the amount of toxins seeping into groundwater from chemical fertilizers and pesticides.
What is the main agency responsible for helping commercial farmers create more sustainable practices?
The United States Department of Agriculture Farm Service Agency (FSA)
What is the focus on in subsistence farming?
the critical need to preserve soil fertility and prevent soil erosion while increasing yields by intensifying land use.
Ex:
In areas that practice shifting cultivation, farmers can replenish the soil and achieve higher yields by rotating fields systematically to include cover crops
Cover crops
plants that protect and nourish the soil.
How does agriculture affect diet and lifestyle choices?
Consumers in many countries have altered their diet in reaction to recent innovations in agriculture.
People are purchasing organically grown foods they believe are better for the environment and for their own bodies.
Organic farmers markets are more popular around the world that ever before.
How are diets and social norms are tied to longstanding agricultural practices in many countries?
Argentina's agricultural history and food traditions since the 16th century has long ranked as a country with the highest levels of beef consumption in the world.
How do roles of women in farming vary tremendously across regions and agriculture types?
Women in agriculture face gender discrimination, but with changes in both agricultural practices and available opportunities, the role of women in agriculture is rapidly changing.
Ex:
In parts of Southeast Asia, women form the majority of the aquaculture workforce. In pastoral nomadic cultures share responsibility for the care of the animals with the men.
How can the loss of small farms harm the social and economic fabric of rural communities?
Large-scale commercial farming dominates most American farmland, and farm families often sell their land to agribusiness corporations when they encounter financial struggles.
When these farms go out of business, rural towns lose population. This creates a sense of loss of community when family farms have been operating for generations.
How can the rise of monocropping makes farmers and consumers vulnerable to sudden changes in prices?
The lack of diversity in crops causes prices to be turbulent, because any single disrupter such as disease or natural disaster can have a major impact on the entire system.
Ex:
In the face of a drought, the prices of corn and all the products made from corn are driven up due to shortages.
Biotechnology
the science of altering living organisms to create new products for specific purposes, such as crops that resist certain pests.
What is one problem with biotechnology?
One issue with biotechnology is sustainability.
Farmers must manage the environment in a way that minimizes pollution in the air, soil, and water, in order to ensure productivity in the future.
Arguments FOR Biotechnology and GMOs
-Increased crop yields
-Resistance to drought, disease, and pests
-Improved nutritional values
-Reduction in the cost of food production
Arguments AGAINST Biotechnology and GMOs
-Possible impact on agricultural biodiversity
-Intensified uses of pesticides, herbicides, and fertilizers
-Possible transfer of genetic material into unmodified plants
-Possible build-up of synthetic fertilizers in the soil, decreasing the soil's fertility
Aquaculture
the controlled cultivation of aquatic organisms (fish, crustaceans, mollusks, algae), and other organisms of value.
The water equivalent of the Green Revolution.
What are the pros of Aquaculture?
-One of the fastest growing food production sectors in the world.
-Has provided thousands of jobs
-Algae fuel is being developed that could potentially replace fossil fuels and reduce energy costs.
Arguments FOR Aquaculture
-Less space and care intensive than other types of agriculture
-Can provide enormous and consistent amounts of fish and seafood
Arguments AGAINST Aquaculture
-Water pollution and the negative impact of antibiotics on the ecosystem
-Possible compromise of native gene pools if farmed fish and native fish interbreed
-Possible transfer of disease and parasites to wild fish populations
Precision agriculture/farming
uses a variety of cutting-edge technologies to apply inputs with pinpoint accuracy to maximize crop yields, reduce waste, and preserve the environment
Farmers can use GIS software to map their fields and develop a micro-level analysis of each field's physical characteristics.
part of a movement that some see as the fourth agricultural revolution.
What are the disadvantages of precision agriculture/farming?
Precision farming can be too expensive for small farmers, and the technology can be challenging to operate.
What are the goals of food choice movements?
eating healthier foods, encouraging sustainable farming, and supporting small, local farmers.
How do some local food movements focus on choosing food grown nearby?
-Some U.S cities have designated small, urban plots of land to provide fresh fruits and vegetables.
-Community Supported Agriculture (CSA), local farms sell shares of their output directly to consumer (mailing service)
How have organic farm products gotten very popular?
Many wealthier consumers are willing to pay higher prices for organic food and fair trade products.
Speciality crops, or value-added crops
transformed from their original state to a more valuable state.
They require production and business skills that may be different from those needed to produce traditional crops.
Ex:
converting milk into cheese or yogurt. Other value added crops are coffee, tea, and chocolate.
What drives the consumer demand for value added crops?
Consumers demand for value added crops can be driven by the desire to eat healthy, nutritious food.
It is waaay easier for people to buy yogurt than to make it themselves.
Food security
reliable access to safe, nutritious food that can support a healthy and active lifestyle.
Food insecurity
the disruption of a household's food intake or eating patterns because of poor access to food
What factors contribute to food insecurity?
-lack of money
-distribution problems
-bad weather
-government instability
-Suburbanization
Suburbanization
the shifting of population from cities into surrounding suburb causing a loss of agricultural land.
Do only peripheral countries suffer from food insecurity?
No. The United States has it as well.
Loss of small farms and farmland have increased the the issues of food insecurity.
How much farmland has shrunk in the U.S.?
The USDA estimates that between 1980 and 2018 the amount of farmland shrank by 13 percent.
How many households are food insecure?
12.3 percent of households and nearly 13 million children in America are food insecure.
Single women with children represent almost 1/3 of that number.
Does poverty always directly affect food insecurity?
Not all people living in poverty experience food insecurity, and not all people living above the poverty line are exempt from it.
What plays a factor in food security, then?
Cost of living can play a factor. Families with children and low wages may not have adequate incomes to purchase enough food.
Contrary to popular belief, most food insecure Americans are employed or live in a household where someone works at least part time.
Undernourishment
dietary energy consumption that is continuously below the minimum requirement for maintaining a healthy life.
How many people suffer from undernourishment?
The UN estimates that 870 million people suffer from undernourishment- 99% of whom live in peripheral countries.
How does conflict and war affect world hunger?
-Warring parties have used food as a weapon by deliberately denying access to it for people associated with the opposition.
-In many cases, food distribution is inadequate or unequal in conflict zones because political systems are poorly managed, corrupt, or in disarray.
-Crops fail when people are displaced by conflict.
How many % of the world hunger is in countries affected by war?
About 60% of the world's hunger-490-million people-live in countries affected by war.
What are countries in conflict with food shortages
Democratic Republic of Congo, Myanmar, Yemen, Afghanistan, Sudan, South Sudan, Nigeria, and Syria.
How does transportation impact both producers and consumers?
Farms, food-processing facilities, and the markets where foods are sold are often located far from one another.
How does storage impact both producers and consumers?
Food insecurity results from poor storage, processing, transportation, or infrastructure along the supply chain. Winter storms are causing major problems in the US.
How does inadequate infrastructure impact both producers and consumers?
Inadequate infrastructure in many peripheral countries means that food grown elsewhere often cannot be transported to those who need it.
Economy of scale
the reduced cost of producing food items as the quantity of production increases.
Economy of scale offers a good way to think about how to best use available resources to meet agricultural needs.
How much % of the world's food do women produce?
Women produce more than 50% of the world's food and make up 43% of the agricultural labor force
Women in Peripheral Countries
-mostly labor in agriculture.
-do not have land rights
-are largely limited to subsistence agriculture
How many farmers in the United States are female?
A third
What challenges do women face?
-Cultural biases block women from borrowing money in some countries.
-Rigid gender roles sometimes keep women from taking their crops to the market.
-In many places, women in agriculture experience difficult working conditions and a poor quality of life.
-In the United States, women work as farmers, ranchers, and land managers, and often face prejudice from male counterparts.
Agricultural empowerment
having the ability to make decisions about land, livestock, seeds, fertilizer, and machinery, as well as control over finances and one's own time.
Traditional Women Roles
In cultures throughout the world, women have traditionally been in charge of selecting, cooking, and serving food to their families.
What happens as women's roles in the workplace change and are empowered?
As women's roles in the workplace change, families may eat out more, and grandmothers or domestic helpers may take over family food purchasing.
What are benefits of empowering rural women?
-Children receive better nutrition and education when their mothers' incomes increase.
-Communities benefit when women have money to spend on schooling and other resources.
-Empowering female farmers may help improve food security for millions.
What are steps to empowering female farmers?
-Education
-Technical support
-Access to capital
-Government policies that promote gender equality