L26 The Somatic Sensory System (Imported from Quizlet)
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
Somatosensory system
What is the somatic sensory system also known as?
The body in the brain
What does the somatic sensory system represent?
Mechanical stimuli (light touch, vibration, pressure and cutaneous tension) and painful stimuli and temperature
What are the 2 major input components of the somatic sensory system?
To identify the shape and texture of objects
To monitor the internal and external forces acting on the body
To detect potentially harmful circumstances
To have a sense of ourselves within our environment and so plan our actions accordingly
What do the input and interpretations of the two major input components enable us?
Sensory
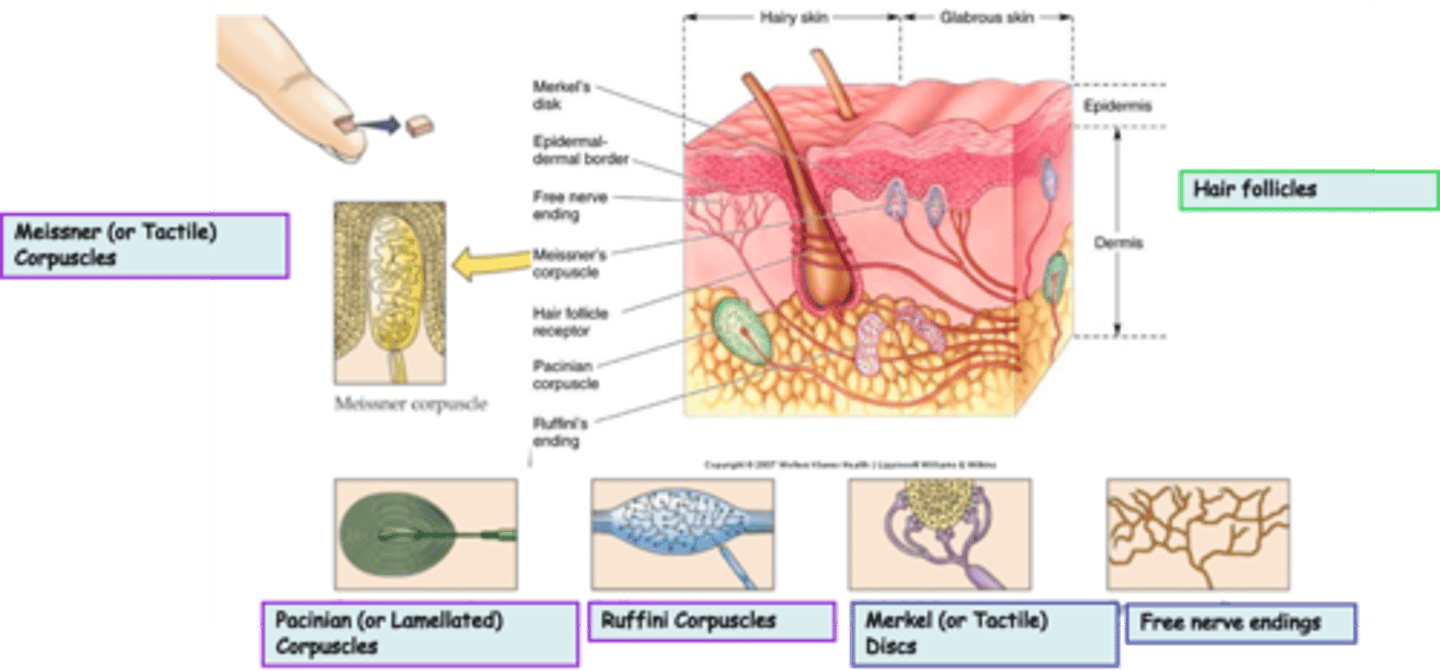
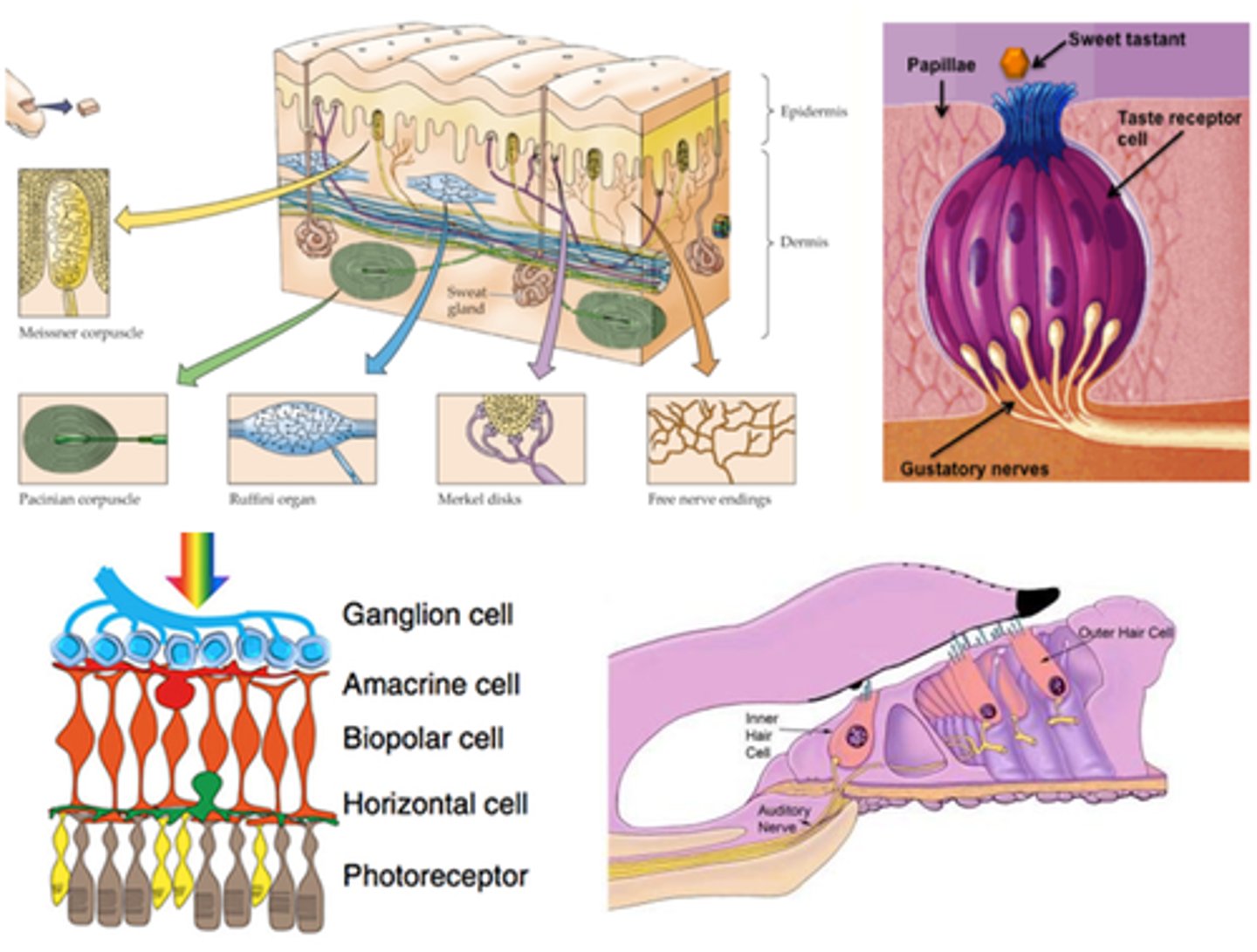
Golgi Tendon Organs and Muscle Spindles are what kind of receptors?
Widespread in epithelia
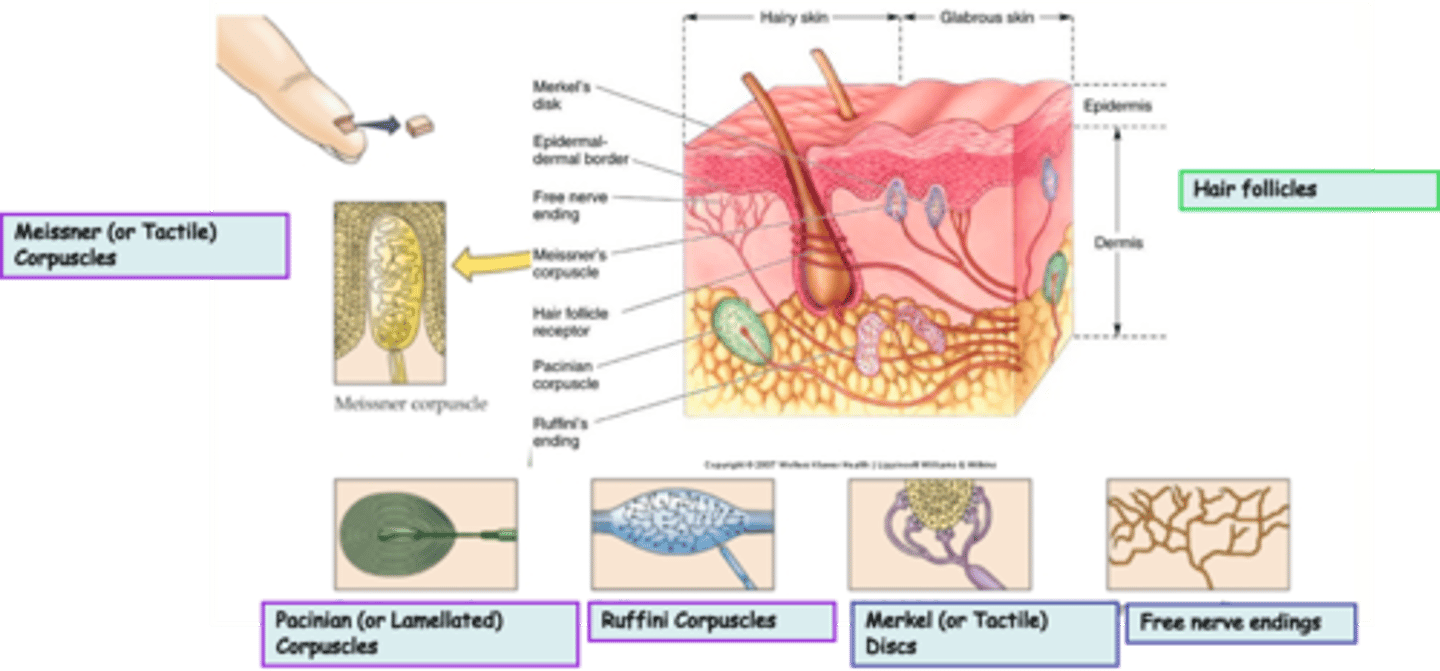
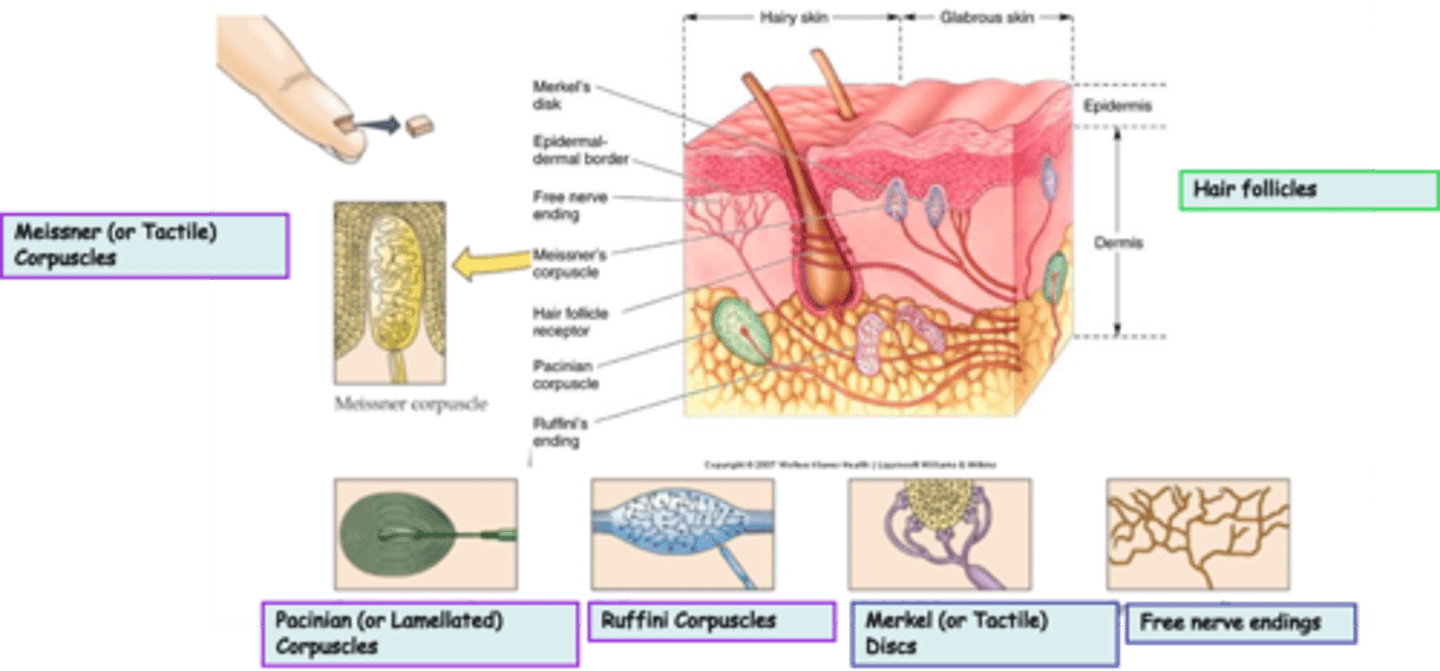
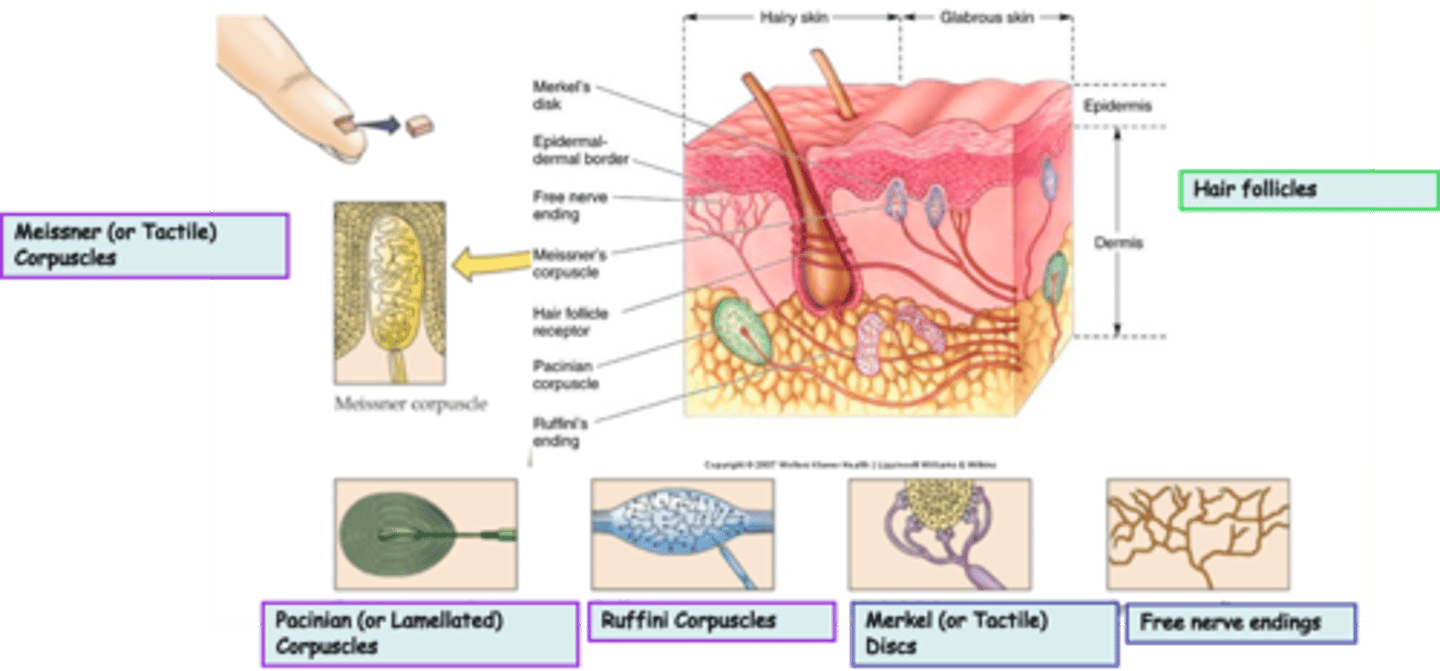
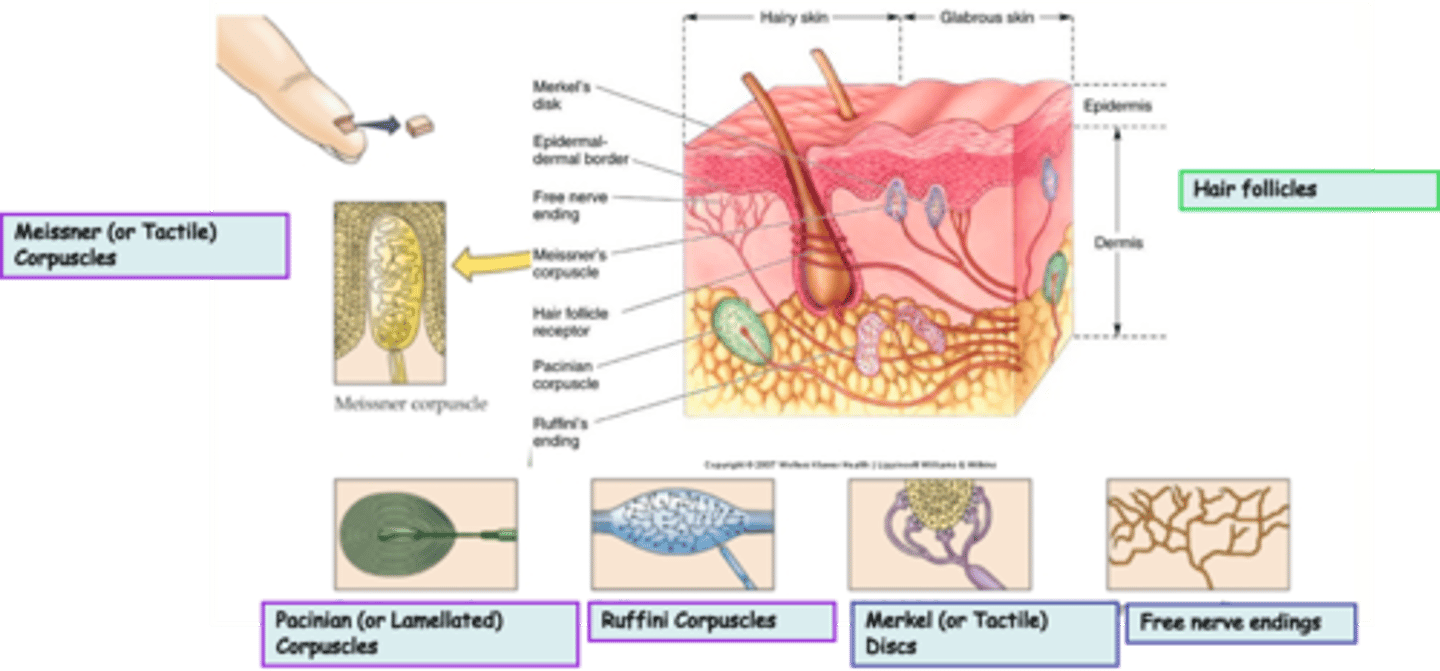
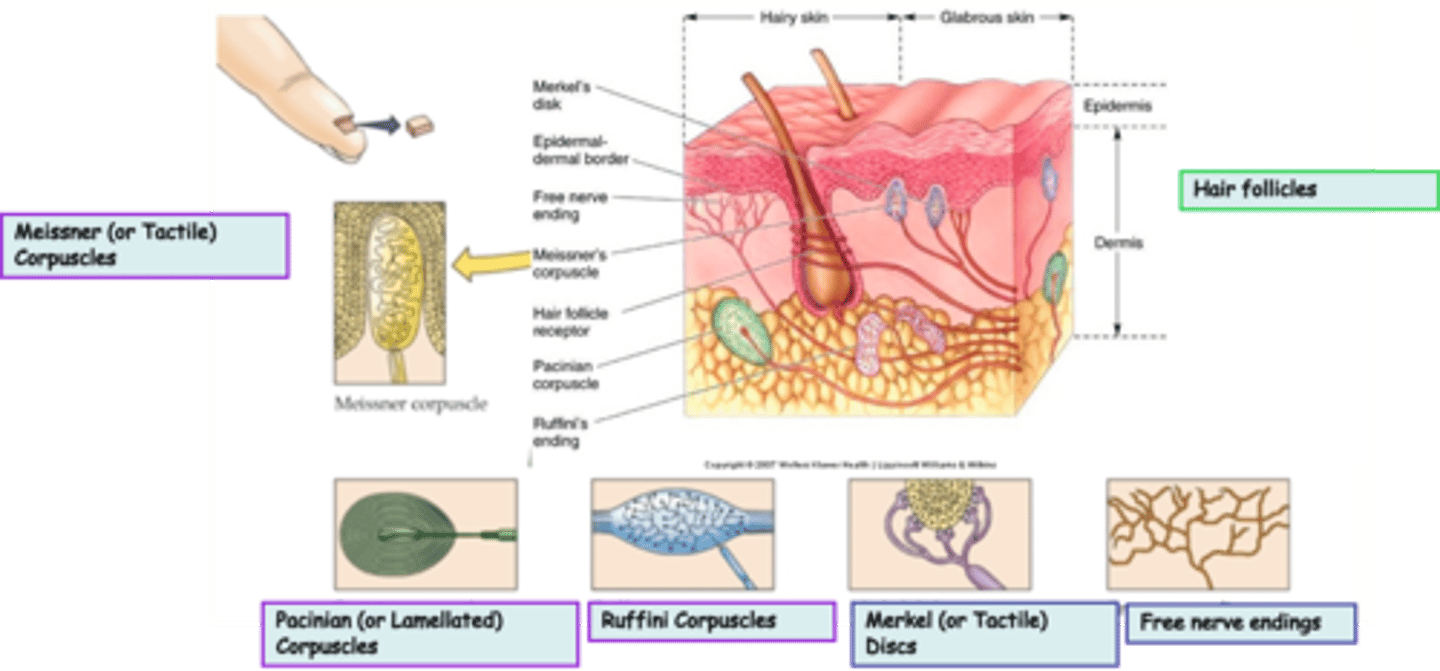
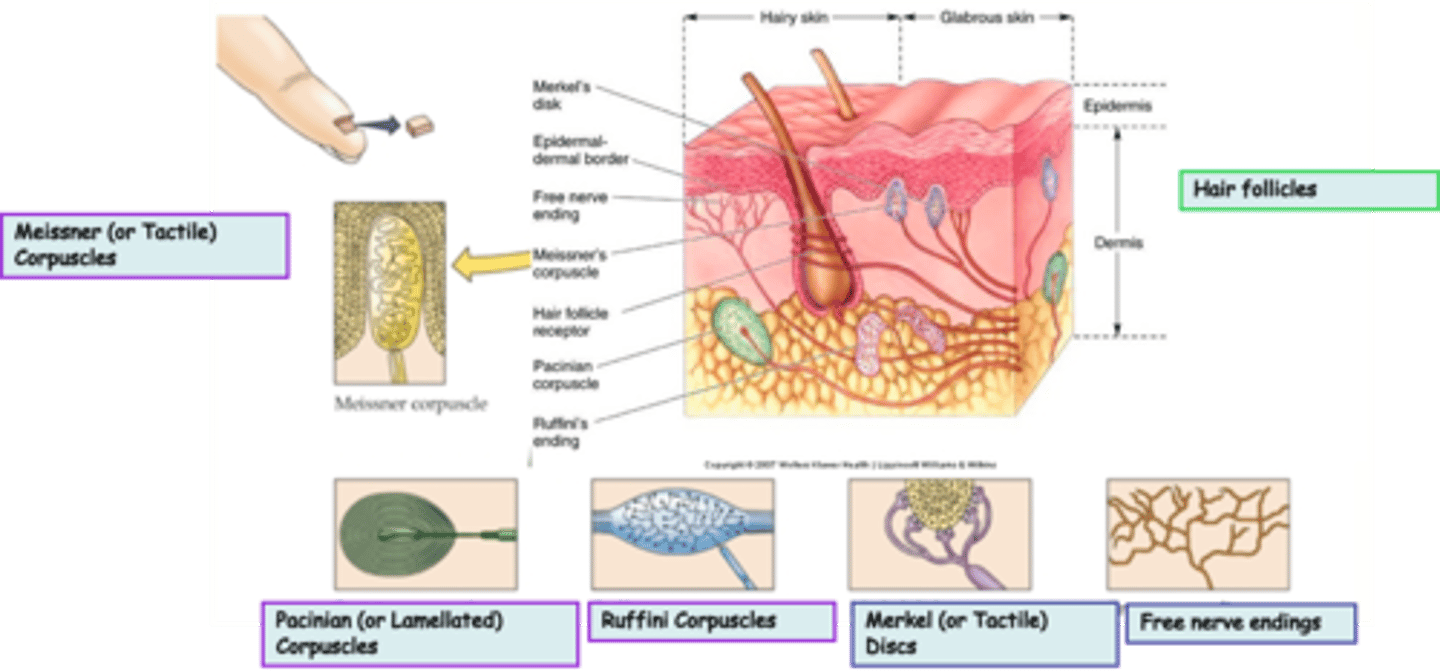
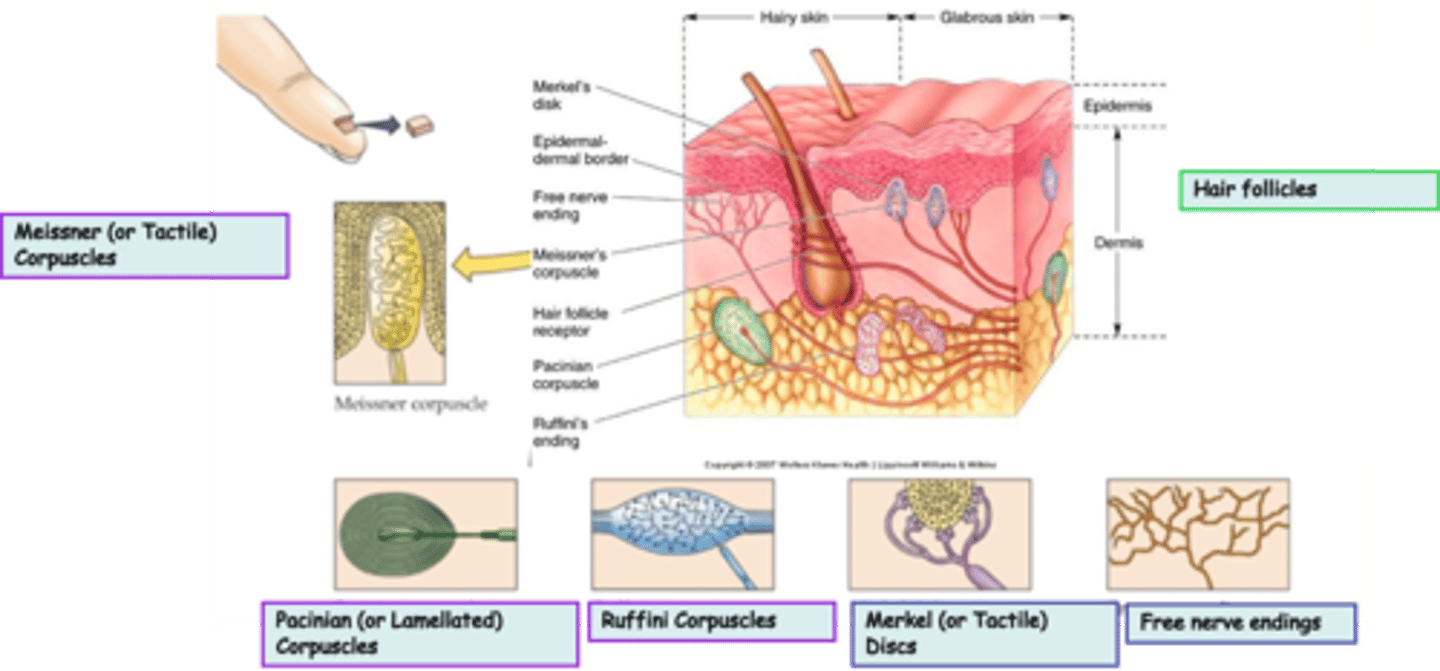
Where are hair follicles located?
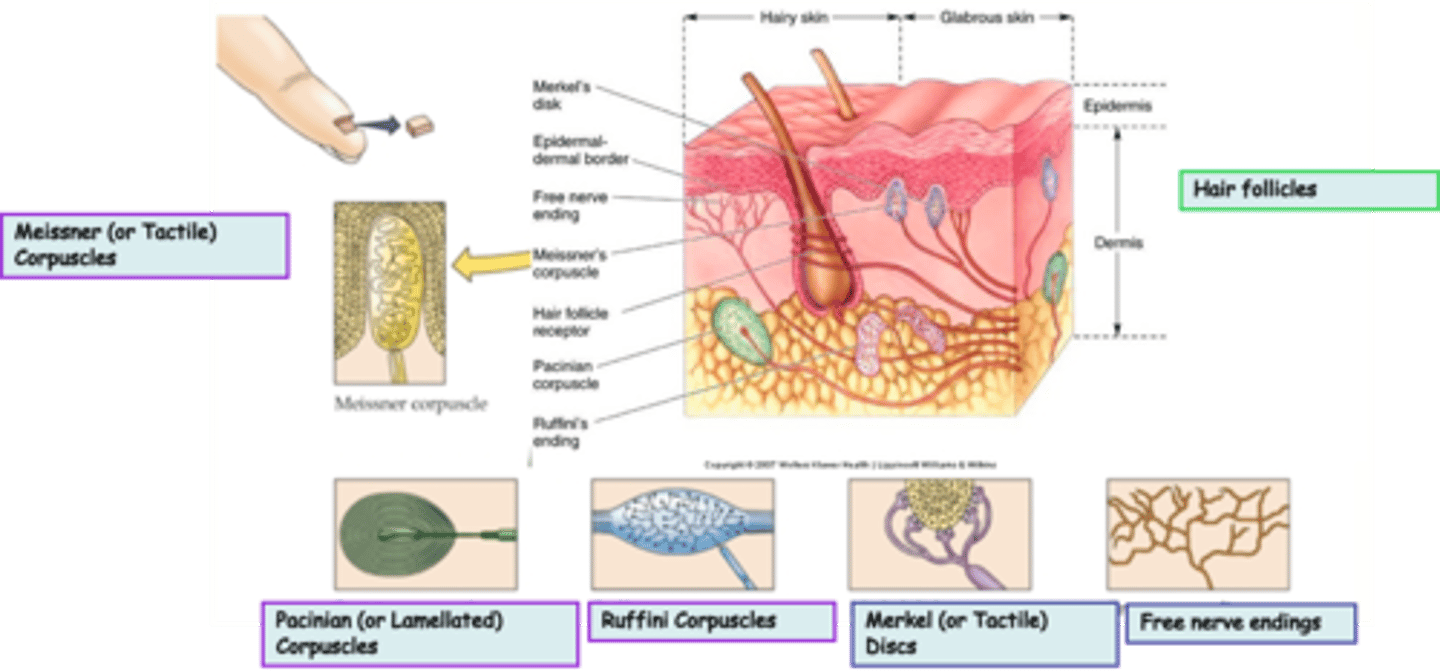
Varied according to type
What is the modality of hair follicles?
Both rapid and slowly adapting
What kind of subtypes do hair follicles have?
Unencapsulated
Free nerve endings are an example of _______________ nerve endings
Widespread in epithelia and connective tissue
Where are free nerve endings located?
Pain, heat, cold
What is the modality of free nerve endings?
Unencapsulated
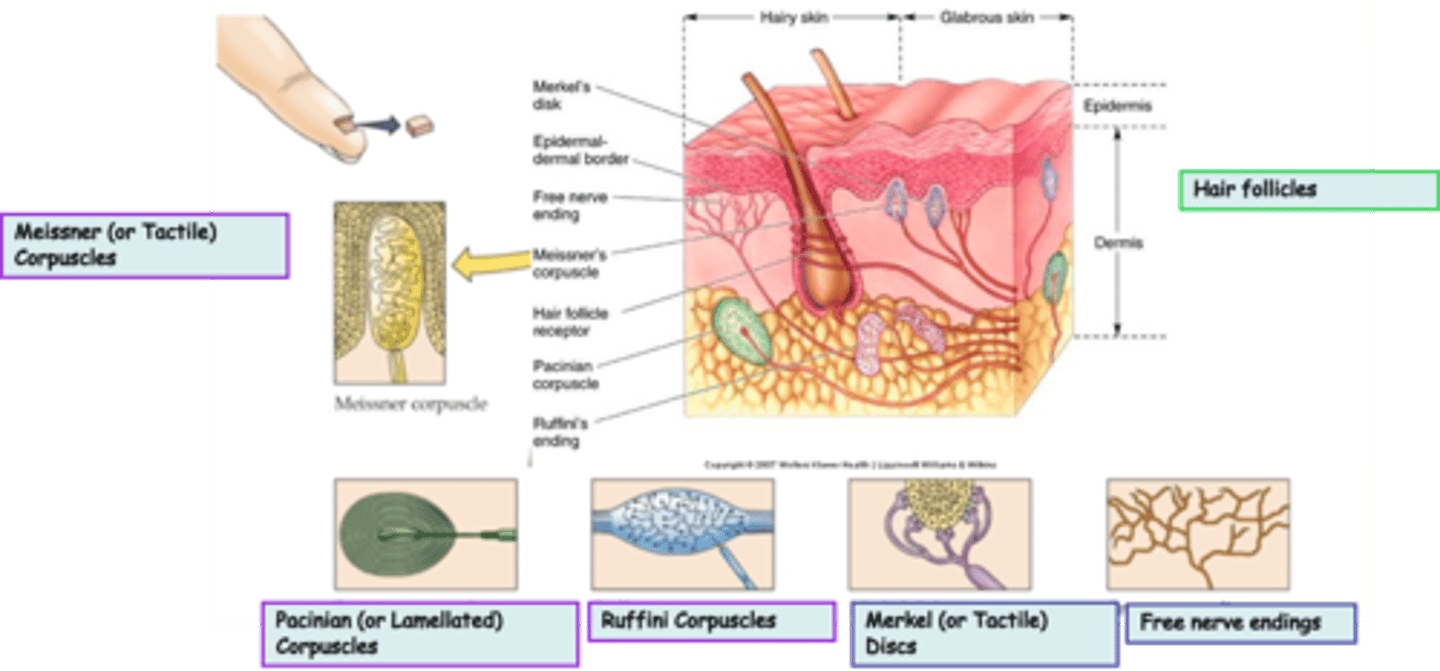
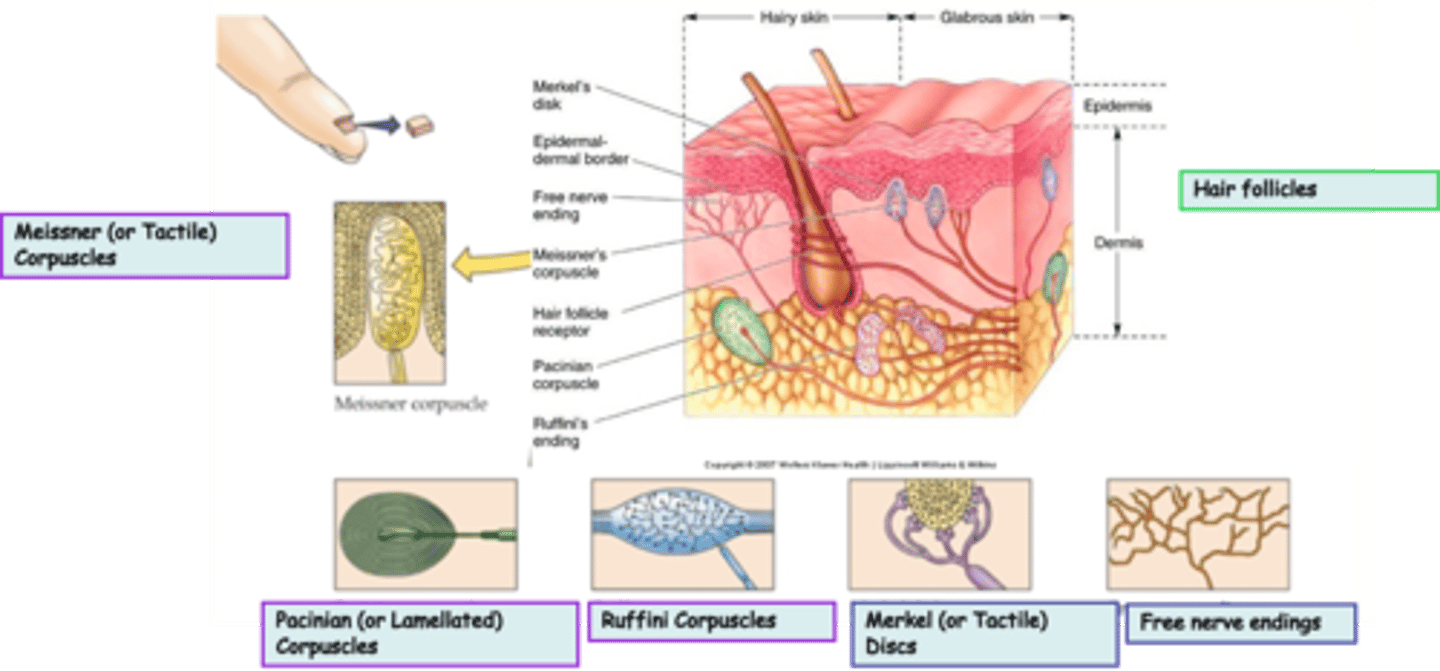
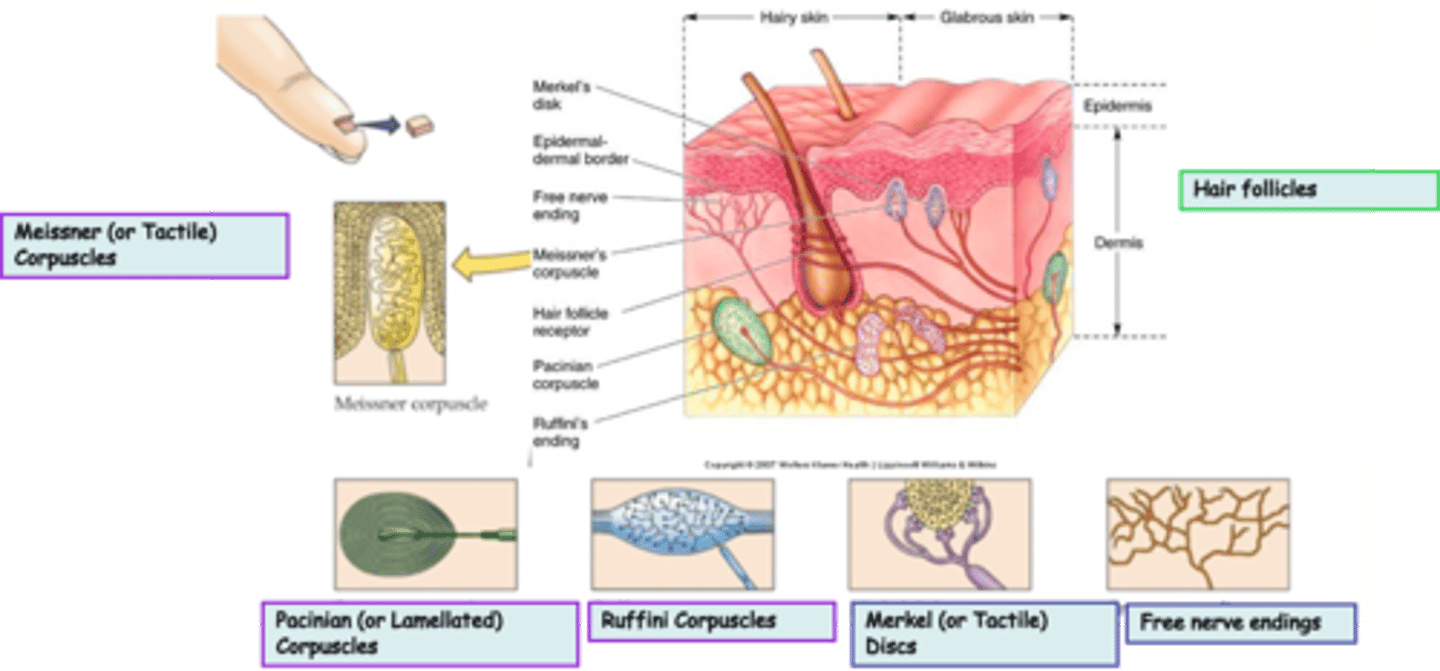
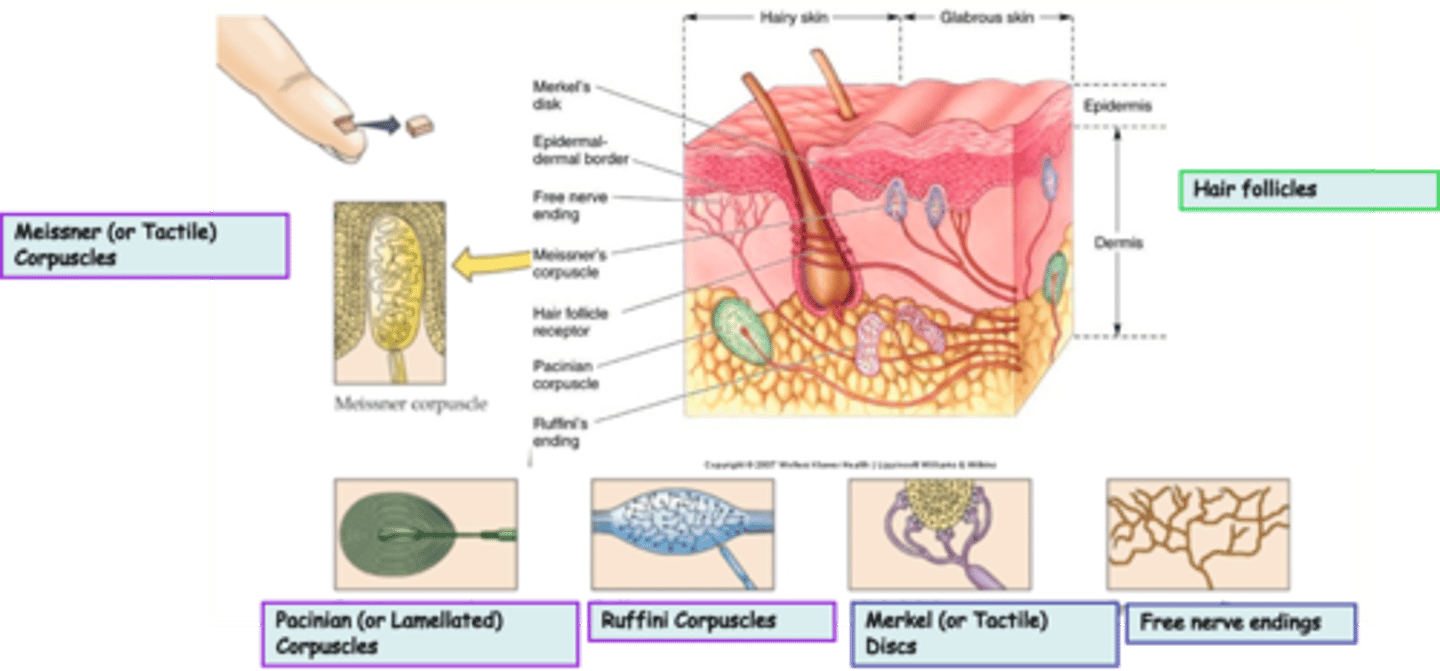
Merkel (or Tactile) Discs are an example of ____________________ nerve endings
Superficial skin (epidermis)
Where are Merkel (or Tactile) Discs located?
Light touch, texture, edges, shapes
What is the modality of Merkel (or Tactile) Discs?
Slowly
Merkel (or Tactile) Discs are __________ adapting
Dermis, subcutaneous tissue, joint capsules
Where are Ruffini Corpuscles located?
Heavy touch, pressure, skin stretch, joint movement, a kind of proprioceptor?
What is the modality of Ruffini Corpuscles?
Slowly
Ruffini Corpuscles are ___________ adapting
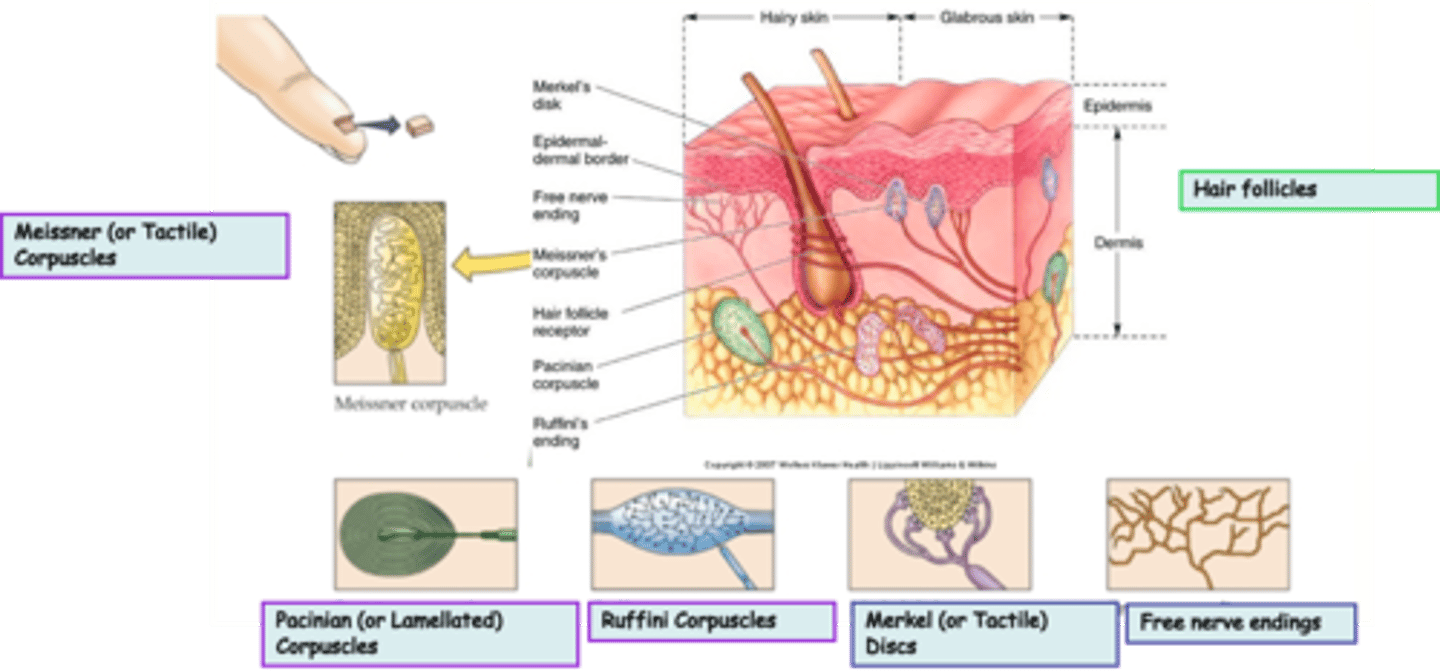
Encapsulated
Pacinian (or Lamellated) Corpuscles are an example of _______________ nerve endings
Dermis, joint capsules, viscera
Where are Pacinian (or Lamellated) Corpuscles located?
Deep pressure, stretch, tickle, vibration
What is the modality of Pacinian (or Lamellated) Corpuscles?
250-350Hz
Pacinian (or Lamellated) Corpuscles are sensitive to ...?
Rapidly
Pacinian (or Lamellated) Corpuscles are ___________ adapting
Encapsulated
Messiner (or Tactile) Corpuscles are an example of ____________________ nerve endings
Dermal papillae of skin, esp. palms, eyelids, lips, tongue, etc
What is the modality of Meissner (or Tactile) Corpuscles?
30-50Hz
Meissner (or Tactile) Corpuscles are sensitive to ...?
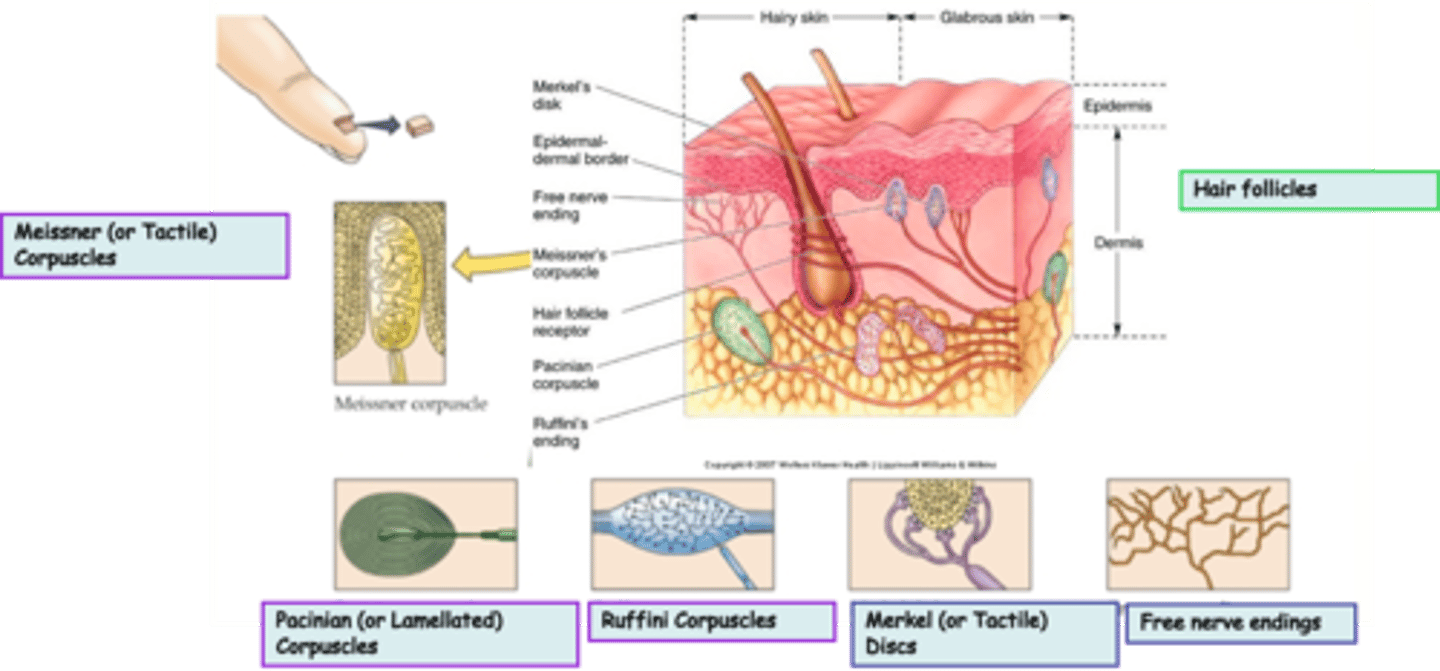
Rapidly
Meissner (or Tactile) Corpuscles are ___________ adapting
A 'device' made of cells that detects changes in the body or the environment
What is a cellular receptor?
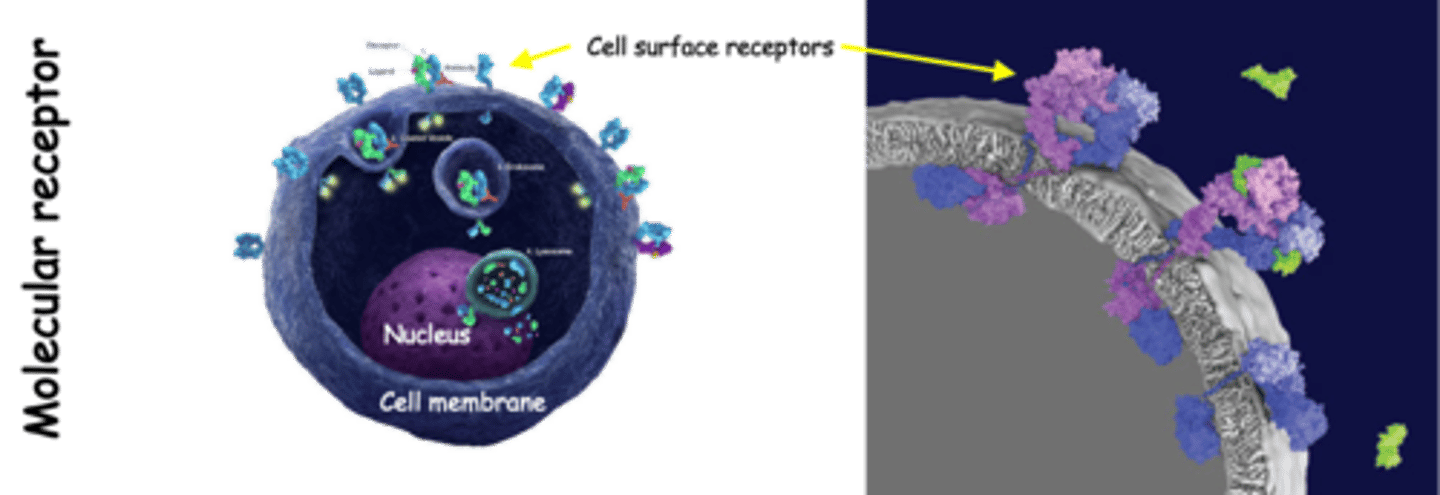
A molecule, usually located on the surface of a cell with a transmembrane linkage to the cytoplasm, that detects changes in molecular environment (e.g. growth factors, hormones, etc)
What is a molecular receptor?
The sensory neurons themselves
In these examples, the sensory receptors - the cells doing the sensing - are actually what?
Photoreceptors, auditory and vestibular hair cells, taste receptors
What are some specialist cell types?
Primary afferent neuron, CNS
In these cases, the specialist cell type synapses with a ____________ ___________ __________ to relay the sensory information to the ____
Phasic and tonic
What are the two different classes of mechanoreceptor responses?
Pacinian (or Lamellated) Corpuscles
What is an example of a phasic mechanoreceptor response?
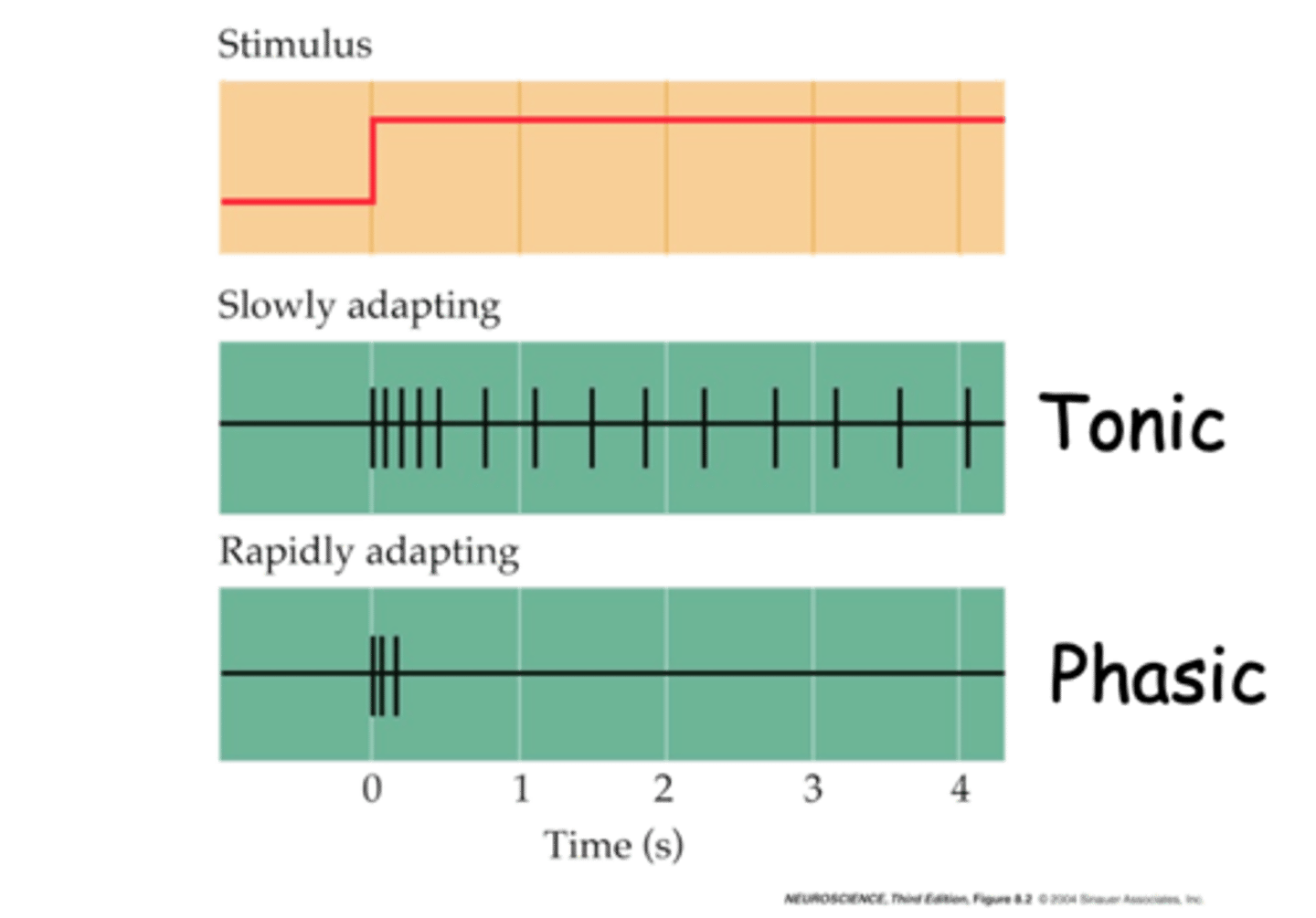
Rapidly
Phasic mechanoreceptors responses are ___________ adapting
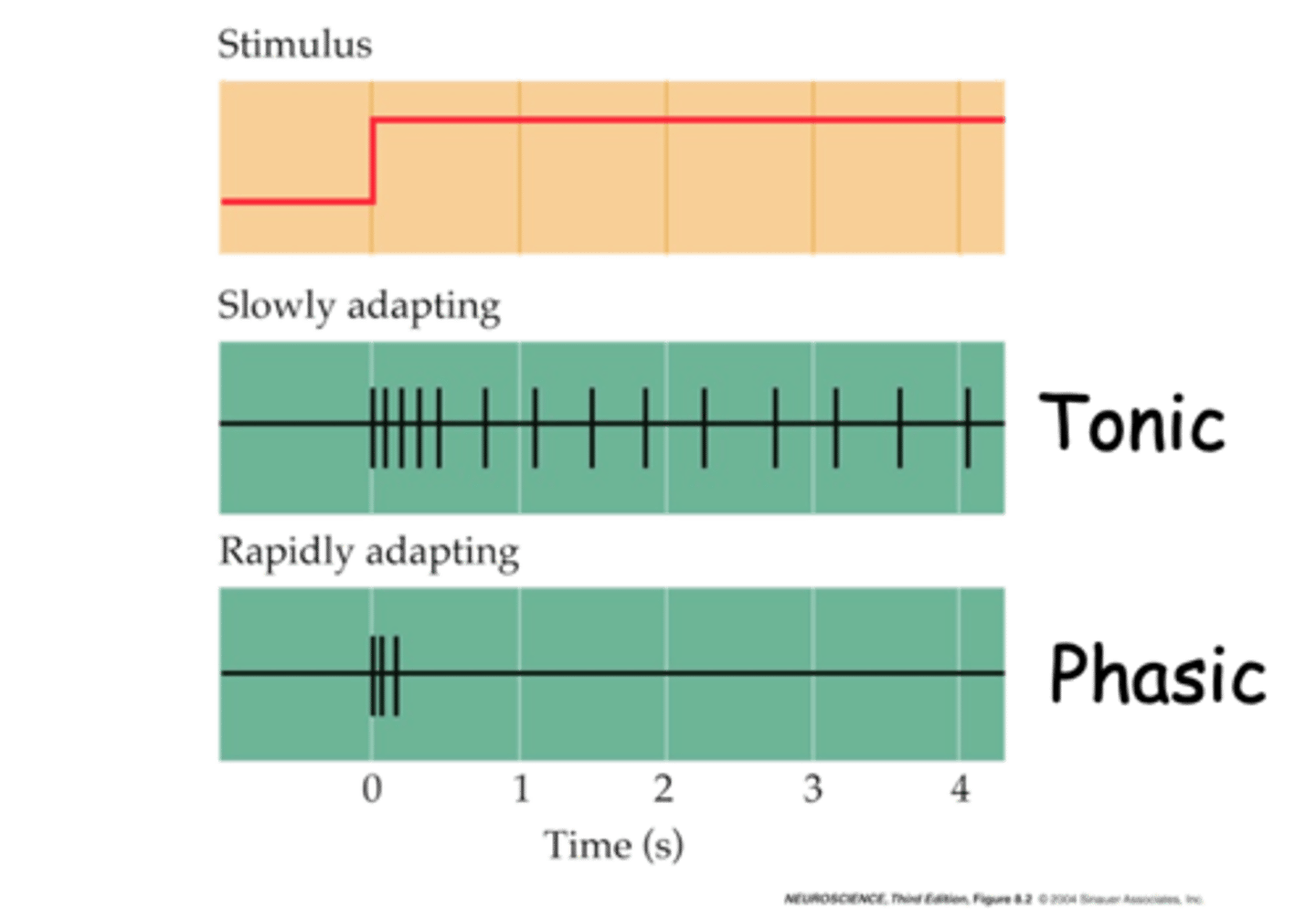
Ruffini Corpuscles
What is an example of a tonic mechanoreceptor response?
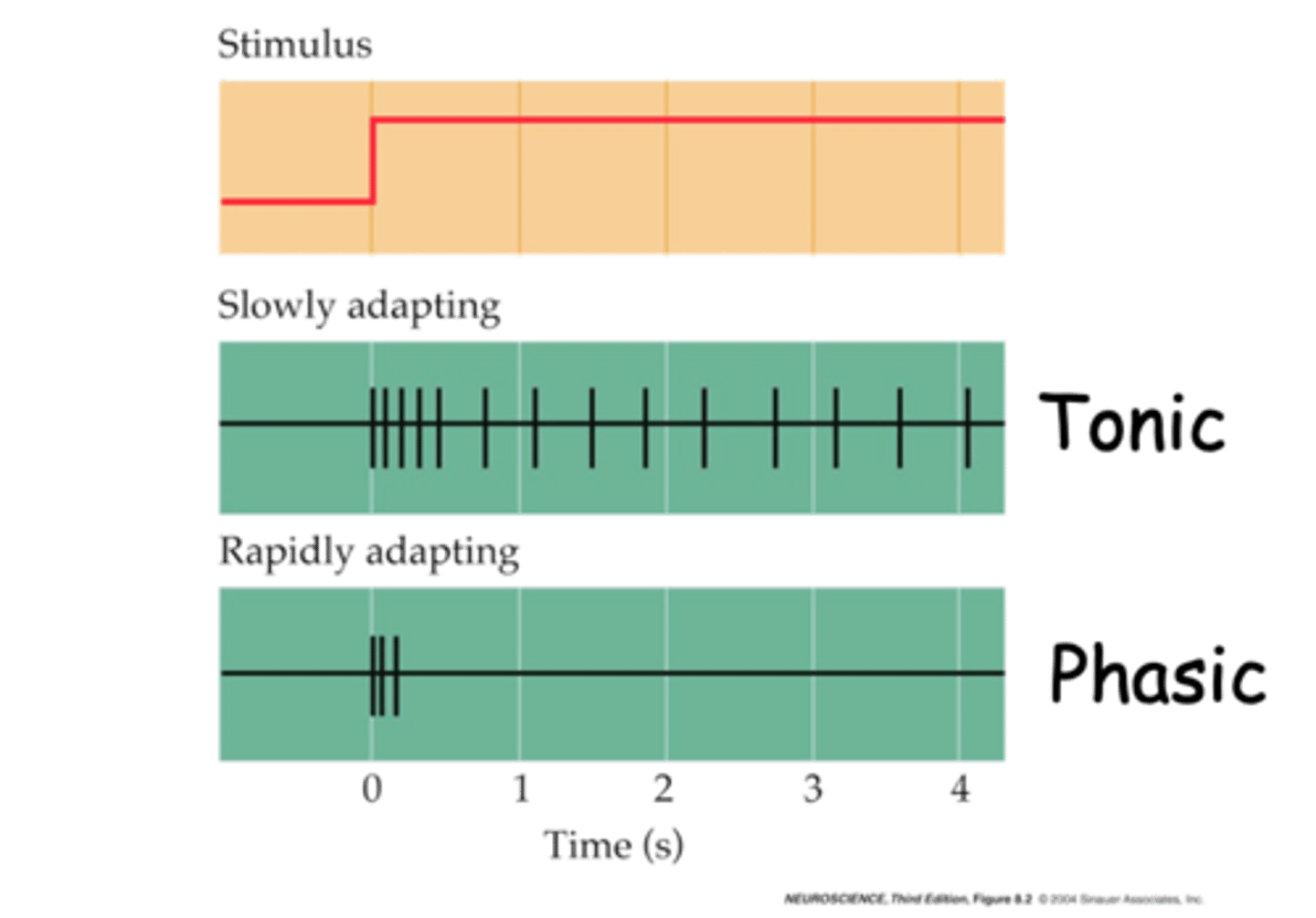
Slowly
Tonic mechanoreceptor responses are ___________ adapting
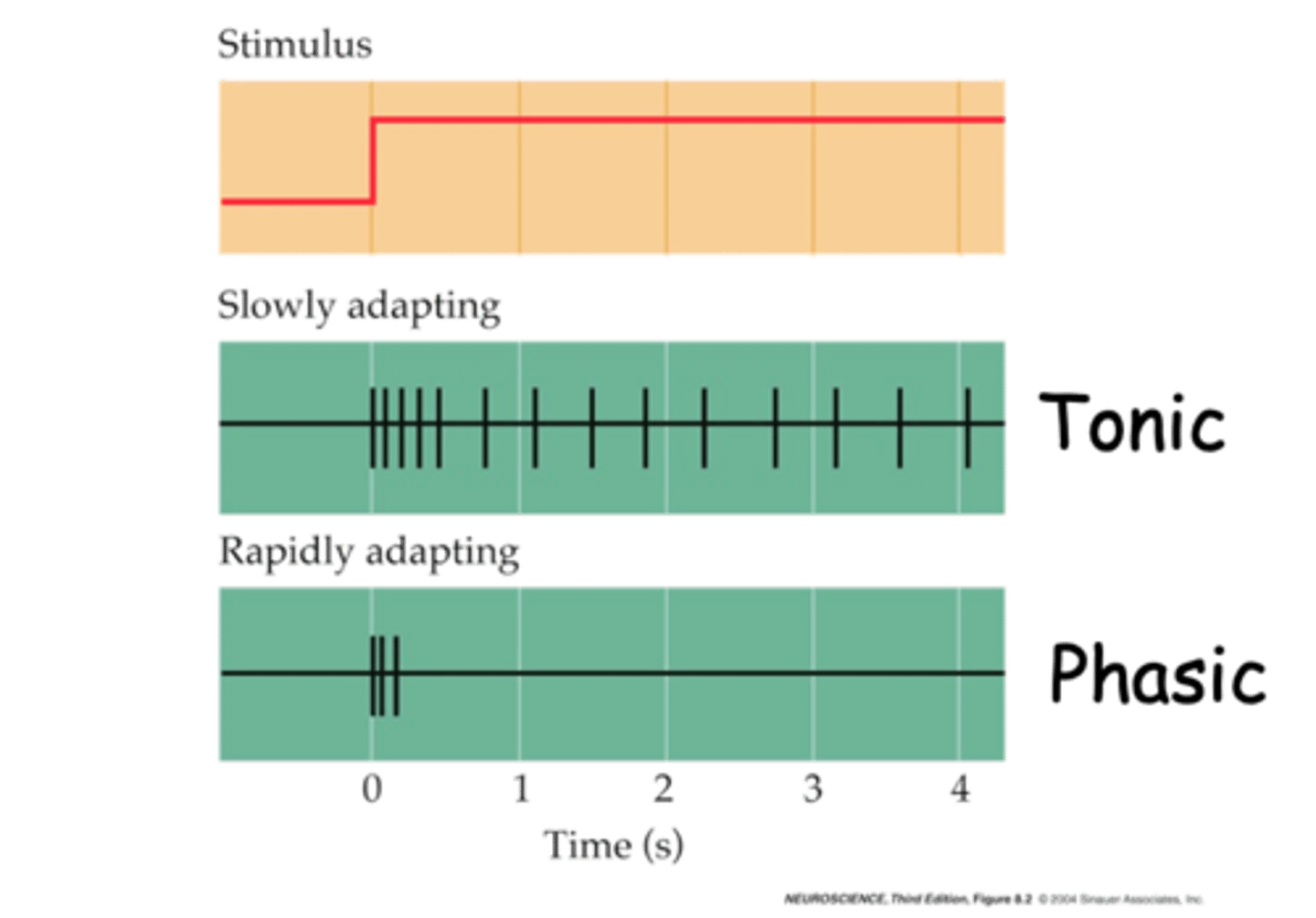
Changes, stimuli
Rapidly adapting or phasic receptors give information about __________ in the __________ e.g. Pacinian Corpuscles
Continue, stimulus, persistence, stimulus
Slowly adapting or tonic receptors, ___________ to respond as long as __________ is present (gives info about ______________ of ___________) e.g. Ruffini Corpuscles
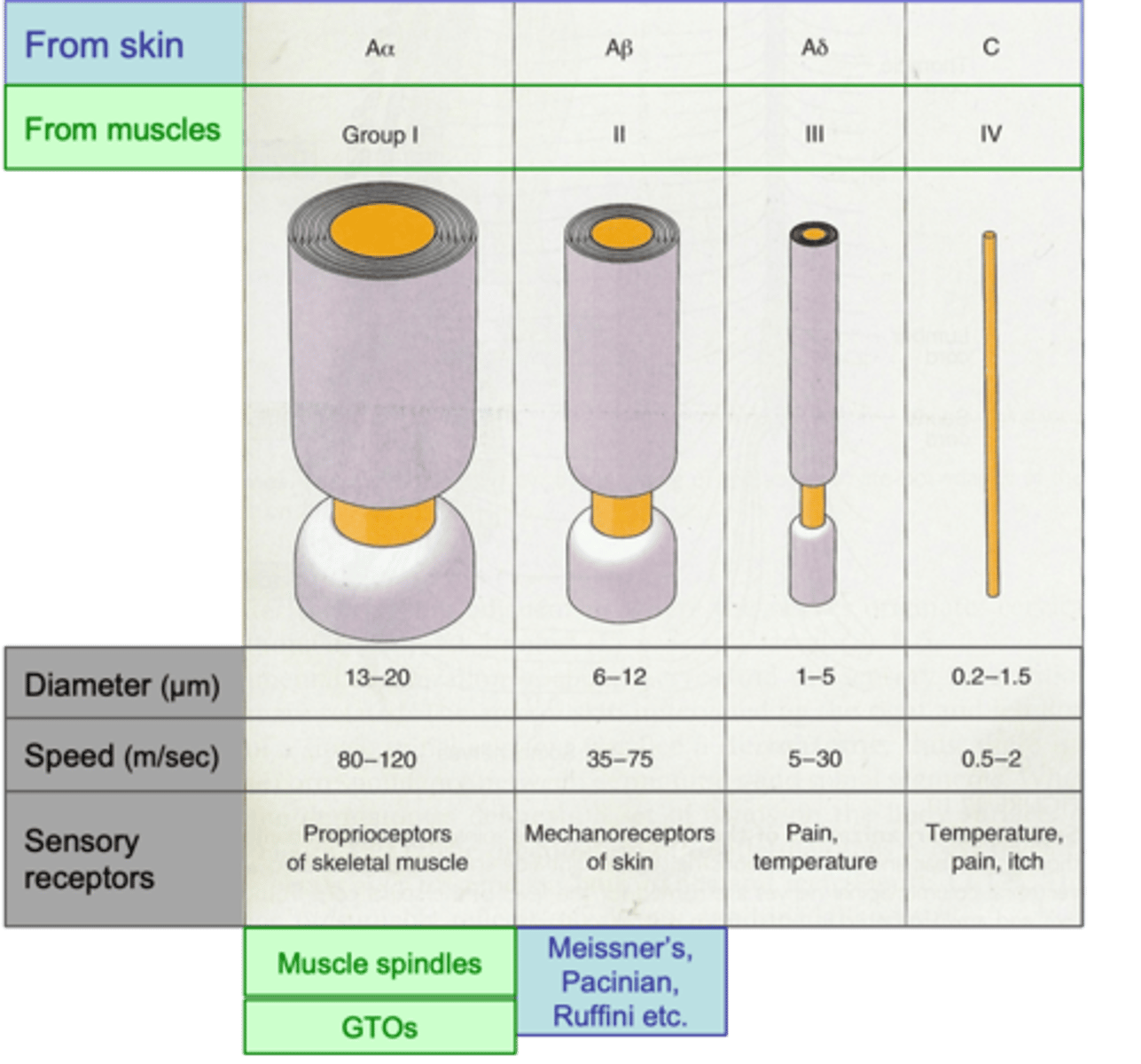
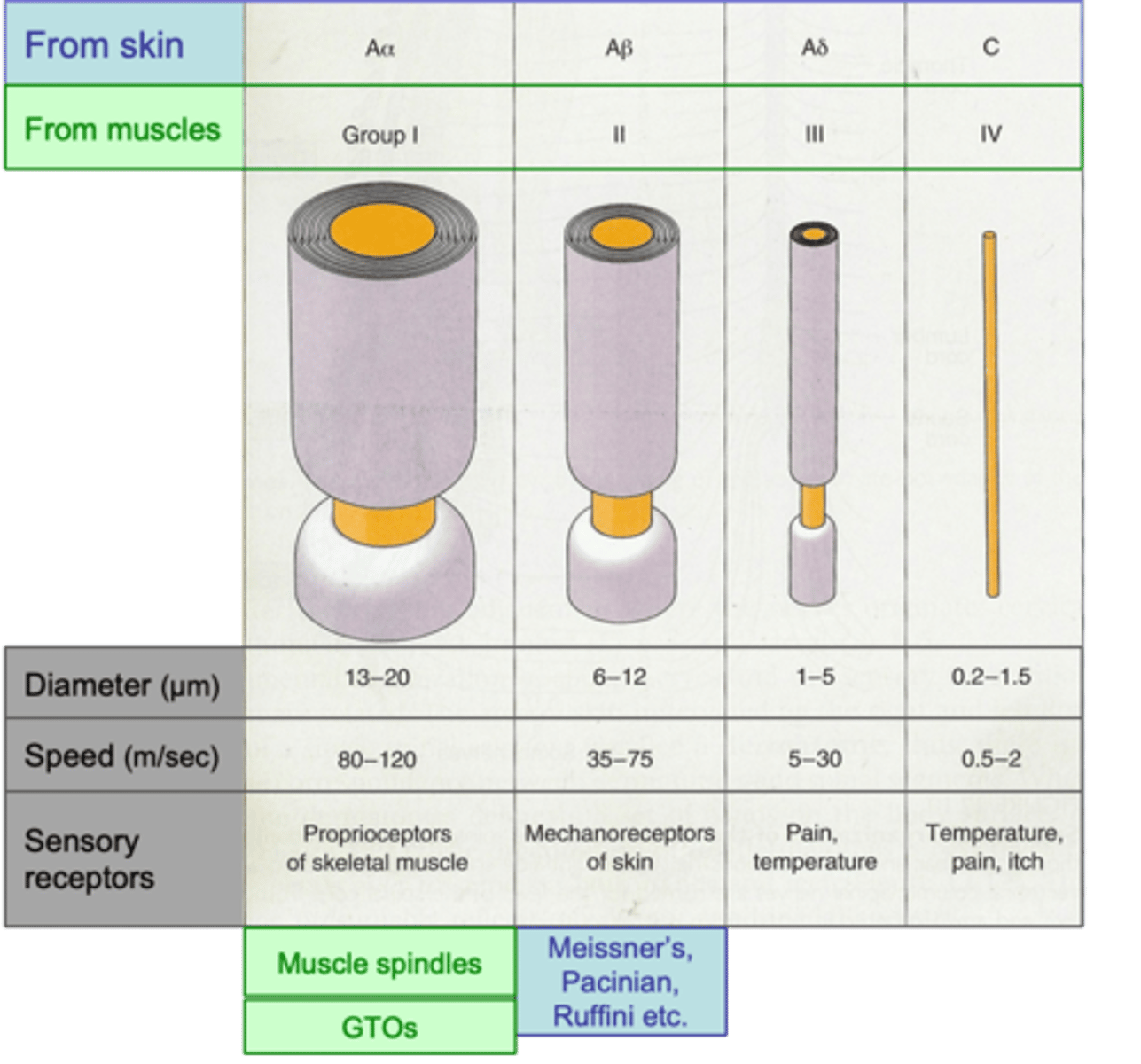
Conduction velocity, which broadly reflects diameter (faster = larger diameter)
Primary afferent axon subtypes are classified according to ...?
Skin
Axons coming from the ______ are designated by letters (A, B, C; A = fastest/largest; C = slowest/smallest)
The A group further broken down by Greek character (α, β, δ, α = fastest; δ = slowest)
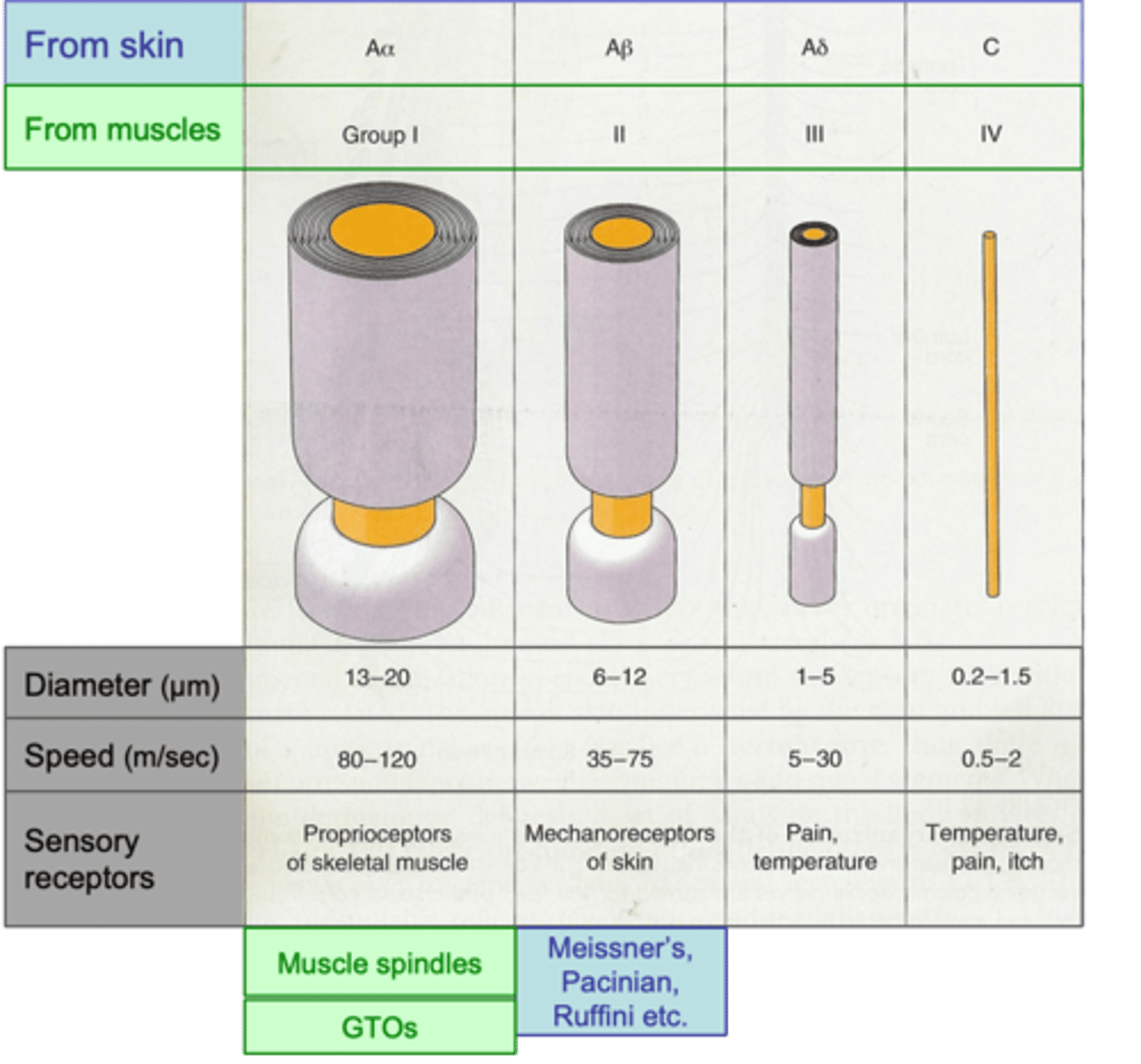
Muscles
Axons coming from the _____________ designated by Roman numerals: I, II, III and IV; I = largest, IV = smallest
Slower
Pain fibres are __________ than proprioceptors
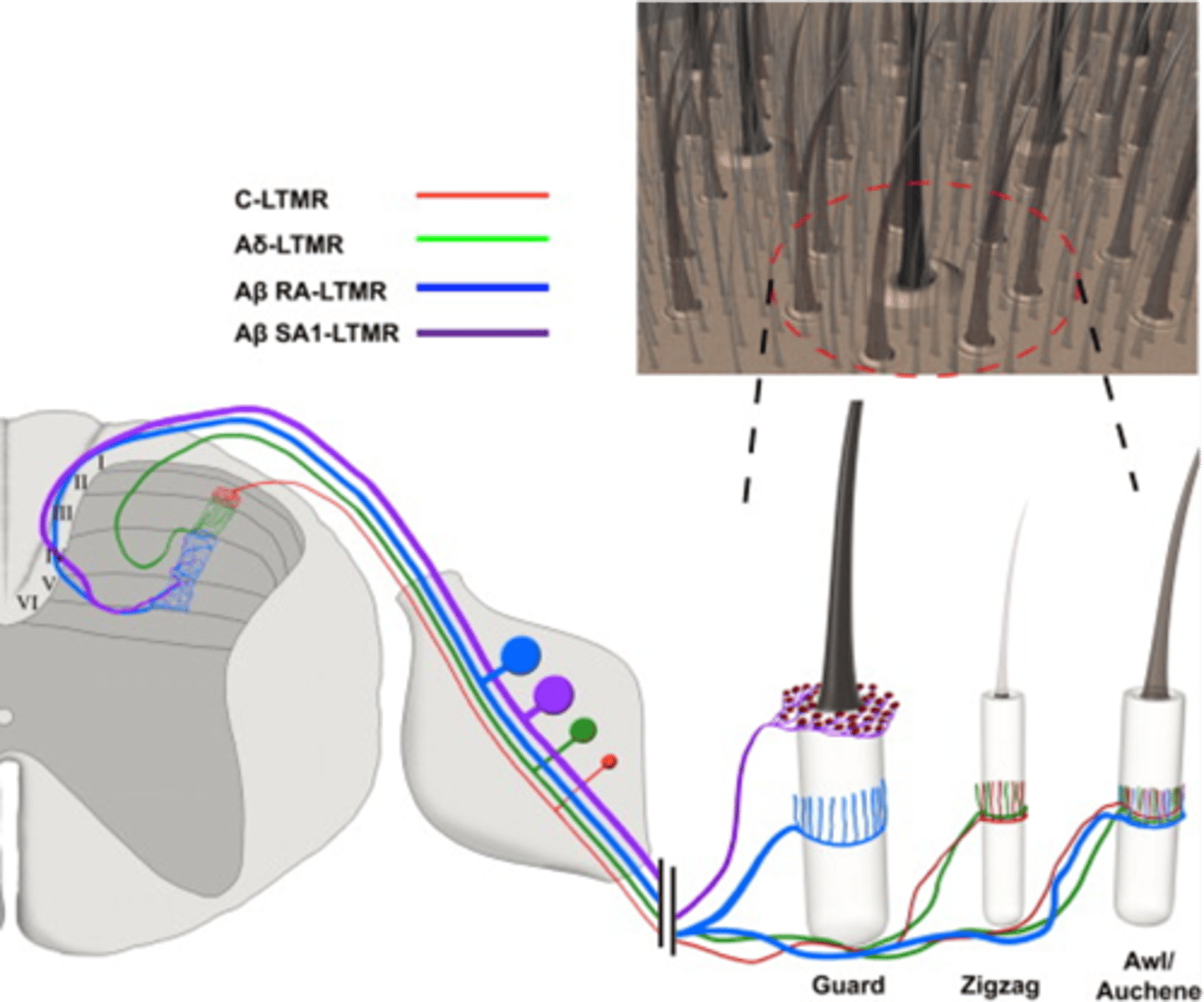
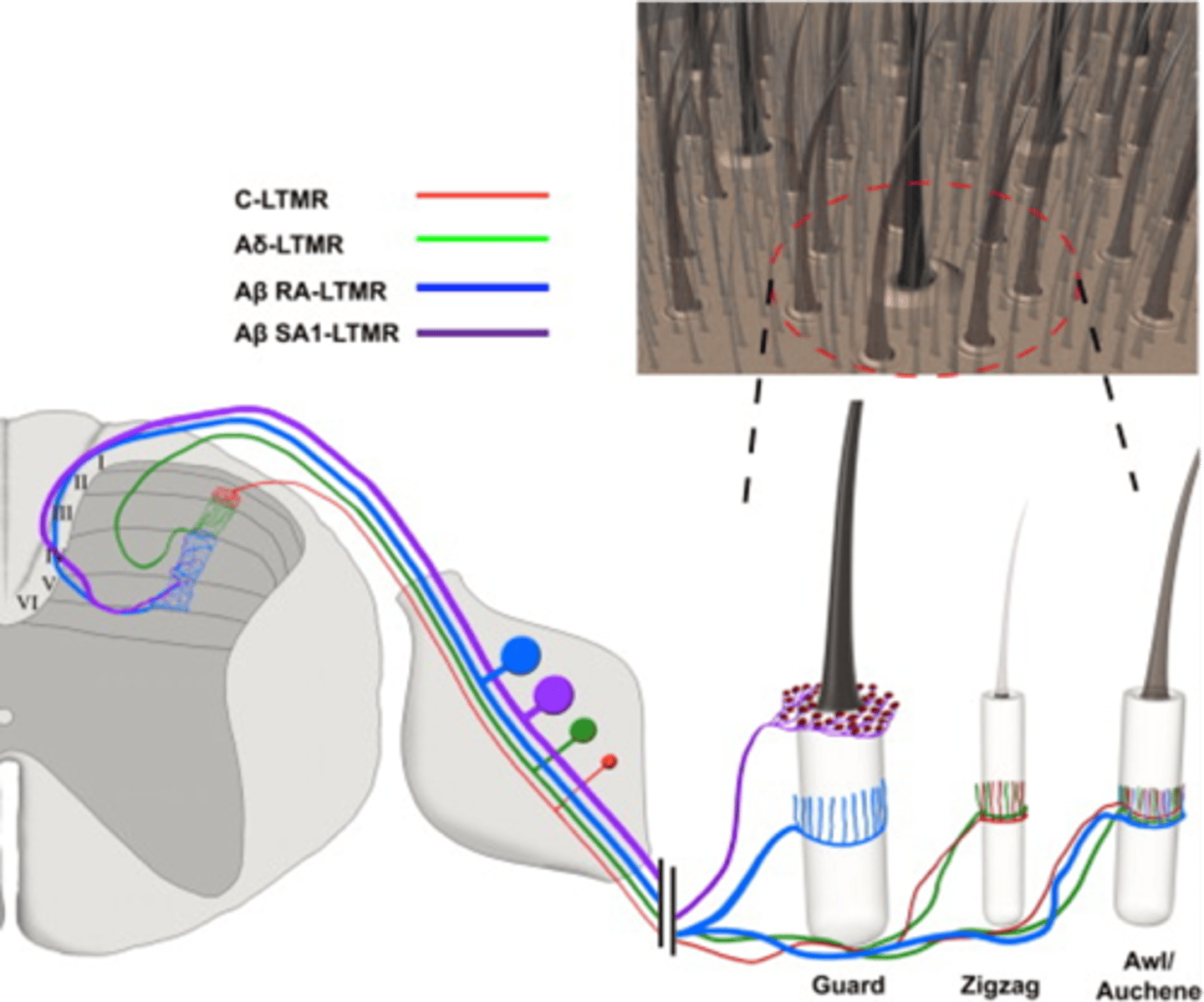
Into layers in the spinal cord dorsal horn
How is sensory information organised?
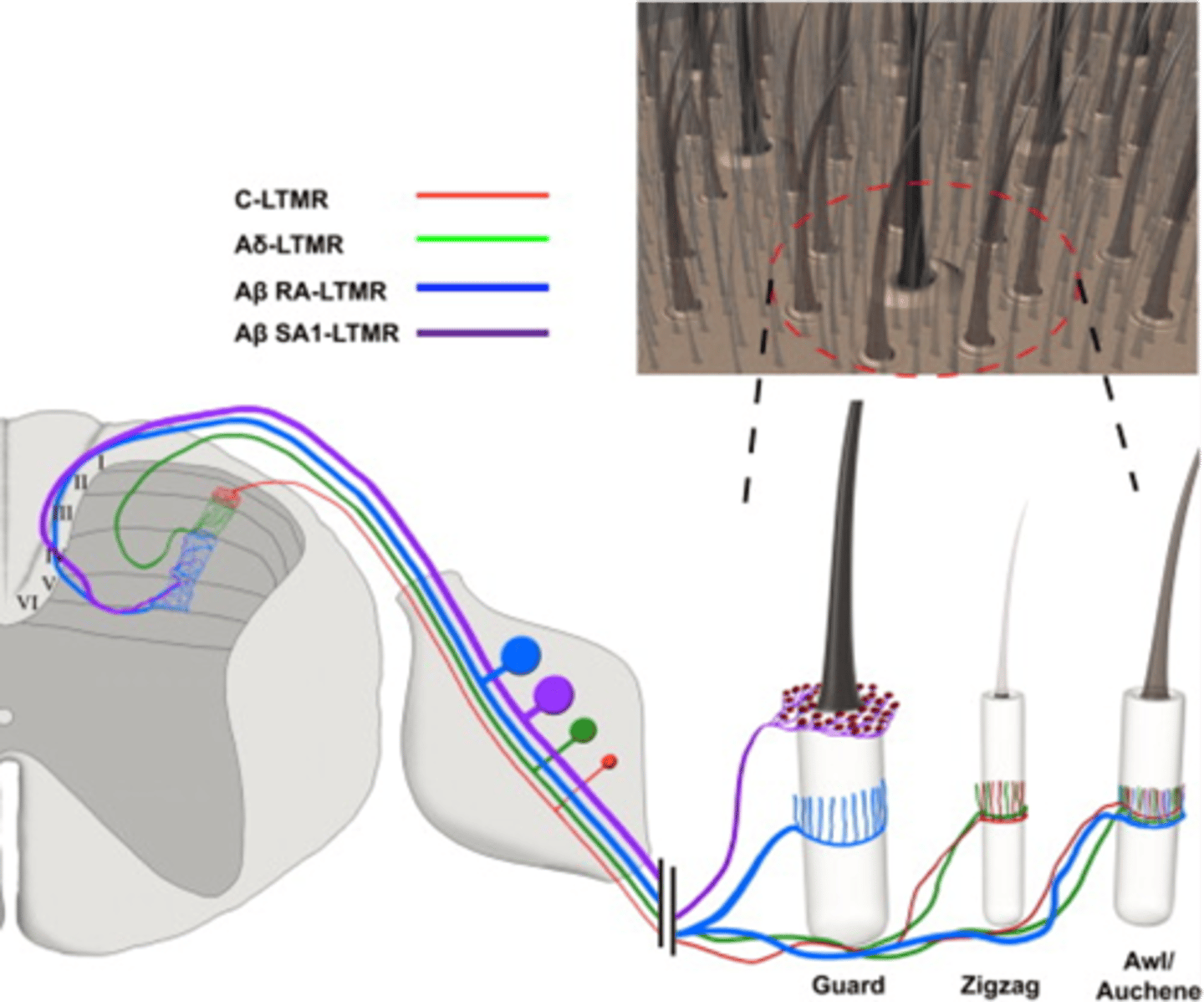
DRG, different layers
The cell bodies of different classes of sensory neuron are group in the ____ and their projections are organised to ______________ ________ of the dorsal horn
Sensory modalities
For example, information from different classes of hair follicle is represented in different layers
Note that this also applies to different ____________ ___________, e.g. pain vs touch
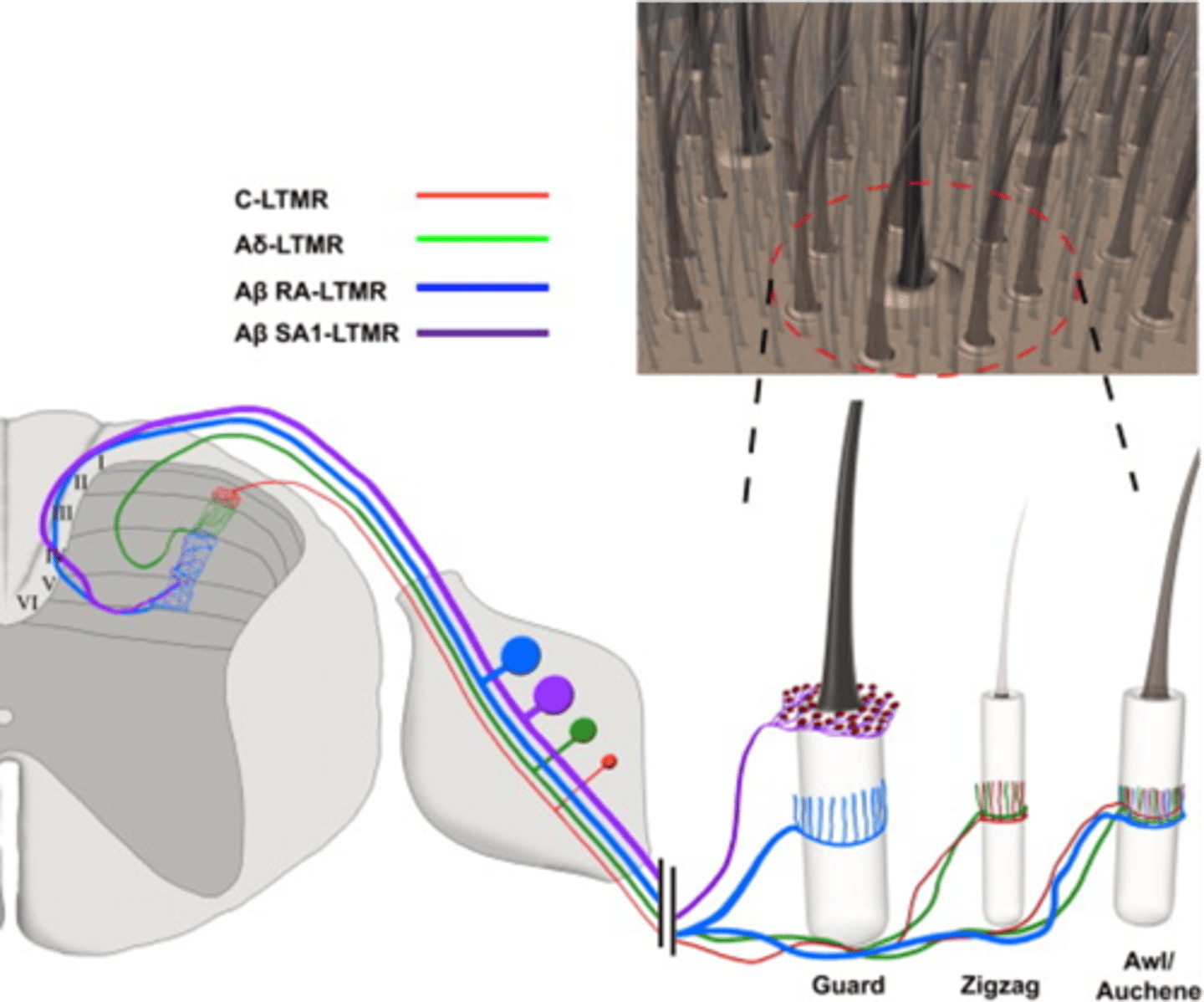
Carried, brain, pathways
Sensory information remains spatially organised as it is ____________ into the ________ by different ___________
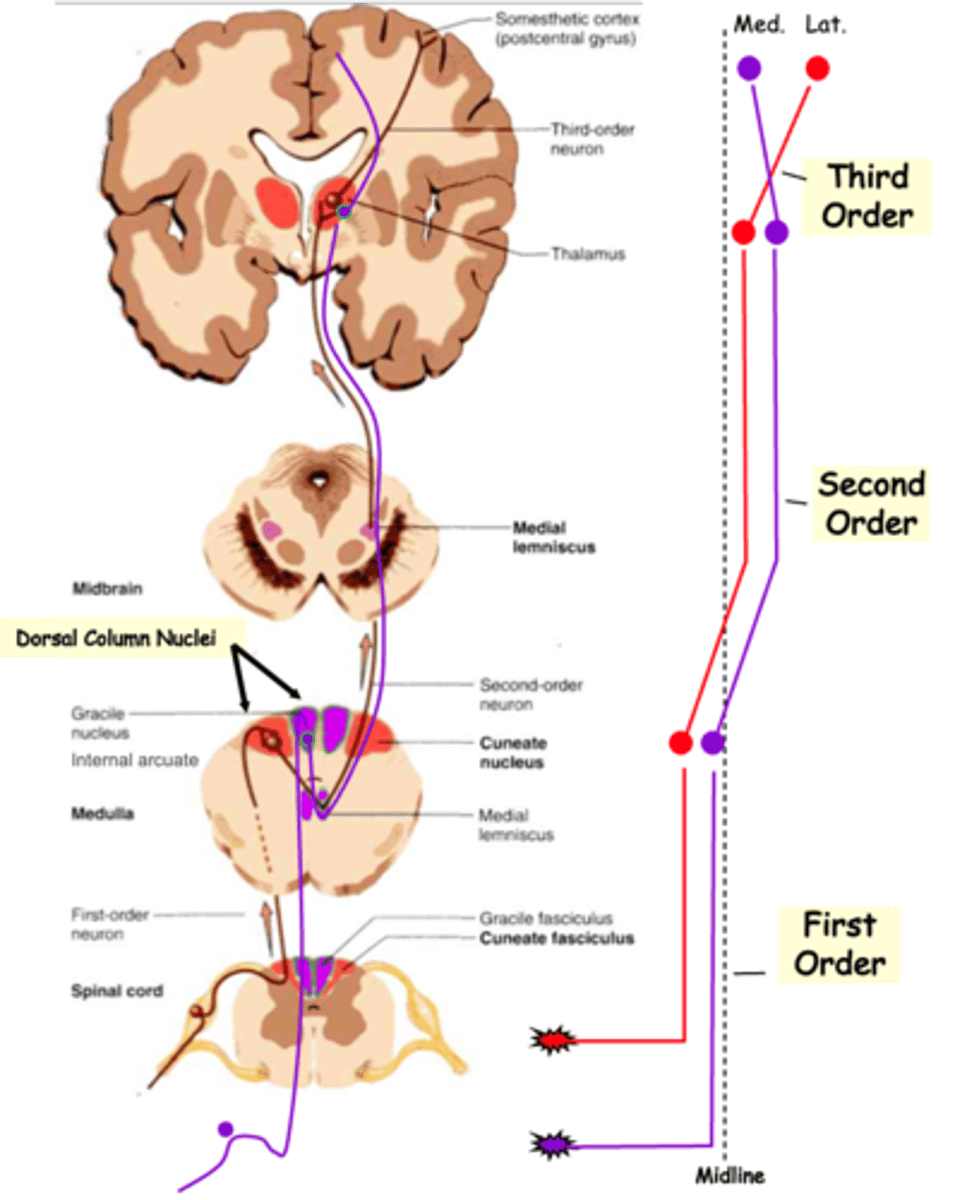
Medial Lemniscal tracts and Spinothalamic tract
The info from all these sensory subtypes gets to the brain via one of the two main routes, what are they?
Mechanoreceptive and proprioceptive signals to the thalamus
What does the medial lemniscal tract carry?
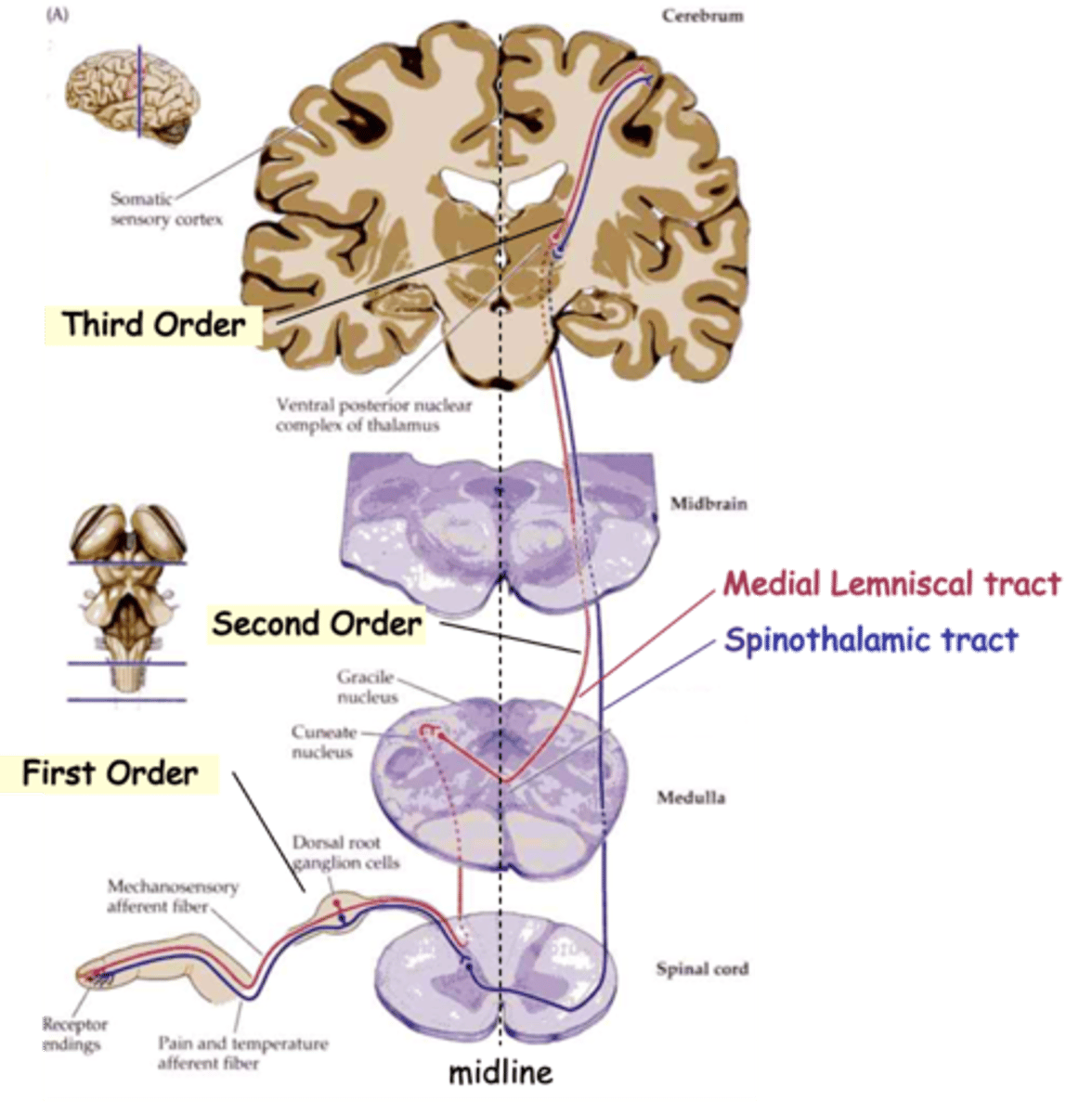
Pain and temperature signals to the thalamus
What does the spinothalamic tract carry?
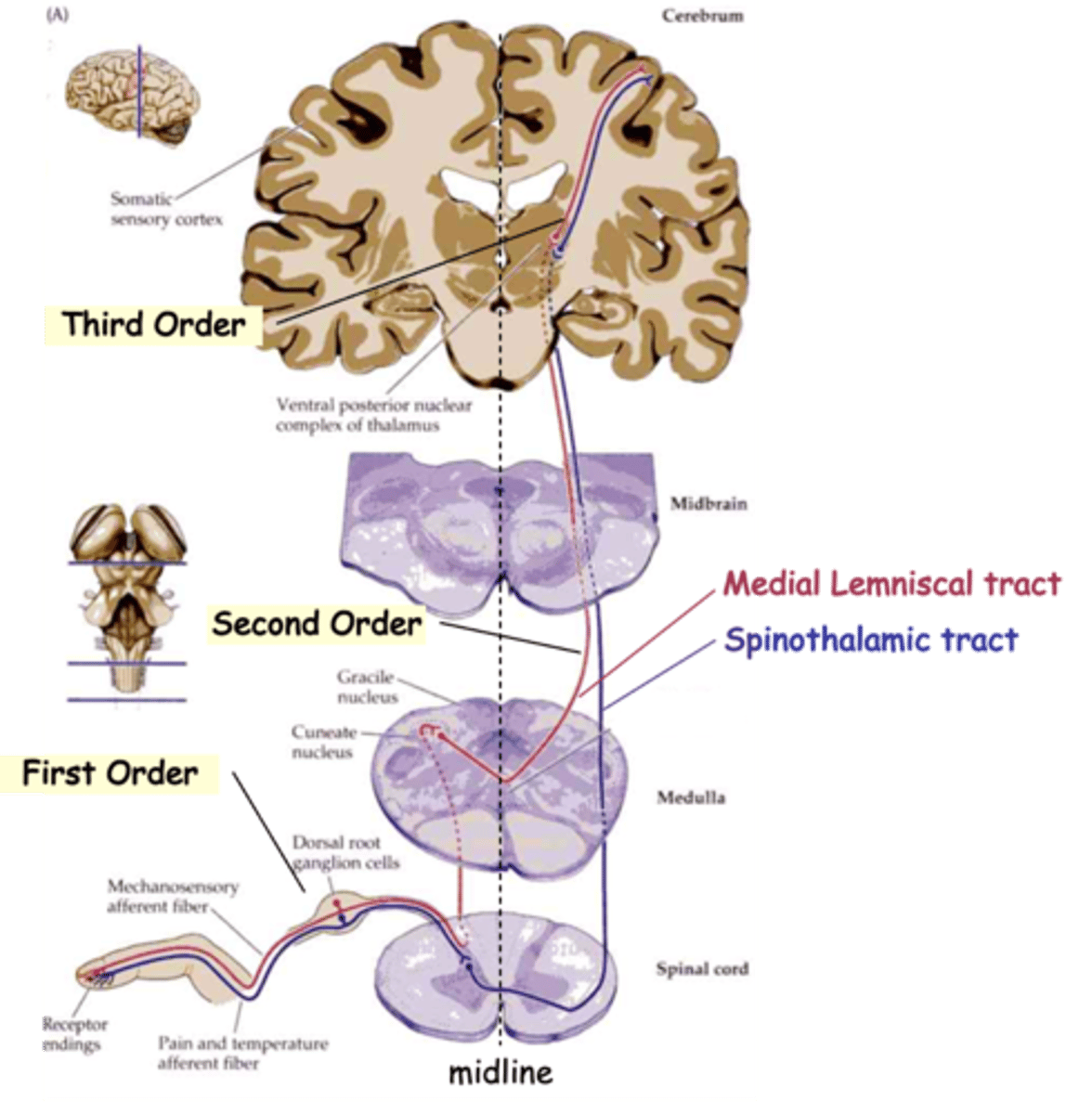
Detect the stimulus and transmit to spinal cord
Typically, sensory information travels through 3 neurons to reach higher centres, what do first-order neurons do?
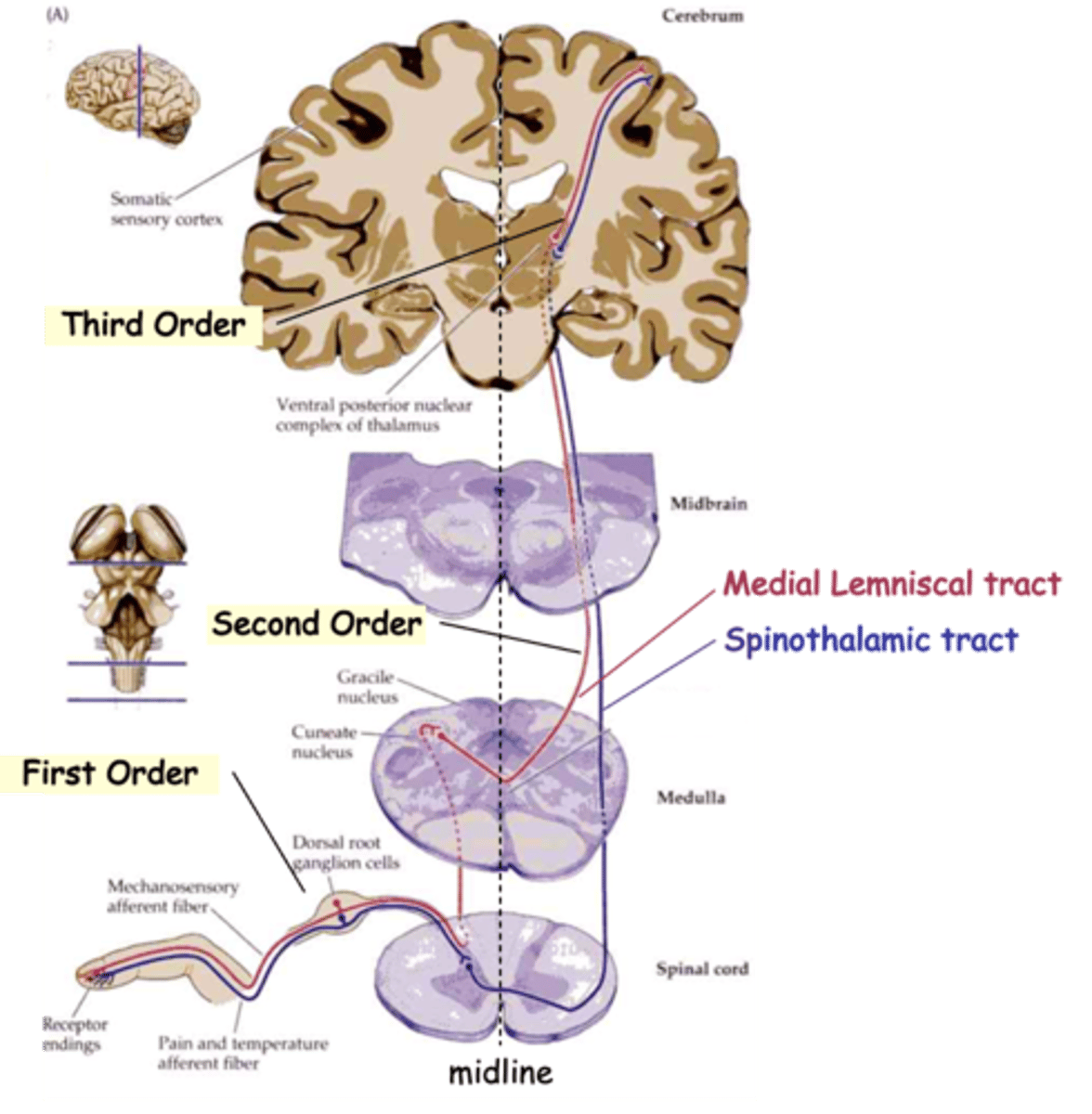
Relay the signal to the thalamus, the 'gateway' to the cortex
Typically, sensory information travels through 3 neurons to reach higher centres, what do second-order neurons do?
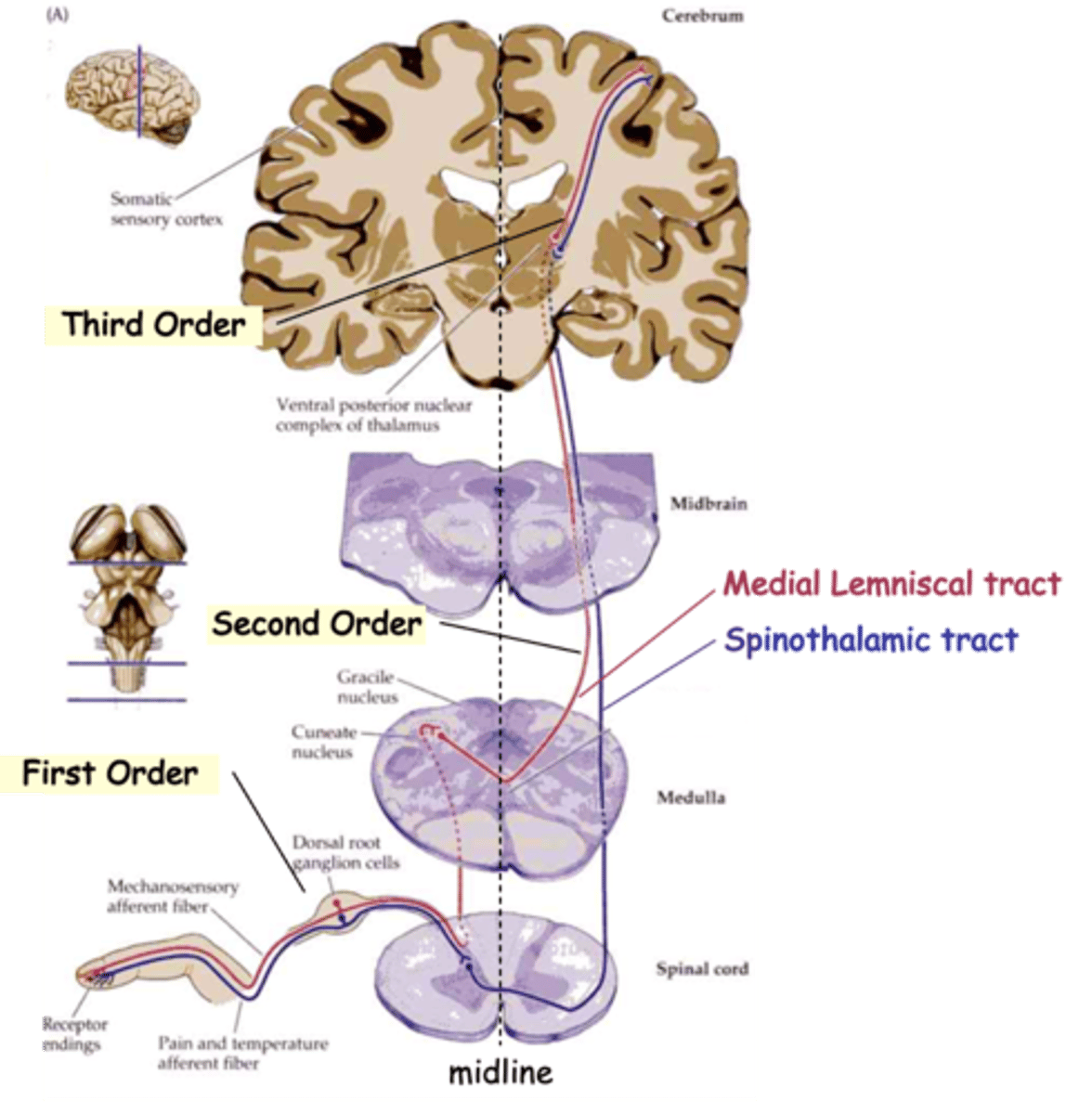
Carry the signal from the thalamus to the cortex
Typically, sensory information travels through 3 neurons to reach higher centres, what do third-order neurons do?
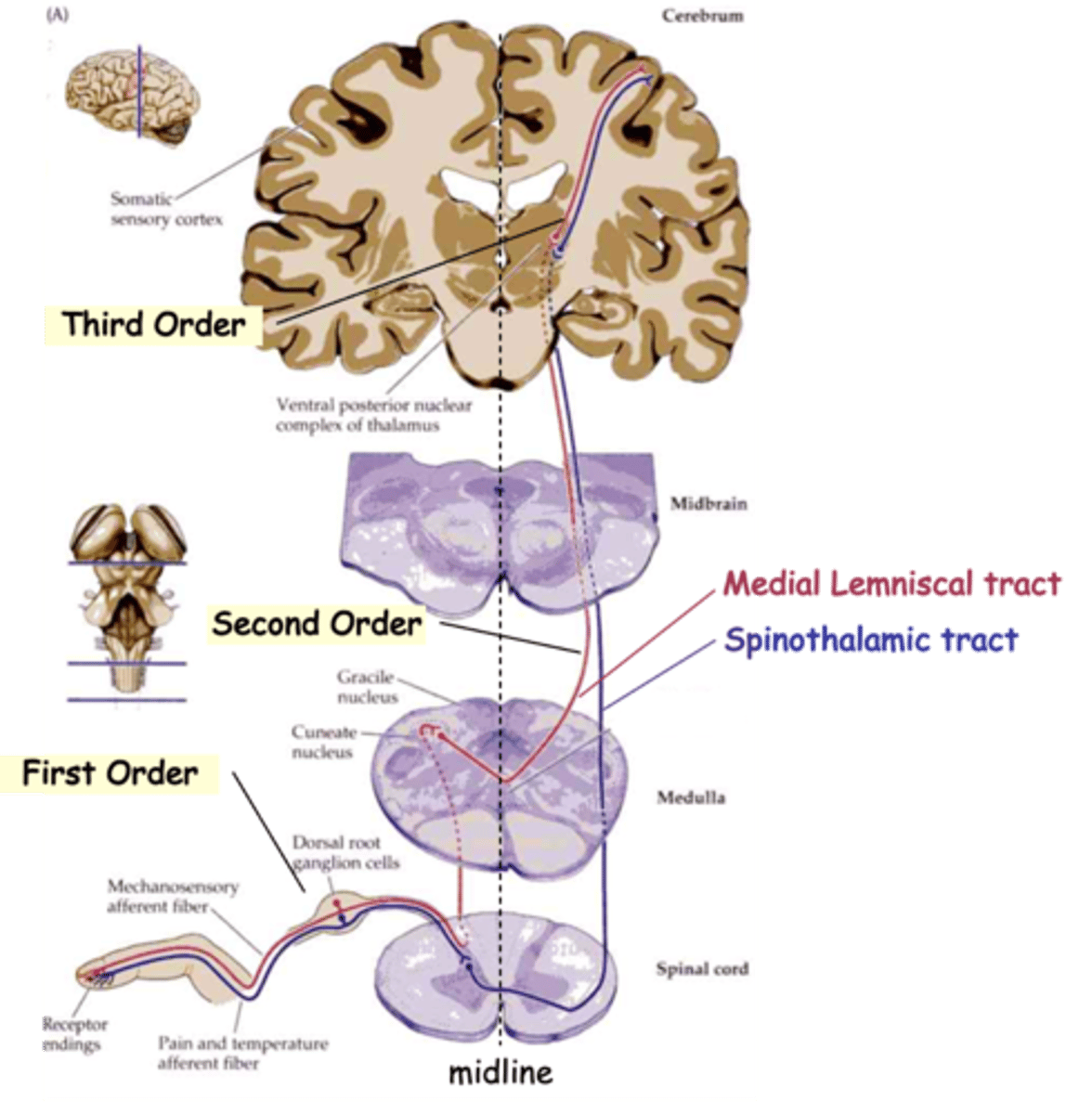
Commissural
In both cases, 2nd order axons cross the midline, i.e are __________________
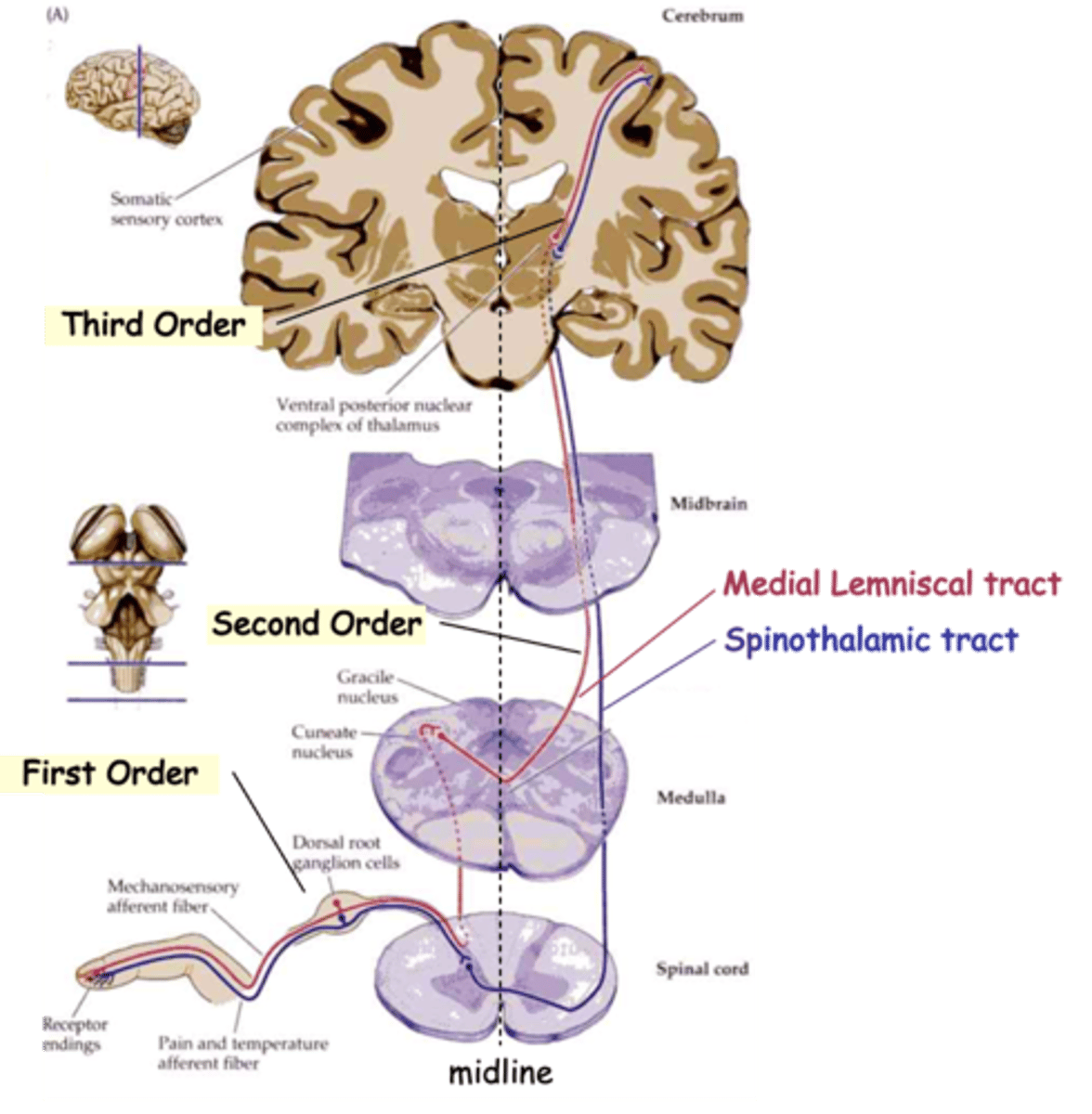
Topologically
Axons of the medial lemniscal pathway are ______________ organised
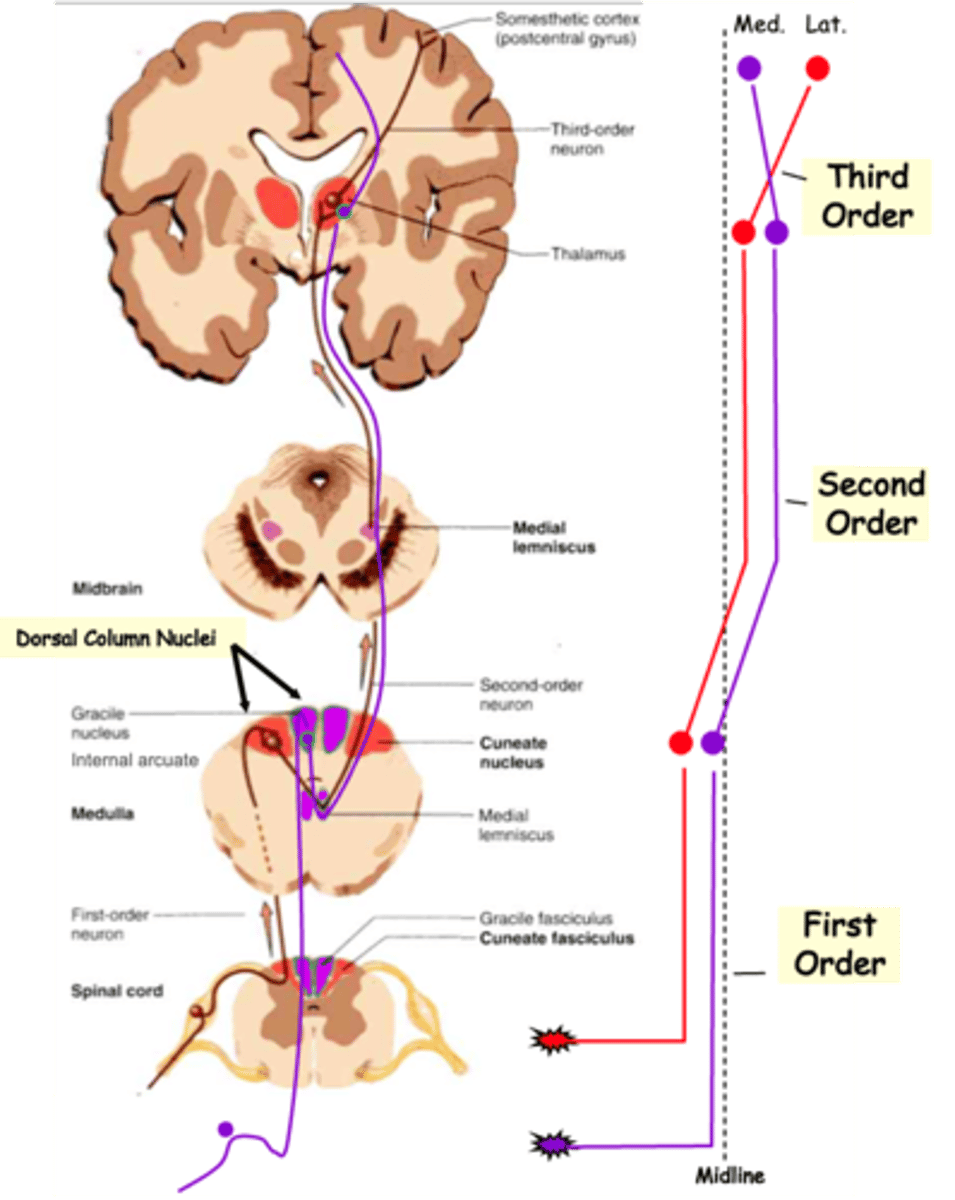
Upper, lateral, cuneate nucleus
1st order axons from the _______ body follow the __________ (red) pathway and synapse on 2nd order neurons in the ___________ __________
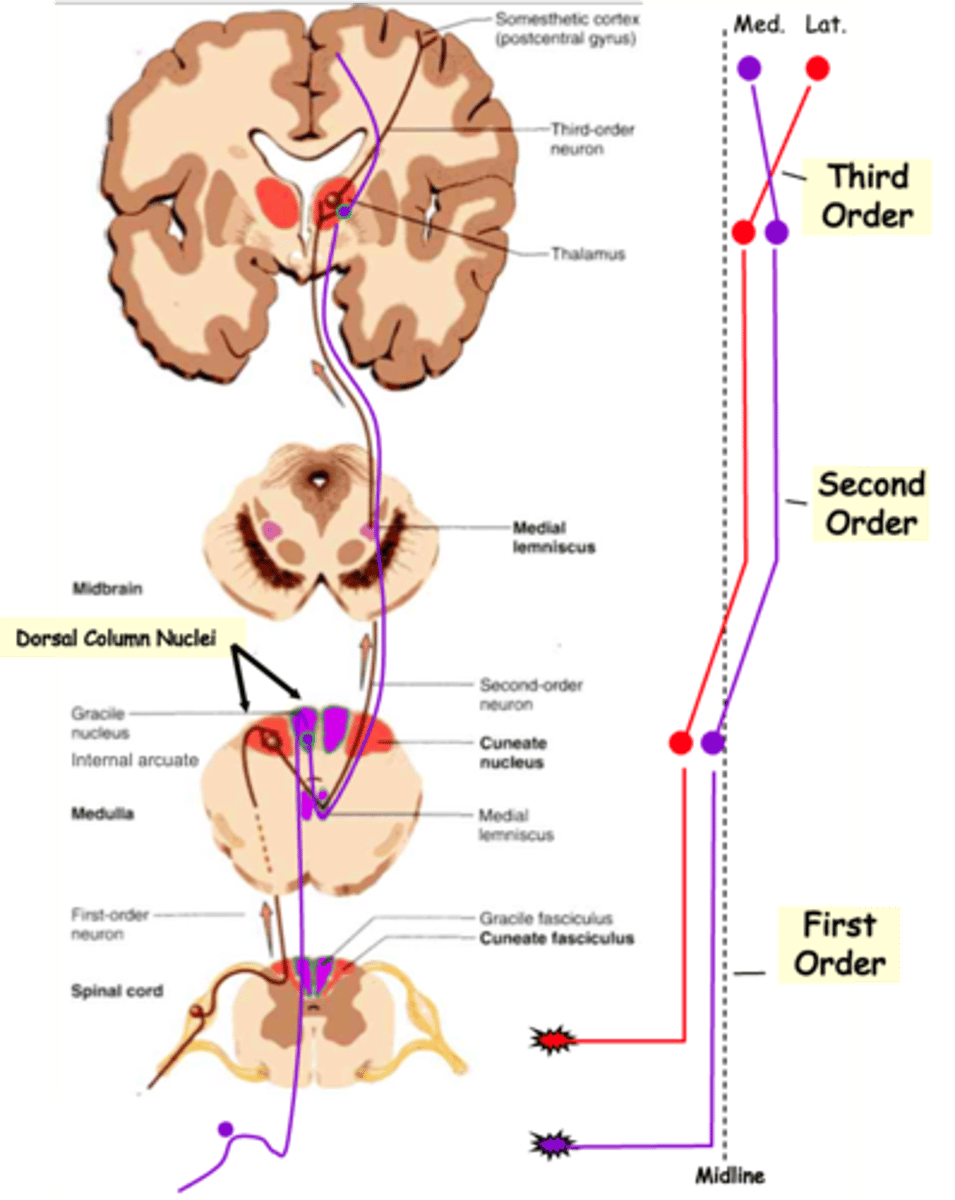
Lower, medial, gracile nucleus, dorsal column nuclei
1st order axons from the _______ body (below vertebra T6) follow the more _________ (purple) pathway and synapse on neurons in the __________ _________
Together these are known as the _________ __________ _________
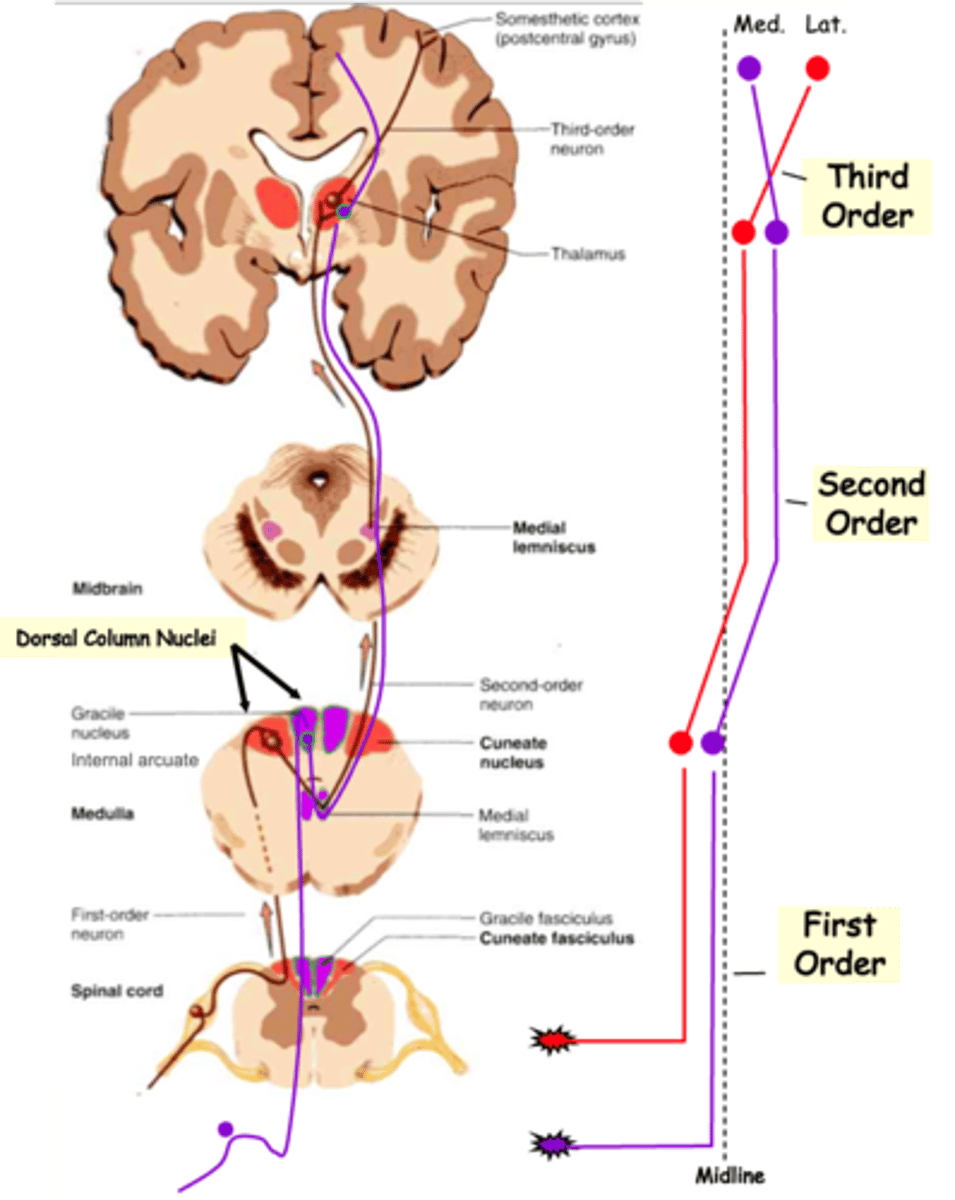
Medial lemniscus, reversed, lateral
2nd order axons cross the midline and ascend in the ___________ __________
In doing so their topology is ____________, relative to the midline, so that lower body axons are more __________ on reaching the thalamus
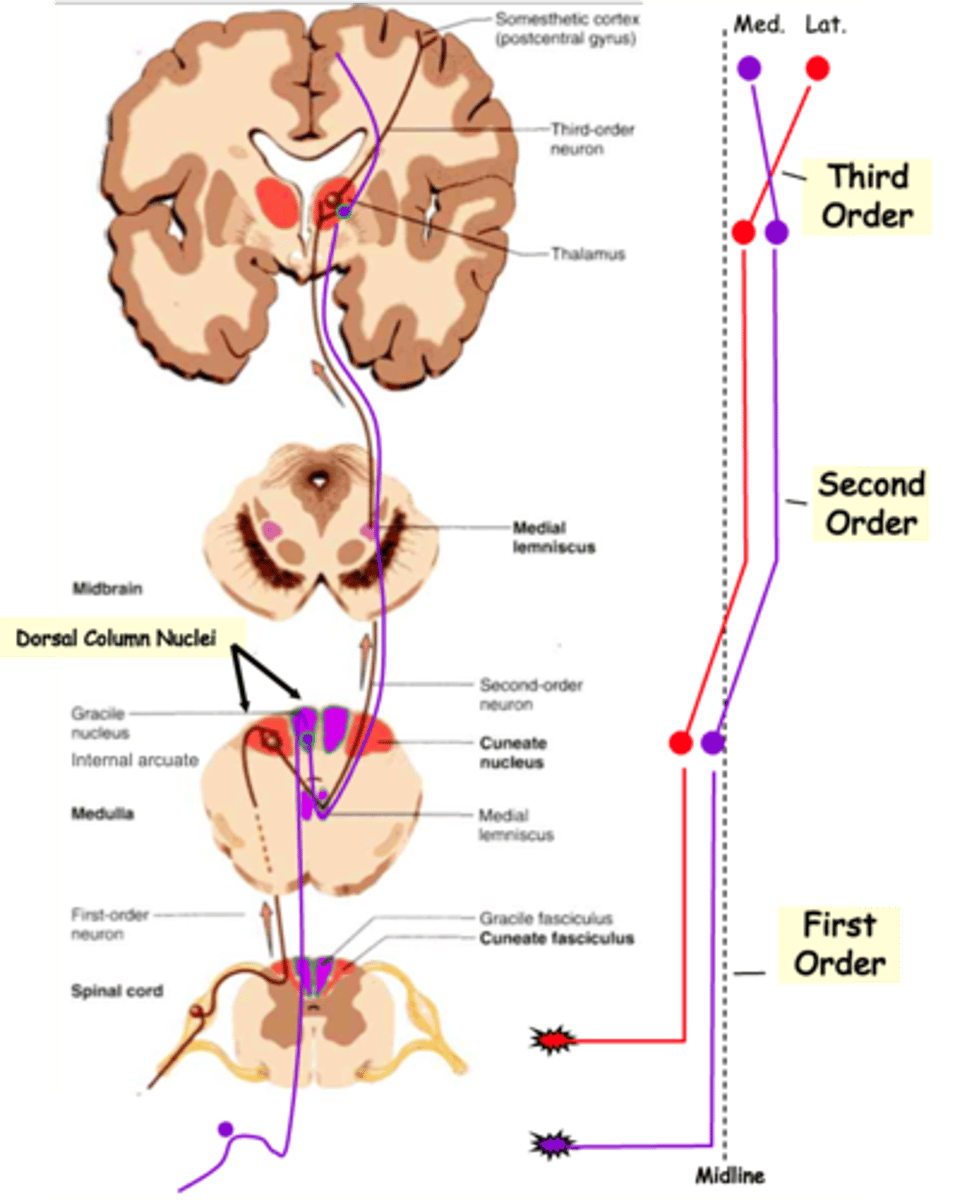
Medial, lateral
Finally, 3rd order axons again reverse the topology so that lower body axons synapse on more __________ cortical neurons, whereas upper body axons 'map' to the _________ cortex
The spatial arrangement of the objects relative to one another
What is topological organisation?
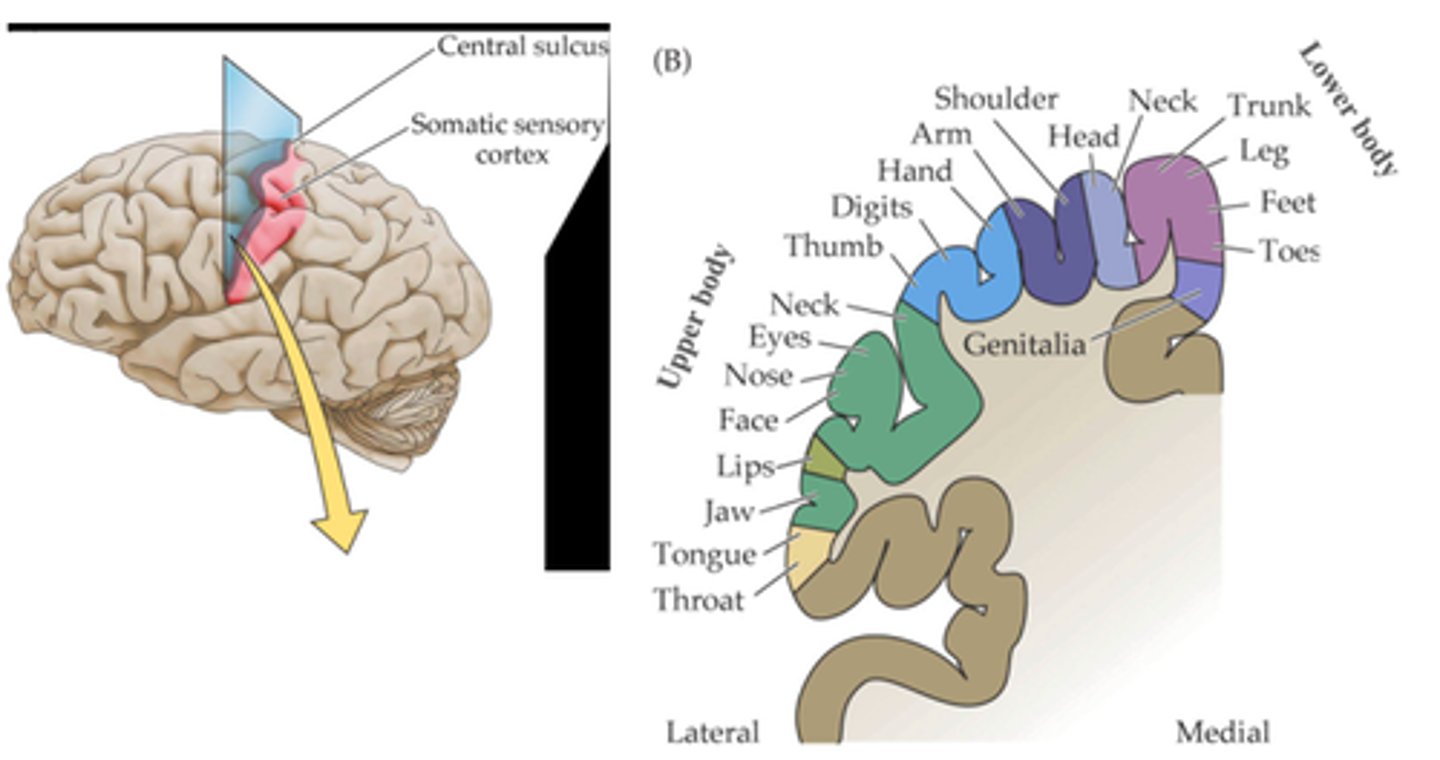
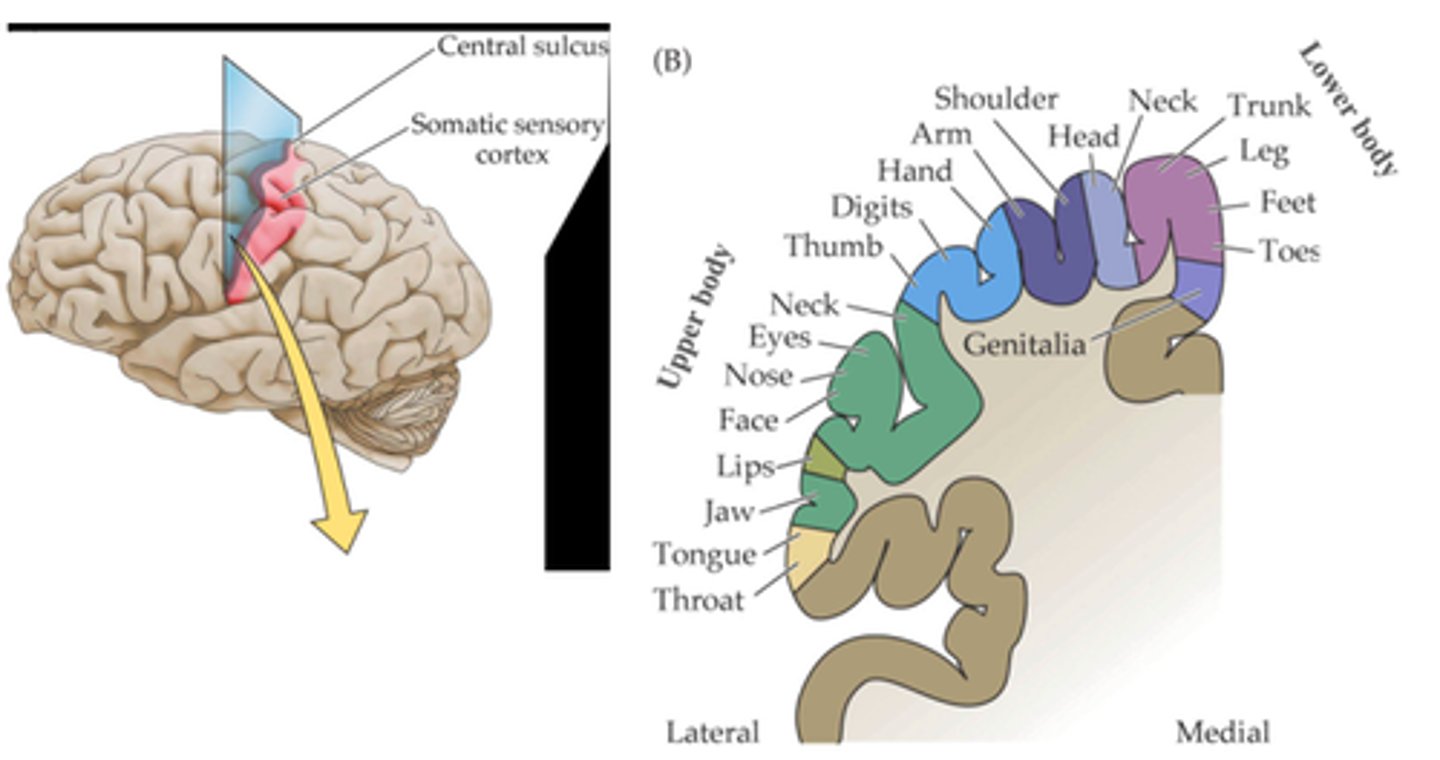
A map of the body in the cortex
What is the result of the topological projection?
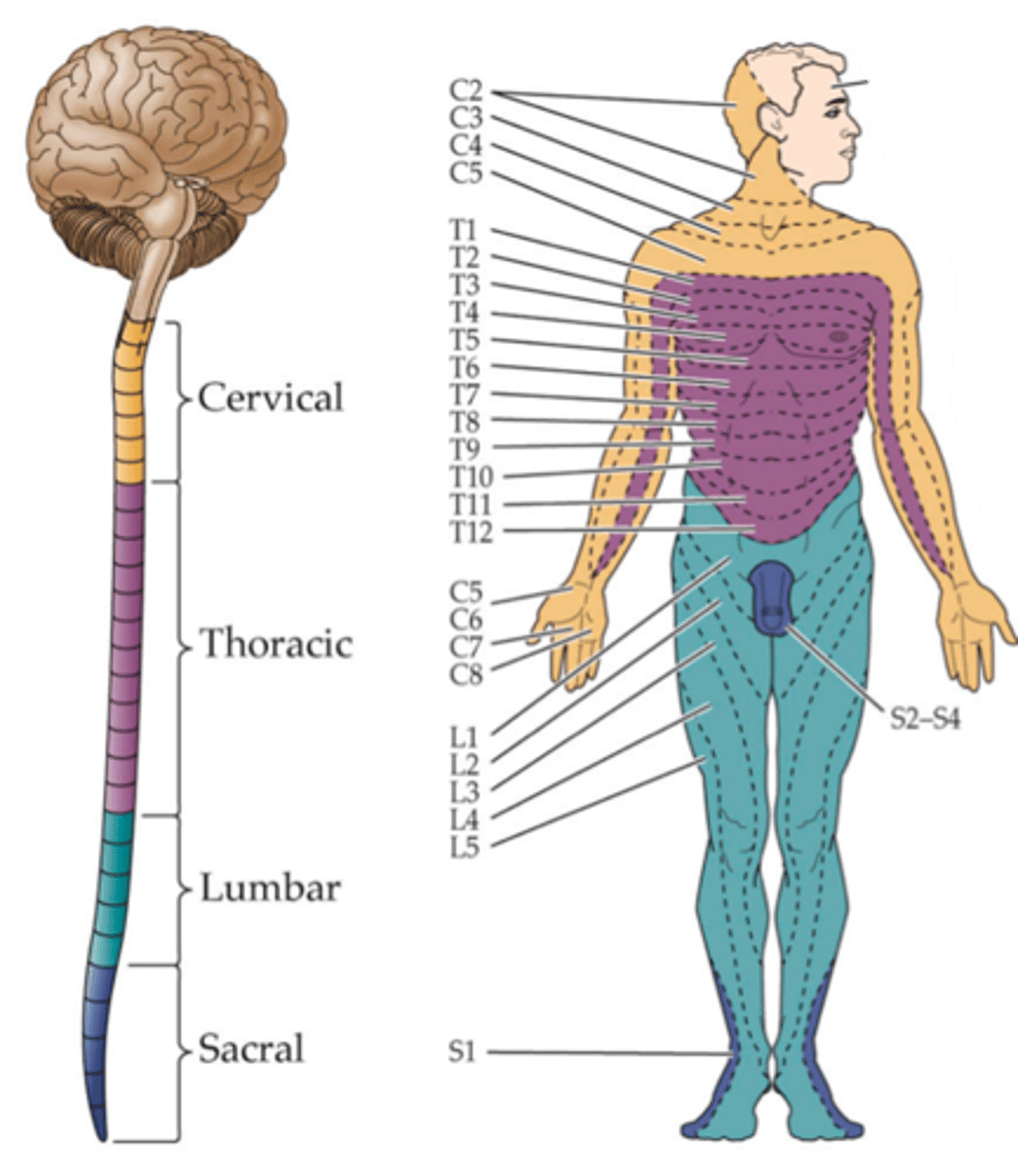
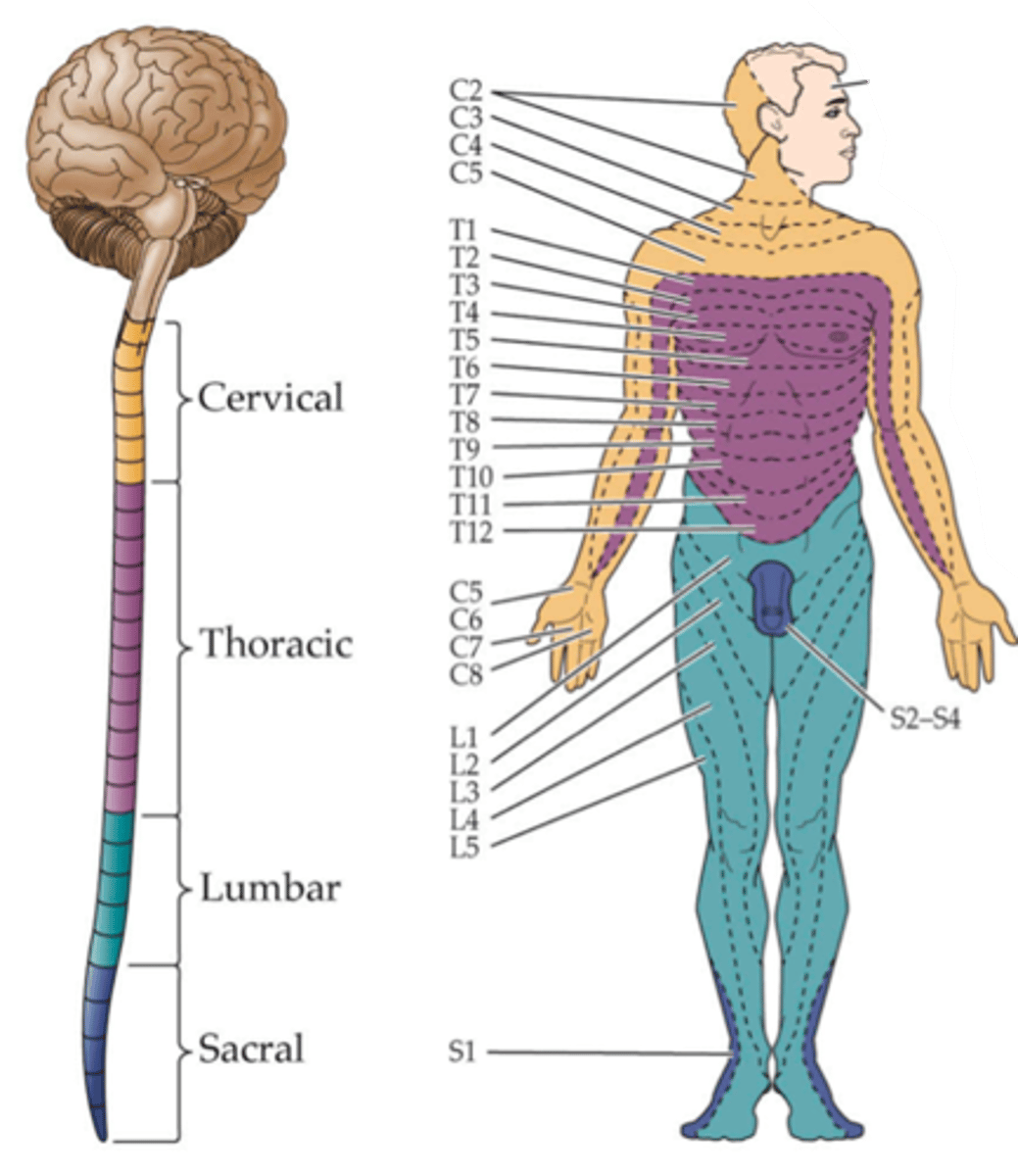
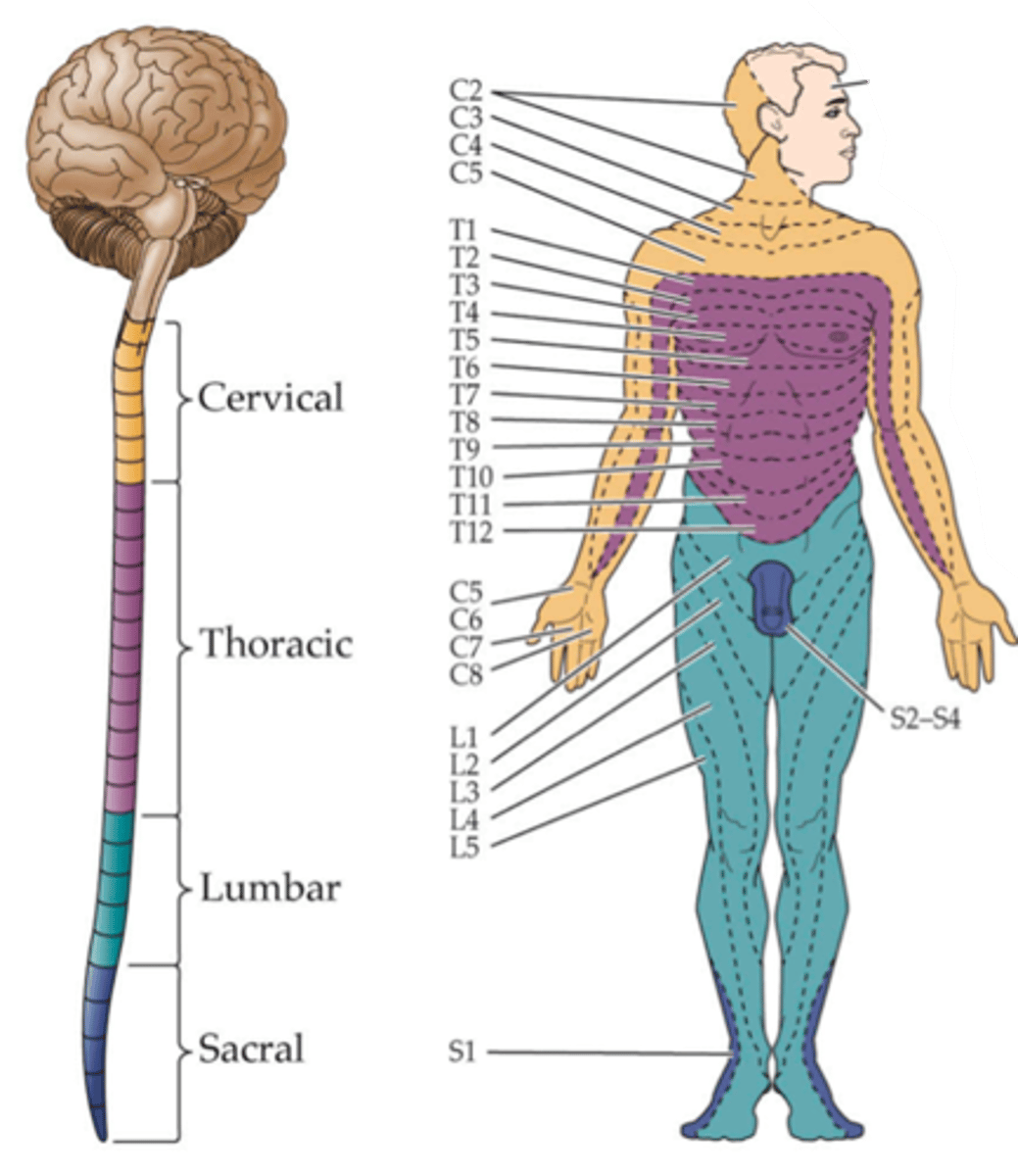
Innervates, dermatome
The map is very fine, not simply lower versus upper body and it reflects the fact that each DRG ____________ a specific domain of the body called a _______________
Dermatome
Each sensory ganglion innervates a specific region of skin called a ...?
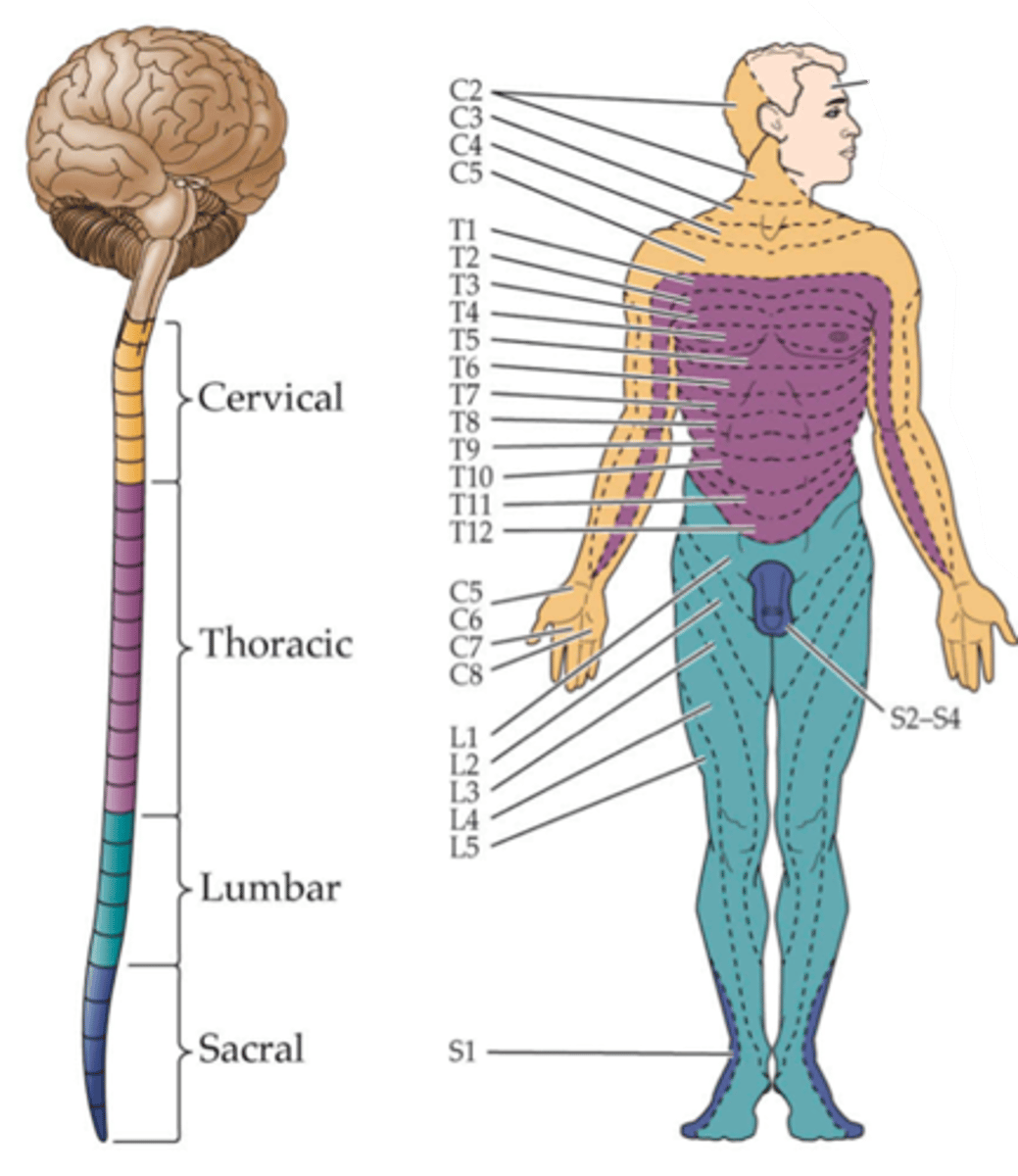
Because the dermis of each region is derived from a specific embryonic structure called the somite
Why do these dermatome regions arise?
Iterated structures that give rise to the underlying musculature and skeleton
What are somites and what do they do?
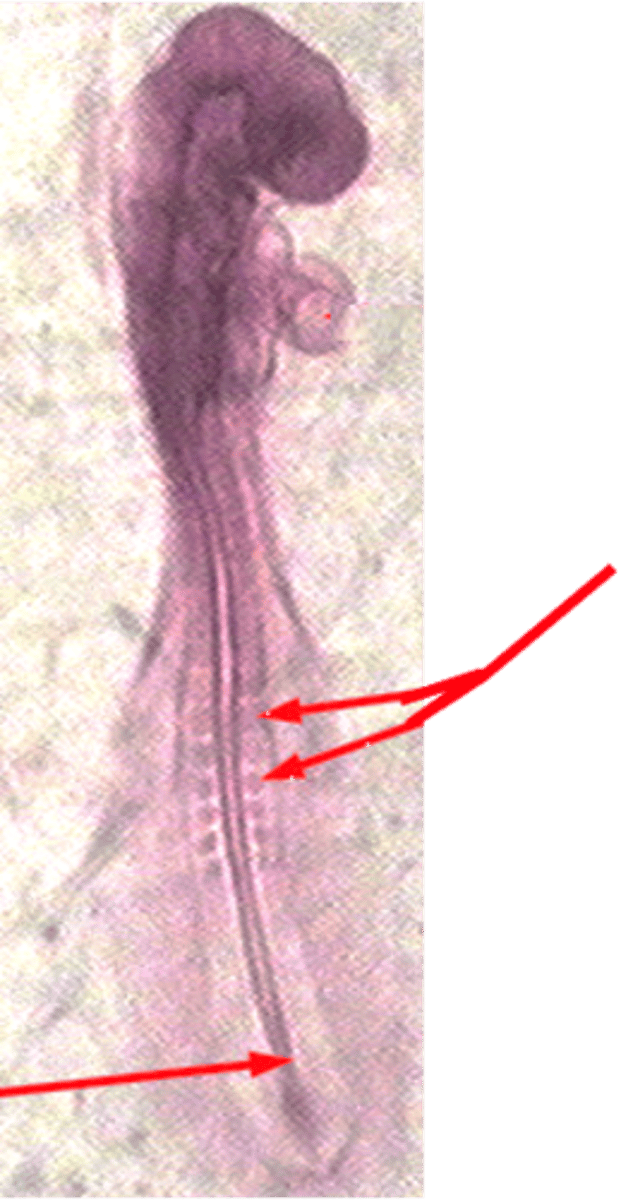
Somite, tissues
In the embryo, each sensory ganglion (DRG) is associated with a specific __________ and subsequently innervates the _________ arising from it
Spinal cord, somatosensory projections
This topological organisation is preserved in the ________ ______ and the ________________ ___________
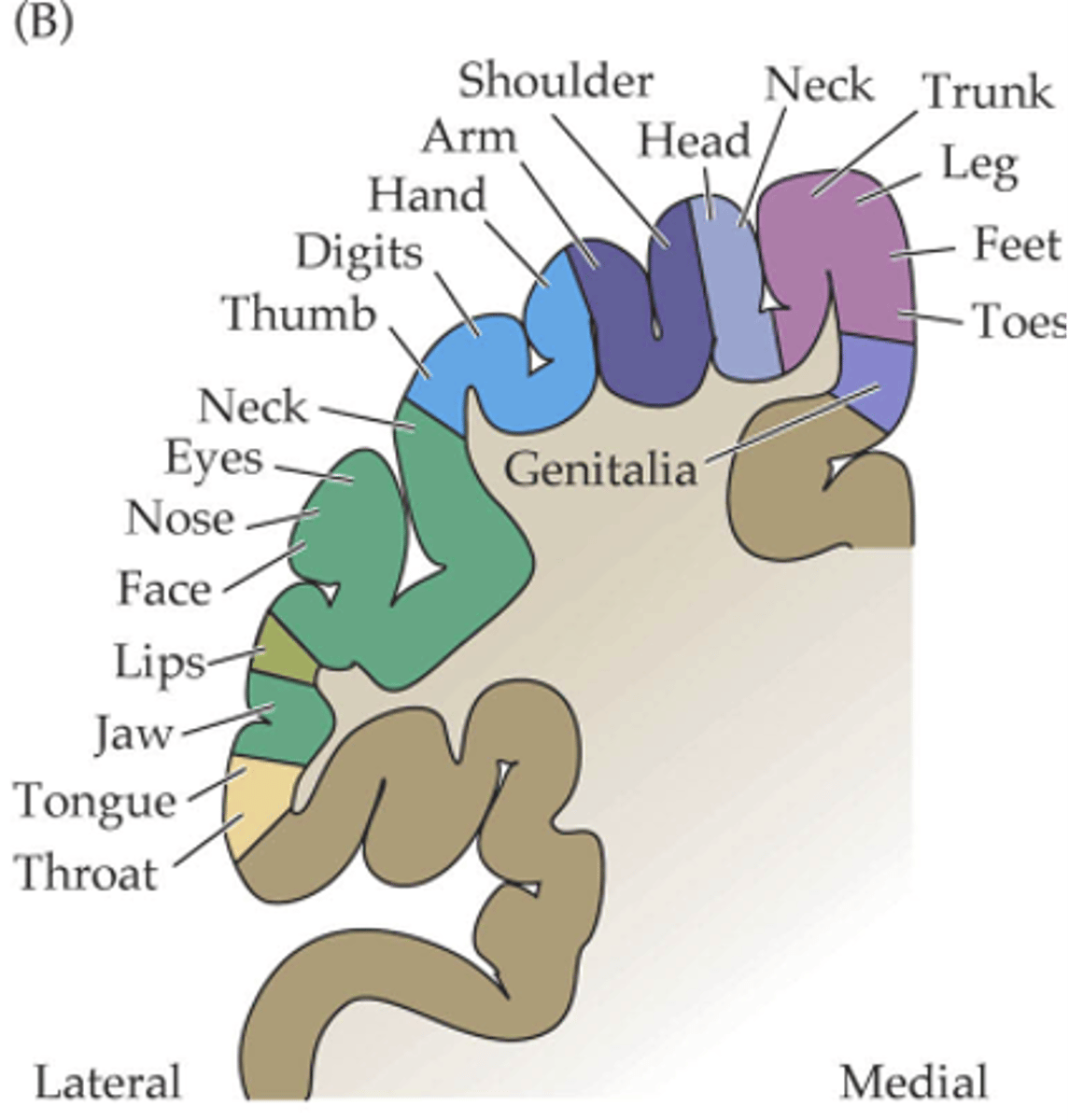
Not proportional
The area occupied by the different regions in the cortex is _____ _______________ to their physical size
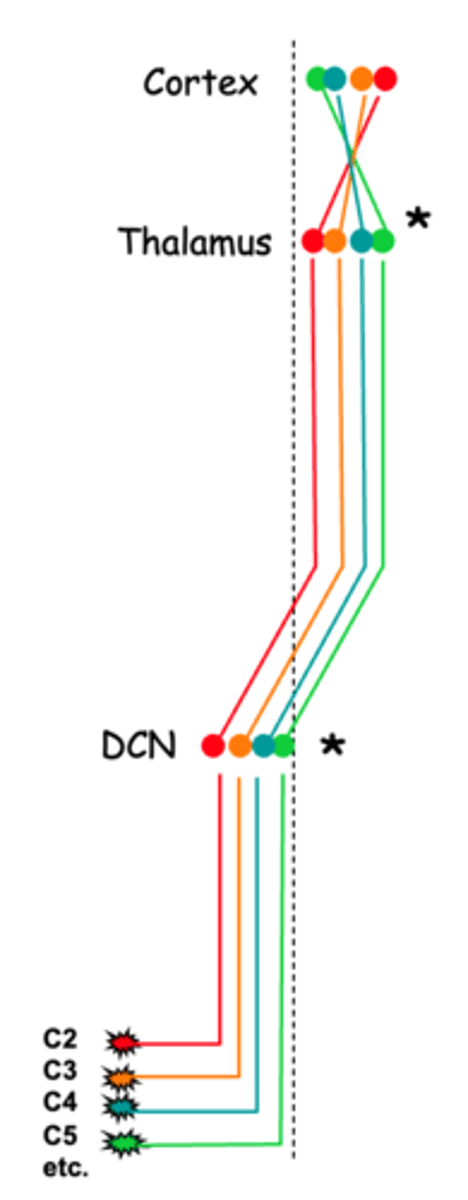
Thalamus, 2nd, 3rd, dorsal column nuclei
Logically, there must also be a map in the __________, the 'way station', between the ____ and ___ order neurons, and in the __________ __________ __________
The way in which constituent parts are interrelated or arranged
What is meant by topological?
Relating to or representing the physical distribution of parts or features on the surface of or within an organ or organism
What is meant by topographical?
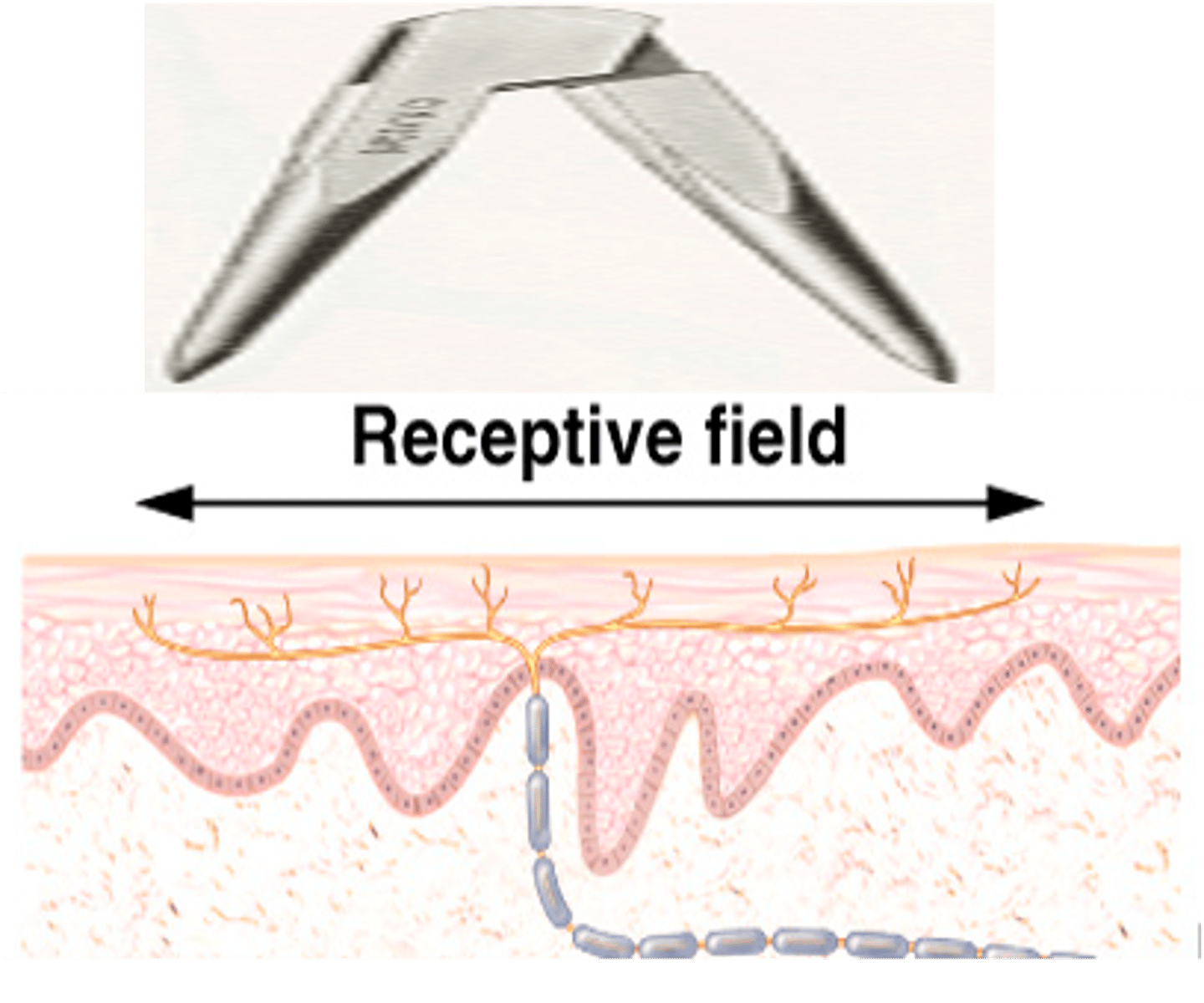
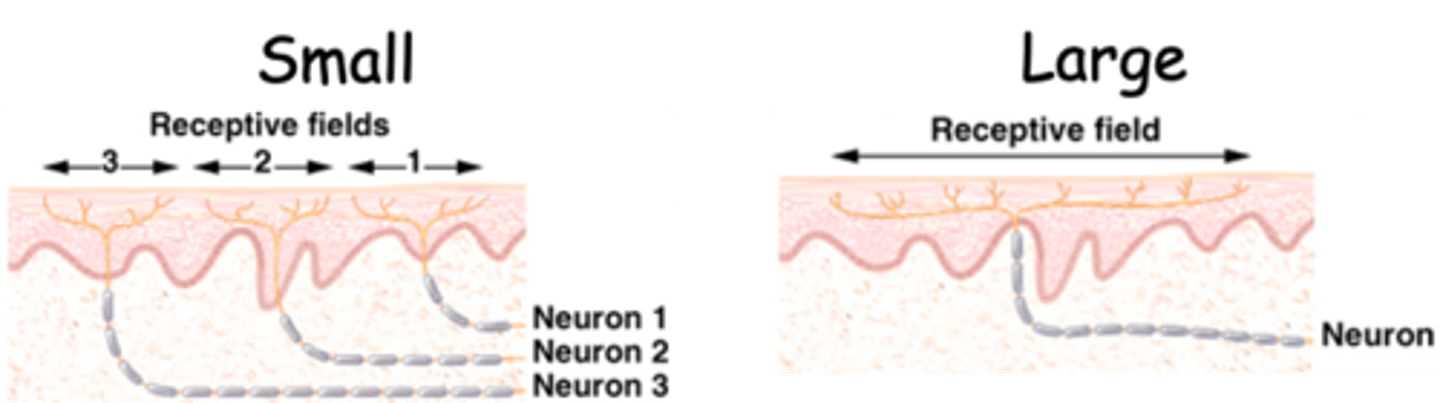
A receptive field
What does each sensory neuron have?
Where it is in the body, some regions have denser innervation than others
The size of the receptive field for any particular neuron will vary depending on what?
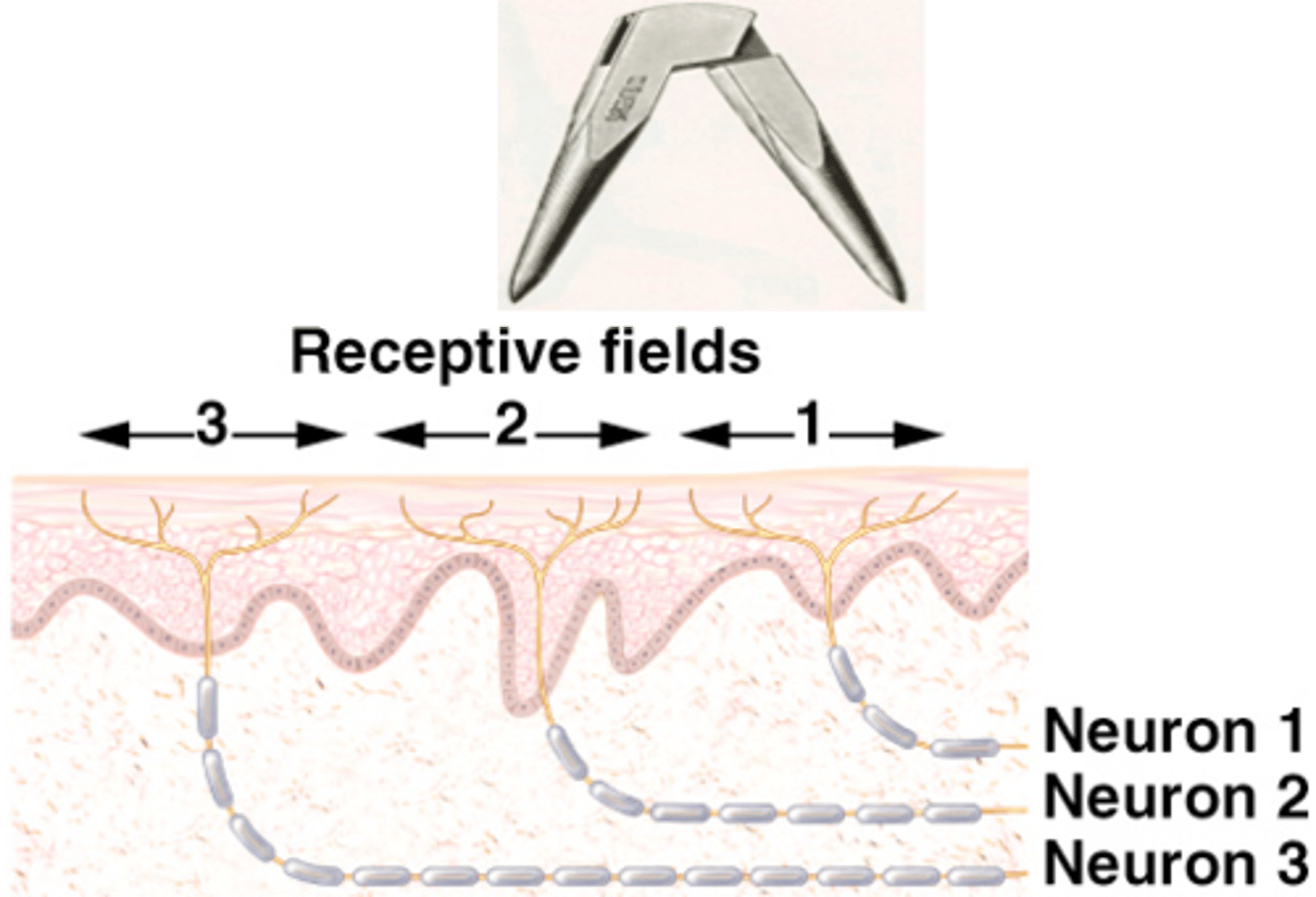
By assessing the ability to discriminate two sharp points set apart at different distances (if the subject feels two pin points then the distance between the points is larger than the receptive field)
How can the size of a receptive field be measured?
Low, high
Where the receptive fields are large, discrimination is ____ (legs and arms), whereas where receptive fields are small, discrimination is _____ (fingers)
Small
More cortex is dedicated to regions where receptive fields are ________
Higher, higher, larger
In these regions, although the number of receptors (nerve endings) per unit area may be similar, the number of endings from different neurons is ________, therefore the amount of derived information is also __________
This results in a _________ number of axons per unit area being represented in the cortex
The behavioural significance of that area
The number of sensory neurons innervating a particular area is related to what?
Behavioural significance
Cortical representation is determined by ...?
Large, dominate
While the representation of the hand is _________ in human cortex, in rodents it is the fields corresponding to whiskers that ____________
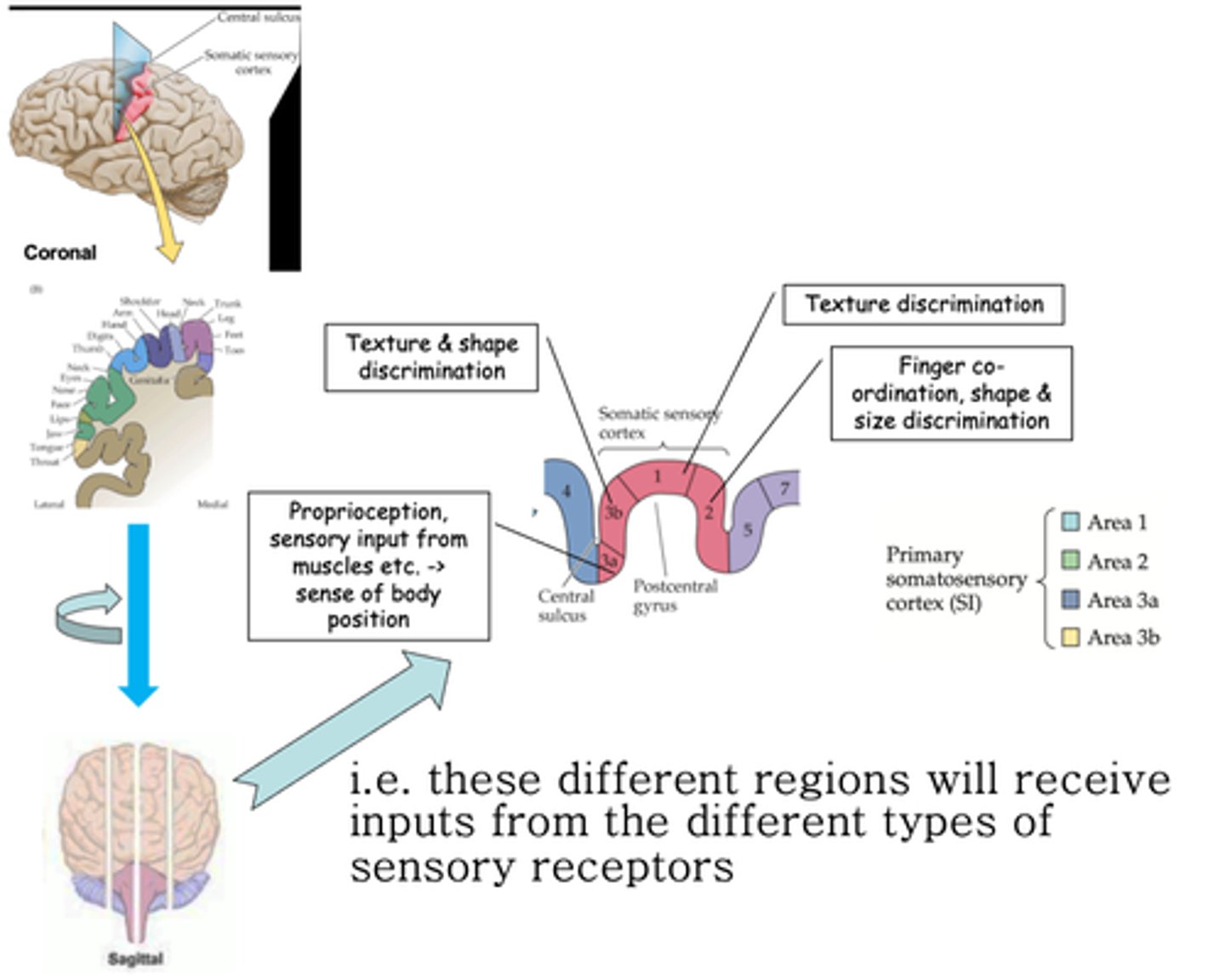
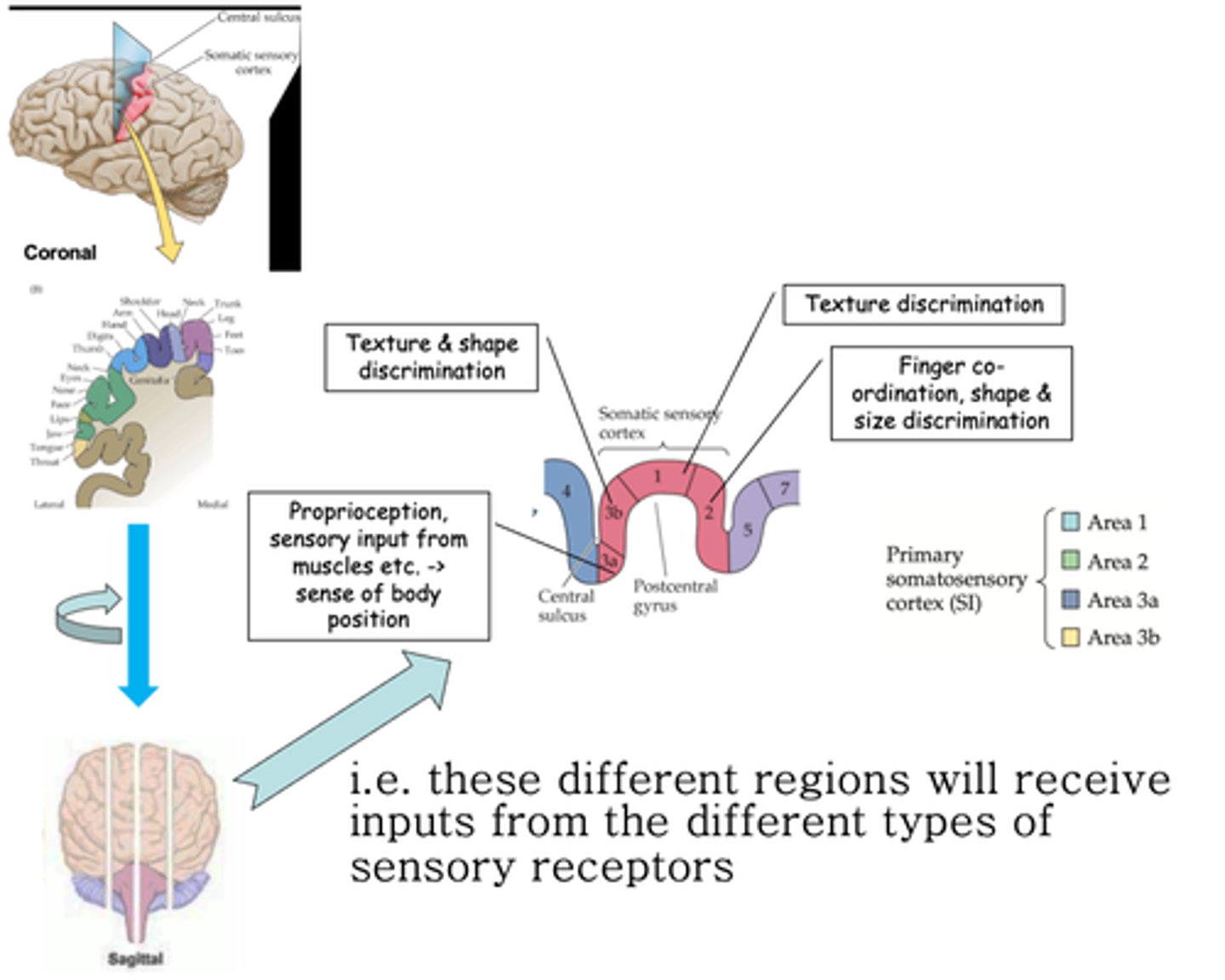
Postcentral gyrus
The somatotopic map is preserved in the coronal plane in the _____________ _______
Sagittal axis
Throughout the post central gyrus, different sensory modalities are localised along the ..?
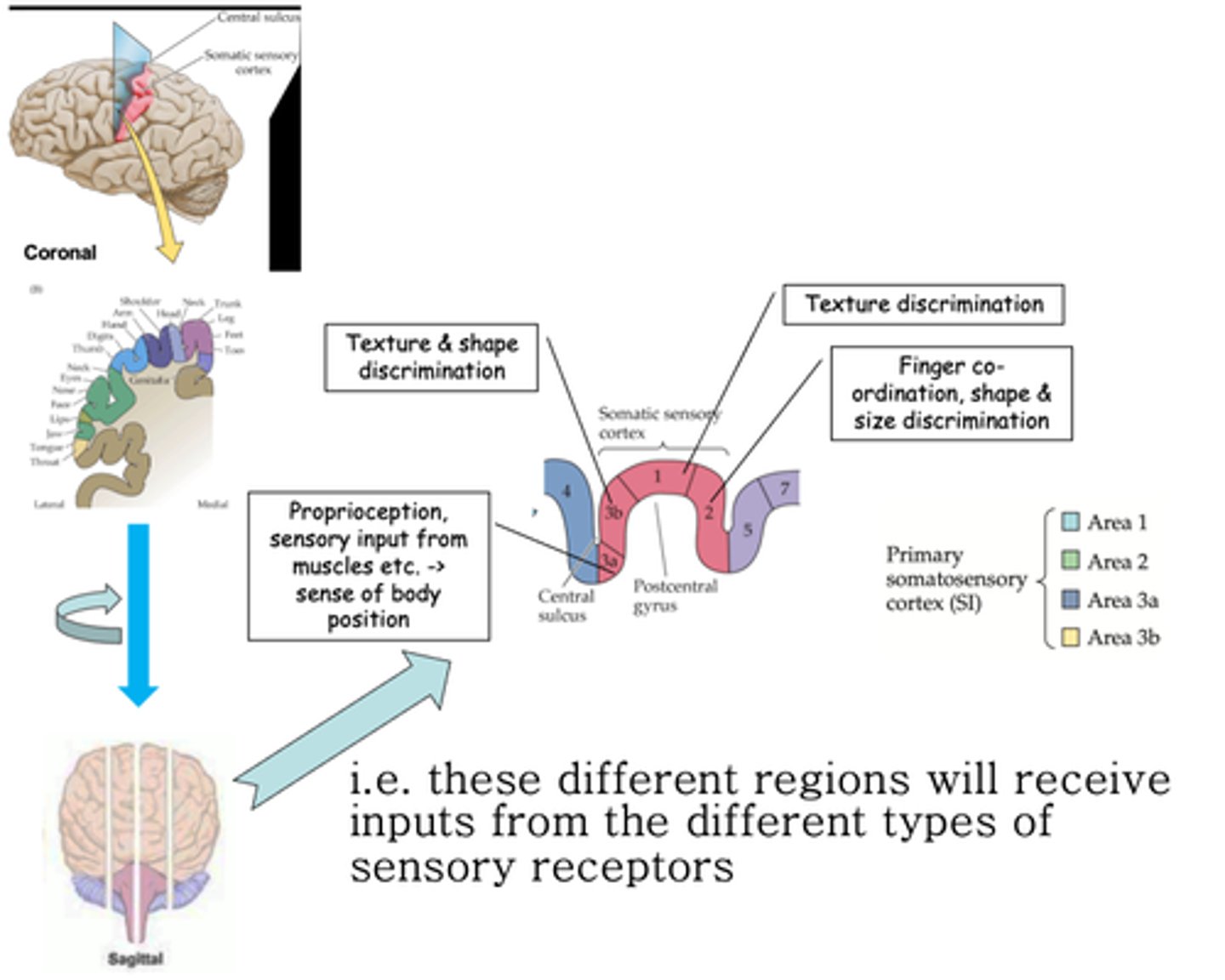
Brodmann areas
What are these areas known as?
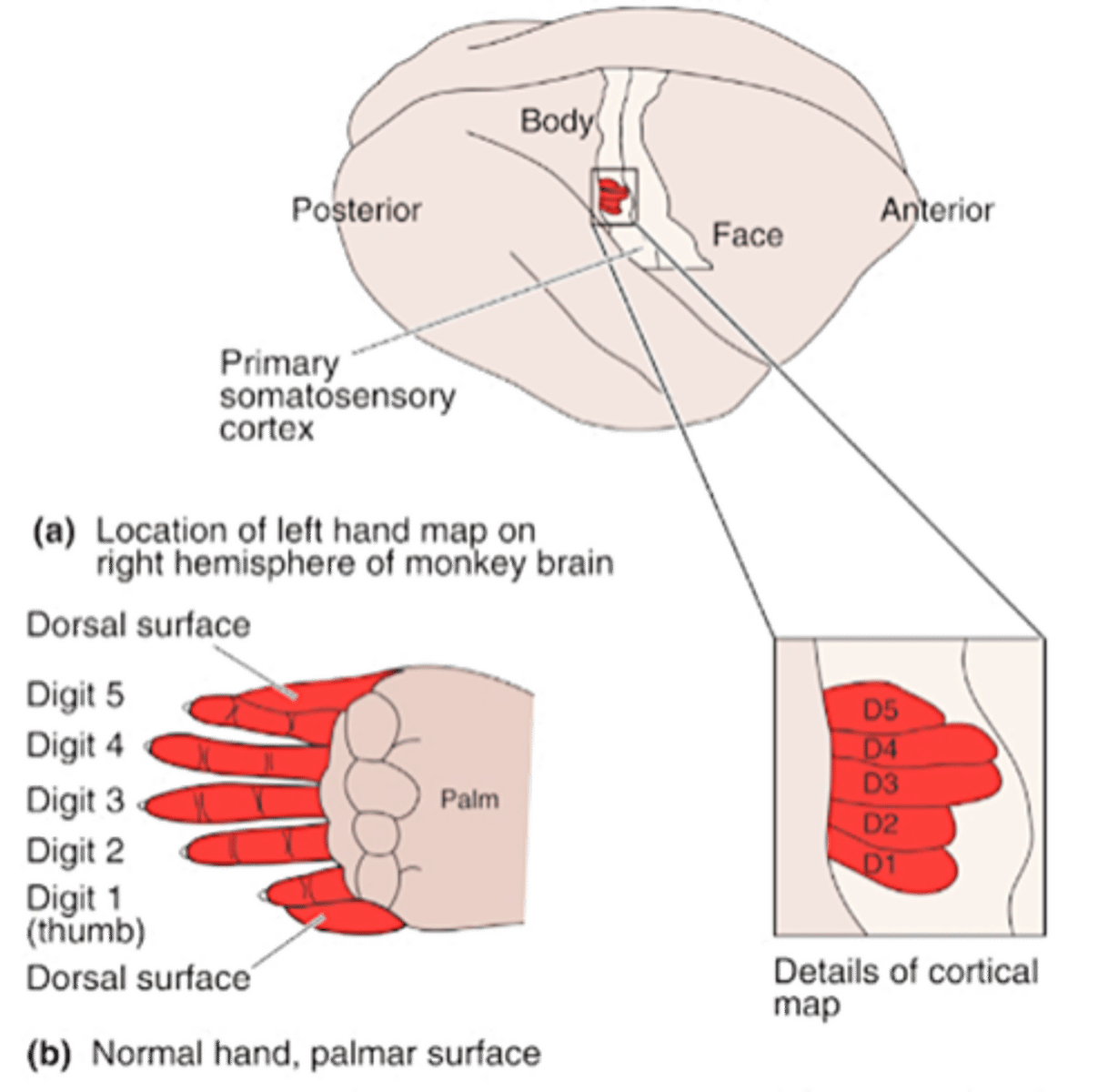
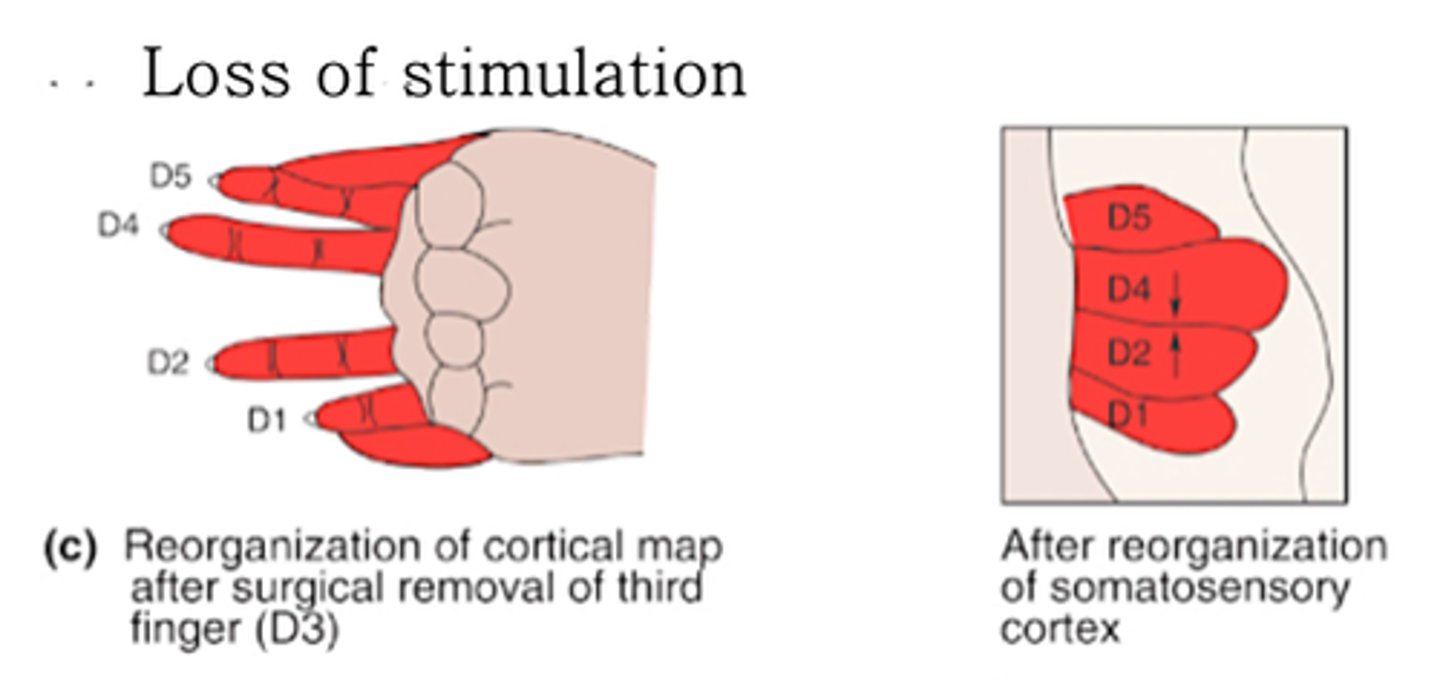
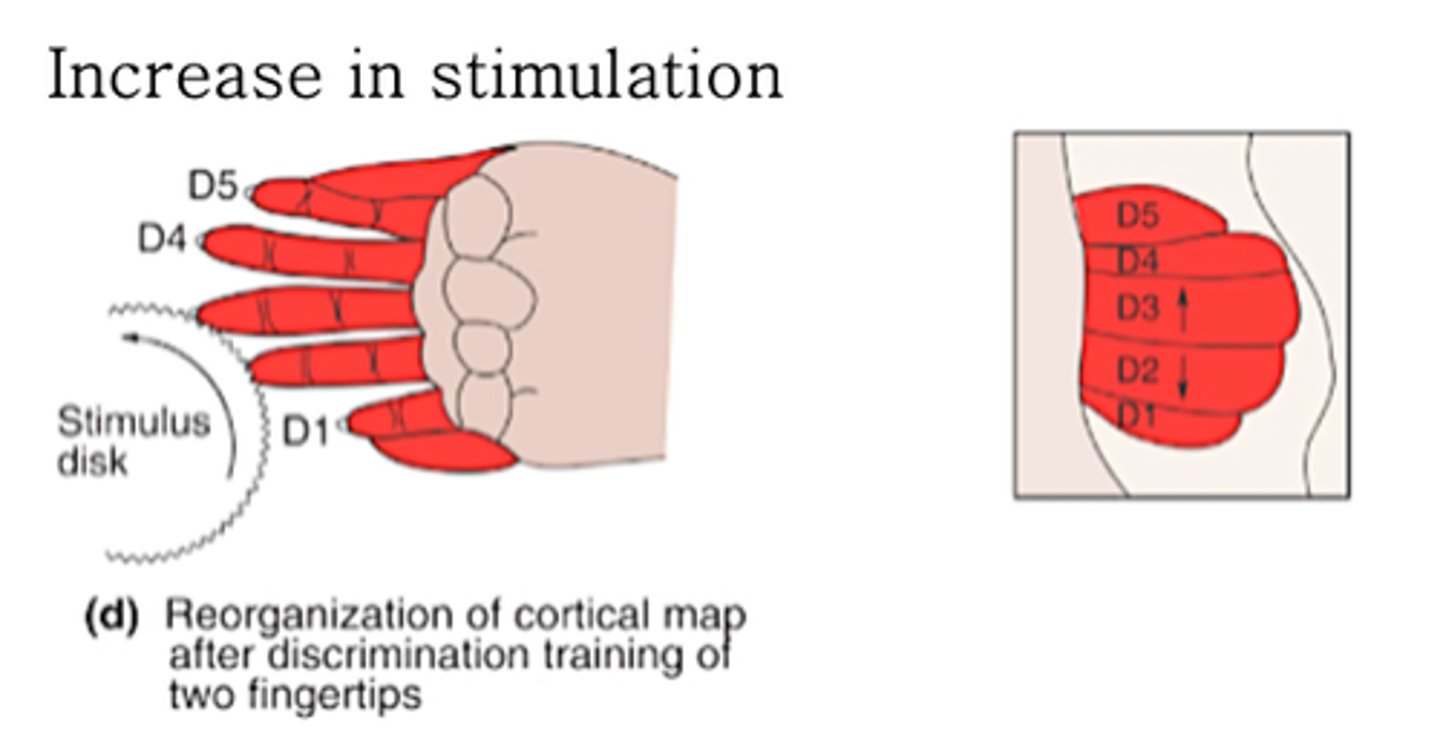
Cortical map plasticity
Disappearance (over several months) of the area normally devoted to the stimulated digits, and increase in that devoted to neighbouring digits
What does loss of stimulation result in?
Increase in the area devoted to the stimulated digits, at the expense of neighbouring, unstimulated areas
What does increase in stimulation result in?
Mechanical stimuli, proprioception
The components of the somatosensory system process information conveyed by ___________ _________ that impinge upon the body surface or that are generated within the body itself (________________)
First, second, third, medial lemniscal, thalamus
This sensory information is relayed via ______, __________ and ________-order neurons from the receptors to the somatosensory cortex via the _________ __________ system and the __________
Dorsal root ganglion, dorsal column nuclei, thalamus
First-order neurones are located in the ________ _______ __________, second-order neurons in the ________ _________ _________, and third-order neurons are found in the ___________
Topographic map, somatosensory cortex
The topology of the axons in the projections is preserved such that a ____________ _____ of the receptors is created in the _______________ ________
Proportional, density, innervation
The area of the cortex dedicated to each area of the body is _______________ to the __________ of ____________ in that area (hence its behavioural significance) not to the physical size of the area
Modality
The __________ of innervation is also represented in the cortex, functionally similar information projecting to the same cortical domain
Plastic
The cortex is highly ___________ and can adapt to changes in its inputs