Organic Chemistry
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
How do you determine the number of protons in an atom?
The number of protons in an atom is equal to its atomic number, which is located above the element symbol.
How do you determine the number of neutrons in an atom?
The number of neutrons in an atom can be found by subtracting the atomic number from the atomic mass.
How do you determine the number of electrons in an atom?
The number of electrons in a neutral atom is equal to the number of protons, which is determined by the atomic number.
How do you draw ionic lewis structures from molecular formulas?
First, identify the cations and anions in the compound. Then, depict the transfer of electrons from the metal to the non-metal, ensuring that the valence shell of each atom is filled according to the octet rule.
How do you identify anions and cations in an ionic compound?
cation: usually metal, loses electrons
anion: usually nonmetal, gains electrons
How do you draw covalent Lewis structures from molecular formulas?
Count total valence electrons, choose central atom (least electronegative, never H), connect atoms and satisfy octets, check formal charges.
How do you use electronegativity properties to predict bond dipole arrows and molecular polarity?
Bond dipole points toward more electronegative atom.
Larger E.N. difference = stronger dipole
dipoles add up => polar molecule
dipoles cancel (symmetrical) => nonpolar molecule
How do you determine formal charge?
Formal charge= # of valence electrons - (atoms attached + dots)
What is the orbital geometry of sp³ hybrid orbital?
Tetrahedral, 109.5 degrees
What is the orbital geometry of the sp² hybrid orbitals?
Trigonal planar, 120 degrees
What is the orbital geometry of the sp hybrid orbital?
Linear, 180 degrees
How do you determine orbital sybritization?
write “sppp”, cross out a p every for every pi bond or more.
for example, a single bond would be sp³, a double bond would be sp², and triple bond or two double bonds would be sp.
What does VSEPR theory tell us about the # of electron groups and their corresponding shapes & bond angles?
linear (2 e groups) → 180 degrees
trigonal planar (3 e groups) → 120 degrees
tetrahedral (4 e groups) → 109.5 degrees
trigonal pyramidal (3 bonds, 1 lone pair) → 107 degrees
bent (2 bonds, 2 lone pairs) → 104.5 degrees
A single line in a lewis structure represents a ___ bond.
sigma
A double line in a lewis structure represents a ___ bond.
pi
what orbitals are present in sigma bonds?
overlap of hybrid orbitals or s orbitals (head on overlap)
what orbitals are present in pi bonds?
overlap of unhybridized p orbitals (side by side overlap)
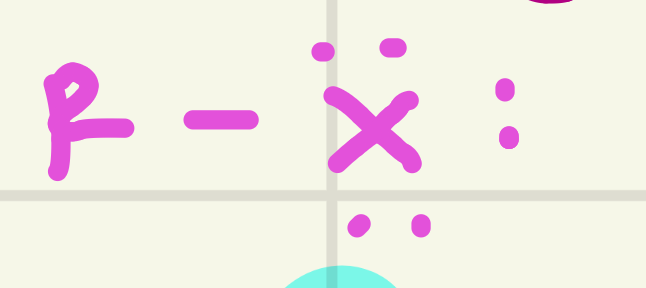
identify this functional group
Halide
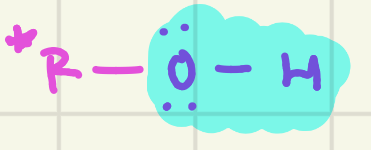
identify this functional group (*R= any carbon based group)
Alcohol (hydroxy)
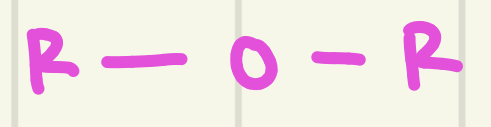
identify this functional group
Ether

identify this functional group
Thiol

identify this functional group
Sulfide
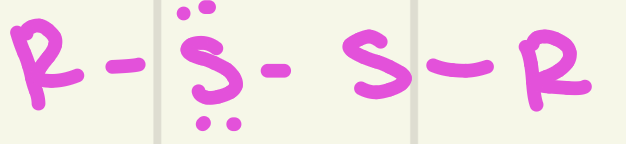
identify this functional group
Disulfide
how do you identify a carbonyl?
Carbonyls have carbons double bonded to oxygen. This does not include Amides; you can identify the difference because amides also have a Nitrogen bonded to the Carbon.
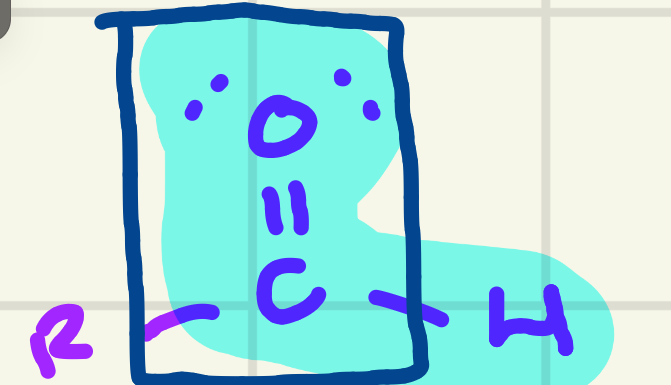
identify the functional group
Aldehyde
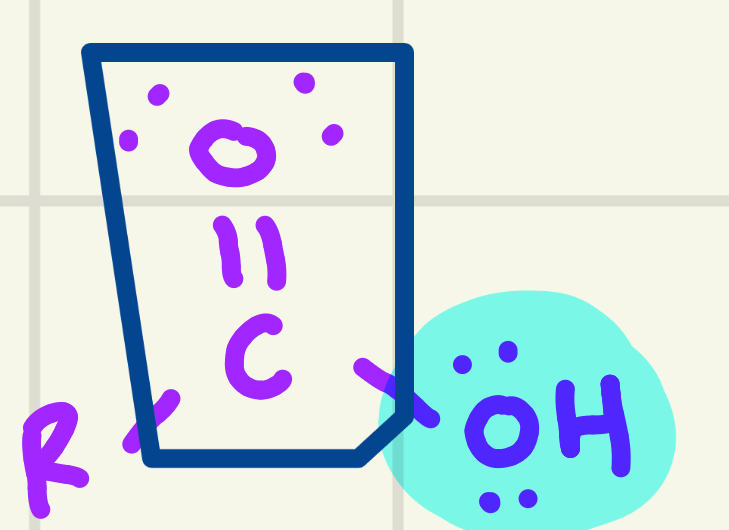
identify the functional group
carboxylic acid
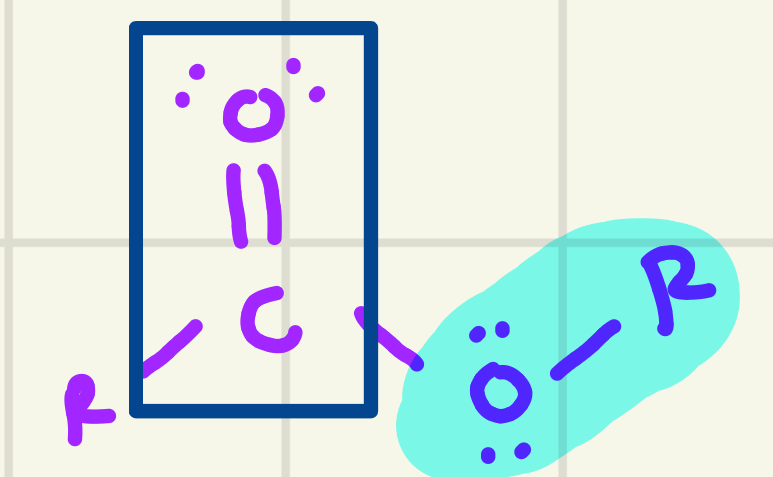
identify the functional group
Ester
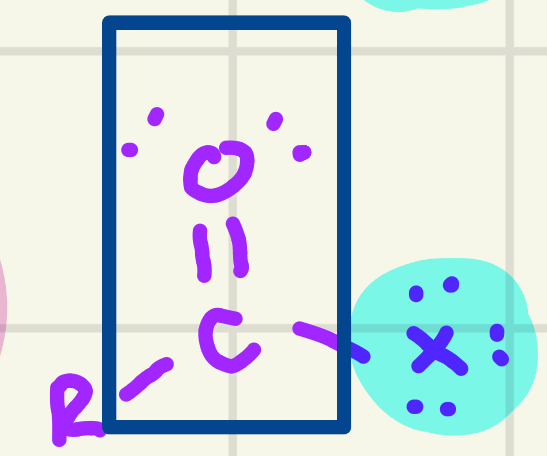
identify the functional group
Acyl Halide
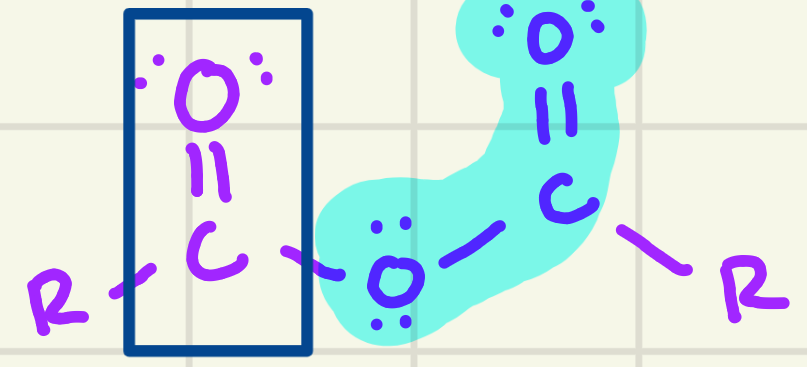
identify the functional group
Anhydride
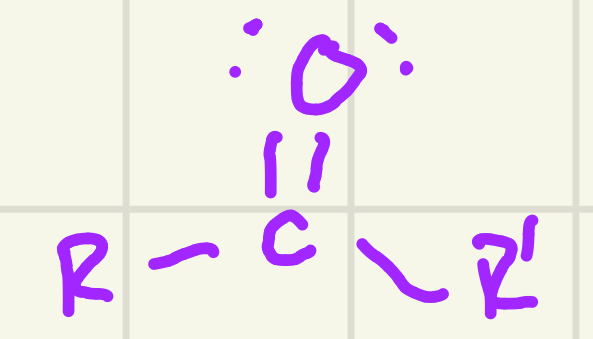
identify the functional group
Ketone
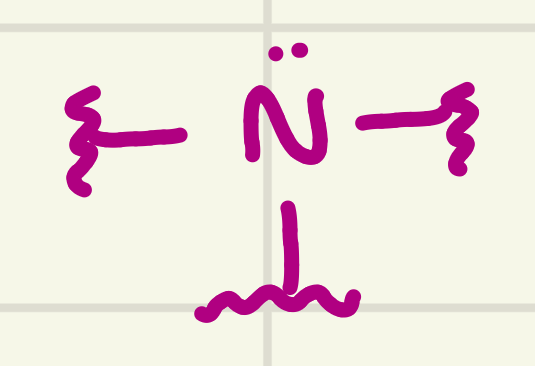
identify the functional group
Amine
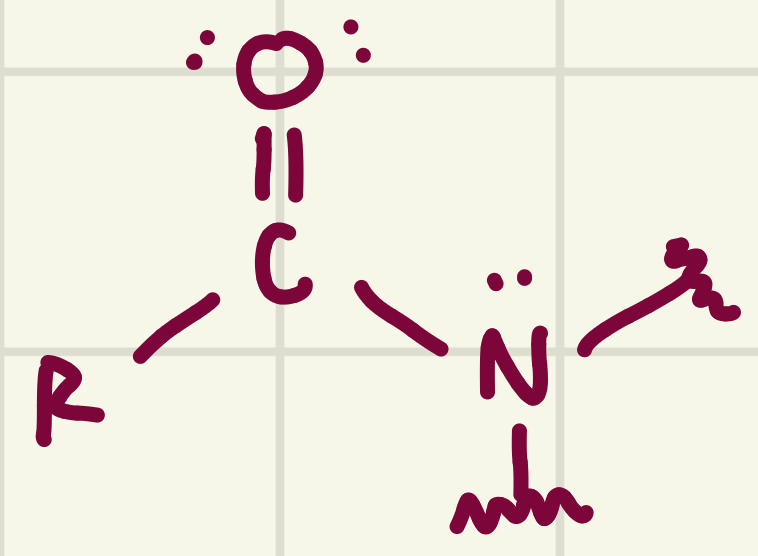
identify the functional group
Amide
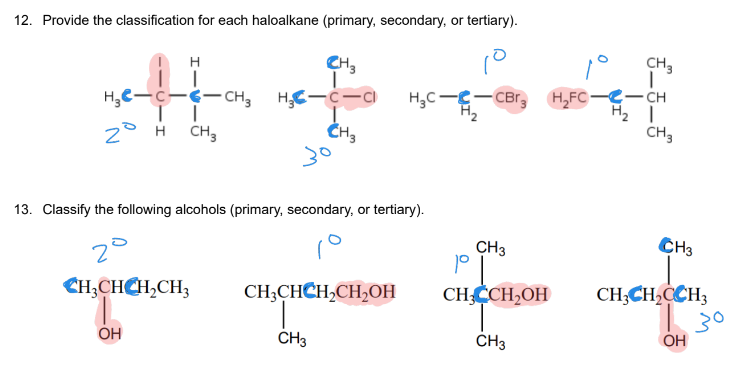
How do you decide whether to classify halides and alcohols as primary, secondary, or tertiary?
track the carbon that the functional group is connected to and count the number of carbons that it’s attached to (1= primary, 2= secondary, 3= tertiary)
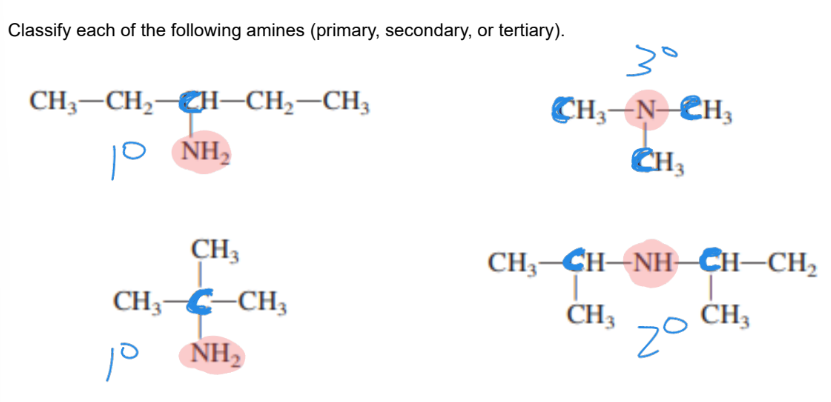
How do you decide whether to classify amines as primary, secondary, or tertiary?
Count the number of R (carbon based) groups connected DIRECTLY to the nitrogen.
What are the characteristics of Arrhenius acids and bases?
Acid → produces H+ in water
Base → produces OH- in water
What are the characteristics of Bronsted-Lowry acids and bases?
Acid → donates H+
Base → accepts H+
What are the characteristics of Lewis acids and bases?
Acid → accepts electron pair
Base → donates an electron pair
Predict the product of the Arrhenius acid-base
H+ moves from acid to OH-, making H2O, and the leftover ions form the salt. (MEMORY TIP: WATER)
Predict the product of the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base
H+ transfer from acid to base, products are conjugate base and conjugate acid. (MEMORY TIP: PROTON MOVE)
Predict the product of the Lewis acid-base
Electron pair moves from base to acid, forming a bonded complex (MEMORY TIP: ELECTRON PAIR MOVE)
What is the relation between Ka, Keq, and pKa and strong acids/bases?
Ka= acid dissociation constant (acid strength)
Larger Ka → stronger acid
pKa= -log(Ka)
smaller pKa → stronger acid
Keq: favors formation of weaker acids and bases
How do you use CARIH to compare acid/base strength?
(Charge, Atom, Resonance, Induction, Hybridization)
Charge: more + → stronger acid, more - → stronger base
Atom: larger/more electroneg. atom stabilizes charge → stronger acid
Resonance: more stabilization (charge/electrons are spread out over mult. atoms) → stronger acid, weaker base
Induction: electron withdrawing groups stabilize charge → stronger acid
Hybridization: more s-character (sp > sp² > sp³) → stronger acid
in a line-bond formula, what do line intersections and ends represent?
Carbon atoms
how are double bonds and triple bonds depicted in line-bond formula?
like usual, two lines for double and three lines for triple
How can you tell how many Hydrogens are attached to Carbon in line-bond formula?
Assume each Carbon has 4 total bonds, so a Carbon with 2 lines has 2 H’s, C with 3 lines has 1 H, C with 4 lines has 0 H’s.
What is a heteroatom and how are they depicted in line-bond formula?
O, N, and halogens depicted by writing them explicitly, with H’s SHOWN if attached
how do you draw valid constututional isomers?
Same molecular formula, rearrange atom connectivity, keep normal valences, avoid duplicates (rotate/flip to check)
how do you determine degrees of unsaturation?
ring or double bond → 1 DoU
triple bond → 2 DoU
how do you name alkanes using IUPAC nomenclature
Identify the parent chain (longest carbon chain)
Number the chain to give substituents (branches) the LOWEST NUMBERS
Name substituents (methyl, ethyl, etc) with their positions
Use prefixes (di-, tri-) for multiples
List substituents alphabetically + parent name
identify the branched alkyl chain: straight 3 carbon chain, branch attached at end
n-propyl (n= normal/straight)
identify the branched alkyl chain: straight 3 carbon chain, branch attached middle carbon
isopropyl (iso= one branch)
identify the branched alkyl chain: straight 4 carbon chain, branch attached at end
n-butyl (n= normal/straight)
identify the branched alkyl chain: straight 4 carbon chain, branch attached second carbon
sec-butyl (sec= attached to secondary carbon)
identify the branched alkyl chain: branched chain, attached at end carbon
isobutyl (iso= one branch)
identify the branched alkyl chain: central carbon attached to three methyl groups
tert-butyl (tert= attached to tertiary carbon)
How do you decide whether to classify carbons as primary, secondary, tertiary, or quaternary?
Count how many other carbons are attached to the carbon.
Primary → C bonded to 1 other C
Secondary → C bonded to 2 other C’s
Tertiary → C bonded to 3 other C’s
Quaternary → C bonded to 4 other C’s