Unit 5 Learning and conditioning
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Learning
the relatively permanent change in behavior resulting from experience or practice
Conditioning
the process of learning associations
behavioral perspective
a psychological view that emphasizes how learned behaviors are shaped by environmental interactions, such as rewards and punishments
classical conditioning
a type of learning where a neutral stimulus becomes associated with an unconditioned stimulus, eventually triggering a conditioned response on its own
associative learning
a psychological process where an organism learns to link or associate one stimulus with another, or an action with a consequence
acquisition
The initial stage of learning, where a new behavior or response is established and strengthened
what is the order of presentation in classical conditioning
stimulus to be conditioned should precede the UCS rather than follow it or occur simultaneously with it
- CS before UCS
Pavlov's studies
classical conditioning. studied dogs. Rung a bell and presented food to the dog at the same time.
Watson's studies
Operant conditioning. Little Albert experiment. presented a white rat and hit a hammer behind little Albert's head.
extinction
the weakening and eventual disappearance of a learned response
- in classical conditioning, it occurs when the conditioned stimulus is no longer paired with the unconditioned stimulus
spontaneous recovery
The reappearance of a learned response after its apparent extinction
stimulus discrimination
the tendency to respond differently to two or more similar stimuli
- in classical conditioning, it occurs when a stimulus similar to the conditioned stimulus fails to evoke a conditioned response
stimulus generalization
in classical conditioning, occurs when a new stimulus that resembles the conditioned stimulus elicits the conditioned response
higher-order conditioning
a neutral stimulus can become a conditioned stimulus by being paired with an existing conditioned stimulus
conditioned emotional responses (CER)
a learned behavior that is paired with an emotion-producing stimulus (classical conditioning...but emotion-based)
counterconditioning
involves the conditioning of an unwanted behavior or response to a stimulus into a wanted behavior or response by the association of positive actions with the stimulus
taste aversions
(one-trial learning)
an animal can develop a strong dislike for a particular food after only experiencing it once, usually paired with feeling sick, meaning it only takes one exposure to forn the aversion
biological preparedness
animals are biologically prepared to make some associations easier than others. Specifically, we are prepared to associate tastes with illness rather than a visual stimulus such as a flash of light.
garcia's research
taste aversion could be considered a survival mechanism, allowing an organism to stay away from substances that seemed to make them sick.
known for his research of radiation on laboratory animals
habituation
decreasing response to a stimulus
Operant conditioning
the process by which a response becomes more or less likely to occur depending on its consequences
reinforcement
increase the target behavior
- positive = add a desired stimulus
- negative = remove an undesired stimulus
punishment
decreases the frequency of a behavior
- positive = add an aversive stimulus
- negative = remove a rewarding stimulus
law of effect
behavior followed by pleasant consequences is likely to be repeated, while any behavior followed by unpleasant consequences is likely to be reduced or stopped
thorndike studies
law of effect. studied cats in boxes
positive reinforcement
Increasing behaviors by presenting positive stimuli, such as food. A positive reinforcer is any stimulus that, when presented after a response, strengthens the response.
negative reinforcement
Increasing behaviors by stopping or reducing negative stimuli, such as shock. A negative reinforcer is any stimulus that, when removed after a response, strengthens the response. (Note: negative reinforcement is not punishment.)
positive punishment
the administration of a stimulus to decrease the probability of a behavior's recurring
negative punishments
subtract something desirable (such as phone privileges) to decrease the likelihood of behavior (such as staying out past curfew).
primary reinforcers
Events that are inherently reinforcing because they satisfy biological needs
ex) food
secondary reinforcers
learned reinforcers, such as money, that develop their reinforcing properties because of their association with primary reinforcers
shaping
the process of training a learned behavior that would not normally occur. for each action closer to the desired outcome, a reinforcemtn or reward is provided until the target behavior is achieved
chaining
the concept of linking multiple complex behaviors together through shaping to get the final result
instinctive drift
the tendency of learned behavior to gradually revert to biologically predisposed patterns
escape conditioning
a learning process where a subject learns to perform a behavior to stop an unpleasant stimulus
avoidance conditioning
happens before experiencing the unpleasant stimulus.
- escape conditioning happens in response to the stimulus which means that it is already occurring
superstitious behavior
a learned response that is mistakenly linked to a specific outcome due to a coincidental association, rather than a logical or scientific one
learned helplessness
when repeatedly faced with traumatic events over which we have no control, we come to feel helpless, hopeless, and depressed.
seligman research
studied learned helplessness, learned optimism, and became a founder of the positive psychology movement
continuous reinforcement
every occurrence of a response is reinforced
- necessary to first teach a new behavior
partial reinforcement
only some occurrences of a response are reinforced
- can be used after a new behavior has been taught
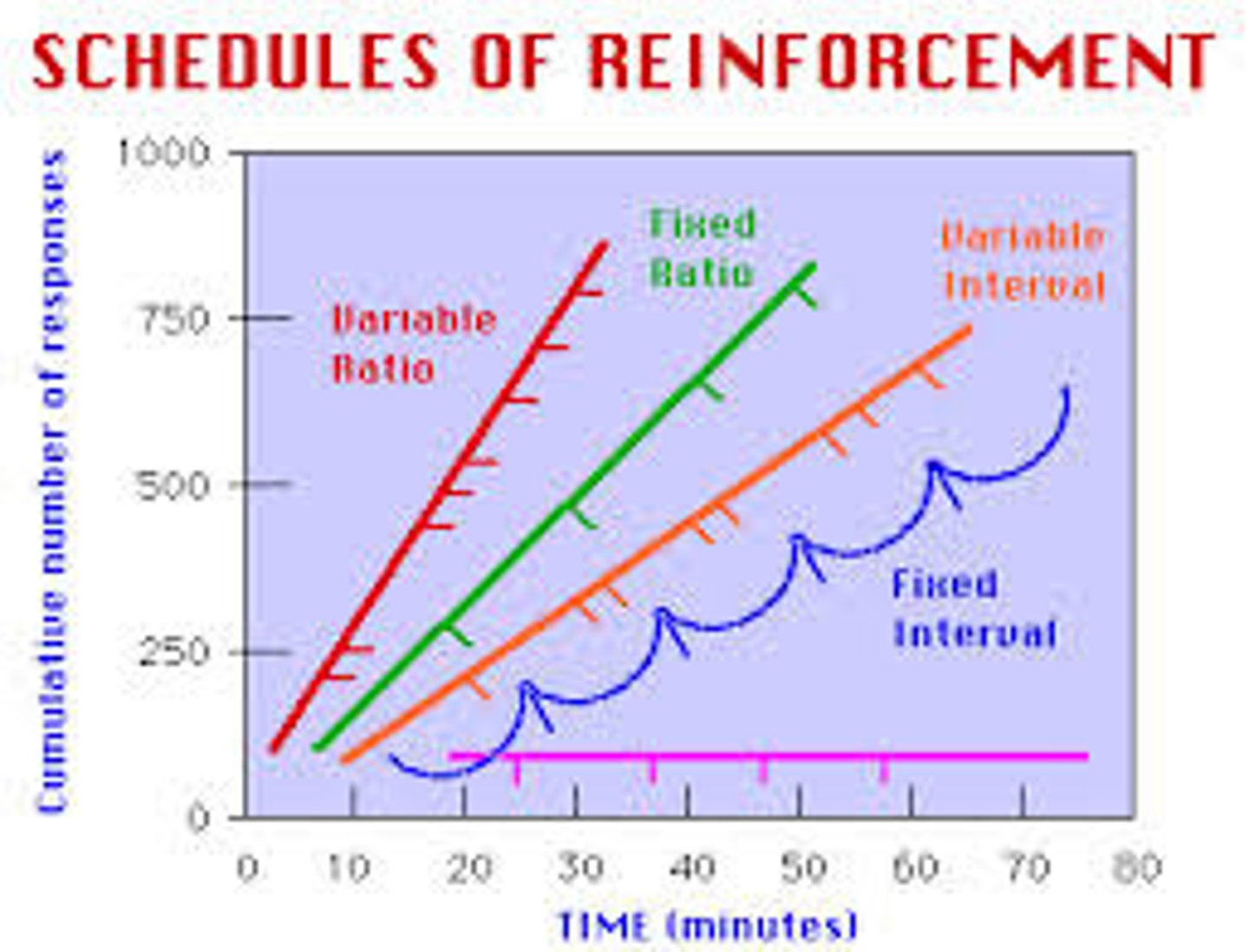
fixed interval
Reinforce the first response after a fixed time period
ex) checking the mail, studying for a weekly test, getting a paycheck every two weeks
- learn that reinforcement is connected with time, not effort
- slower response rate
variable interval
Reinforce the first response after varying time intervals
ex) checking email, studying for a pop quiz
- steady, continuous behavior
- effective for maintaining consistent behavior
fixed ratio
Reinforce behavior after a set number of responses
ex) workers paid per product unit produced, lose your driver's license after five violations
- high rate of response (learn quickly)
- usually a short pause after reinforcement before behavior resumes
variable ratio
Provide reinforcers after a seemingly unpredictable number of responses
ex) slot machines, gambling, fishing
- high rates of responding
- strong and consistent behavior
- no (predictable pauses in behavior)
- one of the most effective reinforcement schedules for building long-term habits, resistant to extinction
- fast rate of learning
graph patterns of partial reinforcement schedules
social learning theory
a comprehensive theory explaining how people acquire new behaviors through observing others, including factors like attention, retention, reproduction, and motivation
vicarious conditioning
a way of learning from the experiences of others, rather than having to go through those experiences directly, through stories, books, and real-life situations
modeling
a type of observational learning where individuals learn new behaviors, skills, and attitudes by watching and imitating others
bandura's studies
social cognitive theory. learning through observation, imitation, and modeling.
- Bobo doll experiments
insight learning
the sudden perception of relationships among various parts of a problem, allowing the solution to the problem to come quickly
"Aha Moment"
kohler's studies
insight learning.
latent learning
learning that occurs but is not apparent until there is an incentive to demonstrate it
cognitive maps
An internal representation of the spatial relationships between objects in an animal's surroundings.
tolman's studies
latent learning
- rats explored a maze without an obvious reward and developed cognitive maps, or mental representations, of the layout of the maze
- when presented with an incentive (reinforcement) the rats quickly navigated the maze