1. Forces & Motion
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
on a distance-time graph, what does the gradient represent?
speed
straight line means constant speed
greater gradient means greater speed
horizontal line means speed is 0 - object is stationary
what is the formula for speed?
speed = distance / time
PRACTICAL: Investigating Motion
how would you investigate the speed of different objects?
measure out a height of 1m
drop the object
use a stopwatch to time how long it takes to fall
record distance travelled and how long it took to fall
do this 2-3 times and take an average
repeat for different heights
calculate average speed
define acceleration
the rate of change in velocity
what is the formula for acceleration?
acceleration = change in velocity / time taken
a in m/s2
Δv in m/s
t in s

on a velocity-time graph, what does the gradient represent?
acceleration
straight line means constant acceleration
greater gradient means greater acceleration
horizontal line means acceleration is 0 - object is either stationary or at constant speed
what does the area under a velocity-time graph represent?
displacement
think speed = distance / time, so distance = speed x time
what equation links final speed, initial speed, acceleration and distance? what kind of objects does this formula apply to?
v2 = u2 + 2as
(final speed)2 = (initial speed)2 + (2 × acceleration × distance moved)
s in m
u in m/s
v in m/s / a in m/s2
objects moving with uniform acceleration
what is a force?
a push or pull that arises from the interaction between objects
what are the different types of forces?
gravitational force (weight)
reaction force
friction
drag
air resistance
thrust
up thrust
electrostatic force
magnetic force
tension
what can force do to an object?
the object could:
change speed
change direction
change shape
what is the difference between distance and displacement?
distance is a measure of how far an object has travelled, regardless of direction - it is a scalar quantity
displacement is a measure of how far it is between two points in space, including the direction - it is a vector quantity
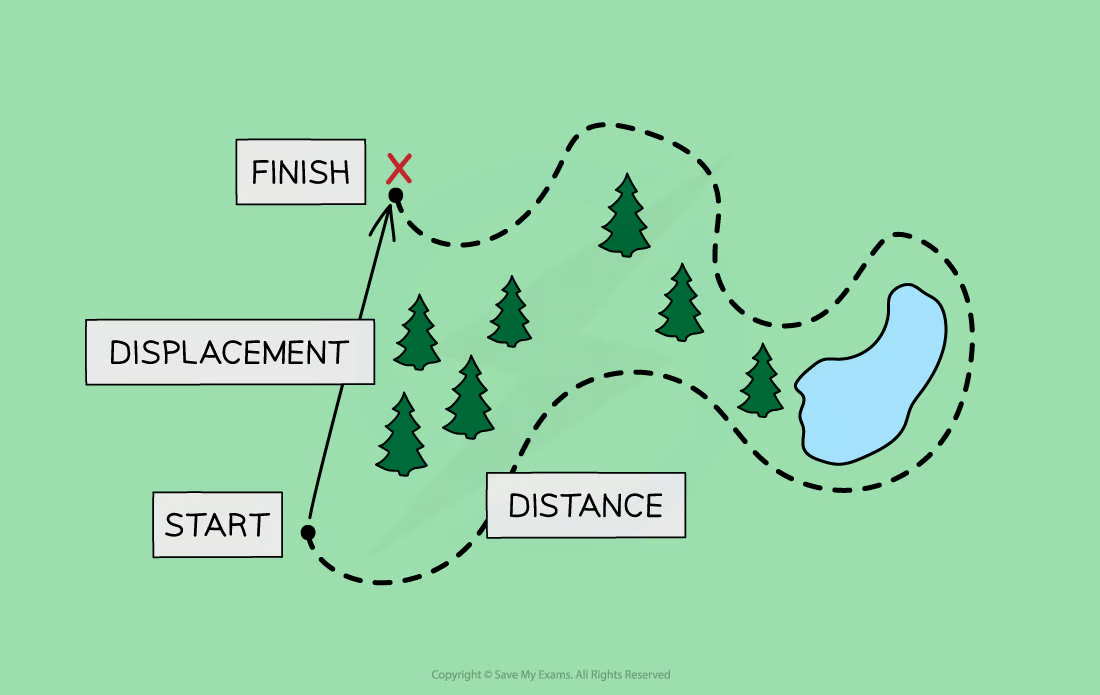
what is the difference between speed and velocity?
speed is a measure of the distance travelled by an object per unit time, regardless of the direction - it is a scalar
velocity is a measure of the displacement of an object per unit time, including the direction - it is a vector
what type of quantity is a force? how could you represent this?
force is a vector quantity, and can be represented by an arrow
the length of the arrow represents the magnitude of the force
the direction of the arrow indicates the direction of the force
what is a resultant force?
a resultant force is a single force that describes all of the forces operating on a body
when multiple forces act on one object, the forces can be combined to produce one net force that describes the combined action of all the forces
the resultant force determines:
the direction in which the object will move
the magnitude of the net force experienced by the object
when writing resultant forces, what 3 info parts should you include?
the magnitude of the force
units for the force
the direction of the force
e.g. 4N to the right
define friction
a force which opposes the motion of an object
how do drag, friction, and air resistance differ?
friction a force which opposes the motion of an object
drag is a type of friction that acts to oppose the motion of objects moving through a fluid (liquid or gas)
air resistance is a type of drag force, and therefore a type of friction, that acts to oppose the motion of objects moving through air
what does balanced forces mean?
balanced forces mean the forces on an object have combined in such a way that they cancel each other out and no resultant force acts on the object
e.g. a book sitting on a table
what does unbalanced forces mean?
unbalanced forces mean that the forces have combined in such a way that they do not cancel out completely and there is a resultant force on the object
e.g. a game of tug of war
what do unbalanced forces cause an object to do?
the resultant force causes the object to accelerate (i.e. change its velocity)
the object might:
speed up
slow down
change direction
what equation links force, mass, and acceleration?
what is this equation also known as?
F = m × a
F in N
m in kg
a in m/s2
define weight
the force experienced by an object with mass when placed in a gravitational field
how are weight and mass different?
mass is a measure of how much matter there is in an object - it is a scalar quantity
weight is a force - it is a vector quantity
what is the equation linking weight, mass, and gravitational field strength?
W = mg
W in N
m in kg
g in N/kg
what is the gravitational field strength of Earth?
10 N/kg
W = mg
what is g also sometimes used to describe?
the acceleration of freefall in a gravitational field
on Earth, it is 10 m/s2
how are mass and weight related?
they are directly proportional
what is stopping distance?
the stopping distance of a car is the total distance travelled during the time it takes to stop in an emergency
the sum of the distance travelled as the driver makes the decision to stop + the distance travelled as the driver applies the brakes
what is the formula for stopping distance? what factors affect it?
stopping distance = thinking distance + braking distance
the speed of th car
the reaction time of the driver
what is thinking distance? what factors affect it?
the distance travelled in the time it takes the driver to react to an emergency and prepare to stop
the speed of the car
the reaction time of the driver
what is reaction time? what factors affect it?
reaction time is a measure of how much time passes between seeing something and reacting to it
the average reaction time of a human is 0.25s
reaction time is increased by:
tiredness
distractions
intoxication
what is breaking distance? what factors affect it?
the distance travelled under the braking force in metres (m)
the greater the speed of the vehicle, the larger the stopping distance
how does speed affect stopping distance?
thinking distance vs braking distance
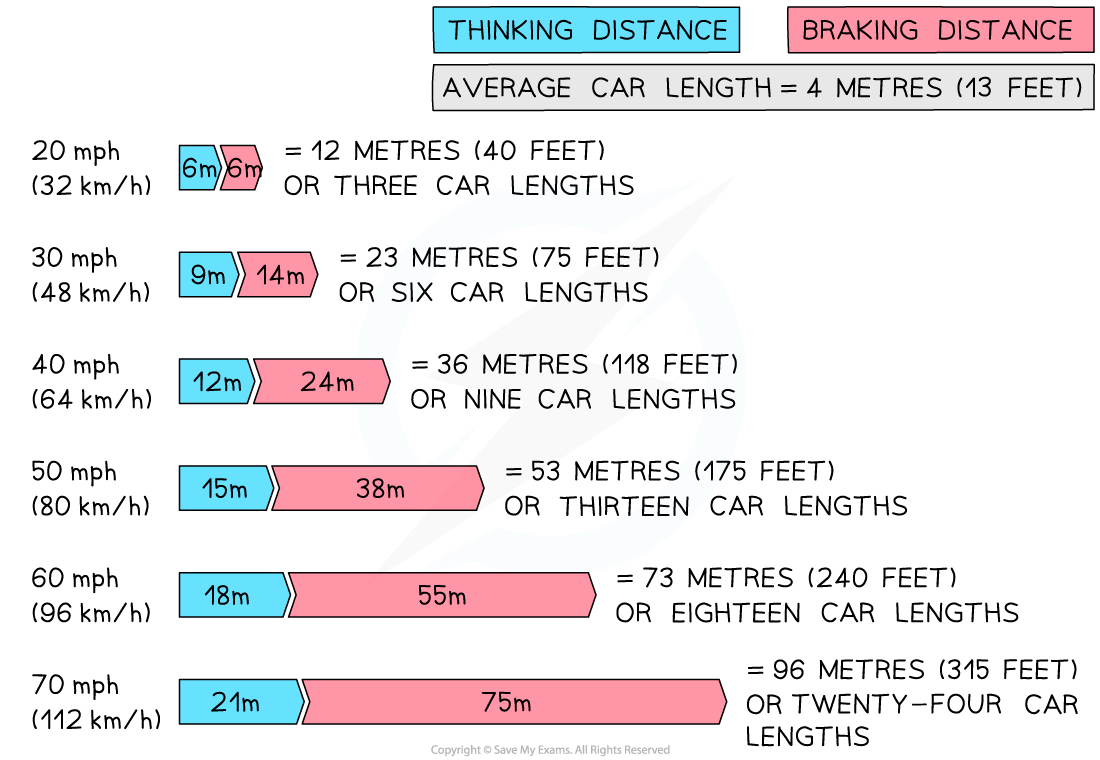
what factors affect stopping distance?
vehicle speed - the greater the speed, the greater the braking distance
vehicle mass - the more massive the vehicle, the more distance it will travel
road conditions - wet or icy roads make the brakes less effective
driver reaction time - distractions, tiredness, and intoxication make reaction time longer
what is terminal velocity? when is it reached?
the fastest speed that an object can reach when falling
terminal velocity is reached when the upward and downward acting forces are balanced
the resultant force on the object reaches zero
the object no longer accelerates and a constant terminal velocity is reached
what two forces do falling objects experience? how do these forces change as an object falls?
weight and air resistance
the air resistance increases as the object’s speed increases (because the object collides with air particles as it falls, and the faster it falls, the more collisions there are)
describe the changing forces a skydiver experiences as they fall
at the instant the skydiver jumps, the support force of the plane is no longer acting on them, but they are not yet falling, so the only force exerted is their weight
there is a downward acting resultant force, equal to the weight force
the skydiver accelerates downward at maximum acceleration
as the skydiver begins to fall, the air resistance is small because the skydiver’s speed is small
there is a downward acting resultant force, equal to the weight force - air resistance
the skydiver accelerates downward but the acceleration decreases
as the skydiver accelerates, their speed increases, so air resistance increases
there is a downward acting resultant force, equal to weight - air resistance
the skydiver accelerates downward but the acceleration continues to decrease
as the skydiver’s acceleration decreases, their speed increases at a slower and slower rate
eventually, the skydiver reaches a speed at which the air resistance is equal to the force of their weight
the forces are balanced, so resultant force is 0
the skydiver no longer accelerates and a constant velocity is reached
this is terminal velocity
what is Hooke’s Law? how is it represented on a graph?
Hookes law states that:
The extension of an elastic object is directly proportional to the force applied, up to the limit of proportionality
the limit of proportionality is the point beyond which the relationship between force and extention is no longer directly proportional, and it varies according to the material

what is elastic behaviour?
the ability of a material to recover its original shape after the forces causing the deformation have been removed
what is deformation?
deformation is a change in the original shape of an object
it can be either elastic or inelastic
elastic deformation is when the object does return to its original shape after the deforming forces are removed
it results in a change in the object’s shape that is not permanent
inelastic deformation is when the object does not return to its original shape after the deforming forces are removed
it results in a change in the object’s shape that is permanent
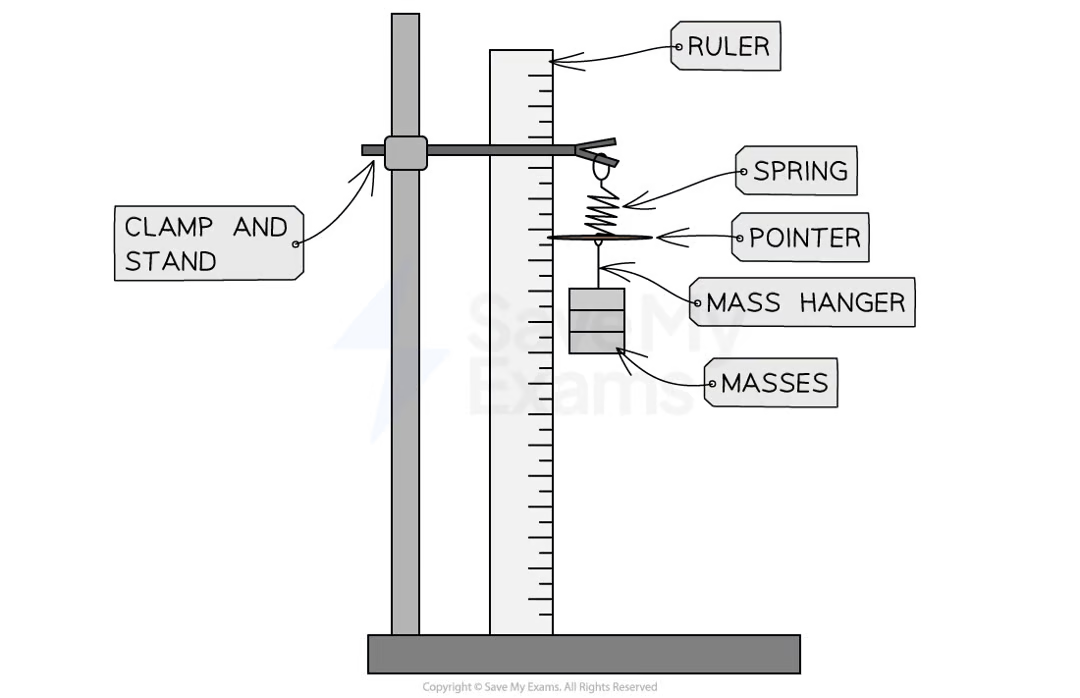
PRACTICAL: Investigating force + extension
IV: Force, F
DV: Extension, e
METHOD:
set up a clamp stand and hang a spring on it. align the stand with a vertical ruler and put a pointer on the bottom of the spring. measure the initial reading on the ruler
add a 100g mass onto the spring and record the mass and new measurement from the pointer
add another 100g and record the new mass and position from the pointer
repeat this process until the desired number of masses has been added
remove the masses and repeat the process again until it has been carried out 3 times, calculate the average length for each mass
what is the equation for momentum? is momentum a scalar or vector quantity?
p = mv
p in kg m/s
m in kg
v in m/s
vector
what does the principle of conservation of momentum state?
in a closed system, the total momentum before an interaction is equal to the total momentum after an interaction
what happens to momentum in a collision?
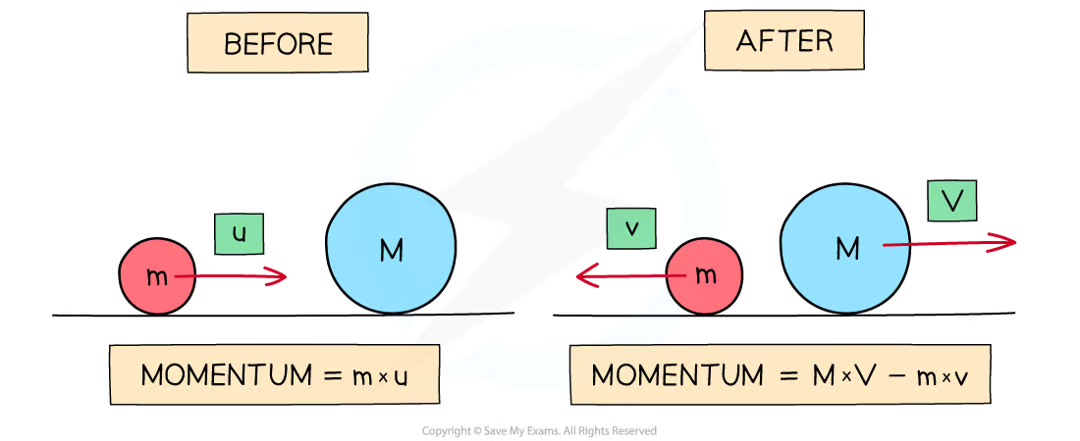
what is the equation for change in momentum?
Δp = mv - mu
Δp in kg m/s
m in kg
v in m/s
u in m/s
what is the equation linking force and change in momentum?
F in N
m in kg
v in m/s
u in m/s
t in s
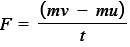
in terms of momentum, what can force be defined as?
rate of change of momentum on a body
the shorter the time over which the momentum changes, the bigger the force
force and time are inversely proportional to each other
what is Newton’s third law?
whenever two objects interact, the forces they exert on each other are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction
what are the three rules to help identify a third law pair?
The two forces in a third law pair act on different objects
The two forces in a third law pair always are equal in size but act in opposite directions
The two forces are always the same type: weight, reaction force, etc
what is newton’s first law?
an object at rest will remain at rest, and an object in motion will remain in motion at a constant velocity unless acted upon by a net, external force
how can the force of an impact in a vehicle collision be decreased?
by increasing the contact time over which the collision occurs
how are vehicle safety features designed to absorb energy? give some examples
they change shape and increase the time for the passenger’s momentum to reach zero
crumple zones, seat belts, and airbags
define a moment
the turning effect of a force about a pivot
what is the equation for the size of a moment?
M = Fd
M in Nm
F in N
d in m
what does the principle of moments state?
if an object is balanced, the total clockwise moment about a pivot equals the total anticlockwise moment about that pivot
what is the centre of gravity of an object?
the point through which the weight of an object acts
for a symmetrical object of uniform density, the centre of gravity is located at the point of symmetry
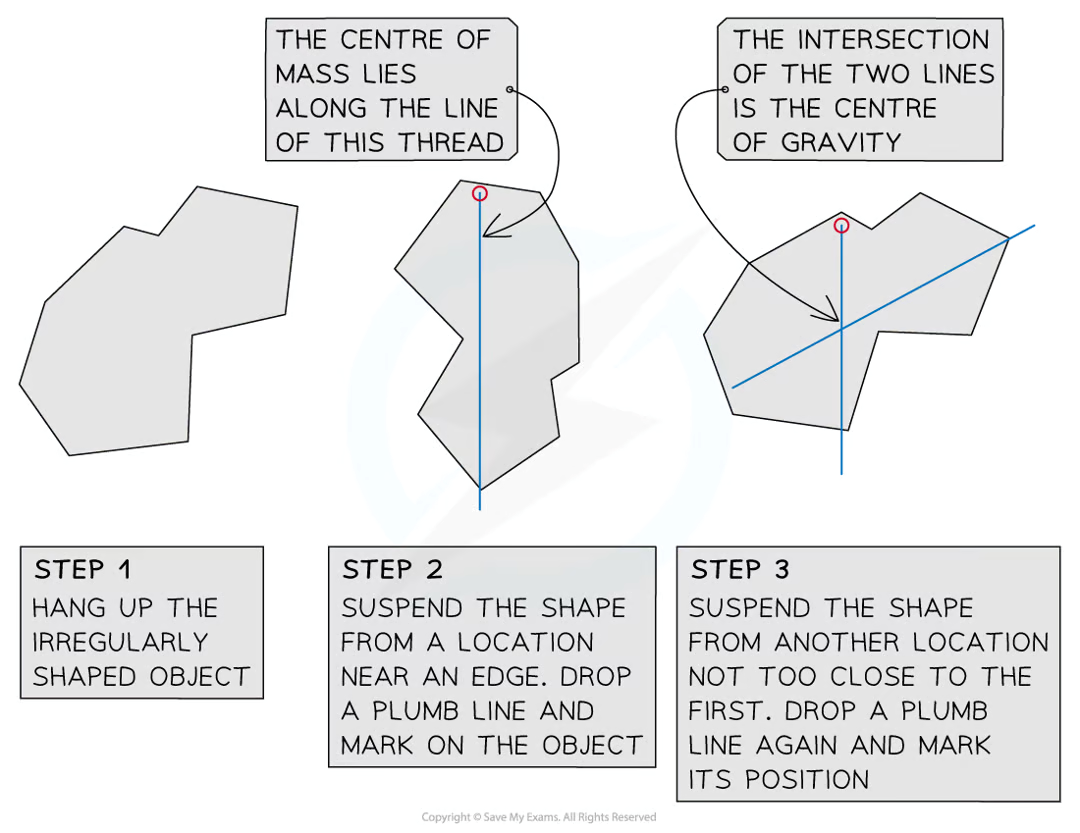
how would you find the centre of gravity of an irregular object?
The irregular shape is suspended from a pivot and allowed to settle
A plumb line (weighted thread) is then held next to the pivot and a pencil is used to draw a vertical line from the pivot (the centre of mass must be somewhere on this line)
The process is then repeated, suspending the shape from two additional points
The centre of mass is located at the point where all three lines cross