Cardiovascular and Respiratory Anatomy: Heart, Vessels, and Lung Structures
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Coronary sulcus
A groove that encircles the heart, marking the boundary between the atria and ventricles.
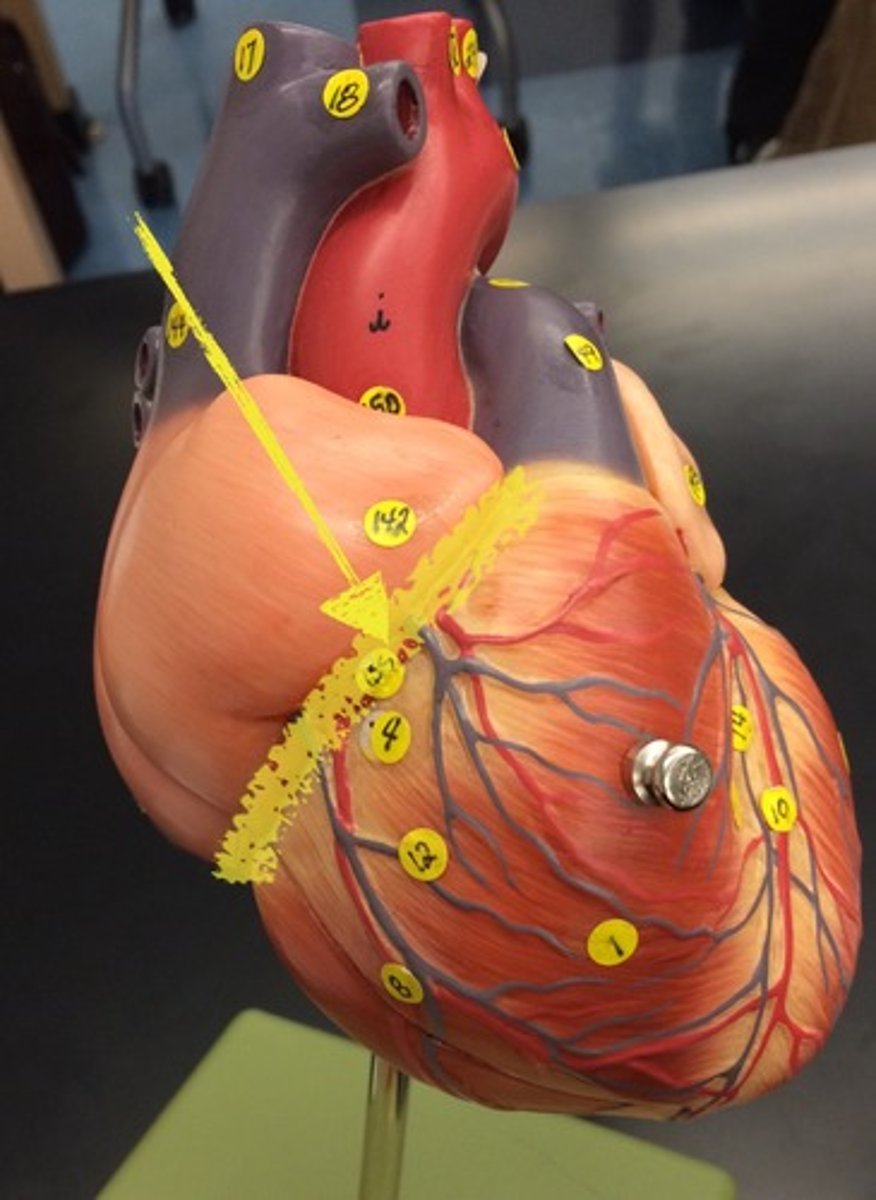
Left anterior descending coronary artery
A major artery supplying blood to the front of the left side of the heart.
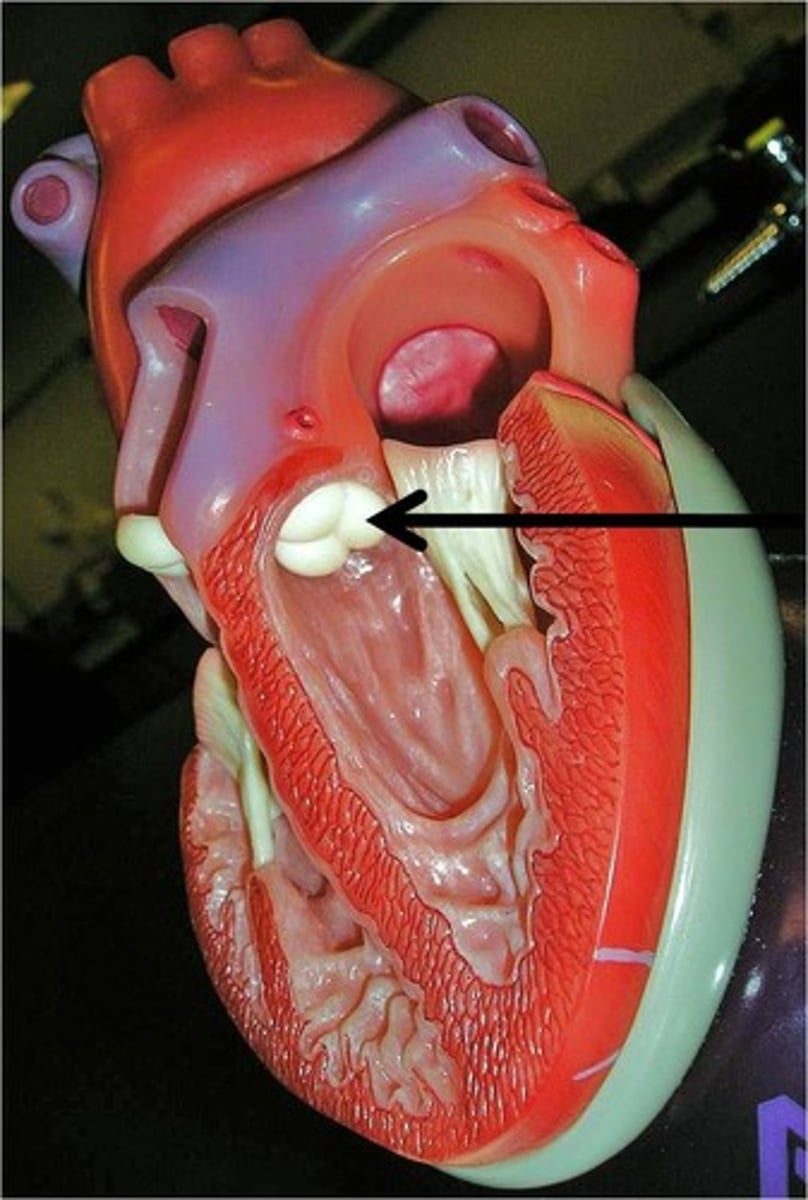
Aortic semilunar valve
A valve located between the left ventricle and the aorta that prevents backflow of blood.
Vena cava
The large vein that carries deoxygenated blood from the body to the right atrium of the heart.
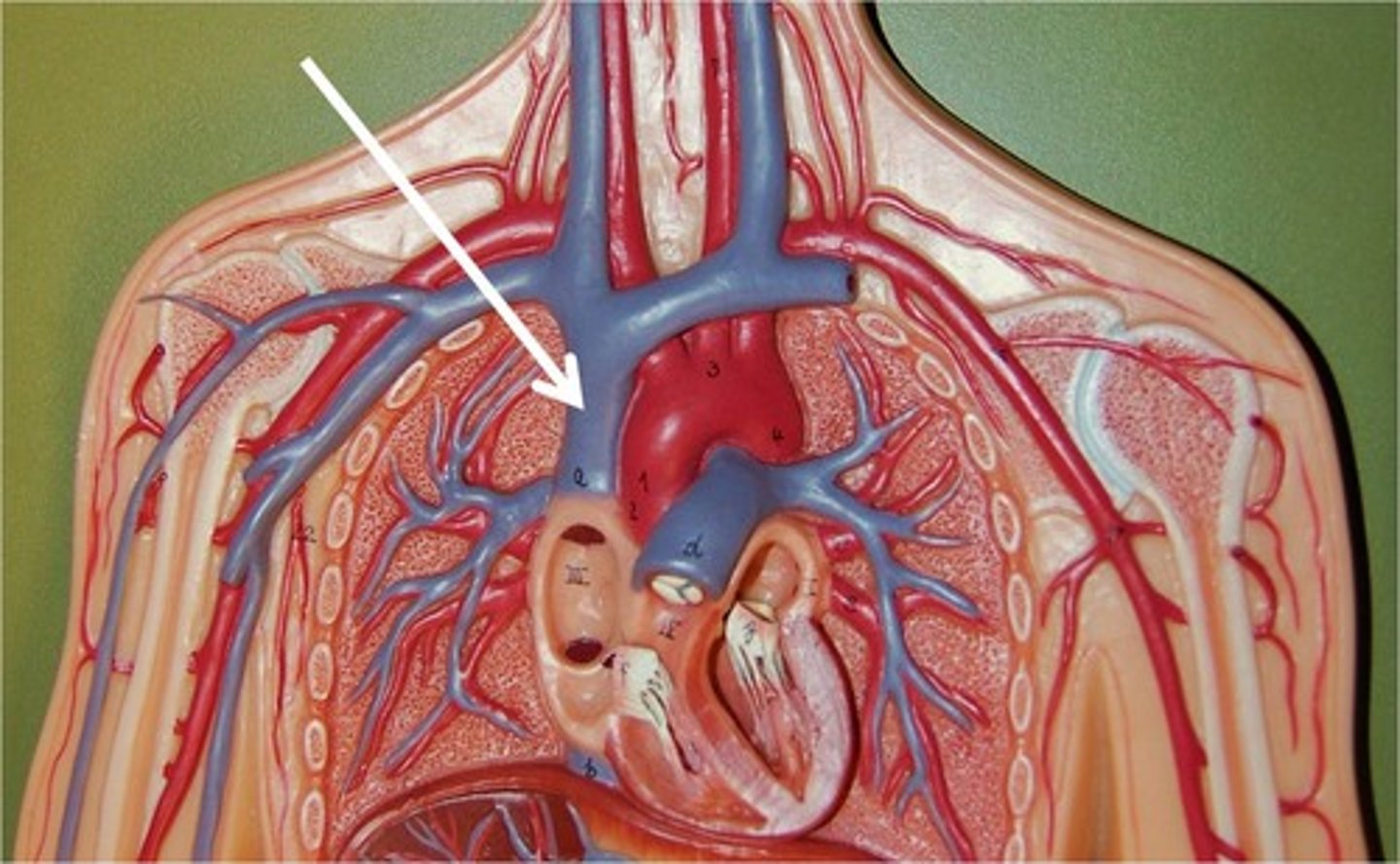
Pulmonary vein
Veins that carry oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart.
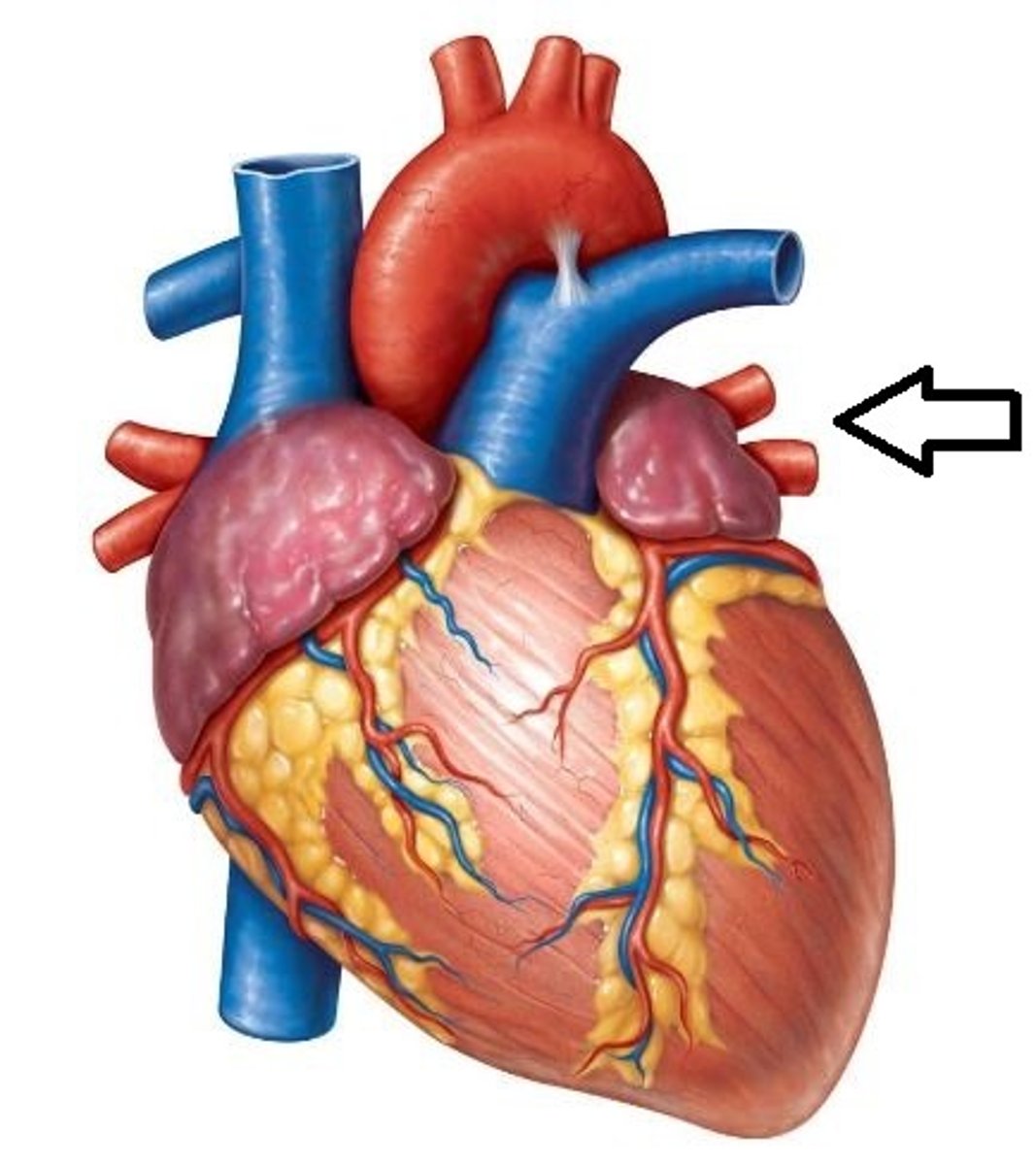
Artery vs vein
Arteries carry blood away from the heart, while veins carry blood toward the heart.
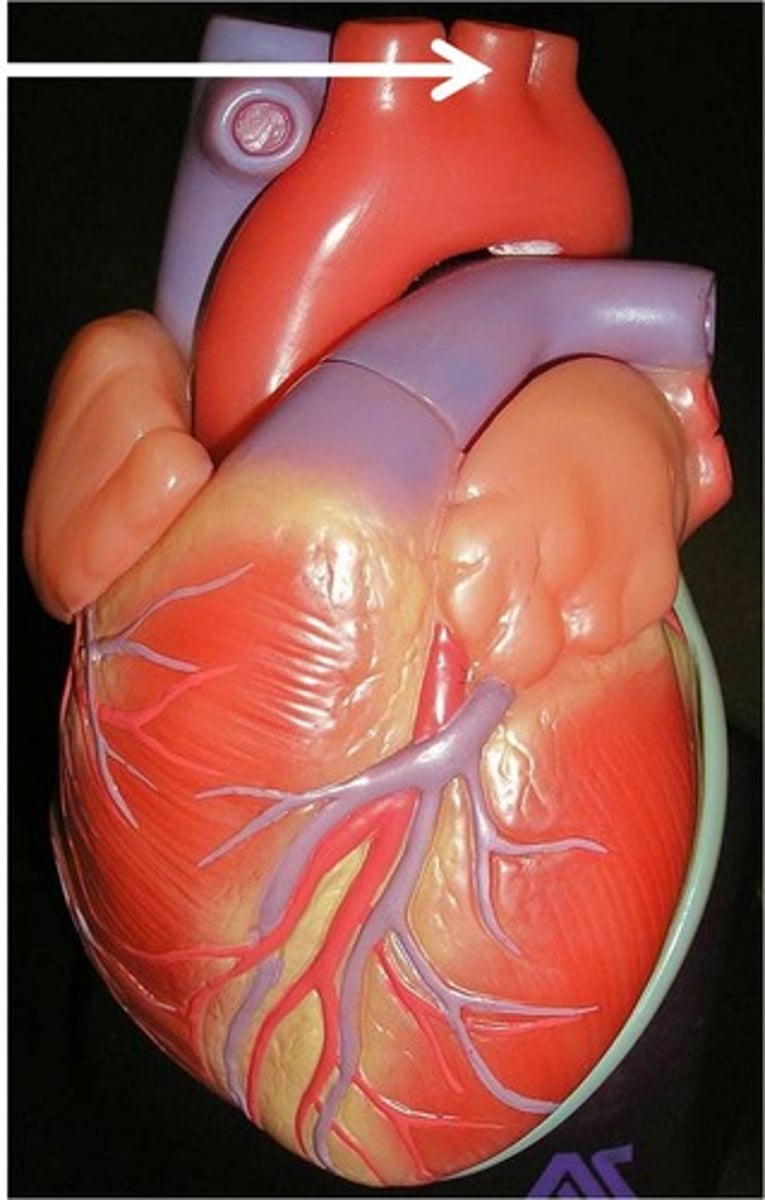
Common carotid artery
An artery that supplies blood to the head and neck.
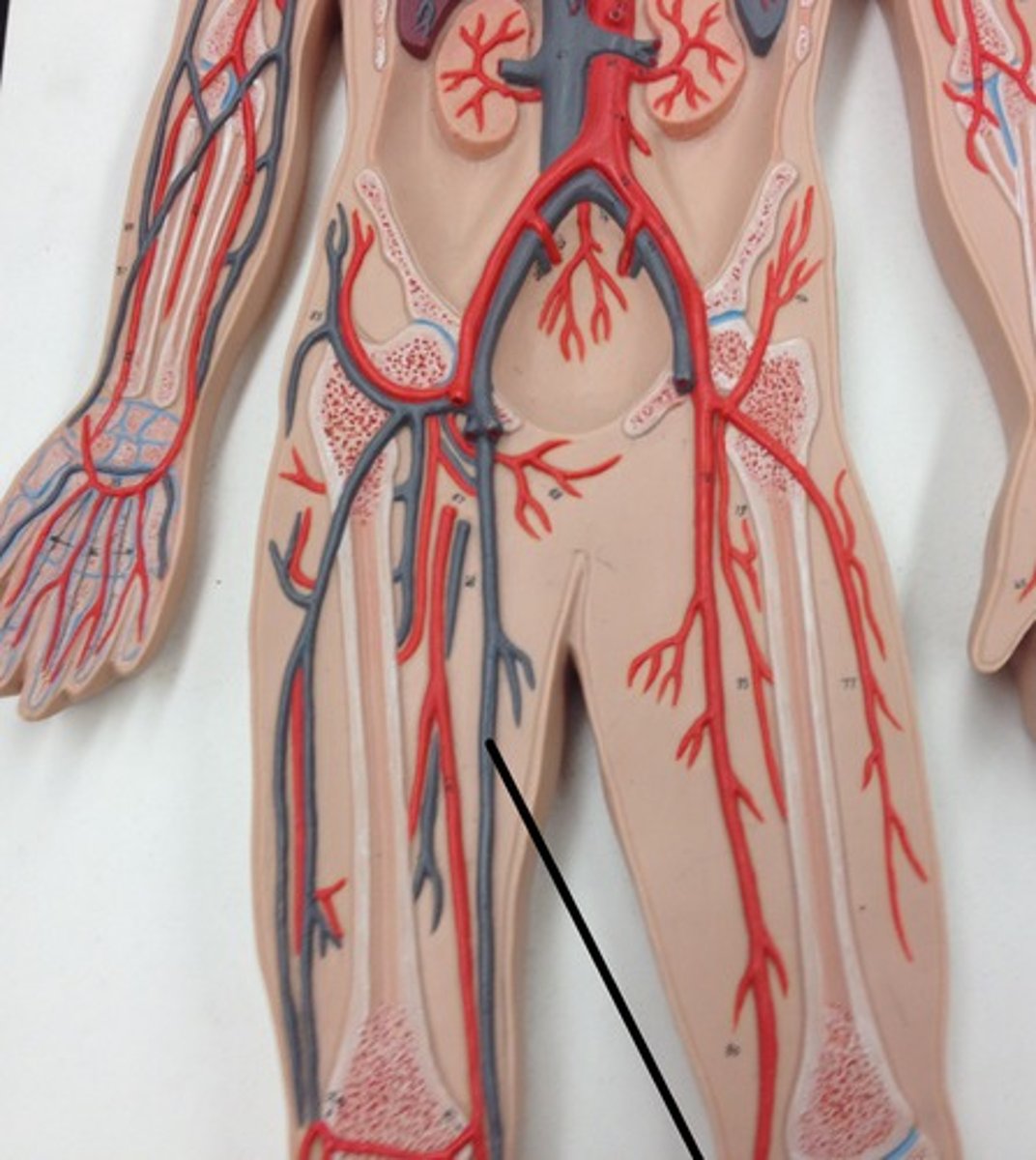
Great saphenous vein
The longest vein in the body, running along the length of the leg and draining into the femoral vein.
Vertebral artery
An artery that supplies blood to the posterior part of the brain and spinal cord.
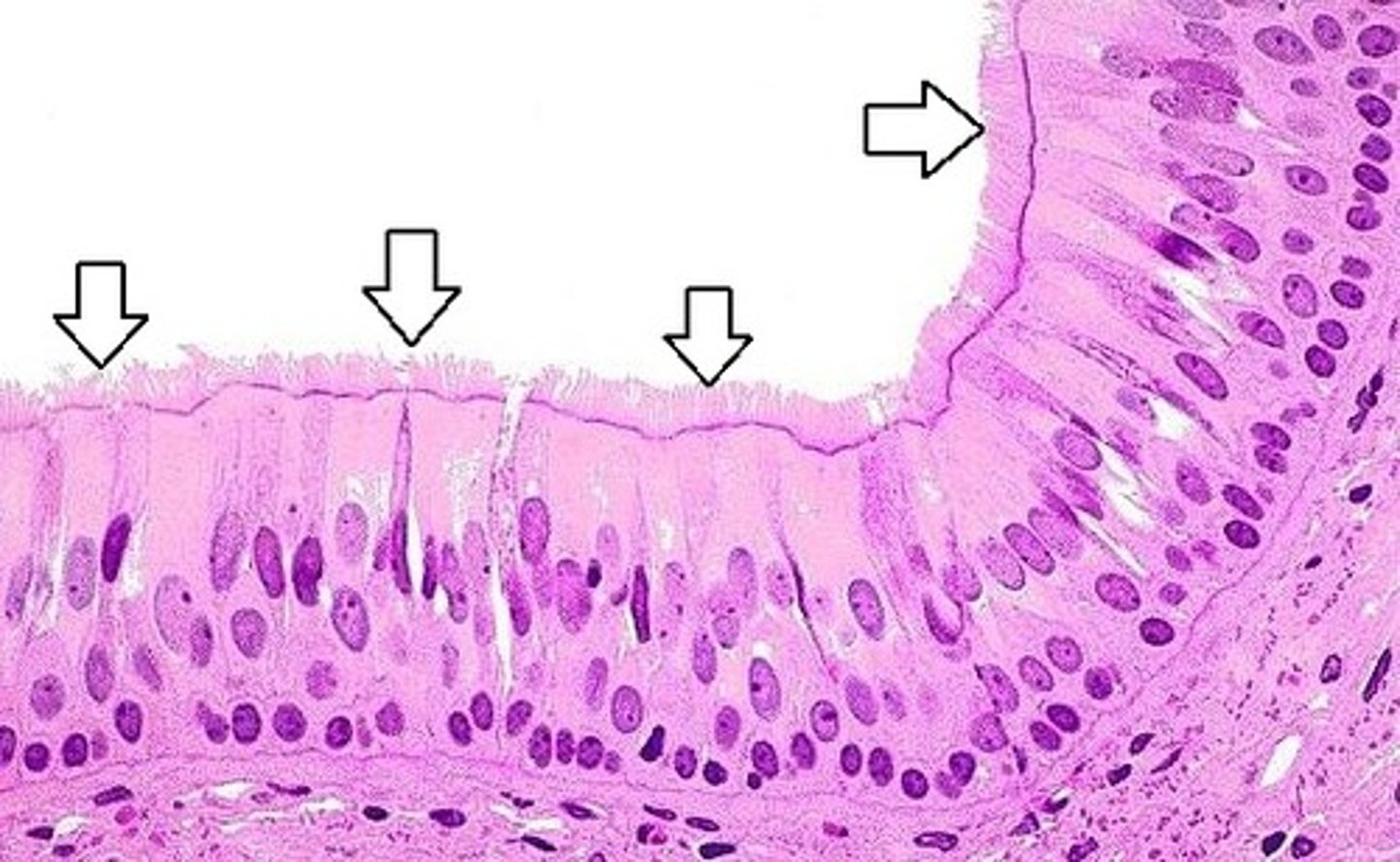
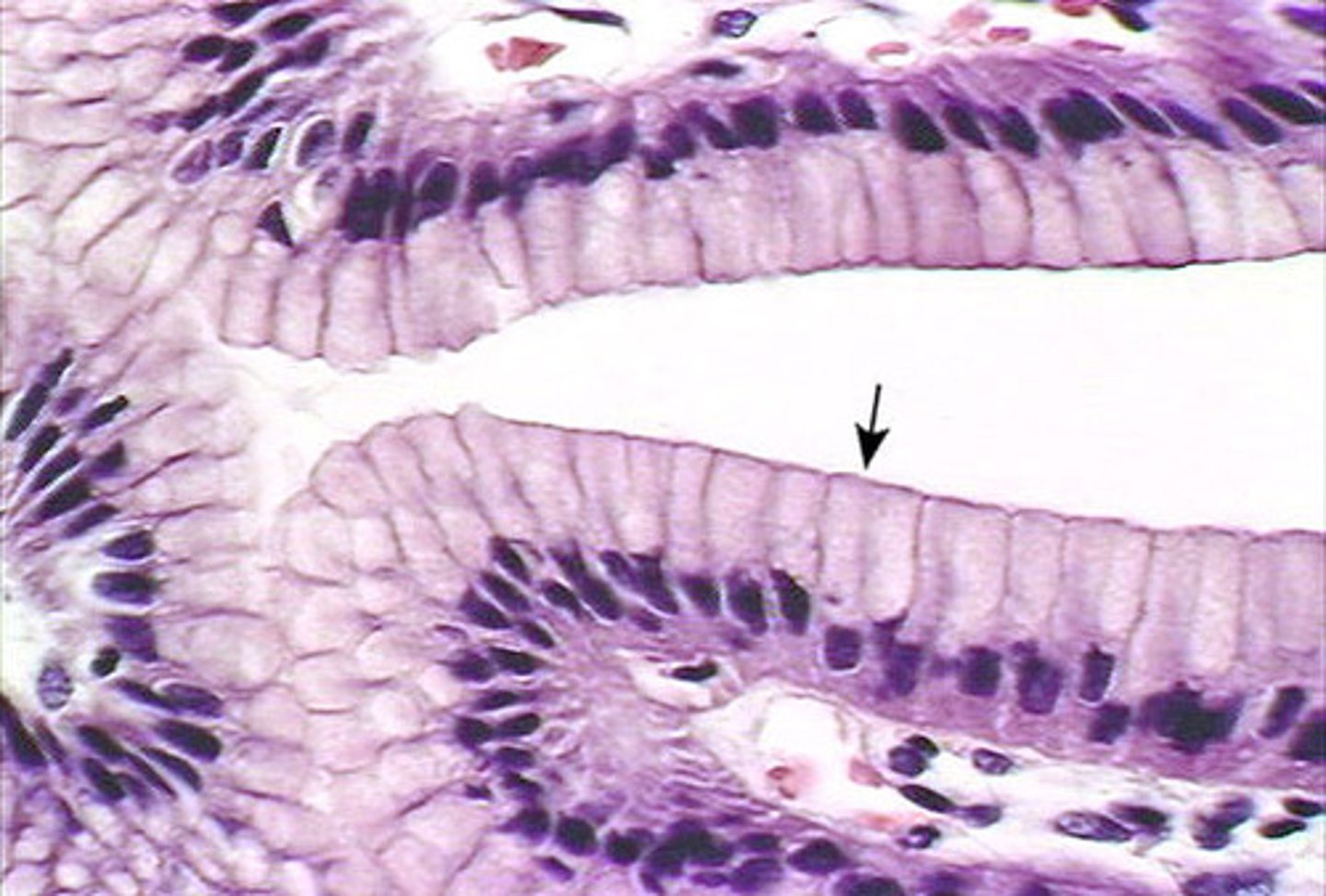
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelial tissue
A type of epithelial tissue that appears to be stratified but is actually a single layer with varying cell heights, often found in the respiratory tract.
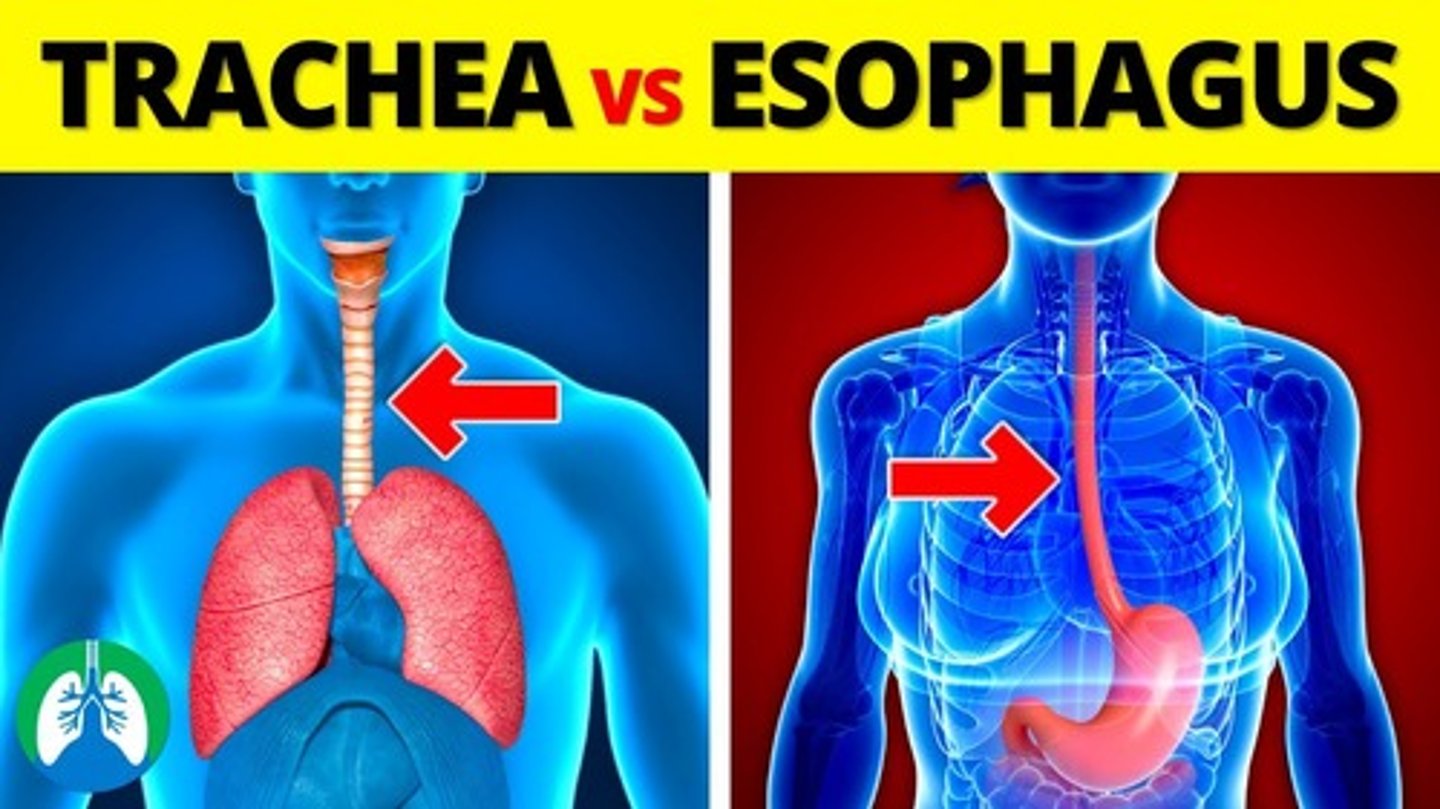
Trachea vs esophagus
The trachea is the airway leading to the lungs, while the esophagus is the tube that carries food to the stomach.
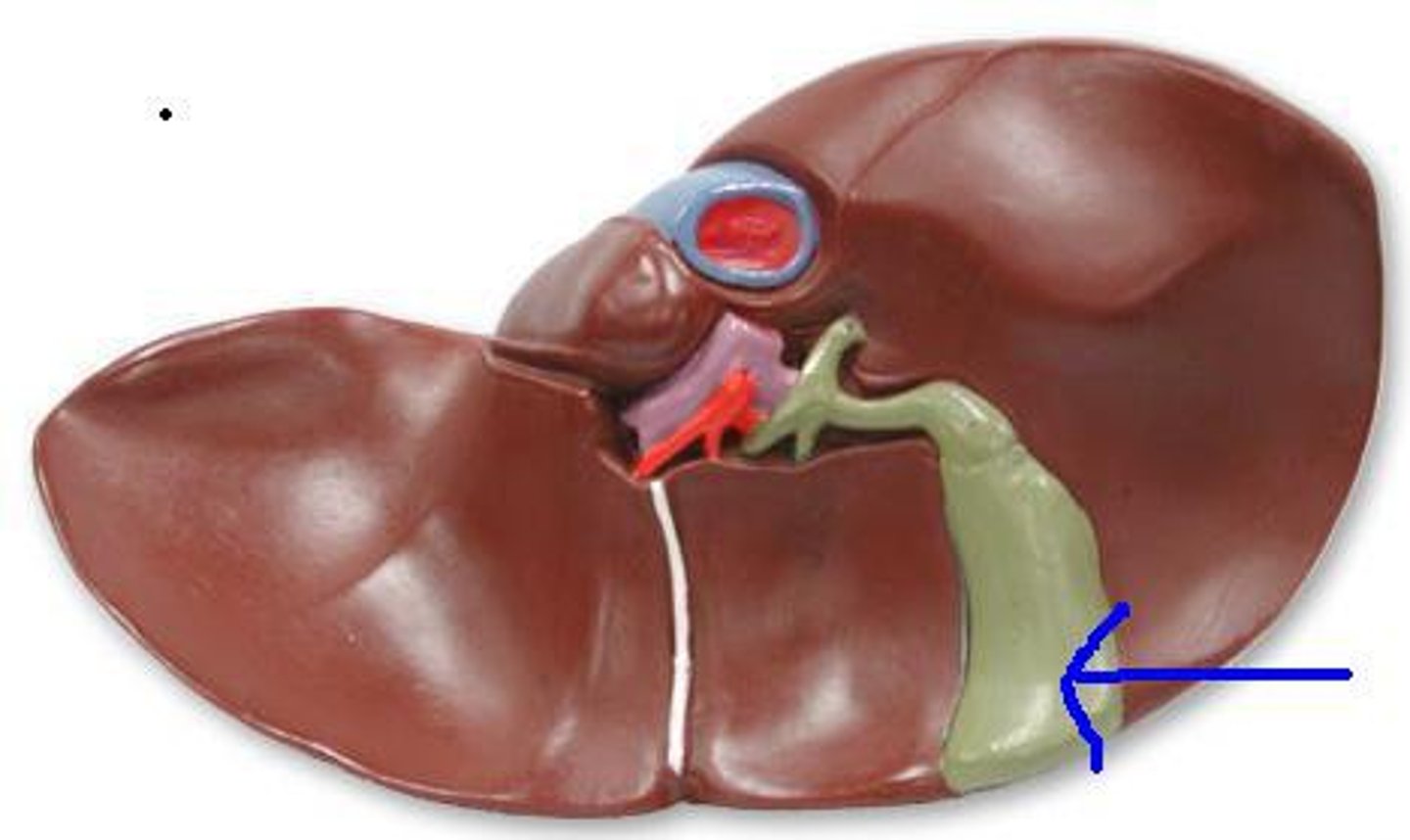
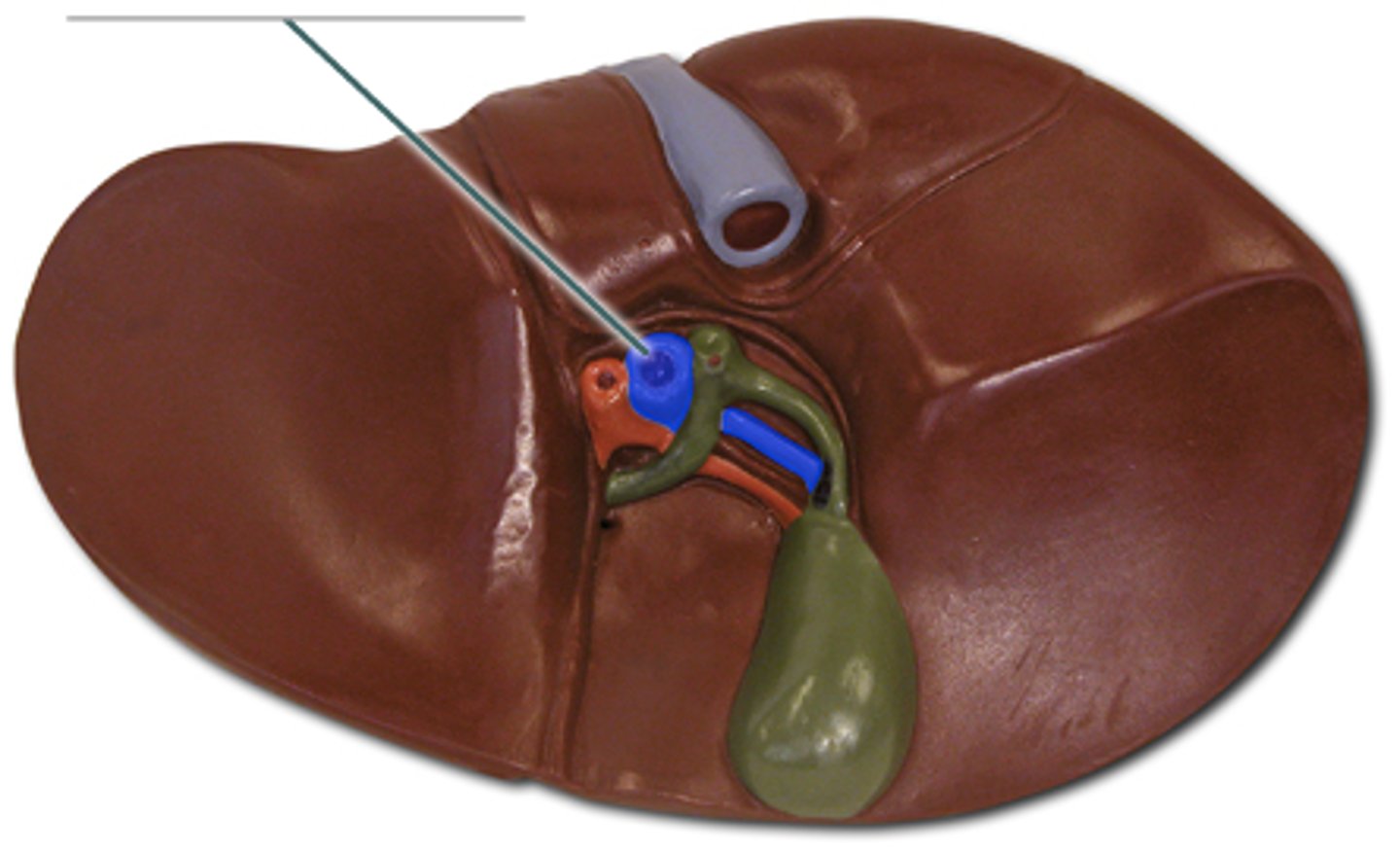
Gallbladder
A small organ that stores bile produced by the liver, aiding in fat digestion.
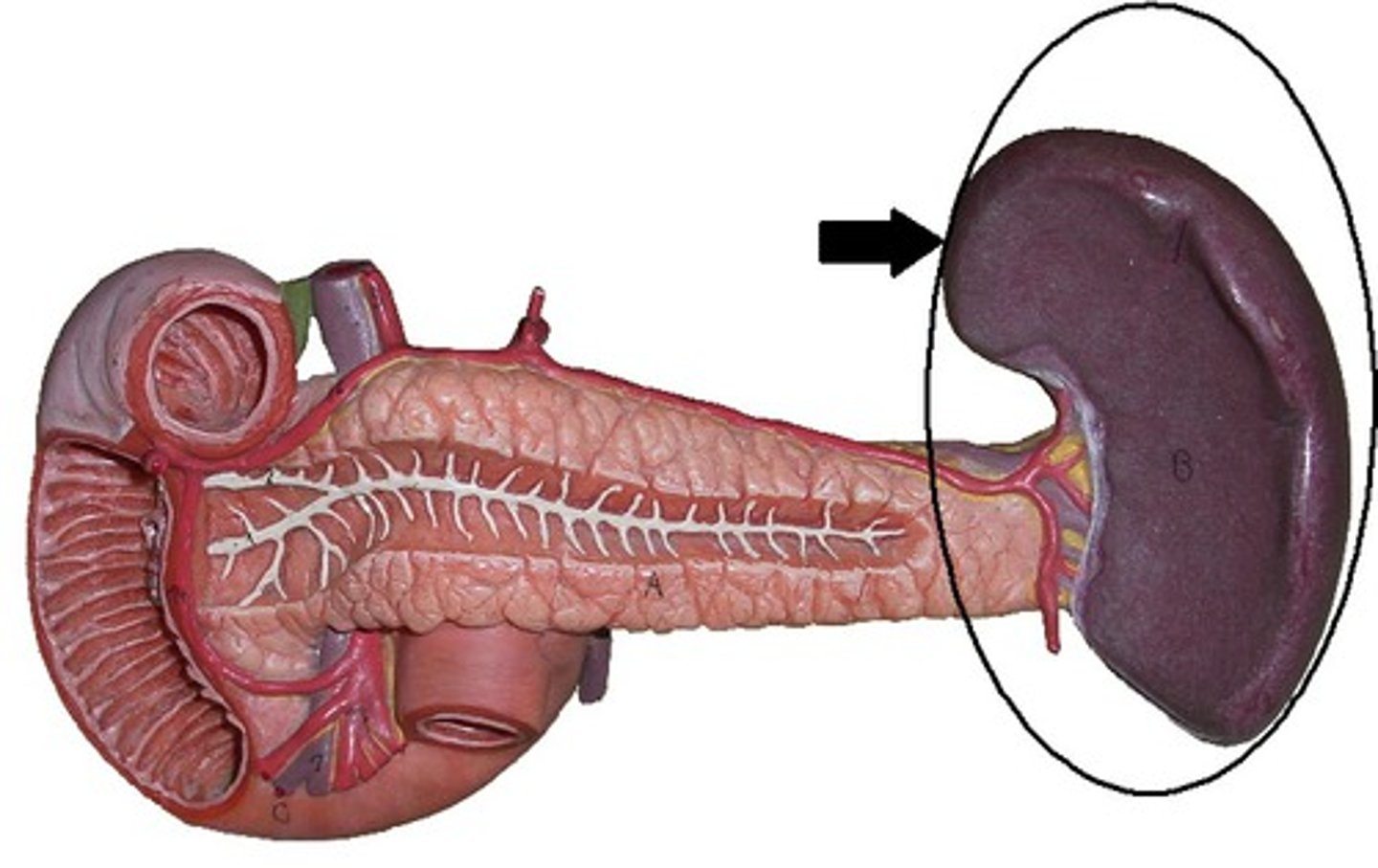
Spleen
An organ involved in filtering blood and recycling iron from red blood cells.
Epiglottis
A flap of tissue that covers the trachea during swallowing to prevent food from entering the airway.
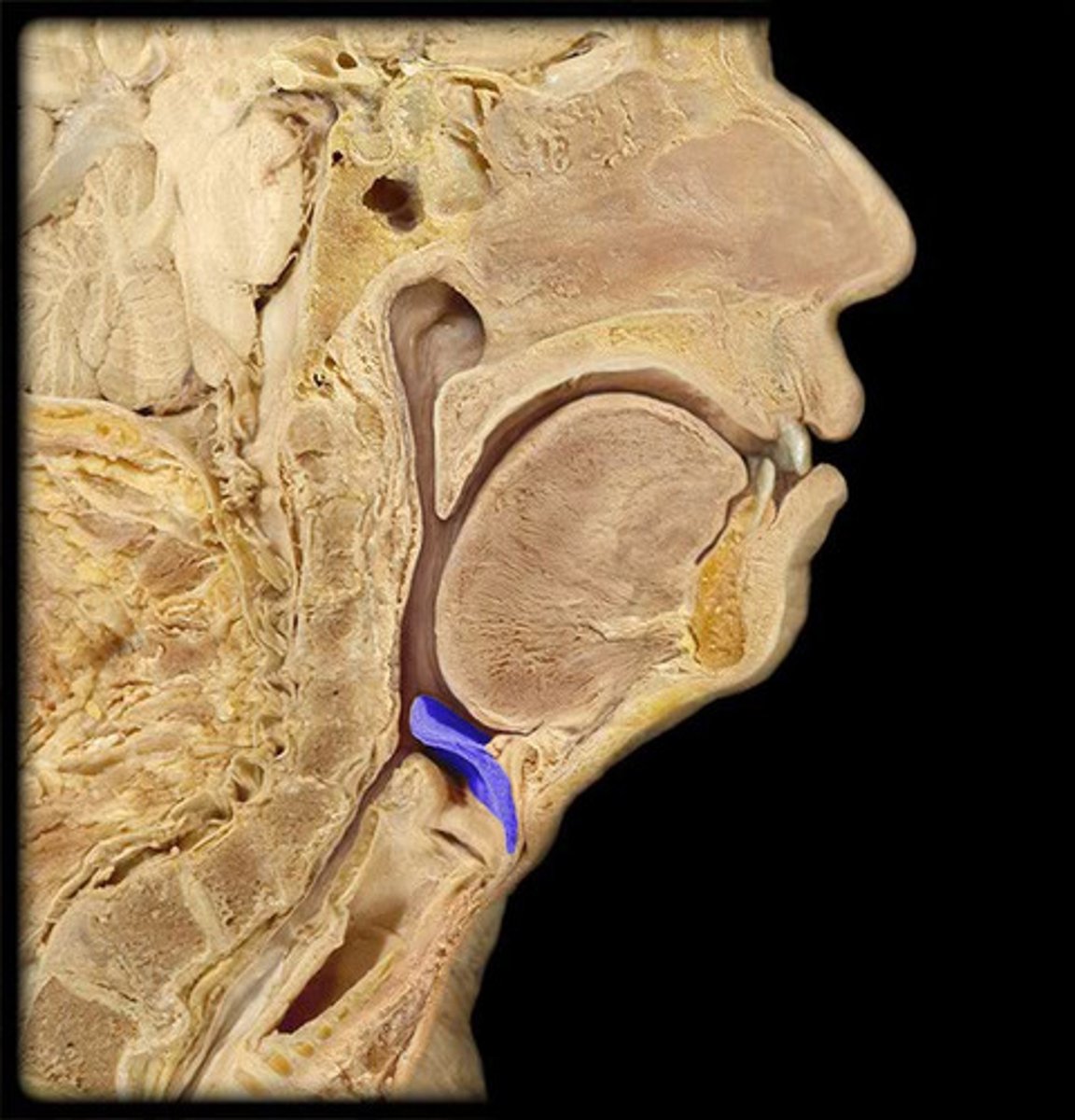
Larynx
The voice box, located in the throat, involved in sound production and protecting the airway.
Hyoid bone
A U-shaped bone in the neck that supports the tongue and is not directly attached to other bones.
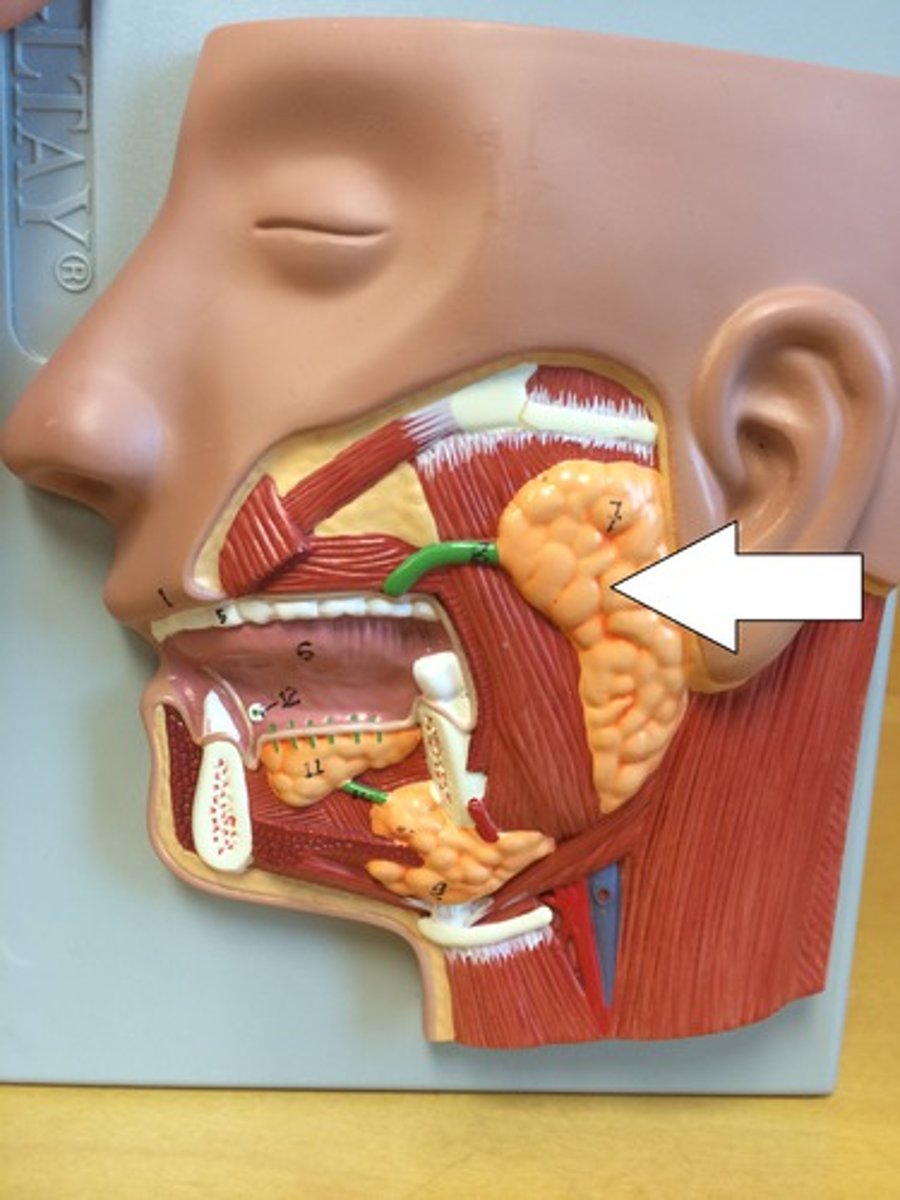
Parotid salivary gland
The largest salivary gland, located near the ear, that produces saliva.
Hepatopancreatic ampulla
The junction where the bile duct and pancreatic duct meet and release their contents into the duodenum.
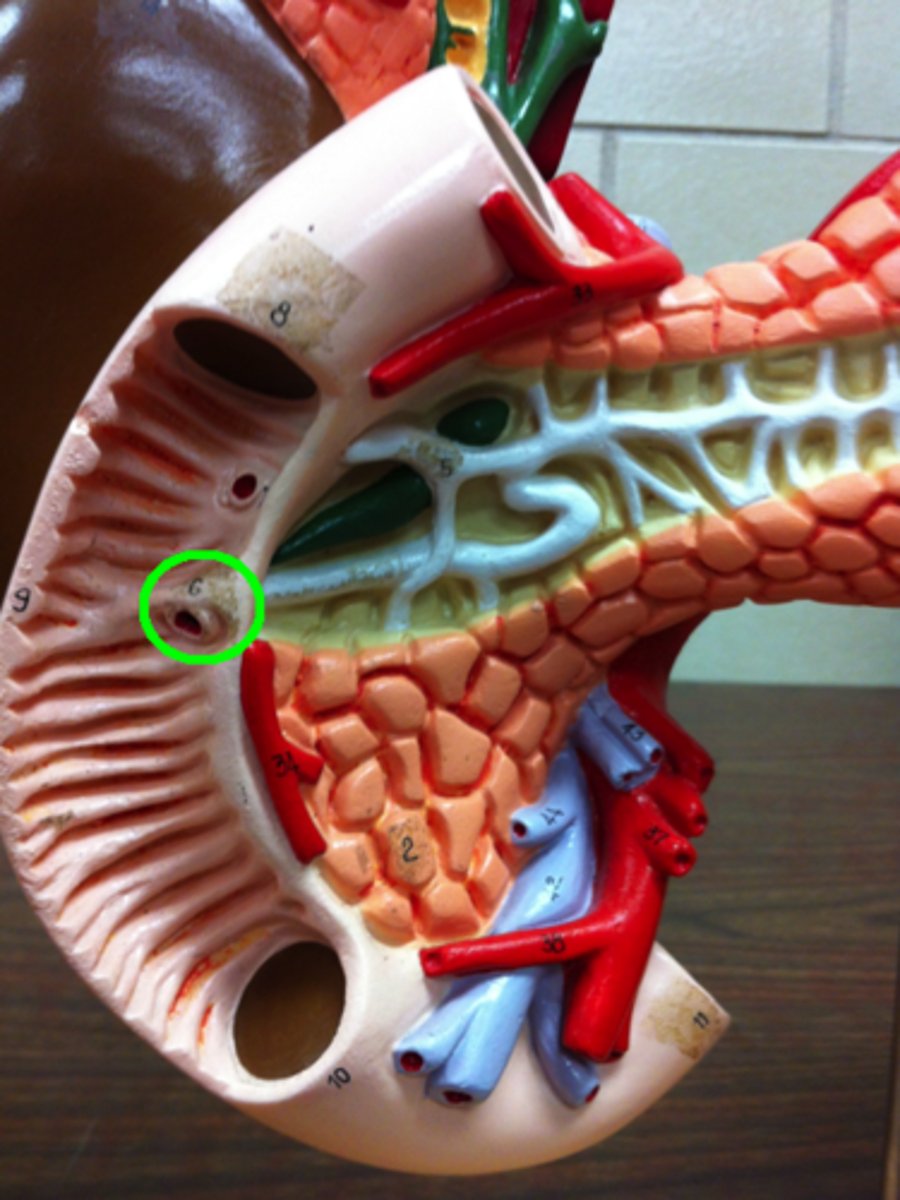
Pancreas
An organ that produces digestive enzymes and hormones, including insulin.
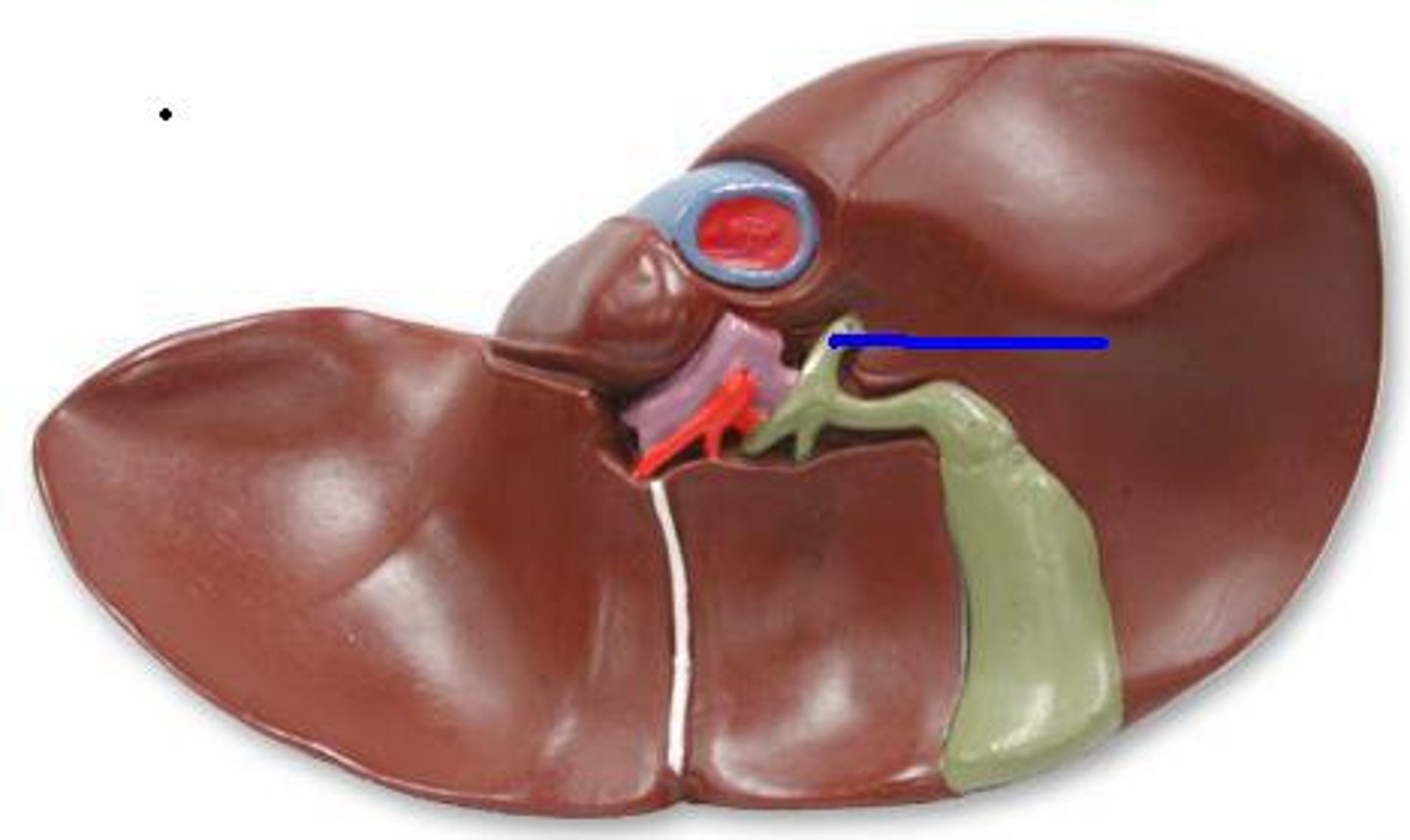
Common bile duct
The duct that carries bile from the liver and gallbladder to the duodenum.
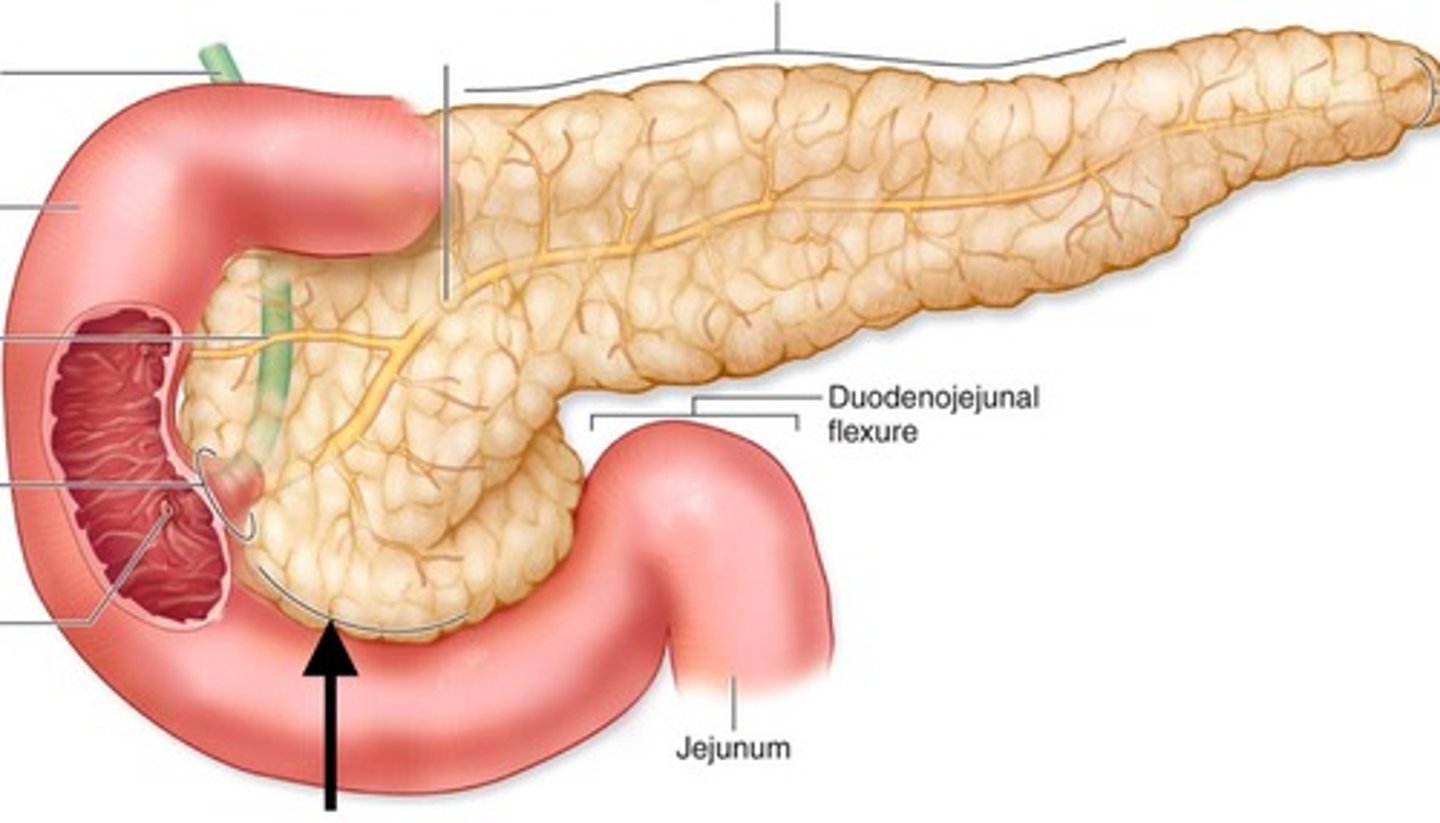
Duodenum
The first section of the small intestine, where most chemical digestion occurs.
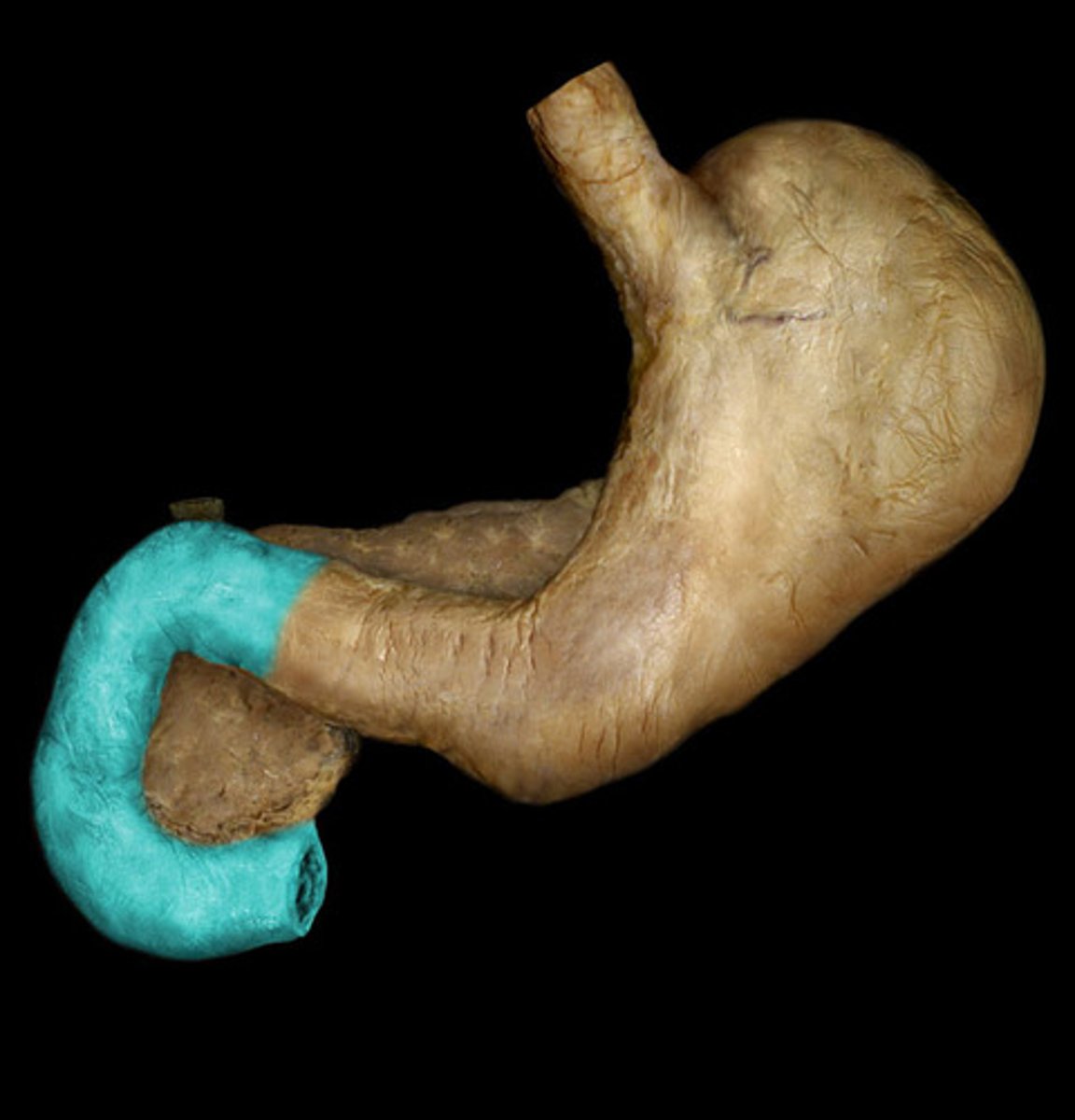
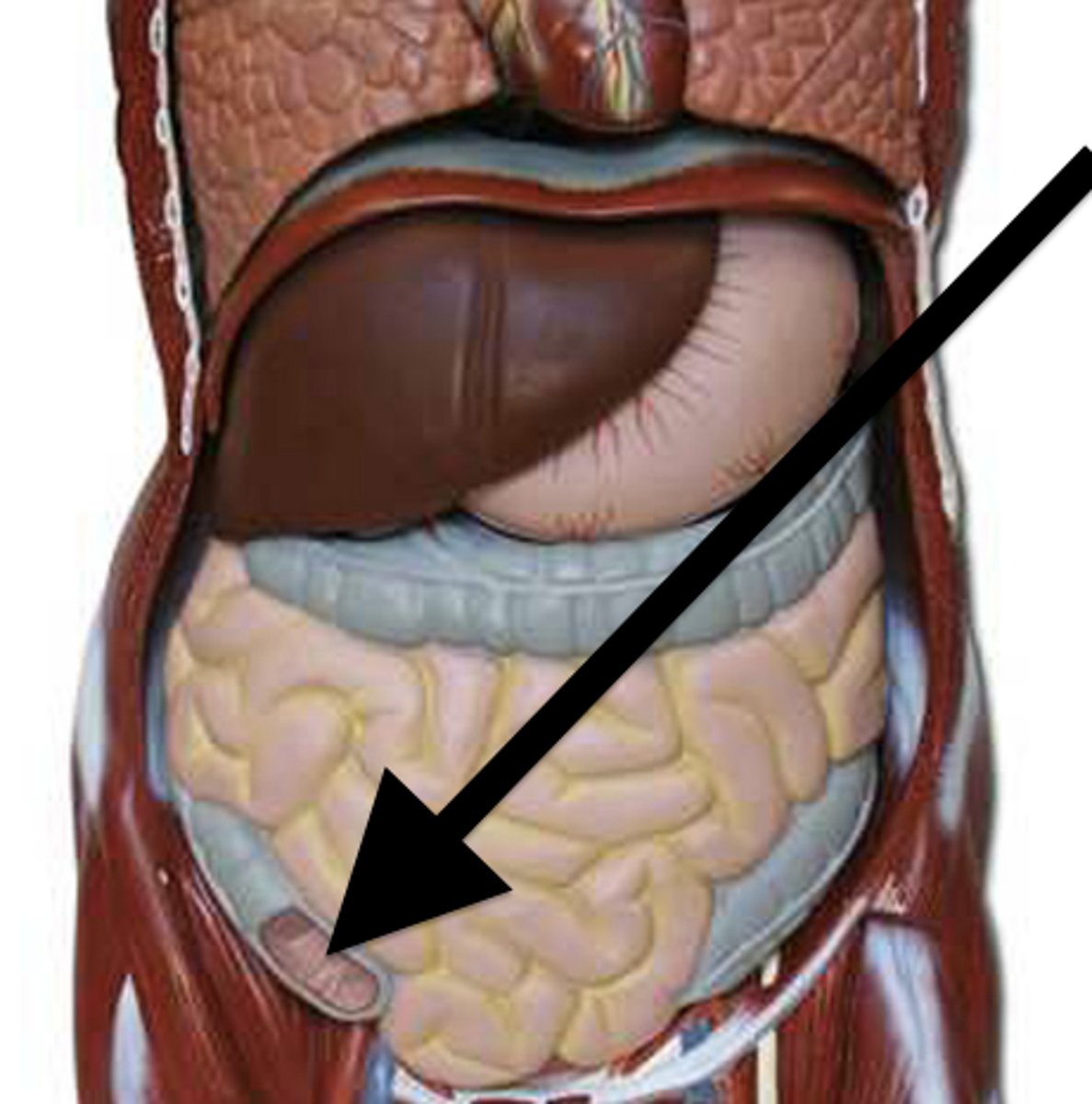
Cecum
The beginning of the large intestine, connecting the ileum of the small intestine to the colon.
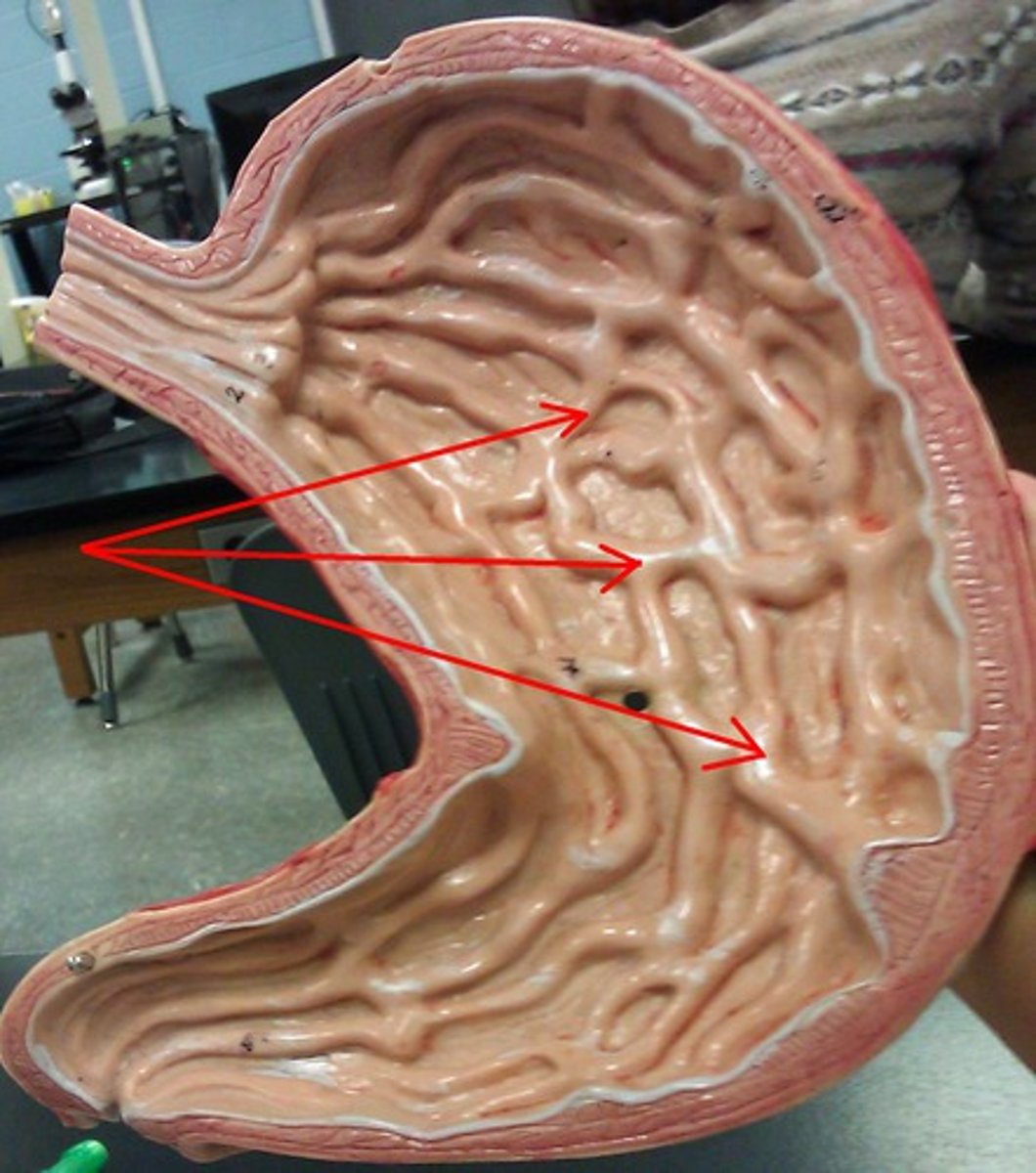
Rugae
Folds in the lining of the stomach that allow for expansion when food enters.
Leukocyte vs erythrocyte
Leukocytes are white blood cells involved in immune response, while erythrocytes are red blood cells that carry oxygen.
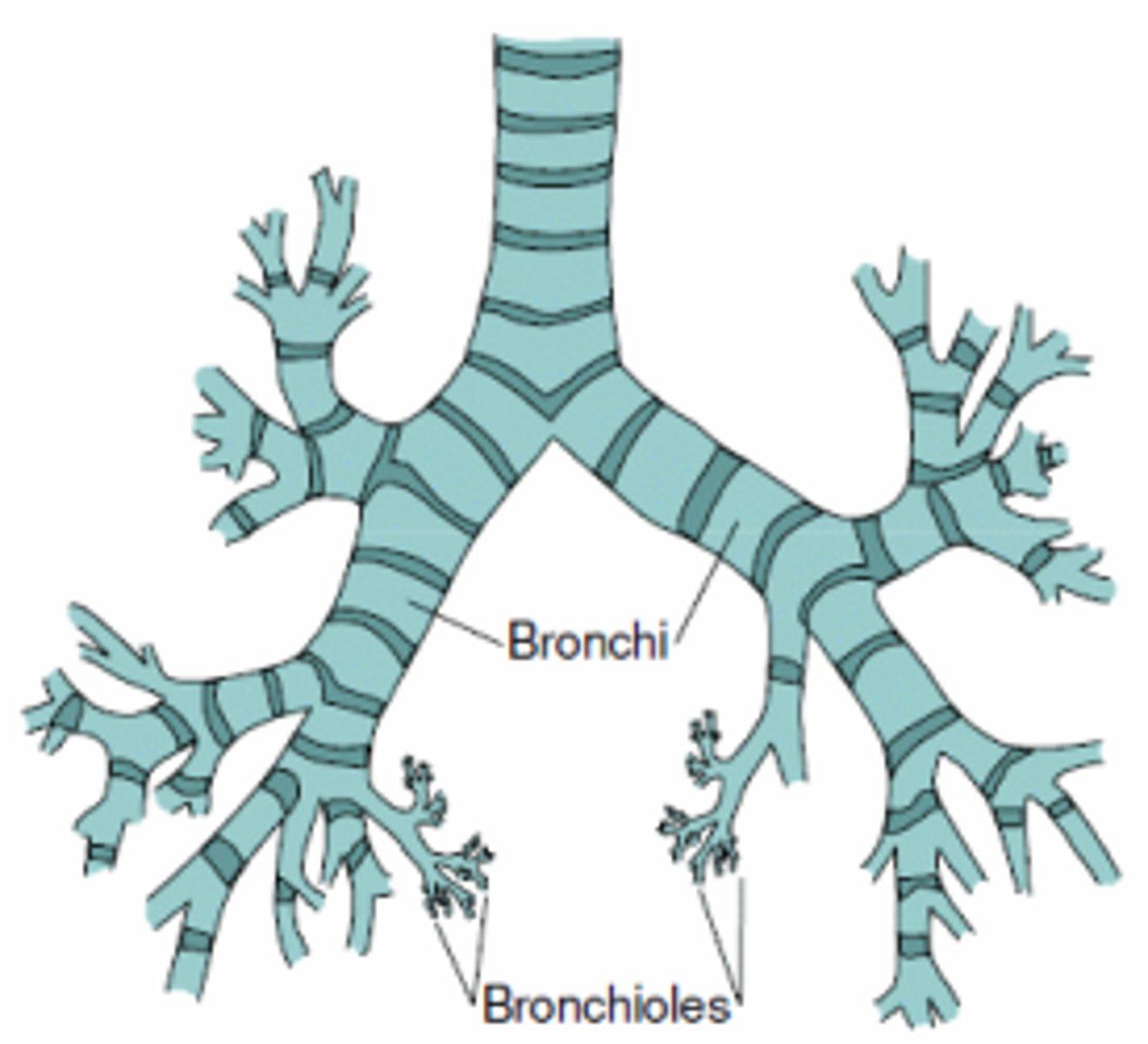
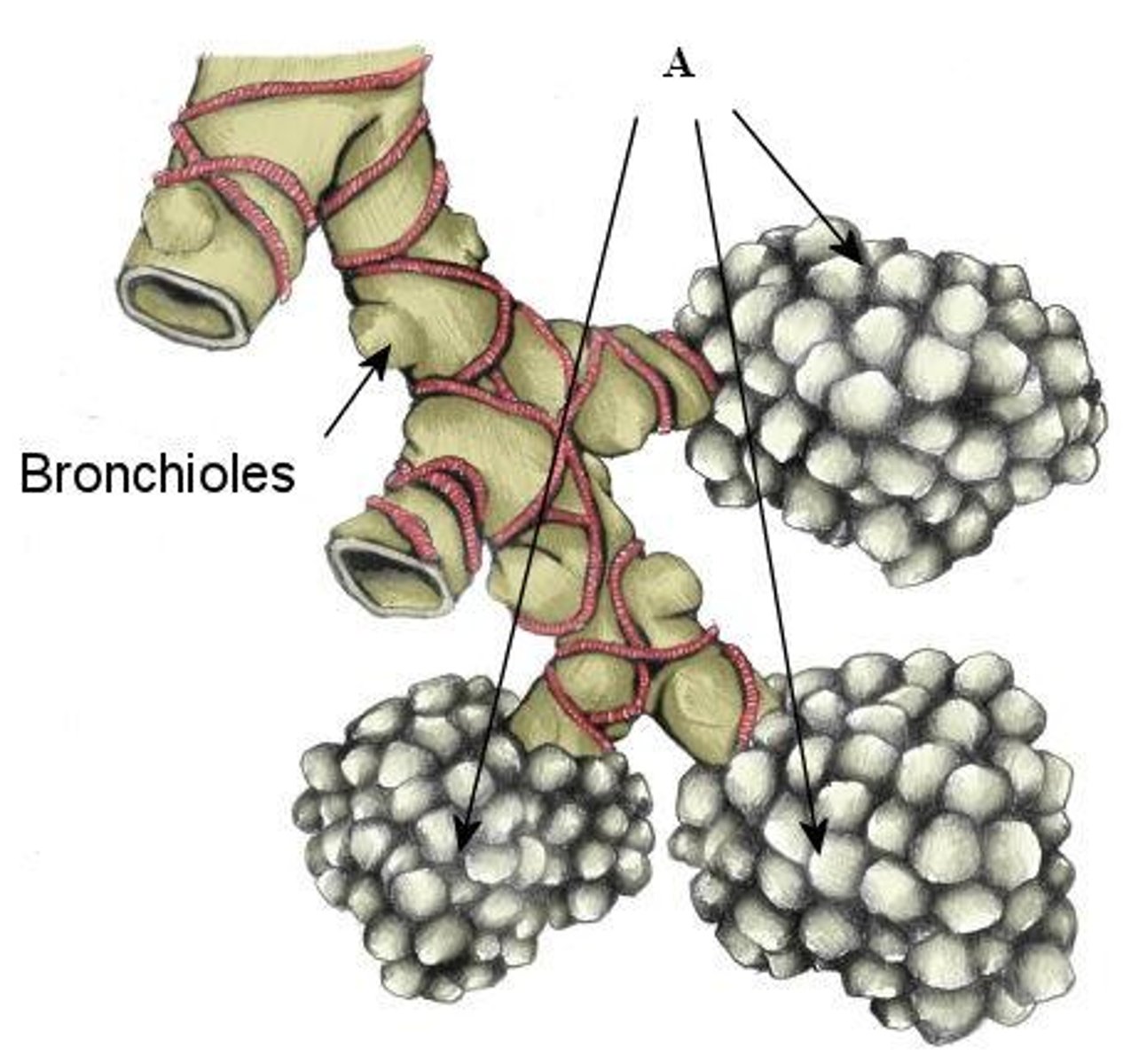
Bronchioles
Small air passages in the lungs that branch from the bronchi and lead to alveoli.
Alveolus
Tiny air sacs in the lungs where gas exchange occurs.
Simple columnar epithelium
A single layer of tall, column-like cells, often found in the digestive tract.
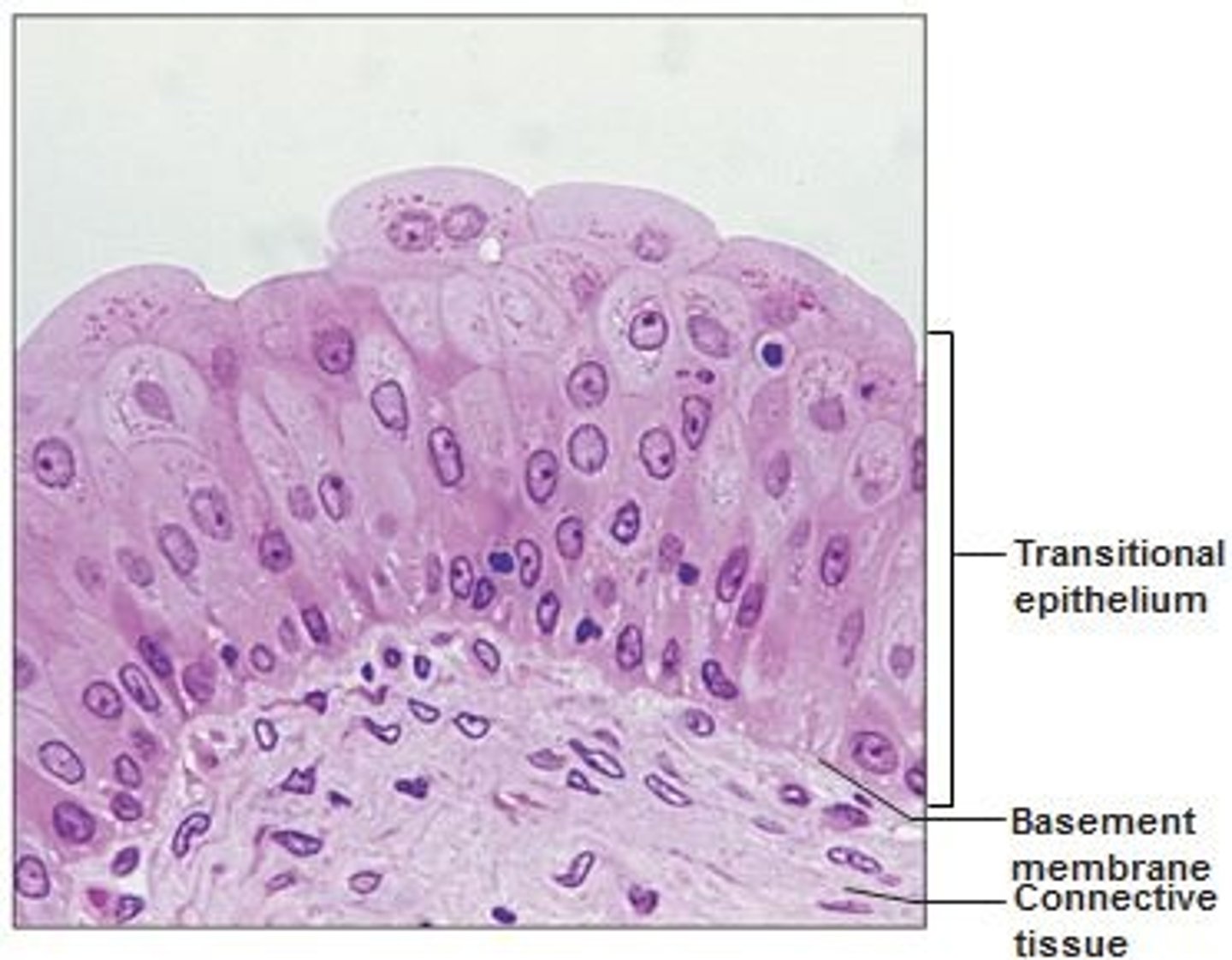
Transitional epithelium
A type of epithelium that can stretch and is found in the bladder.
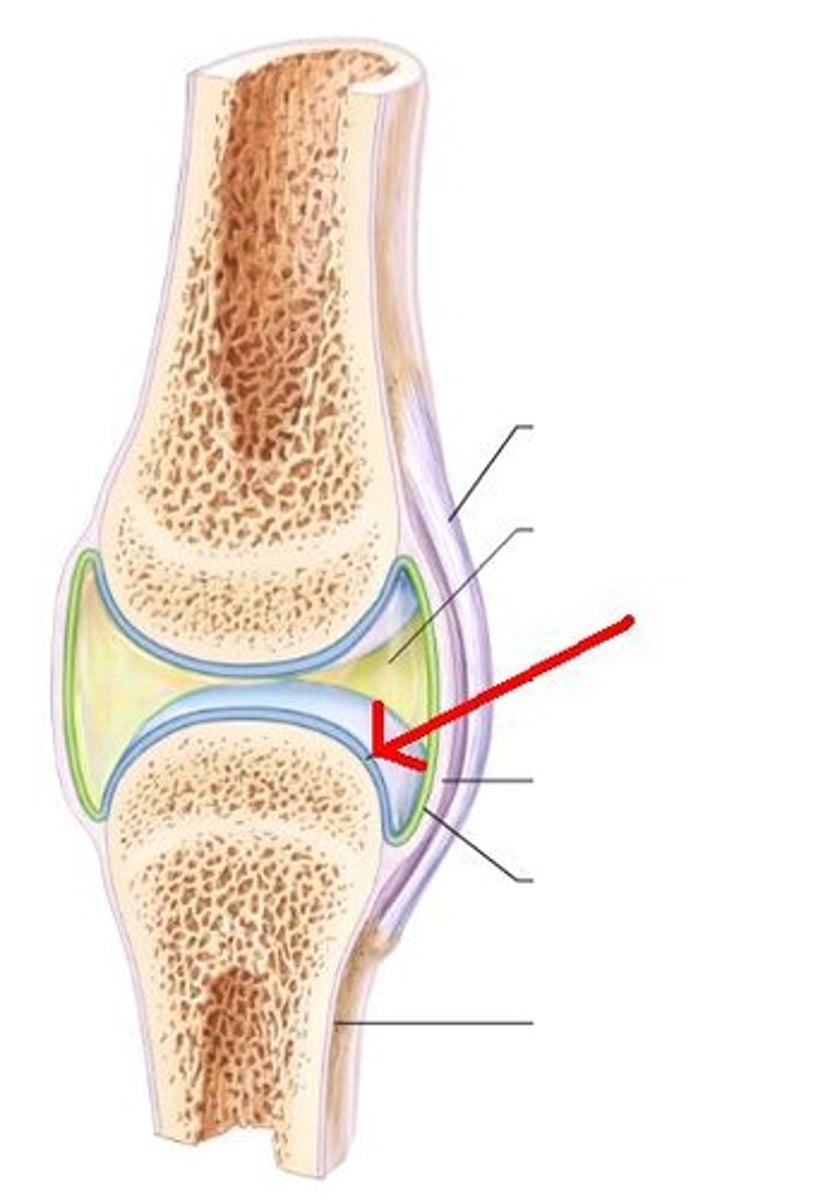
Hyaline cartilage
A type of cartilage that is smooth and glassy, providing support and flexibility.
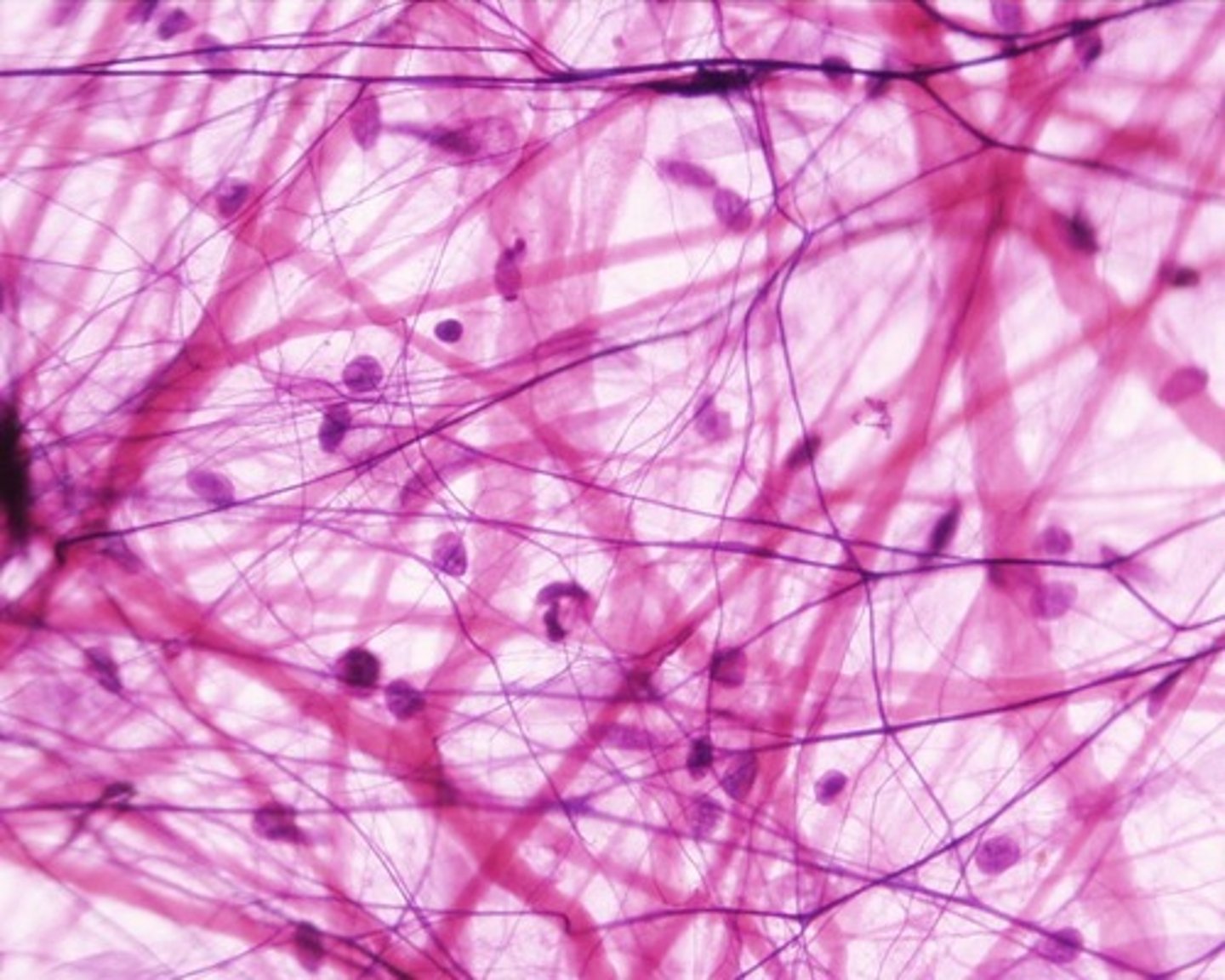
Areolar connective tissue
A loose connective tissue that provides support and elasticity to organs.
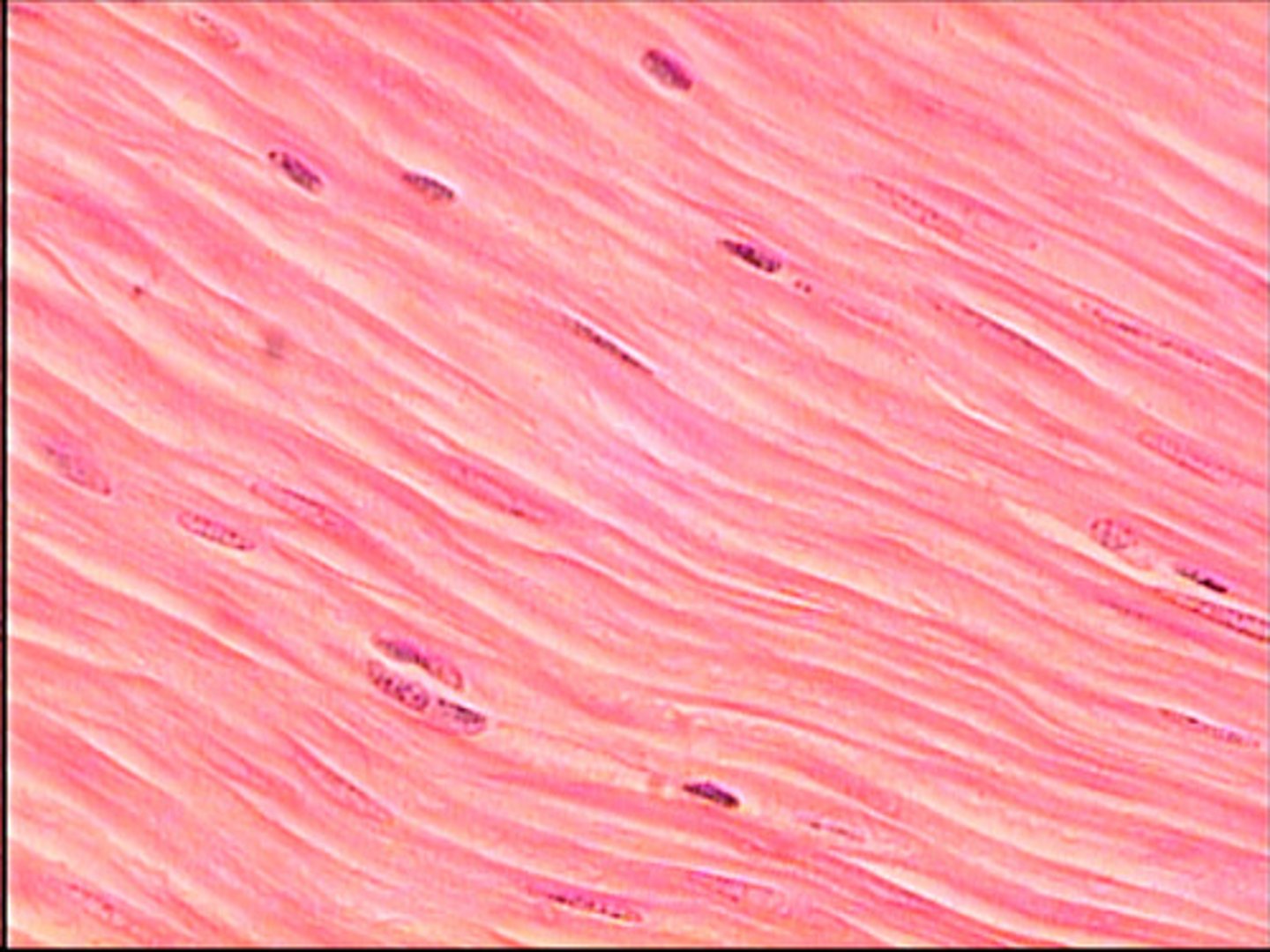
Smooth muscle tissue
Involuntary muscle found in walls of hollow organs, such as the intestines and blood vessels.
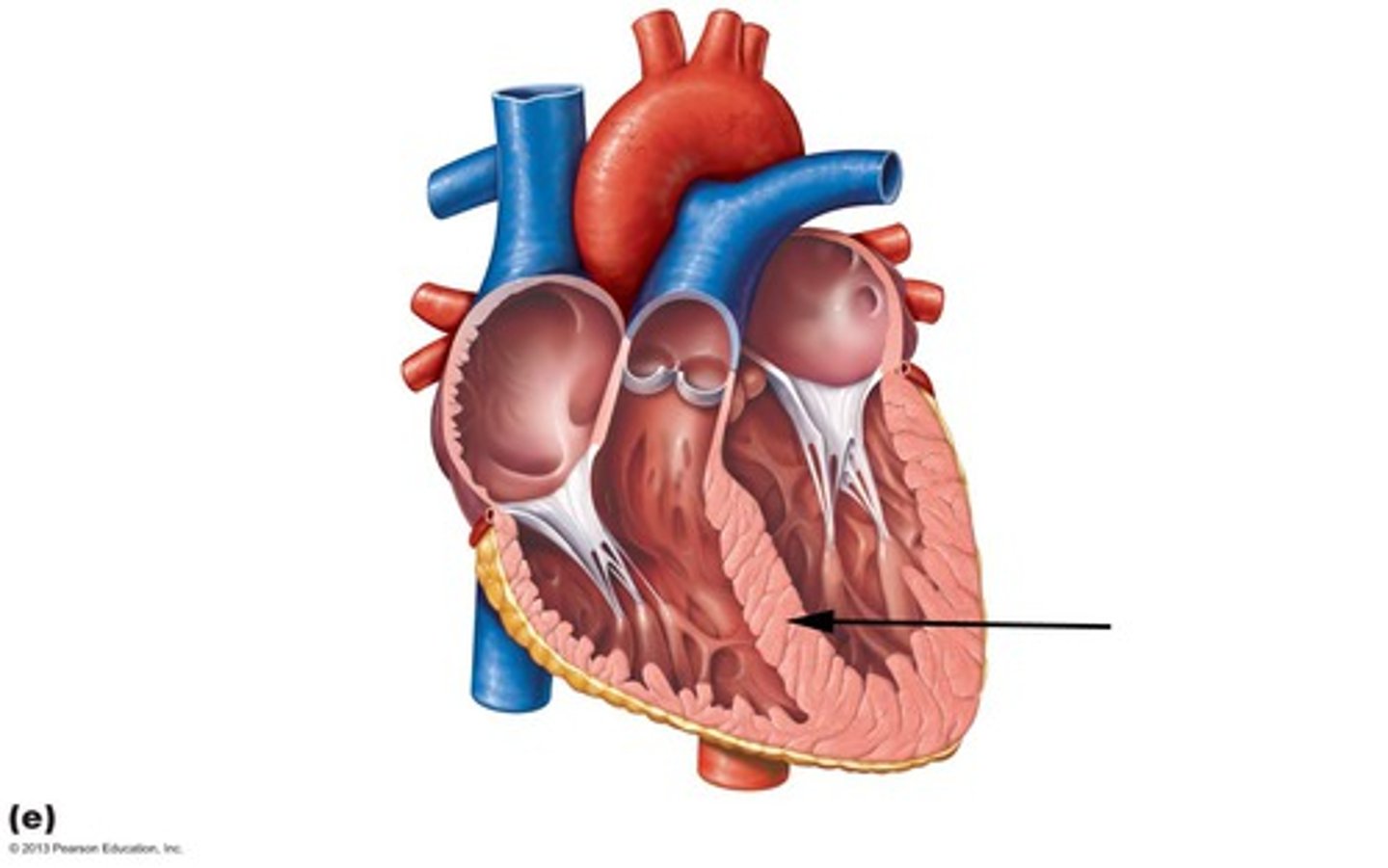
Interventricular septum
The wall that separates the left and right ventricles of the heart.
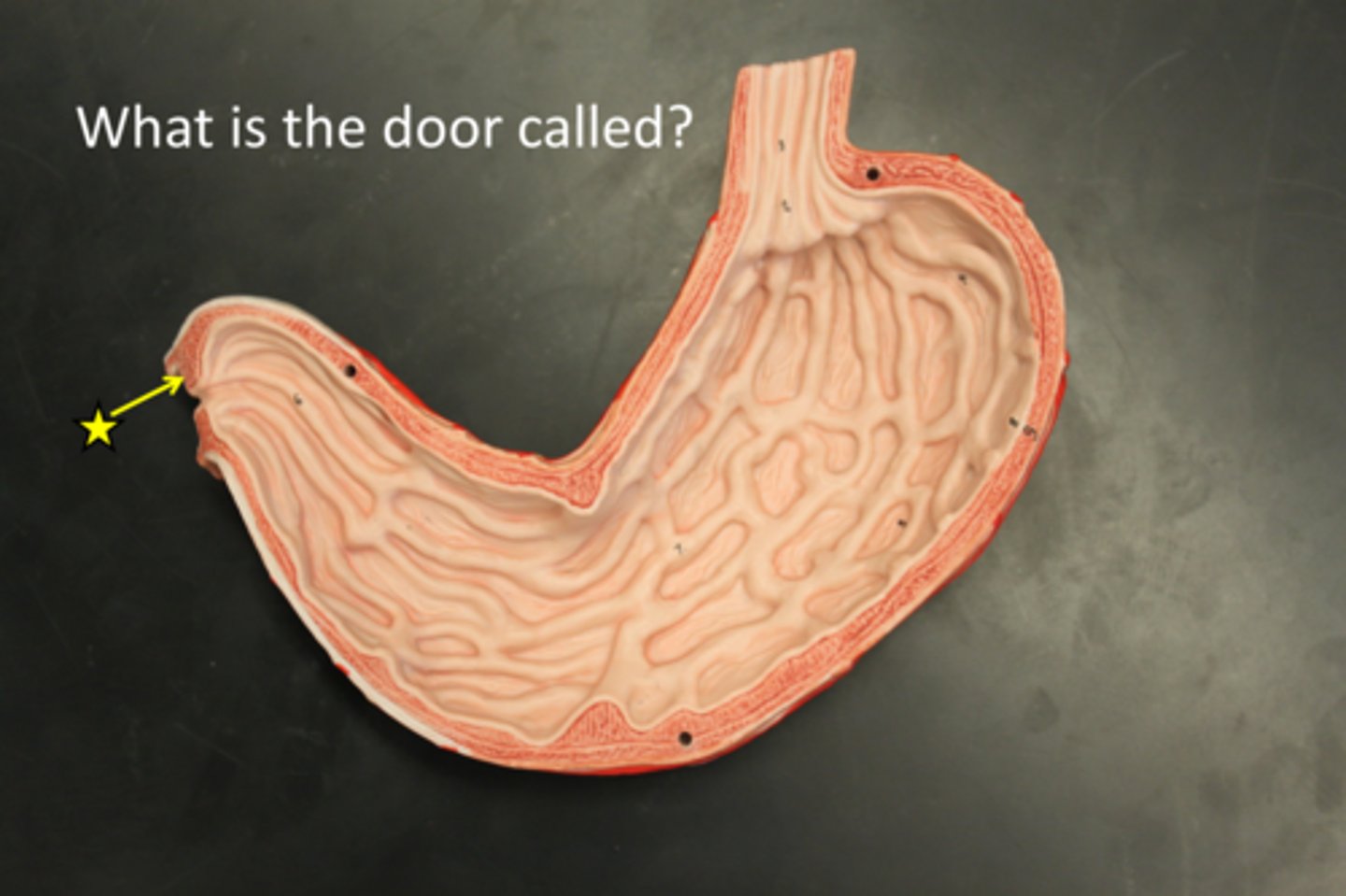
Pyloric sphincter
A valve that controls the passage of food from the stomach to the duodenum.
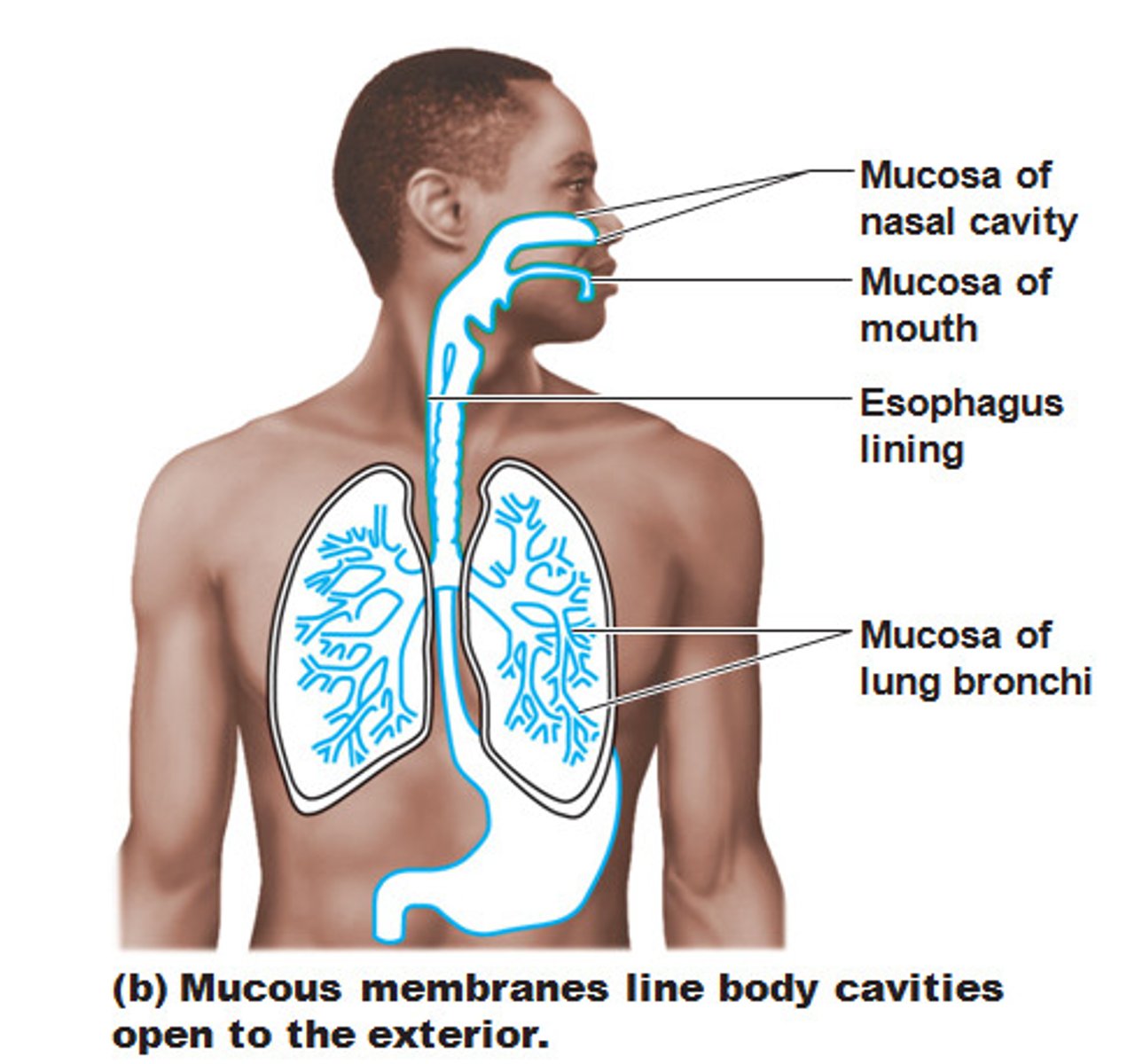
Mucous membrane
A membrane that lines body cavities and secretes mucus for lubrication.
Ligamentum arteriosum
A remnant of the ductus arteriosus, connecting the pulmonary artery to the aorta in fetal development.
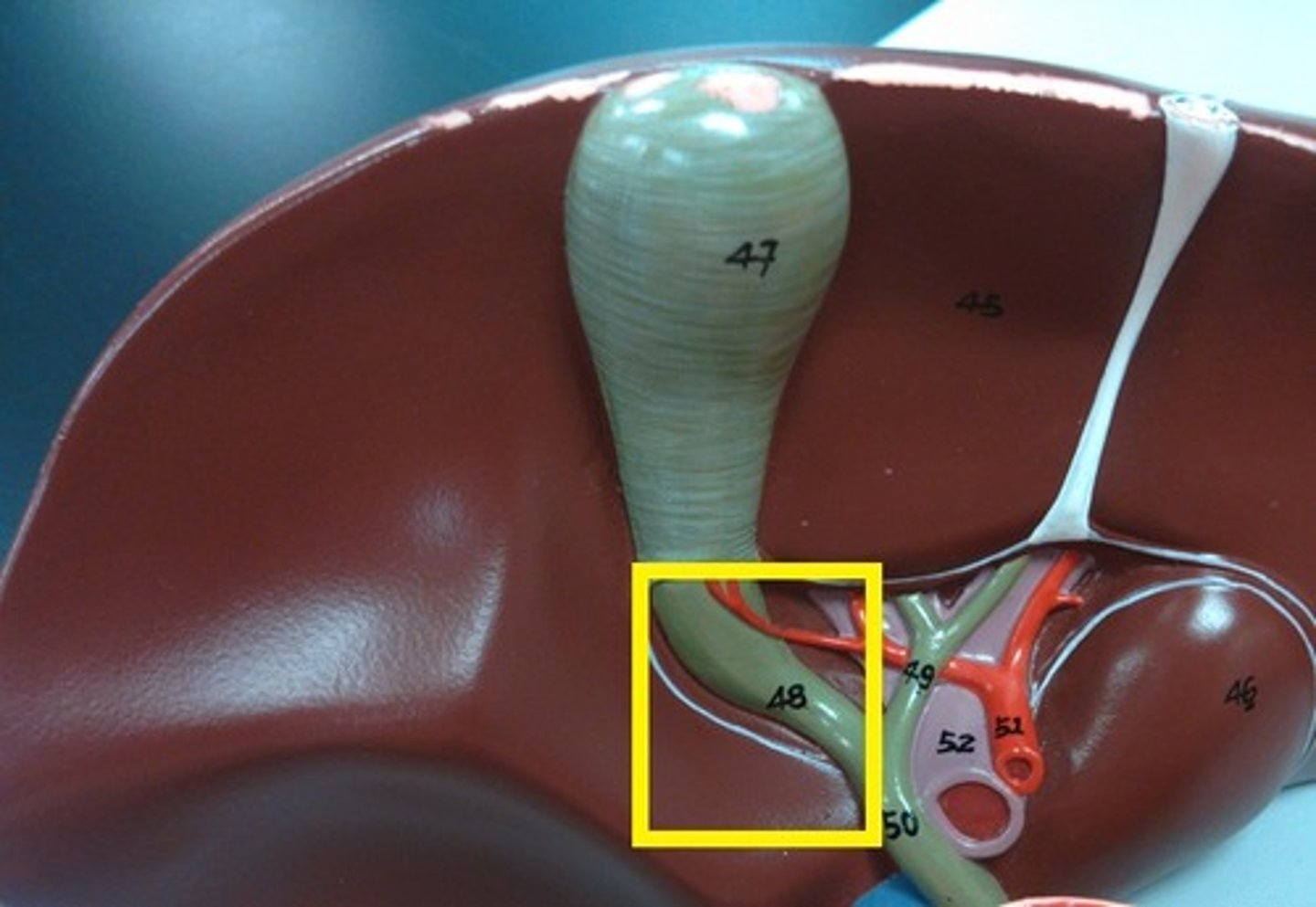
Cystic duct
The duct that carries bile to and from the gallbladder.
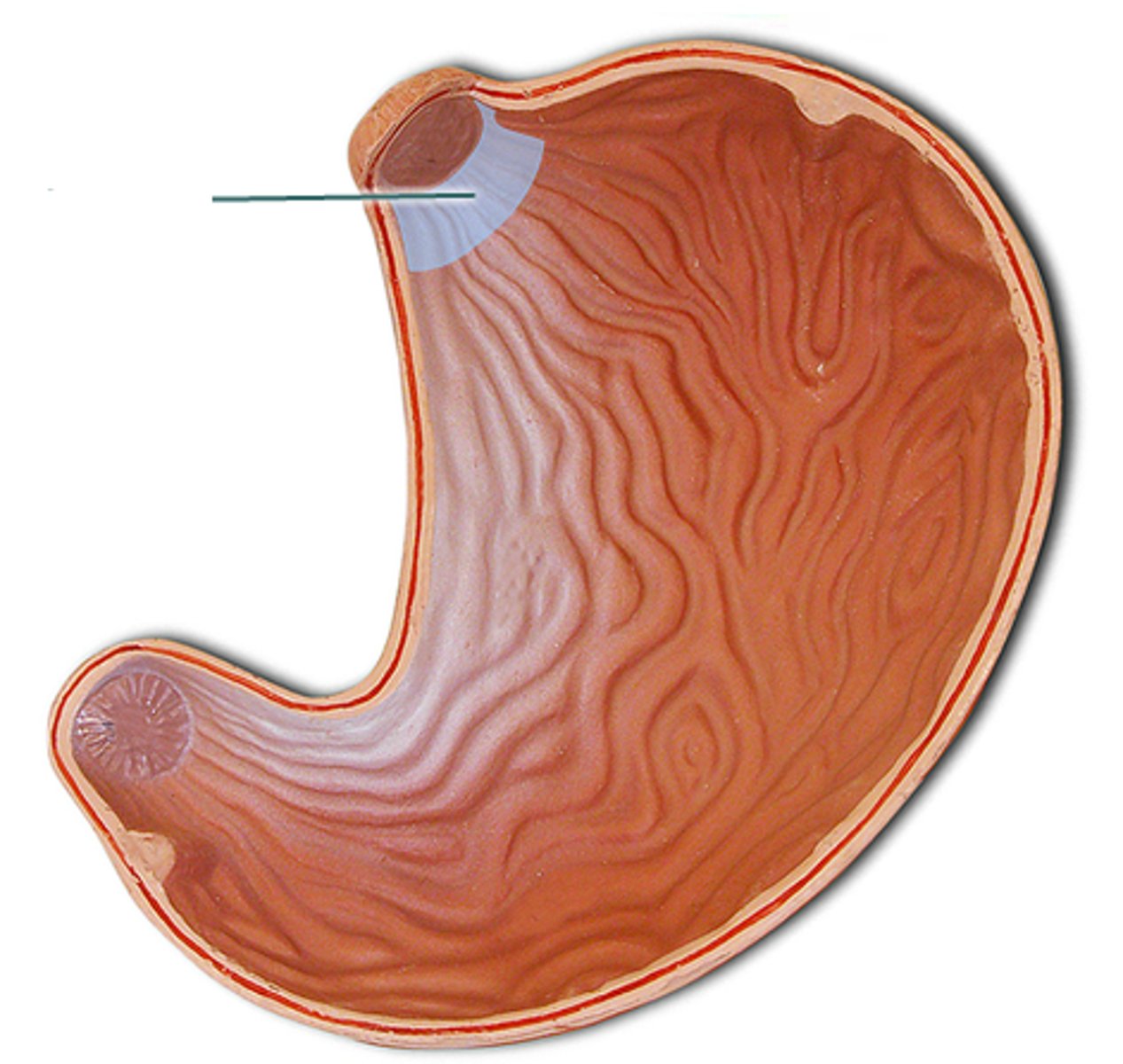
Cardia
The region of the stomach nearest to the esophagus.
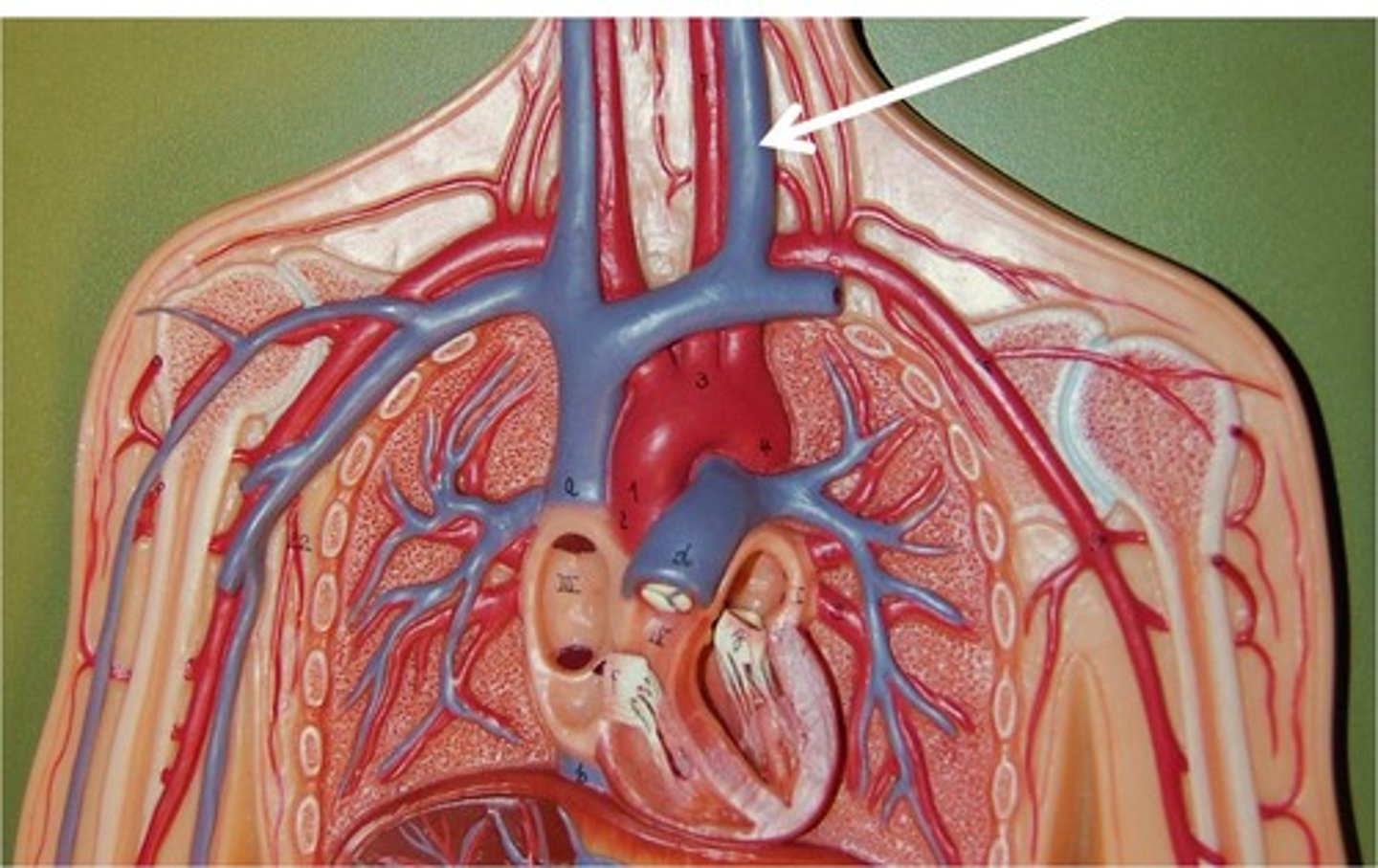
Internal jugular vein
A major vein that drains blood from the brain and neck.
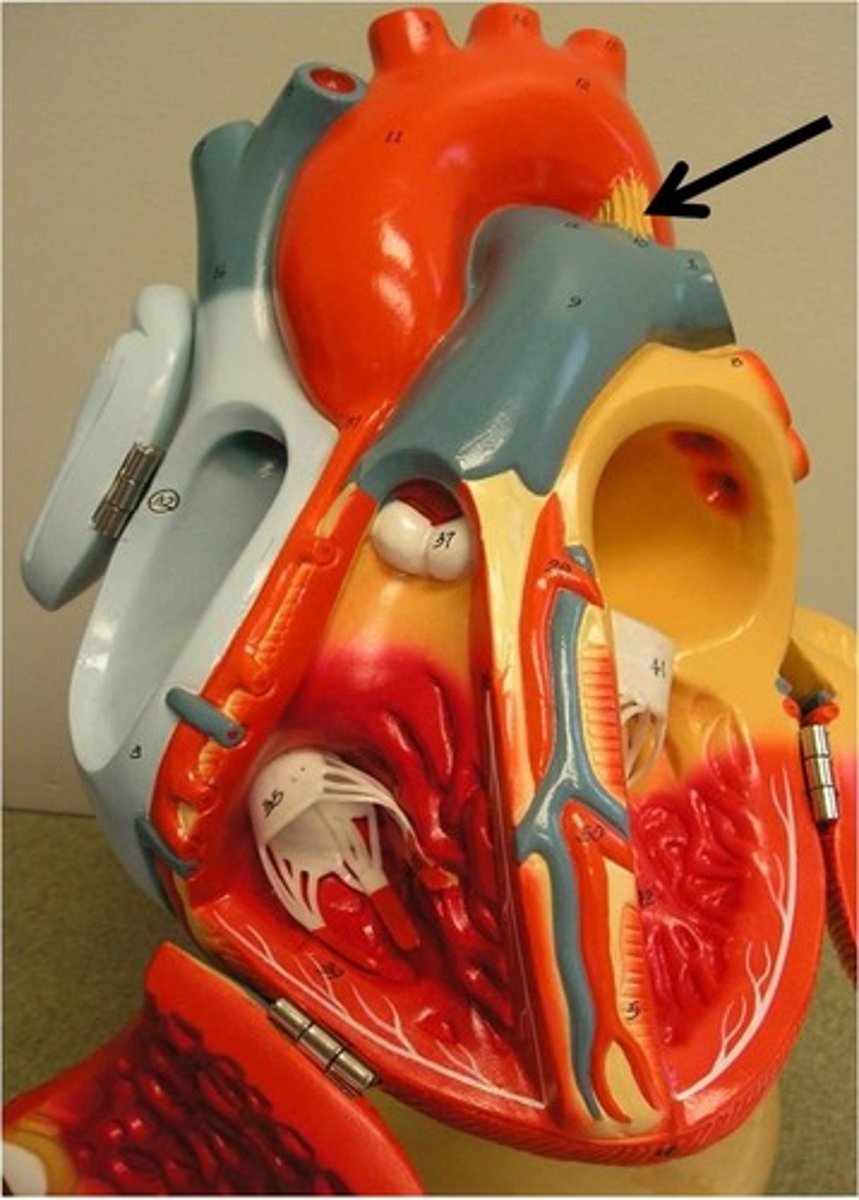
Falciform ligament
A ligament that attaches the liver to the anterior abdominal wall.
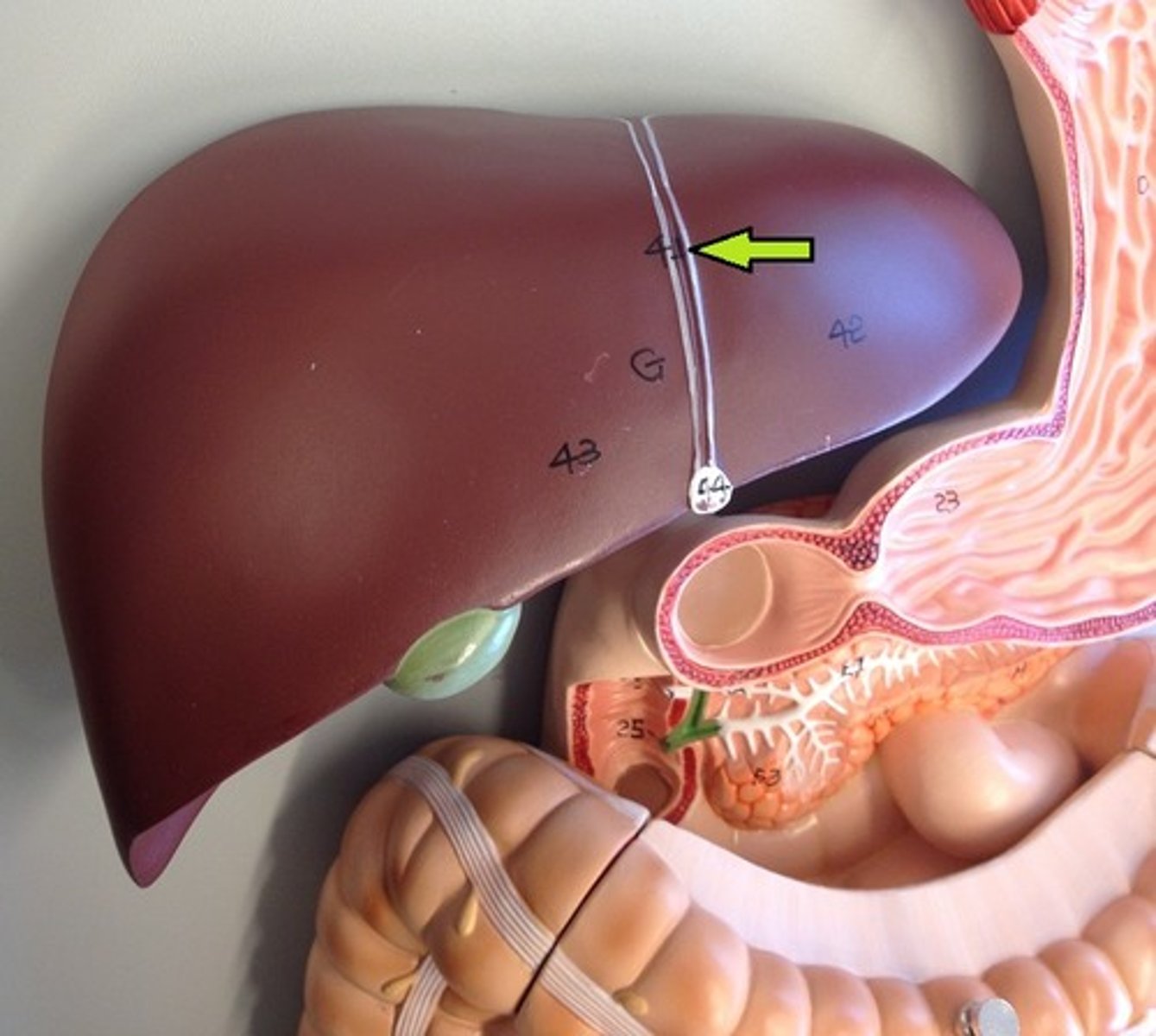
Portal vein
A vein that carries blood from the gastrointestinal tract and spleen to the liver.
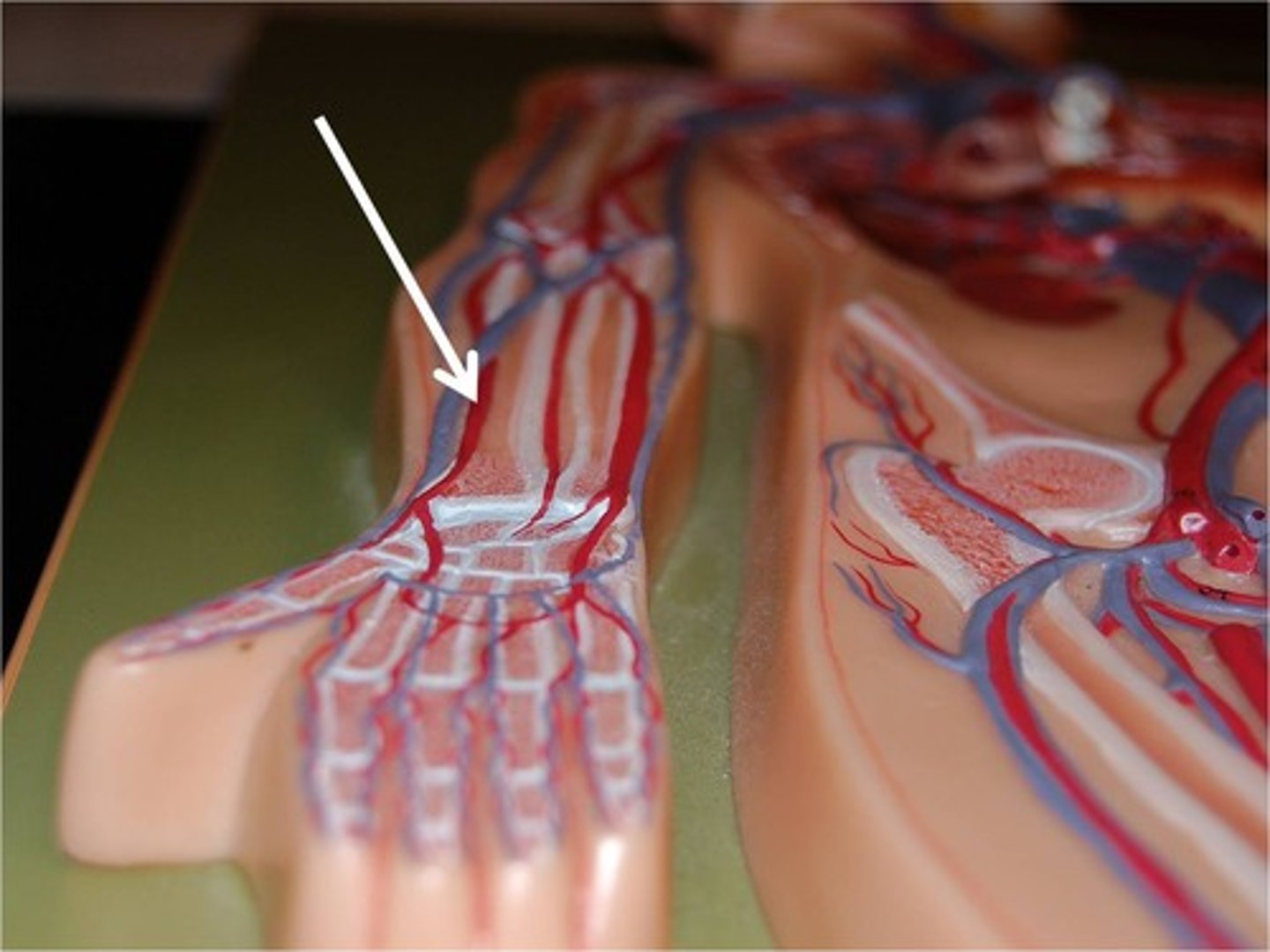
Radial artery
An artery in the forearm that supplies blood to the lateral aspect of the arm.
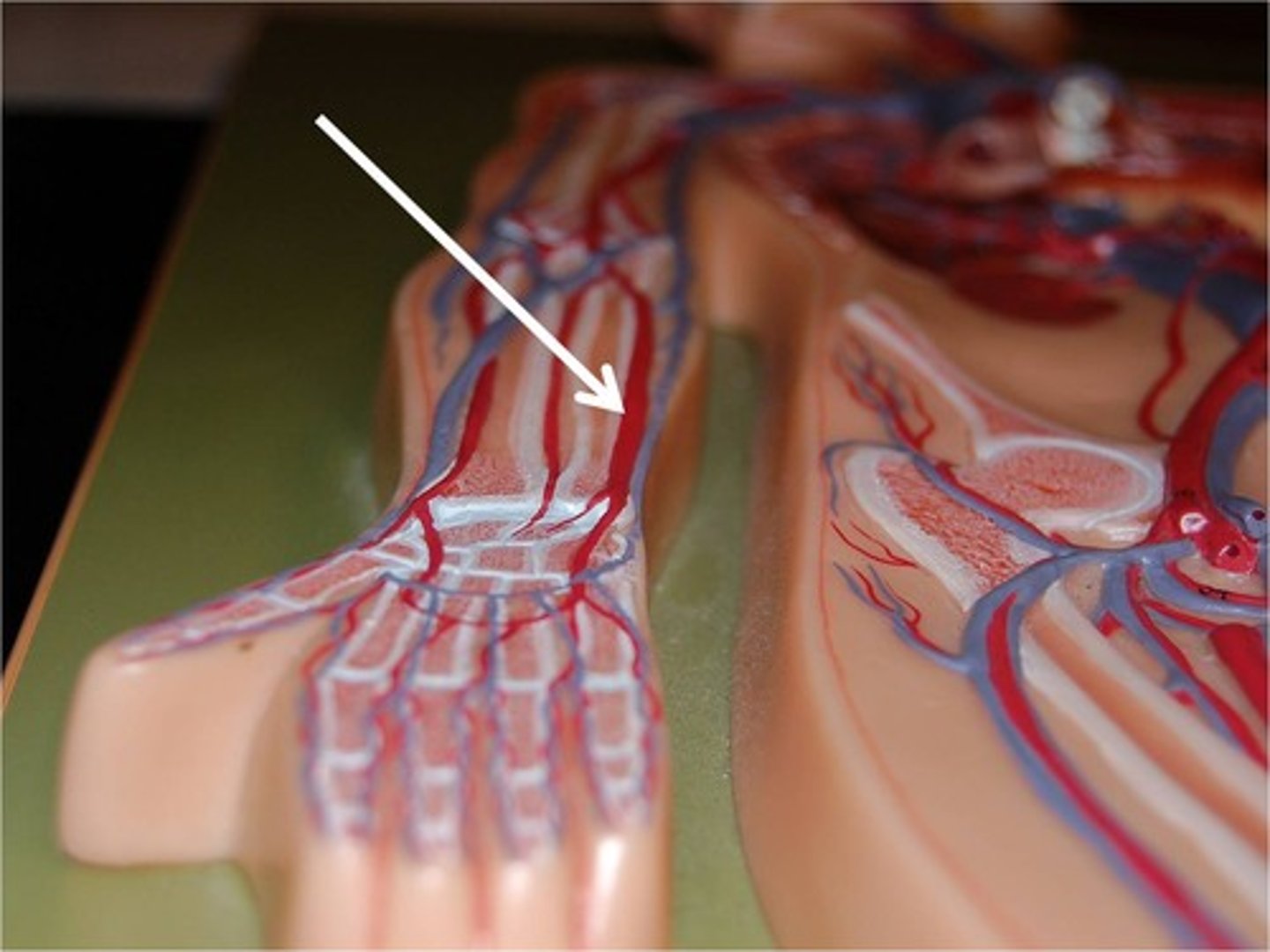
Ulnar artery
An artery in the forearm that supplies blood to the medial aspect of the arm.
Bicuspid valve
A valve in the heart between the left atrium and left ventricle, also known as the mitral valve.
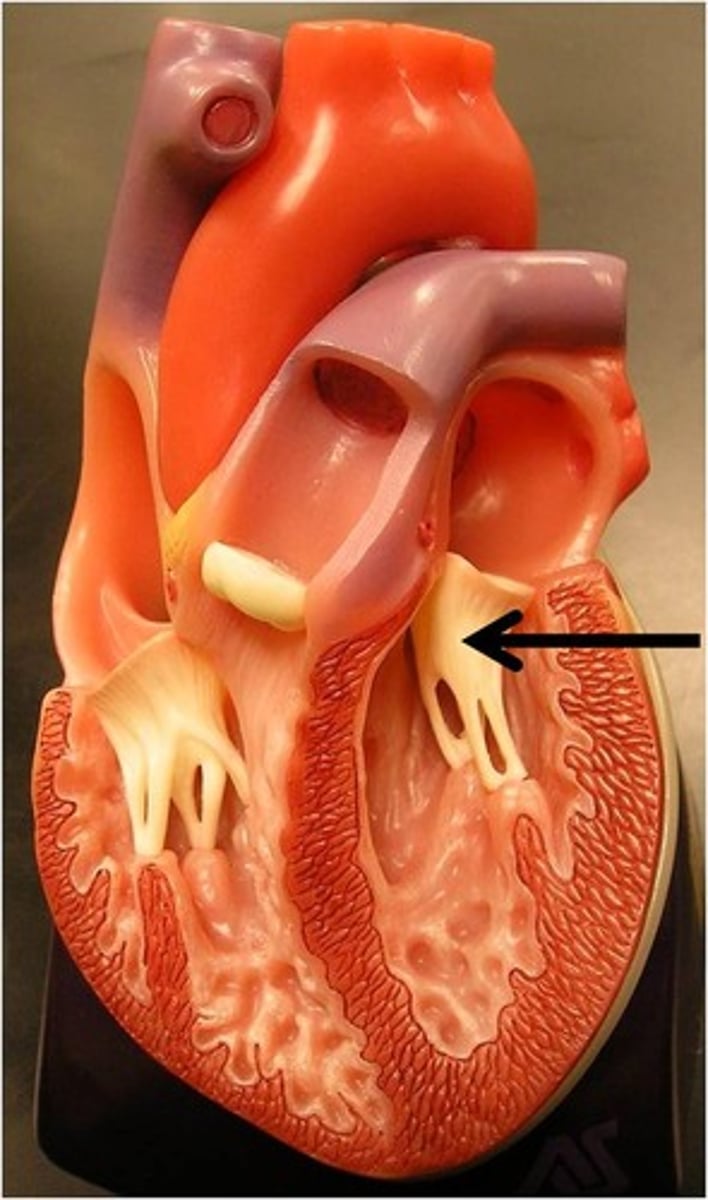
Base of heart
The top part of the heart where major blood vessels enter and exit.