Chapter 20, Carboxylic acids and derivatives
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
geometry of a carbonyl group
what hybridization is the carbon?
trigonal planar
SP2
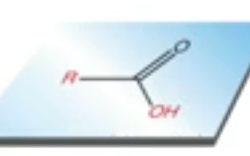
(T/F) acidic part of a molecule with a CA is not capable of H-bonding
false
(T/F) carboxylic acids have a lower boiling point than alcohols due to hydrogen bonding
false, hydrogen bonding increases bp
carboxylic acids are (weak/strong) acids and exist as _____ in the presence of a base
weak; carboxylate salt
pKa of most CAs are between ___-___
4-5
a lower pKa indicates a (weaker/stronger) acid
stronger
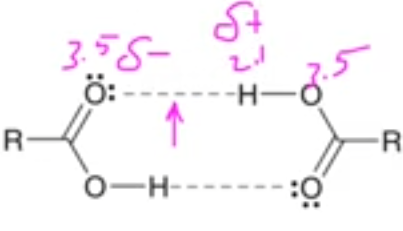
while is carboxylate stable?
draw this reason
resonance
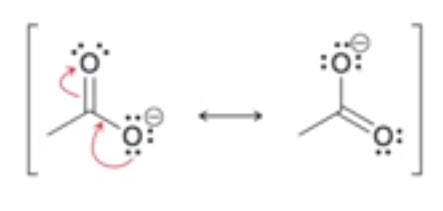
what is the physiological pH?
show ratio of carboxylate ion to carboxylic acid at physiological pH
7.3
(Carboxylate)1000:1(CA)
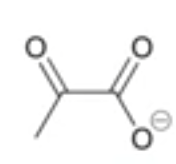
how many oxygen atoms is the negative charge delocalized across?
2
effect of EWGs on pKa carboxylic acids
(lower/higher) pKa indicates a stronger acid
The stronger and/or closer they are to the acidic proton, the lower the pKa.
lower pKa indicates a stronger acid
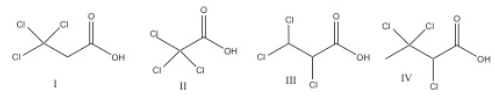
which CA is the least acidic? which one is the most acidic?
1: least acidic due to distance of EWGs from acidic proton
2: most acidic due to proximity EWGs to the acidic proton
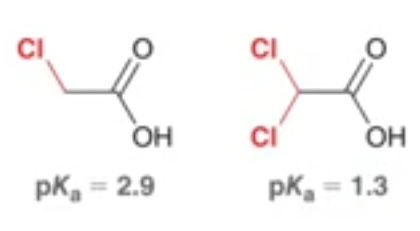
which molecule is more acidic, and by how much more acidic is that molecule
the right molecule is 10^1.6 times more acidic than the left molecule
If an EWG is attached to benzoic acid, the CA is (more/less) acidic
If an EDG is attached to benzoic acid, the CA is (more/less) acidic
more
less
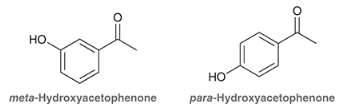
which is more acidic and why?
the para isomer is more acidic due to its conjugate base having more resonance structures than the meta isomer
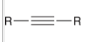
how to generate a CA from this molecule?
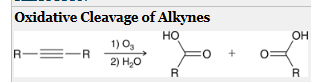
how to generate a CA from this molecule?
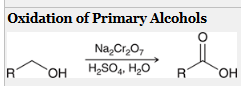
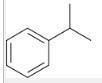
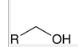
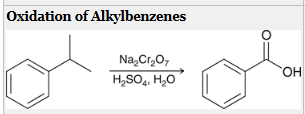
how to generate a CA from this molecule?
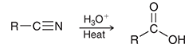
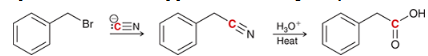
how may a CA be made from a nitrile?
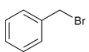
show a two-step synthesis of converting this alkyl halide to a carboxylic acid (hint: this synthesis would not work on tertiary alkyl halides)
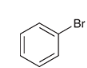
show a two-step synthesis of converting this alkyl halide to a carboxylic acid (hint: this synthesis works on vinyl or aryl alkyl halides)
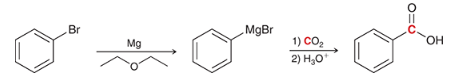
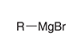
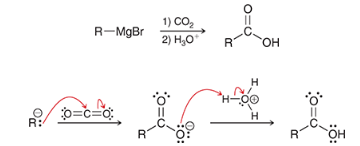
show the overall reaction and mechanism for converting this into a CA
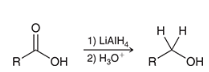
how may a carboxylic acid be reduced a primary alcohol using a strong reducing agent
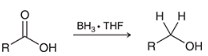
How may a carboxylic acid be reduced to a primary alcohol using a weaker reducing agent
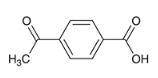
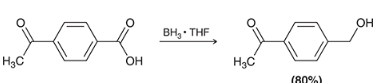
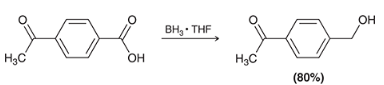
how may you reduce only the carboxylic acid on this molecule to a alcohol
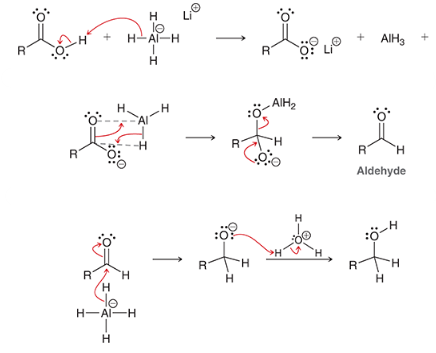
show the mechanism of reducing a CA via lithium aluminum hydride
when would you use BH3 instead of LAH when reducing a CA?
BH3 allows for the reduction of a carboxylic acid without reducing other carbonyl groups in the molecule. LAH will reduce everything on the molecule.