Introduction to Ecology
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
the study of relationships among organisms and between organisms and the physical environment
ecology
enumerate importance’s of ecology
understands nature: how living thing interact
protects environment: prevents pollution and climate change
maintains balance in nature: ecology shows how plants animals and humans depend on each other to survive
prevents disease spread: understanding ecology helps stop the spread of disease between animals, humans, and plants
aids conservation: protects endangered species
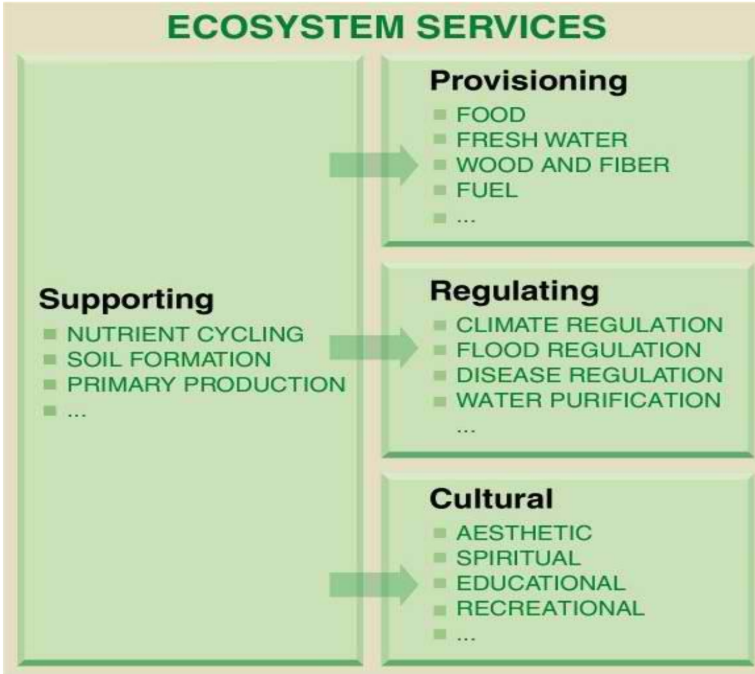
enumerate the ecosystem services
supporting services: these are the basic processes that make life possible
provisioning services: these provides things we use from nature
regulating services: these keep nature balanced and protect us
cultural services: these give us enjoyment, knowledge, and spiritual value
focuses on meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generation to meet their needs
ex: using water wisely so it doesnt run out
sustainability
is about long-term balance
is the goal of maintaining natural resources and the environment for future generations
connotes a process by which human potential is improved and the environment (the resource base) is used and managed to supply humanity on a long-term basis
ex: building eco-friendly houses using renewable energy
sustainable development
is about actions taken to achieve sustainability
- is the process of meeting human needs while protecting nature
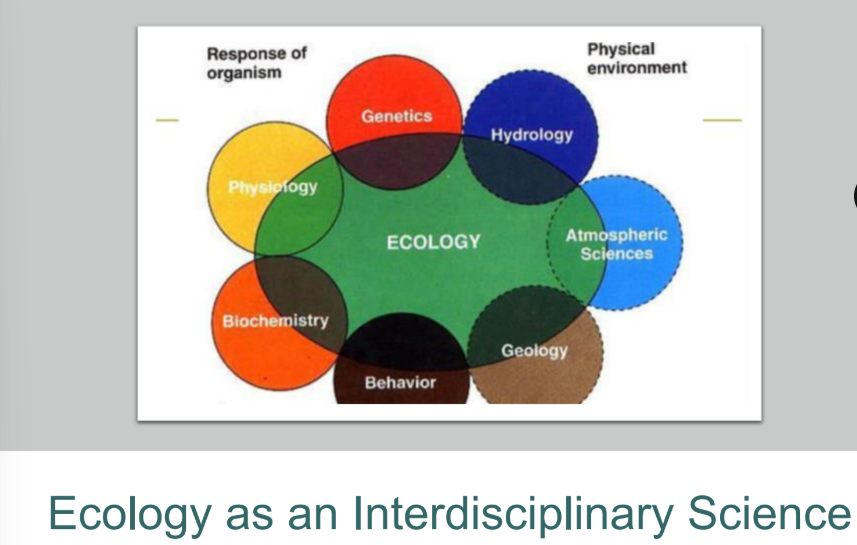
why is ecology as an interdisciplinary science?
ecology is an interdisciplinary science because it combines knowledge from different fields to understand how living things interact with their environment
what are the other sciences ecology relates to?
physiological ecology
evolutionary ecology
political ecology
behavioral ecology
ecological genetics
ecological climatology
system ecology
landscape ecology
concerned with how the individual organism meets the challenges of its physicochemical environment and how the organism’s limits of tolerance for environmental stresses determine where it can live
physiological ecology
studies the evolutionary histories of species and their interactions ex. distribution and abundance of organisms are products of long term evolutionary changes as well as ongoing interactions with the environment
evolutionary ecology
connects politics and economy to problems of environmental control and ecological change
political ecology
examines the roles of behavior in enabling an animal to adapt to its environment
behavioral ecology
studies the extension of our modern knowledge in molecular genetics to studies of viability, gene expression and gene movements in natural environments
ecological genetics
examines how ecosystems are affected by climate
ecological climatology
focuses on the study, development and organization of ecological systems from a holistic perspective
system ecology
concerned with spatial patterns in the landscape and how they develop, with an emphasis on the role of disturbance, including human impacts. The goal is to predict the responses of different organisms to changes in landscape, to ultimately facilitate ecosystem management
landscape ecology
is the study of individual organisms in their environment or simply the ecology of the individual organisms
autecology

what are the subdivisions of ecology
synecology and autecology
is the study of interrelationships between groups of organisms (populations or communities) and the environment
synecology
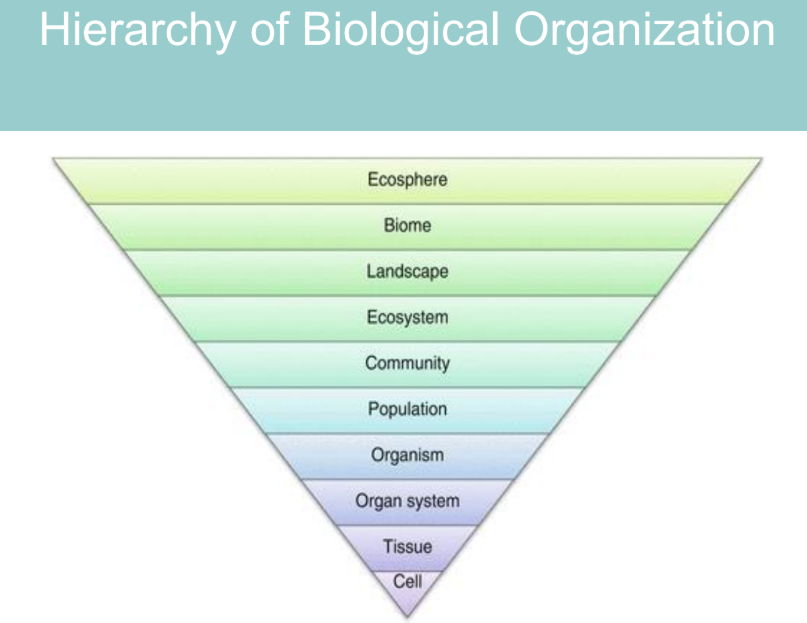
enumerate the hierarchy of biological organization
cell- the basic unit of life
tissue- a group of similar cells working together
organ system- a group of organs performing specific functions in an organism
organisms- a single living individual
population- a group of organisms of the same species living in the same area
community- different populations interacting in the same environment
ecosystem- the interaction of communities with abiotic (non-living) factors
landscape- a collection of ecosystems in a region
biome- large- scale ecosystems categorized by climate and dominant vegetation (e.g desert, rainforest)
ecosphere (biosphere)- the sum of all ecosystems on earth, including all life and environments
ecology starts at the organisms level and extends to the biosphere (ecosphere)
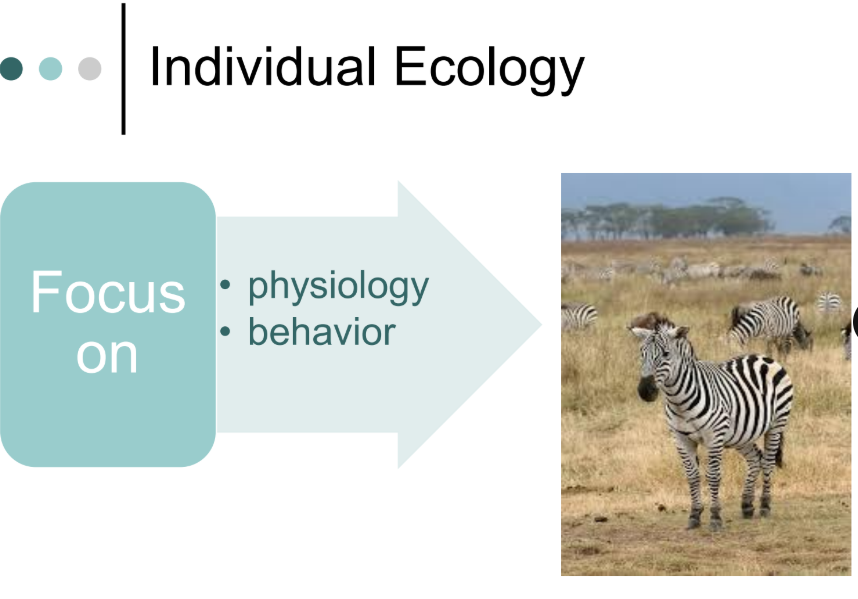
focus on: physiology and behavior
- this looks at how a single living thing (an organism) interacts with its environment
ex: how a penguin survives in the cold
individual ecology
centered on the factors influencing population structure and process
this focuses on a group of the same species living in one area and how they grow, reproduced, and survive.
ex: studying why a deer population is increasing or decreasing
population ecology
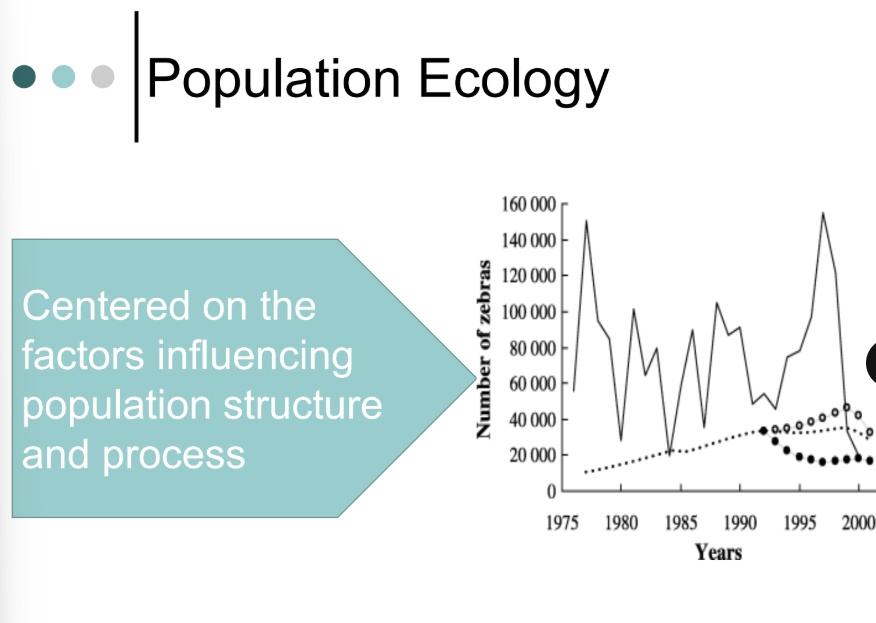
concentrates on the organisms inhabiting an area
this studies how different species in area interact with each other.
ex: how bees pollinate flowers, or how wolves hunt deer
community ecology

includes physical and chemical factors influencing the community
this looks at how living things (plants, animals, bacteria) interact with non-living things (water, air, soil, sunlight)
ex: how a forest recovers after a wildfire
ecosystem ecology

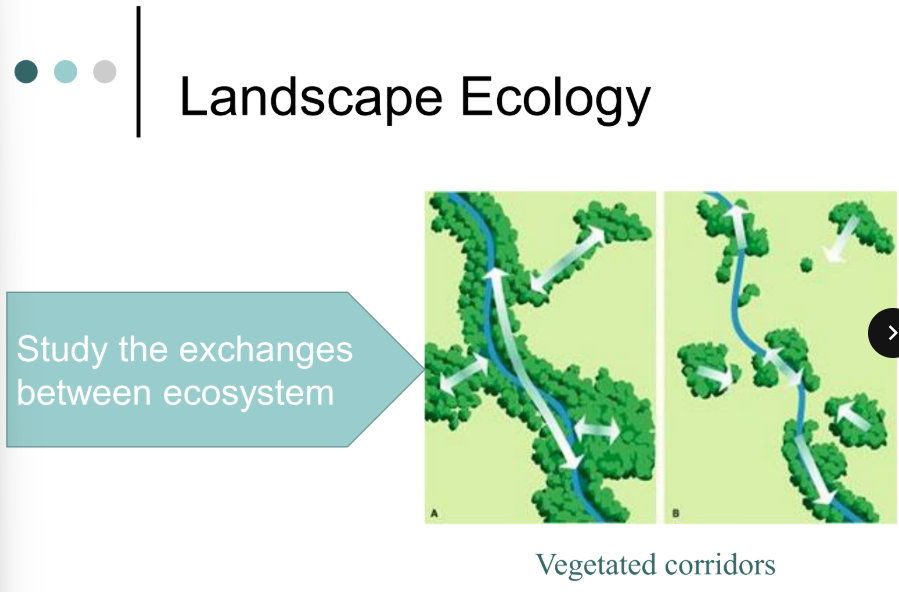
study the exchanges between ecosystem
this studies how multiple ecosystem are connected and affect each other
ex: how cutting down a forest affects nearby rivers and animals
landscape ecology
this focuses on large areas with similar cilmates and life forms, like deserts, rainforests, and tundras
ex: how climate change affects the amazon
biome ecology
a group of ecosystems that have the same climate and similar dominant communities
biome ecology: biome
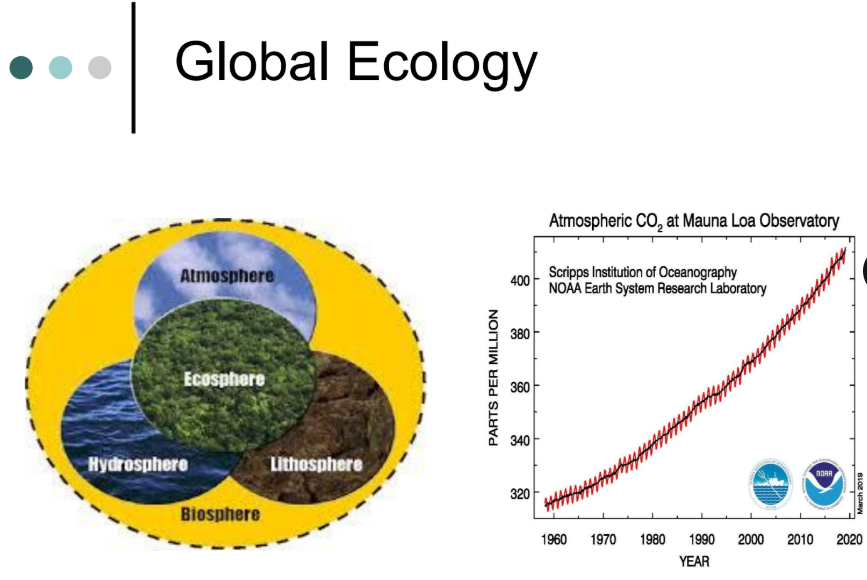
this looks at the earth as a whole and how different ecosystems interact worldwide
ex: How pollution in one country affects the entire planet’s climate
global ecology
is a characteristics an entity gains when it becomes part of a bigger system
ex: a single neuron cant think, but a network of neurons creates thoughts
emergent property
emergent properties help living organisms better adapt to their environments and increase their chances of survival
means the whole is greater than the sum of its parts, making emergent properties possible
ex: one musician plays a melody, but an orchestra creates a symphony
basic functions that operate at all levels in the hierarchy (happens when something goes beyond its original purpose or limits to create new abilities or effects)
ex: a smartphone was made for calling, but it now serves as a camera, GPS, and computer-going beyond its basic function
positive and negative feedback controls are universal
transcending functions
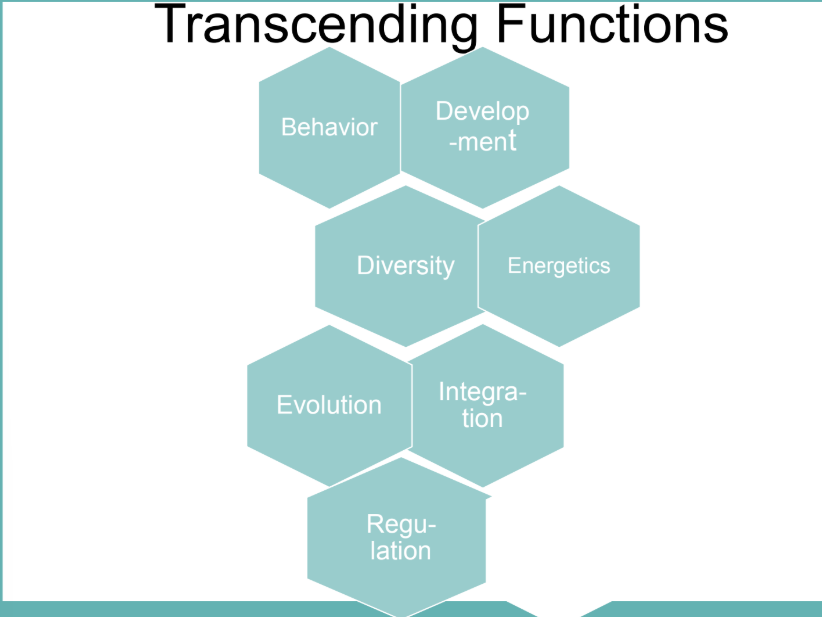
why are this transcending functions


Homeorhesis

Homeostasis

Homeostasis
is the way living things keep their internal conditions stable, like keeping body temperature or blood sugar at the right level
it helps organisms survive by adjusting to changes in the environment
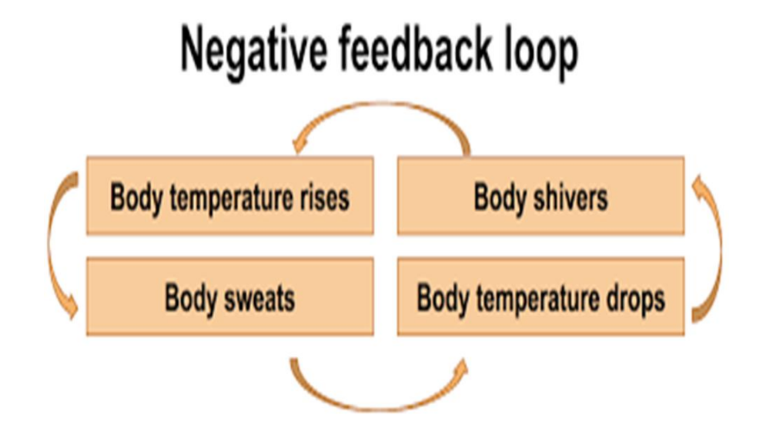
what is the negative feedback loop?
helps bring things back to normal when they go too high or too low.
ex: if your body gets too hot, you start sweating to cool down. If it gets too cold, you shiver to warm up. This process stops extreme changes and keeps balance inside the body
Homeorhesis
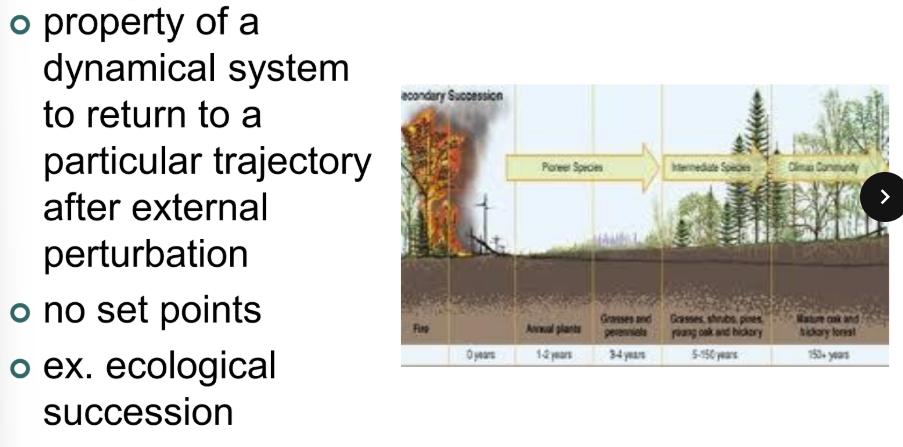
what sis Homeorhesis?
is the way living things adjust their internal conditions over time to stay on the right path for growth and development. Unlike homeostasis, which keeps things stable, homeorhesis allows change to happen in a controlled way
For example, a growing baby doesn’t stay the same size—it keeps changing but follows a natural pattern. Similarly, a river might change its shape over time but still flows in the same general direction. Homeorhesis guides changes in a smooth and balanced way instead of just keeping things the same.