Viruses
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
1
New cards
What are viruses?
* Tiny (only seen on an electron microscope)
* Obligate parasites (need a host to reproduce)
* Classified by their shape
* Are considered to be living and non-living
* Obligate parasites (need a host to reproduce)
* Classified by their shape
* Are considered to be living and non-living
2
New cards
Describe the structure of a virus
1. Capsid (protein coat): protects the virus
2. Nucleic Acid: DNA or RNA
* no organelles
* no metabolic machinery
3
New cards
What are the arguments for viruses being both __living__ and __non-living__?
__Living:__
* A virus contains genetic material
* Contains a protein coat
* Can replicate (though requires a host)
\
__Non-Living:__
* Non-cellular
* Cannot reproduce by themselves
* No cell organelles
* Only have one type of nucleic acid
* A virus contains genetic material
* Contains a protein coat
* Can replicate (though requires a host)
\
__Non-Living:__
* Non-cellular
* Cannot reproduce by themselves
* No cell organelles
* Only have one type of nucleic acid
4
New cards
Why is a virus described as an “obligate parasite”?
* They need a host to reproduce
5
New cards
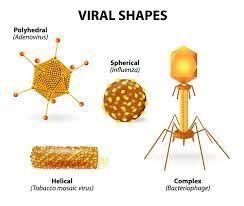
How are viruses classified?
Viruses are classified according to their shape:
1. Round (ex. influenza)
2. Rod-shaped (ex. Tobacco Mosaic)
3. Complex (ex. bacteriophage)
1. Round (ex. influenza)
2. Rod-shaped (ex. Tobacco Mosaic)
3. Complex (ex. bacteriophage)
6
New cards
Why are antibiotics ineffective against viruses?
1. antibiotics target bacteria
2. antibiotics target cell organelles, a virus doesn’t have any
7
New cards
Viral Replication. How do viruses replicate?
* Viruses are obligate parasites- need a host to reproduce ex. bacteriophage is a virus that infects bacteria to replicate.
* There are 5 stages of replication
* There are 5 stages of replication
8
New cards
List the 5 stages in Virus Replication
1. Attachement
2. Entry
3. Synthesis
4. Assembly
5. Release
9
New cards
List and explain the stages of Viral Replication
1. __Attachement:__ Virus attaches to host (bacteria)
2. __Entry:__ Virus makes a hole in bacteria cell wall and injects nucleic acid (DNA or RNA)
3. __Synthesis:__ Host DNA is made inactive, viral DNA uses bacteria organelles to produce new viral nucleic acid and proteins
4. __Assembly:__ New viruses are made inside the infected cell.
5. __Release:__ Bursting of cell (lysis) occurs releasing thousands of viruses.
10
New cards
What is lysis?
__Bursting of a cell__, which causes the release of thousands of viruses. Occurs during the release stage of viral replication.
11
New cards
Attachement stage of viral replication
1. __Attachement:__ Virus attaches to host (bacteria)
12
New cards
Entry stage of viral replication
2. __Entry:__ Virus makes a hole in bacteria cell wall and injects nucleic acid (DNA or RNA)
\
13
New cards
Synthesis stage of viral replication
\
3. __Synthesis:__ Host DNA is made inactive, viral DNA uses bacteria organelles to produce new viral nucleic acid and proteins
\
3. __Synthesis:__ Host DNA is made inactive, viral DNA uses bacteria organelles to produce new viral nucleic acid and proteins
\
14
New cards
Assembly stage of viral replication
\
4. __Assembly:__ New viruses are made inside the infected cell.
4. __Assembly:__ New viruses are made inside the infected cell.
15
New cards
Release stage of viral replication
5. __Release:__ Bursting of cell (lysis) occurs releasing thousands of viruses.
16
New cards
Acronym for stages in viral replication
RASEA- reversed
1. __Attachement:__ Virus attaches to host (bacteria)
2. __Entry:__ Virus makes a hole in bacteria cell wall and injects nucleic acid (DNA or RNA)
3. __Synthesis:__ Host DNA is made inactive, viral DNA uses bacteria organelles to produce new viral nucleic acid and proteins
4. __Assembly:__ New viruses are made inside the infected cell.
5. __Release:__ Bursting of cell (lysis) occurs releasing thousands of viruses.
1. __Attachement:__ Virus attaches to host (bacteria)
2. __Entry:__ Virus makes a hole in bacteria cell wall and injects nucleic acid (DNA or RNA)
3. __Synthesis:__ Host DNA is made inactive, viral DNA uses bacteria organelles to produce new viral nucleic acid and proteins
4. __Assembly:__ New viruses are made inside the infected cell.
5. __Release:__ Bursting of cell (lysis) occurs releasing thousands of viruses.
17
New cards
What are virus disadvantages?
disease…duh.
18
New cards
3 examples of human diseases caused by viruses
1. Influenza
2. AIDs
3. Mumps
19
New cards
2 examples of plant diseases caused by viruses
1. Potato mosaic disease
2. Tobacco mosaic disease
20
New cards
2 examples of animal diseases caused by viruses
1. Foot and mouth
2. Rabies
21
New cards
Give an example of 2 virus benefits
1. Genetic Engineering
2. Infection Control
22
New cards
How is Infection Control beneficial?
bacteriophages can be used to control bacterial infections which may reduce the number of antibiotic-resistant bacteria
23
New cards
How is Genetic Engineering beneficial?
Transfer of genes using viruses e.g vectors
24
New cards
Explain why viruses are described as obligate parasites
They require a host to reproduce
25
New cards
Explain in detail the term vaccination
Vaccination is a non disease causing dose of a disease. It is a form of artificial active immunity and it is long lasting since the body is learning how to produce the antibodies itself.
26
New cards
Name a harmful virus, other than Cov-2
mumps, aids, influenza
27
New cards
From which biochemical component are viral coats made?
protein
28
New cards
Name the main chemical component of a virus
nucleic acid
29
New cards
Immunity is the ability to resist infection. Name two types of induced immunity
1. Passive Immunity
2. Active immunity
30
New cards
Which type of immunity occurs after a vaccination?
active
31
New cards
Give one difference between the types of induced immunity
1. Active immunity- long lasting
2. Passive immunity- short term
32
New cards
Discuss the statement: “Viruses are not considered to be living organisms”
* They are obligate parasites-cannot reproduce independently
* They contain no organelles and no metabolic mechanisms
* They are made of only one type of nucleic acid
* They contain no organelles and no metabolic mechanisms
* They are made of only one type of nucleic acid
33
New cards
What is the main constituent of a capsid coat?
protein
34
New cards
What virus causes disease in plants?
Tobacco mosaic virus
35
New cards
How to distinguish between viruses?
shape
36
New cards
Give one way in which viruses are metabolically important.
Biotechnology and genetic engineering- transfer of genes using viruses
37
New cards
DISCUSS THE STATEMENT “VIRUSES ARE NOT CONSIDERED TO BE LIVING”
* Viruses have __**some features**__ of living things, e.g. containing RNA or DNA, being able to replicate and having a protein coat.
* However, other characteristics of living things are missing, e.g. viruses are non-cellular and **cannot reproduce** on their own. Viruses do not have cell organelle and **only contain one kind** of nucleic acid while most living things have both RNA and DNA.
* However, other characteristics of living things are missing, e.g. viruses are non-cellular and **cannot reproduce** on their own. Viruses do not have cell organelle and **only contain one kind** of nucleic acid while most living things have both RNA and DNA.
38
New cards
**DESCRIBE HOW THE VIRUS REPLICATES**
1. Virus attaches to a host cell and inserts its nucleic acid into the cell cytoplasm.
2. The viral enzyme __destroys the host cell’s nucleus__
3. The virus uses host cell’s machinery to make more viral dna and protein coats
4. New viruses are assembled and burst out of the host to infect other cells
39
New cards
**GIVE ONE EXAMPLE OF A BENEFICIAL VIRUS**
Bacteriophages can be used to control bacterial infections
40
New cards
**WHY ARE VIRUSES DIFFICULT TO CLASSIFY INTO A KINGDOM?**
Because they are not made up of cells and are unable to carry out metabolic reactions on their own.
41
New cards
**HOW DO SCIENTISTS DISTINGUISH BETWEEN DIFFERENT VIRUSES**
According to their shape, round, rod or complex