4.1.4.4 Economies and diseconomies of scale
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
When do economies of scale occur?
fall in average total cost as the scale of production increases
When do Diseconomies of scale occur?
rise in average total cost as the scale or production increases
When do internal economies of scale occur?
A fall in avg costs due to growth of the firm
When do external economies of scale occur?
Fall in average cost due to factors outside of the firm
Economies of scale take a variety of forms, what are they?
Purchasing economies
o Discounts for bulk-buying
Technical economies
o The use of specialist, often expensive, capital e.g. machines
Managerial economies
o Specialist labour e.g. accountants, lawyers, technical
Financial economies
o Better credit ratings as large firms are seen to be less likely to fail and can borrow money at lower interest rates
What is an example of purchasing economies of scale?
Discounts for bulk-buying
Firms buys a lot - > able to secure lower prices per unit.
Big firms use influence to get better deals when bulk-buying & better terms when bulk-marketing their own products.
What are technical economies of scale?
The use of specialist capital e.g. machines
Large firms spend more on bigger & more efficient machinery
spread fixed costs over greater output
obtain lower costs per unit through this method- > increasing competitiveness
spend more money on scientific Research and technical Development (R&D)
What is meant by managerial economies of scale?
Employing specialist labour e.g. accountants, lawyers, technical
Division of labour allows staff to focus on particular areas
As the employee is allowed to concentrate on a specific job they are likely to be:
better qualified
more experienced
more efficient
The manager of a small firm will often do the accounts, marketing and look after human resource management issues i.e. a ‘Jack of all trades’
What is meant by external economies of scale?
A fall in average total cost due to factors outside of the control of the firm.
They will impact on firms within the same industry or geographical region
Creating positive externalities
What are examples of external economies of scale?
➢ improved transport infrastructure
➢ a pool of skilled workers
➢ more advanced communication systems
Diseconomies of scale take a variety of forms, what are they?
Communication
o Larger firms find it more difficult to communicate efficiently within the organisation
o There will be an increased cost for communication methods within the firm
o The manager of a small firm will be able to communicate effectively with all members of the workforce
Coordination
o Larger firms find it more difficult to manage the increased number of personnel and customers
o It might become increasingly difficult to delegate to and motivate
What does higher average costs mean for larger firms?
discourages them from growing as this could lead to a fall in profits or a move into loss
The firm will have to weigh up the benefits involved e.g. greater market share against the costs involved e.g. overtrading where the firm takes on too many orders
What does the LRAC curve look like?
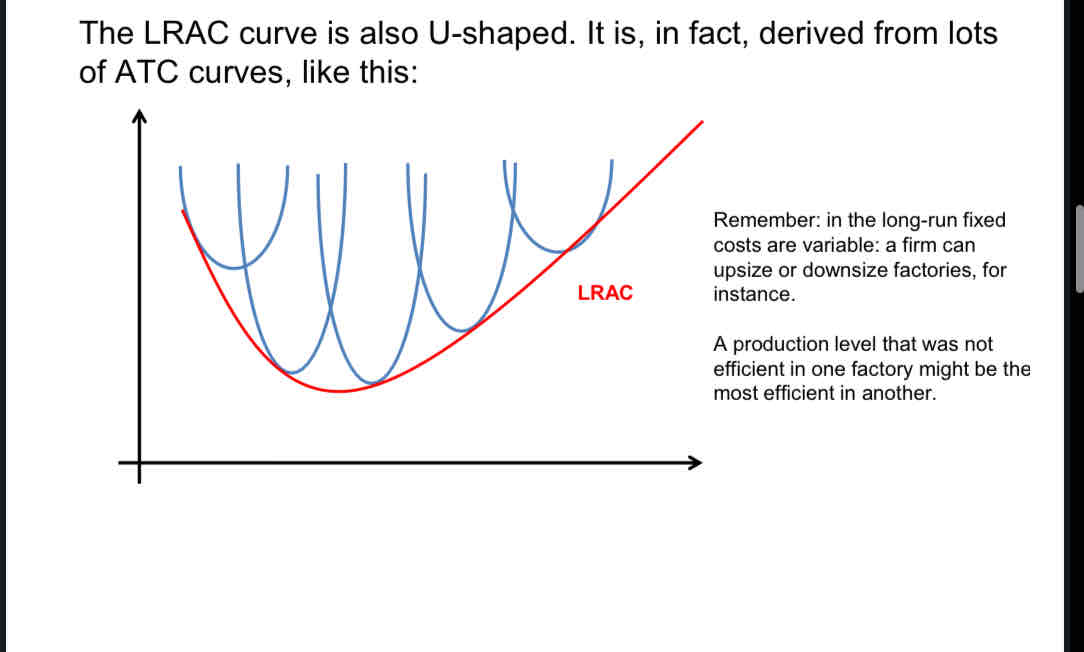
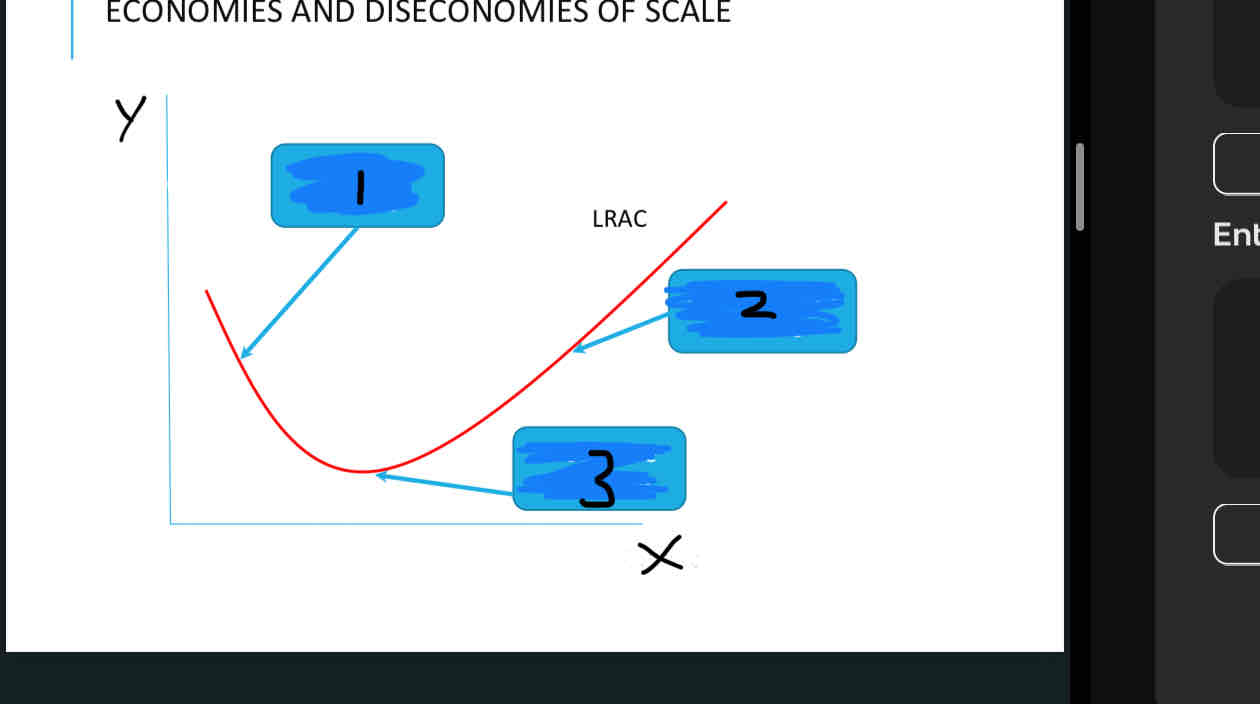
Label this diagram
X = outputs
Y = costs
Economies of scale
Diseconomies of scale
Productive efficiency
When do EOS & DEOS operate?
At the same time
At first unit costs fall due to economies of scale. At this point economies outweigh diseconomies.
The optimum output occurs when unit costs are at a minimum (productive efficiency).
After this unit costs rise and diseconomies outweigh economies.