Biology 9 weeks exam
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
The four compounds are
Carbohydrates, Lipids, Protein, and Nucleic acids
Macromolecules are made by
removing a water molecule from two polymers in a process called dehydration synthesis
Process of Hydrolysis
adds a molecule of water to break down larger molecules into smaller monomers
Carbohydrates Monosaccharide:
Glucose, Fructose, Galactose
Carbohydrates Disaccaride:
Sucrose and Lactose
Carbohydrates Polysaccharides:
Glucose and Cellulose
Carbohydrates Function
short term energy storage
Lipids Monomer:
Glycerol and Fatty acids
Lipids Polymer:
Fats and Oils
Lipids Function:
Long term energy storage, makes up the plasma membrane as phospholipids, hormones messenger
Nucleic Acid Monomers:
Nucleotides made of sugar, phosphate and a nitrogen base
Nucleic Acid Polymer:
DNA and RNA
Nucleic Acid Function:
Store and transmit hereditary information
Protein Monomers:
Amino acids
Protein Polymer:
Chains of amino acids a.k.a polypeptides
Protein Function:
act as enzymes, hormones, and transporters. Enzymes speed up reactions but are affected by pH and temperature.
Structure if an Amino Acid
Can be identified by a nitrogen atom also the R in the structure different elements that make up 20 different kids of amino acids
Enzymes
are a special group of proteins that act acts catalysts to speed up the rate of chemical reactions, lower the energy to activate the chemical reaction
Hydrolysis
a large substrate being broke down into 2 smaller products
Cellular Respiration
The process by which cells make energy from glucose, with the help of oxygen. Occurs in the mitochondria
Light energy
Transferred to the bonds in a molecule of glucose
Active Transport
When cell is using energy to move substances across the cell membrane
Protein Pumps
Moved individual ions across the membrane against the concentration gradient
Homologous Chromosomes
they carry genes that code for the same types of traits
Passive Transport
Moves molecules across the membrane through diffusion
Diffusion
moves molecules from high to low concentration. Substances that dissolve in liquids can easily diffuse across the liquid barrier
Facilitated diffusion
Substances that are larger, like glucose, or electrically charge, like ions, will move across the protein channel
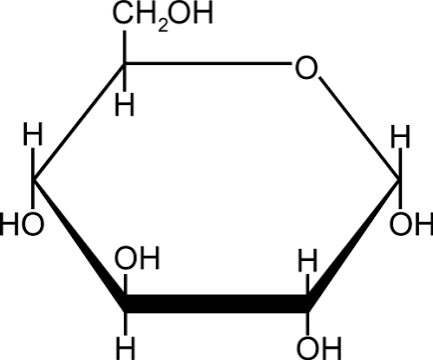
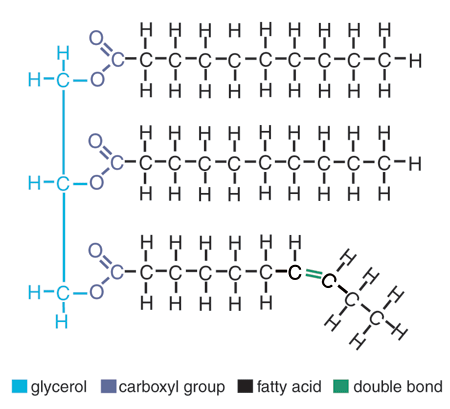
Lipids
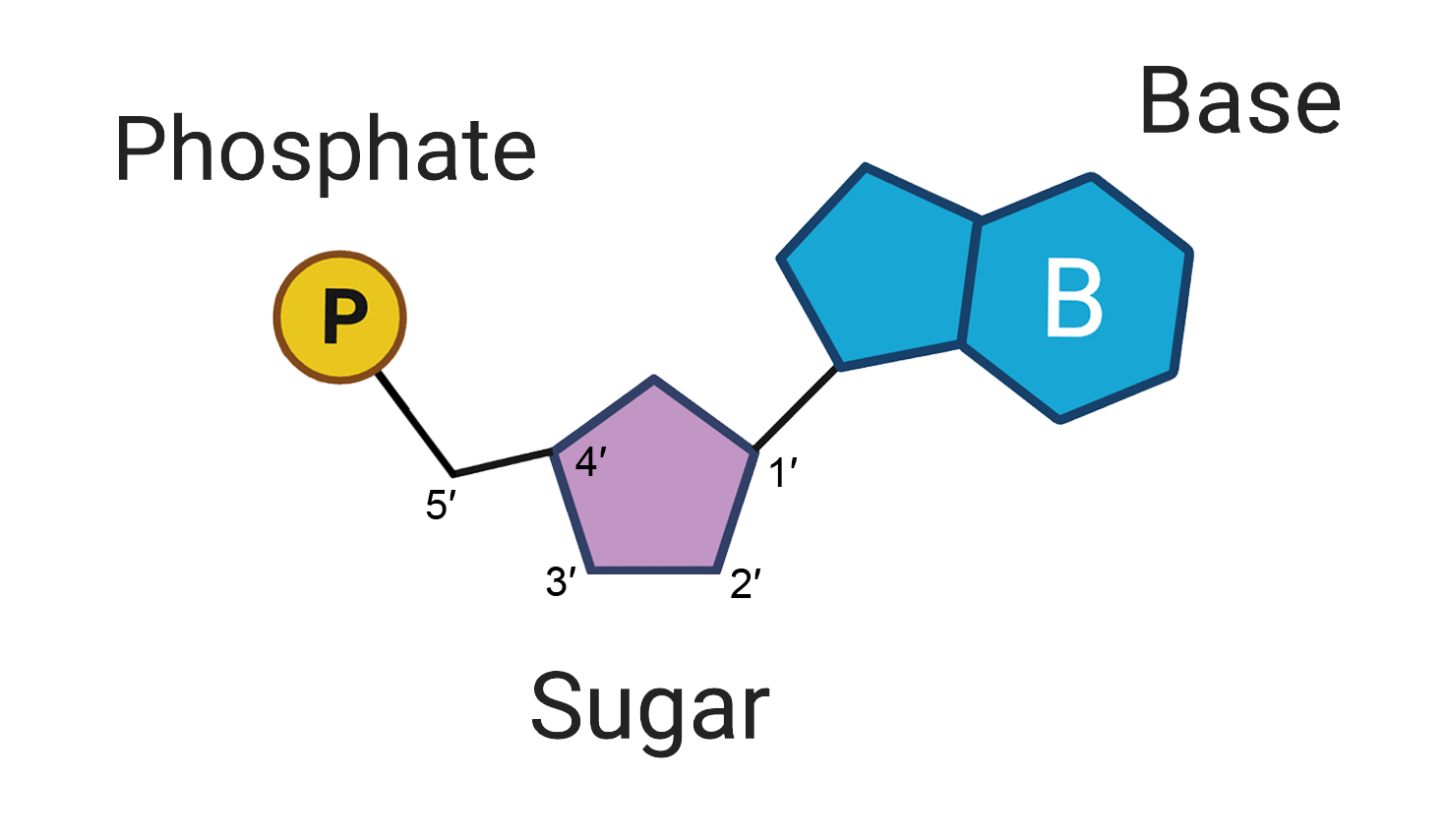
Nucleic Acid
Pyrimidines
Single rings
Purines
Double Rings
Subunits of DNA
Nucleotides, Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine and Thymine
Polymerase
is like glue
Prokaryotic
Single-celled organisms that dont have a nucleus or other membrane-bonds also located in the cytoplasm and also bacteria and archea
Rough ER
Transport Protein
Nucleus
Control center of the cell, house cell DNA
Lysosome
Contains strong digestive enzymes
Golgi Complex
Modifies and packages proteins
Makes proteins for the cell
Ribosomes
Cytoplasm
Site of various chemical reaction
Chloroplast
Make sugar and oxygen using the process of Photosynthesis
Smooth ER
Makes Lipids
Living things smallest to largest
Organelles, cells, tissue, organs, organ systems, organism
Eukaryotic
Single-called or multicellular and includes animals, plants fungi, and protests also have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles
Cell membrane / Plasma membrane
Regulates what enters and exits the cell/ semi-permeable
Adhesion
Water molecules stick to other stuff
Cohesion
Water molecules stick together because they are attached to each other
High specific heat
it takes a lot of energy to rise the temperature of water
Good at cooling organisms
When you sweat, it cools you off because water takes a lot of heat energy with it as it evaporates
High heat evaporation
It takes a lot of heat energy to make liquid water molecules evaporate as gas molecules