Anatomical Kines Unit 1 - Relevant Anatomy
1/138
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
139 Terms
kinesiology
study of body movement
anatomical kinesiology
study of structures most relevant to body movement
organelles
make up cells
cells
make up tissues (smallest function of life)
tissues
make up diff organs
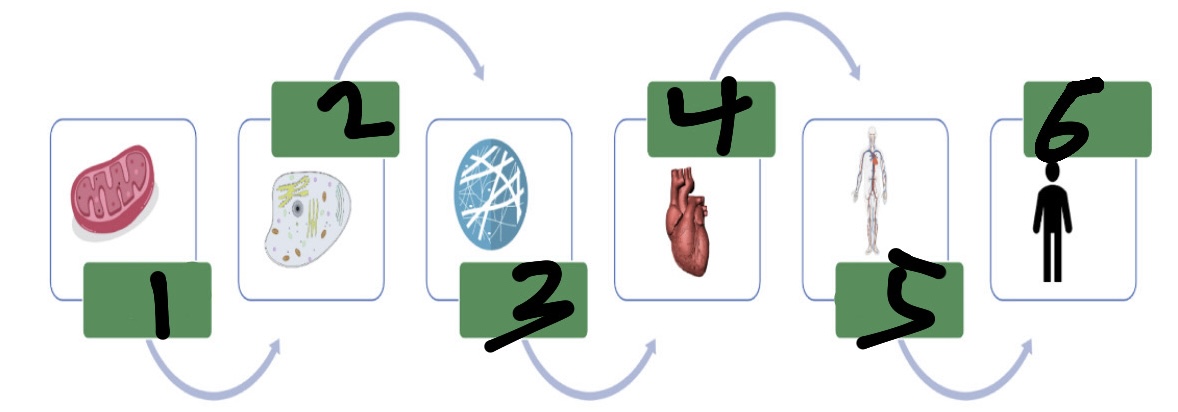
What’s 1?
organelle
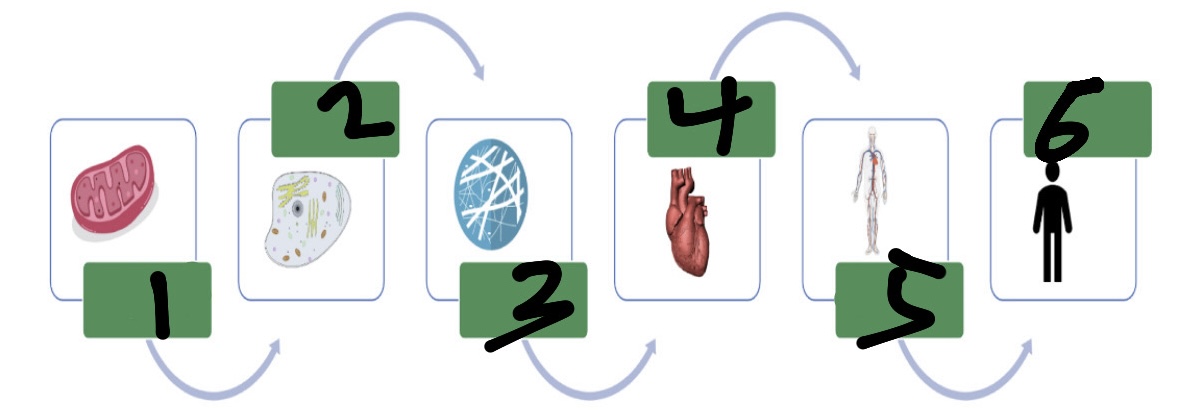
What’s 2?
cell
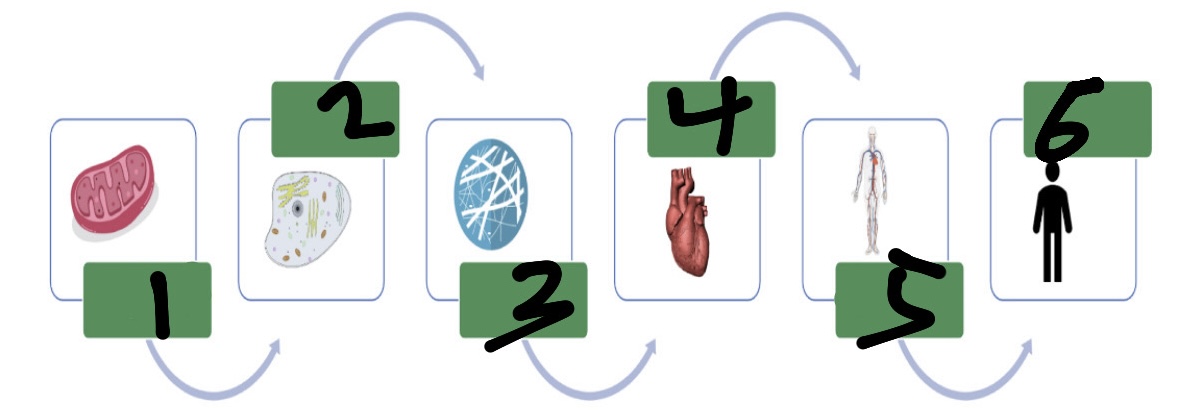
What’s 3?
tissue
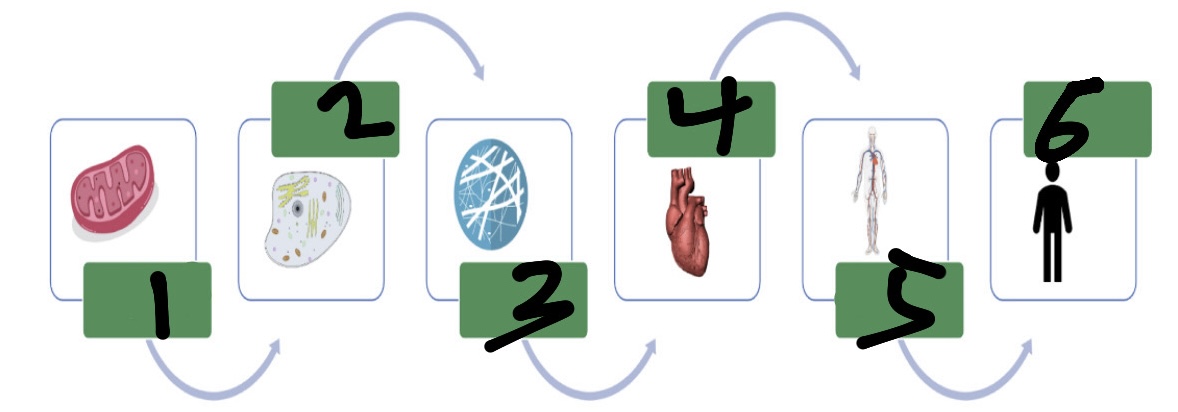
What’s 4?
organ
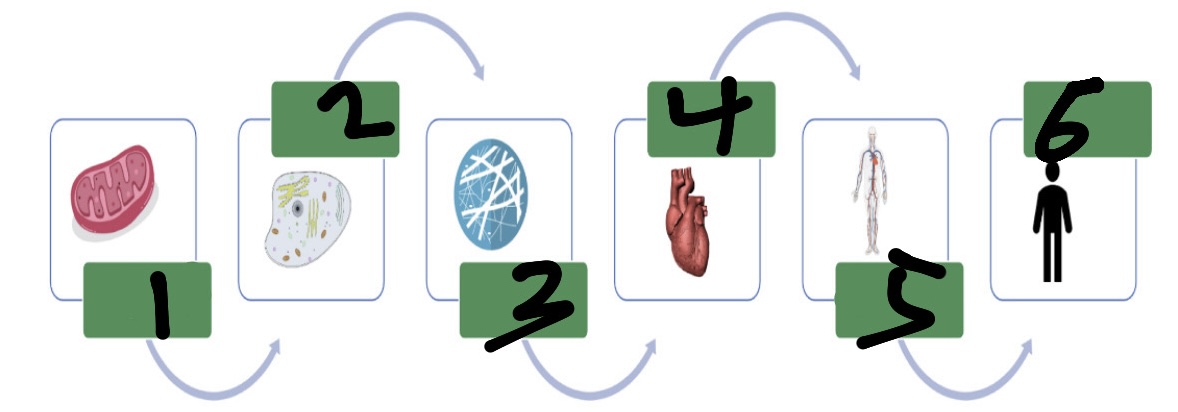
What’s 5?
organ system
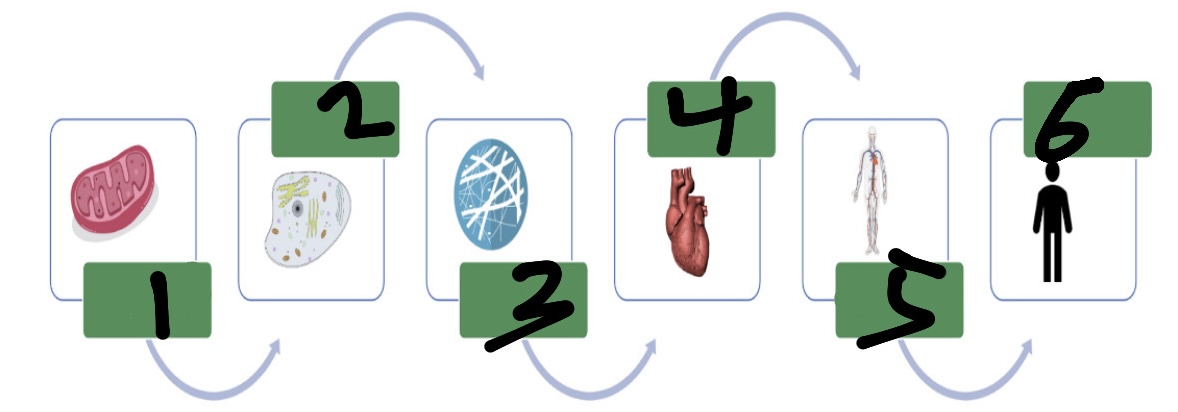
What’s 6?
organism
cell
smallest functional “unit of life” (consists of organelles, cell membrane, cytoplasm, and nucleus)
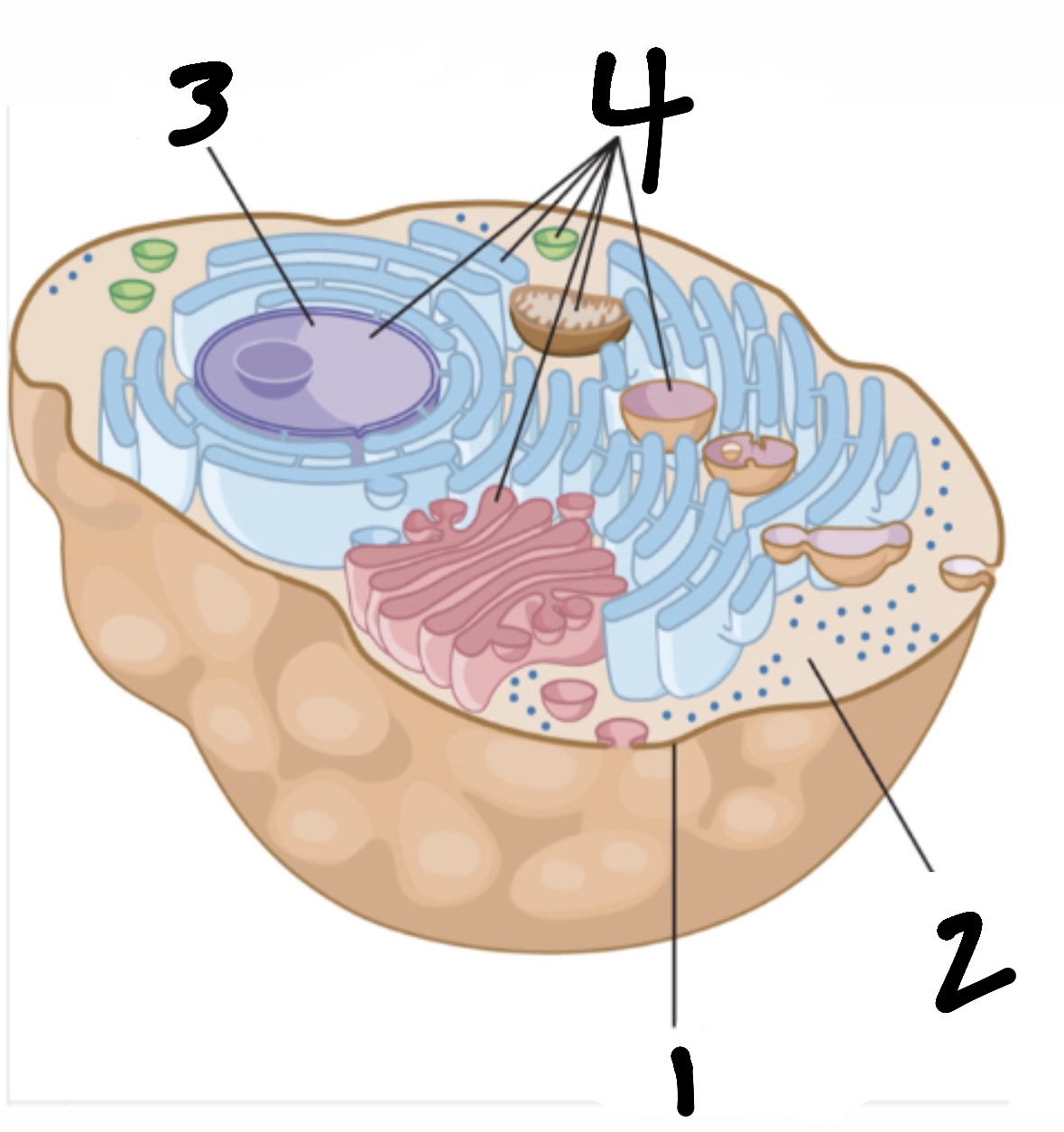
What’s 1?
cell membrane
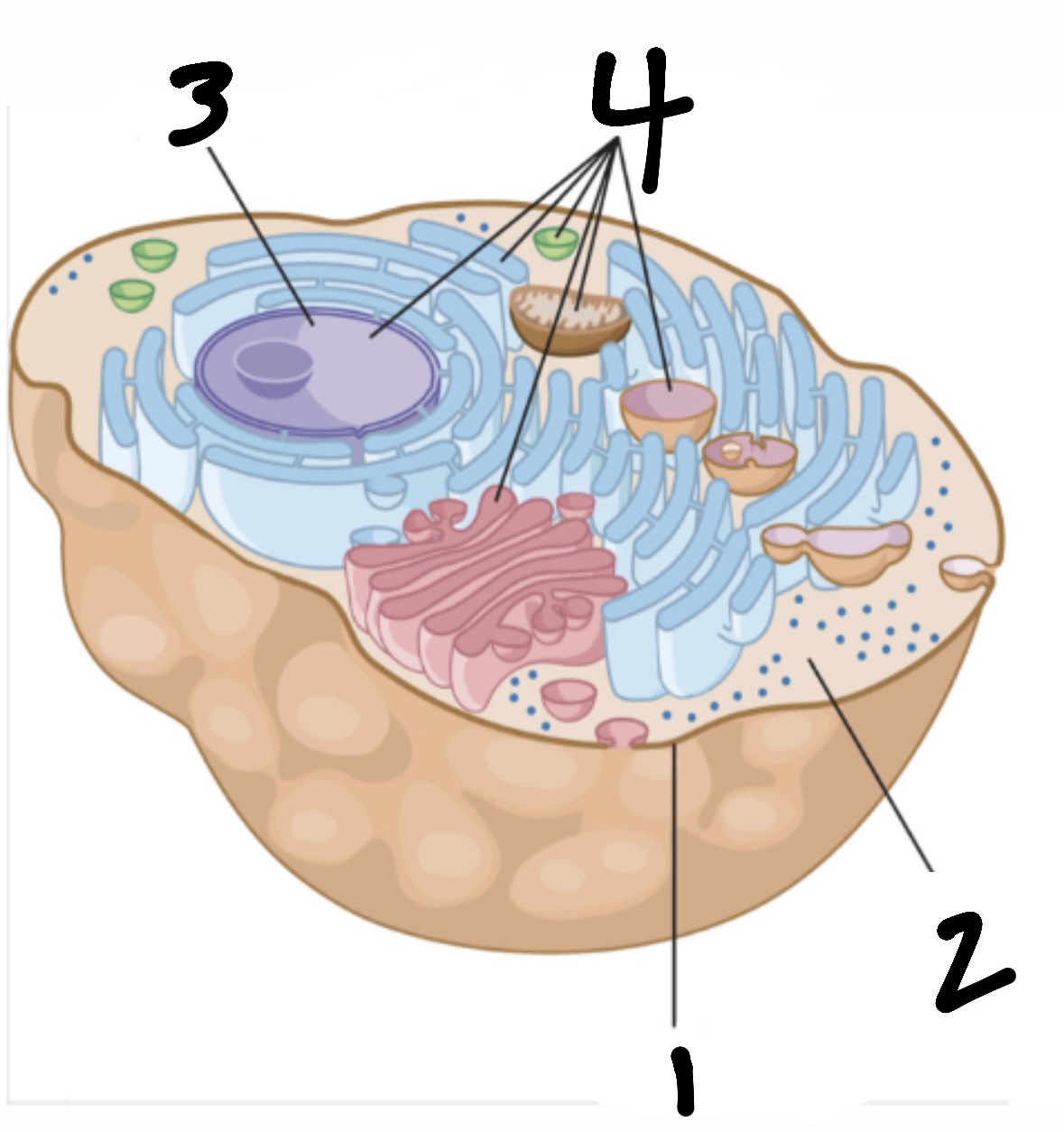
What’s 2?
cytoplasm
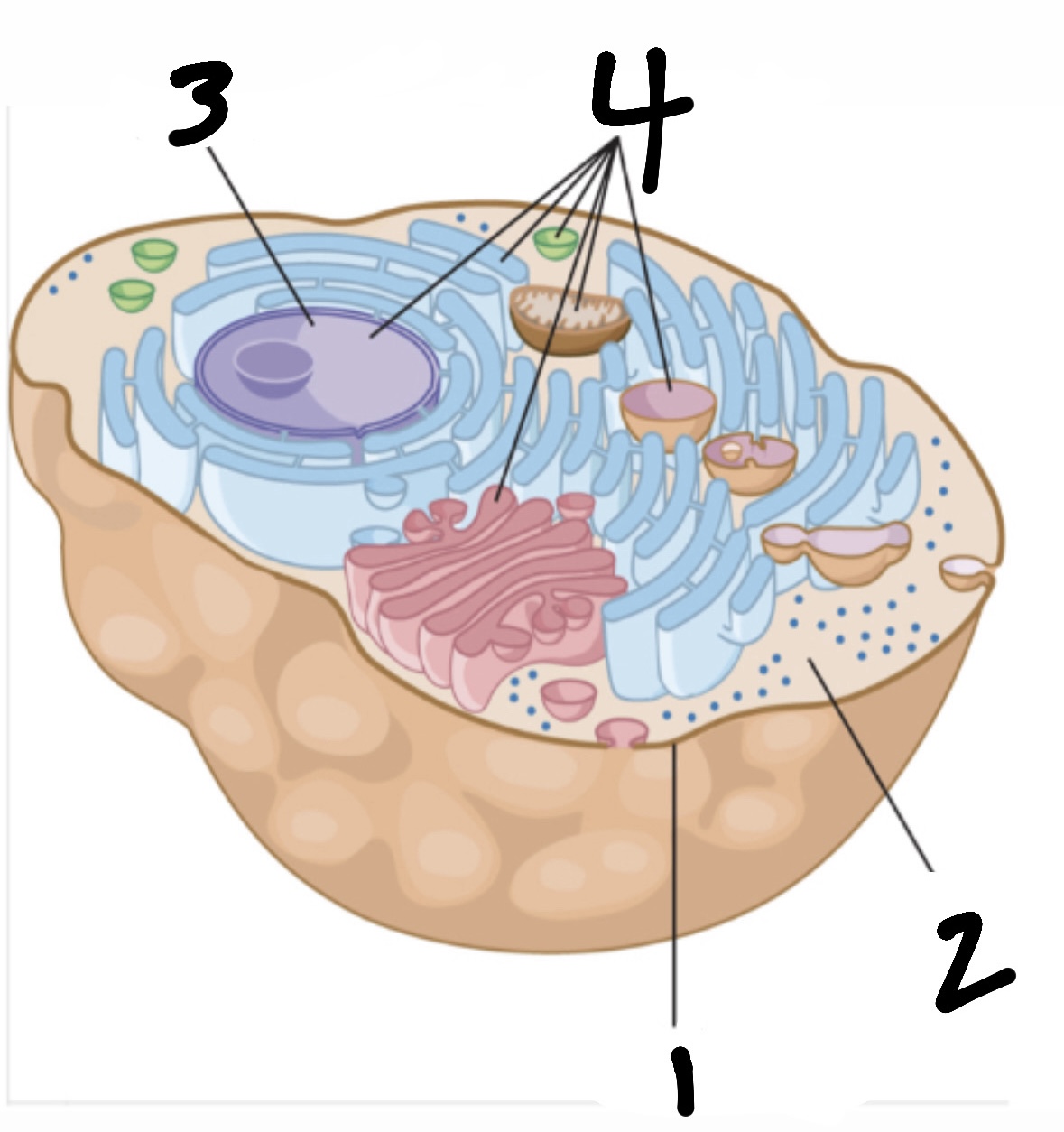
What’s 3?
nucleus
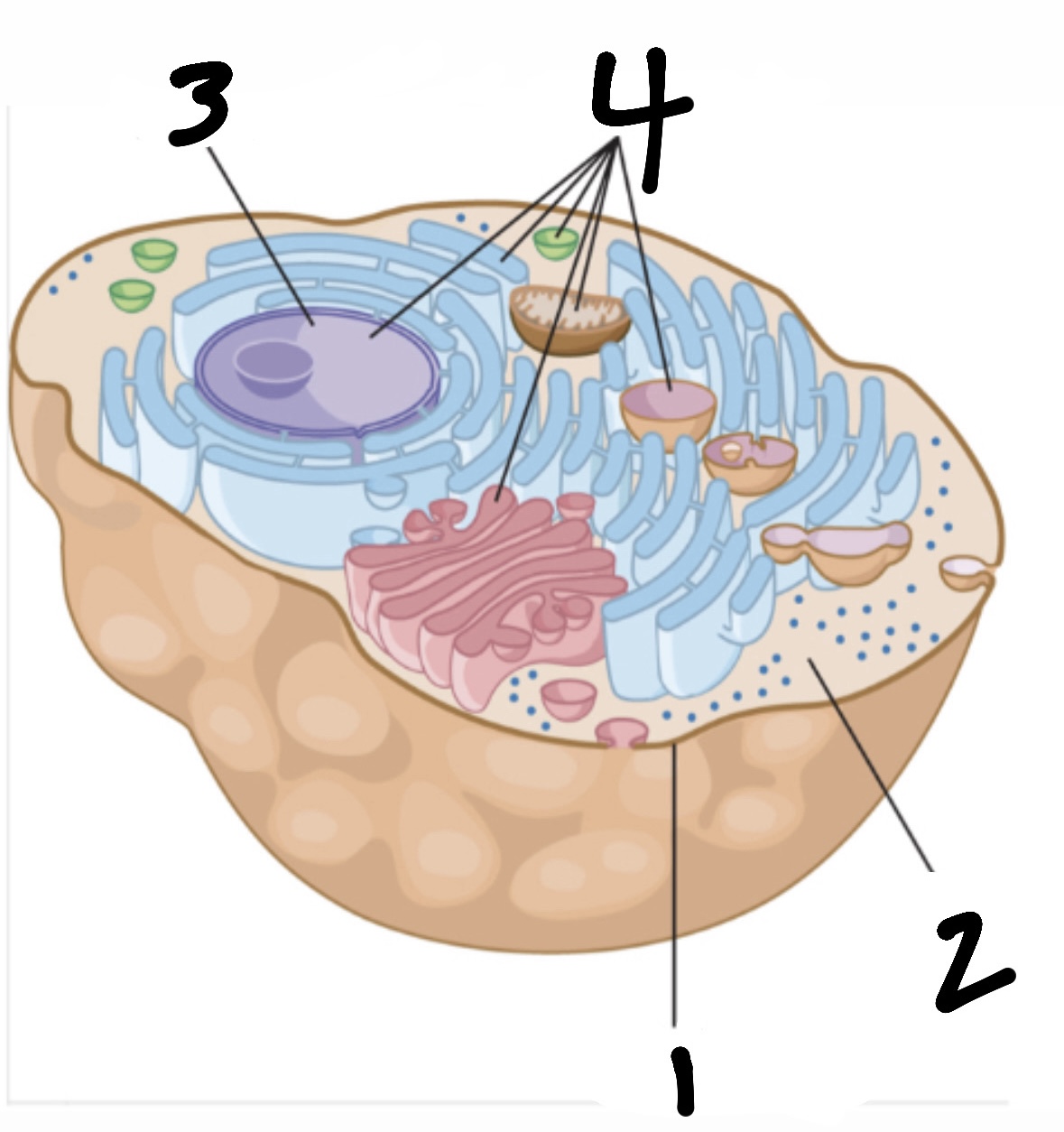
What’s 4?
organelles
tissue
group of similar types of cells and fluid in between them called intracellular fluid or tissue
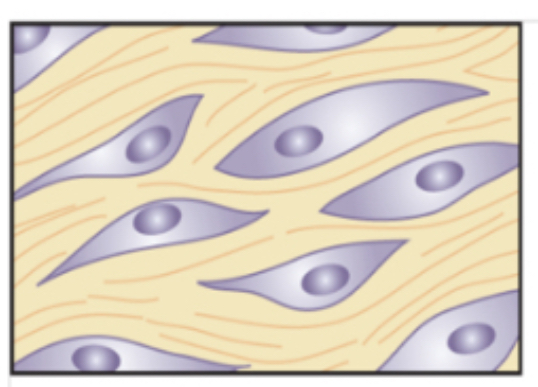
connective
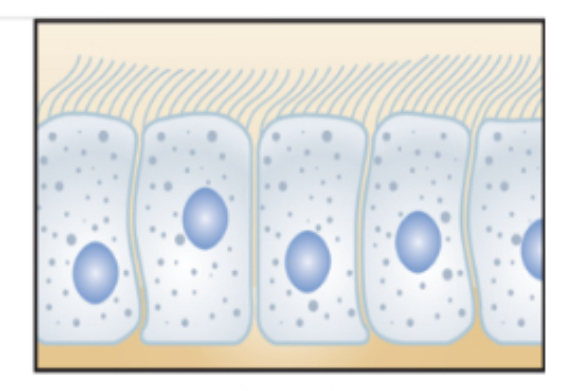
epithelial
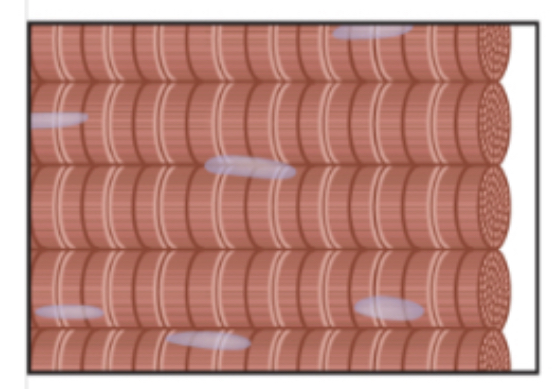
muscular (cardiac and skeletal muscle tissue)
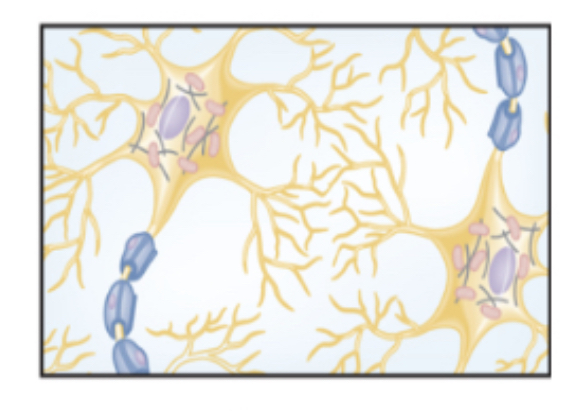
nervous
organs
groups of diff tissues that perform more complex function than any single tissue or cell
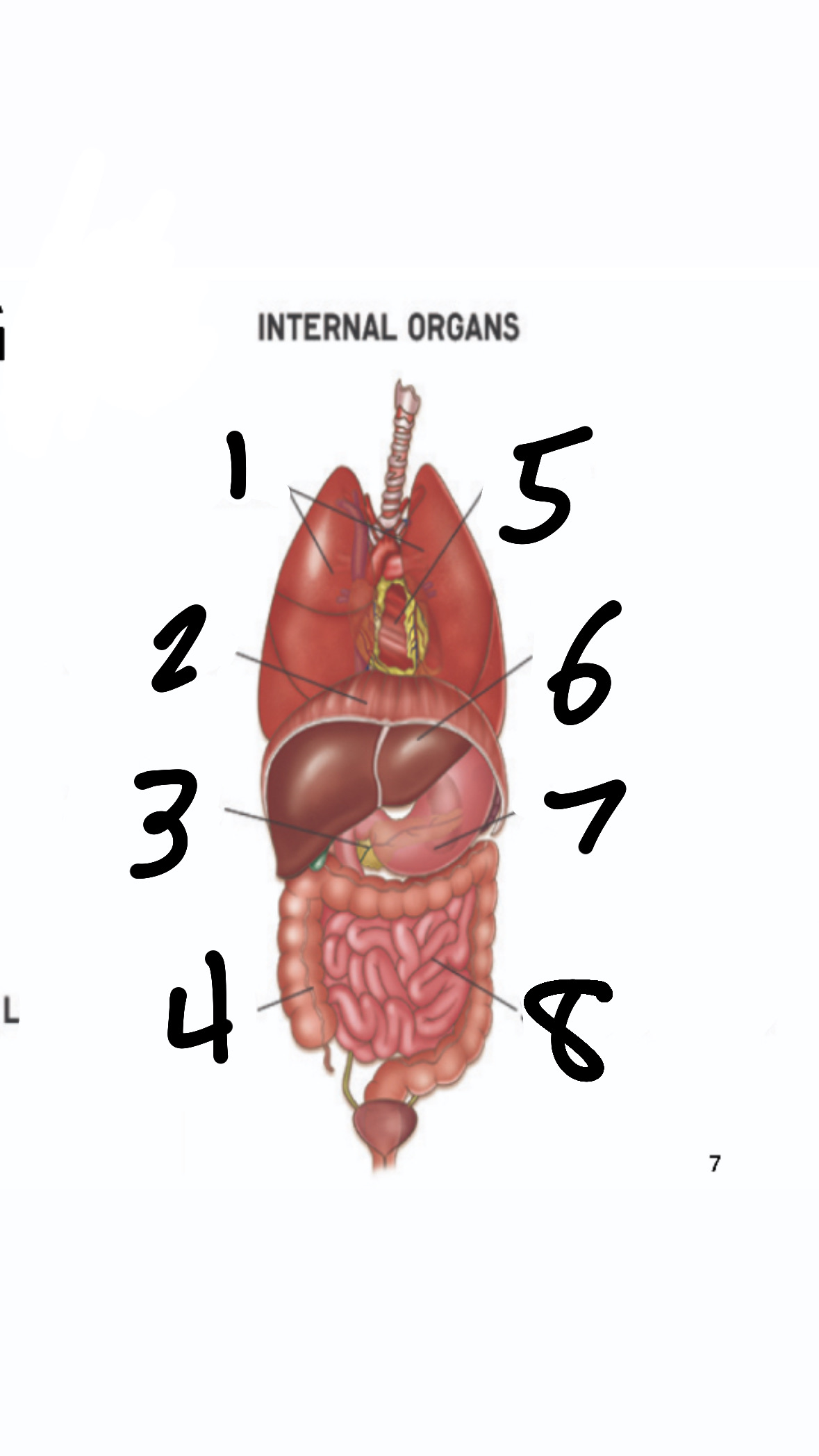
What’s 1?
lungs
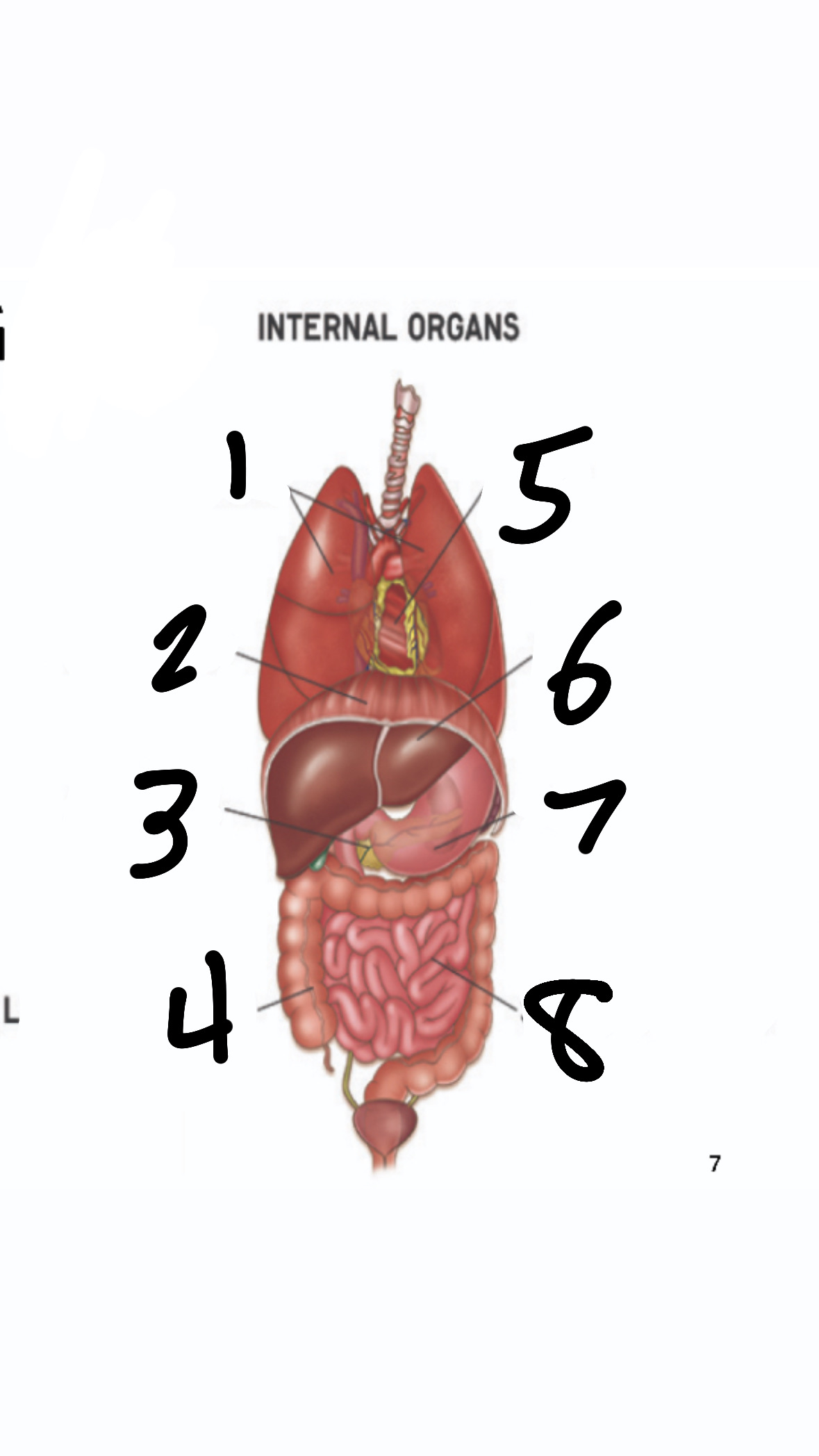
What’s 2?
diaphragm
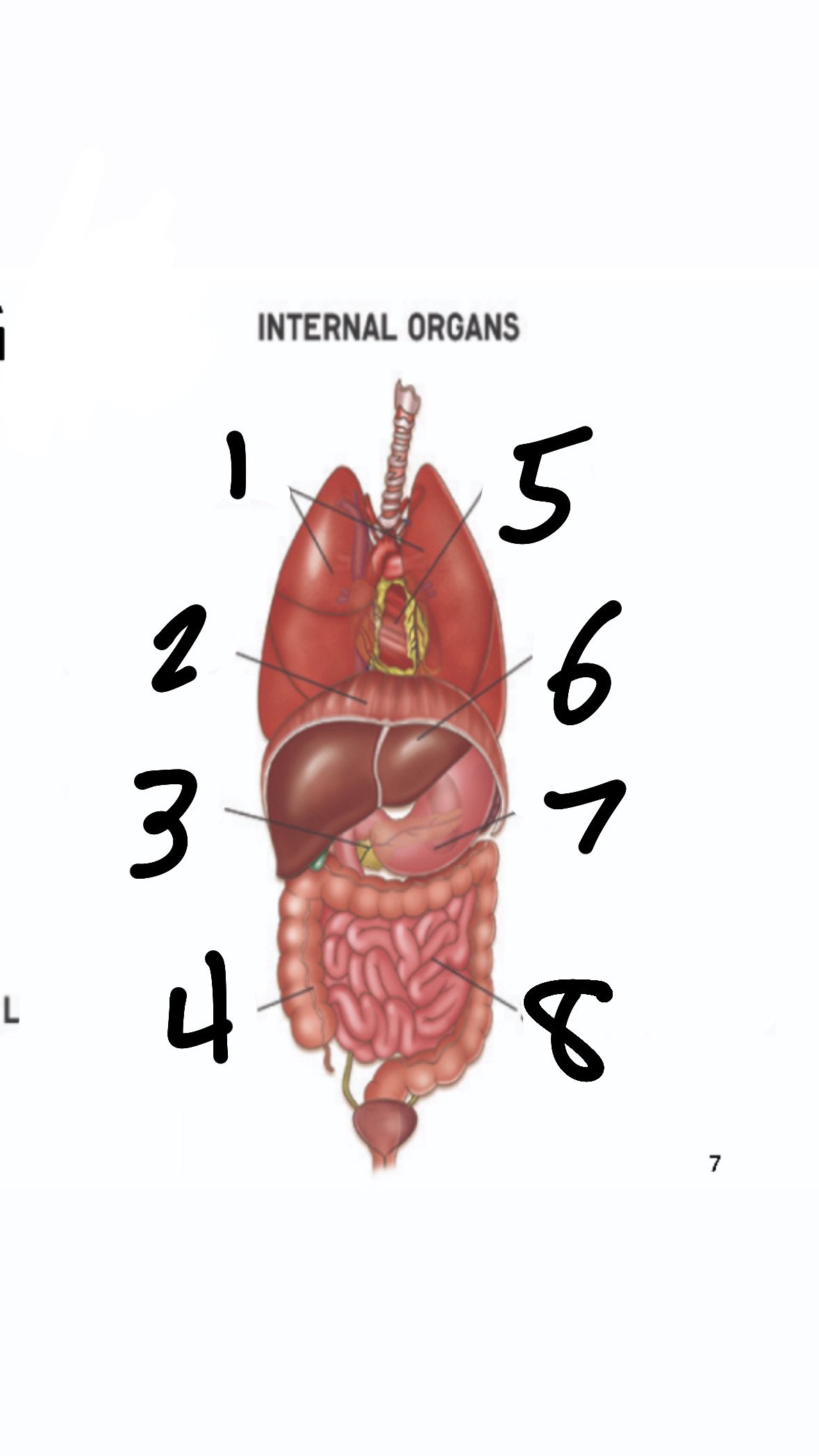
What’s 3?
pancreas
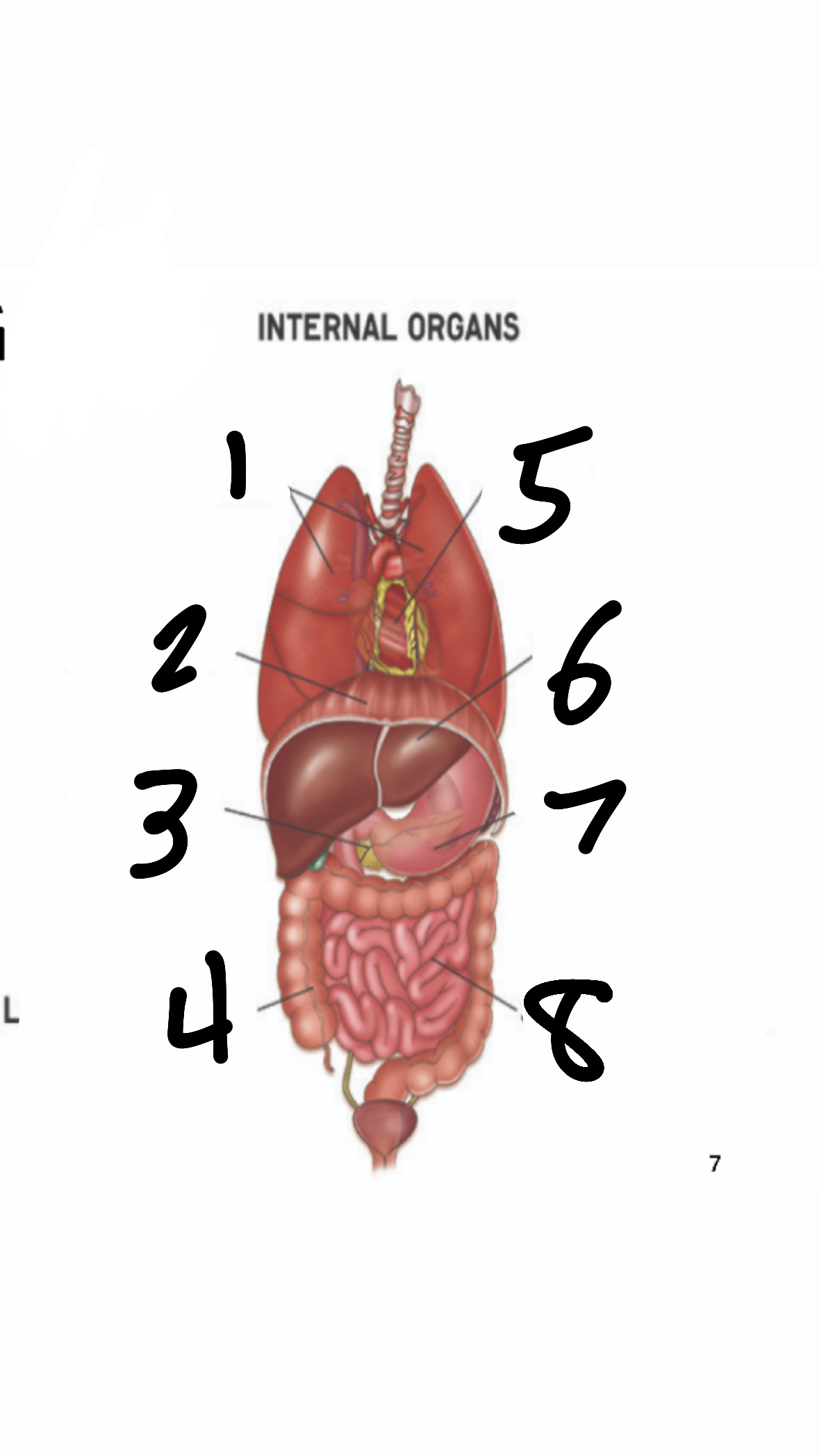
What’s 4?
large intestine
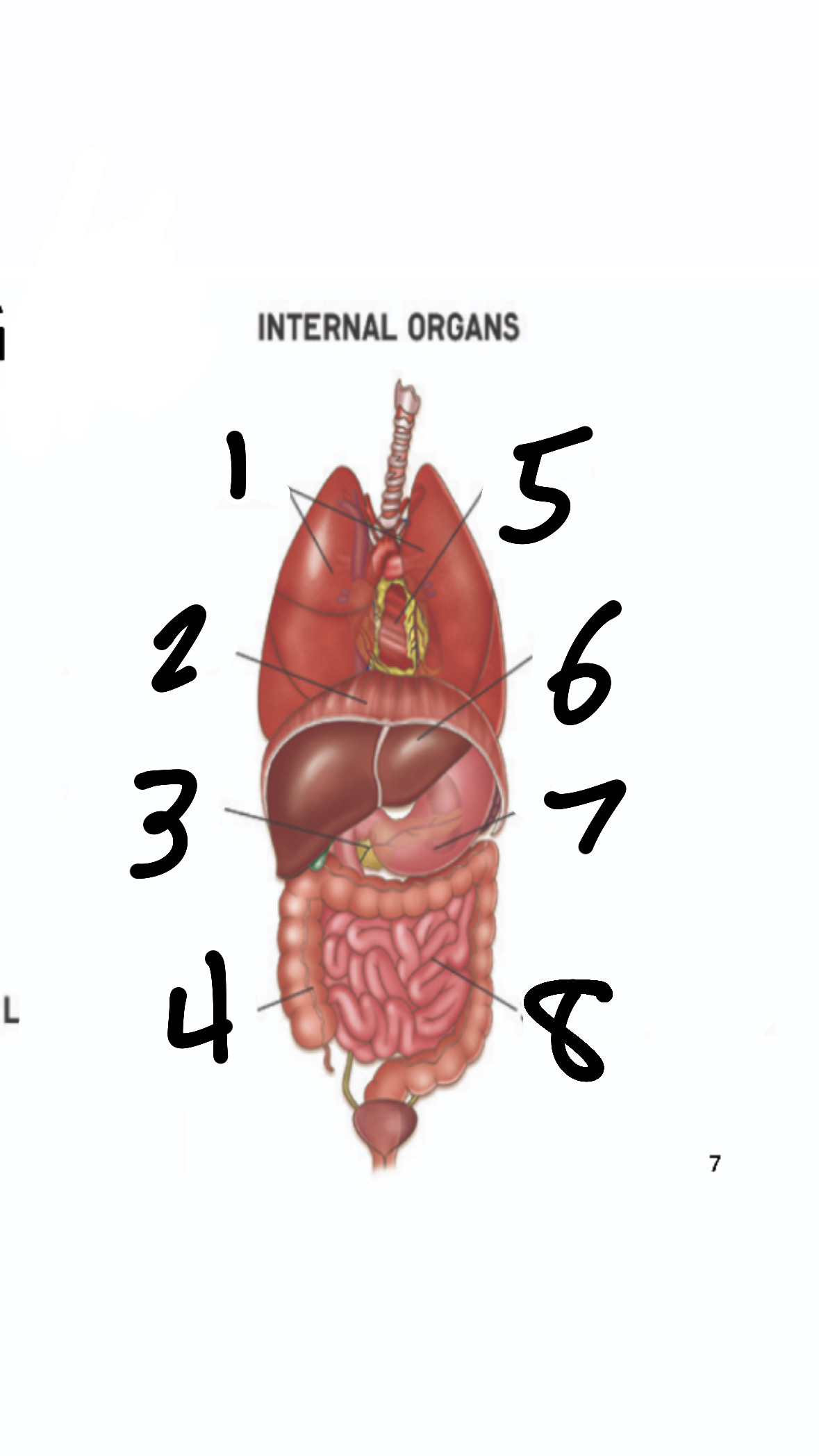
What’s 5?
heart
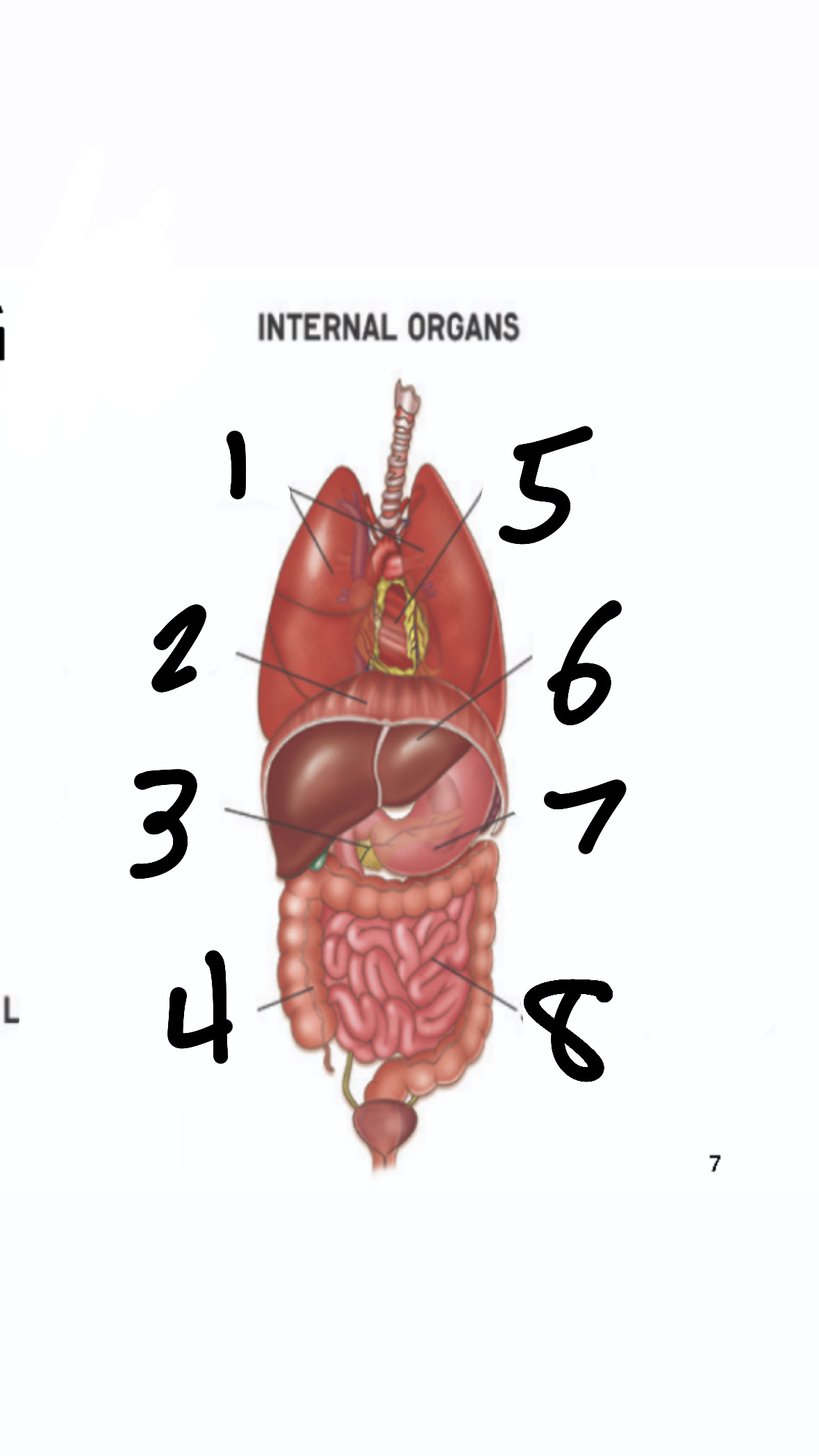
What’s 6?
liver
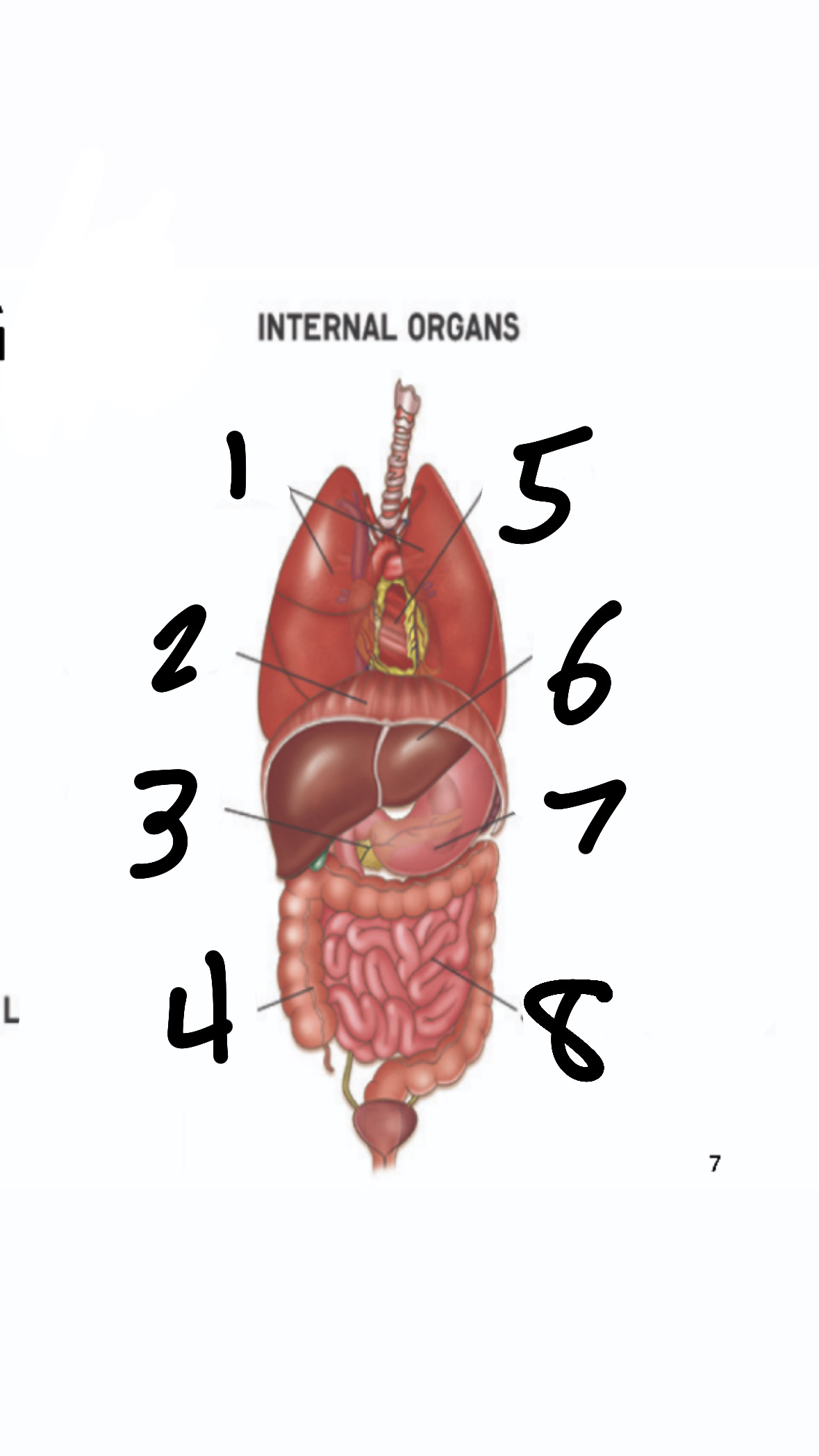
What’s 7?
stomach
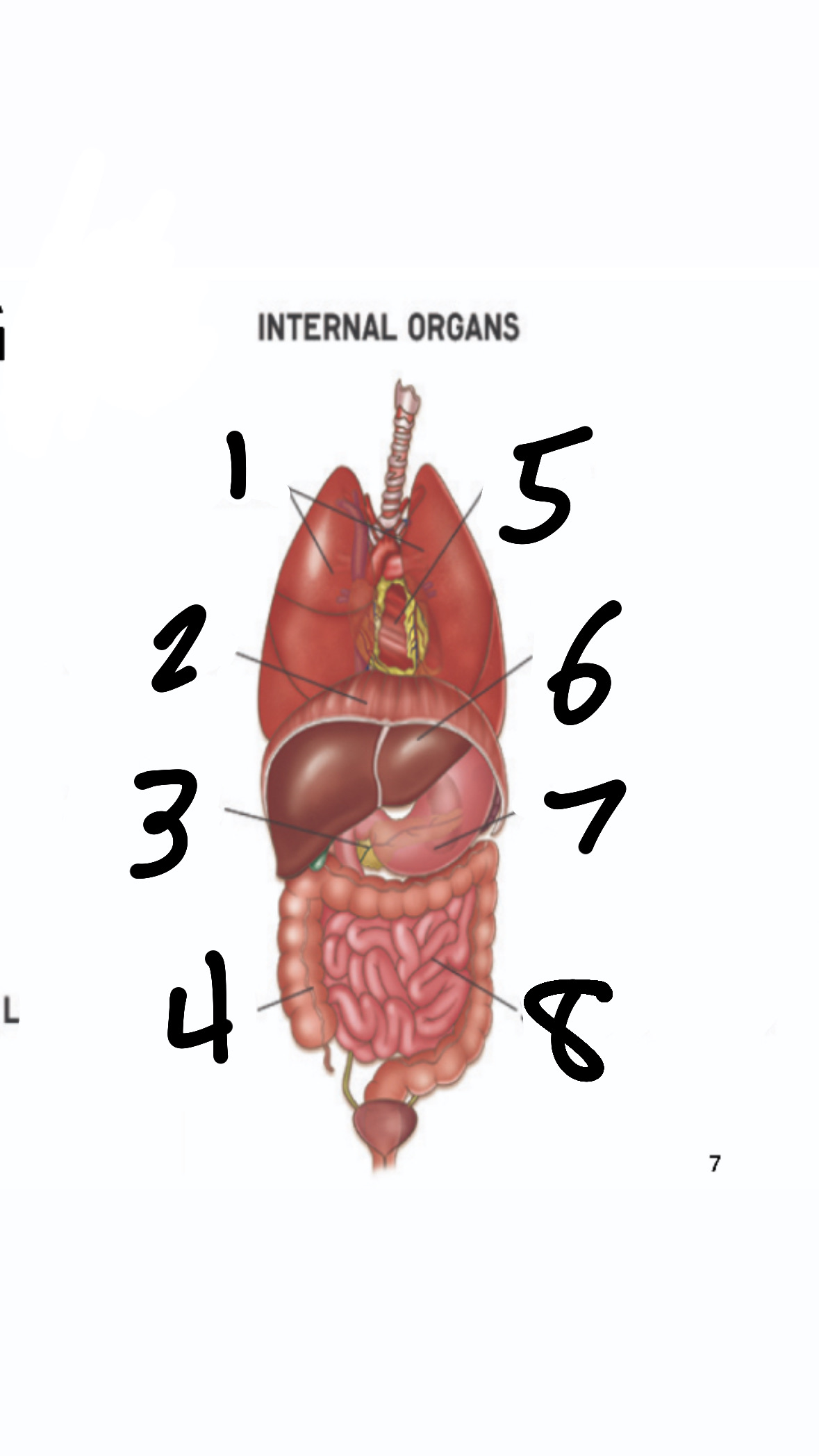
What’s 8?
small intestine
cardiovascular
endocrine
digestive
integumentary
lymphatic
muscular
nervous
reproductive
urinary
skeletal
anatomical position
established reference point for body position
supine
refers to body lying flat on back
prone
refers to body lying face down
anterior
towards front
posterior
towards back
ventral
towards belly/ towards front
dorsal
used interchangeably w/ posterior
cephalic
towards head (same as superior)
caudal
towards tail (same as inferior)
deep
penetrates farther into skin
medial
towards midline
lateral
farther away from midline
proximal
closer to attachment point or origin
distal
farther to attachment point or origin
bilateral
compare normal to other side
unilateral
one side
contralateral
opposite/ other side
ipsilateral
same side
axial region
includes head, neck, and trunk
appendicular region
includes four extremities (arms and legs)
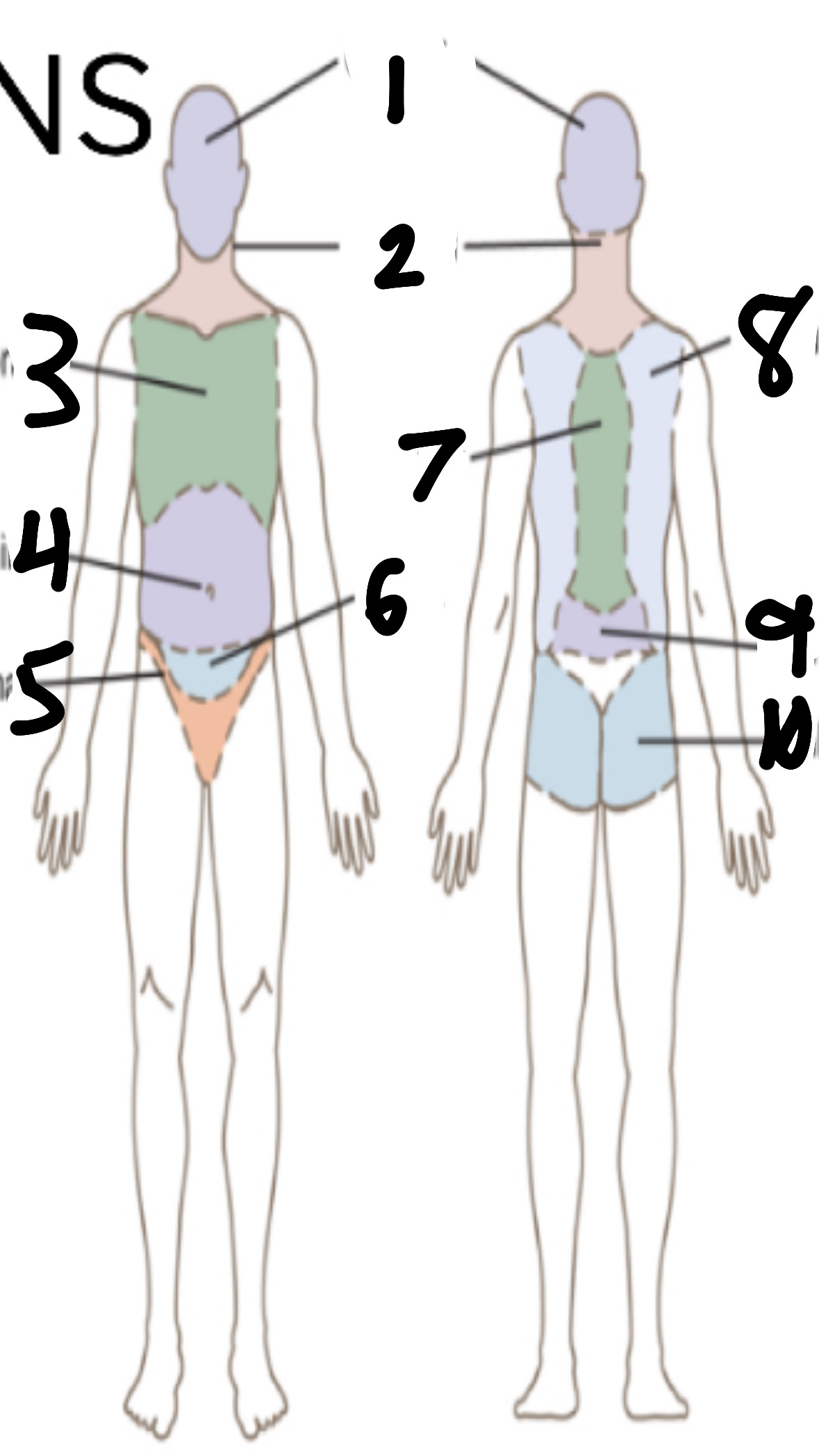
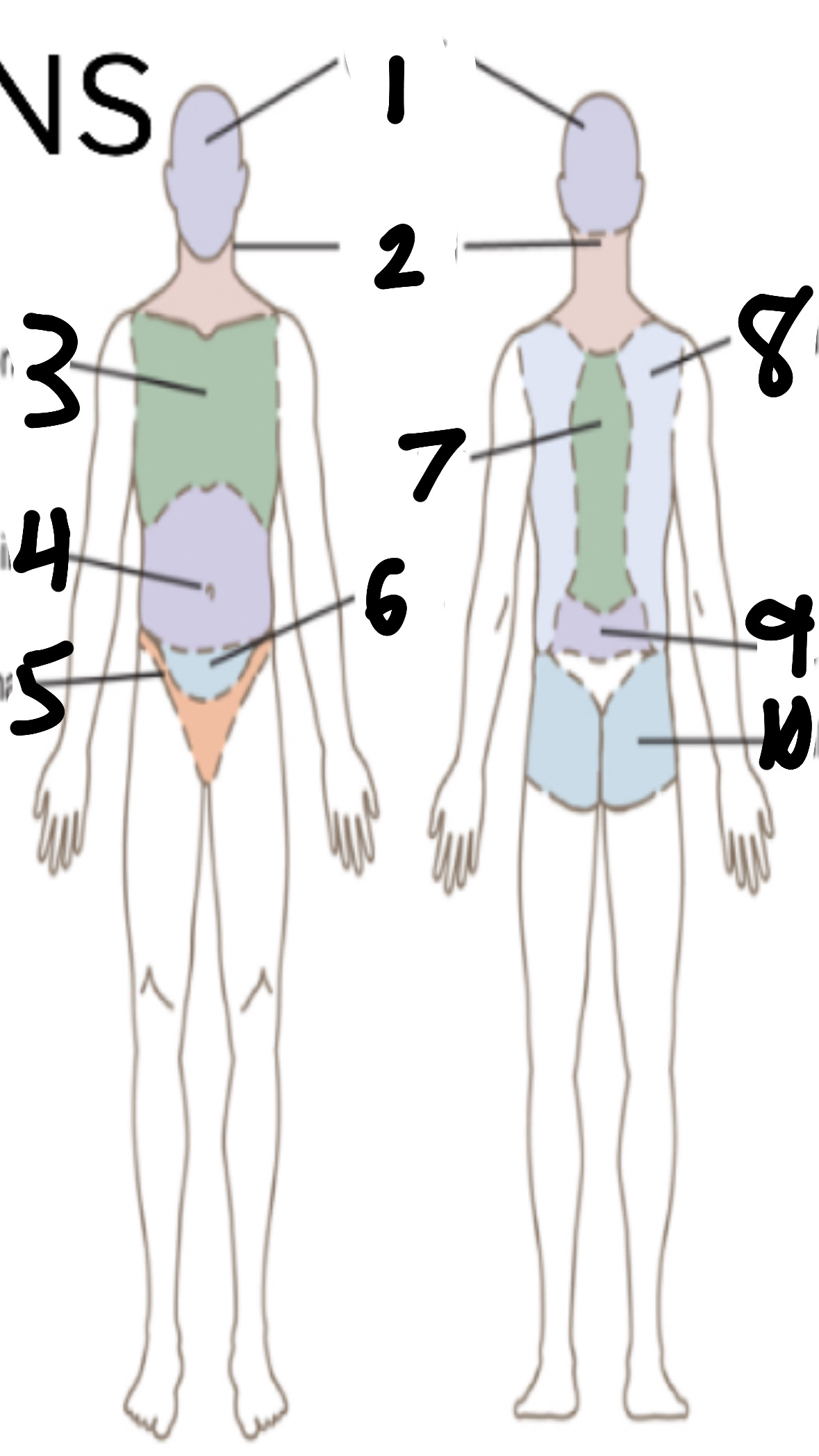
What’s 1?
cephalic
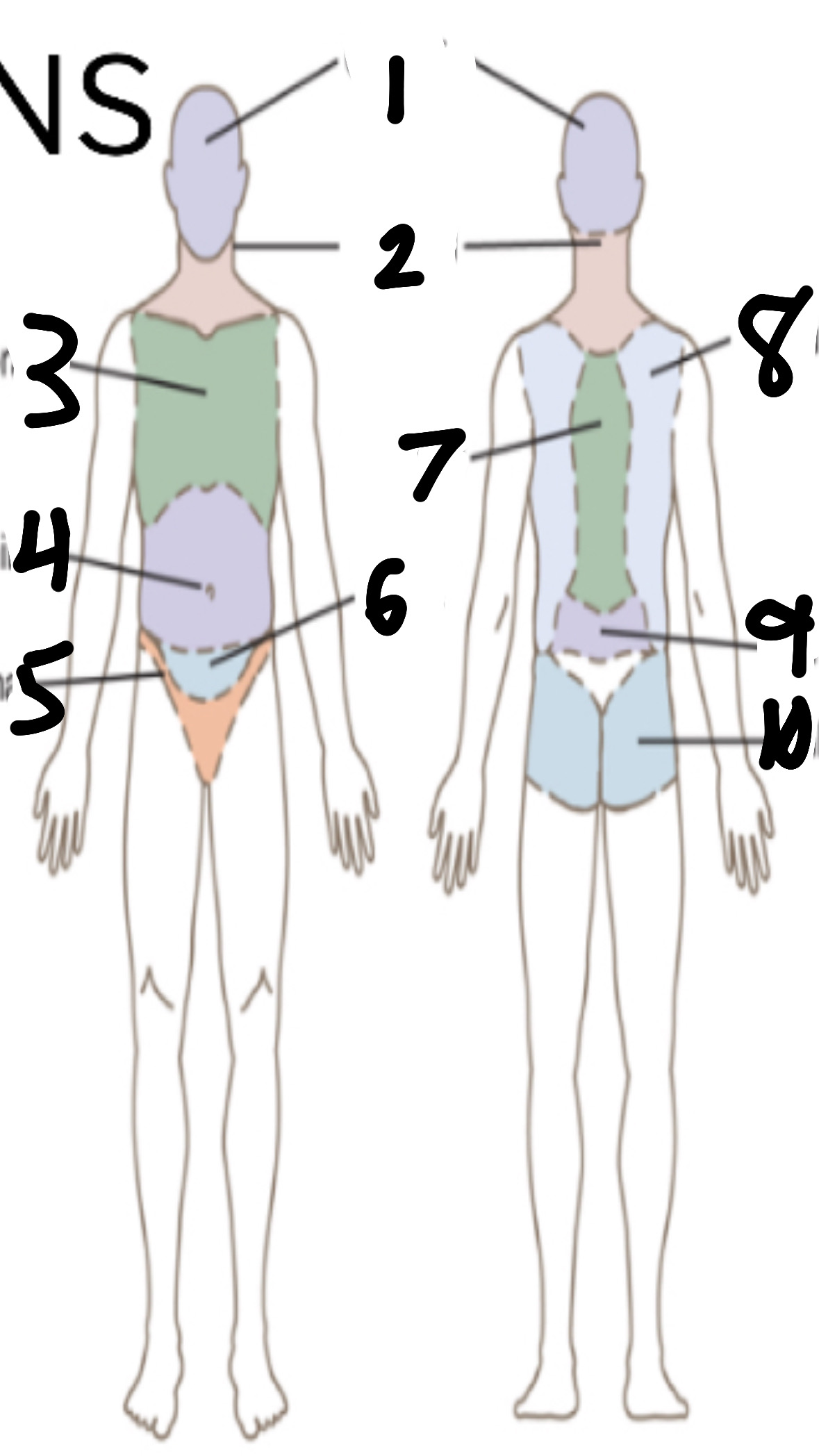
What’s 2?
cervical
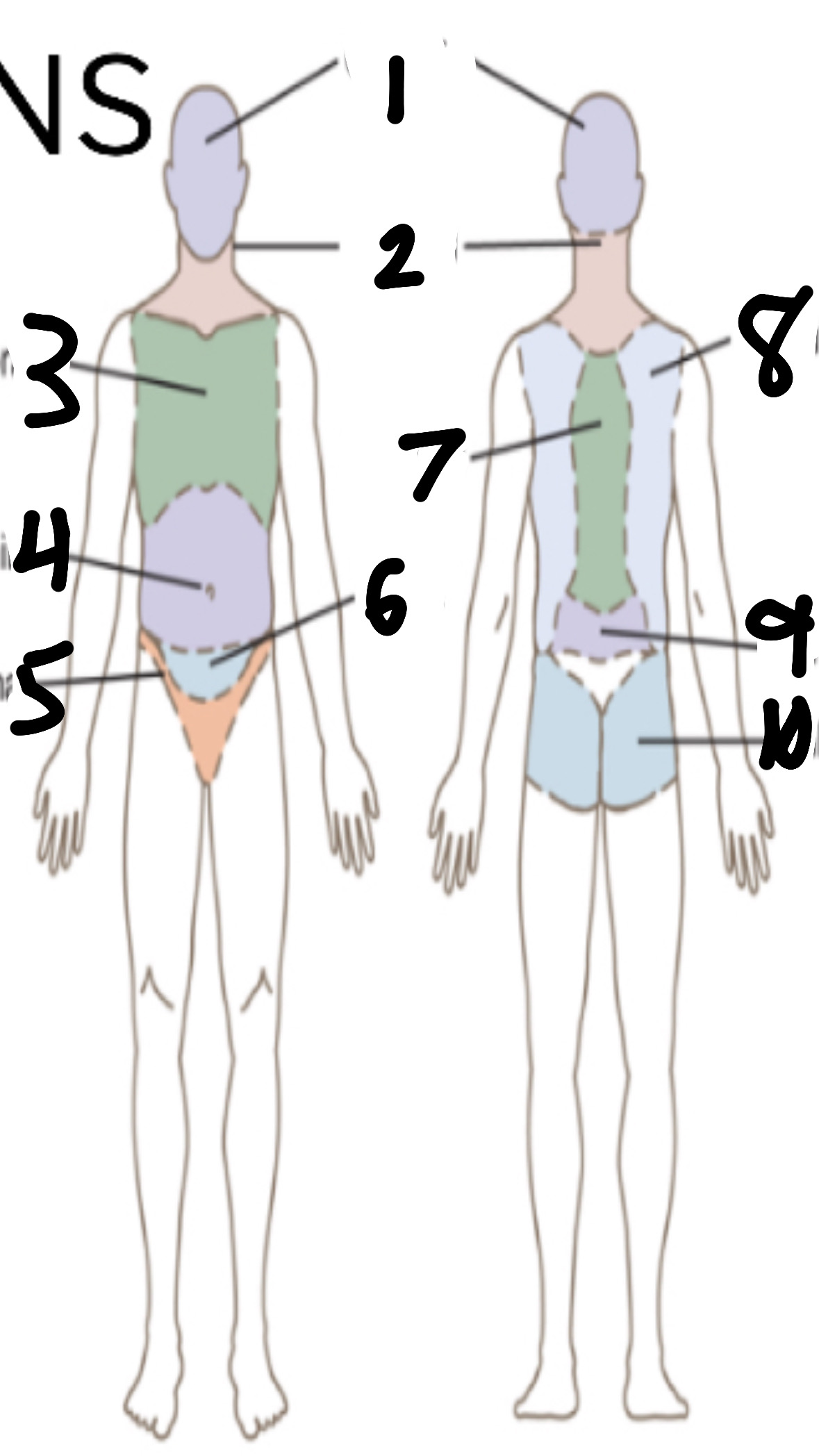
What’s 3?
thoracic
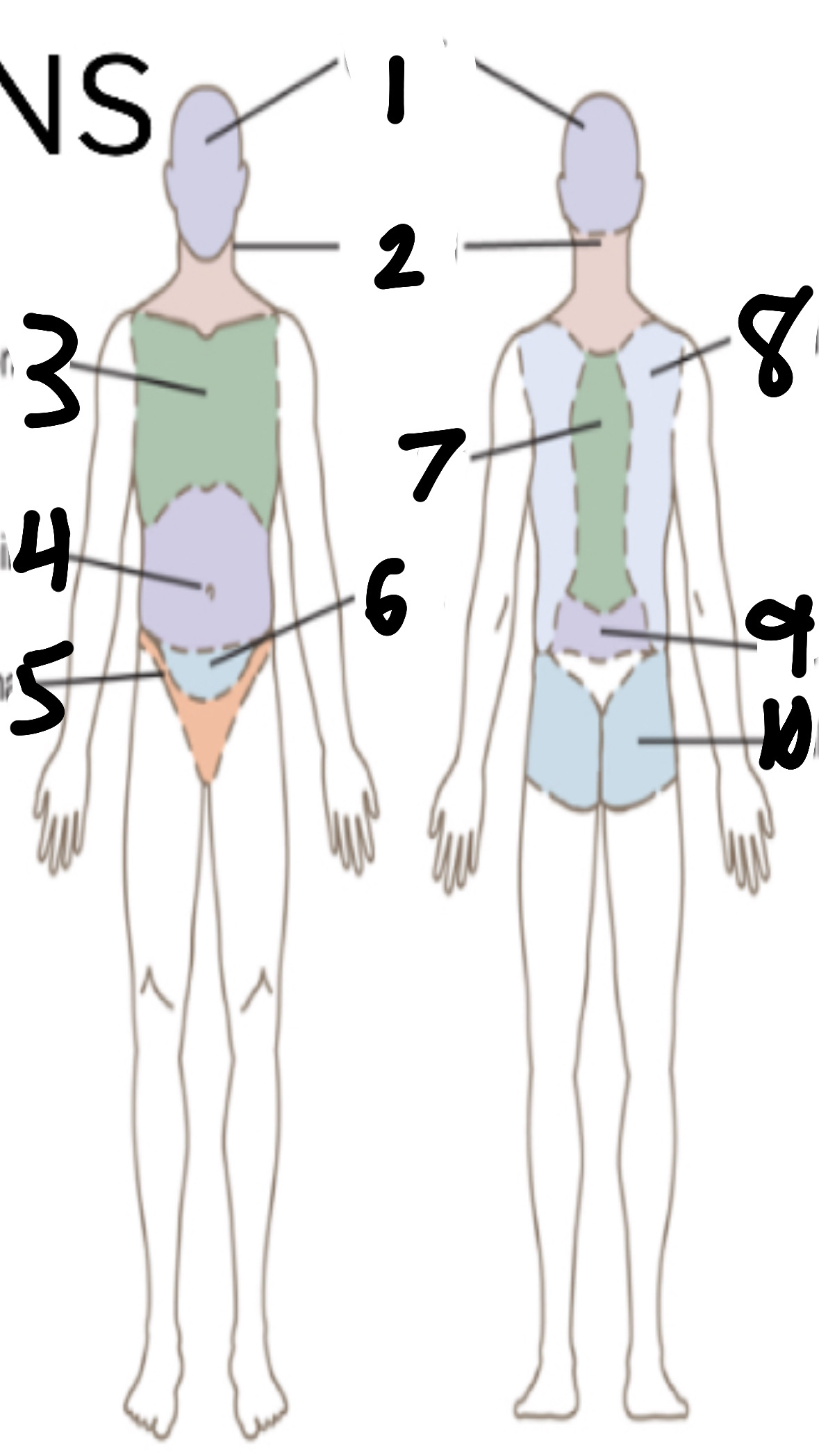
What’s 4?
abdominal
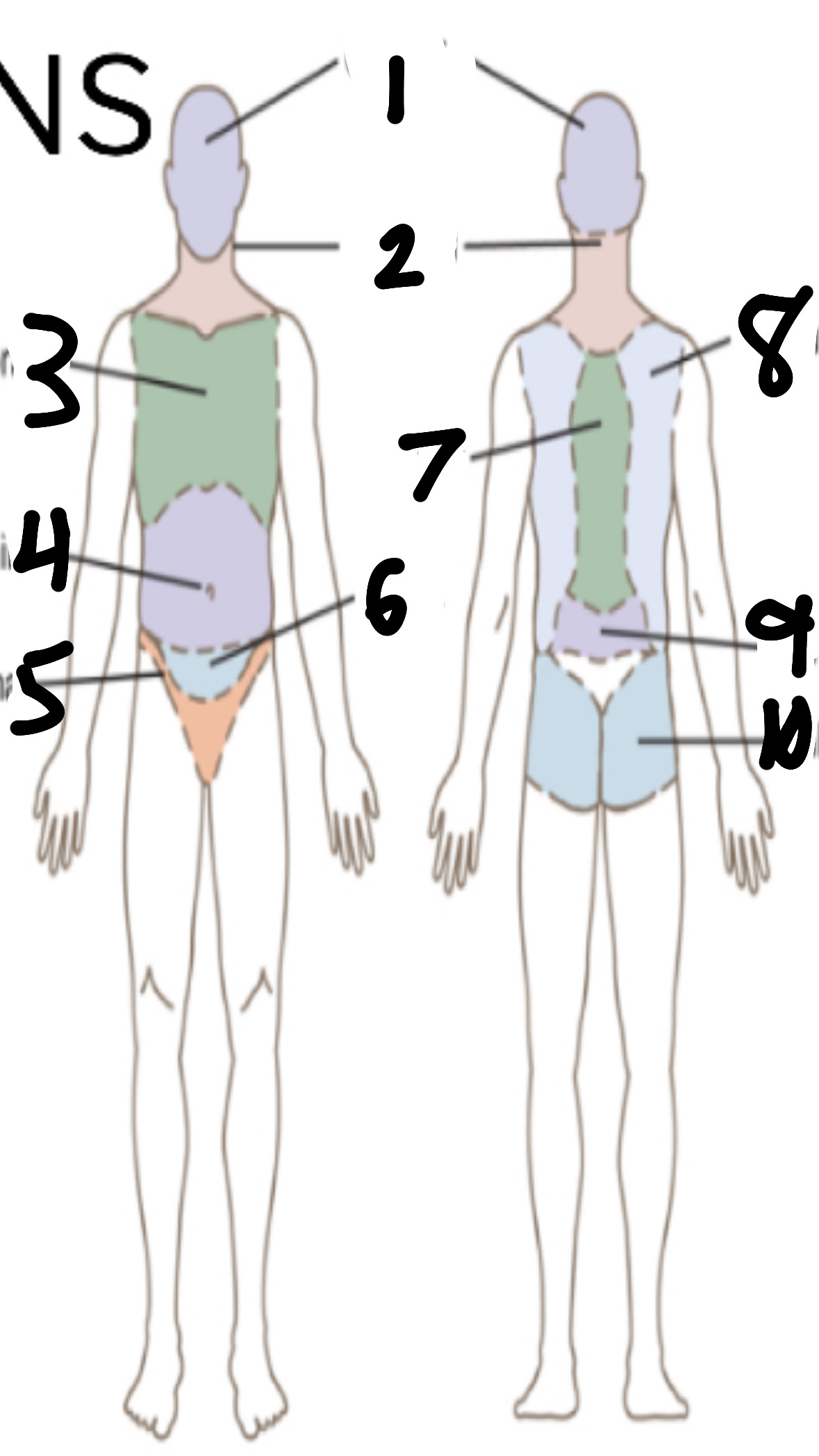
What’s 5?
inguinal
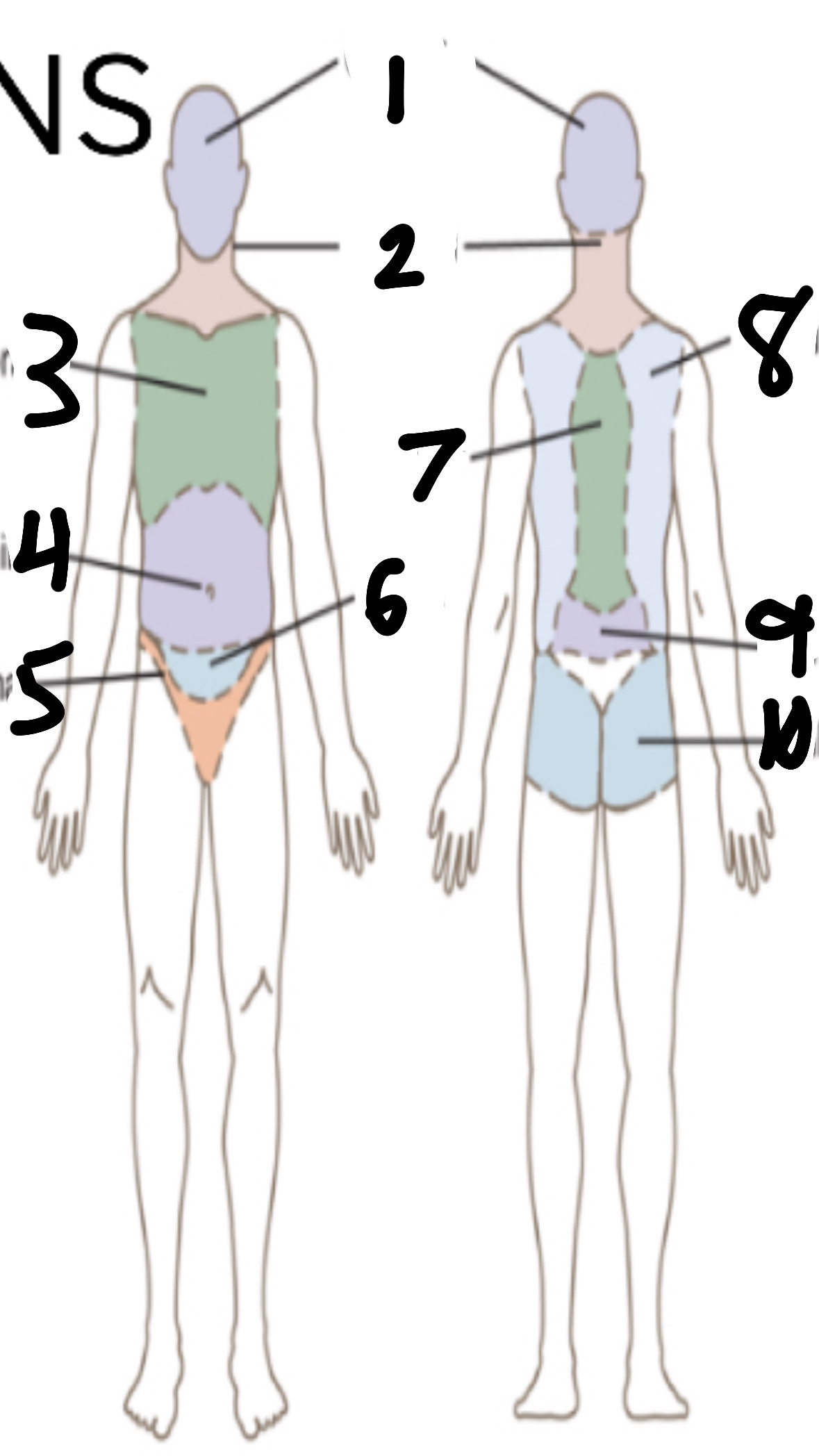
What’s 6?
pelvic
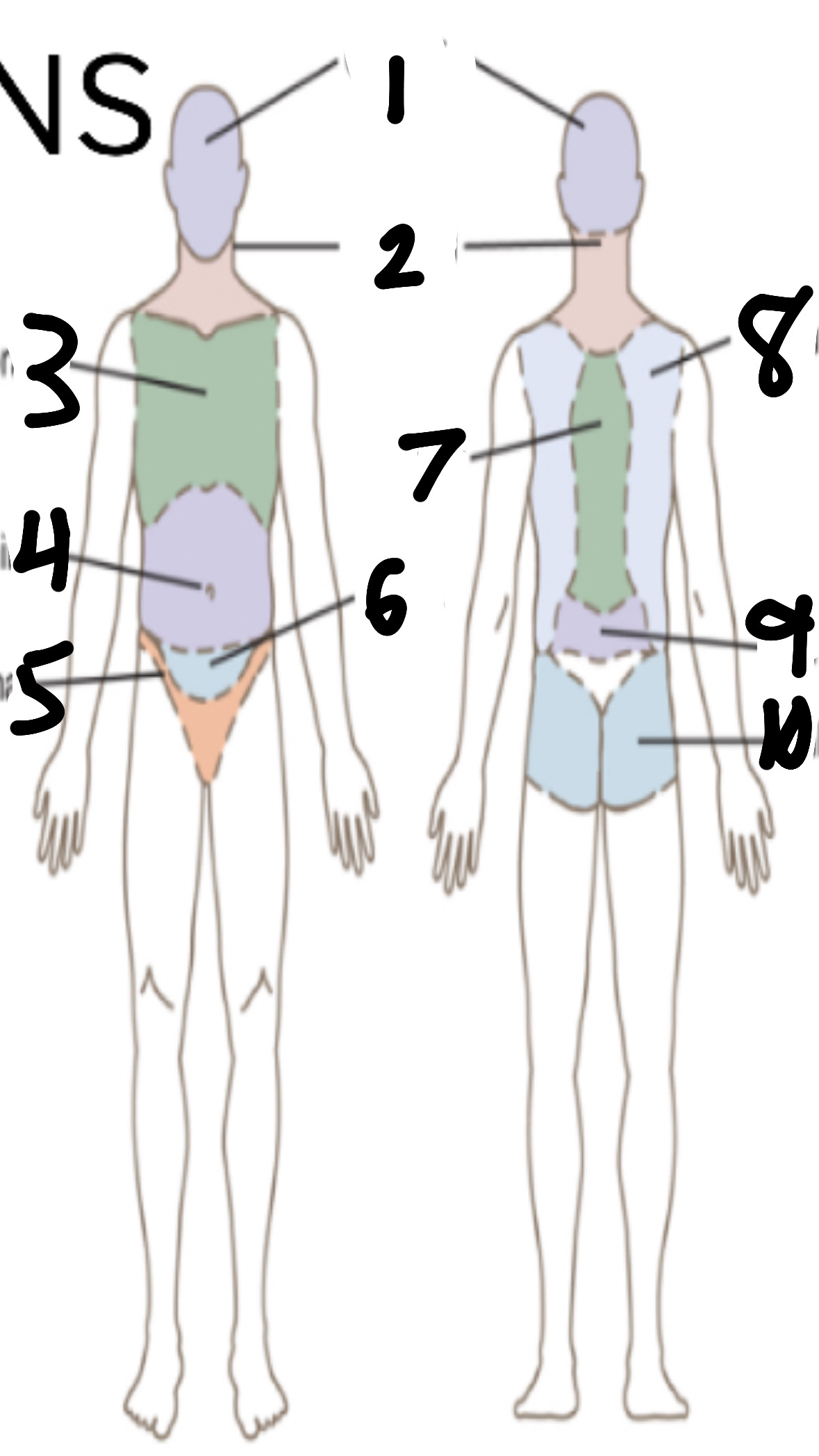
What’s 7?
vertebral
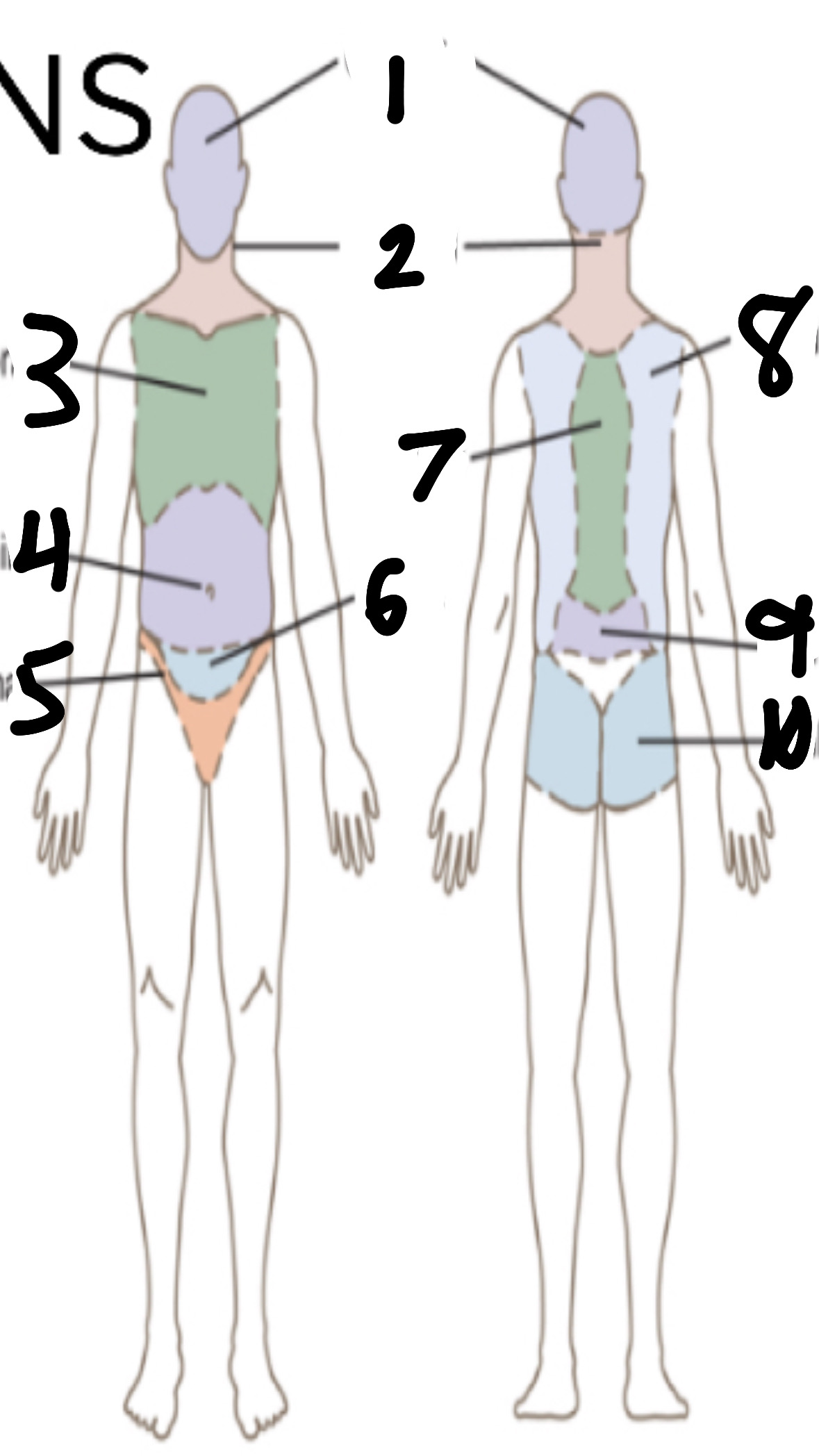
What’s 8?
scapular
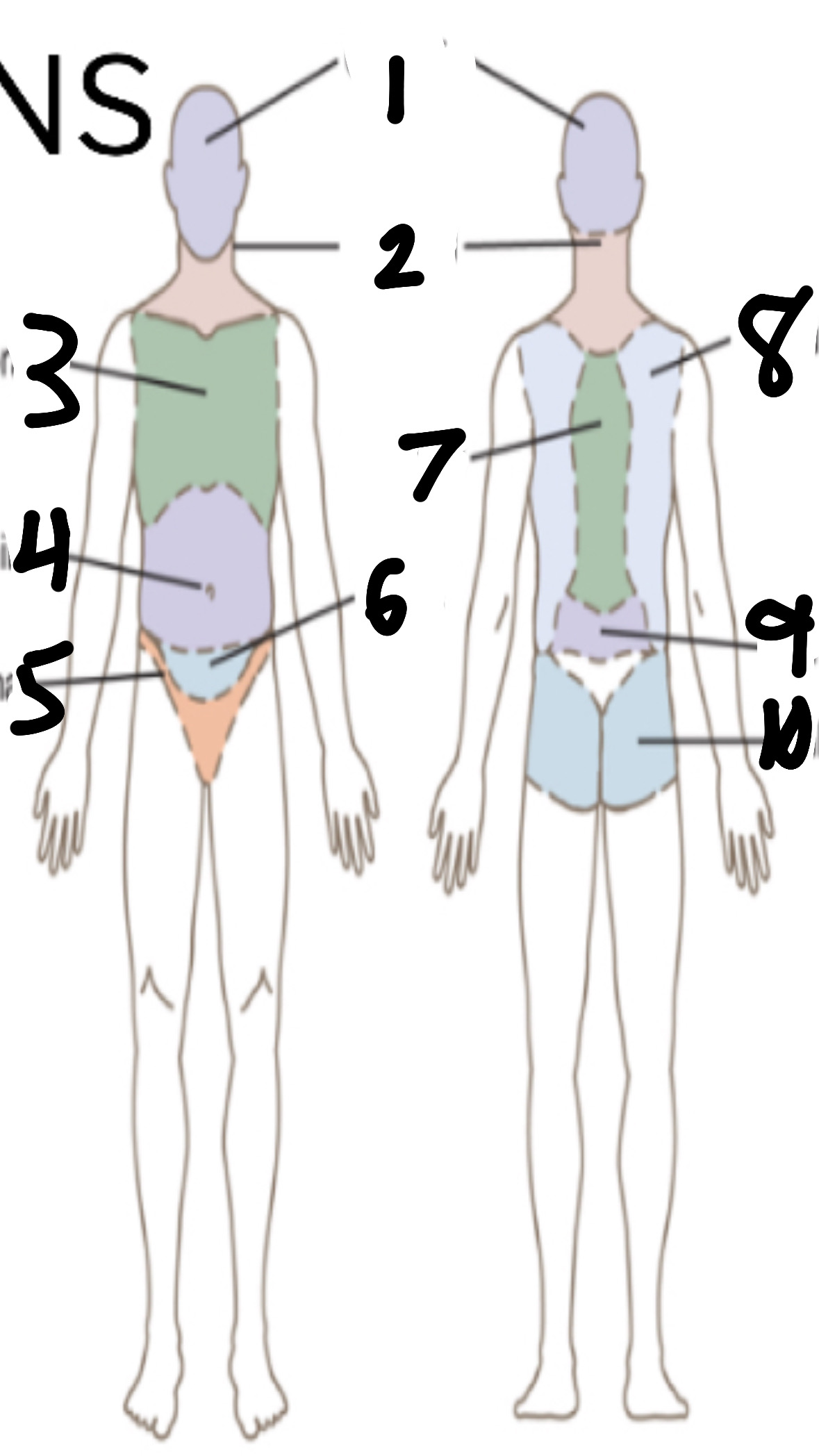
What’s 9?
lumbar
What’s 10?
gluteal
frontal plane
midsagittal plane
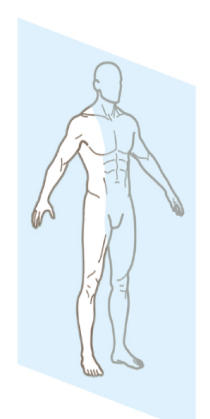
sagittal plane (not on midline)
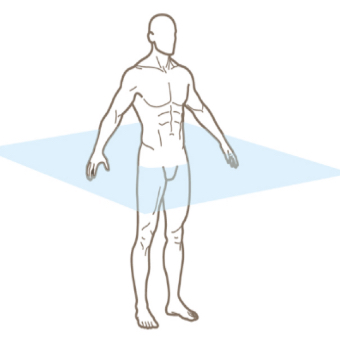
transverse plane
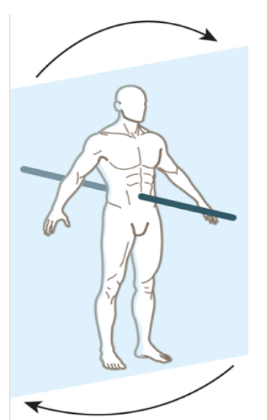
frontal plane, sagittal axis (abduction of arm, flexion of elbow)
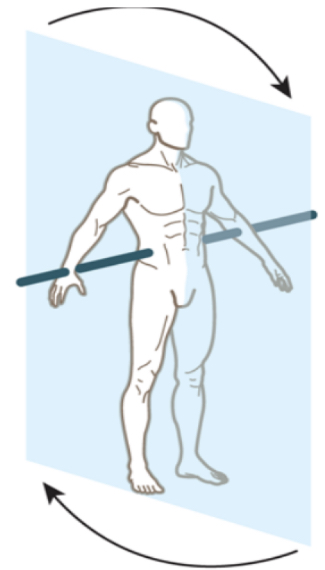
sagittal plane, frontal axis (flexion of shoulder)
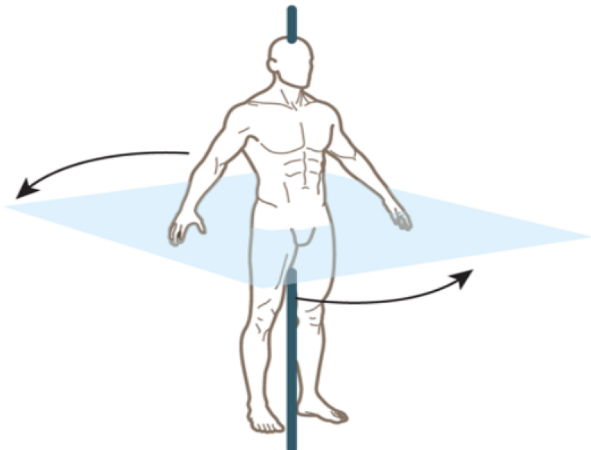
transverse plane, vertical axis
functions of skeletal system
movement
protection
produce blood cells (hemopoeisis, produced in long bones)
store fats and minerals
support
osseous tissue
specific tissue of bone that is comprised of bone cells (compact and spongy)
bone marrow
soft tissue that occupies spaces of spongy tissue and passageways of compact osseous tissue (red bone marrow and yellow bone marrow)
flat bones
cranial bones, ribs, scapulae, sternum, clavicle, and ilium
short bones
7 tarsals and 8 carpals
long bones
humerus, radius, ulna, metacarpal, metatarsal, phalanges, tibia, fibula, and femur (longest bone)
irregular bones
vertebrae and sacrum
sesamoid bone
patella
features of bones
projections
depressions
articulations
passageways
synarthrosis “synarthrodial”
non-moveable/ bony structure
amphiarthrosis “amphiarthrodial”
slightly moveable/ cartilagenous and fibrous structure
diarthrosis “diarthrodial”
freely moveable/ synovial structure
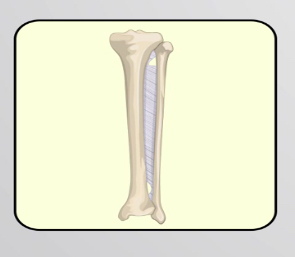
fibrous
cartilaginous
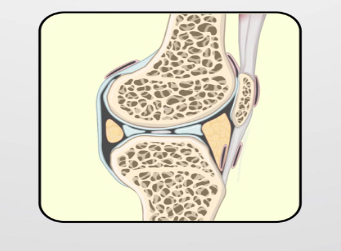
synovial
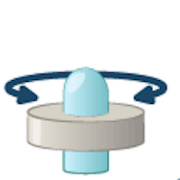
pivot joint (radioulnar)
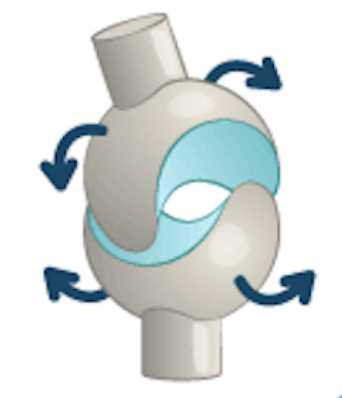
saddle joint (thumb)
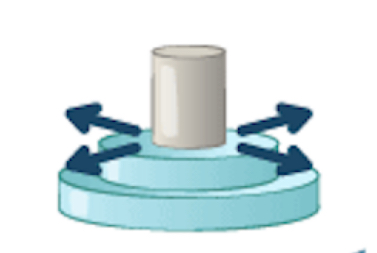
plane “gliding” joint (ankle, wrists, and vertebrae)
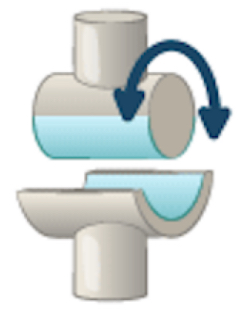
hinge joint (elbow, knee and ankle)
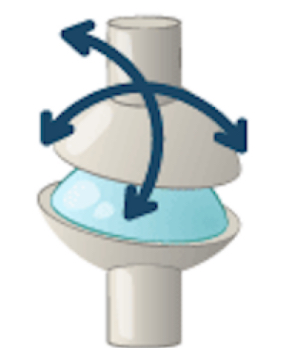
condyloid joint (wrist and hands (metacarpal phalangeal joints))
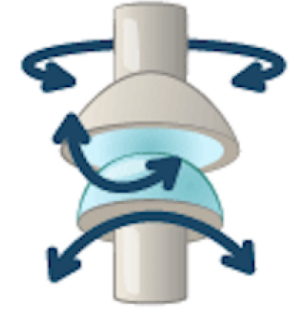
ball and socket joint (hip and shoulder, most movement allowed in body)
muscular system
overall purpose is to move body and body fluids
muscular contraction
causing of tension (force)