astrocytes
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
protein that gives astrocytes star-like shape
glial fibrillary acidic protein
astrocyte morphology (4)
innumerable fine processes
GFAP highly expressed → doesn’t exist in processes
plasma membrane protein anchored green fluorescent (LCK-GFP) → enables visualization
astrocytes don’t overlap w e/o
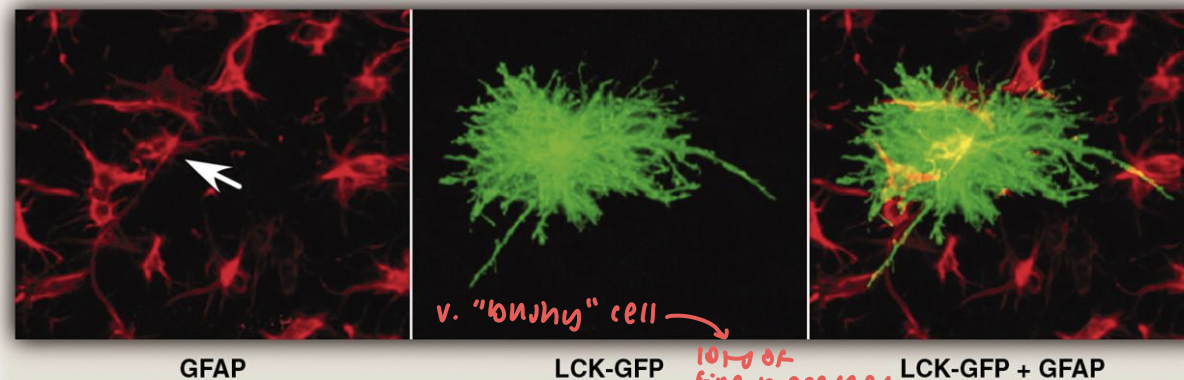
astrocytes form
gap junctions from cell to cell → have connect cytosols
excitability of an astrocyte (3)
v. little when injected w current bc resting membrane potential ~85mV
highly permeable to K+ → membrane potential close to K+ equilibrium potential
v. leaky
astrocyte interaction w synapses (3)
help support synaptic functioning
make extensive contact w multiple dendrites/neurons
1 astrocyte can interact w 100,000 synapses
what are astrocytes doing in the brain (6)
support + influence the synapse
ionic homeostasis → ie. external K+ clearance
feed synapses w glucose/lactate
secrete growth factors for synaptogenesis
neurotrans clearance + recycling
modulate synaptic transmission
glutamate clearance via _______ generates an _______________
excitatory amino acid transporters (EAAT1 + 2)
inward Na+ current that can be recorded in voltage clamp
EAATs (4)
use Na+ driving force to bring in glutamate
3 Na+ for 1 Glu- and 1 H+
can work w/o ATP
+2 ve
glutamine synthetase
converts glutamate into glutamine which is shuttled back into presynapse for reconversion + use in synaptic transmission
how can EAATs shape neuronal excitability
↑/↓ EAATs can produce longer lasting depolarization
Ca2+ signalling in astrocytes (3)
poking astrocyte w pipette initiates wave of Ca2+ → propagates as a wave
ATP/glutamate can start waves too
intracellular propagation through IP3
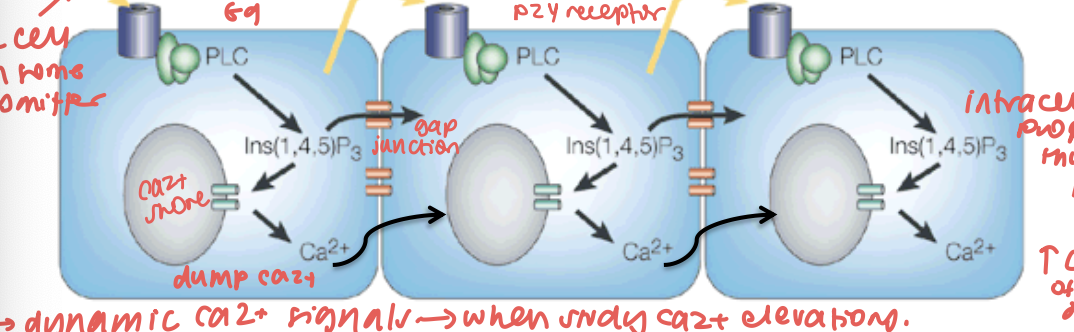
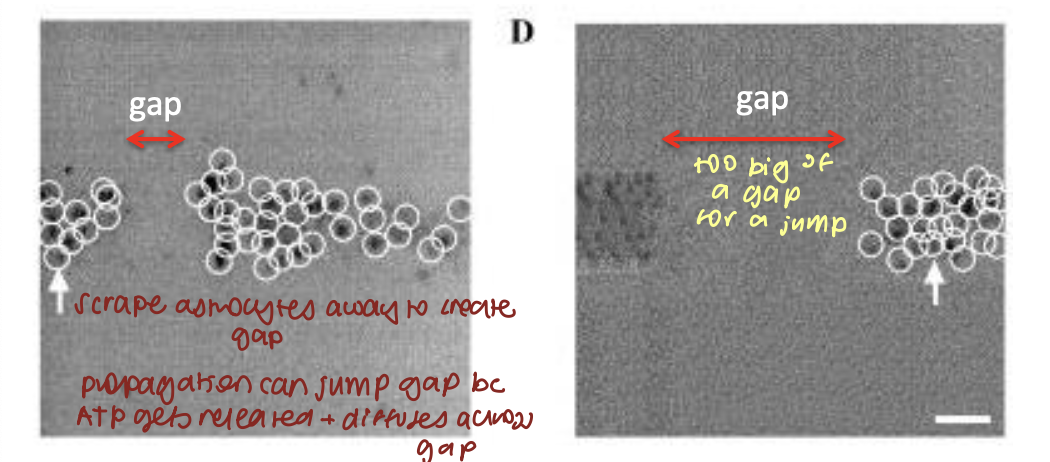
what/how did paracrine ATP signalling show in astrocytes (3)
gap jumping
astrocytes releasing diffusible messenger (ATP)
large gaps cannot be jumped → not enough ATP
Synaptically evoked astrocyte Ca2+ via metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR)
strong synaptic activity ↑s astrocyte free intracellular Ca2+
weak synaptic activity does not cause astrocyte signal
needs lots of glutamate release to overcome uptake → spill out of the synapse + activate astrocyte mGluRs
bad experimental technique to stimulate astrocytes vs better technique
BAD
injection of current → v. high current to ∆ MP of v. leaky astrocyte membrane
BETTER
light-sensitive, caged Ca2+ molecules