Microeconomics: Government Intervention
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
Why is government intervention required at times?
The free market can result in a misallocation of resources (or market failures). Governments can intervene to correct these market failures.
Why would government intervention be needed to meet basic needs?
In a market-based economy, a consumer's ability to consume goods and services depends on their income and wealth.
If a consumer has a low income, they may not be able to afford basic goods to satisfy their needs.
The market is under-providing these goods and this can be a source of market failure.
Why would government interventions be needed for over consuming demerit goods.
Demerit goods like cigarettes may be over consumed. Taxes or bans may be interventions to solve this issue.
Why would government interventions be needed for irrationality?
The UK government has a nudge unit, which implies that consumers may not be rational agents and need guidance.
Why would government interventions be needed for under consuming merit goods?
Governments may want people to consume more things like education, which have positive externalities.
Subsidies or free state provision may be used to encourage the consumption of merit goods.
What is market failure?
When the market fails to allocate society's resources efficiently.
What are the 4 reasons for Government intervention?
Over consuming demerit goods
Irrationality
Meeting basic needs
Under consuming merit goods
What are 3 government objectives for interventions? Explain them
Improving information- Reducing the asymmetry of information by giving consumers as much information about the choices they make.
Efficiency- Some policies are needed to reach government goals. Some industries benefit from nationalisation because they do not function well under the price mechanism, e.g. train lines.
Focus on SMEs- Small to medium size businesses benefit from deregulation so government intervention is required to achieve their goals.
What does competition policy do? Who is in charge of it?
Competition policy aims to reduce the amount of anti-competitive behaviours in markets and to protect consumers.
It is undertaken by the competition and markets authority. (CMA)
How is regulation a form of competition policy?
The power of monopolies can be reduced by regulation, e.g. the introduction of a price ceiling by the government restricts the amount firms can raise their prices. Reducing the potential losses in efficiency.
Alternatively, the government could tax excessive profits, or set performance targets for monopolies.
How M&A policy a form of competition policy?
The CMA is also responsible for monitoring merger and acquisition (M&A) activity in the UK.
Any firms which looks to merge or acquire other firms in the market which leads them to be considered and investigated by the CMA. They will then decide if the transaction would lead to a lack of competition in that market and so excessive monopoly power.
If they believe it will lead to excessive monopoly power, they can block the deal.
What are the principles of UK competition policy?
UK competition policy looks for anti-competitive play in the market. This can come from different sources such as monopolies, mergers, cartels or financial support.
There are also industries that have their own regulatory bodies, e.g. OFCOM deal with communications industry and are in charge of ensuring fair play within it.
Why do the government want to prevent monopolies?
Monopolies are formed through mergers or agreements can often be inefficient. This is because they restrict quantity and agree to raise price to a level that isn't allocatively efficient.
What powers do the CMA have?
The CMA can force the break up of firms which have become too powerful in a market. If they believe a firm is abusing its monopoly power, they can force the firm to split or sell some of its assets to increase competition. It is rate to break up firms which have gained power through internal growth.
Give 3 reasons why governments encourage competition? Explain each one?
Lower prices - If there is competition in the market, firms have to make their products more attractive to consumers. This means they will have to lower prices so households can consume more.
Higher quality - consumers would chose goods which have higher quality so firms would have to improve their products to keep up. This leads to more utility and improved welfare.
Technological advances -Firms' investment in technology leads to positive spill over effects as the technology is shared through an economy. Each technological breakthrough pushes society further forward and again leads improved welfare.
How does the quality of information affect the effectiveness of competition policy?
If the information received is trustworthy, governments can take action and punish anti-competitive behaviour. This will help to improve efficiency and the allocation of resources.
But this is not possible if not enough information is received, or the information is unreliable.
Also, there is an opportunity cost to collecting this information. This could be seen as government failure if there is no action resulting from the collation of information.
How does deregulation impact contestability?
Contestability in markets can be improved through deregulation. This is because barriers to entry have been lowered. This is good for competition in an industry.
Why do the regulators need to have powers?
For firms' behaviour to be influenced by regulation, the regulator (the CMA in the UK) needs to have sufficient powers and to be well-resourced.
The CMA's ability to impose large fines and even imprison directors of companies means that firms are likely to think twice before engaging in price-fixing or joining an illegal cartel.
What did the CMA do when BT wanted to buy EE?
The CMA investigated BT's proposed purchase of mobile network EE.
BT are also involved with telephone and internet services. The deal was eventually allowed to go ahead, but only after BT agreed to the CMA's suggestion that they sell off certain parts of their business to make sure that they would not be too powerful in certain markets.
How does price capping relate to utility industries?
In the UK utilities industries, the respective regulators set a cap on how much prices can rise year on year based on the rate of inflation and planned levels of investment.
The government can impose a maximum price on goods and services, this reduces the benefit to firms of constricting output to increase the price.
Consumers can then access the goods and services at what the government deems a fair price.
What is state provision?
Goods and services provided directly by the government.
How can state provision be offered?
The government could either provide state provision directly (e.g. state education) or provides free goods or services to the public that they have bought from the private sector.
What are the advantages of state provision?
State provision can reduce inequality by redistributing money from the wealthy to the poor. This is something the market doesn't always do.
Without state provision, some services might not exist as they aren't profitable, e.g. unprofitable train routes.
Value judgements need to be made about what the state can and can't provide well.
What are the disadvantages of state provision?
Without a drive for profit, there is less incentive to make a service as efficient as possible. The economic incentives for efficiency could be eroded.
There is an opportunity cost of providing one service over another.
With asymmetric information, there is a risk of government failure.
What is privatisation?
The change of ownership of an industry from the government to private shareholders.
What are the advantages of privatisation?
The incentive for profit means that resources will be allocated more efficiently.
When the government sell off their enterprise, they will gain revenue that can be put to alternative use.
What are the disadvantages of privatisation?
The drive for efficiency means that an element of humanity might be lost. Efficiency may come in the way of delivering a fair service.
There is a moral argument against providing some services profitably.
Safety and spending on safety measures may be worse in privatised industry that are judged only on profits.
How does the government contract out provision of goods? Give an advantage and disadvantage of contracting out.
The government pays for the contract and distributes it as if it had been publicly provided.
By contracting certain jobs out, the government can get jobs done by specialist firms who service other customers and benefits from economies of scale.
But by contracting out certain jobs, the government becomes reliant on other firms. There are risks that a firm with a contract goes bankrupt or faces strikes from its workforce.
What is tendering? Why does the government put out jobs to tender? What's a negative to tendering?
Tendering is a competitive process with firms giving their best offers in order to win contracts.
Governments can put out jobs to tender, giving prospective suppliers the chance to bid for contracts to supply goods or services.
However, because the tendering process is based on what firms promise they can deliver, it is common for firms to over promise and under provide which can lead to large unexpected costs and reduced quality.
What is regulation and deregulation?
Regulation involves setting rules that firms must comply with. These rules are imposed by the government to try and correct market failures. Deregulation is a loosening of these rules.
What are the benefits of regulation?
Regulation can correct market failures that arise from externaties, e.g. pollution.
Regulation can control monopolies and stop them from taxing advantage of customers and reducing welfare.
Legislation provides a means of punishing firms for their anti-competitive behaviour.
Regulation can be used to protect environment.
What are the problems with regulation?
It's hard to know which industries to regulate, and how to regulate them. This often needs a value judgement.
It can be expensive to monitor firms to enforce regulation, and there is an opportunity cost attached to this.
It can be expensive to follow regulations. Some firms may end up closing or relocating because of high costs.
What are the benefits of deregulation?
The allocation of resource will improve as the government will reduce their interference with the free market.
By reducing the bureaucracy associated with legislation, efficiency and will.
What are the problems of deregulation?
Customers are no longer protected from the anti-competitive behaviour of firms and might lose.
There are some market failures it cannot fix, such as the problem with externalities.
Some natural monopolies need regulation.
What is a regulatory capture?
It is a situation in which a firm being regulated successfully influences the regulatory agency's actions to benefit the interests of the firm, rather than the public interest.
What is a monopsony employer?
A monopsony occurs when there is a sole or dominant employer within a labour market
What are taxes? What are the difference between direct and indirect taxes?
Taxes are sums of money paid to the government.
Direct taxes are taxes on income or wealth while indirect taxes are on consumption.
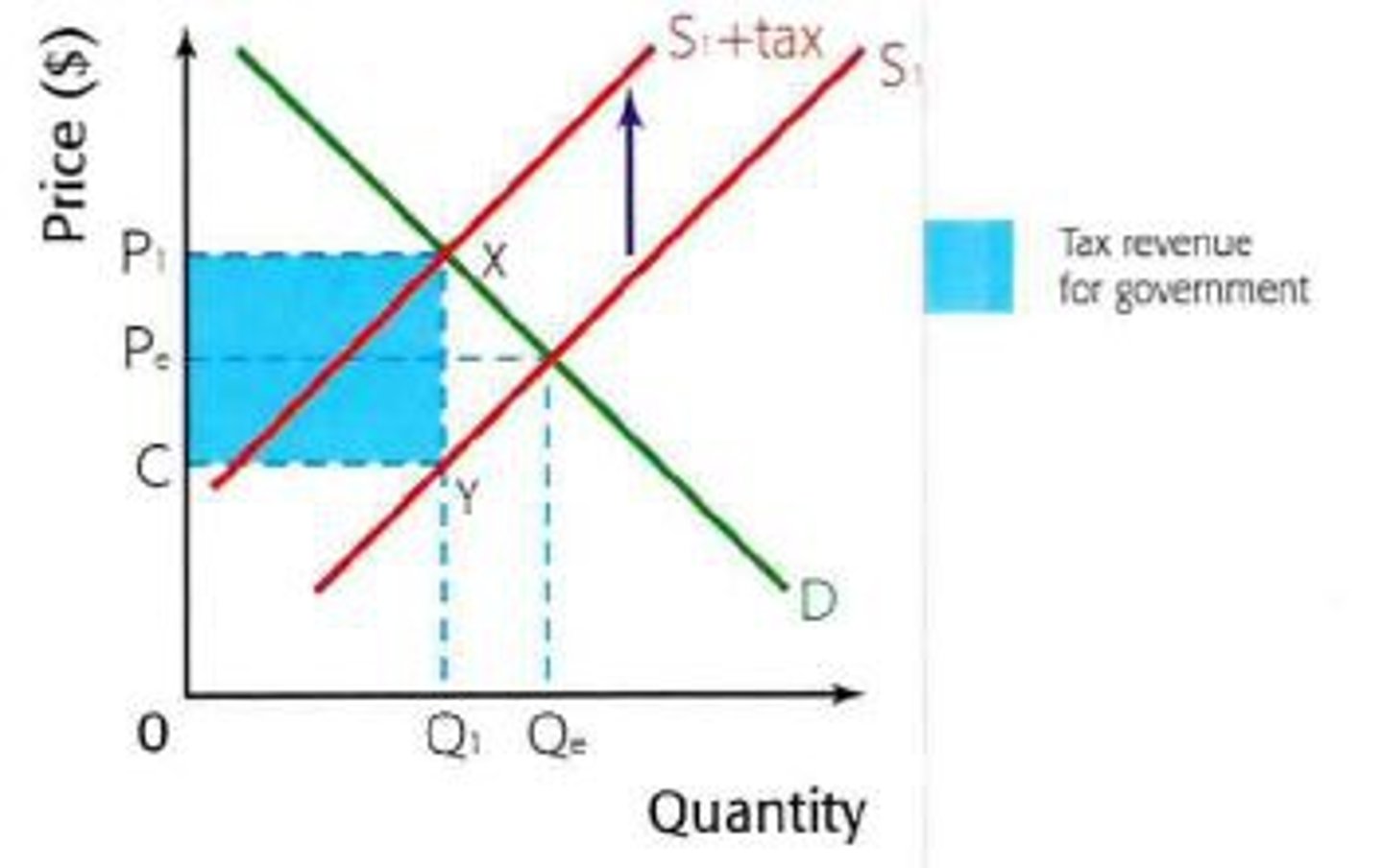
Explain what are specific taxes? How do they affect the supply? Give an example?
Specific taxes increase the costs of production by the tax amount on each unit which leads to a decrease in supply. They are fixed per unit and are the same for all units.
The vertical distances between the supply curves represent the value of the tax.
An example would be the 58p tax per litre on the consumption of petrol.
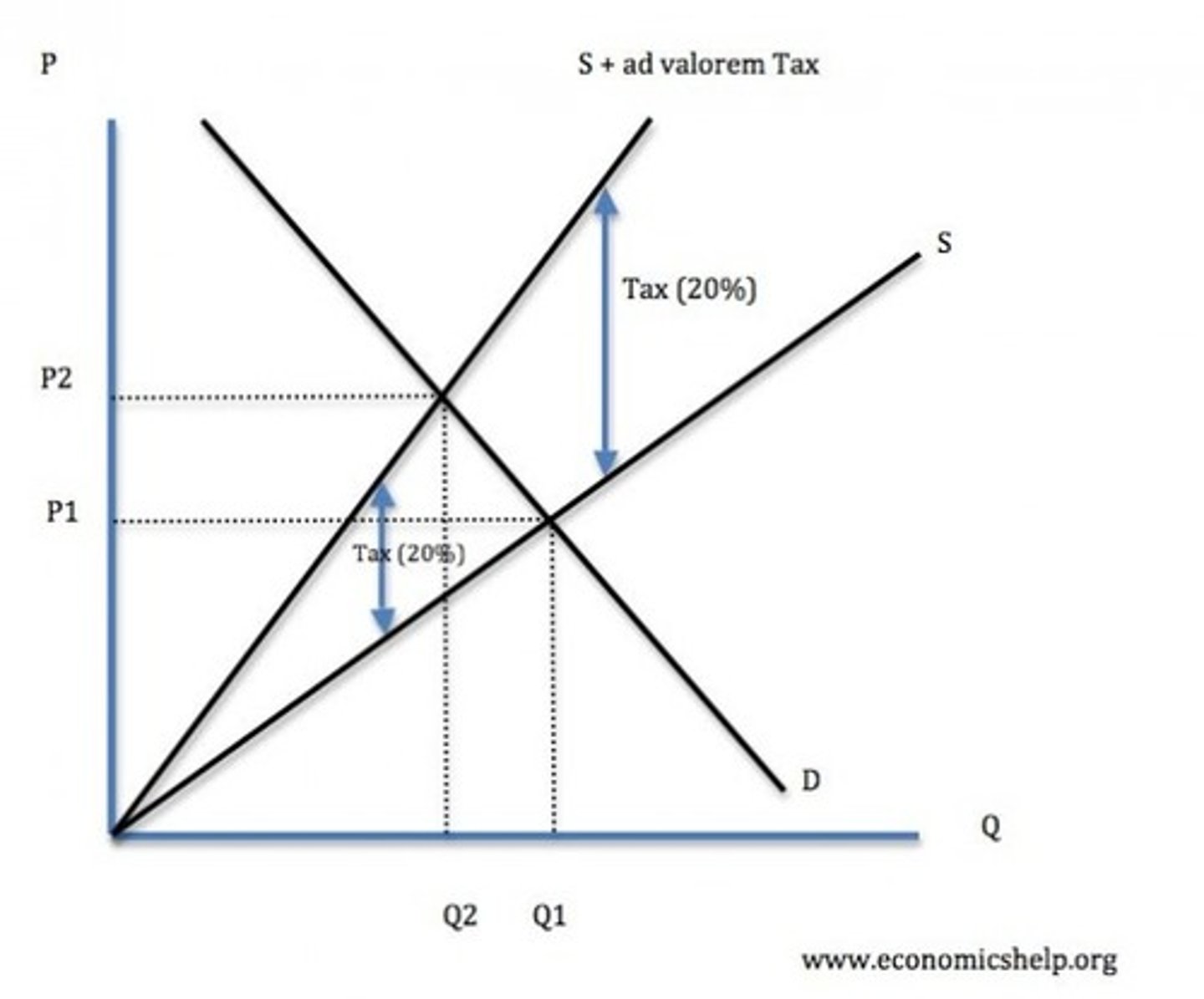
Explain what are AD Valorem taxes? How do they affect the supply? Give an example?
Ad Valorem taxes are based on the value of the good being sold. They increase the price by a fixed percentage.
The supply curve pivots to the left because the size of the tax increases further up the curve where the price is higher which means the tax is also higher.
An example of this is the 20% VAT.
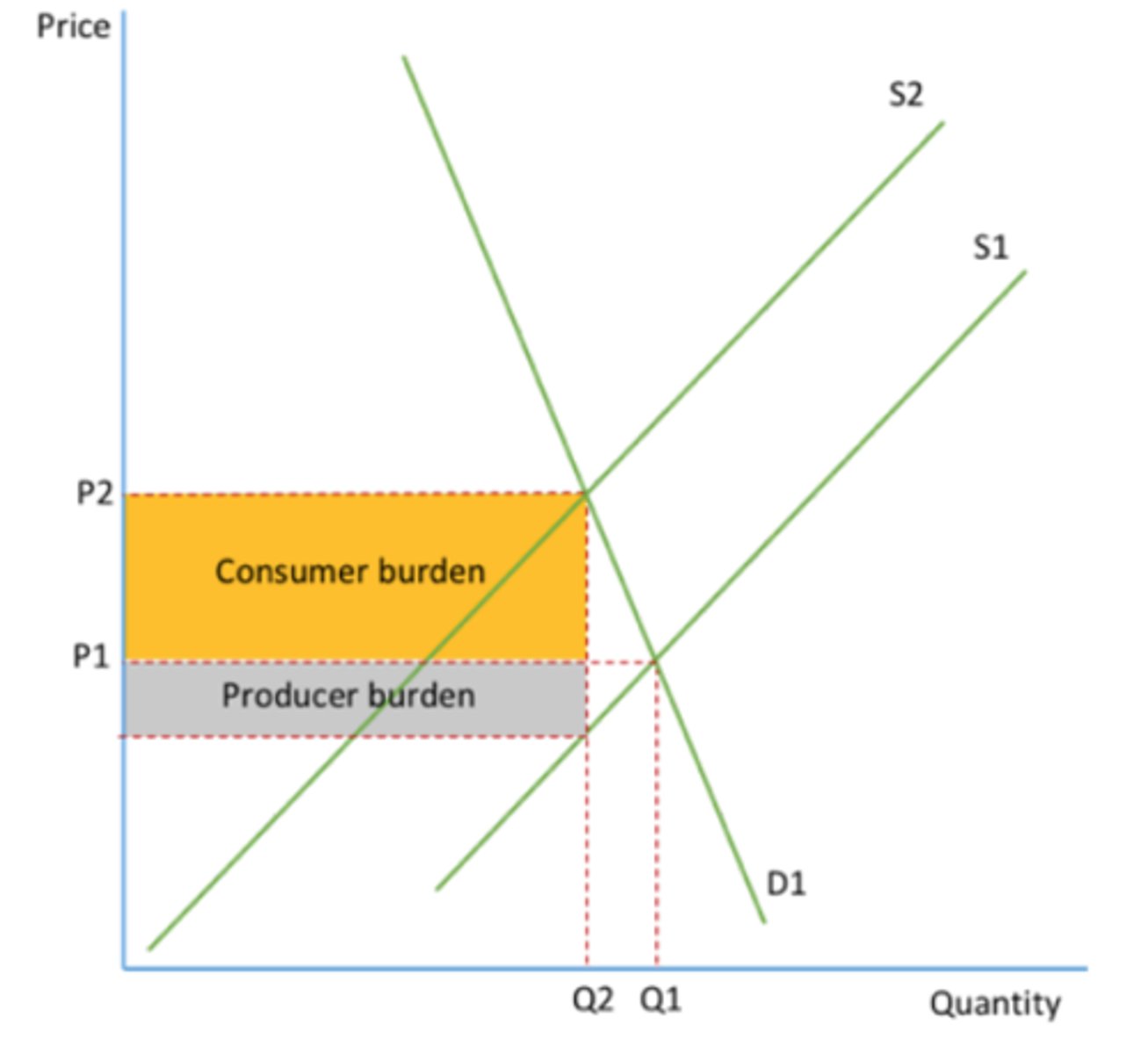
Explain what the burden of a tax is? What affects the proportion of tax passed on? Give an example of burden?
When a tax is imposed, the producer may pass on some of this cost to the consumer in the form of a higher price and absorb the remaining cost.
The proportion of the tax passed to the consumer depends on the elasticity of demand. The more inelastic the demand, the more of a tax is passed on and less absorbed.
An example is the demand for cigarettes is inelastic so producers would pass more of the tax onto consumers knowing the demand wont decrease much.
What are the advantages of taxes?
Taxes could help fund government expenditure which could include correcting the adverse effects of the goods they are taxing.
Taxing demerit goods can lead to consumers choosing less damaging substitutes.
What are the disadvantages of taxes?
Taxes can lead to an increase in inequality. For example, taxes on alcohol are regressive, as they take up a disproportionate amount of poor people's income.
If a tax is too low, then the market failure remains.
If a tax is too high, it will reduce competitiveness of firms and over-correct market failure. Governments need very good information to implement taxes properly.
What is an indirect tax?
A tax on household spending and consumption and is applied to goods and services.
How can indirect taxes help resolve market failure?
The government can implement an indirect tax on goods (can either be specific or ad valorem). This raises the cost of production shifting the supply curve towards a more socially optimum level.
How can subsidies resolve market failure?
Subsidies can correct market failure by encouraging the consumption and production of a good with positive externalities. This is represented by a shift in the right of supply, towards a more socially optimal level.
What are the advantages of subsidies?
Subsidies can reduce the cost of a product and allow firms to exploit EoS. (this will improve long-run efficiency and competitiveness )
Consumer preferences may change as a result of a subsidy.
What are the disadvantages of subsidies?
Subsidies may encourage laziness from producers because they do not have to be as efficient.
There are opportunity costs to a subsidy.
Elasticity of demand determines how effective a subsidy is.
Subsidised goods may be of a lower standard than alternatives they're trying to replace.
What is the impact of indirect taxes on the government?
Indirect taxes make revenue for the government, this can be spent on capital investments or transfer payments.
If demand was perfectly inelastic, quantity consumed will remain the same but tax revenues will increase and the burden will fall completely on consumers. If this was a market made up of poor consumers, then this may not be a good intervention for the government.
What is the impact of indirect taxes on consumers and producers?
If demand is inelastic, then consumers bear the whole burden of an indirect tax.
If demand is elastic then producers bear the whole burden of an indirect tax.
What is the impact of subsidies on consumer and producer surplus, for consumers, producers and the government?
Consumers: consumer surplus rises as the price that consumer pay has fallen and output has risen.
Producers: producer surplus rises because the price consumers pay + subsidy is higher than the price at the previous market equilibrium.
Government: Producer surplus and consumer surplus rise, so the government must pay the total amount of the subsidy. This involves the government generating money by borrowing/ using tax revenues.
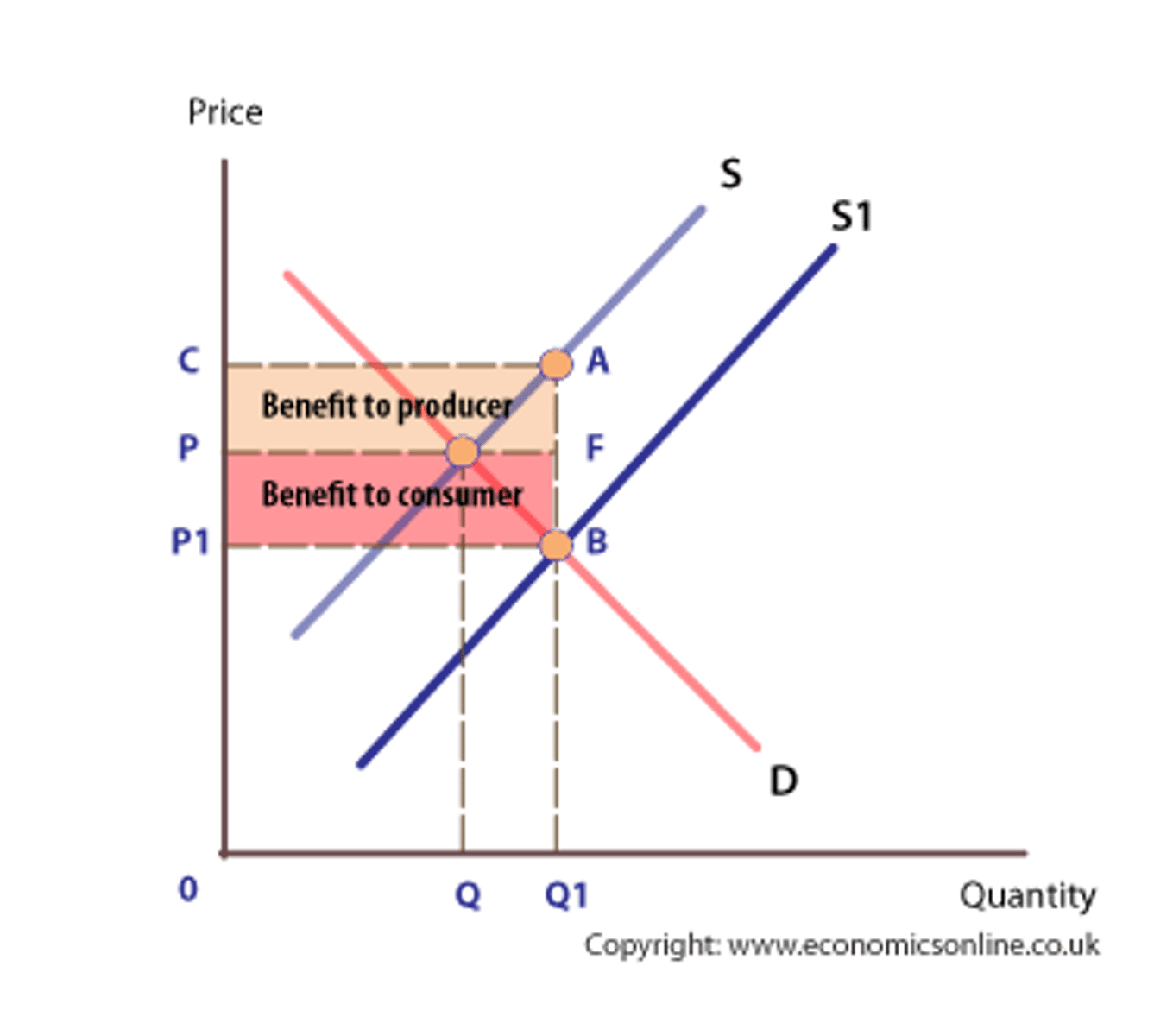
What are trade pollution permits?
Governments can set an optional limit on pollution by allocating permits to firms which can be traded by the price mechanism.
The European Union emissions trading system (ETS) gives governments permits which are then allocated to firms. The ETS annually cuts the number of permits, which incentives firms to reduce emissions because they may be forced to buy more permits for not doing so.
What are the benefits of trade pollution permits?
This system can put a cap on the level of pollution.
The lower the pollution of a firm, the more they can benefit. This encourages firms to lower their pollution levels.
Governments can make revenue
What are the disadvantages of trade pollution permits?
There is a cost to implementing the scheme.
Deciding on the level of pollution is hard.
The market for permits is subject to failure also.
What is the common agricultural policy (CAP)?
The CAP was introduced by the EU in 1962 as a means of supporting farmers in producing particular crops like wheat through subsidies.
It addressed market failures of farmed goods being an under consumed merit good.
It encouraged environmentally sustainable farming (reducing negative externalities) and encouraged farmers to take care of the country side (tragedy of the commons).
Advantages of CAP?
EU farmers have benefited from the cap as they have found it easier to earn a living by producing goods in a way that entitles them to the subsidy.
By effectively lowering the cost of production, it has led to lower prices for farmed goods.
It has also encouraged more sustainable farming practices and encouraged the protection of the countryside.
Disadvantages of CAP?
CAP is very expensive, costing around 40% of the EU's total budget, roughly £50bn in 2017.
By paying fixed amounts for certain crops, it has led to overproduction of these crops, resulting in huge stockpiles which can spoil and go to waste if not sold.
With only certainly crops subsidised, other crops have had a shortage and led to worsening inequality between those formers that do and do not produced subsidies crops.
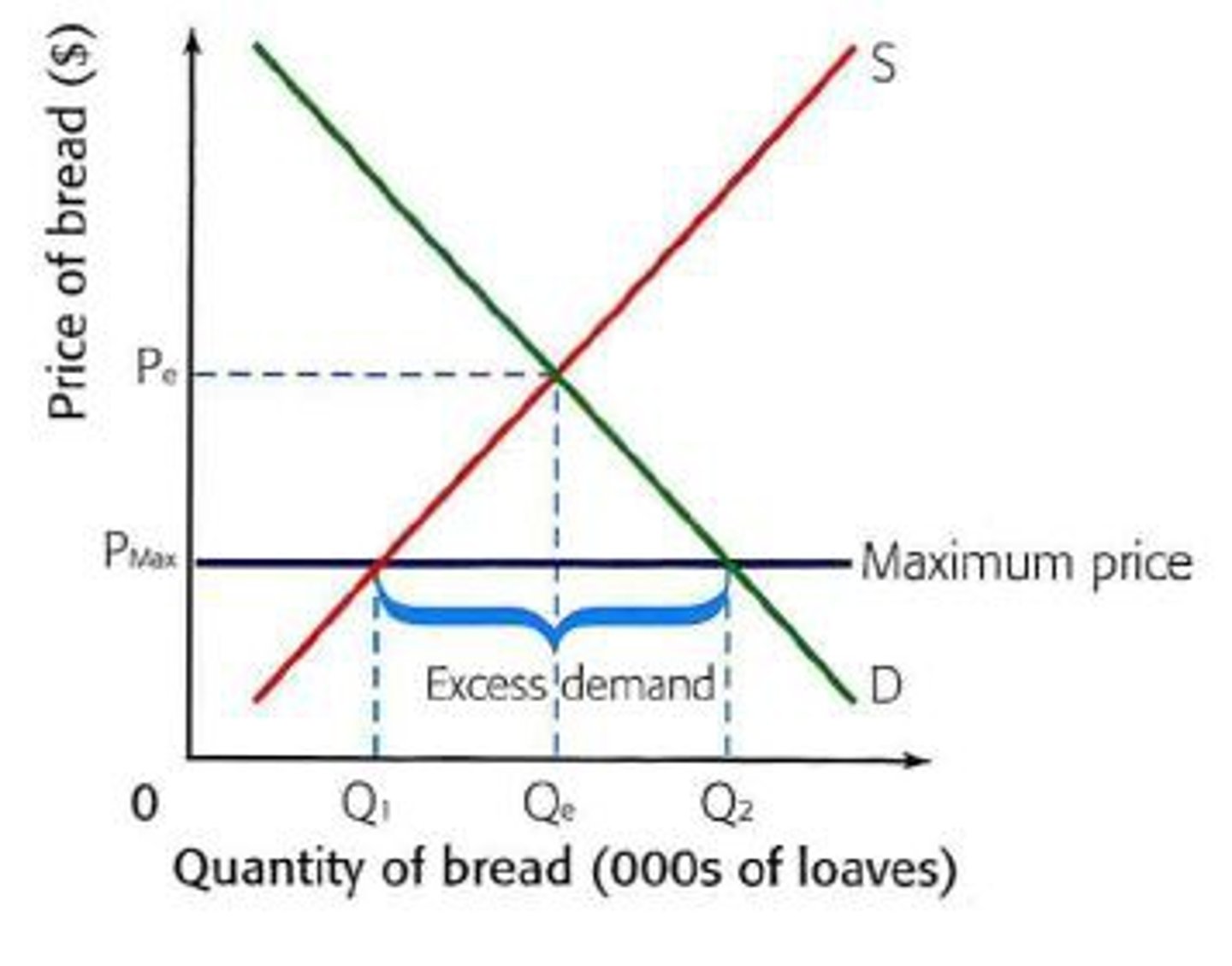
Explain maximum price. How is it influenced by equilibrium? How does this link to a black market?
A maximum price is a policy to increase consumption levels of a good.
If the new maximum price is above equilibrium, there will be no change, while if the new maximum price is below equilibrium, there will be more demand but a shortage of supply leading to an excess of demand.
So although more people can now afford the good, less people can have it as the supply is restricted. This might lead to the good being sold in a black market.
Explain minimum price. How is it influenced by equilibrium?
A minimum price can be used to correct failures that can happen under monopsony power.
If the new minimum price is below equilibrium, there will be no change. If the new minimum price is above equilibrium, there will be less demand but increased supply, leading to excess supply.
Advantages of maximum price?
It protects consumers from exploitation.
It could make sure that firms are more efficient by forcing them to pay more attention to costs.
Disadvantages of maximum price?
A maximum price could deter firms from entering the market.
It could also limit investment into the industry as the amount of profit firms can make is limited.
Firms could cut costs too aggressively in an attempt to boost profit, leading to poor quality goods.
Advantage of minimum price?
By having a minimum price, suppliers can get a reasonable price for their goods.
Disadvantages of minimum price?
Consumers will be paying more for their goods.
Resources are wasted when excess goods are destroyed.
Resources are allocated inefficiently, as they could be used elsewhere instead of producing excess supply.
Potentially high opportunity cost, as the government could spend on other schemes.
Explain the government intervention of public transport in London.
Transport for London is a government body in charge of the provision for buses and underground trains in London.
25% of its revenue comes from government subsidies.
This subsidy leads to lower prices, encouraging commuters and tourists to use the transport instead of more polluting alternatives. As a result, the effects of the negative externalities are reduced. This is an expensive intervention, costing the government £2.5bn in 2017
What is government failure?
Government failure is the unintended worsening allocation of resources as a consequence of a policy the government has implemented to correct a market failure. It produces a netwelfare loss.
How can government failure happen because of imperfect information?
In a world of perfect information, governments should be able to make the right decisions to improve allocation. Asymmetric information limits the governments ability to critically assess market failures and possible solutions. So the right decision isn't always made and government failure can arise.
How can government failure happen because of administrative costs?
Resources are needed to implement government intervention. If the cost is too high, the intervention may not be worthwhile.
How can government failure happen because of bureaucracy?
The private sector has the incentive to maximise profits, but individuals working for governments rarely get the benefits.
Governments are also very large and may suffer from material diseconomies of scale.
Why is conflicting policy objectives a consequence of government failure?
In trying to satisfy one objective, others may be compromised, e.g. by causing firms to cut down emissions, their growth may be limited which is bad for the economy.
Politicians may also be influenced by what's politically acceptable or unacceptable, e.g. government wont ban car use to cut down gas emissions because people rely on cars for convenience.
What is a market distortion?
A market distortion occurs when market forces of supply and demand are disrupted, preventing the market from allocating resources efficiently. This leads to outcomes where prices, quantities, or both deviate from what would occur in a perfectly competitive market.
How is market distortions a consequence for government failure?
Market distortions can be caused by a government intervention, for example:
Income taxes give people less incentive to work hard, which reduces efficiency.
Subsidies may allow firms to make profit without being efficient, this is distortionary.
Minimum and maximum price controls can distort price signals