5 - SI Joint Examination and Treatment
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
anterior aspect of the SIJ
two innominants with the pubic symphysis, forming a ring
posterior aspect of the SIJ
wedge shaped sacrum
Auricular (ear shaped) surface forms
rough, irregular joint to increase fibrous connection and stability
Interarticular fibrous connections form with...
age (more stiff)
Movement of SIJ
deformations and slight gliding motions
SIJ - degrees of rotation
0.2 - 2 degrees
SIJ - amount of translation available
1 - 2mm
nutation is associated with
increased lumbar lordosis and extension
counternutation is associated with
decreased lumbar lordosis and flexion
Nutation - sacral tilt
anterior (superior aspect nods ant and inferior)
Nutation - iliac tilt
posterior
what posture increases nutation?
standing
Counternutation - sacral tilt
posterior and superior
Counternutation - iliac tilt
anterior
what position favors counternutation?
supine --> risk
Closed packed position of SIJ
Nutation
Loose packed position of SIJ
Counternutation
anterior ligamentous reinforcements of SIJ
comparatively weak
- resists anterior distraction and nutation
Interosseous ligament
strong, short, deep to dorsal ligament
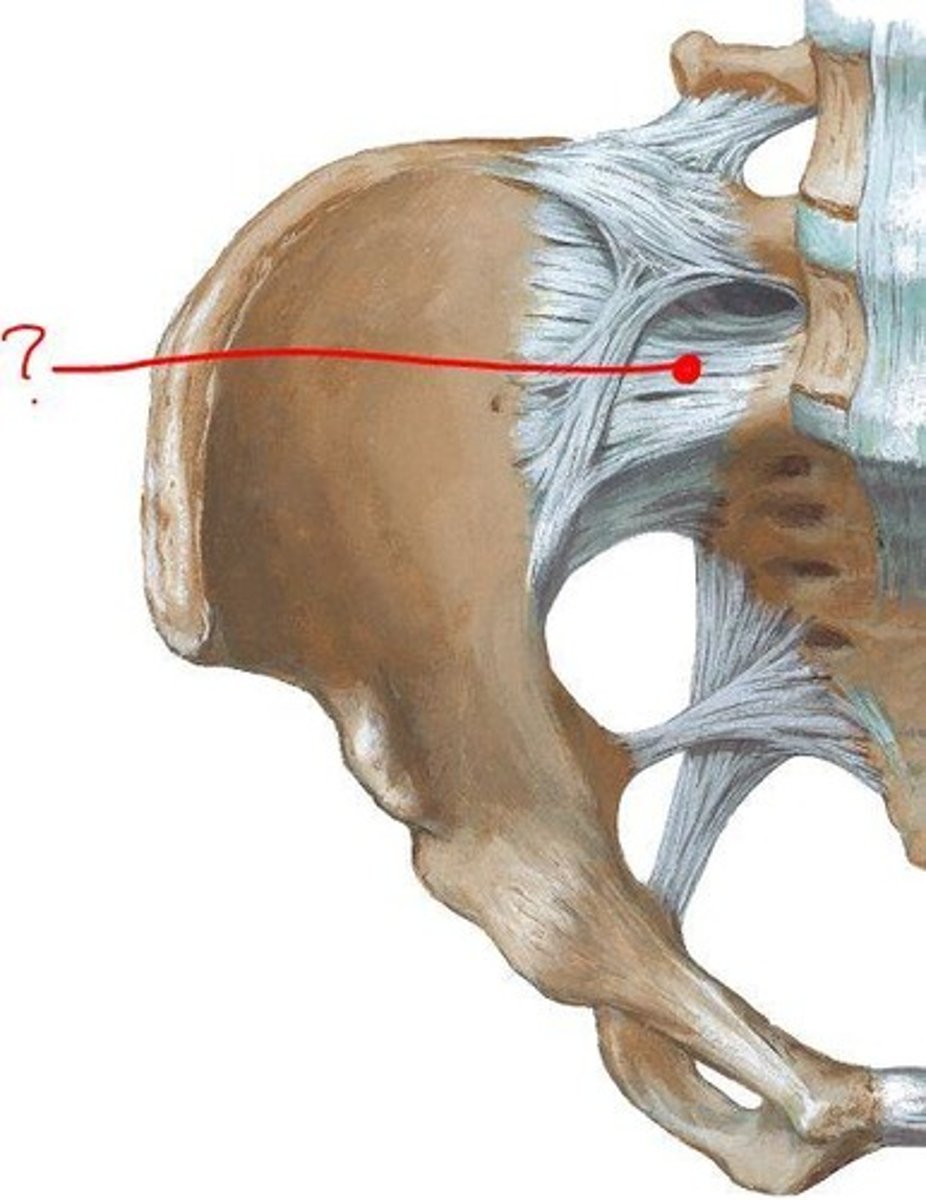
posterior or Dorsal SIJ ligaments
- strong w/ multidirectional fibers
- palpable caudal to PSIS
Posterior/dorsal ligaments resists
counternutation
the posterior/dorsal ligaments attach to what 3 things? what is it continuous with?
- attach to: erector spinae, multifidi, thoracodorsal fascia
- inferiorly cont. w sacrotuberous ligament
extra-articular ligamentous support (2)
- sacrotuberous
- sacrospinous
Sacrotuberous ligament bony attachments
- lateral sacrum
- PSIS
- ischial tuberosity
sacrotuberous ligament - muscle attachments
- gluteus maximus
- piriformis
- continuous with biceps femoris
sacrotuberous resists what movement?
nutation and cranial (superior) migration
sacrospinous ligament attachments
lateral sacrum to spine of ischium
sacrospinous resists what movement?
nutation
Pubic symphysis
far from AOR at SIJ
Pubic symphysis is supported by
anterior, inferior, posterior and superior ligaments
pubic symphysis - type of pain
common source of groin pain
what muscles attach to both innominates and sacrum? (3)
- piriformis
- gluteus maximus
- iliacus
other muscles of interest for SIJ
- erector spinae
- multifidi
- Bicep femoris LH
- Transverse abd
- internal/external obliques
Glute max arises from (5)
- innominate
- sacrum and coccyx
- aponeurosis of erector spinae
- superficial thoracodorsal fascia
- fascia of glut. Med
Glute max inserts on
gluteal tuberosity
Glute max ipsilaterally blends w/
multifidus via fascia
Glute max contralaterally blends w/
latissimus dorsi via fascia and sacrotuberous ligament
Form closure
stability of jt due solely to anatomy
- shape and congruency of joint surfaces
- integrity of ligaments
Force closure
Stability of joint due to dynamic interacting forces of gravity, ligamentous tension, fascial and muscle forces.
~ what we can alter as PTs
Active muscle force ~ force closure
- Erector spinae - pushes up posterior on sacrum
- Rectus abdominus pulls innominate up
- Active force counteracts and creates stability (self locking mechanism)
Train pts to facilitate muscles ~
- Abdominus, hamstrings, erector spinae - to get stability before doing torsional movements
- Exercises with hip ext while firing opposite erector spinae bc they have cross-fascial connection that stabilizes joints
All components create self locking mechanism in
force closure
What is key of in force closure in SIJ?
nutation of sacrum
- winds up ligaments, utilizes gravity favorably
muscles that assist in force closure (5)
- erector spinae
- rectus abdominus
- gluteus maximus
- latissimus dorsi
- bicep femoris
What reduces the self locking mechanism of SIJ?
counternutation
What position reduces the self locking mechanism of SIJ? (hint: counternutation) (3)
- end range forward bending
- sacral sitting
- long sitting
What can also result in counter nutation and reduce force closure, predisposing SI joint to injury?
Weakness or imbalance in lumbar/hip/pelvis region
In the absence of very clear diagnostic criteria: if lumbar or hip S/S are present
treat those first
When do you focus on treating SIJ?
after lumbar or hip S/S are resolved, if symptoms still present
MOJ for SIJ
- unilateral trauma (stepping down hard on one foor or falling on one hip/isch tub)
torsion results via
femur through acetabulum or isch tub
--> foundation of leg length discrepancy association w SIJ Patho
Typical SI joint Pain
Unilateral pain with no referral below knee
- sharp pain or catching during mvmt
- esp transitional mvmts (STS, rolling)
groin pain is often associated with...
pubic symphysis dysfunction
- may be related to SIJ
Typical aggravating factors of SIJ pain (6)
- Reciprocally going down stairs
- Getting in/out of cars
- Holding child on one hip
- Sitting with legs crossed (post tilt)
- Walking with long stride length
- Traditional positioning (missionary position)
- Anything that creates torsion
Chronic SIJ mechanisms of injury may be associated with
-Ligamentous laxity
-Asymmetrical Postures
Ligamentous laxity may be due to
Recent pregnancy/meds/cyclical symptoms
Asymmetrical Postures can be from
• Work postures
• Child care
Observations of SIJ dysfunction
Visual or palpable asymmetry
Functional Tests - palpate during these:
-Unilateral stance, IR/ER (like thessaly)
-Gillets (march)
-Forward Flexion
APR in sitting
pain free (if pelvis is stabilized and WB is symmetrical)
Palpation unique to SIJ
greater chance that pubic symphysis may be involved, far from AOR
Special tests for SIJ (6)
• Ganslens
• Gillet (March)
• Forward flexion
• Primary stress tests (anterior and posterior gapping)
• Fabers/Patrick
• Joint play (flutter)
Conditioning of SIJ, it is best to move from...
- bilateral to unilatereal
- symmetry to asymmetry
- opposire some lumbar progressions
- seated before standing
- opposite of exercise progression from disk
~ Strengthen muscles that control ant/post tilt of pelvis
~ Extensors, ab/adductors
Length and strength
Consider position in frontal + sagittal plane
SIJ treatment aims to reduce _____________ and increase ___________.
torsional forces initially; stability
- SIJ belt
what should be emphasized in treatment?
conditioning of muscles that maintain force closure AND core stability
- diagonal relationship of lats to glutes --> tensions TLF over SIJ (fascial connections)
what position should be encouraged for stability?
nutation
what shoudl be corrected during treatment?
correct length/strength deficiencies that undermine stability via imbalace or asymmetry