Macroeconomics
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
Aggregate Demand
Total planned expenditure on goods and services in an economy
Components of AD
C
I
G
X - M
GDP
Total monetary value of all finished goods and services within a country’s borders
Unemployment
A proportion of the population who are out of work, but is willing, able and searching for work.
Injections
Additions to the circular flow of income that increases total spending
Economic Growth
An increase in the monetary value of goods and services produced as measured by the annual change % in real GDP.
Macroeconomic Objectives
Economic Growth (a positive GDP)
Low unemployment
Low and stable inflation
Have a balanced current and financial account
Leakage
A factor that removes money from the circular flow of income
Different leakages
T
S
M
Circular Flow of Income
How money is passed through the economy
Households
Factors of Productions → Firms
Consumer Expenditure → Firms
Firms
Goods and Services → Households
Factor Incomes → Households
Aggregate Demand shift to the right
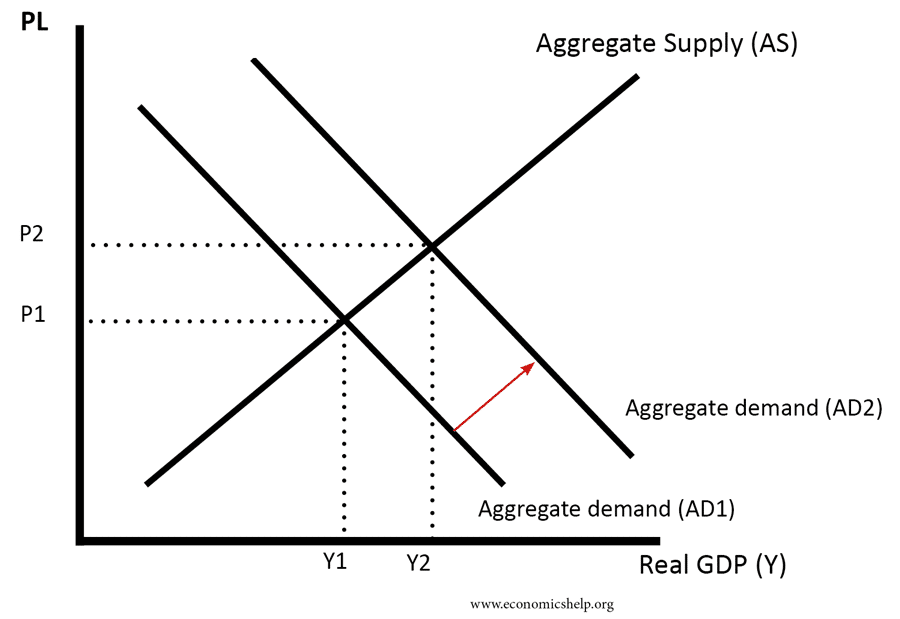
Wealth effect
Purchasing power of income increases therefore consumption increases as price level has fallen and therefore making goods and services more affordable due to increases in Real Income.
Trade effect
The decreasing of the price level makes exports more competitive and imports less competitive
Interest effect
Price level decreasing equates to a low inflation hence interest rates are kept low by central banks to meet inflation targets due to lower inflationary pressure which stimulate higher consumption and higher investment.
Interest Rates & Investment
Lower interest rates allow firms to invest more as cost of borrowing is lower.
What is investment
A firms spending on capital
Interest Rates & Exchange Rate
Low interest rates reduces value of exchange rate which increases net export performance.
Lower Price Level
Reduces inflationary pressure
Increasing MPC causes
Lower Interest Rates as it encourages borrowing as consumers are more likely to take out loans to buy big purchases
Increased animal spirits which are increased consumer confidence as consumers are more optimistic about the economy.
Multiplier effect
An initial increase in a component of aggregate demand leads to a bigger increase in real GDP
Accelerator effect
An increase in real GDP leads to an increase in investment
MPC
The willingness to spend any additional income a household earns.
Increased by animal spirits.
Lower interest rates.
Determinants of consumption
Real disposable income
Interest rates
Consumer confidence (animal spirits)
Asset prices (house prices)
Disposable income causes
Income taxes
Current Spending
Maintenance of public sector services
Payment of public sector wages
Capital Spending
Infrastructure spending
Welfare Spending
Benefits and pensions
Budget Deficit
G > T in a fiscal year
Budget surplus
T > G in a fiscal year
National Debt
Total stock of debts over time
SRAS Shift Causes
Costs of production
Costs of Production
Wages
Raw resources
Business Taxes (VAT)
Oil prices
LRAS Shift Causes
Due to the quality of factors of production
Quality & Quantity of FOP
R & D, Capital Investment
Infrastructure
Monetary Policy
Actions taken by the central bank to influence the circulation of money such as lower interest rates and purchasing of government bonds.
Fiscal Policy
Actions taken by the government to influence the economy such as government spending and taxation.
Expansionary Monetary Policy
Actions taken by the central bank to stimulate economic growth such as lower interest rates by purchasing government bonds to increase the money supply and encourage lending.
Contractionary Monetary Policy
Actions taken by the central bank to slow economic growth and control inflation, such as increasing interest rates by selling government bonds and reducing the money supply to discourage borrowing.
Weaker Pound
More exports
Less imports
Stronger Pound
More imports
Less exports
Economic Development
An improvement in living standards, higher incomes, education, reduced poverty
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
Investment by foreign firms into productive assets such as infrastructure or factories
Market Failure
When markets fail to allocate resources efficiently leading to welfare loss.
How governments can fix unemployment
Re-education
Apprenticeships
Labour market information
Geographical mobility
Capital Account
Records a country’s transactions with the rest of the world
Financial Account
Records the financial assets of all residents and non-residents.
Current Account deficit
Spending more on imports and exports.
Direct Taxation
Taxies levied directly on income or wealth, such as income tax and corporation tax.
Indirect Taxation
Taxied levied on spending such as VAT.
Regressive as lower income households spend a bigger proportion of their income on taxed goods and services.
Increases income inequality which reduces living standards for lower income households.
Increases disposal income especially for higher earners.
Leads to cost-push inflation.
Regressive Tax
A tax that takes a higher proportion of income from low-income earners and high income earners.
Progressive Tax
A tax that takes a higher proportion of income from high-earners than low-earners.
Disposal Income
Income left after direct taxes have been paid, such as taxes and bills.
Inflation
A sustained increase in the general price level.