Introductory physics: Chapter 2- Newton's first law of Motion- Inertia
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 6:41 PM on 9/1/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
1
New cards
What are two things Galileo discovered?
1) Objects of different weight fall to the ground at the same rate in the absence of air resistance(Free fall)
2) A moving object needs no force to keep it moving in the absence of friction(Inertia)
2) A moving object needs no force to keep it moving in the absence of friction(Inertia)
2
New cards
What is a force?
* push or pull
3
New cards
What is inertia?
* property of matter to resist changes in motion
* depends on mass of object
* depends on mass of object
4
New cards
What was Galileo’s main discovery on his incline experiment?
* He found that if a ball comes to rest, it is due to friction
* Ball moves forever when no force acts on it
* Ball moves forever when no force acts on it
5
New cards
What are the two conditions of Newton’s first law of motion state?
1) An object at rest will stay at rest unless acted on by a force
2) An object in motion will stay in motion at constant speed in a straight line unless acted on by a force
2) An object in motion will stay in motion at constant speed in a straight line unless acted on by a force
6
New cards
What is a vector quantity?
* quantity that has both magnitude and direction
* represented by arrows drawn to scale→ vector
* Ex: force, velocity, acceleration
* represented by arrows drawn to scale→ vector
* Ex: force, velocity, acceleration
7
New cards
What is “T” or tension force?
* force that’s involved with ropes
8
New cards
What is the net force?
* combination of all forces that change an object’s state of motion
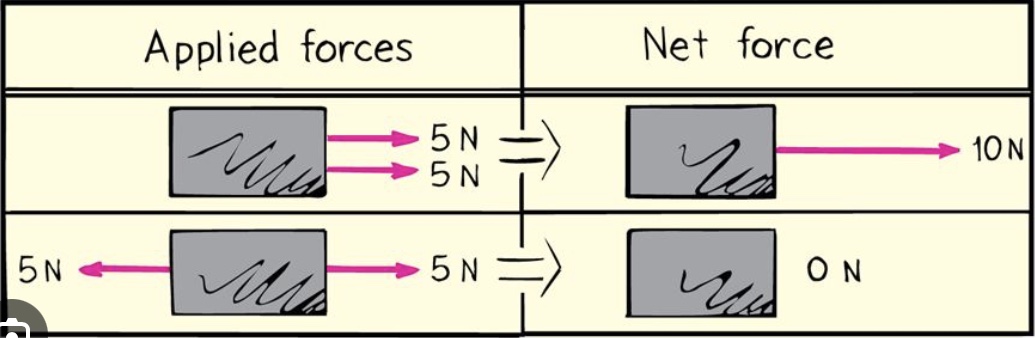
9
New cards
What is the equilibrium rule?
* the vector sum of forces acting on a non-accelerating object equals zero
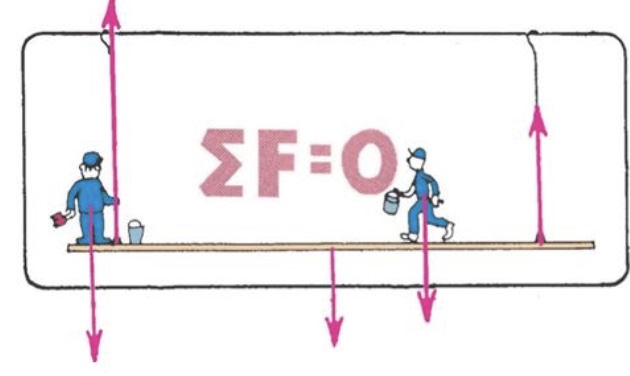
10
New cards
What is equilibrium?
* no change in speed with net force acting = 0
11
New cards
What are the two types of equilibrium?
* static equilibrium- object at rest stays at rest
* dynamic equilibrium- object in motion stays in motion at constant speed
* dynamic equilibrium- object in motion stays in motion at constant speed