Vet A&P Tissues + Body Cavities
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
132 Terms
4 types of tissue
epithelial
connective
muscle
nervous
__ tissue lines body cavities and can be absorbent or secretory
epithelial
__ tissue connect/support body parts, carries nutrients/waste
connective
__ tissue provides movement
muscle (striated, smooth, cardiac)
__ tissue conducts nerve impulses
nervous
Each tissue consists of three main components:
Cells - one type forms the majority
Intercellular products - produced by cells
Fluid - interstitial fluid flows through specialized channels
_____ is epithelium inside the heart, blood vessels, and lymph vessels
endothelium
Simple epithelium is ____ cell thick
one
Stratified or compound epithelium is ____ cell thick
more than one
Squamous cells are ___ in shape
flattened
Cuboidal cells are ___ in shape
square or cube
Columnar cells are __ in shape
column (height > width)
The least specialized type of epithelium is ___
simple cuboidal
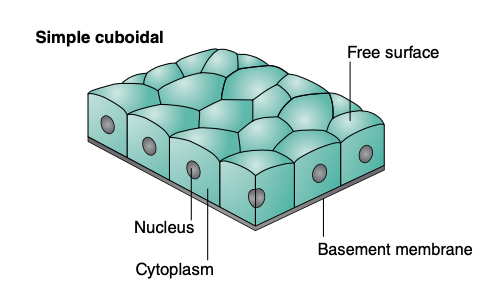
Simple cuboidal epithelium is ___ thick
Found in ____
Absorptive or secretory?
one cell thick
glands and ducts
both
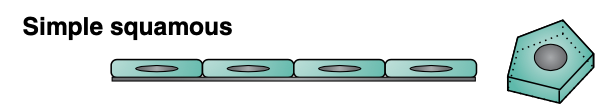
Simple squamous epithelium is ____ thick and must be _____
Found lining the ____
one cell thick (thin and delicate)
easily permeable to oxygen
lining blood vessels and alveoli
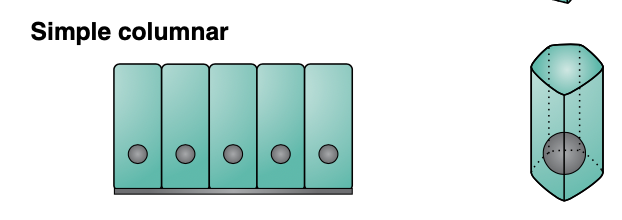
Simple columnar epithelium is ____ thick and the cells are ___
Absorptive or secretary?
one cell thick
cells are tall and narrow
absorptive (small + large intestine)
secretory (digestive glands)
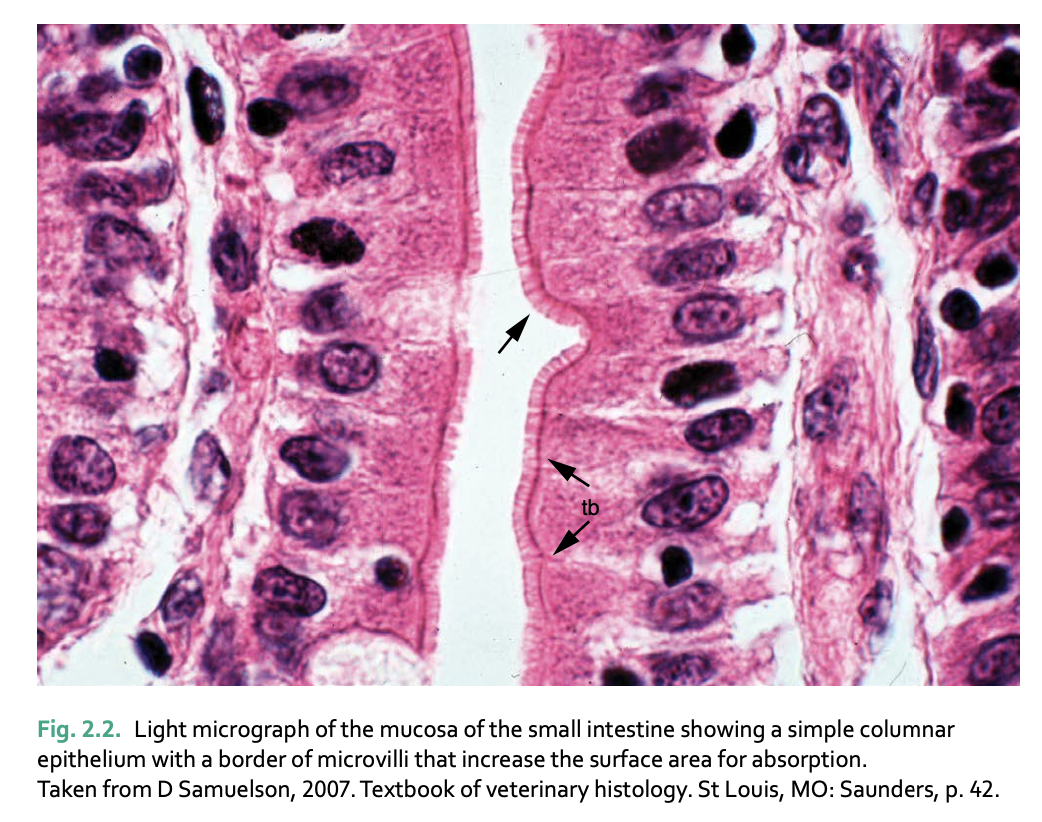
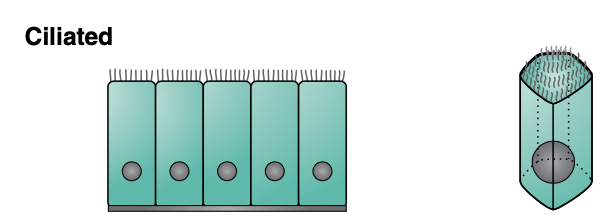
Ciliated epithelium functions to _____
Found in _____
waft particles along the epithelial surface
upper respiratory tract (trap inhaled solid particles)
uterine tubes (move fertilized egg along tract)
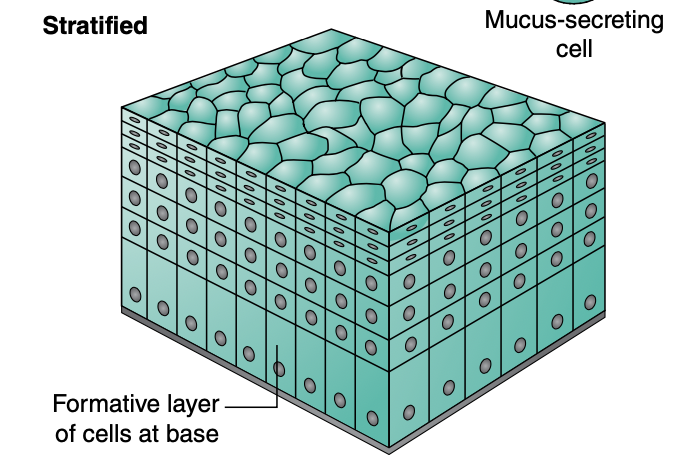
Stratified epithelium is ____ and found in ___
multilayered (thicker and tougher)
in areas subject to shearing forces (epidermis)
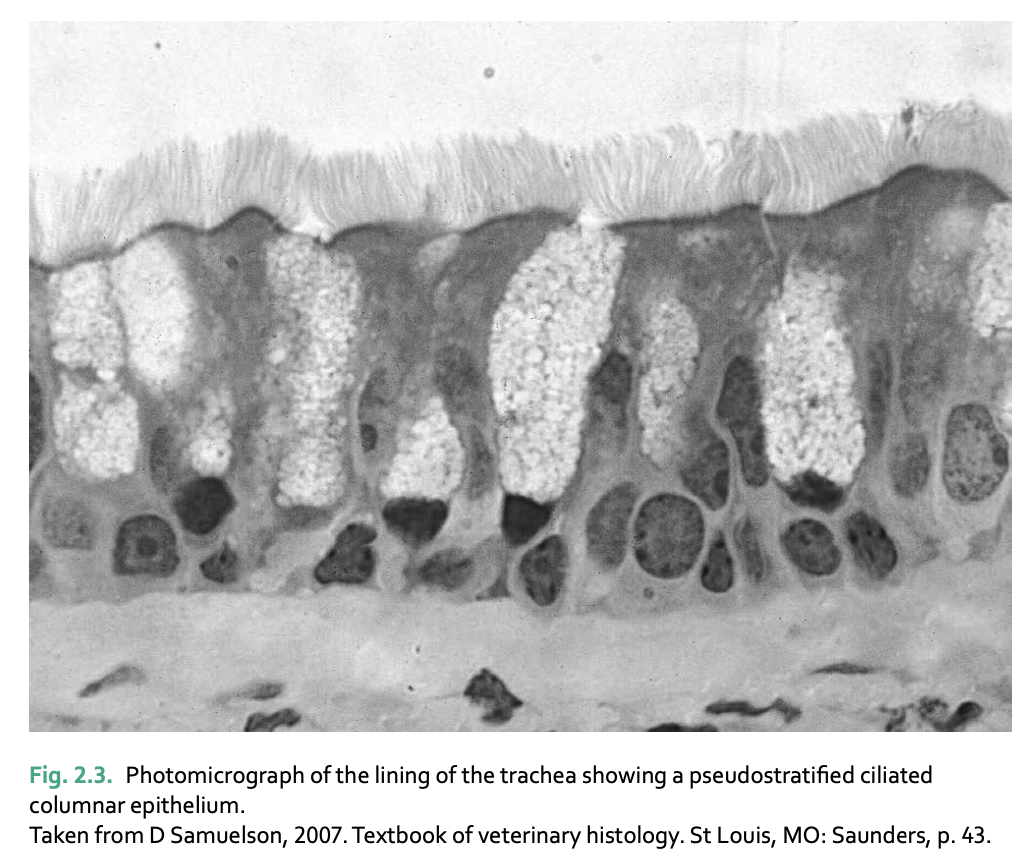
Pseudostratified epithelium is ___ thick, but appears ____ because ____
ONLY ONE LAYER, but appears mutilayered bc of irregular nuclei (found in trachea)
squamous cell carcinoma originates from ____
adenoma develops in ______ tissue
transitional cell carcinoma develops in _______
squamous cells in the skin
glandular
bladder wall
______ is most at risk for canine parvovirus (CPV)
unvaccinated puppies between 6 weeks to 6 months
canine parvovirus (CPV) targets _____ cells
highly infectious virus targets rapidly dividing cells (intestinal epithelium) affecting absorption of nutrients and increasing fluid loss
symptoms of canine parvovirus
hemorrhagic (bloody) diarrhea and vomiting
puppy rapidly becomes weak and dehydrated
T/F there is no drug that can cure canine parvovirus (CPV)
True
treatment plan for canine parvovirus (CPV)
supportive care and management of symptoms (IV fluid, nutrient replacement, drugs to reduce vomiting, antibiotics if there is secondary bacterial infection due to weak immune system)
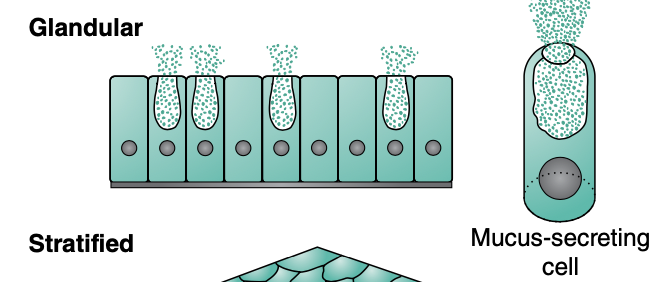
Glandular tissue
modification of epithelial tissue
secretory membrane
unicellular or multicellular
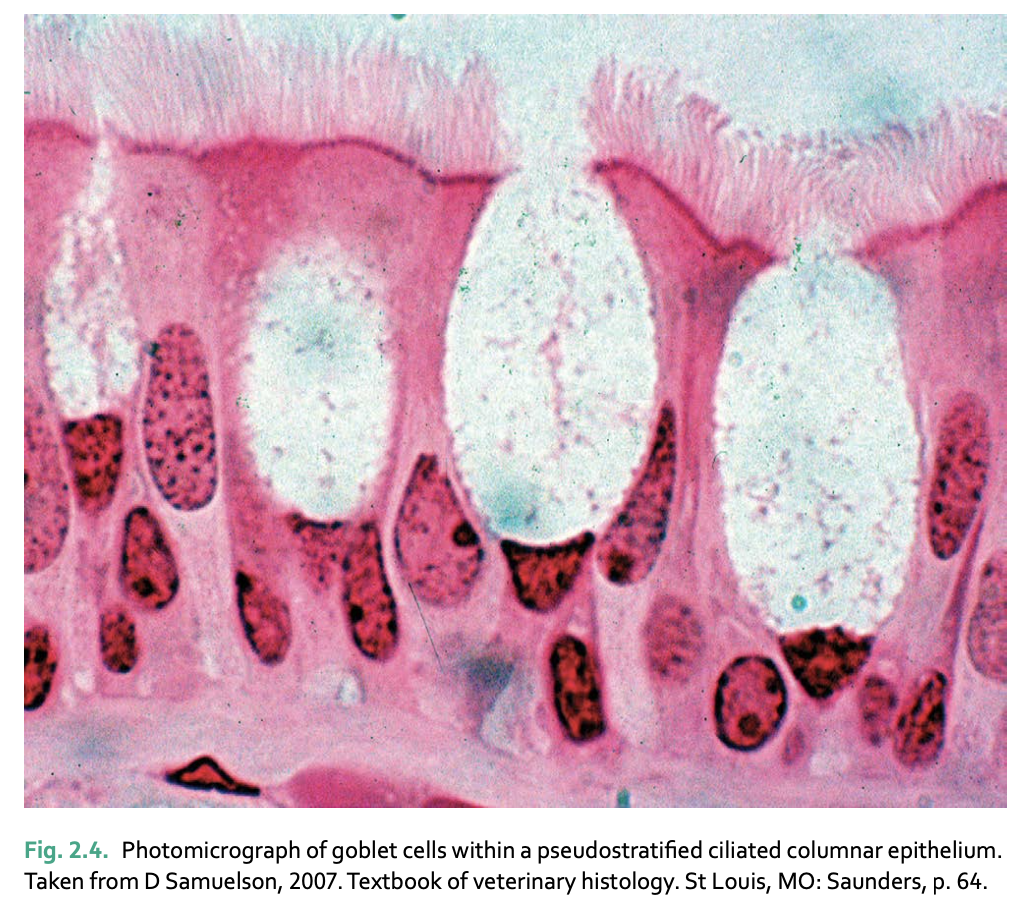
Unicellular glands
individual secretory cells interspersed throughout tissue
goblet cell (secrets mucus directly on membrane)
Epithelium is aka __ membrane that functions to __ and is found in __
mucous; traps particles, extra protection, lubricates
found covering oral cavity, vagina, trachea
Multicellular gland
many secretory cells folded to form complex gland
exocrine glands
system of ducts through which secretory products are transported directly to site
endocrine glands
ductless glands; secretions (hormones) carried by blood to target organ
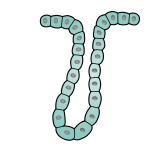
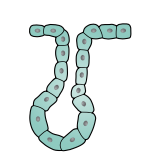
Simple tubular gland
Stomach, intestine
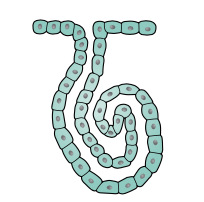
Simple coiled tubular
Sweat glands
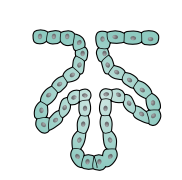
Simple branched tubular
Stomach, mouth, tongue, oesophagus
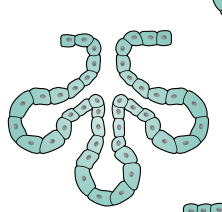
Simple alveolar
Sebaceous glands
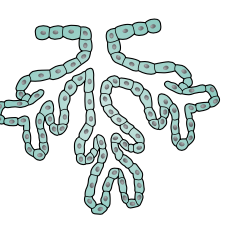
Branched alveolar (acinar)
Sebaceous glands
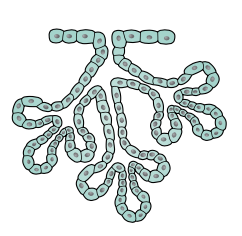
Compound tubular
Bulbourethral glands, mammary glands, kidney tubules, testes, mucous glands of the mouth
Compound alveolar gland
mammary glands
Compound tubuloalveolar
salivary glands, pancreas, respiratory passages
Connective tissue consists of cells embedded in an _______
extracellular matrix or ground substance (properties depend of type of connective tissue)
7 types of connective tissue in order of increasing density
blood
haemopoietic tissue
areolar tissue or loose connective tissue
adipose or fatty tissue
fibrous connective tissue or dense connective tissue
cartilage
bone
Blood functions to ____ and cells are in a ground substance called _____
carry nutrients and oxygen to cells, carry waste to organs of excretion
plasma
haemopoietic tissue
jelly-like tissue forms in bone marrow of long bones
responsible for formation of blood cells
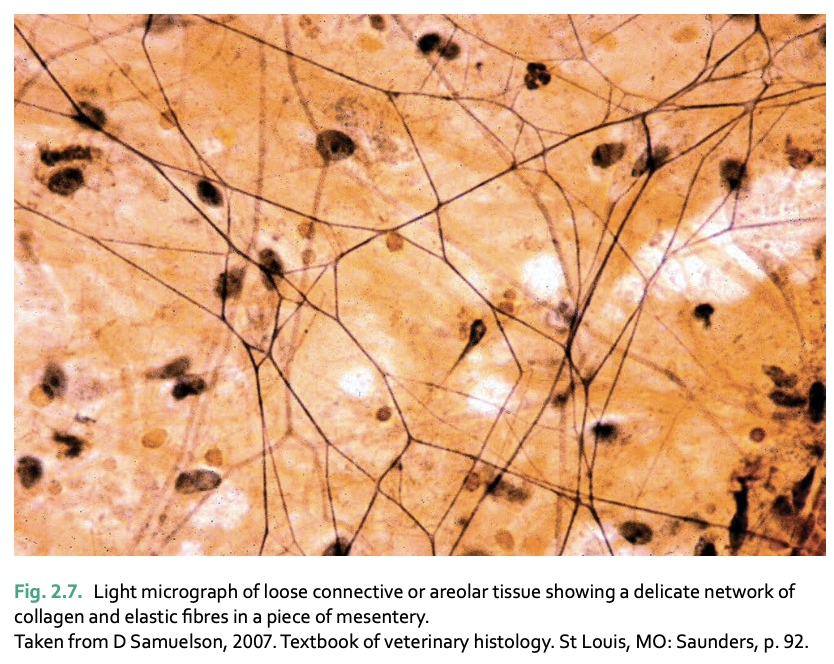
areolar tissue is found __
areolar (spaces)
beneath skin, around vessels/nerves, between organs and muscle bundles
the most widely distributed connective tissue is __
areolar tissue
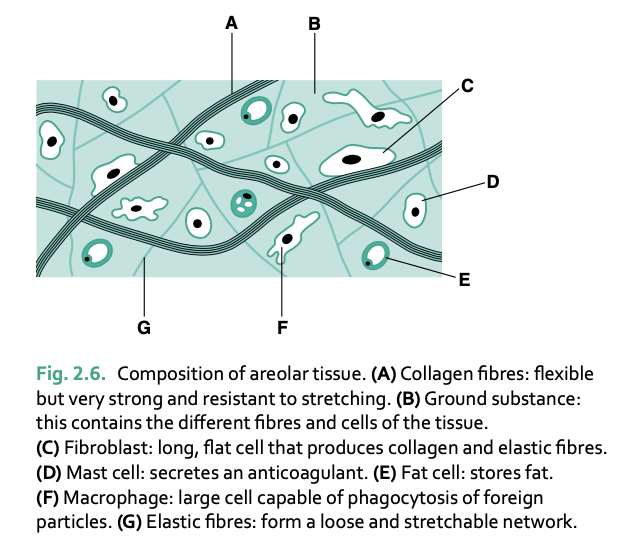
the ground substance of areolar tissue contains ___ (4 things)
collagen fibers - high tensile strength secreted by fibroblasts
elastic fibers - enable tissue to stretch and return to former shape
fat cells - varying quantities depending on location/obesity
macrophages - phagocytosis
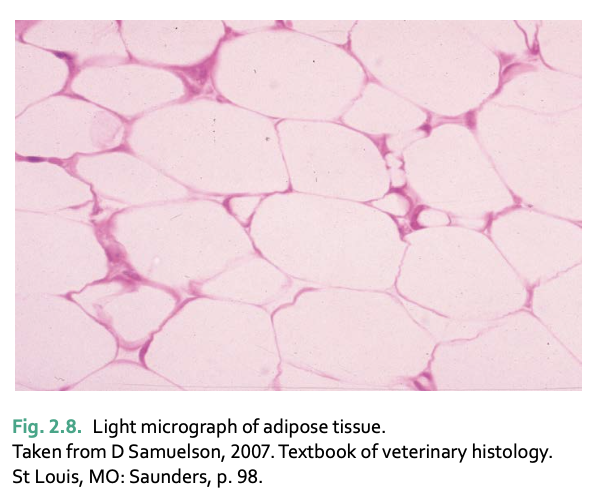
adipose tissue is made of __ and is found __
matrix of fat filled cells closely packed together
around kidney (protective)
__ tissue acts as an energy reserve, insulates, and reduces heat loss
adipose
lipoma
common benign tumor that develops in adipose tissue
frequently in older dogs
can become very large if not removed
may cause discomfort depending on position
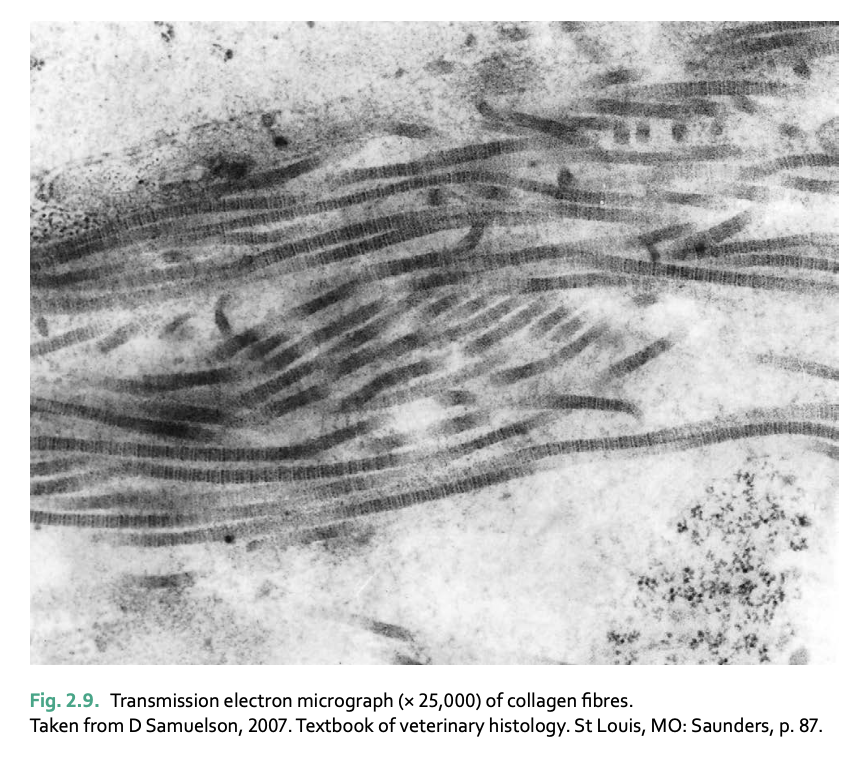
dense connective tissue is composed of __
densely packed collagen fibre bundles with few fibroblasts or other cells
arrangements of dense connective tissue can be ____
Parallel - regular fibrous connective tissue
Irregularly interwoven fibers - forms sheets, fascia, aponeuroses
parallel arrangement of dense connective tissue is found in __
tendons and ligaments
irregularly interwoven fibers arrangement of dense connective tissue is found in __
dermis of skin, capsules of joints, testes, lymph nodes
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) causes _____
defective collagen synthesis
cutaneous asthenia (weakness)
rare inherited condition that affects connective tissue
skin is excessively stretchy, loose, fragile, and tears easily
can affect joint stability
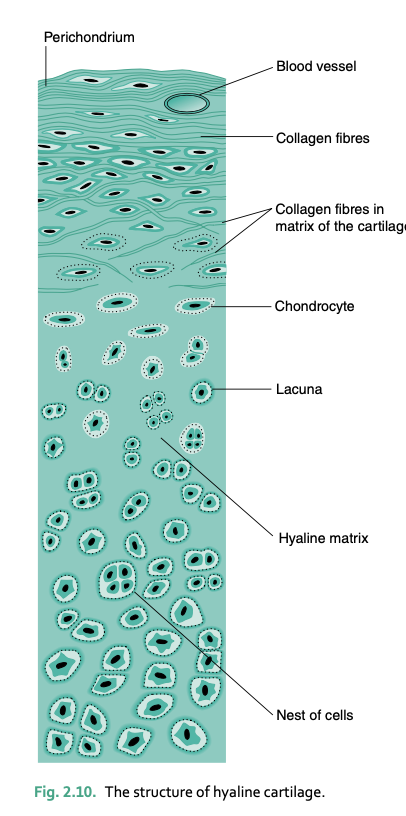
cartilage
rigid but flexible, resilient, able to bear weight
cartilage is composed of __
chondrocytes and fibers with gel-like ground substance
cartilage has no _____ and nutrition us provided by ___
blood supply, fibrous sheath (perichondrium)
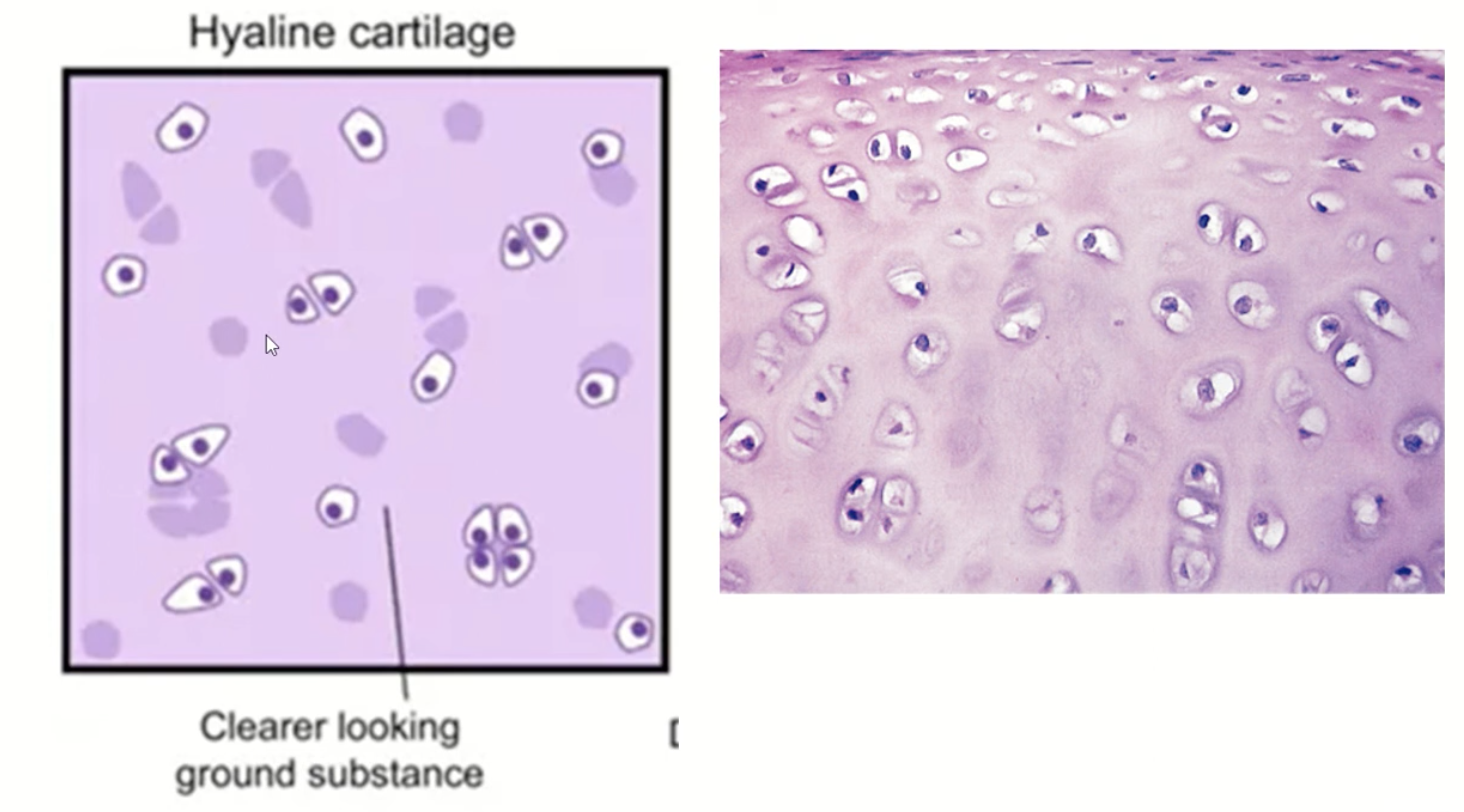
hylaine cartilage is __ in color and forms __
translucent, blue-white
articular surfaces of joints
__ cartilage provides support in the nose, larynx, trachea, and bronchi
hylaine
why can’t you see hylaine cartialge under a microscope?
same refractive index as gel matrix
__ cartilage is the most common type of cartialge
hylaine
__ cartilage forms skeleton of embryo before endochondral ossification
hylaine
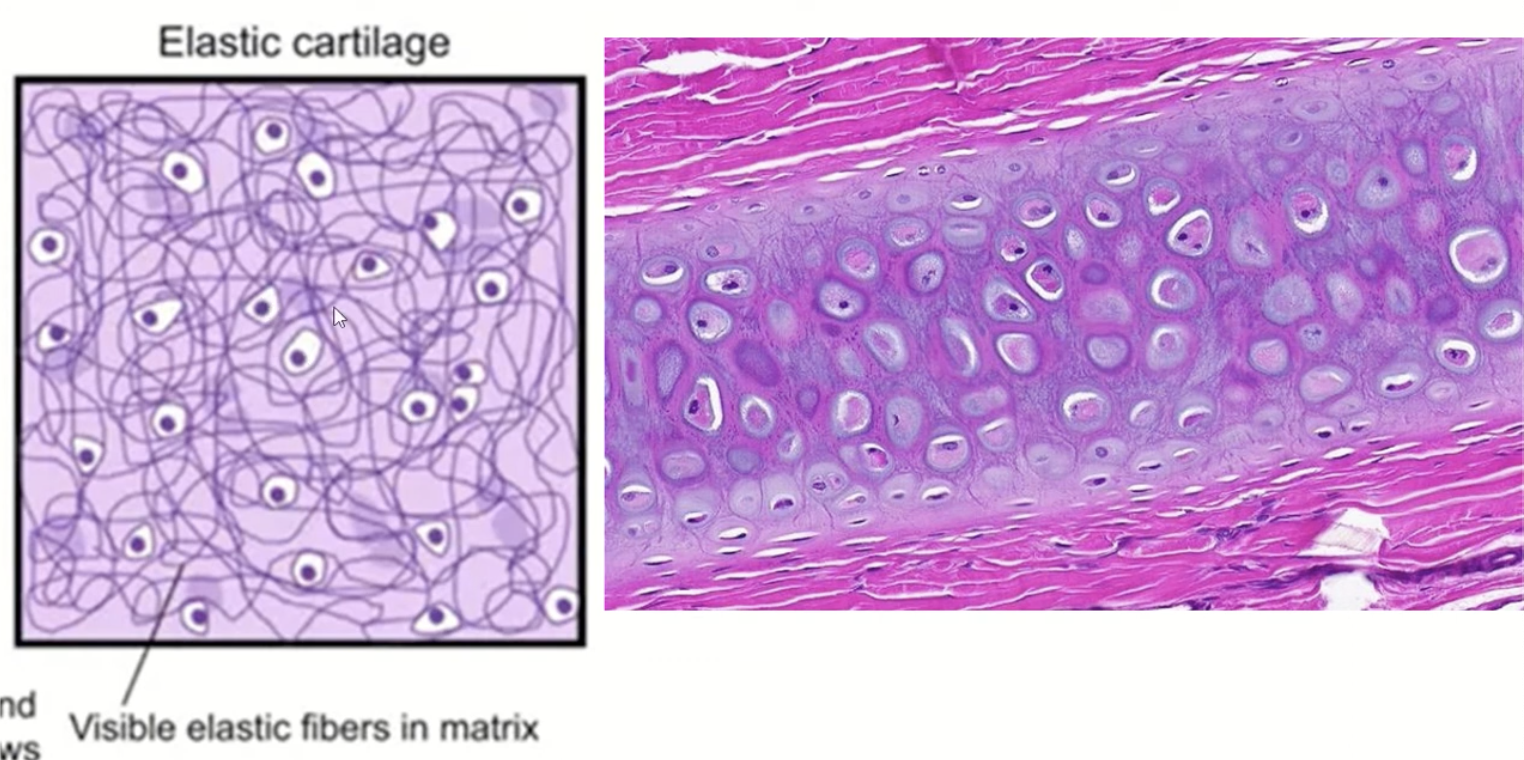
elastic cartilage is made of __
chondrocytes within a matrix and numerous elastic fibers
__ cartilage provides support and flexibility (external ear, epiglottis)
elastic
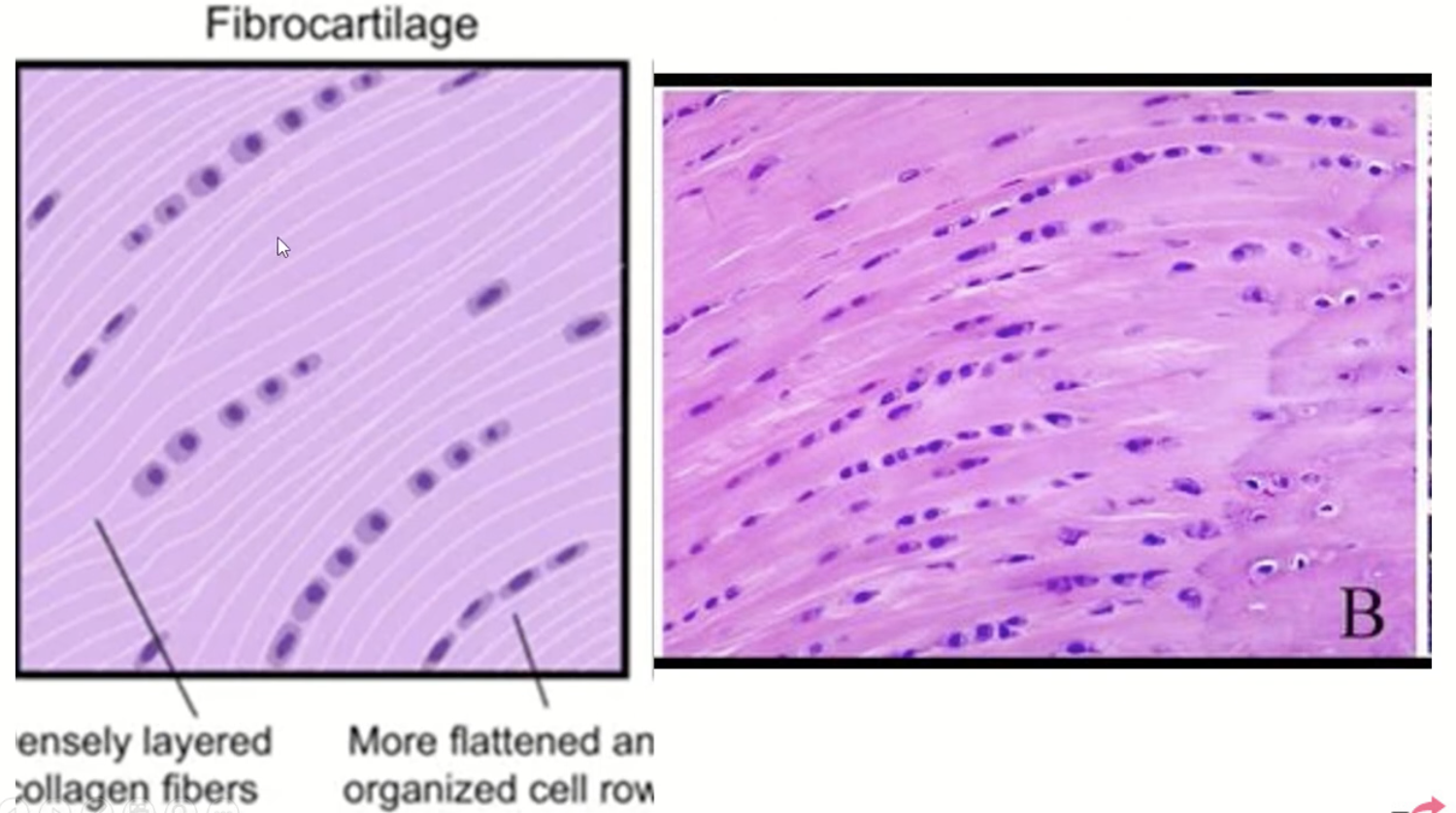
fibrocartilage is made of __
higher proportion of collagen fibers
__ cartilage is found in intervertebral discs and menisci of stifle joint
fibrocartilage
__ cartilage attaches tendons and ligaments to bone
fibrocartilage
osteoarthritis
degeneration of articular cartilage
rickets
young animals on a diet in which there is imbalance of calcium and vitamin D
signs related to problems with ossification of growing bones
osteochondritis dissecans (OCD)
disturbance in endochondral ossification
intermittent lameness in shoulder and elbow joints of large breeds (Great Dane)
panosteitis
young dogs
idiopathic inflammation of all bone tissues
presenting as pain in long bones
bone is a ____tissue
living, capable of remodeling and repairing itself
provides rigid supportive framework
forms a system of levers for locomotion
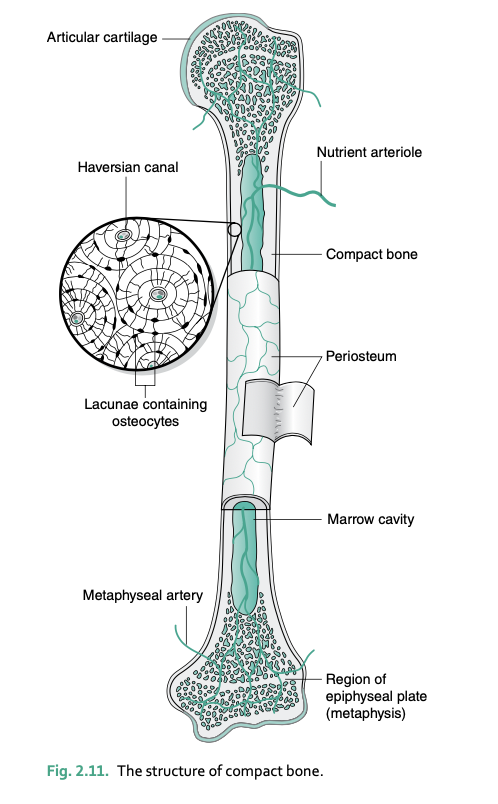
Bone extracellular matrix contains the protein ____ and _____ fibers, which forms the organic material called _____
osteonectin, collagen
form osteoid (unmineralized component of bone matrix before calcification)
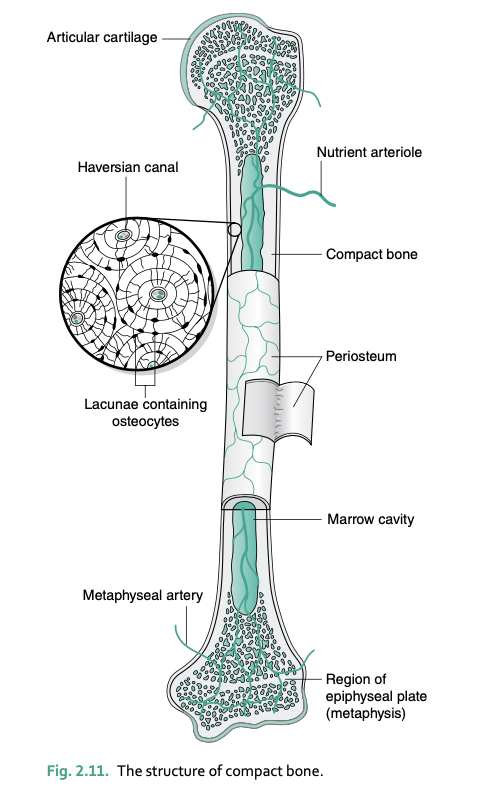
calcification causes _____ to become trapped in______
osteocytes, lacunae spaces
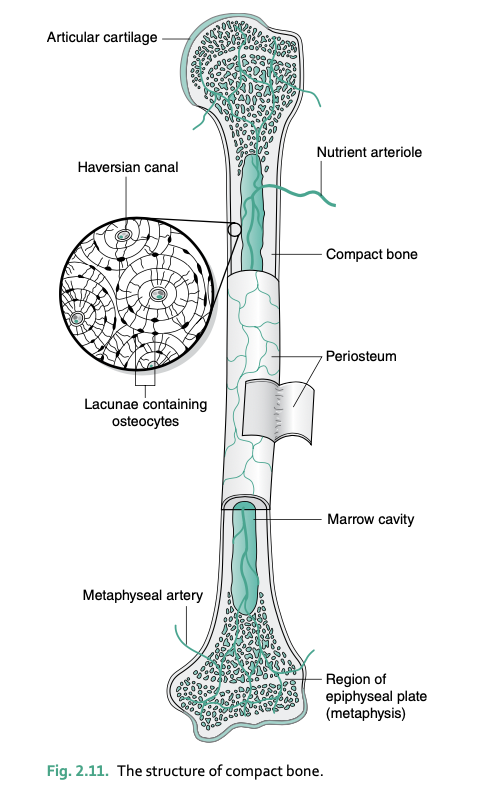
Haversian canals carry ___ and are surrounded by ___
blood vessels and nerves
lamellae (series of concentric cylinders of matrix material) and osteocytes in lacunae
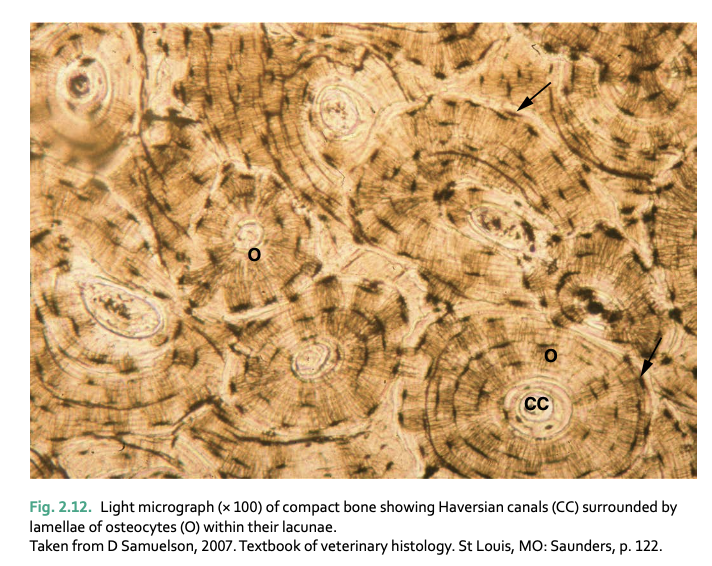
compact bone is ___ and found ____
solid and hard
found in outer later of all types of bone
Haversian systems densely packed together
Cancellous (spongy) bone consists of _____
internal meshwork of trabeculae, spaces between filled with red bone marrow
found in ends of long bones, core of short, irregular and flat bones
osteosarcoma
most common type of malignant tumor of bone tissue
affects any breed of dog, most commonly in large breeds
affects limbs but can occur anywhere
can spread rapidly
affected limb is often amputated
Muscle tissue is responsible for _____
The 3 types are ___-
organized movement of the body
skeletal/striated, smooth, cardiac
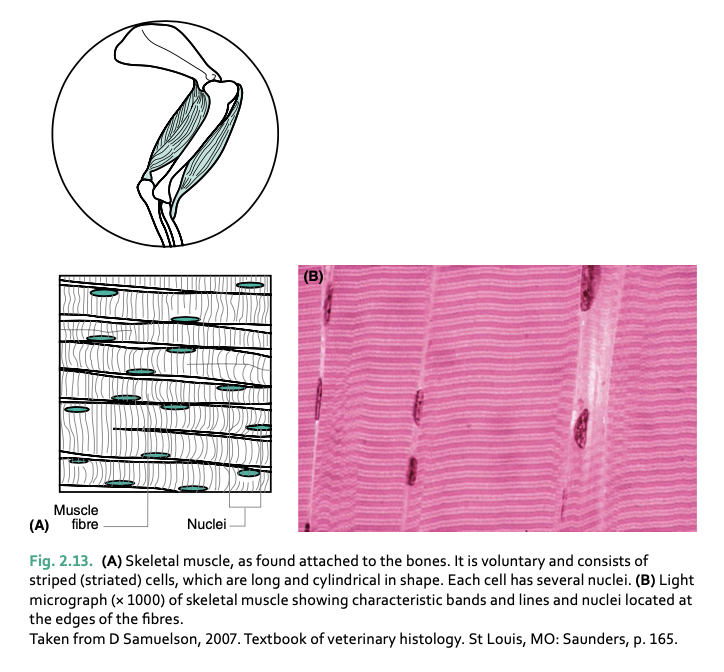
skeletal/striated muscle is found __
attached to skeleton and brings about movement
skeletal muscle fibers are __
long/cylindrical, lie parallel to each other
__ muscle is under voluntary and conscious control
skeletal/striated
skeletal muscle cells are multi____ because __
multinucleated due to the fusion of multiple precursor myoblasts during development.
leads to single, long muscle fiber containing multiple nuclei
Skeletal muscle is composed of bundles of ______ made of ___ and ___
microfilaments (myofibrils)
actin (thin filaments) and myosin (thick filaments)
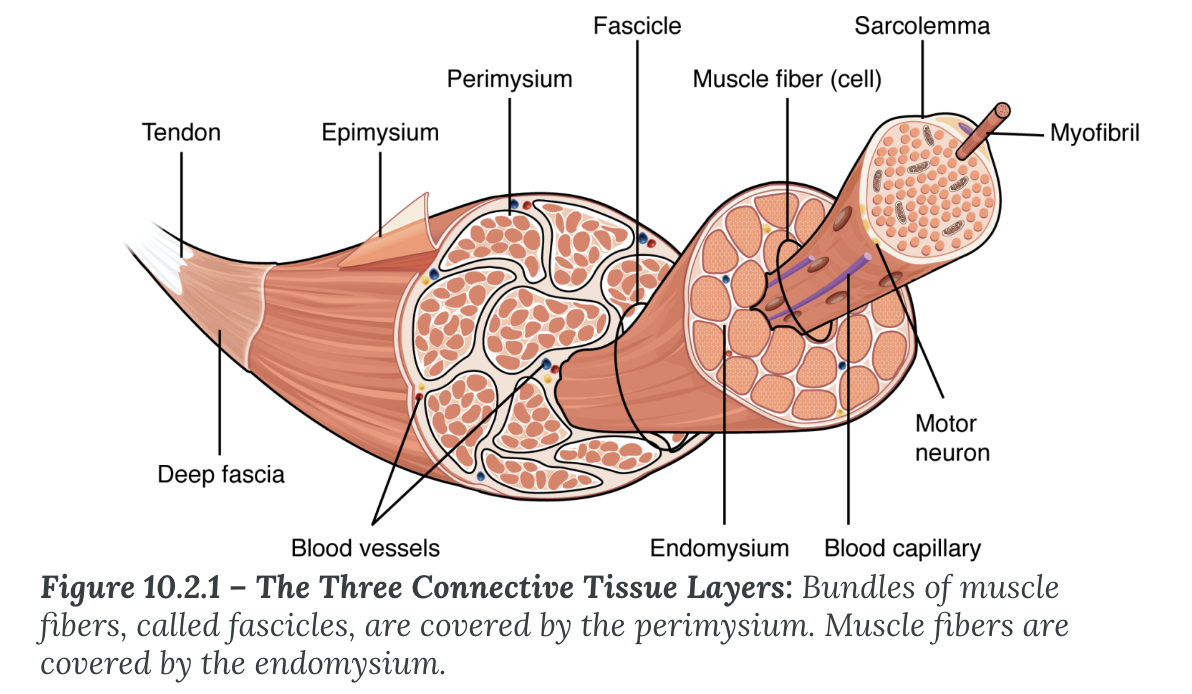
Muscle fibers are grouped together in bundles called ___
fasicles
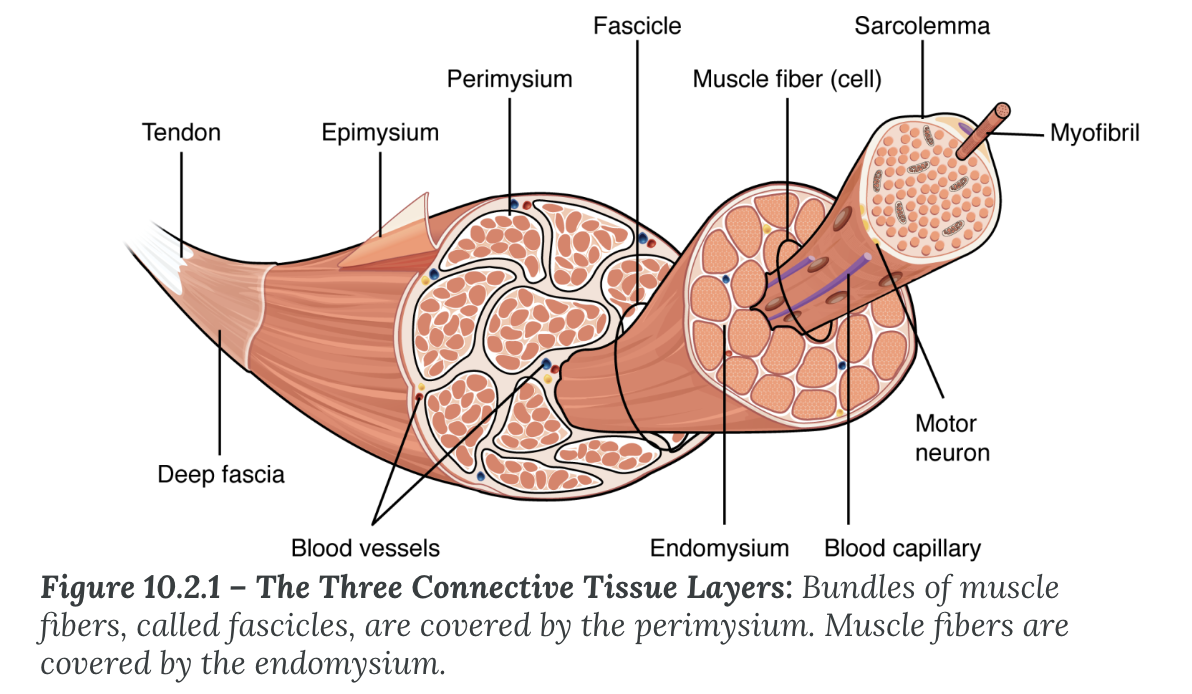
Muscle fibers (cells) are surrounded by ____
Fascicles are surrounded by ___
The entire muscle is surrounded by
endomysium
perimysium
epimysium (continuous with tendon)
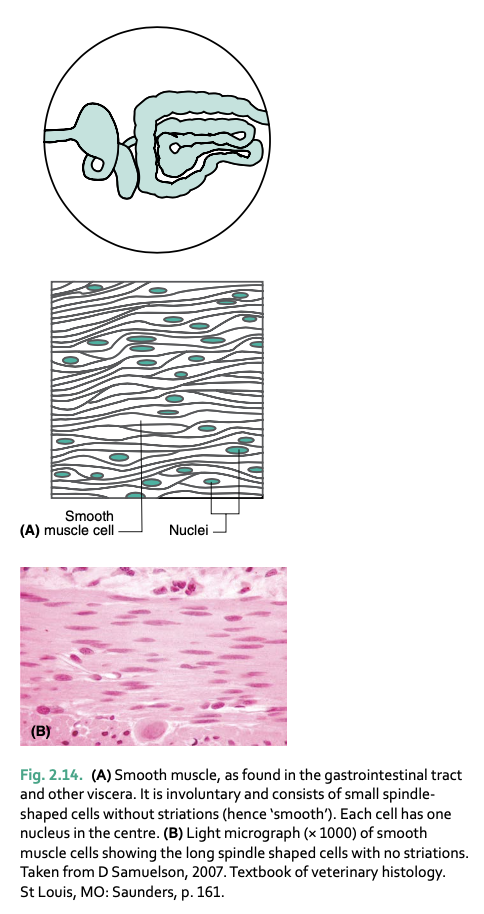
smooth muscle is controlled by _____
autonomic nervous system
smooth muscle is surrounded by __
small amounts of connective tissue that bind cells into sheets/layers
smooth muscle is found __
in walls of blood vessels, digestive tract, respiratory tact, bladder, uterus
__ muscle is under involuntary control
smooth
smooth muscle fibers are __ shaped
long, spindle shaped
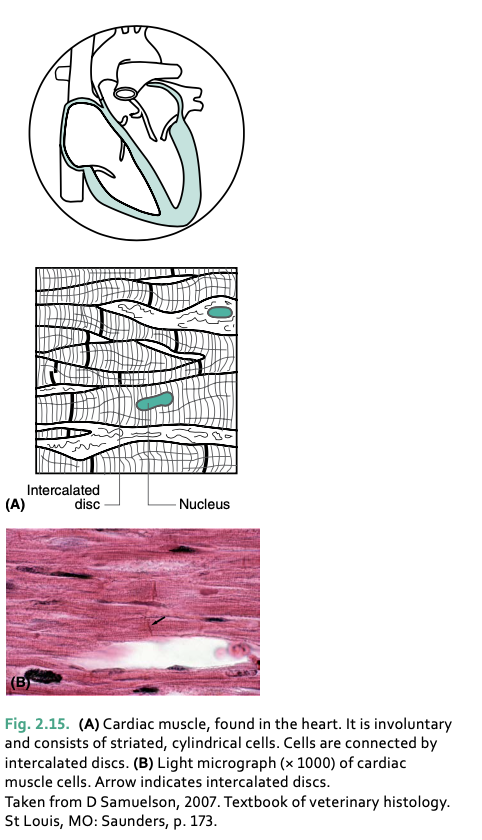
cardiac muscle forms the ___
myocardium of the heart
responsible for rhythmic and automatic contraction, involuntary and unconscious
cardiac muscle is increased or slowed by __
nerves supplying the heart
__ muscle is only found in the heart
cardiac
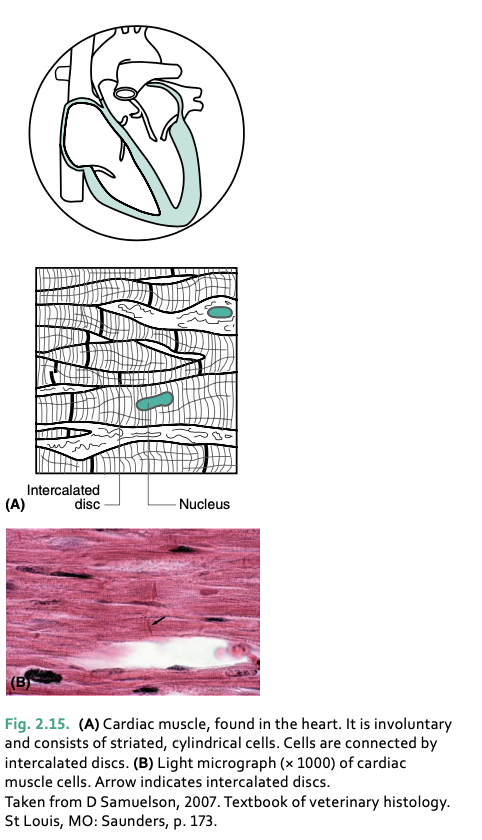
cardiac muscle cells branch to form _____ which are linked by ____ that enable ____
a network of fibers, intercalated discs, nerve impulses to be conveyed across the myocardium quickly
cardiac muscle is __ in shape
striated and cylindrical
Toxoplasmosis
caused by protozoan parasite toxoplasma gondii
inflammation of muscle tissue (myositis)
Cushing’s disease
generalized myopathy
muscular weakness, muscle wasting, atrophy
Myasthenia gravis
lack of receptors for acetyl choline at neuromuscular junctions
presents as chronic fatigue
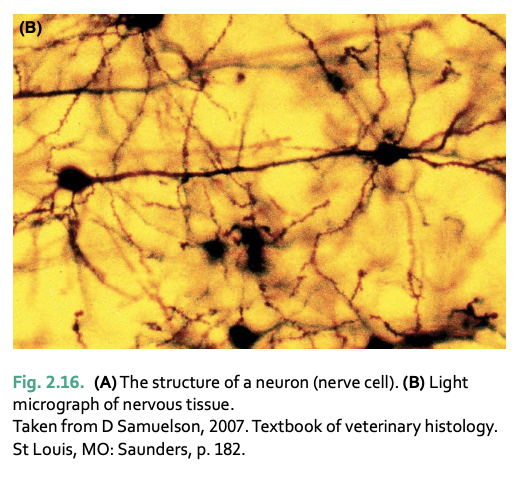
nervous tissue is formed by __
neurons