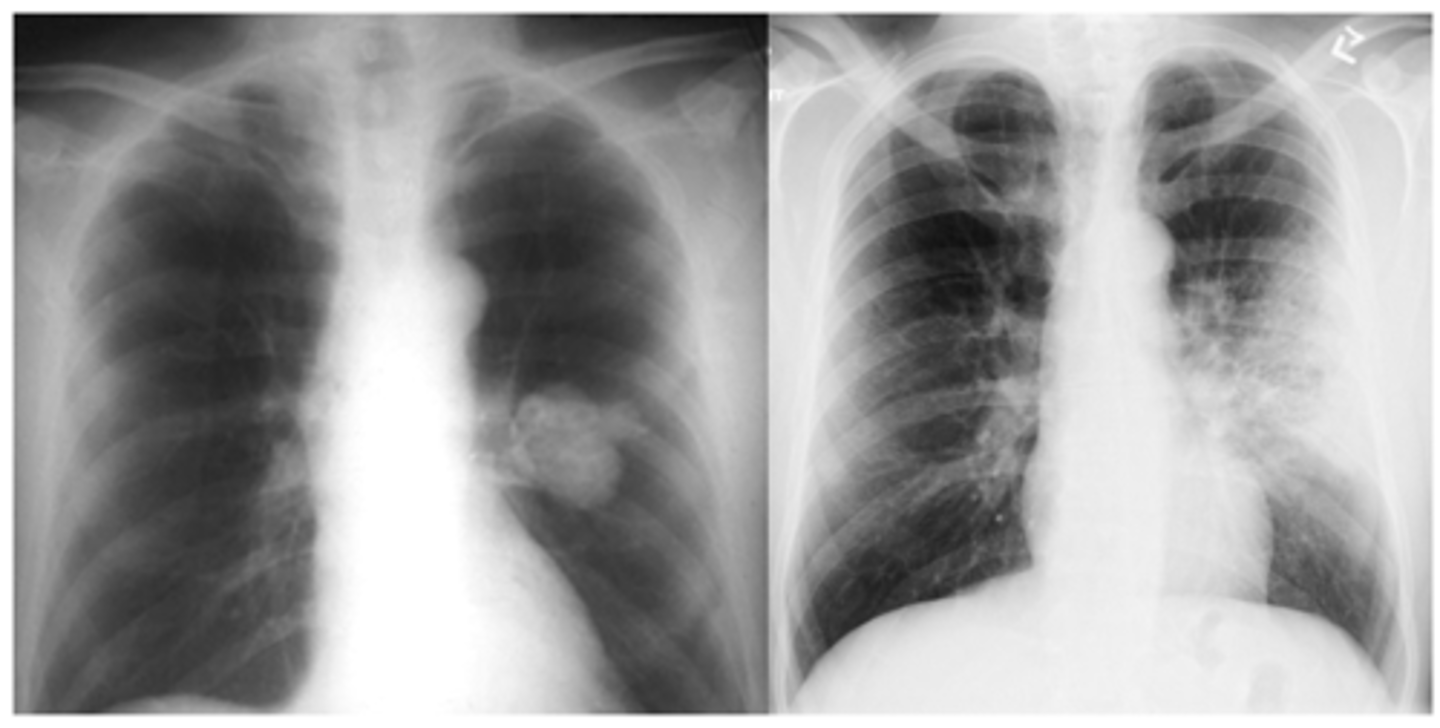
CXR (E1)
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What is always the first step of XRay interpretation?
CONFIRM PT details!! (name, dob, etc)
What does RIPE stand for?
Acronym used to assess image quality
Rotation
• The medial aspect of each clavicle should be
equidistant from the spinous processes. The spinous processes should also be vertically aligned.
•Inspiration
⚬The 5-6 anterior ribs, lung apices, both costophrenic angles and the lateral rib edges should be visible.
•Projection
⚬Note if the film is AP or PA: if there is no label, then assume it’s a PA film
⚬PA = XR beam is posterior (patient’s back)
XR film is anterior (patient’s chest)
⚬AP = XR beam is anterior (patient’s chest)
XR film is posterior (patient’s back)
•Exposure)
⚬The left hemidiaphragm should be visible to the spine, and the vertebrae should be visible behind the heart.
What does ABCDE stand for?
•Airway:
⚬trachea, carina, bronchi and hilar structures.
•Breathing:
⚬lungs and pleura.
•Cardiac:
⚬heart size and borders.
•Diaphragm:
⚬including assessment of costophrenic angles.
•Everything else:
⚬ mediastinal contours, bones, soft tissues, tubes, valves, pacemakers and
For airway, what are 2 main structures to identify and why?
1.Carina and bronchi
⚬The carina is cartilage situated at the point at which the trachea divides into the left and right main bronchus.
•On appropriately exposed chest X-ray, this division should be clearly visible.
•The carina is an important landmark when assessing nasogastric (NG) tube placement, as the NG tube should bisect the carina if it is correctly placed in the gastrointestinal tract.
2. The right main bronchus is wider, shorter and more vertical than the left main bronchus.
•As a result of this difference in size and orientation, it is more common for inhaled foreign objects to become lodged in the right main bronchus.
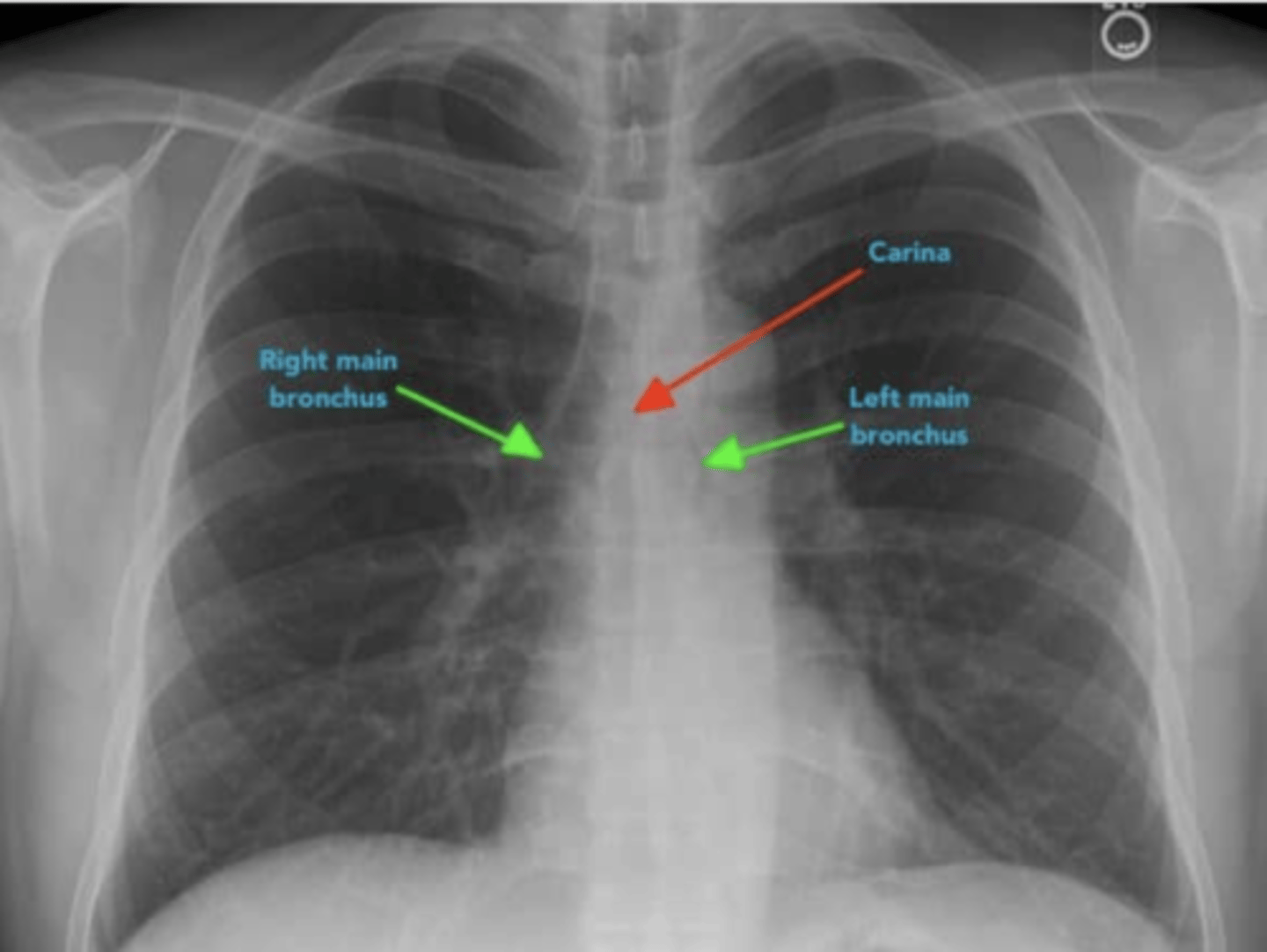
What do the Hilar structures consist of? Is the L or R positioned higher? Why is it important to ID this structure?
•The hilar consist of the main pulmonary vasculature and the major bronchi. (wedge shaped area on central portion of each lung)
•Each hilar also has a collection of lymph nodes which aren’t usually visible in healthy individuals.
•The left hilum is often positioned slightly higher than the right, but there is a wide degree of variability between individuals.
•The hilar are usually the same size, so asymmetry should raise suspicion of pathology.
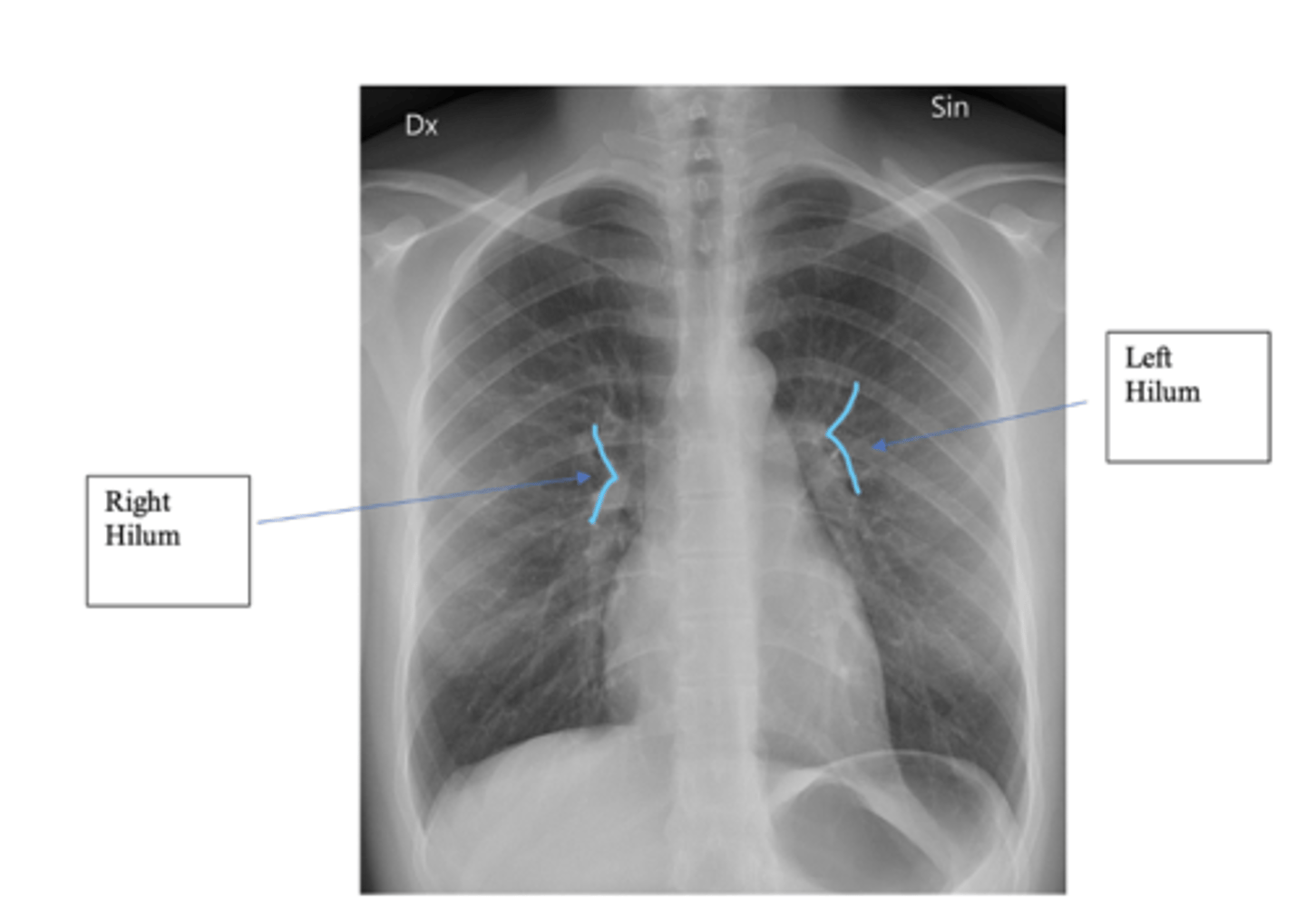
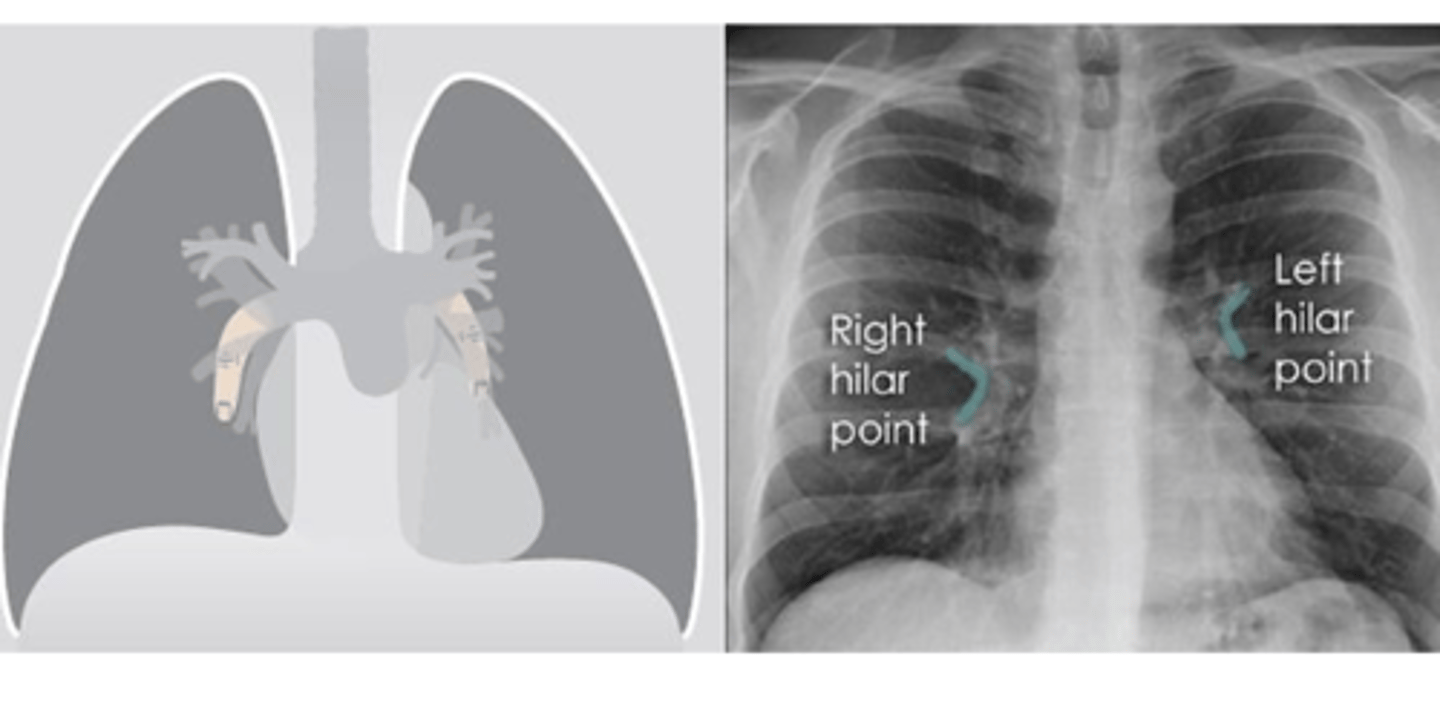
What is the significance of the hilar point?
⚬where the descending pulmonary artery intersects the superior pulmonary vein.
⚬When this is lost, consider the possibility of a lesion here (e.g. lung tumour or enlarged lymph nodes).
What are 8 things to remember when reading a CXR?
•1. Determine age, sex and history
•2. What type of film? AP, PA, portable or lateral? Correct exposure?
•3. What is position of patient? Upright, supine or decubitus?
•4. Is there good inspiratory effort? Is the diaphragm below the 7th rib?
•5. Identify structures and abnormalities
•6. Recheck "Blind spots" •7. Check old films for any changes
•8. Decide what your findings are and a differential diagnosis.
What do routine CXRs inculde and what are 4 other types of CXRs?
•Routine CXRs include PA and lateral views with the patient in the upright position.
Other types of CXRs
⚬AP and supine (portable) films make the heart appear enlarged and the lungs hypoinflated.
⚬A lateral decubitus film can aid in identifying a pleural effusion.
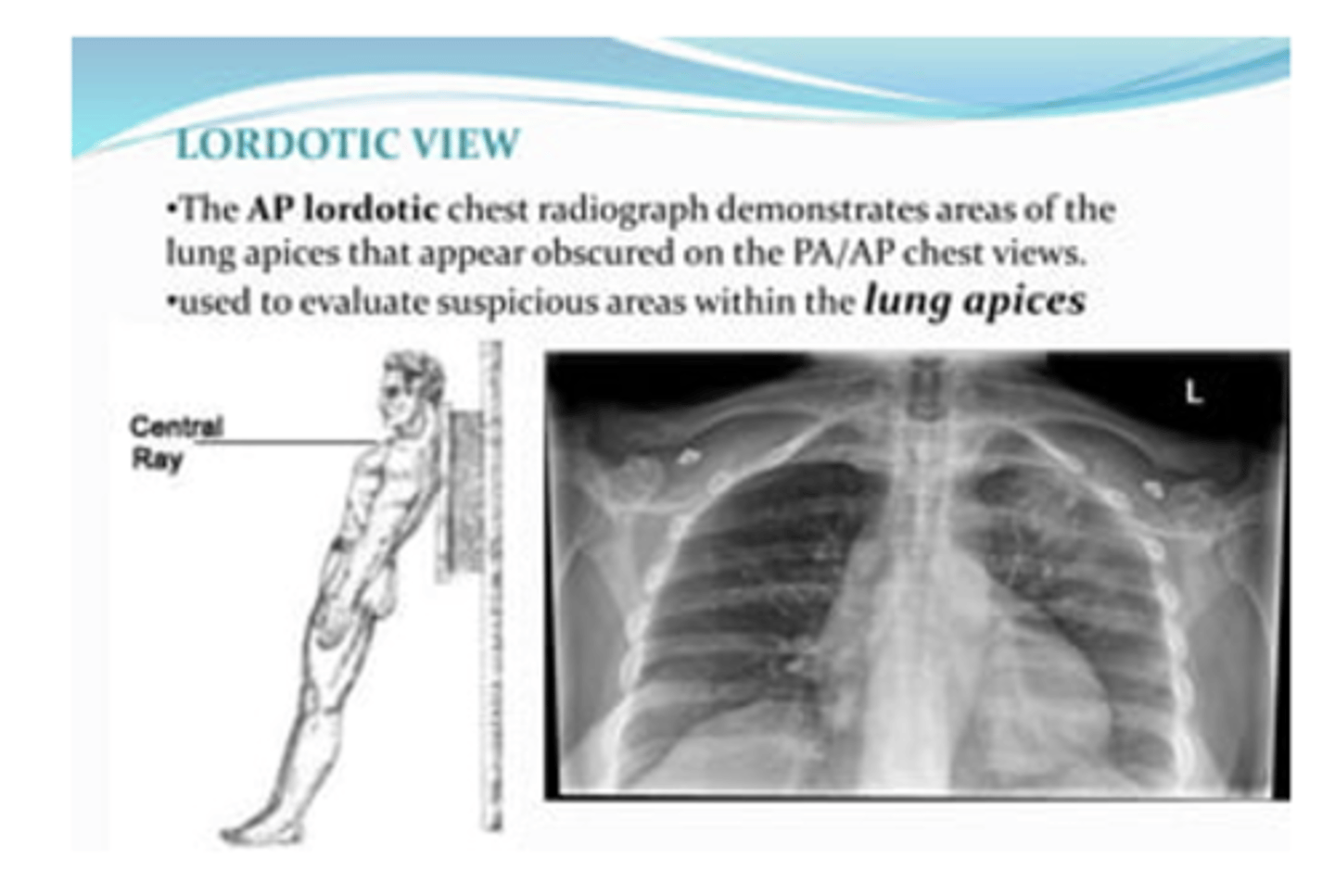
⚬Lordotic films are used to view the apices of the lungs
⚬Expiratory view may be helpful for pneumothorax
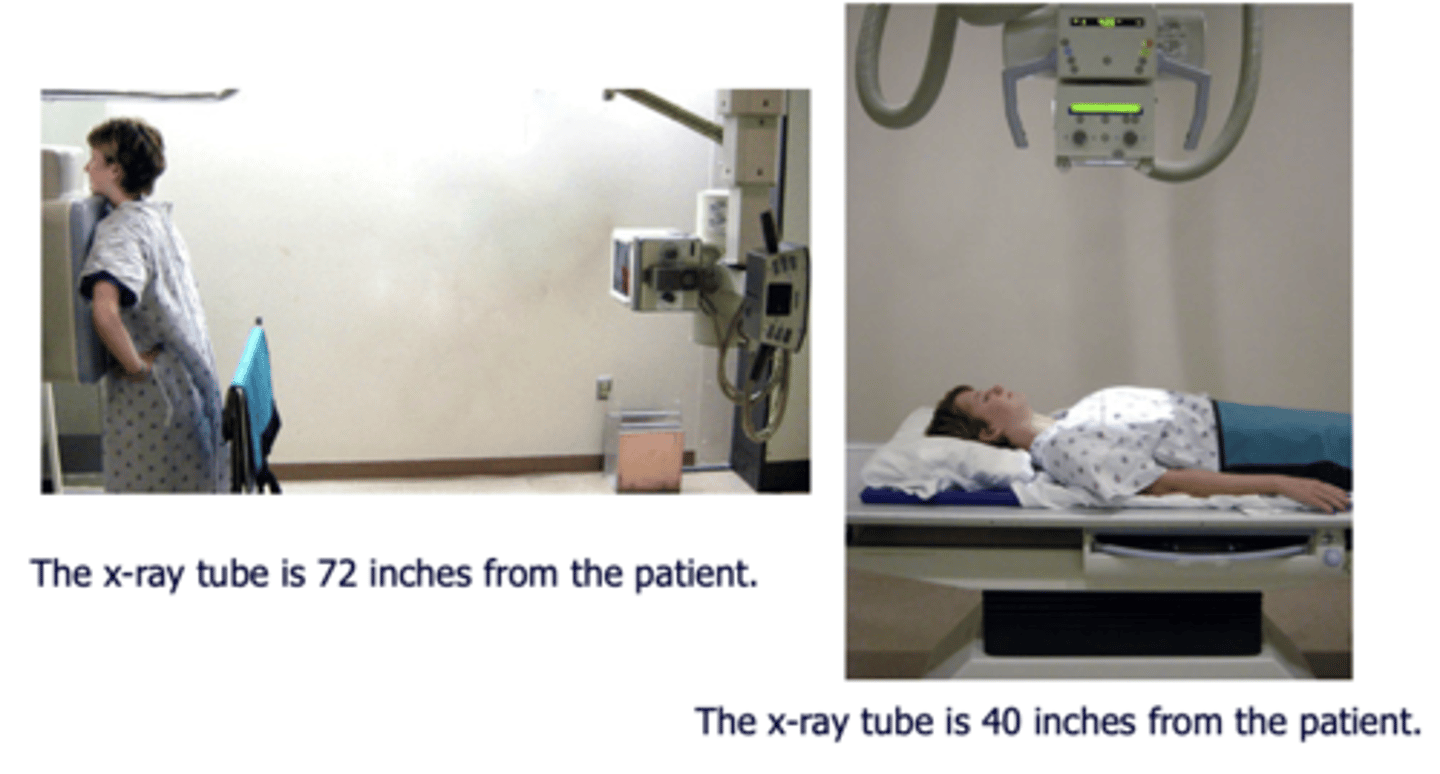
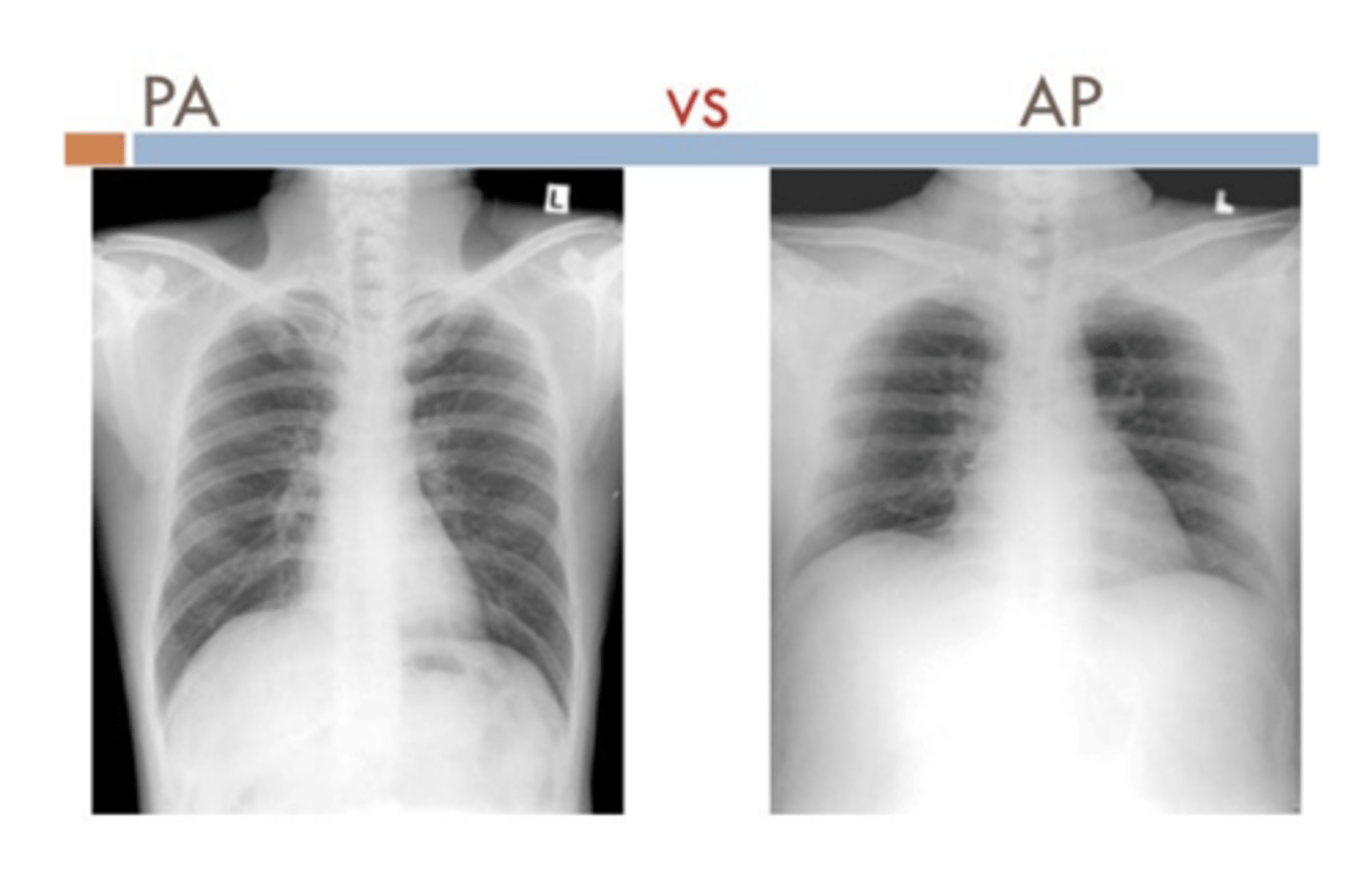
What structures are more visible PA vs AP?
PA
⚬Scapula in periphery
⚬Clavicles project over lung fields
⚬Posterior ribs are distinct
AP
⚬Scapula are over the lung field
⚬Clavicles above apex of lung
⚬Anterior ribs are distinct
What is a lordotic view CXR typicallyl used for?
To evaluate suspicious areas within the lung apices
What is the standard for normal exposure?
visualization of the vessels to at least the peripheral 2/3 of the lung.
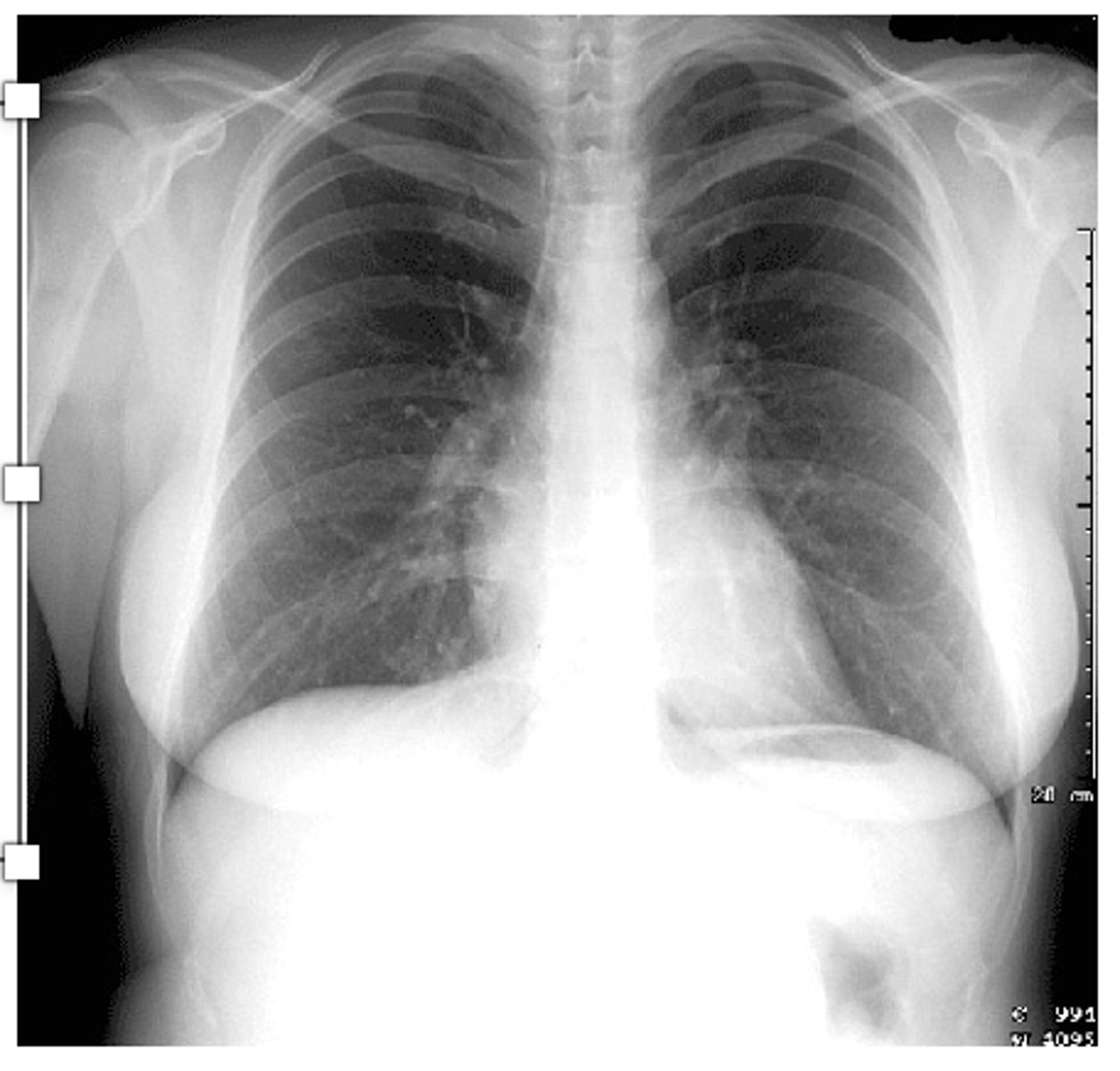
What is normal visualization of inspiratory efffort?
Visualization of more than 7 ribs indicates adequate inspiratory effort.
What is mediastinal shift? How can you ID?
Left hilum should be higher than the right hilum. Often due to mediastinal mass

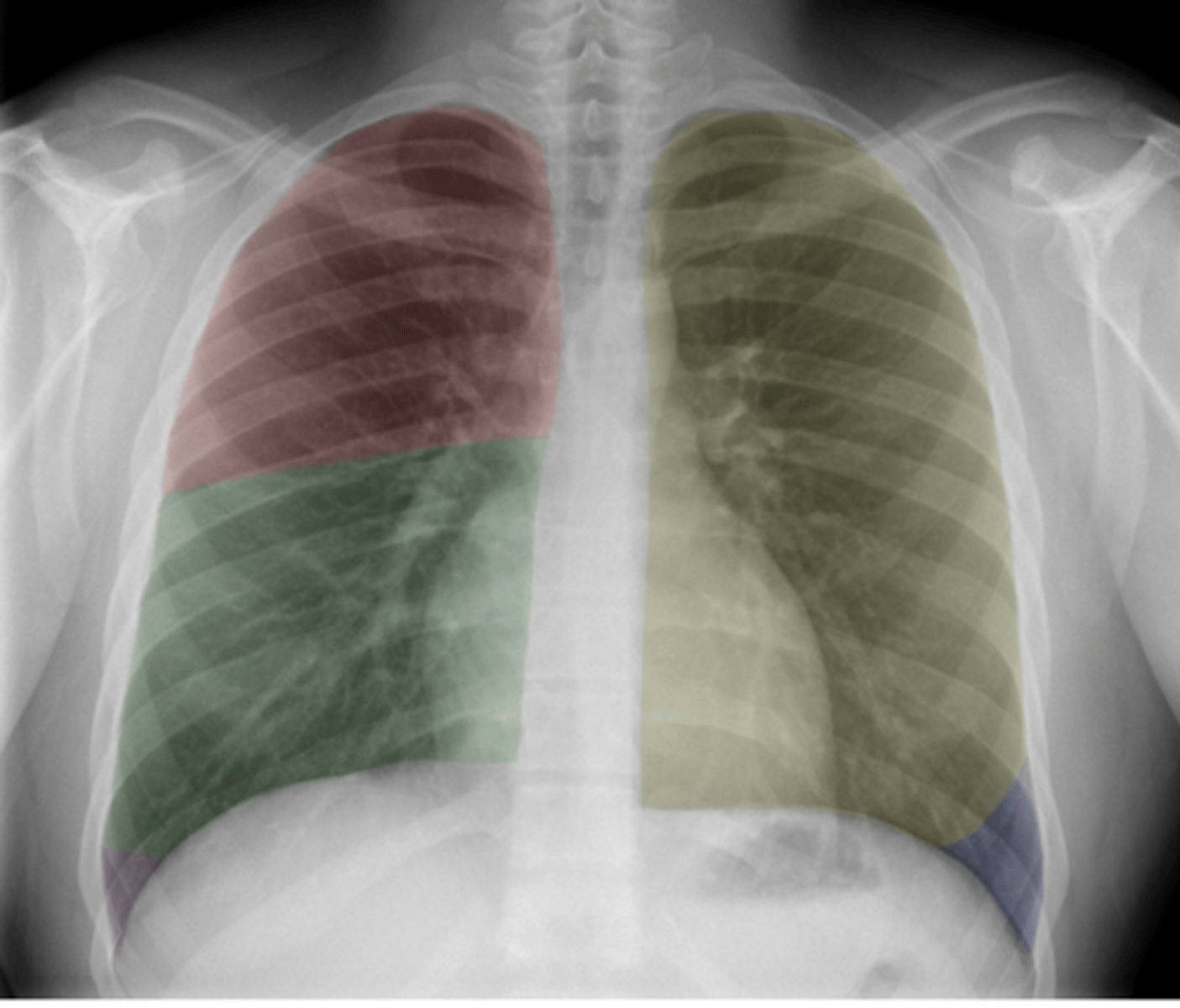
ID lobes of lungs on back (anterior)
•Red: Right upper lobe (RUL)
•Green: Right middle lobe (RML)
•Purple: Right lower lobe (RLL)
•Yellow: Left upper lobe (LUL)
•Blue: Left lower lobe (LLL)
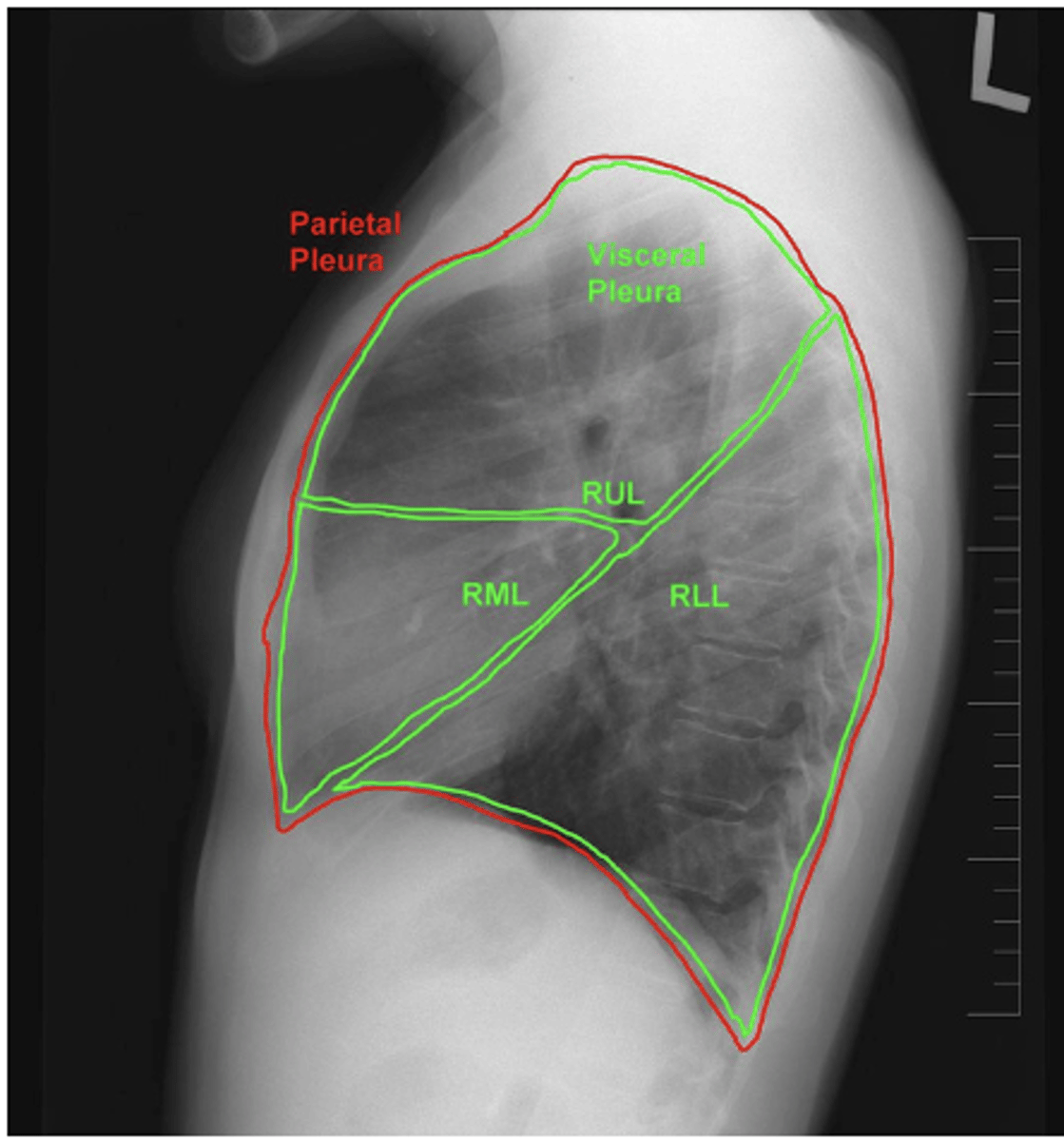
ID lobes of lungs on back of card (lateral right)
refer to picture
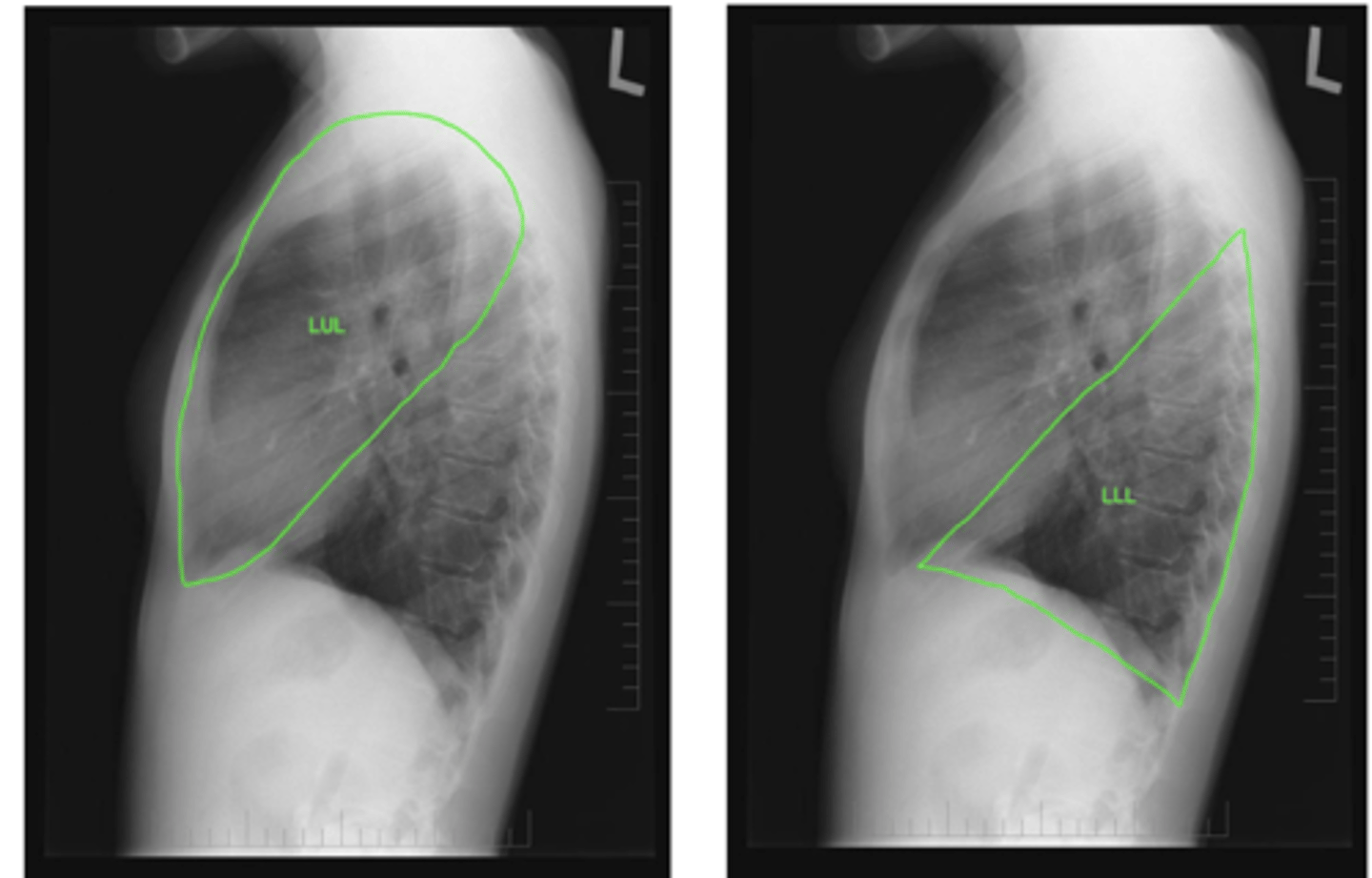
ID lobes of lungs on back of card (lateral left)
refer to pic
dx on back
left lower lobe pneumonia
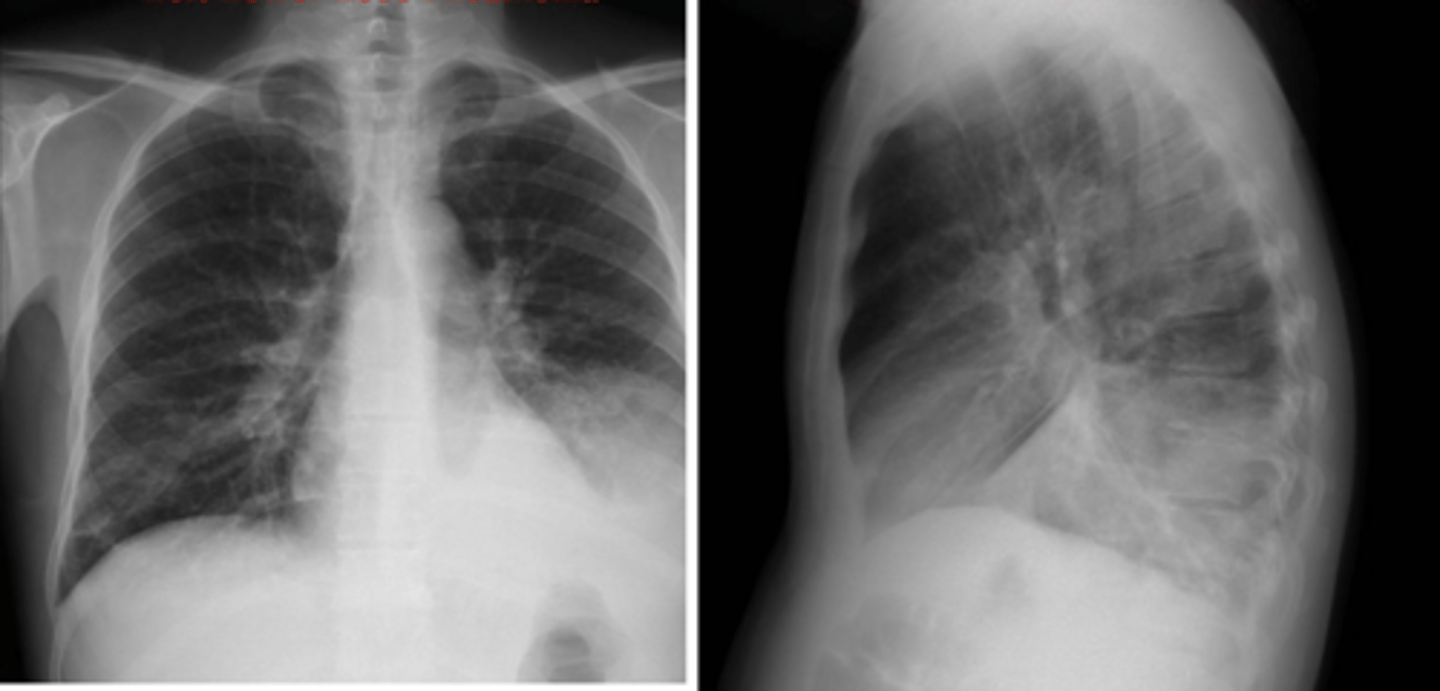
ID mass and infiltrate on back
mass Left
infiltrate R