Feudalism and Medieval Europe Vocabulary
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key vocabulary and concepts from a lecture on Feudalism and Medieval Europe.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
What was the state of Europe after the fall of Rome?
After the fall of western rome people did not have enough money, food, and resources. The turned to aristocrats and other of high power. This led them to the establishment of the feudal order. POLITICAL INSTABILITY
Feudalism/The Feudal Order/System
A system describing the medieval system of land tenure and vassalage.
Feudalism
Social and political system that was used during the Middle Ages.
Manorialism
Economic system that was used during the Middle Ages. Has deep connections to feudalism but it is a distinct regime.
SELF SUFFICENT
Feudal order heirachy
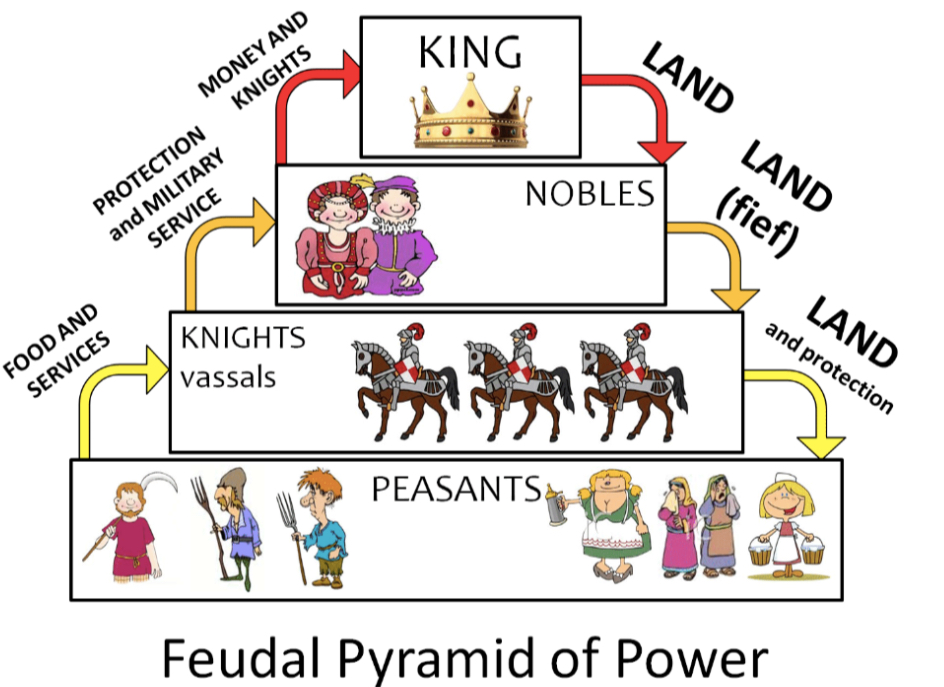
Clergy
The body of people ordained (officially give someone religious duties) such as priests, bishops, deacons, etc.
Laity
The body of religious worshipers.
Doctrine
An official body of teachings from the Church.
Secular
Designates something non-religious or worldly.
Sacraments
Religious rites/ceremonies that followers had to perform if they wished to God/heaven (baptism, confirmation, priest conducts marriage).
Canon Law
Church law that applied religious teachings to clergy, marriages, moral behavior.
Excommunication
Exclusion from the church. Not allowed to get sacraments (and thus can’t get to heaven).
Interdiction
Denial of sacraments (a whole town, kingdom, etc could be denied).
Monasteries/Convents
Places of strict religious worship, usually located in isolated areas.
Benedictine Rule
A set of rules for monks & nuns.
Papal Supremacy
The doctrine that gives the Pope, as Christ’s representative on Earth, full, supreme, and universal power over the Christian Church.
St. Peter
Was chosen by Jesus to build the Christian church, making him Jesus’ successor. He was the first Bishop of Rome.
crucified by Nero in Rome hence why it’s so holy
What was the sequence of events after the collapse of Rome?
Barbarians took over, split up Europe, lots of little nations/empores, those empires were then consolidated to bigger empires, still of invading barbariands
—>THE FRANKISH EMPIRE!
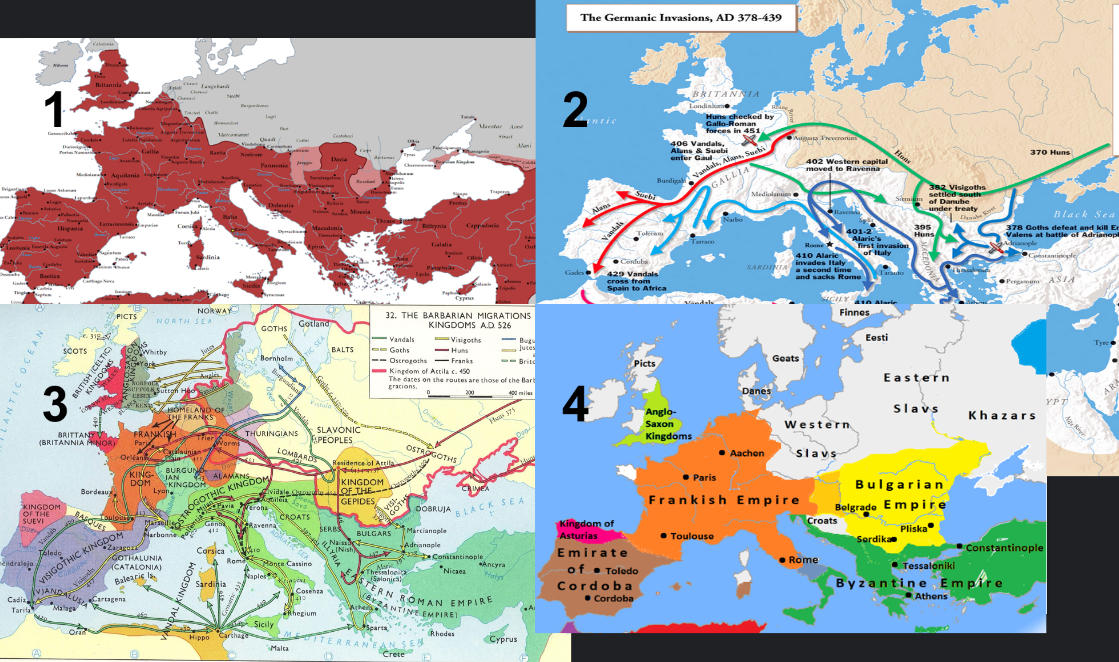
Is feudal order
Decentralized government
Benefit of Clovis converting to Christianity
They were trying to expand territory into Rome. Rome was primarily catholic!
Merovingian versus caroliginian
Both Frankish families who ruled
Merovingian first, then carologian
Pepin (son of Charles Martel) took over to start the Carolinian because pope helped
Pilgrimage
A journey to a shrine, which often housed the relics of a saint, or some other location of importance to a person's religion.
What was the battle of tours
732 AD victory by franks led by Charles Martel against invading Muslim army. Significant for halting the Islamic expansion into western Europe and preserving Christianity as a dominant religion
Who was Charlemagne and how did he take over
Charmaine was a Frankish team who ruled from and is considered the first holy empire it took over the combination of inheritance, military conquest, and the pope/ He is part of the carolgian. His goal was to unite all Western Rome and Central Europe under his rule and for all Germanic people to become Christian
The crowning of Charlemagne by the pope
The pope crowned Charlemagne as the holy Roman empire was originally hesitant because this showed the pope had more power, but in the end, this helped him build our alliance with the church, allowing him to conquer more land
Missi Dominic I
Royal officials in the Frankish Kingdom, particularly used by Charlemagne, who were sent out to oversee the administration of justice and insure authority, particularly with compliance to Christianity is helped to rule a really big empire
Carolinian renaissance
Charlemagne valued knowledge and education.
Wanted to make his capital, Aachen, a “Second Rome”.
Set up a palace school and brought scholars from all over the world to Aachen.
Alcuin of York → ran the palace school.
Copied ancient manuscripts and Latin works of history & science.
Helped spread Christianity throughout Medieval Europe.
Treaty of verdun
Divided his empire into three parts for his three successors after Frankish tradition. Shortly after the carolingian empire col-assed because it was divided and weakened, faced with more Viking invasion
Crusade
A medieval military expedition, one of a series made by Europeans to recover the Holy Land from the Muslims in the 11th, 12th, and 13th centuries.
Relations between empowers and clergy
700’s/800’s: The relationship was amicable between the Pope and western Europe’s first true emperor since the fall of Rome—Charlemagne.
Remember, the Pope crowned Charlemagne and Charlemagne protected the Pope.The Cluny Reforms gave the Church more power in the 900’s:
To try to improve Catholicism Abbot Berno of Cluny revived Benedictine rules and enforced them more strictly.
He excluded nobles from monastery affairs, and only filled monasteries with devoted monks.
Investiture Controversy
1056-1122
Only the Pope has power to invest bishops & church leaders.
Pope can depose kings, absolve subjects of oaths of fealty.
All princes have to kiss the Pope’s feet.
The Church is infallible.

Lay investiture
Popular debate of the time was: Should lay investiture be allowed?
lay investiture= Kings appointed bishops to their positions.
Many church officials owned land AND had gov’t jobs so King Henry IV felt that this was a fair practice.
But the Pope did not want kings appointing bishops that secretly were loyal to monarchs over the Church.
Who kisses the popes feet
1076- When Henry refuses to give Pope Gregory VII the power to choose officials, Henry is excommunicated by the Pope.
Henry IV now faced revolts at home so he had to make peace. He goes to the Pope and begs for forgiveness. (How embarrassing!)
Pope Gregory knew Henry was just trying to save his throne, but as a Catholic he had to practice forgiveness, so he revoked the interdict.
1122 (50 years later!) The two finally settle the dispute at the Concordat of Worms:
Church could elect bishops.
But the king still had the right to give them fiefs, and thus have political alliances in their countries.
The quarrel between Popes and Kings will go on for a few hundred years.
For the most part, the Church wins (the Crusades happening at the same time helps to boost Papal power).
But the power of the monarchs will gradually grow as nations form…
Lay investiture, is the clergy taxed, who gets to try (trial) the clergy
How did they try and convert people and how didn’t it work
They d]tried to convert people to Christianity through missionaries, preaching, and cutting down of pagan traditional stuff like the tree. This failed because the Catholic Church mass was very closed off, things were not done in vernacular and no one understood anything.A majority of the population could not read or speak Latin, so they could not understand what was being read at mass.
Instead peasants would rely on images to understand their faith → hence the importance of icons.
Mass was not given consistently because of the lack of priests.
A majority of people had a very basic understanding of their faith.
Jesus was the central figure and one God.
Crusades
The Crusades (1096-1291):
Series of holy wars launched by Christian states against Muslims in “the kingdom of Jerusalem” (modern day Israel).

Why the crusades
pope urban ll imitated the crusades to reclaim the holy land from Muslim control and to aid the Byzantine empire to establish Christian dominance and reclaim Jerusalem
Byzantine facing pressure from Seljuk Turks requested help from Western European Christian’s
Seljuk Turks = Muslim conquered Anatolia
Good leverage to end schism (bysazntine )
Would unite against one enemy, instead of fighting each other
This was a way to unite Western Christians who were currently fighting each other. (Feudal society was divided into competing kingdoms.)
Also, remember that Popes and monarchs were competing for power (lay investiture).
A religious fight against a new enemy—the Muslims– would give the Pope and the Church more power and demonstrate supremacy.
It was also a power play against the “antipope” who had invaded and taken over Rome - ignoring Pope Urban II’s election to the papacy.
(Pope Urban was ruling from Claremont, France where he had built the largest church in the world at Cluny.)
Mass communication
Letters used to tell more people to join the crusades (religious war) and journey to the holy land
HOW DID CHRISTIANS AND MUSLIMS TREAT EACH OTHER DURING THE CRUSADES?
Both used violence to achieve their ends.
Both sides tried to garner support by creating a negative portrayal, “demonizing” the other side.
Europeans called the Muslims “infidels” and called the wars “crusades” to motivate Christians.
Muslims called the Europeans “barbarians” and called the wars a jihad to motivate Muslims.
HOW MIGHT USING NAMES LIKE THESE HELP EACH SIDE GATHER SUPPORT?
There were times when each side showed mercy. But for the most part, a negative impact of the Crusades was that it created religious intolerance.
What were the results of the Crusades?
1099 A.D. - Christians captured Jerusalem.
Crusaders struck the Muslims at a time when
their forces were not united. (Sunni and Shiites fighting one another.)It felt good to be Christian at this time!
The Holy Land was back in their control!
Crusades result
Battle of Hattin: This refers to Partner B’s reading!
The Christians were tired and thirsty. The Muslims blocked them from getting water and other resources. Muslims surrounded and killed them.
Christian forces sent troops to help, but the forces were too weak to get there in time.
However, it was during this second crusade that Christian kings started personally joining the fight…that sent a strong message!
Saladin (Muslim leader) then led his army to capture Jerusalem. The Christian forces easily fell. Saladin was considered a hero.
Richard the Lionheart marched on to Jerusalem, but turned around because he knew the Christians would never be able to defend it long term.
Saladin came to a truce with Richard:
Muslims owned Jerusalem.
Christians granted safe passage into Jerusalem for religious reasons.
Reasons for Christian failure:
The Byzantine emperor and Catholic Pope disgreed.
The trek was too long for Western Christians to complete.
The Christians lacked people to populate areas they captured.
They lost the “crusading spirit”.
Positive changes of crusades?
Social changes In Western Europe:
The Europeans are exposed to Muslim learning and knowledge. They start to (gradually) look again at the works of the ancients
The Europeans noticed that Muslims supported and pushed for education. This will gradually inspire Europeans to do the same
Europeans are also exposed now to new cultures! They begin have a wider worldview and want to learn more!
So even though the Christians hated the Muslims, they had a lot to thank them for!
How did the Crusades alter the economic and political climate in Europe?
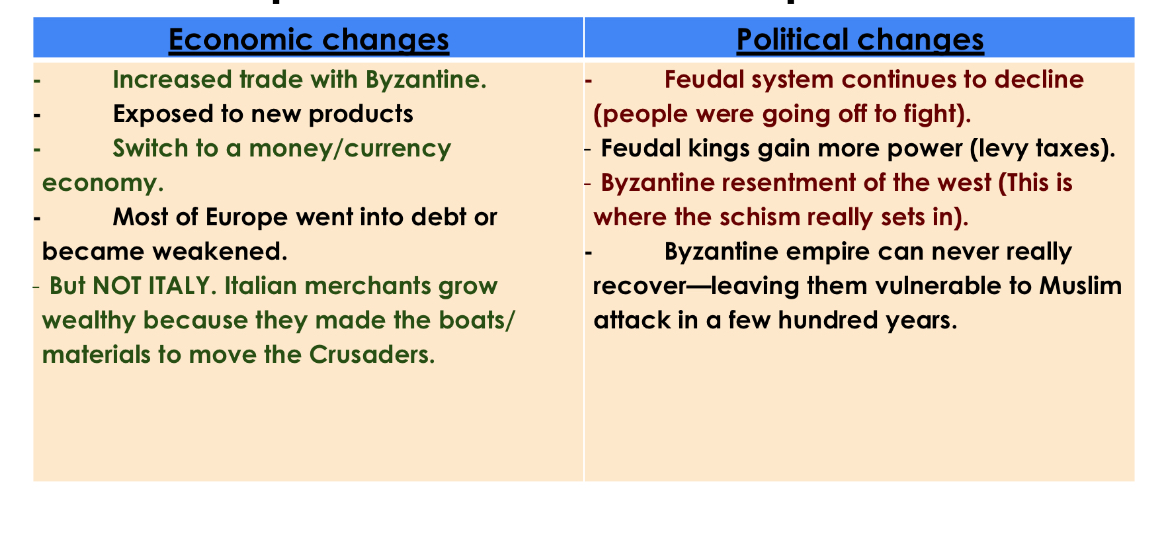
AGRICULTURAL REVOLUTION
Improvements in agricultural technology, which would lead to more food and rise in populations.
Heavy plough: allowed serfs/peasants to cut through deep, wet, and heavy soils of Northern Europe.
Plow horse: horses were much faster & could work longer hours than oxen.
Invention of the horseshoe (horse hooves would not crack in the cold & wet soil) and the horse collar (allowed horses to increase pulling power- from 1000 lbs to 5000 lbs).
Commercial revolution
REVIVAL OF TRADE! —> from manors, no movement to lots of movement becuase things can be traded
Just like the Neolithic Revolution, the fact that Medieval Europe had a stable food supply and the population of Medieval Europe grew.
Not everyone had to be farming all the time!
Feudalism provided the structure for this to happen!
At the same time, this also disrupted feudalism because people started leaving manors for better opportunities.
What are the two agricultural revolutions in history?
Neolithic and medieval
Agricultural revolution impact
NEW CLASS, MERCHANTS, FARMERS, CRAFTSMEN
Towns after agricultural revolution?
Towns were granted “charters,” which exempted them from feudal obligations.
This was given by the king or (less commonly) the lords.
Towns provided the king with money and in a way they were only loyal to the king, not their lord.
“Burgs”
Now alo]lowed to leave differently from manors
Usury
Lending money at interest.
The Church forbade Christians to lend money at interest.
This rule did not apply to Jews!
They were often not allowed to work in other professions so they turned to money-lending.
This becomes critical for the growth of the Medieval economy.
Tensions between Christians & Jews grow over resentment to paying back loans.
Medical guilds
Controlled membership
apprentice → journeyman → master craftsmanControlled quality of the product
Controlled prices
Promoted town/region products
Medieval period was a dark age? :(
Crusades were dark but…
There was some education supported in monasteries.
There was increased trade and new business practices as a result of the agricultural and commercial revolution.
There was a growing middle class.
In some countries, certain liberties were written down.
Philosophy
Math
Literature
Architecture
Scholasticism
The application of logic and reason to philosophical considerations of religious beliefs.
To deal with the challenge of FAITH vs. SCIENCE, scholars engaged in “SCHOLASTICISM”: the application of logic and reason to philosophical considerations of religious beliefs.
Thomas Aquinas was one of the most famous medieval philosophers.
Adopted Arabic number system (easier).
Solve this math problem: MCMLXXX + MMCCCLX
Now solve this one: 1980 + 2360
- no church basking
What types of advancements do you think happened in science (astrology, chemistry, etc)?
Not much…
Vernacular
Writing started to appear in the vernacular of the everyday people instead of Latin.
= more people could learn!
DANTE Alighieri - one of the most famous medieval Italian poets who wrote in the vernacular.
wrote DANTE’S INFERNO