Ch 12 Substance Use and Impulse Control
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
why is substance abuse rate rising?
increased accessibility of drugs, increased life stresses
Physical Consequences of Substance Abuse
damage to vital organs
decreased immune system
neurological impairment
overdose (can be fatal, often a miscalculation)
Psychological Consequences of Substance Abuse
increased anxiety, depression, emotional instability
impaired judgment and decision-making
development or worsening of mental health problems
Social Consequences of Substance Abuse
strained relationships with peers
social isolation and withdrawal
difficulties in work
legal problems
Life Consequences of Substance ABuse
money issues
legal issues
loss of employment or academic opportunities
Substance Use
ingestion of psychoactive substances
Intoxication
physiological reaction to ingestion of a substance
Substance Abuse
loss of control of use of a particular substance
Tolerance
increasingly more of a substance needed to experience the same effect
or diminished effect with continued use
Withdrawal
negative symptoms from cessation or reduction of use of a drug
Craving
psychological intent to get a drug, drive behavioural responses (drug-seeking behaviour)
Substance Use Disorder- Diagnosis
loss of control of substance use
unsuccessful attempts to stop
significant time spent obtaining & using substance
craving or strong desires to use
continued use despite social problems, physical hazards, health problems
tolerance & withdrawal
Depressants
decrease CNS activity
sedative, hypnotic, and anxiolytic drugs
What type of drugs are most likely to produce tolerance and withdrawal?
depressants
Alcohol Use Disorder- Diagnosis
2 criteria over 12 months
cravings for alcohol
impaired control of alcohol use
preoccupation with using or obtaining alcohol
tolerance & withdrawal
neglect of responsibilities due to use
continued use despite health, social, or interpersonal issues
absorption of alcohol into body
stomach → small intestine → heart → liver
long-term alcohol use- problems
major loss of brain tissue, severe liver damage
Alcohol Withdrawn Delirium
symptoms resulting from alcohol withdrawal: agitation, insomnia, disorientation to time and place, hallucinations
Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome
severe thiamine deficiency → cognitive issues and muscle problems
Wernicke-Korsakoff: Cognitive Issues
confusion, issues with planning, problem-solving, attention
confabulation: making stuff up
speech problems
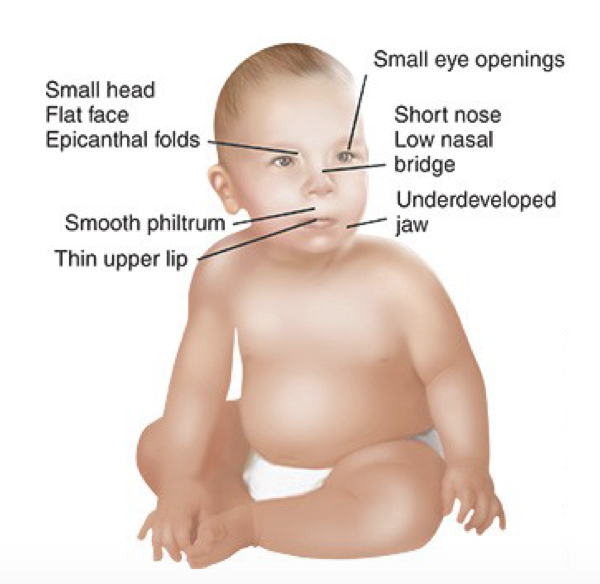
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome
excessive alcohol during pregnancy → severe effects on infant
growth retardation, cognitive/behaviour/learning issues, anatomical abnormalities
sedatives
calming
hypnotic drugs
sleep-inducing
Anxiolytic drugs
anxiety-reducing
barbiturates
CNS depressants that enhance GABA activity (inhibitory)
produce sedative and calming effects
uses: anesthesia, anxiety relief, seizure treatment
BARBitals
barbiturates risks
dependence, overdose, respiratory depression, withdrawal
Benzodiazepines (benzos)
enhance GABA activity (GABA-A) → calming, anxiolytic, sedative, muscle-relaxant and anticonvulsant effects
end in -am
Sedative-, hypnotic-, and anxiolytic-related disorders- Diagnosis
use despite physical or psychological problems from substance
repeated unsuccessful attempts to reduce use
significant impairment or distress from use
tolerance & withdrawal
recurrent use in physically hazardous situations
Prescription excess
overprescription of sedative and hypnotic drugs (benzos, sleeping pills)
especially to vulnerable populations (elderly, ppl wit substance abuse issues) → may have negative consequences
Stimulants
caffeine, nicotine, amphetamines, cocaine
What class of drugs is the most commonly consumed?
Stimulants (ie. nicotine, caffeine)
Stimulant Use Disorder- Diagnosis
excessive stimulation use
unsuccessful attempts to quit
time spent using/obtaining stimulants
cravings, tolerance, withdrawal
failure to fulfill life roles
continued use despite health, social or interpersonal problems
Amphetamines- uses
historically: asthma treatment
now: weight loss, energy, staying awake/alert
ADHD treatment
Amphetamine Intoxication- Psychological
euphoria
changes in sociability
anxiety, tension, anger
stereotyped behaviours
impaired judgment
impaired social or occupational functioning
hallucinations
Amphetamine intoxication- Physiological
increases in heart rate
blood pressure changes
perspiration or chills
nausea/vomiting
weight loss
respiratory depression
seizures
coma
respiratory depression
shallow breathing → deprivation of oxygen
from opioids, benzos, barbiturates
Cocaine- history
stimulant derived from coca leaves
high cost - used by wealthy people
Cocaine - ingestion
snorted, crack cocaine is smoked
Cocaine- long term use
cardiovascular damage
neurological effects: seizures, strokes, neurotoxicity
paranoia, hallucinations
addiction, dependence
respiratory problems: damaged nasal tissue, chronic runny nose
GI problems: decreased blood flow and bowel ischemia
dental decay (“crack mouth”): severe tooth decay and gum disease
auditory deficits in infants
amphetamine- NT effects
stimulates dopamine & norepinephrine release, blocks reuptake
Cocaine- NT effects
blocks dopamine reuptake
What is the effect of increased dopamine (reuptake blocked) from stimulants?
euphoria
Dopamine Theory of Addiction
people with a genetic predisposition to experience less dopamine release from reward (less satisfaction) → more prone to addiction from dopamine reuptake blockers (stimulants)
Nicotine
psychoactive substance that produces dependence, tolerance, and withdrawal
Tobacco-recent rates
decreases in recent years, approximately 10% of population
Tobacco Withdrawal
depressed mood, insomnia, irritability, anxiety, concentration issues, restlessness, increased appetite and weight gain
Caffeine-Related Disorders
most commonly used psychoactive substance (90%)
gentle stimulant- least harmful addictive drug
Caffeine in low doses
increase energy and mood, decrease fatigue
Caffeine-high doses
agitation, sleep disturbances
caffeine withdrawal
headache, drowsiness, irritability
Caffeine- mechanism of action
Influences adenosine (neuromodulator)
Opiates
chemical compounds extracted from natural plant matter
used as pain medication post-medical procedures
opium, morphine, codeine, heroin
Opioids
synthetic compounds that mimic opiates
oxycontin, percoset, demerol, fentanyl
Narcotics
sleep inducing opiates and opioids
Opioid use disorder
increased opioid use over a long period of period
unsuccessful efforts to cut down use
time spent using or obtaining
cravings, tolerance withdrawal
failure to fulfill life roles due to opioid use
continued use despite health, social and interpersonal issues caused by use
recurrent use in physically hazardous situations
Hallucinogens- Discovery
Albert Hoffman discovered LSD in fungus that grows on grain kernels
LSD (d-lysergic acid diethlyamide)
aka acid
Timothy Leary discovered and said he wanted every child and adult try the drug
Psilocybin
magic mushrooms
DMT (dimethyltryptamine)
found in virola tree
Mescalline
found in peyote cactus plant
Phencyclidine (PCP)
synthetic hallucinogen
Cannabis
hallucinogen with both depressant and stimulant effects
Marijuana
name given to dried cannabis or hemp plant
high use rates of cannabis
people with mental health problems
can lead to psychosis in at risk individuals (schizo)
cannabis- psychological effects
humour
dreamlike state
heightened sense
vivid colours
distorted time perception
Drug Use- Causes
genetic
psychological
cognitive
cravings
conditioning
denial of problem
family modelling
social incluso (peer pressure)
Genetic predisposition to drug use
some people experience greater positive/negative effects of certain drugs
Conditioning of drug use
positive value of drinking (ie. going out and having fun)
family modelling of drug use
family history of alcohol → becomes normative → family models alcohol use
Psychological causes of drug use
reducing distress
numbed or reduced by substance (positive feelings)
self-medication of mental health problems
short-term gain, but causes long-term problems
Biological Treatments of opioid use disorder
focus on treating cravings & withdrawal symptoms by switching to another drug that does not cause withdrawal, slowly wean off OG drug
replacement drugs do not produce high
Methadone
long-acting opioid receptor agonist, reduces cravings & withdrawal
Buprenorphine
partial opioid agonist that alleviates withdrawal & diminishes cravings without producing high
Naltrexone
opioid antagonist that blocks the positive effects off opioids, reducing relapse risk
Disulfiram (Antabuse)
causes unpleasant reactions when alcohol is consumed → deters from alcohol use
Naltrexone (Alcohol)
blocks enjoyable effects of alcohol (eliminates positive value) → reduces cravings & rewarding effects
Acamprosate
normalizes brain systems disrupted by chronic alcohol use, reduces symptoms of protracted withdrawal
Nicotine Replacement Therapy
lozenges, patches, gum, nasal spray- slowly reduce nicotine use & break habit of smoking
Buproprion
antidepressant that reduces nicotine cravings & withdrawal suymptoms
varenicline (Chantix)
partial nicotine receptor agonist, reduces cravings & withdrawal
goals of psychological treatments of substance abuse
teach person better coping mechanisms to reduce reliance on substances, or reduce existing stressors
CBT
recognize and rework negative cognition patterns related to substance abuse
developing coping strategies to deal with stress (over substance)
developing better emotional regulation
avoidance of triggering environments that lead to use

Motivational Interview
client-centred approach focusing on building intrinsic motivation to quit
engagement (personal acknowledgment of wanting to change), focusing (on obstacles to quitting), evoking, planning

12-step facilitation therapy
group therapy where people share their experiences with the same struggles (AA, NA, etc)
emphasizes acceptance, surrender, active involvement in group support
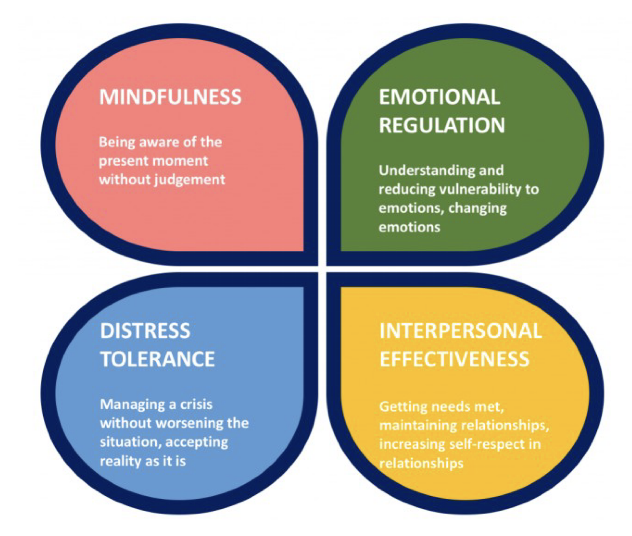
Dialectical Behaviour Therapy
focuses on tolerance of distress and decreasing sense of urgency that leads one to turn to substance use
combines CBT & mindfulness to help people manage negative emotions
drug rehabilitation centers
24/7 care, highly structured program w/ medical supervision, helps manage withdrawal esp in severe cases where going cold turkey would be dangerous
Prevention
public health, education/information about drugs
Intermittent Explosive Disorder
recurrent aggressive/angry emotional outbursts, out of proportion to situation
Intermittent Explosive Disorder- Causes
serotonin dysregulation
family history of aggression
childhood trauma
IED- Treatment
SSRIs or mood stabilizers
CBT for anger management
Kleptomania
recurrent stealing
tension → stealing → relief
Klepto- Causes
comorbid w/ mood disorders
deficits in impulse-control and emotional regulation
Klepto- Treatment
CBT for triggers and steering urges
SSRIs
treat comorbid mood disorders
Pyromania
deliberate fire setting
tension → fire → pleasure/relief
Pyro- Causes
very rare, so limited research
comorbid with other emotional/behavioural disorders
Pyro- Treatment
CBT for triggers and coping strategies
fire-safety education
family interventions in childhood