PSK4U - Unit 2 (Muscular System)
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
Tissue
Masses of cells that have similar functions and form.
Muscle Tissue
Collection of cells that shorten during contraction, there fore creating tension that results in movement.
Over 600
How many muscles in the body?
Smooth, Cardiac, and Skeletal
What are the 3 main muscle groups?
Surrounding the internal organs
Smooth muscle is found where?
Involuntary
Smooth muscle is voluntary or involuntary?
Like dense sheets
Smooth muscle looks...
Found only in the heart
Cardiac muscle is found where?
Involuntary
Cardiac muscle is voluntary or involuntary?
Striated (light and dark strips)
Cardiac muscle looks...
Attached to bones and tendons
Skeletal muscle is found where?
Voluntary
Skeletal muscle is voluntary or involuntary?
Striated (light and dark strips)
Skeletal muscle looks...
Irritability
Ability of muscle to respond to stimulus
Contractibilty
Ability of muscle to shorten in length
Elasticity
Ability of muscle to stretch and return to normal position
Extensibility
Ability of muscle to extend in length
Conductivity
Ability to transmit nerve impulses
The muscular system and the nervous system
Complex Linkages are formed between which two systems?
Neuromuscular junction
Actual meeting point between between nervous system and muscular system
Acetylcholine (ACH)
Which chemical is released as a neurotransmitter?
It causes the muscle to contract
What does ACH do to the muscle?
Motor unit
1 Nerve cell and all of its connecting muscle fibres
Muscle twitch
Single nervous impulse and its resulting contraction (involuntary)
All or none law
When a motor unit is stimulated to contract it does so to its fullest potential (full out or not at all)
Action of Muscle
Flexion, extension, rotation, abduction, etc
Direction of fibres
Rectus (straight), transverse (across), etc
Location of muscle
Anterior, posterior, lateral, medial, intermediate, etc
Number of divisions
Number of heads (2 or 3)
Shape of muscle
Deltoid (Greek letter delta), Trapezius (trapezoid)
Point of attachment
Origins and inserts
Relative size
Maximus (largest), minimus (smallest), longus (long), brevis (short)
Isotonic and isometric
What are the two types of muscle contractions?
Isotonic Contraction
Muscle changes length as it contracts and moves a load
Concentric and eccentric
What are two types of isotonic contractions?
Concentric contraction
Muscle shortens as it contracts
Eccentric contraction
muscle contracts as it lengthens
Isometric contraction
Muscle has no change in length as it contracts
Skeletal muscles
Which muscle is arranged in opposing pairs?
Agonist
Prime mover
Antagonist
counteracts agonist
Synergists
Aids agonist by promoting same movement or becomes a joint stabilizer to reduce effort
Fixators
Immobilize one or more bones to form stable base
Origin
Point where muscle attaches to a more stationary bone
Insertion
Point where muscle attaches to a more moved bone
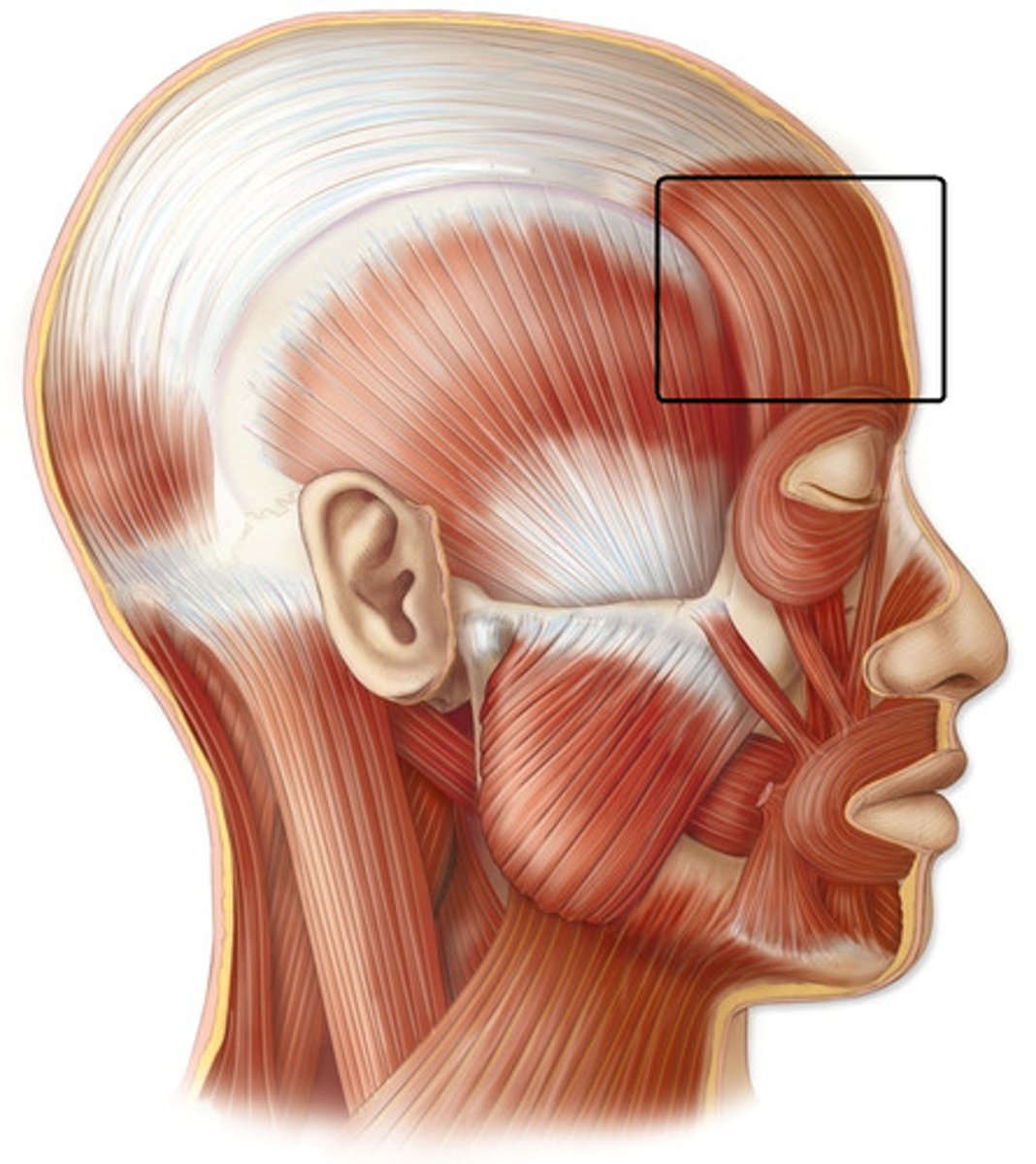
Frontalis
Orbicularis oculi

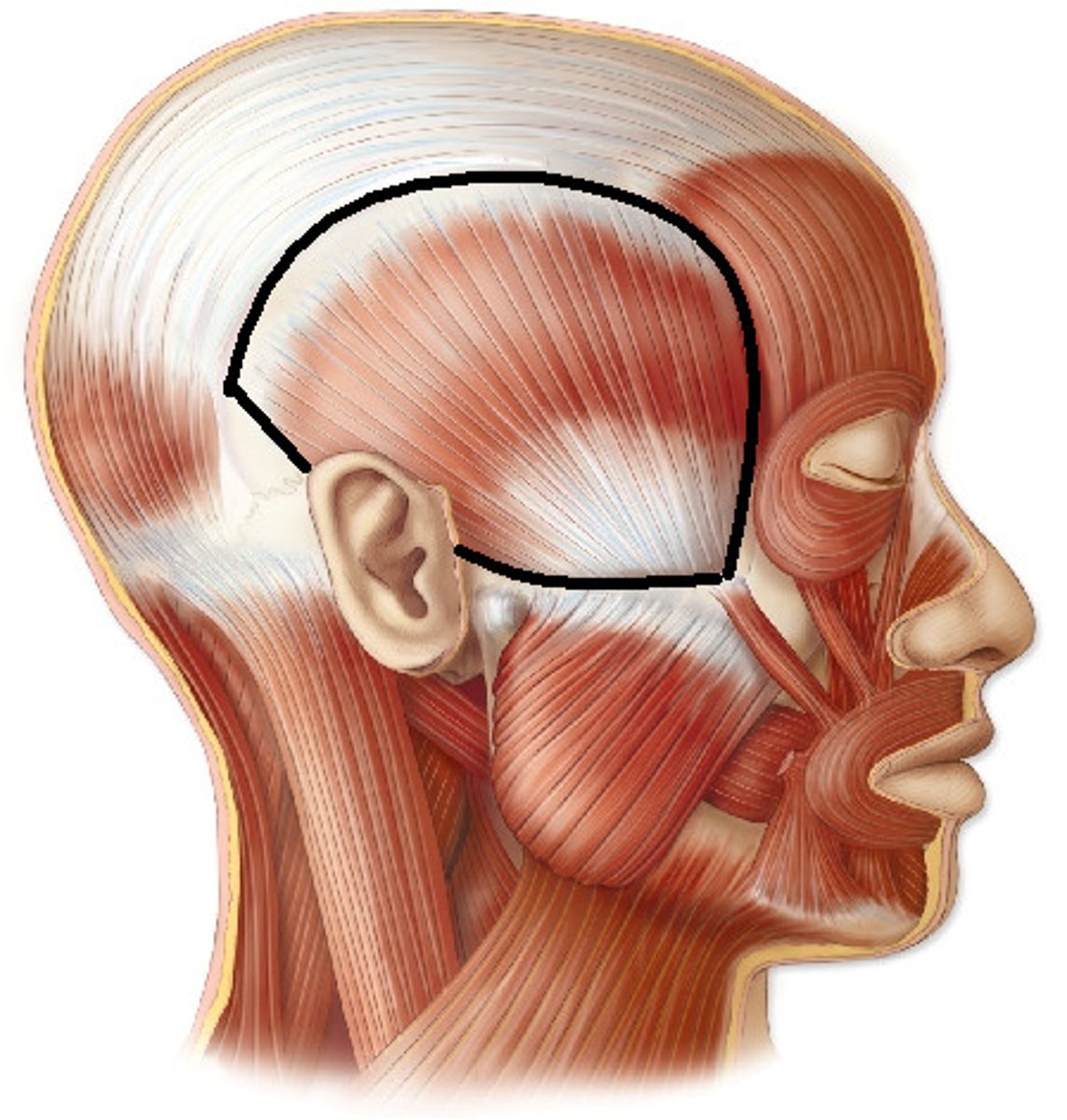
Temporalis
Zygomaticus
Orbicularis oris
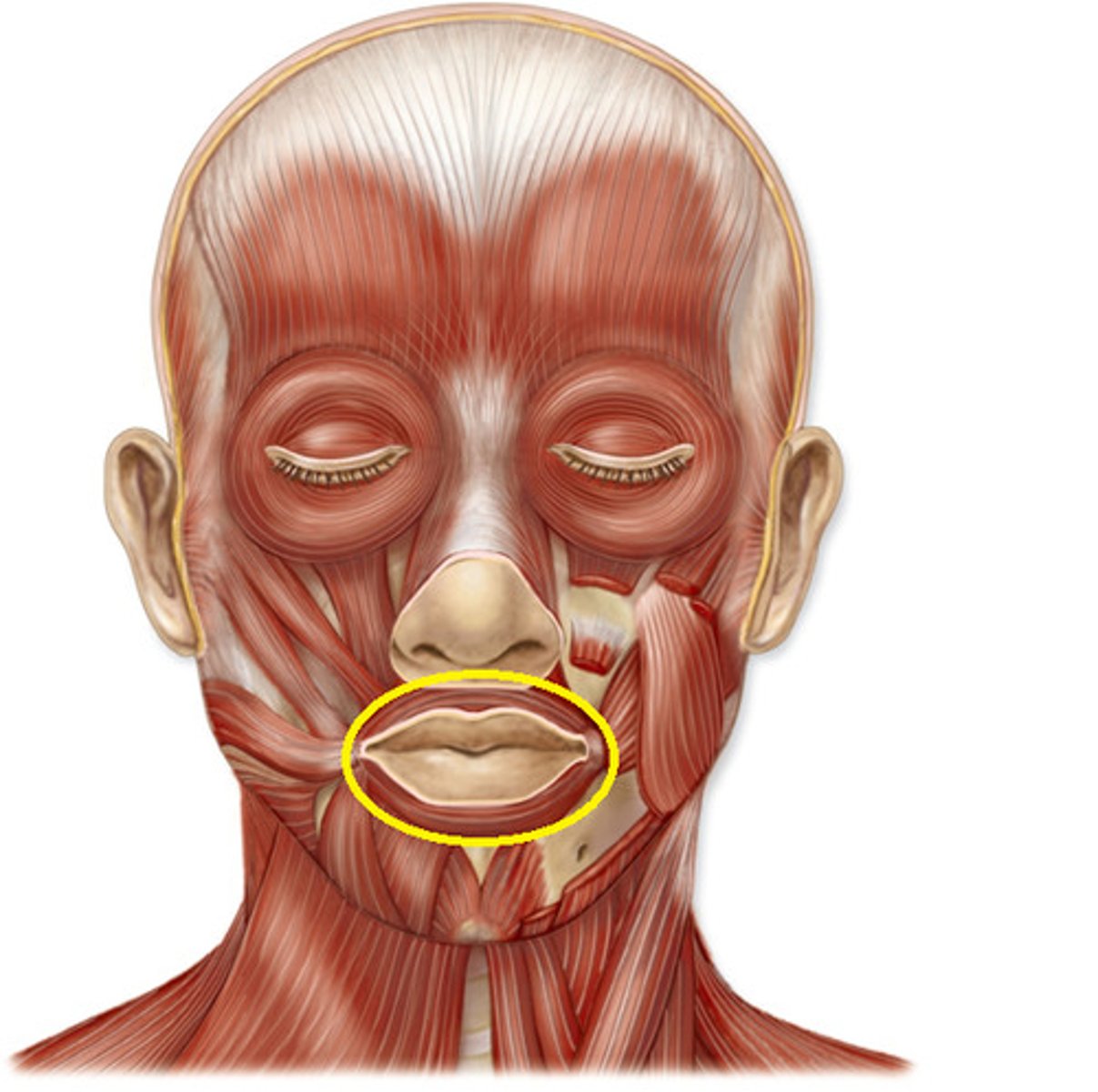
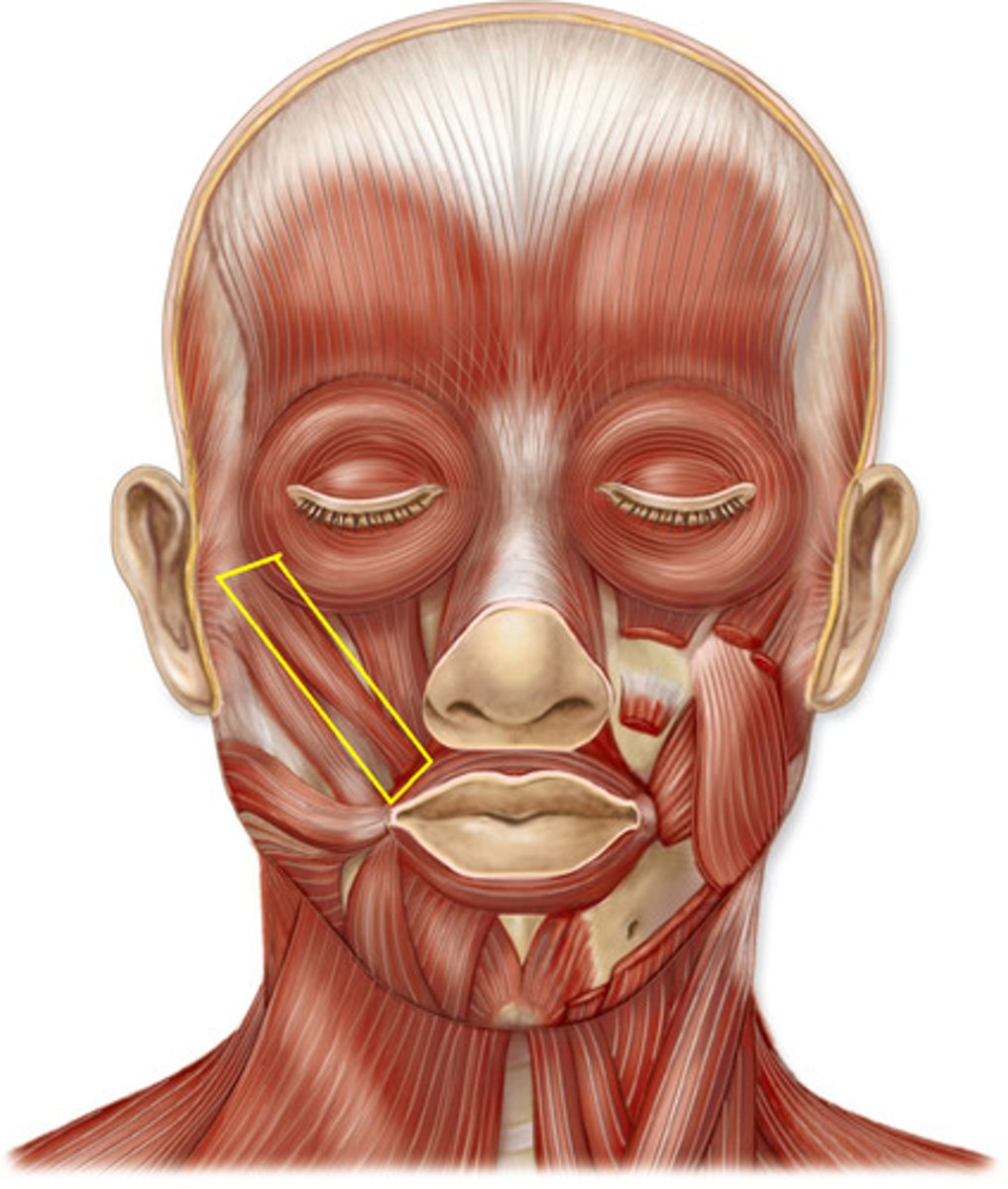
Buccinator
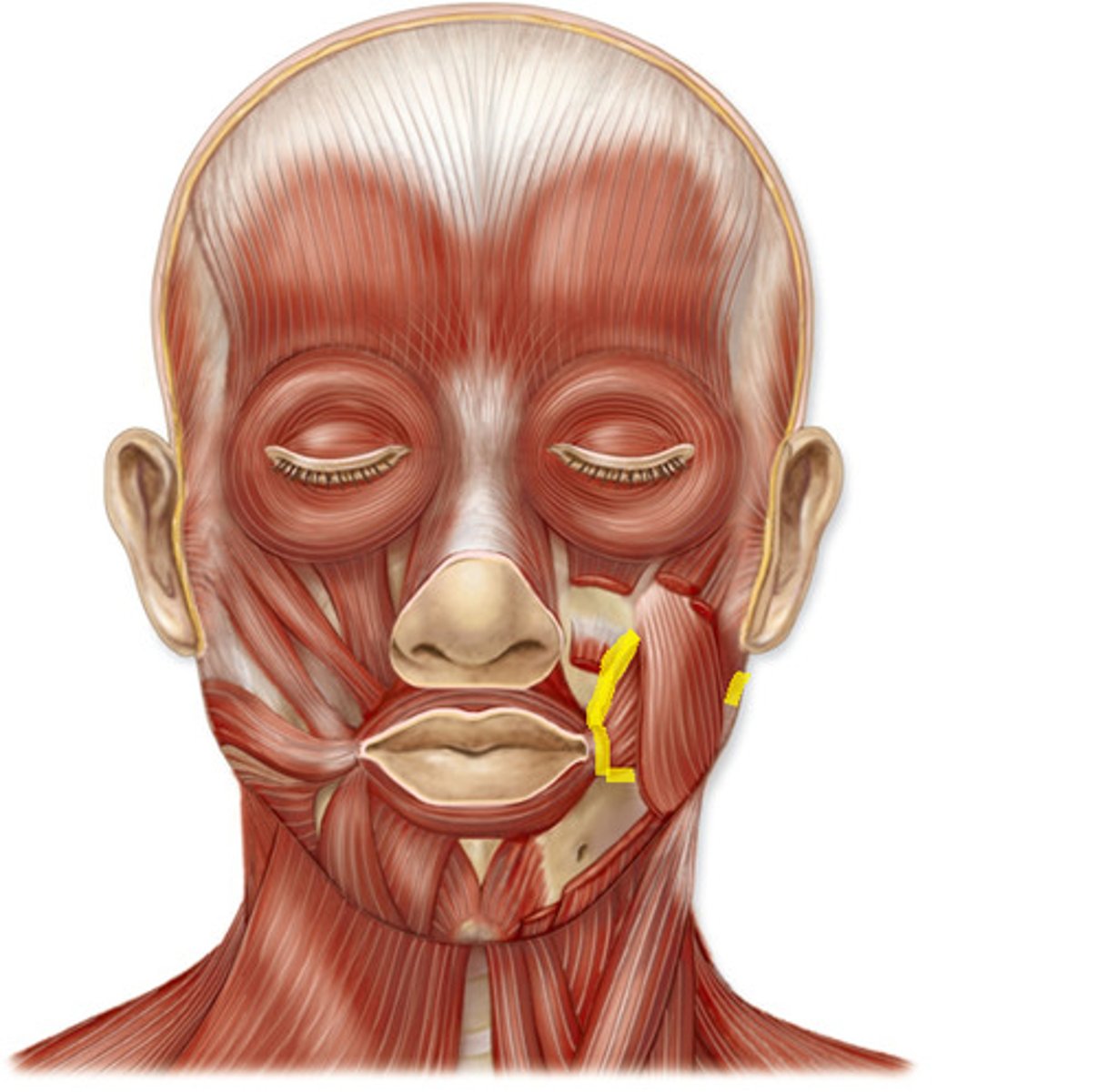
Masseter
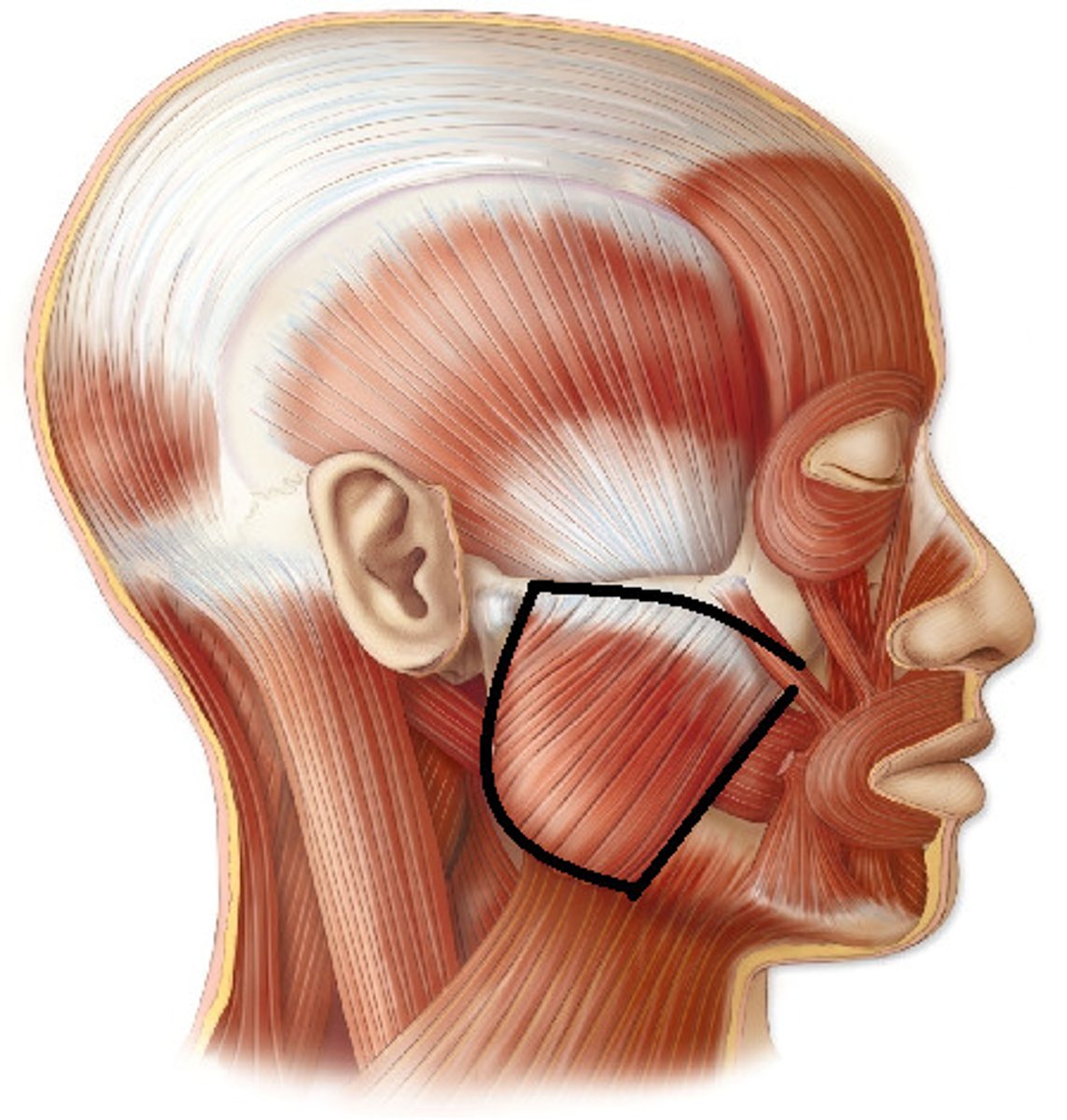
Triangularis
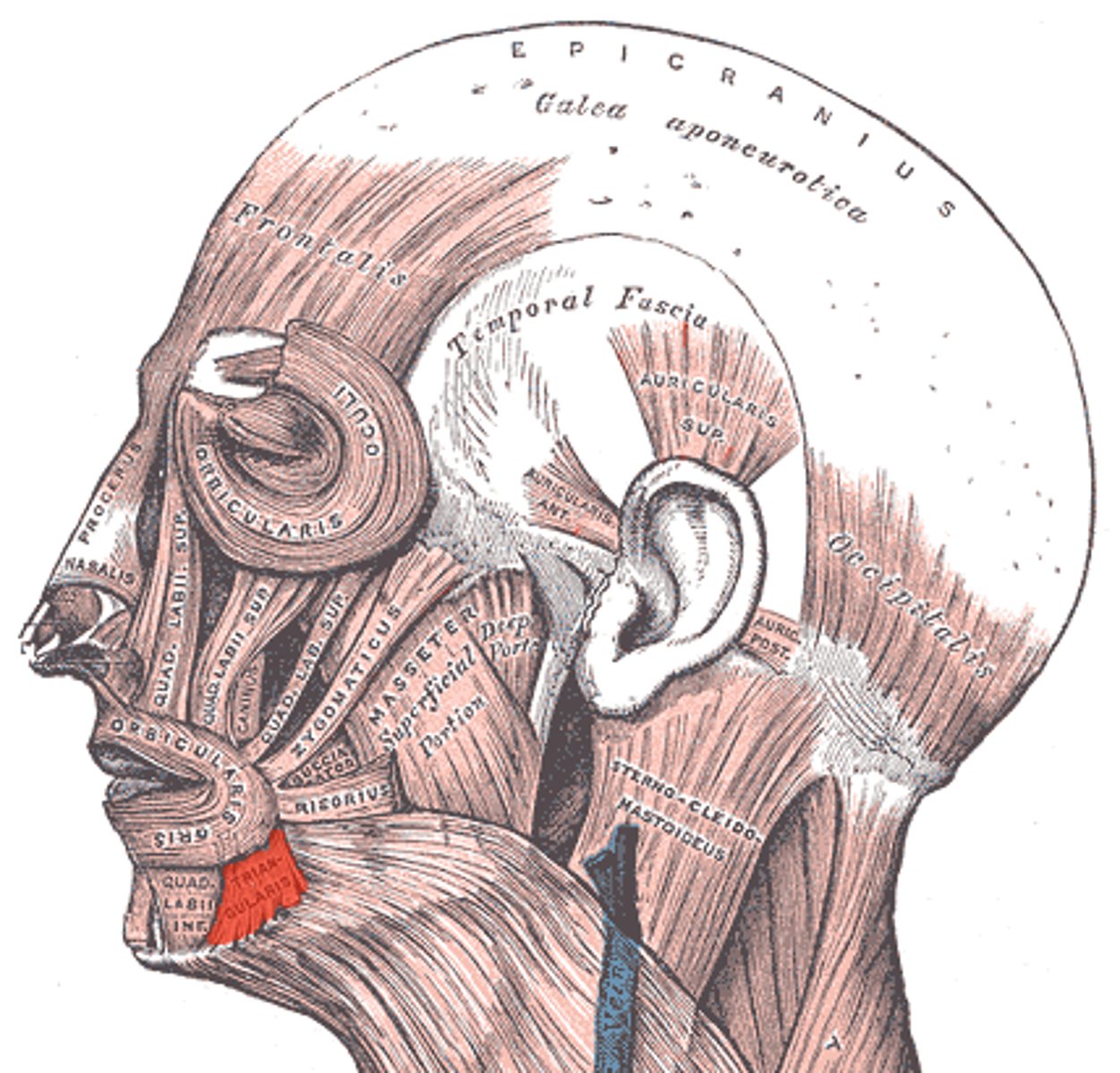
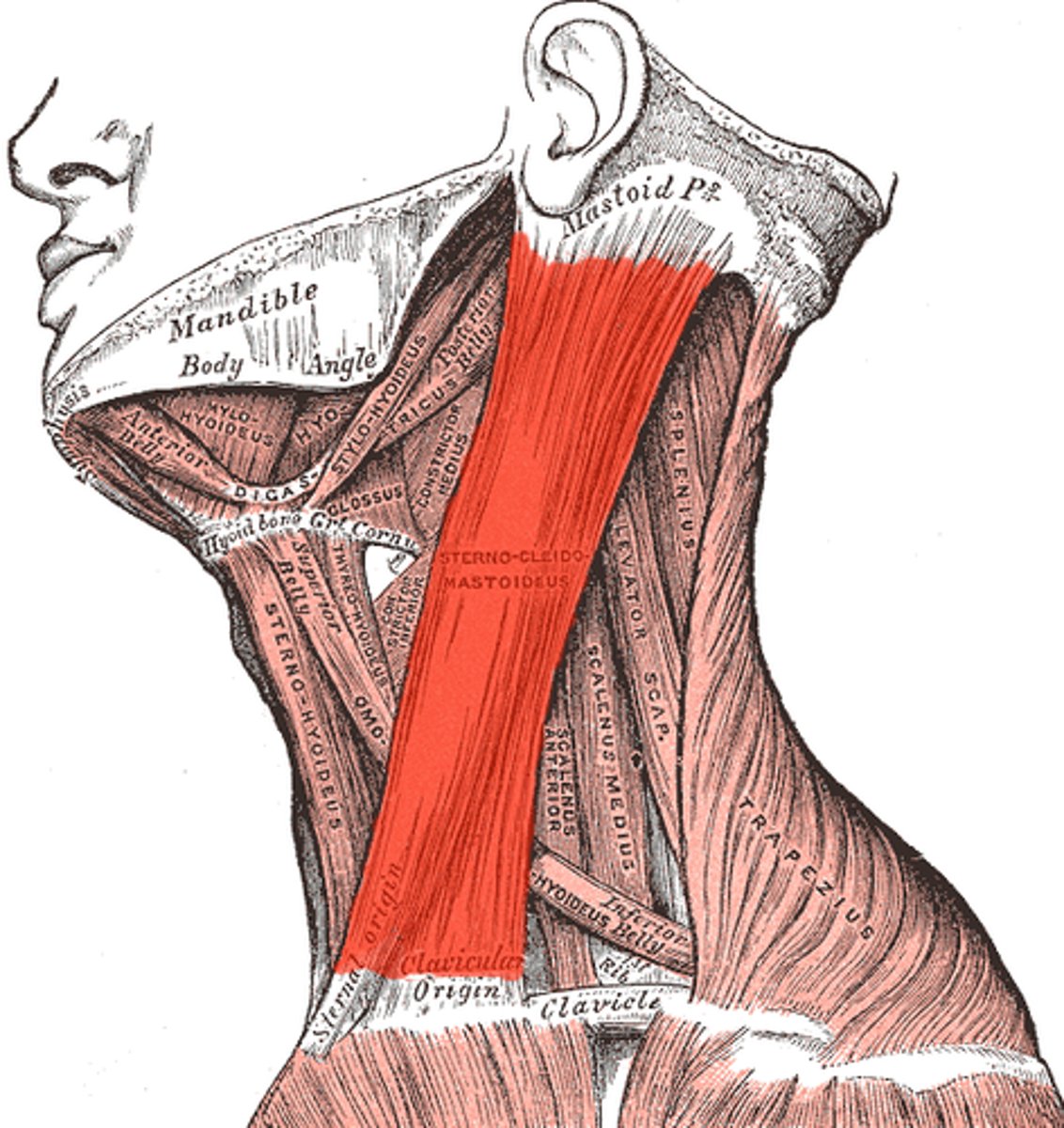
Sternocleidomastoid
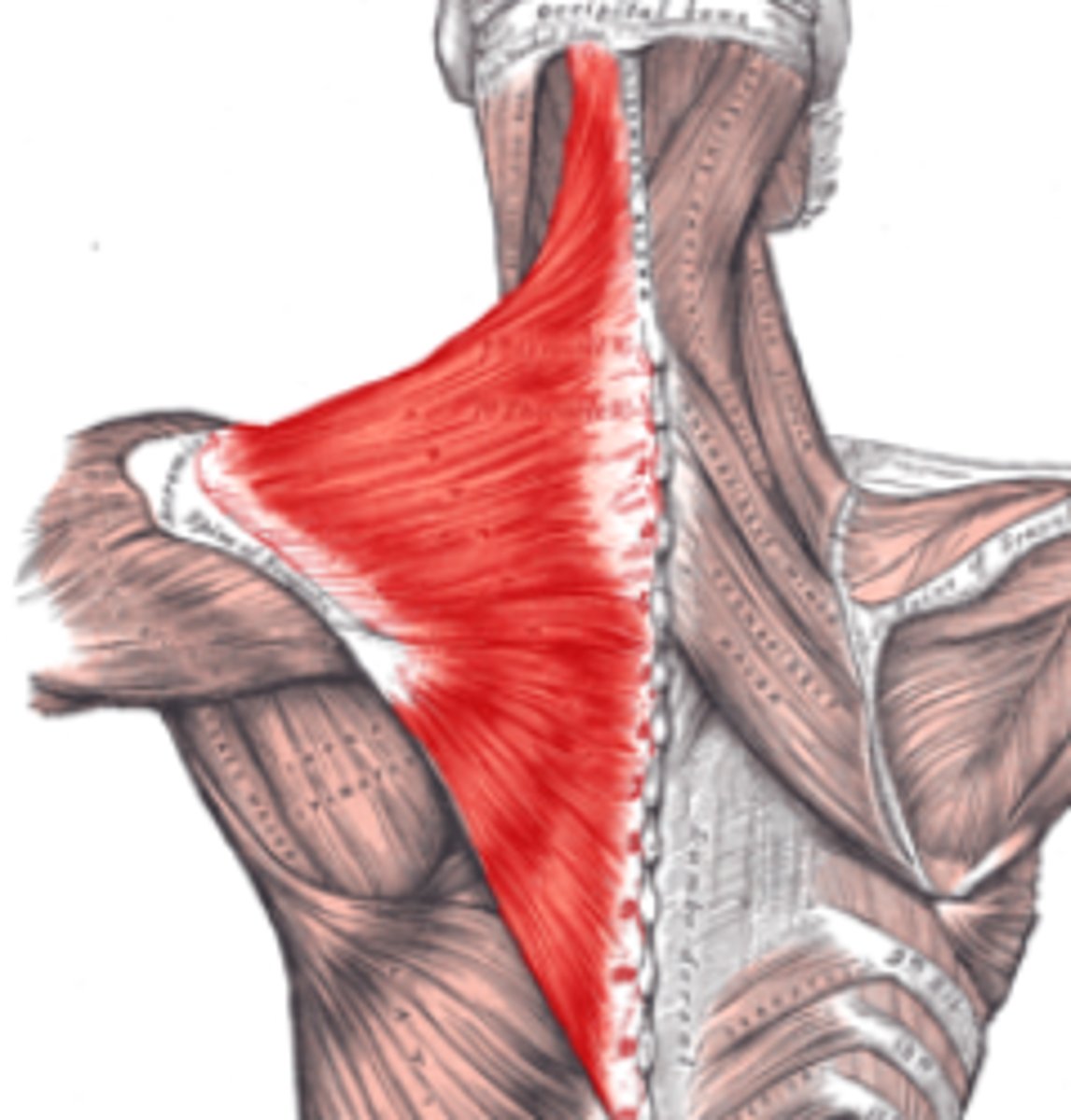
Trapezius
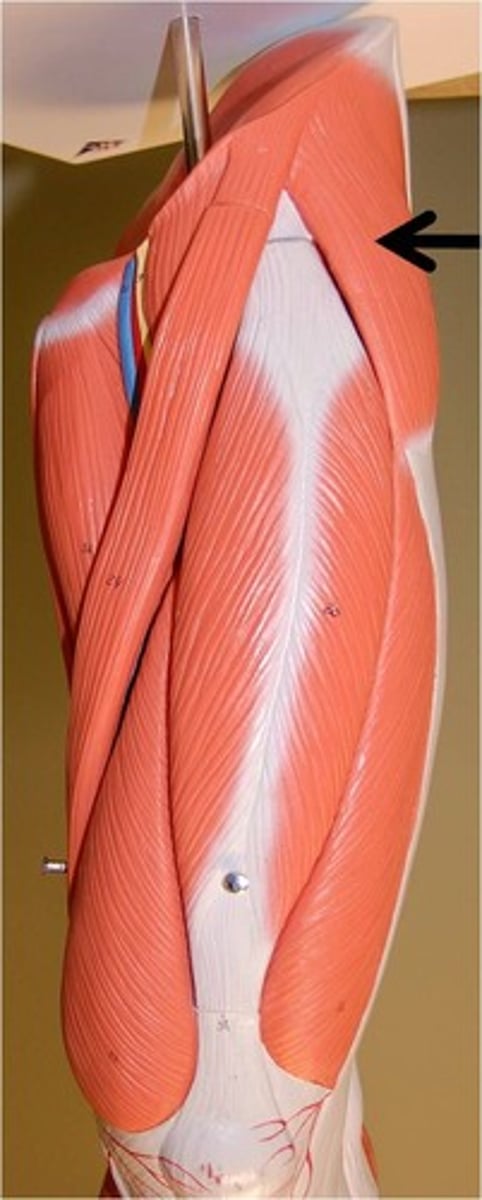
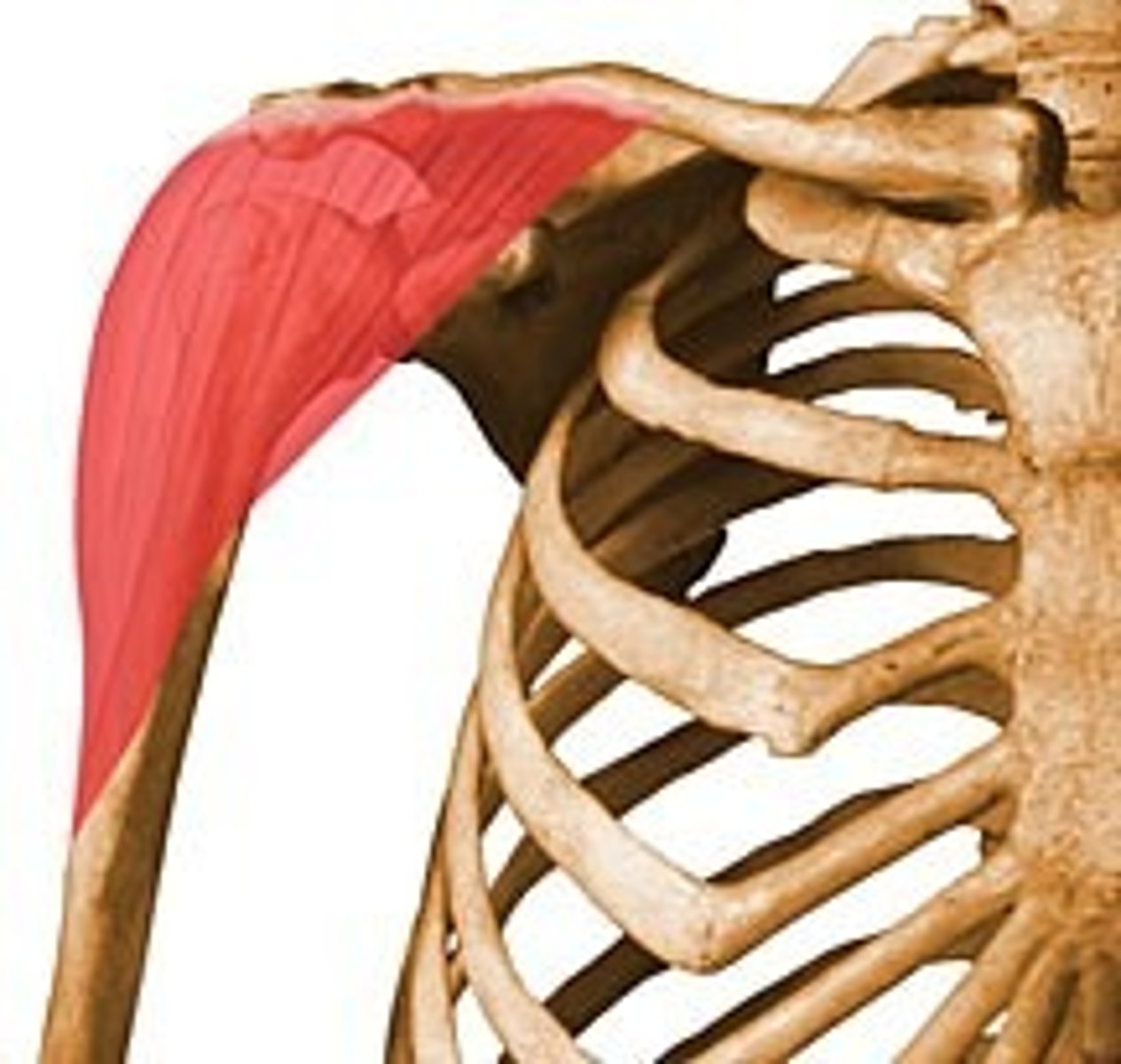
Deltoid
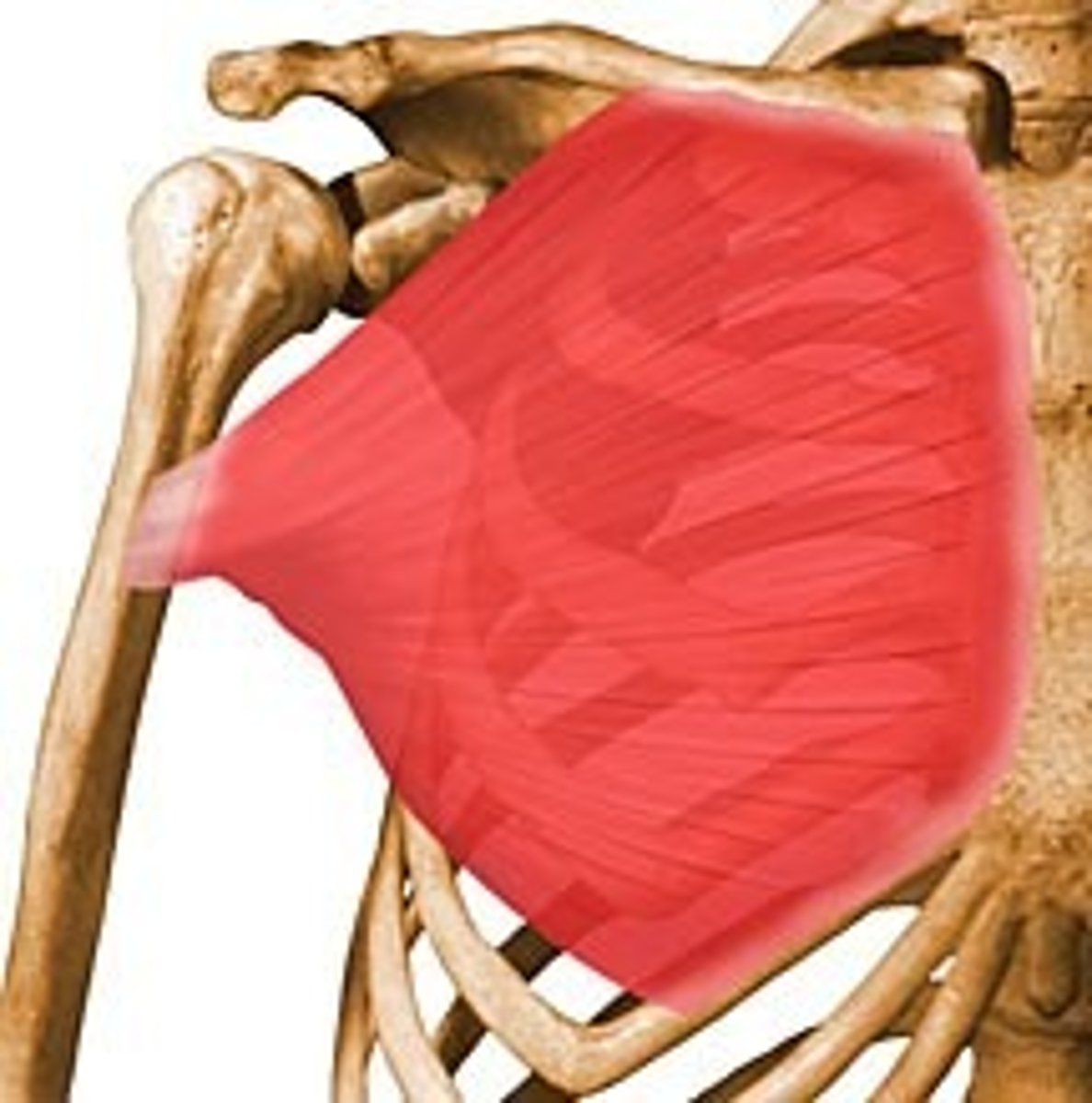
Pectoralis Major
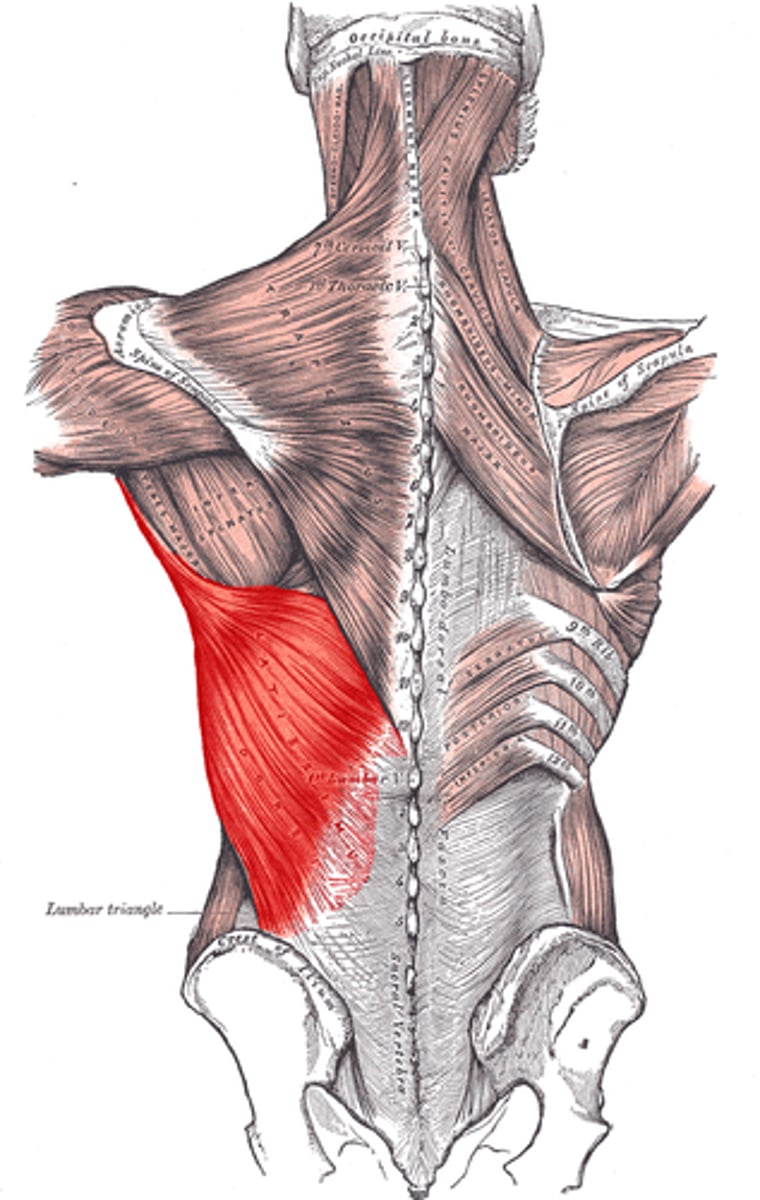
Latissimus dorsi
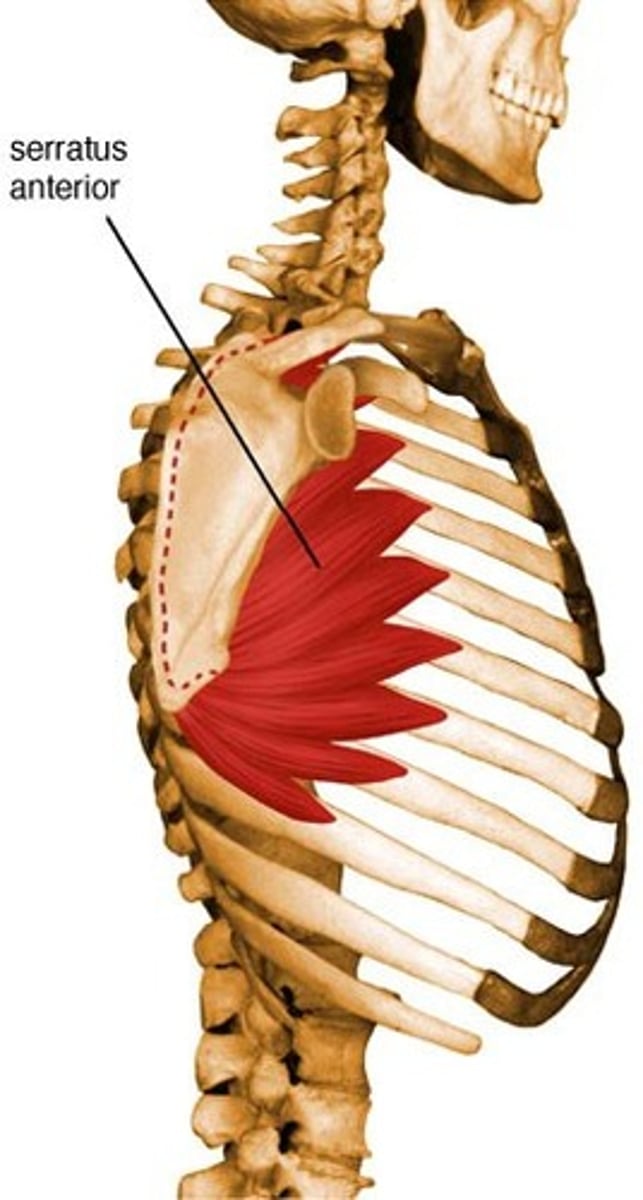
Serratus Anterior
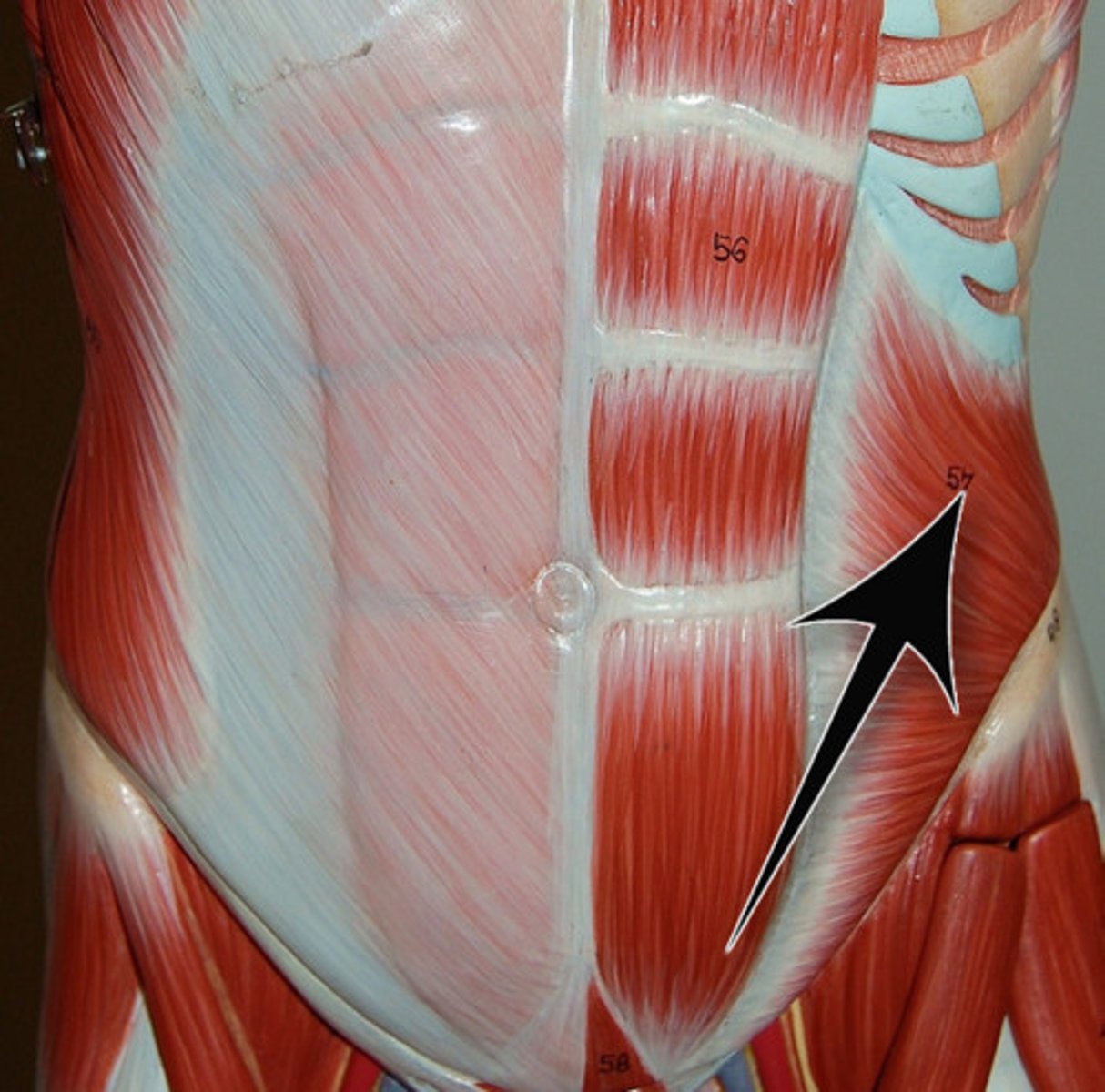
External oblique
Internal oblique
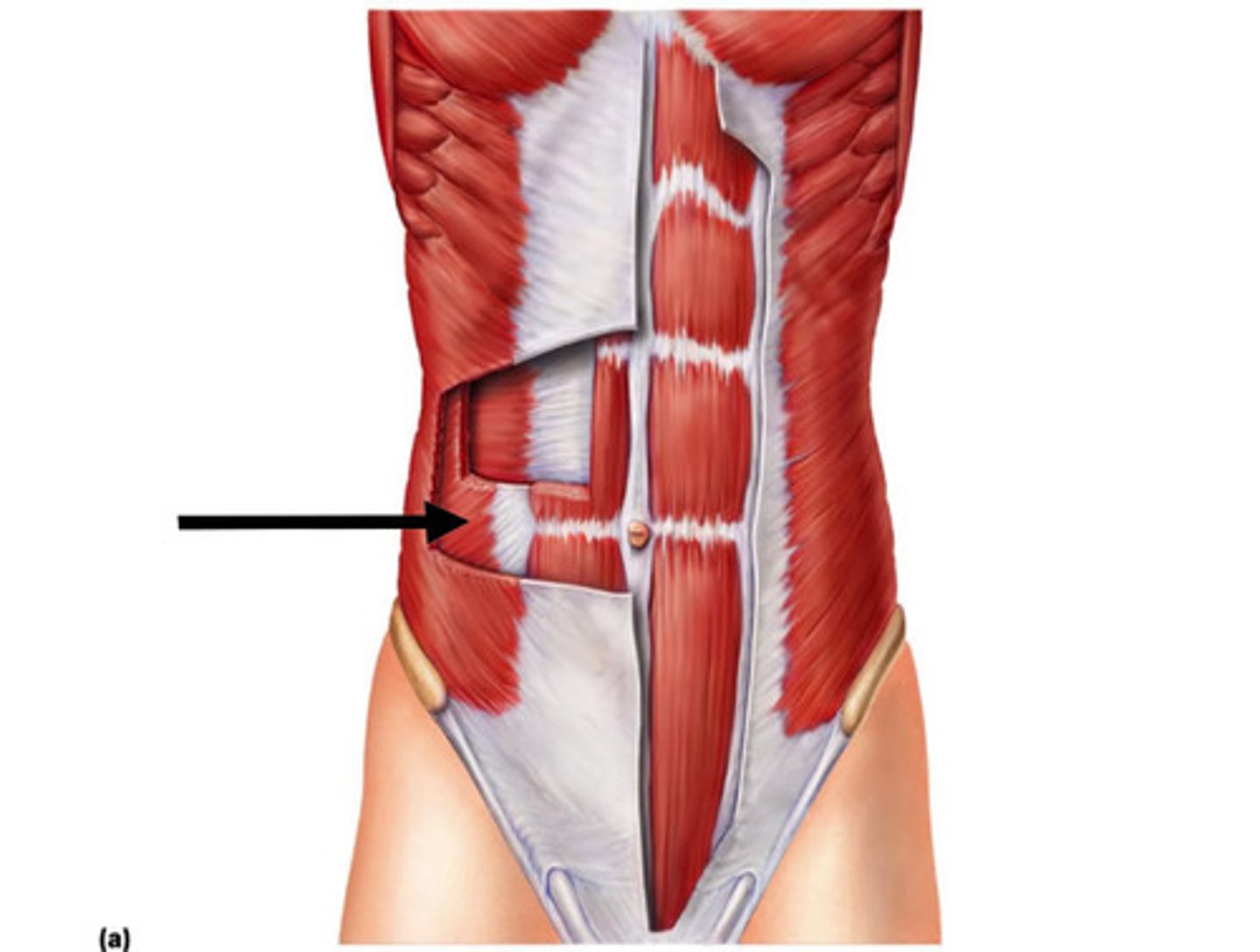
Rectus abdominus
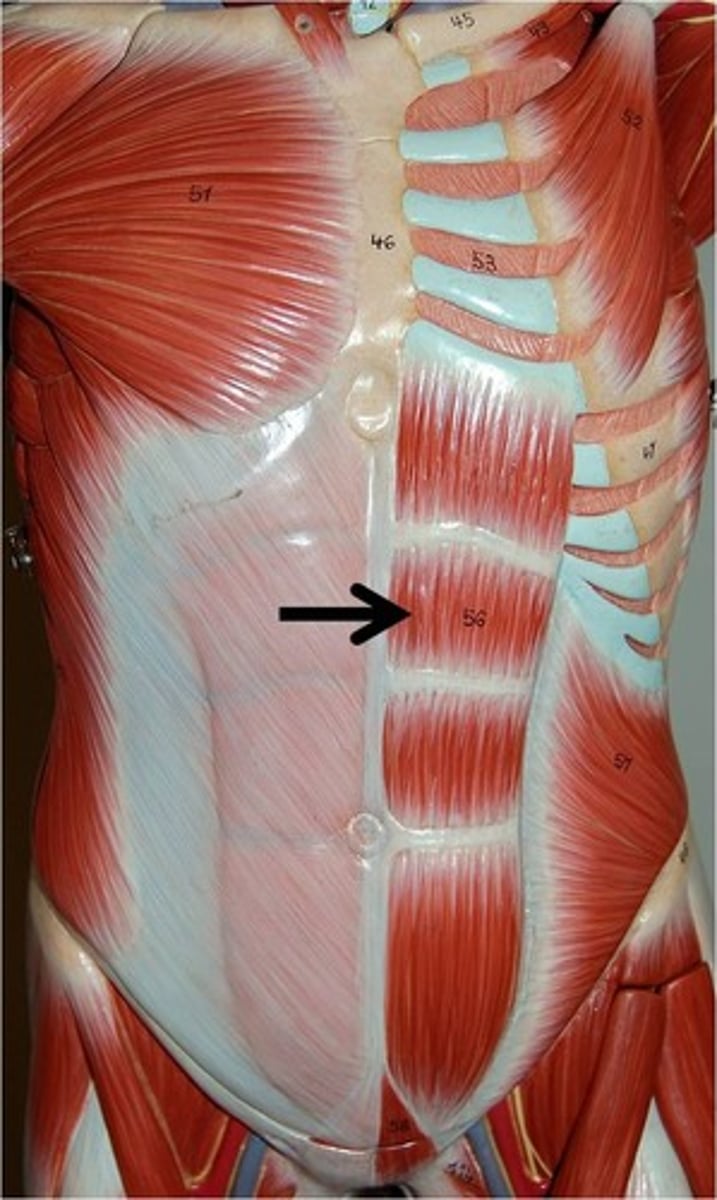
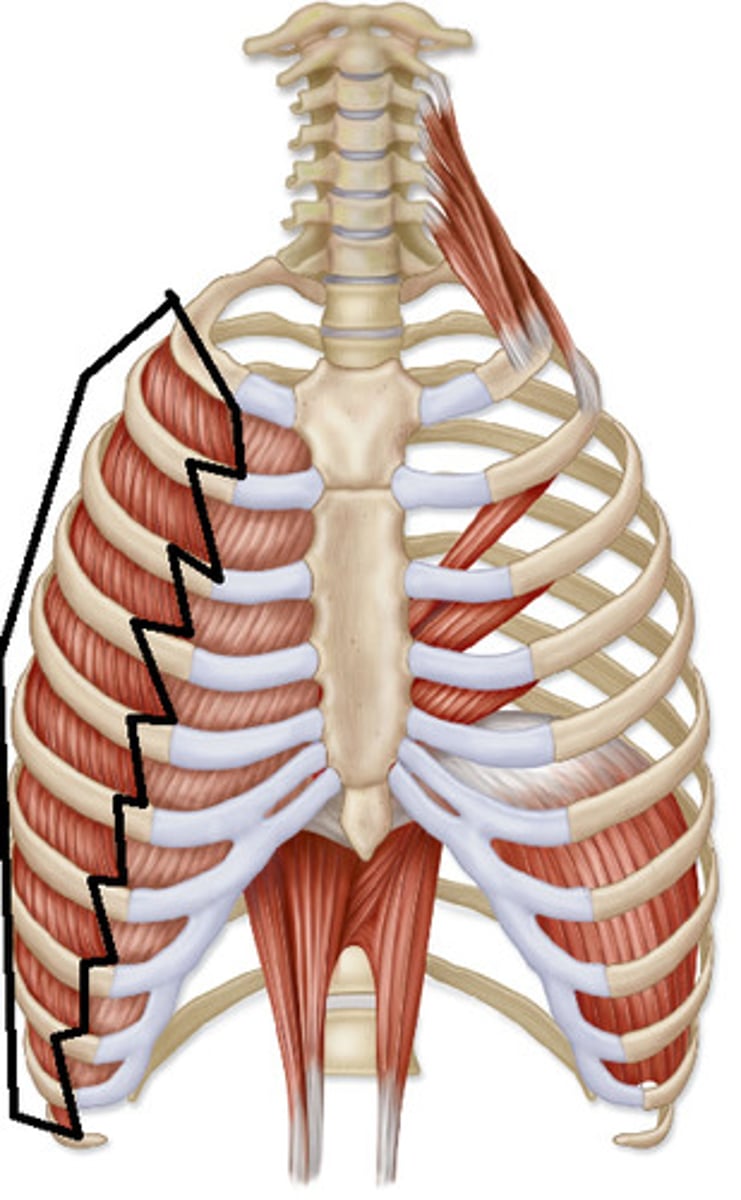
External intercostals
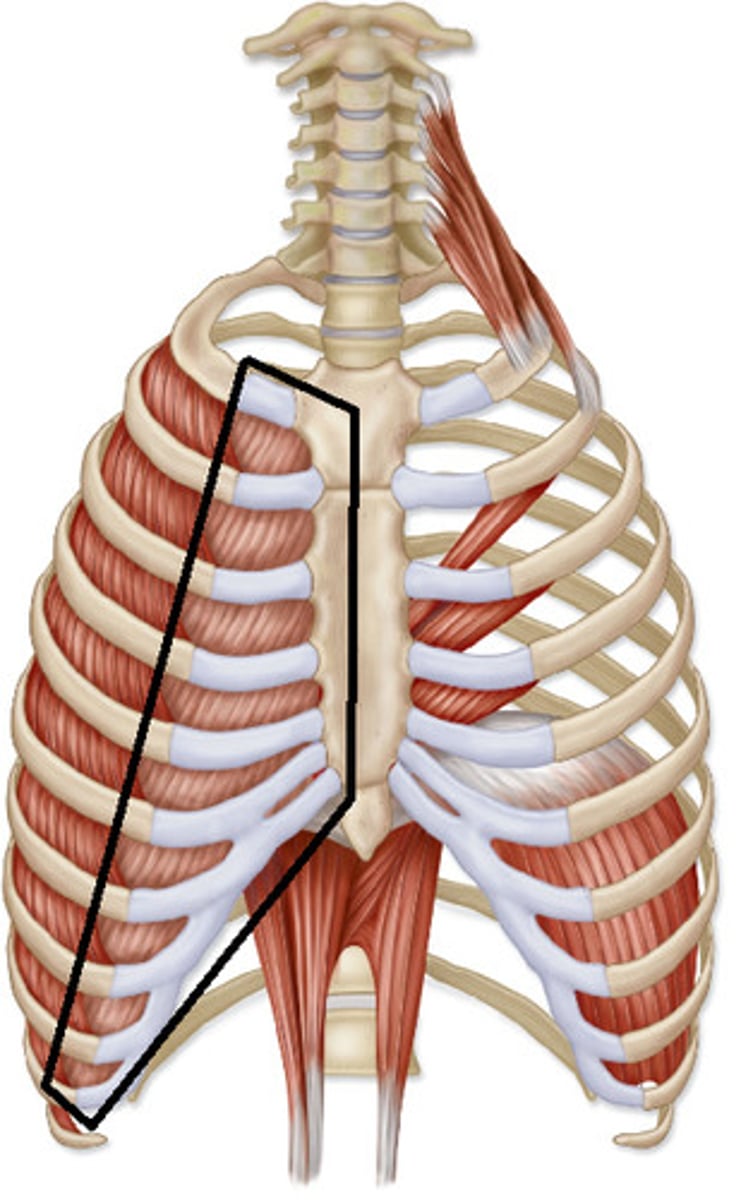
Internal intercostals
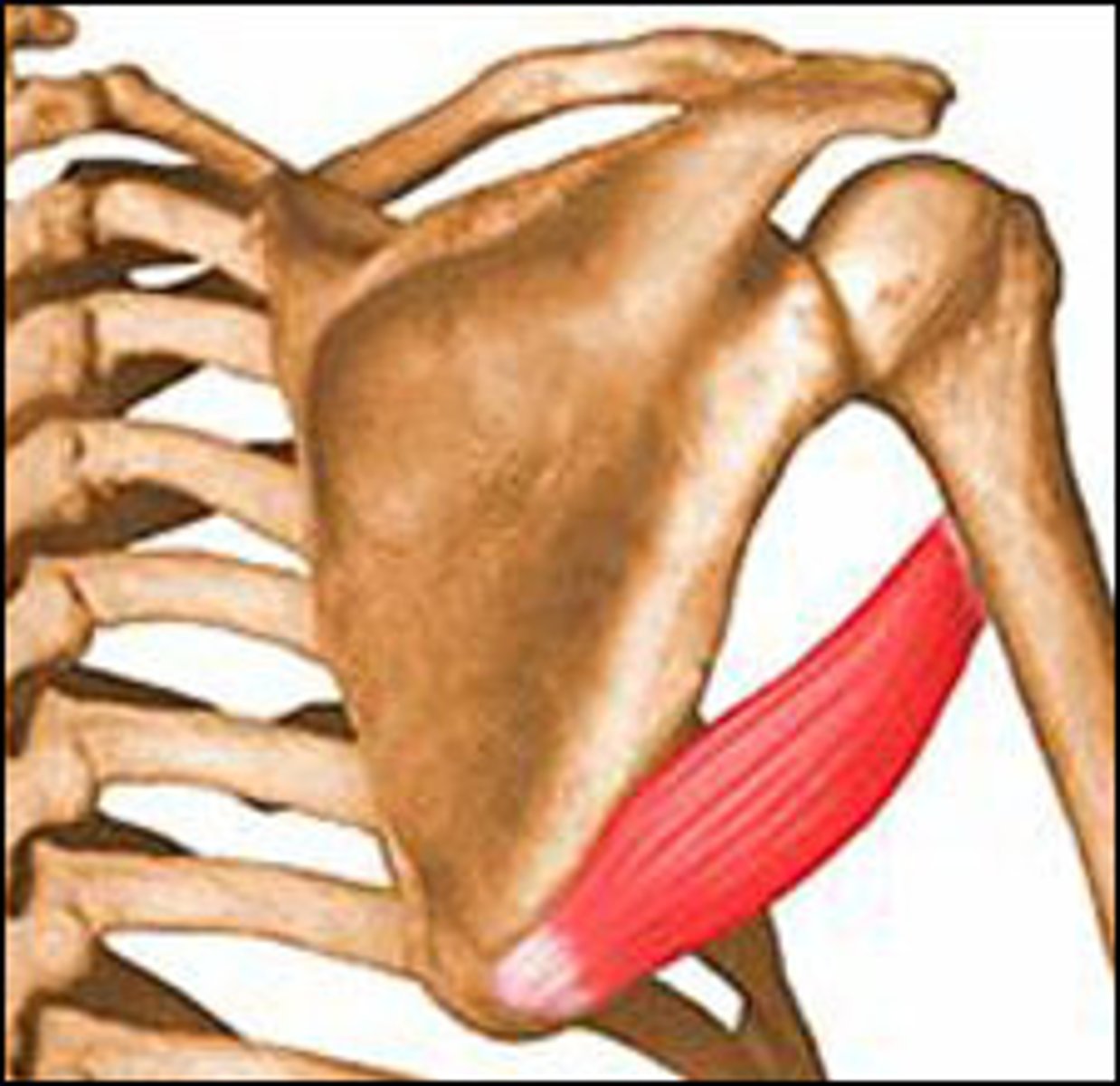
Teres major
Supraspinatus
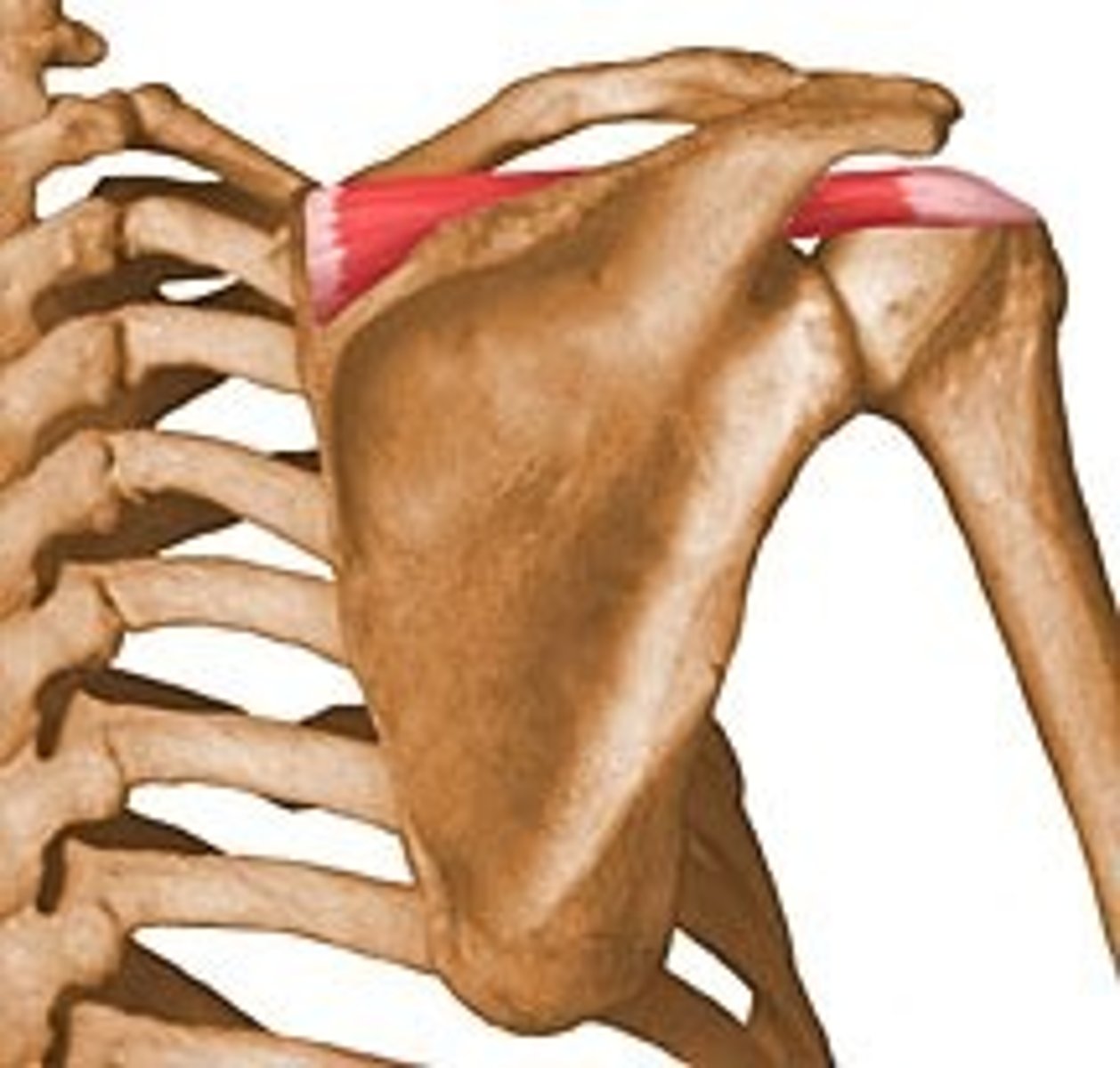
Infraspinatus
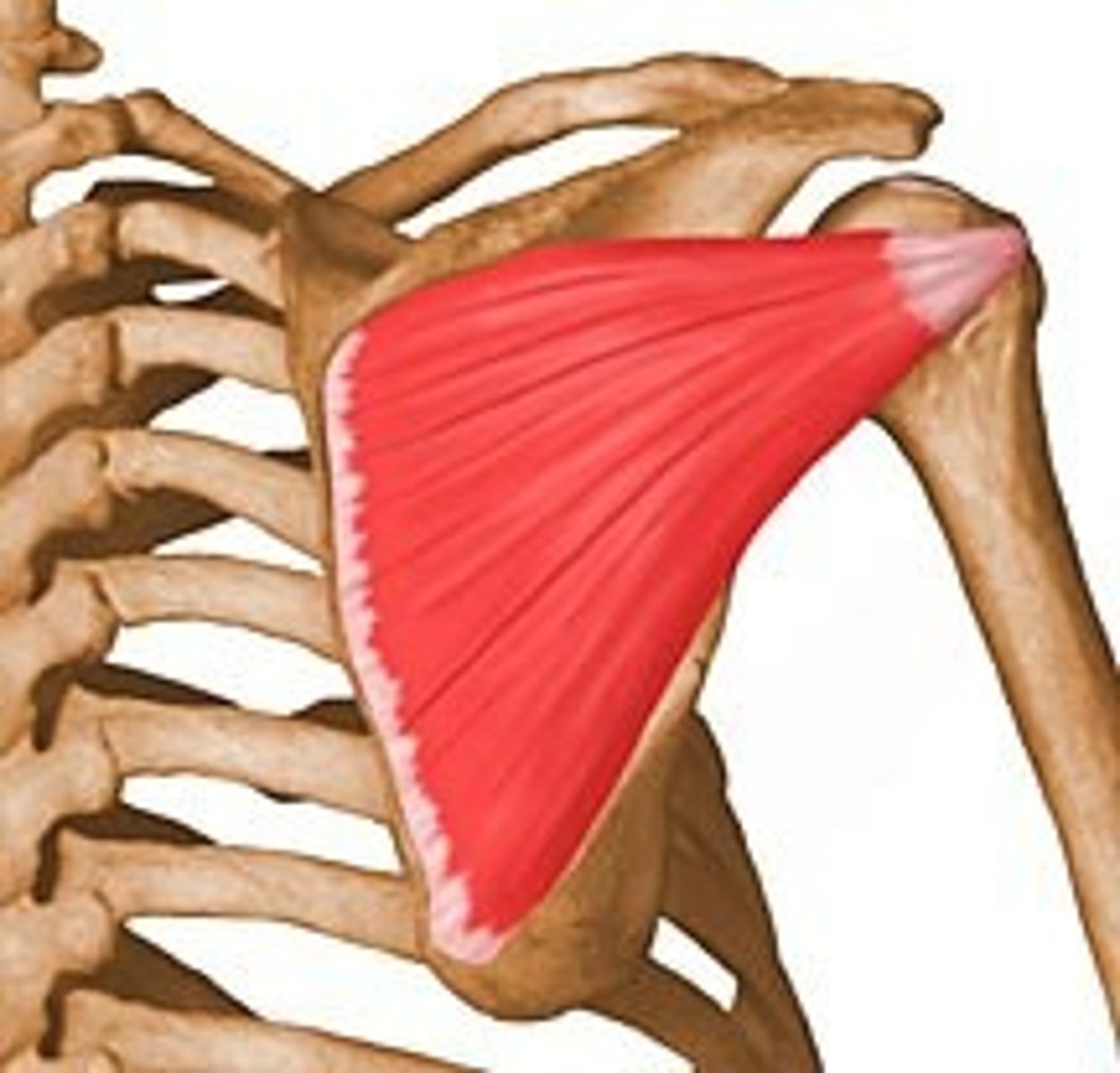
Teres minor
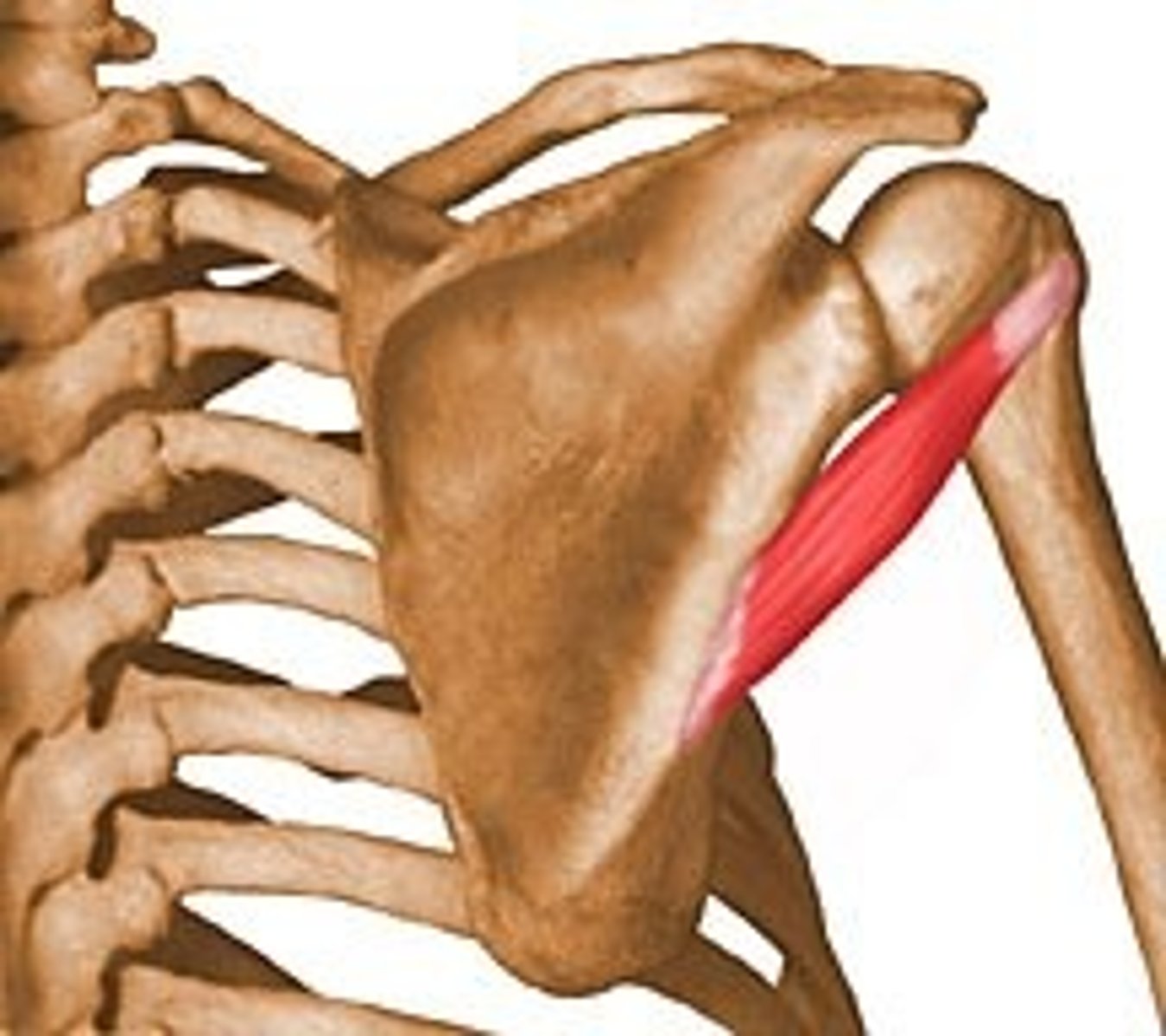
Subscapularis
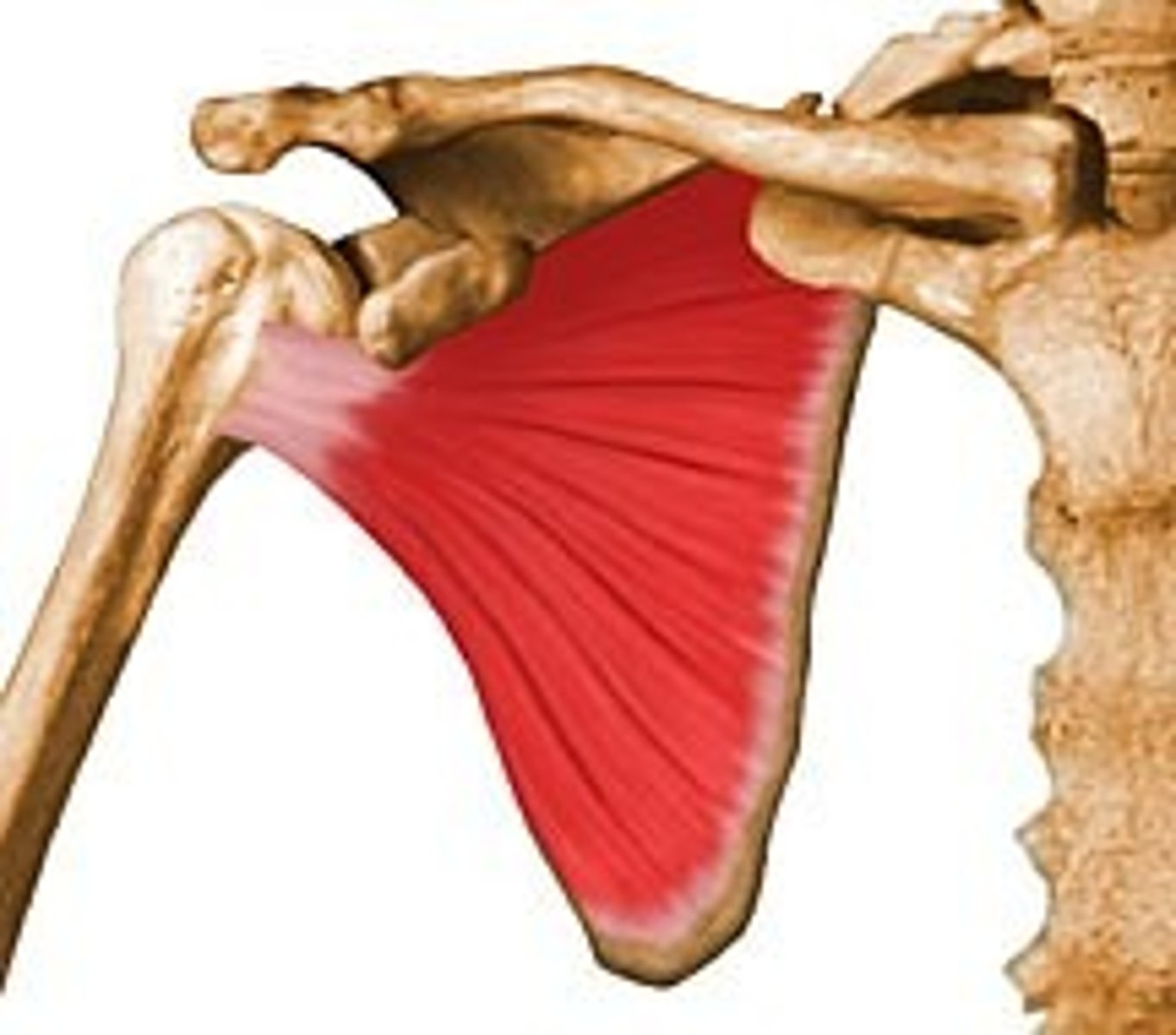
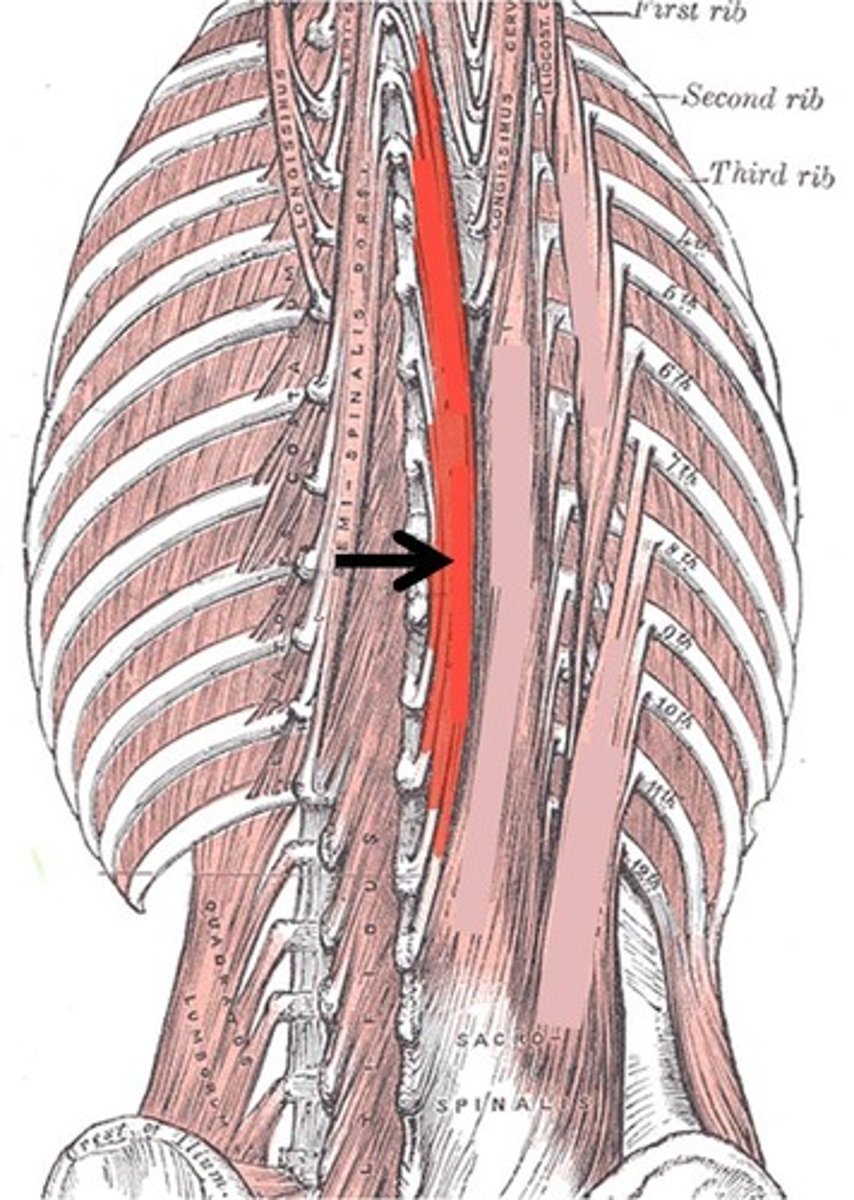
Spinalis
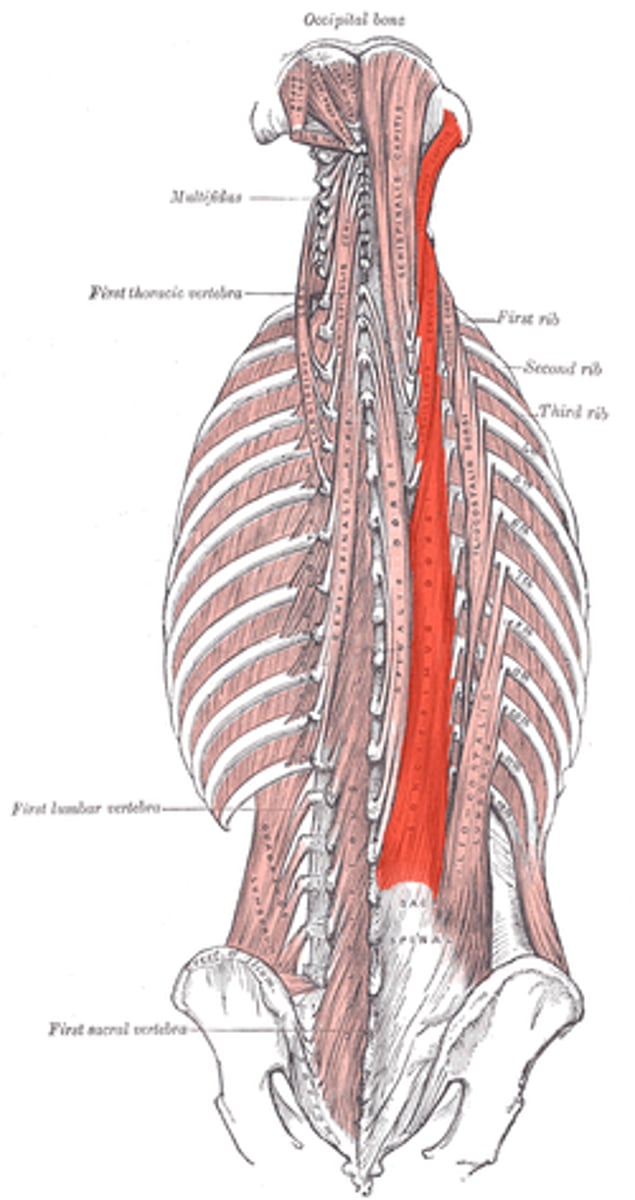
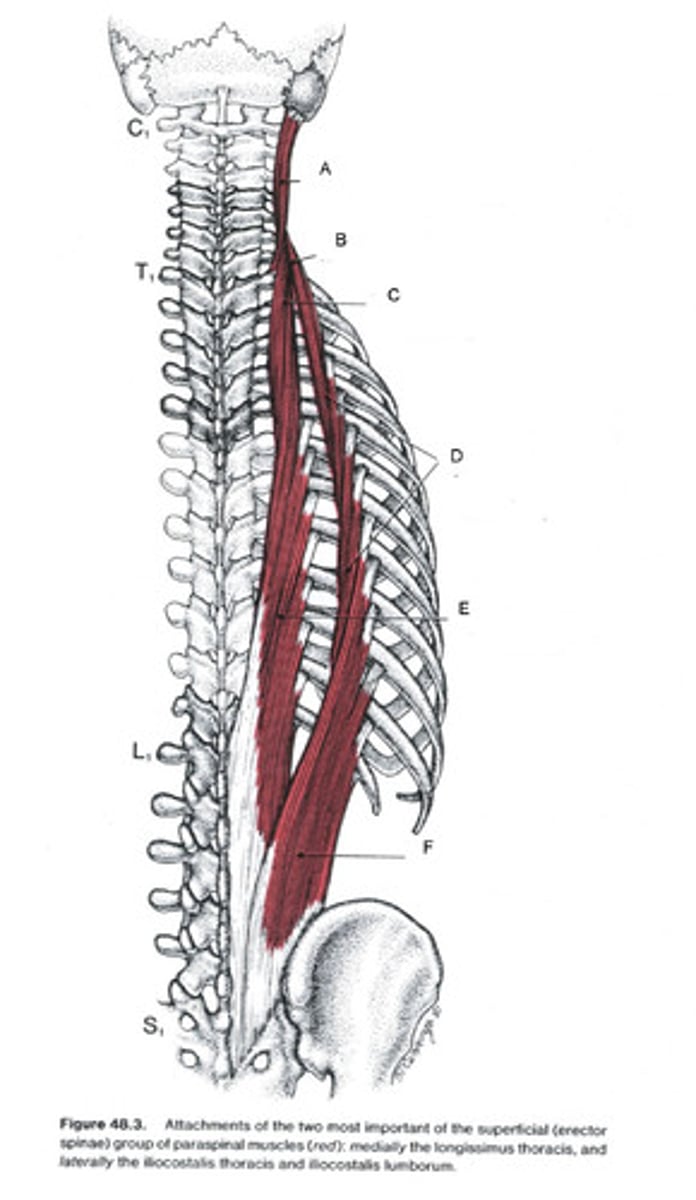
Longissimus
Ilocostalis
Triceps
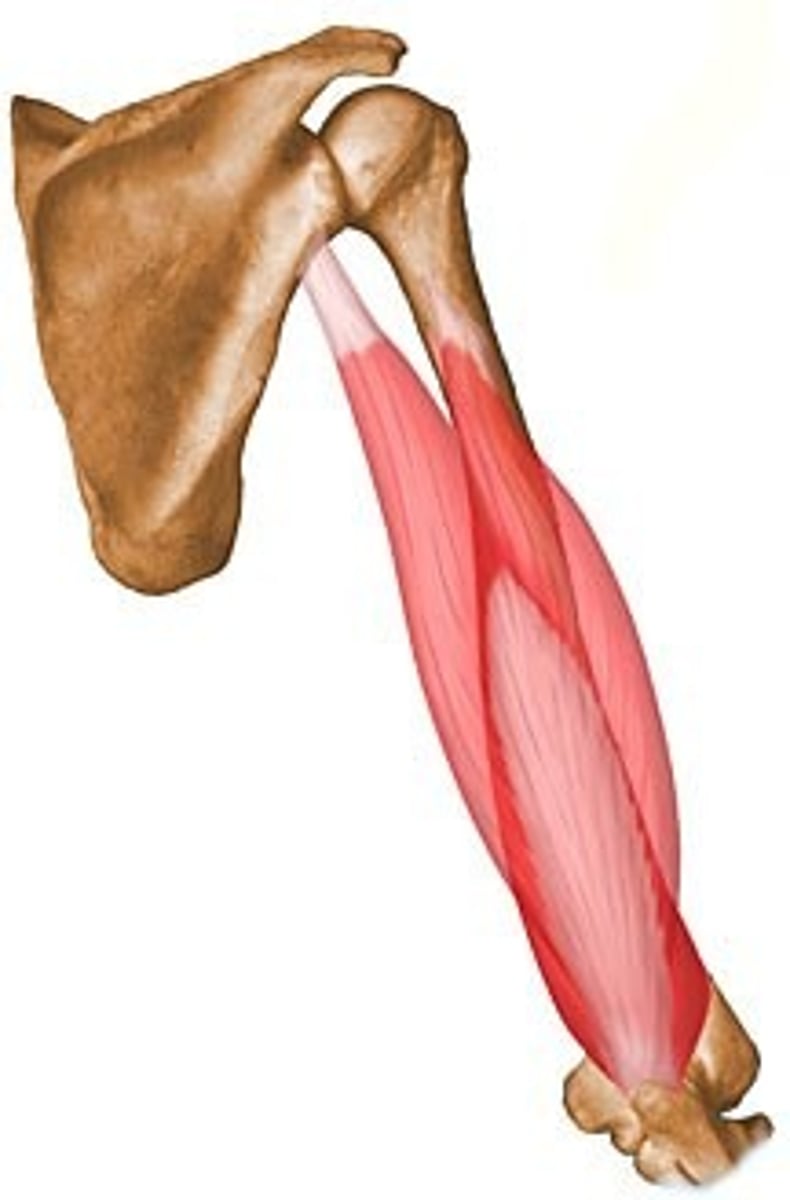
Biceps
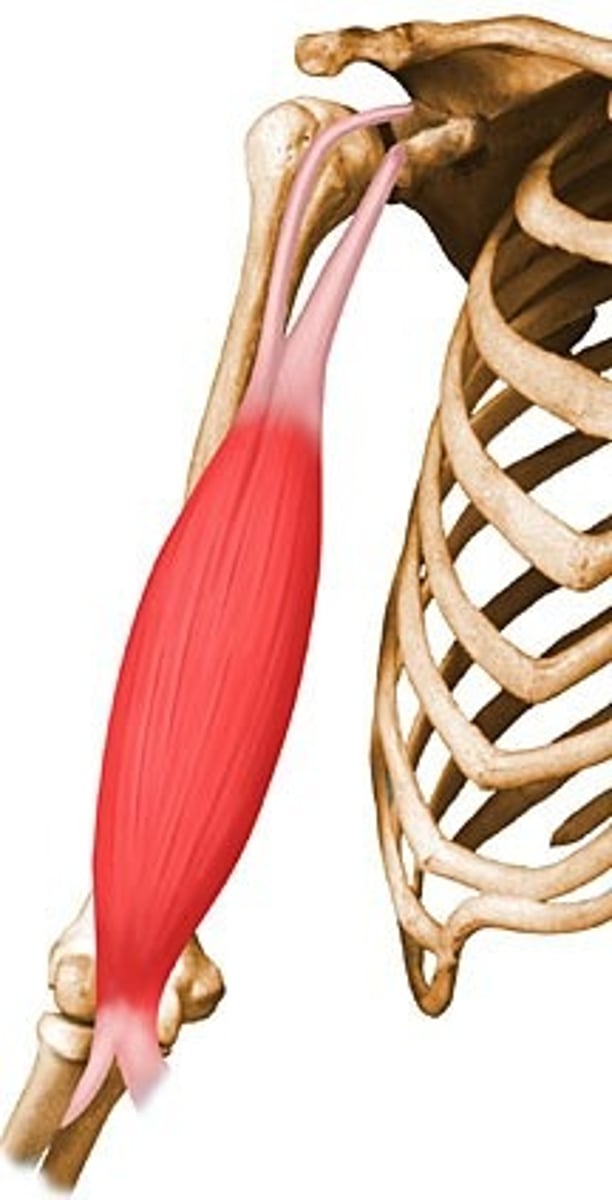
Brachialis
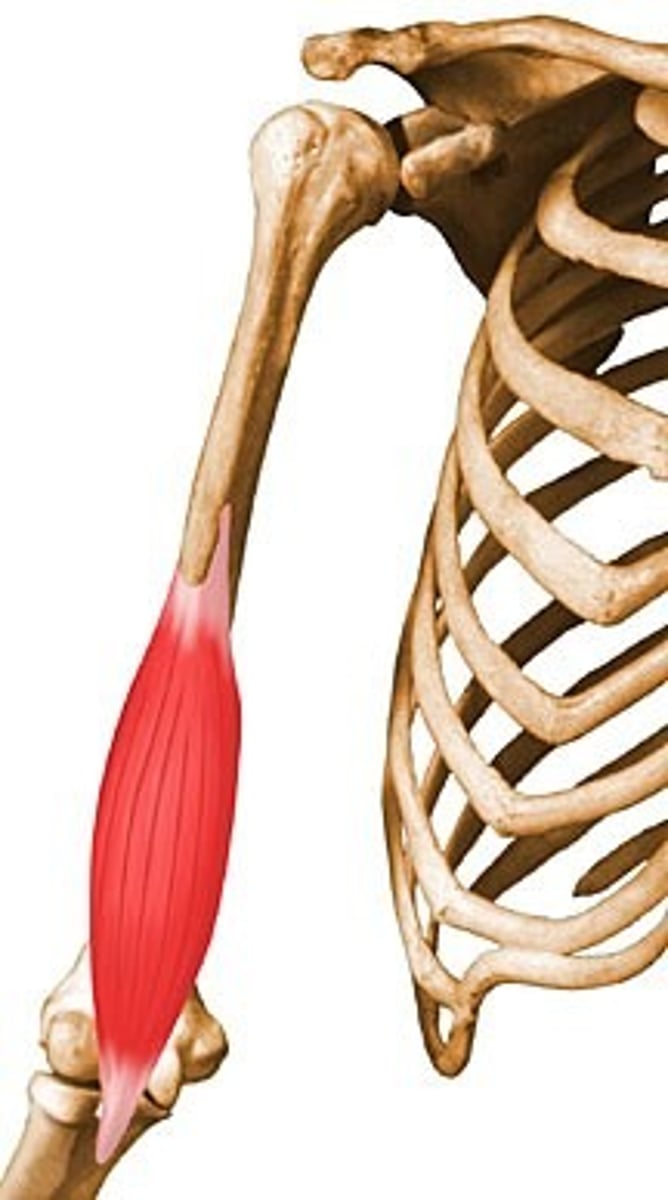
Pronator teres
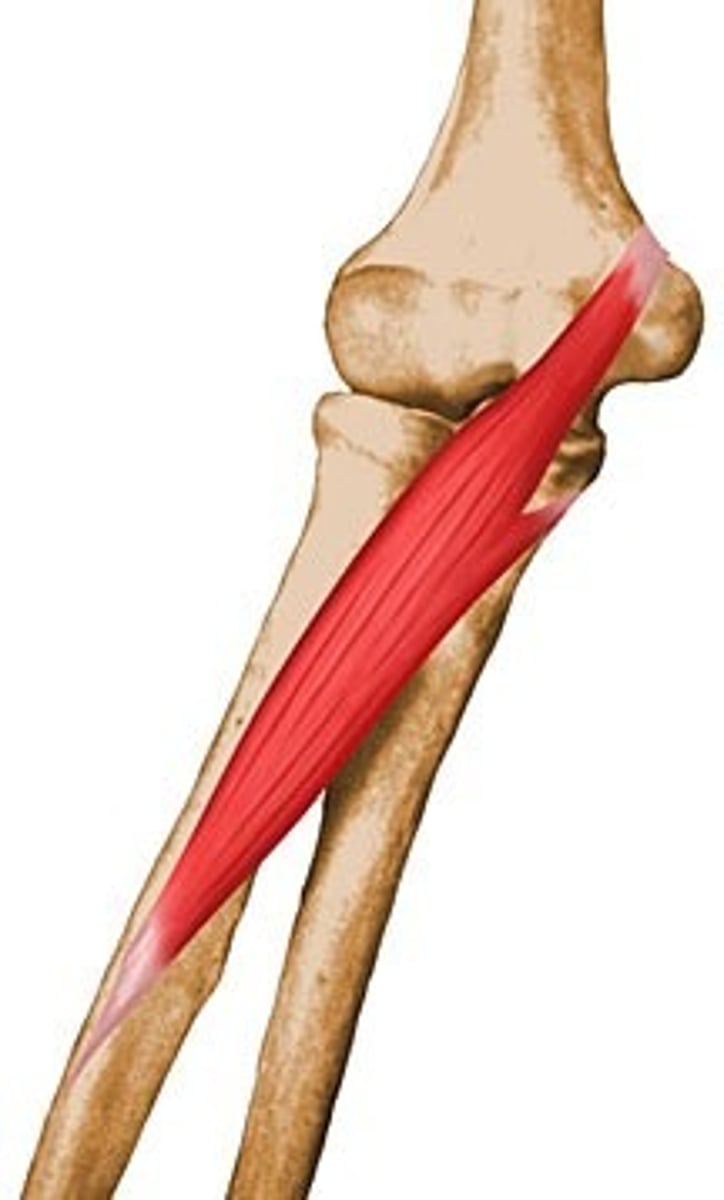
Brachioradialis
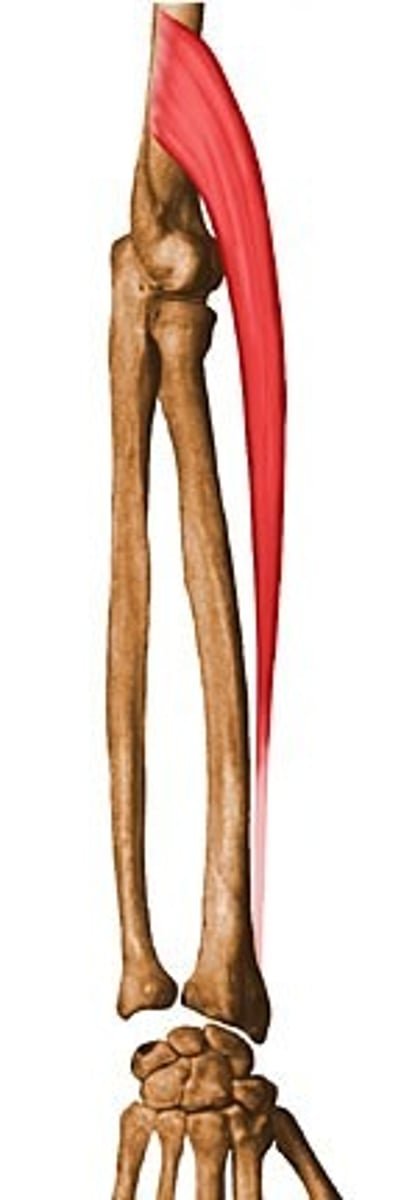

Flexor carpi radialis
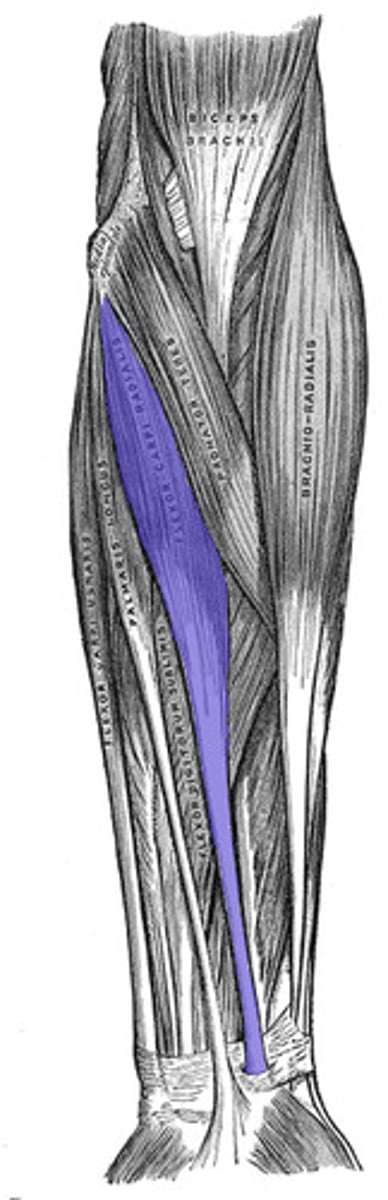
Palmaris longus
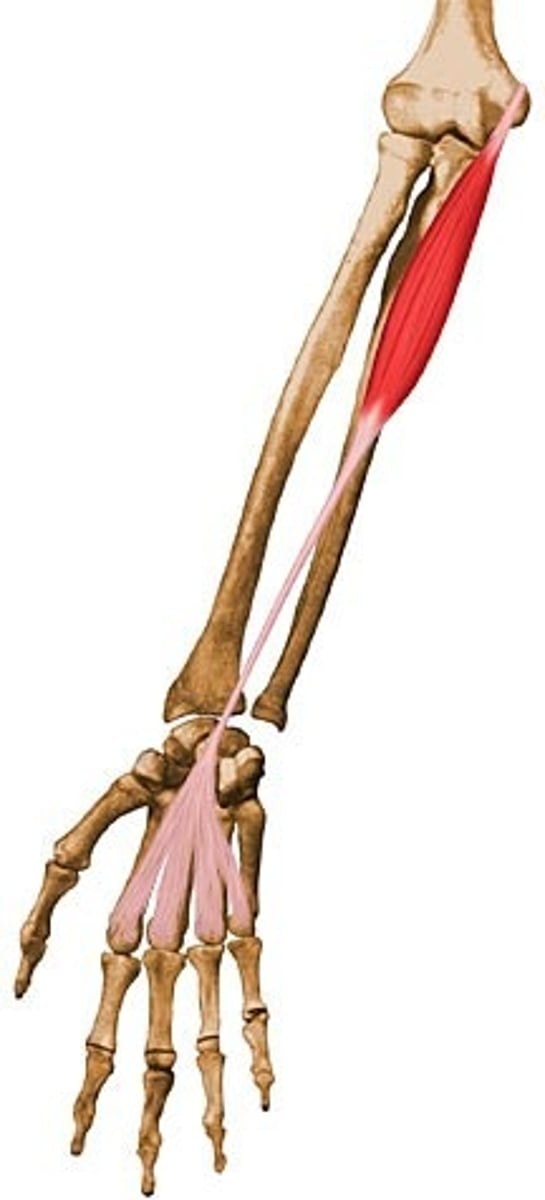
Flexor carpi ulnaris
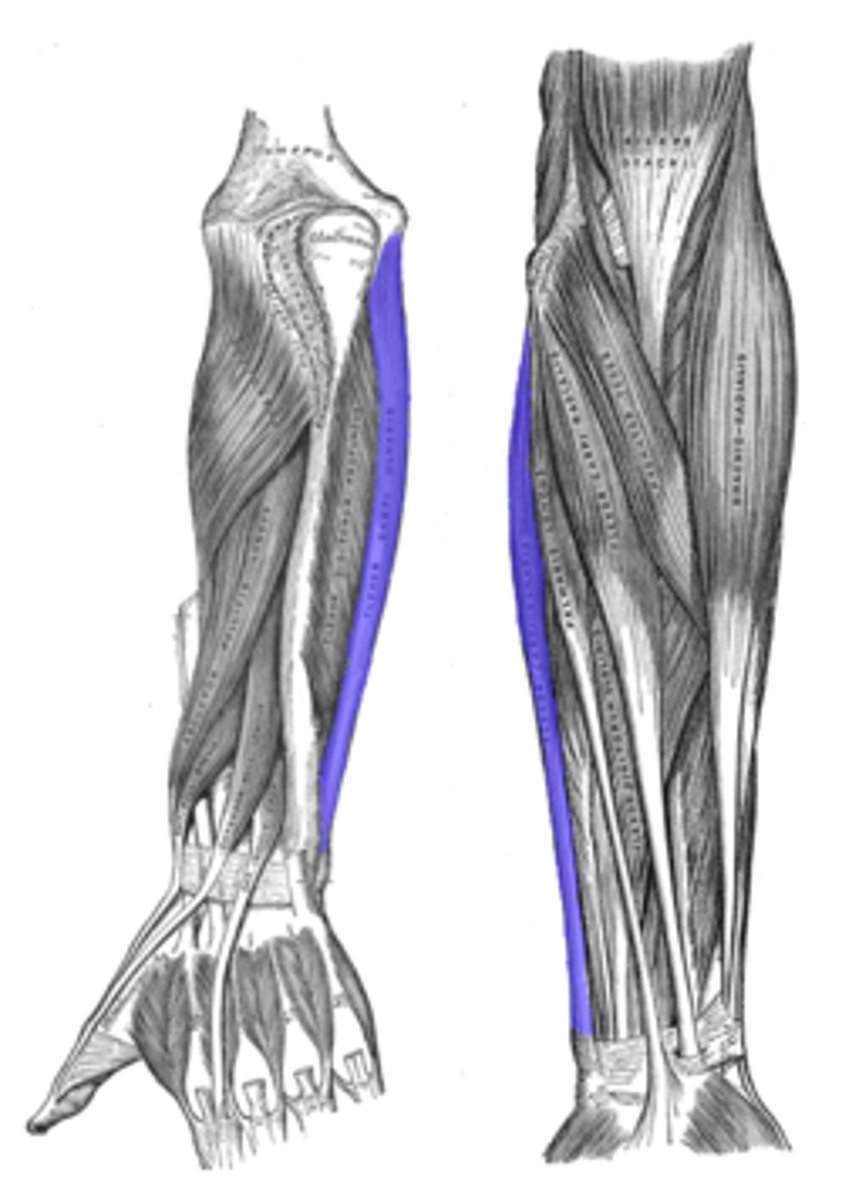
Flexor digitorum superficialis
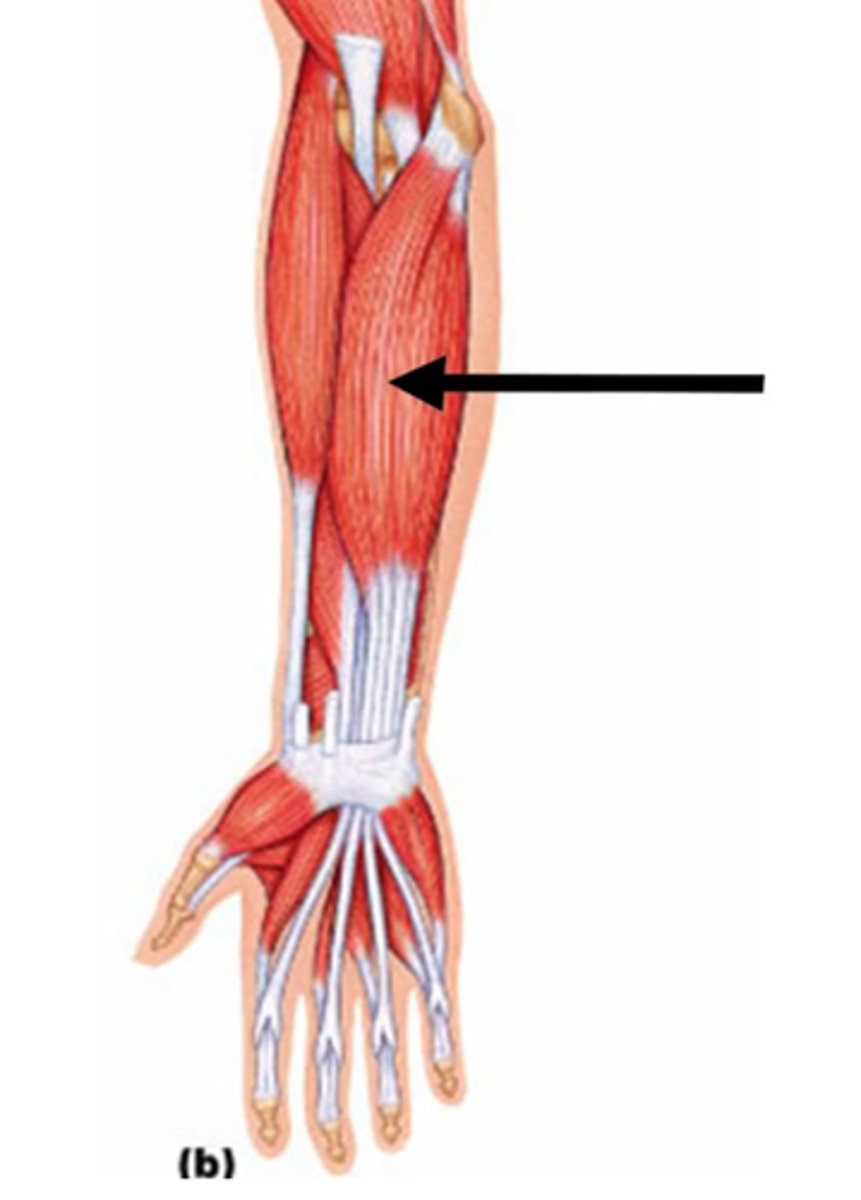
Extensor digitorum
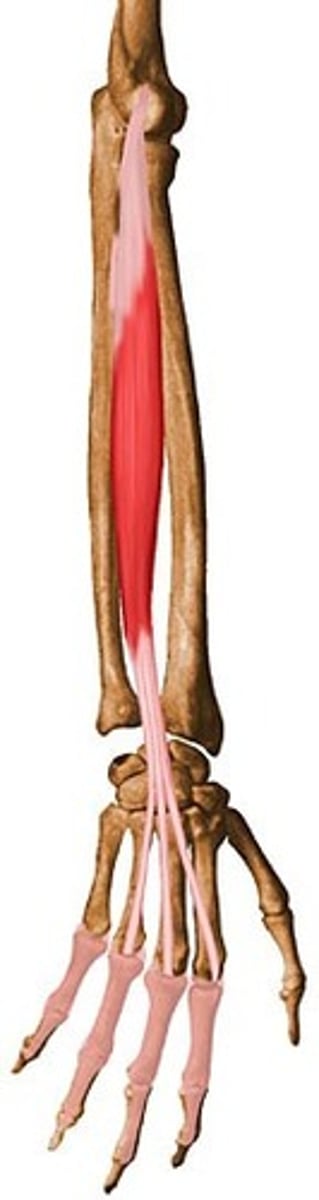
Gluteus Maximus
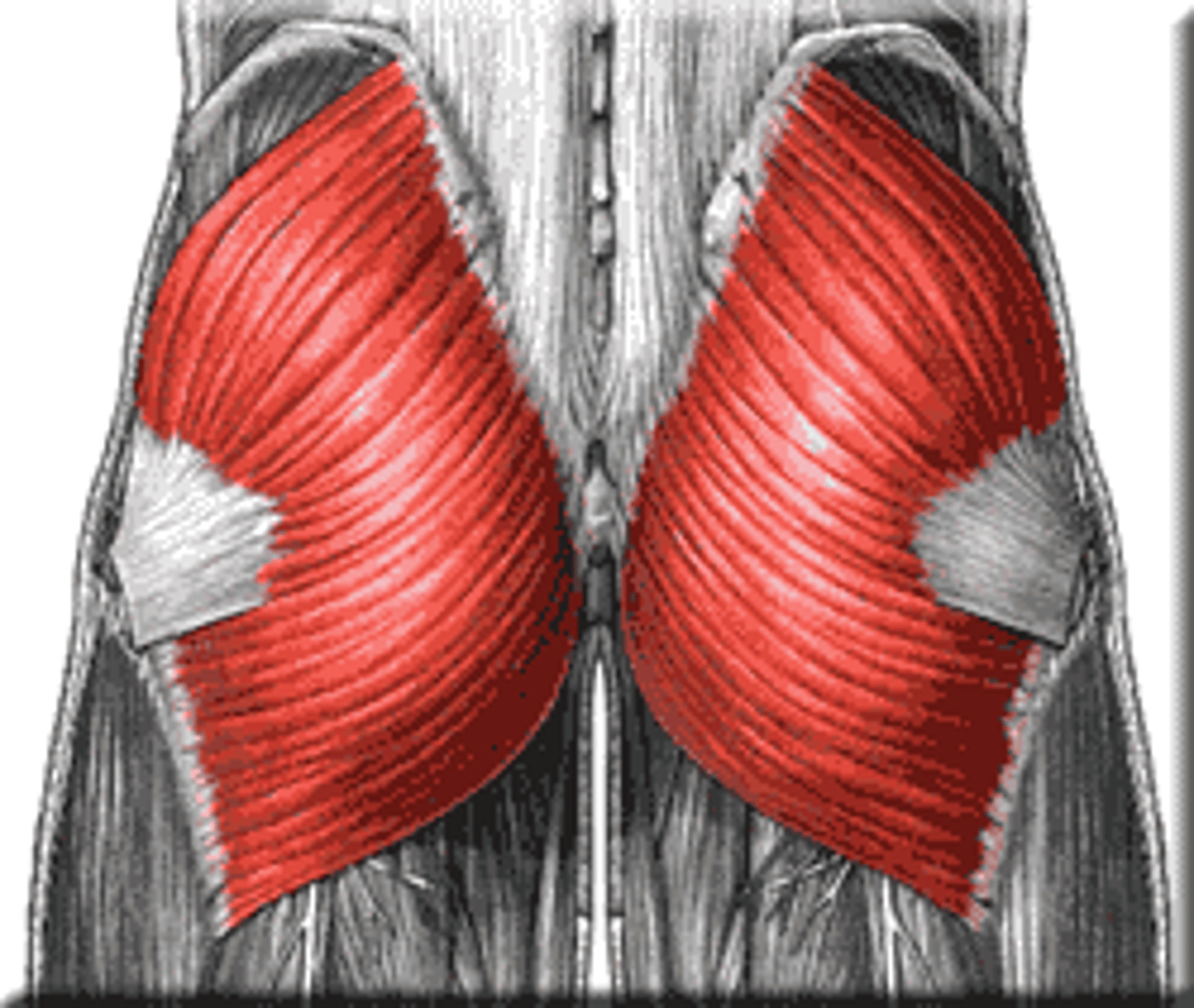
Gluteus medius
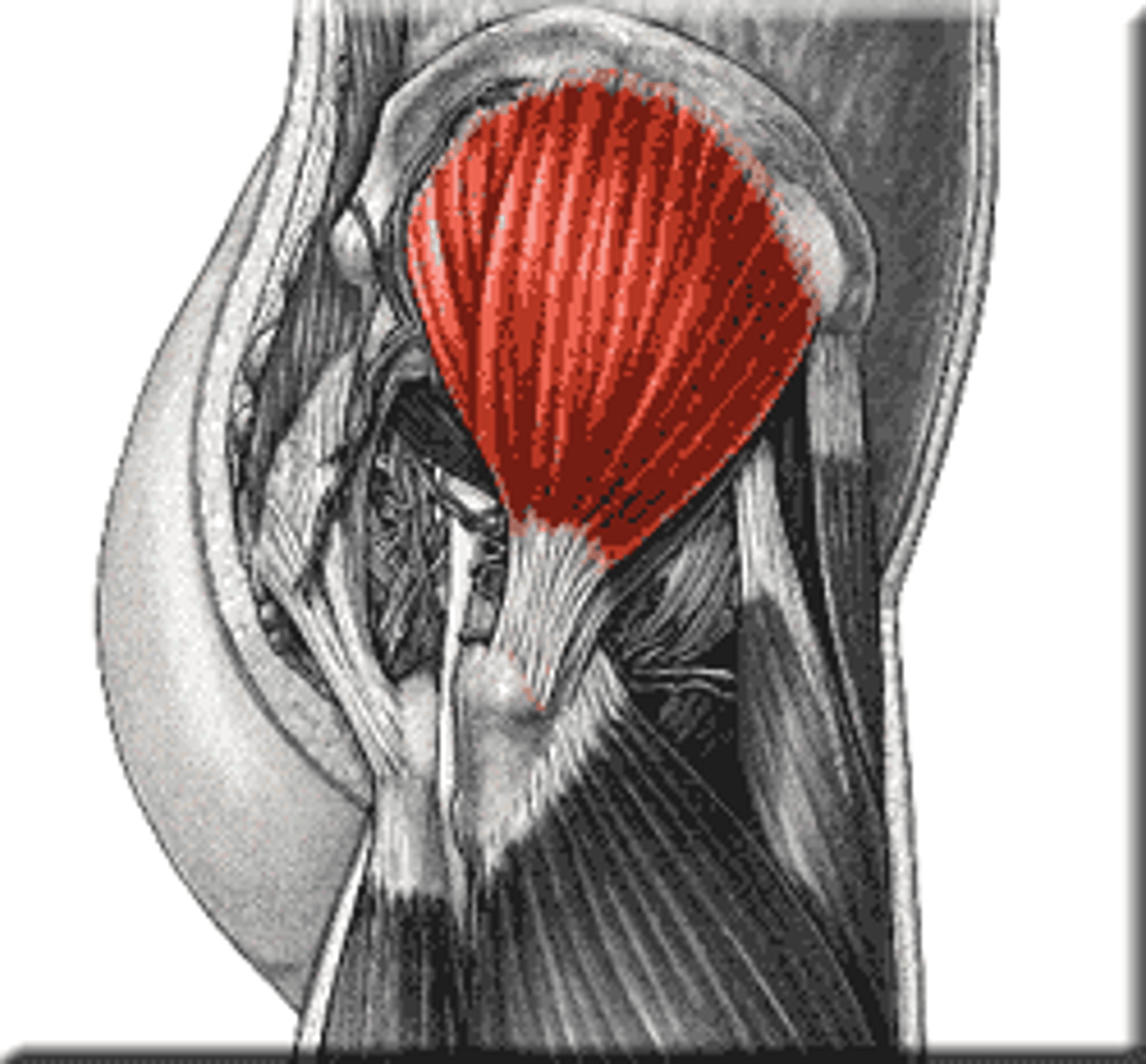
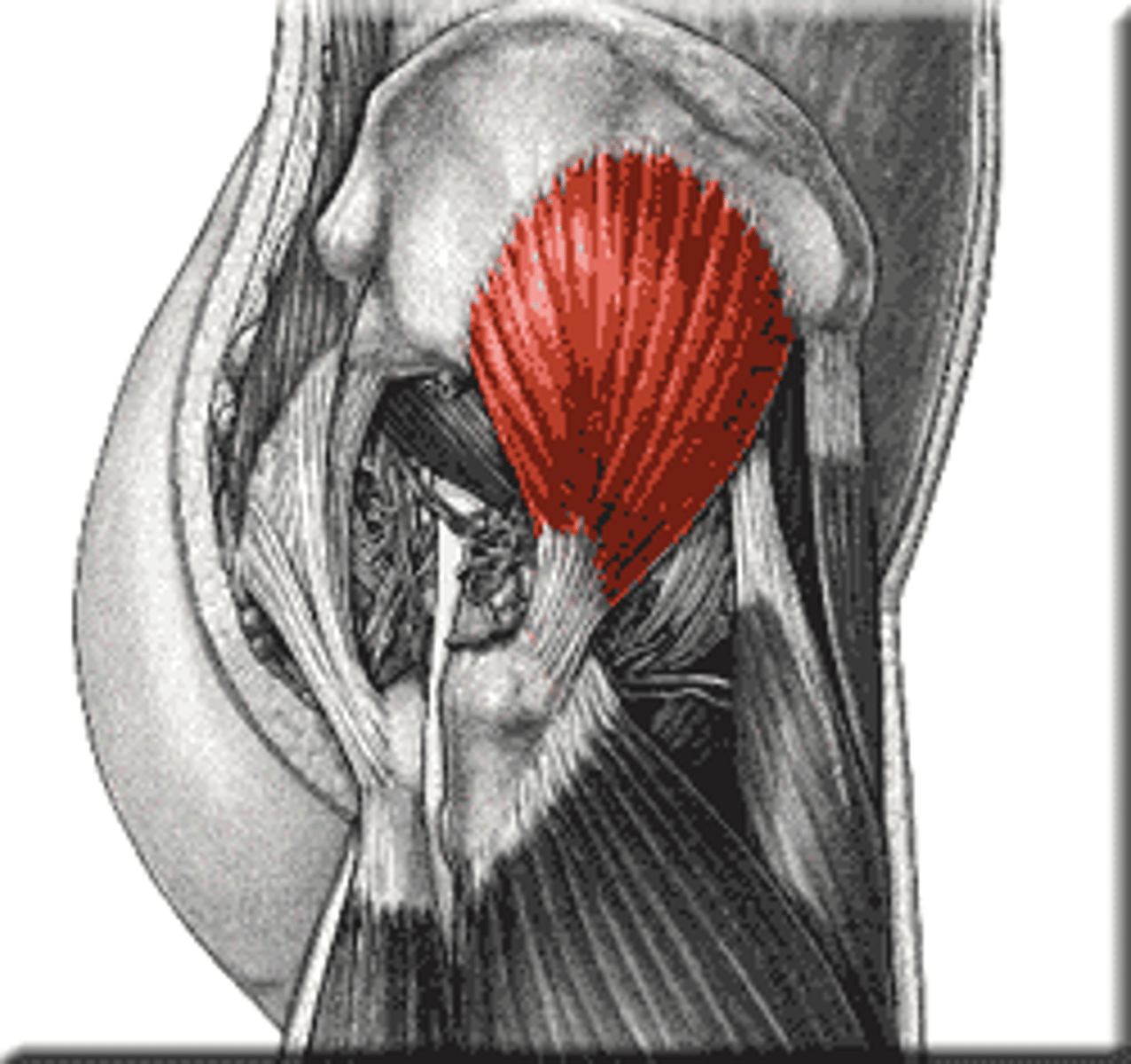
Gluteus minimus
Satorius
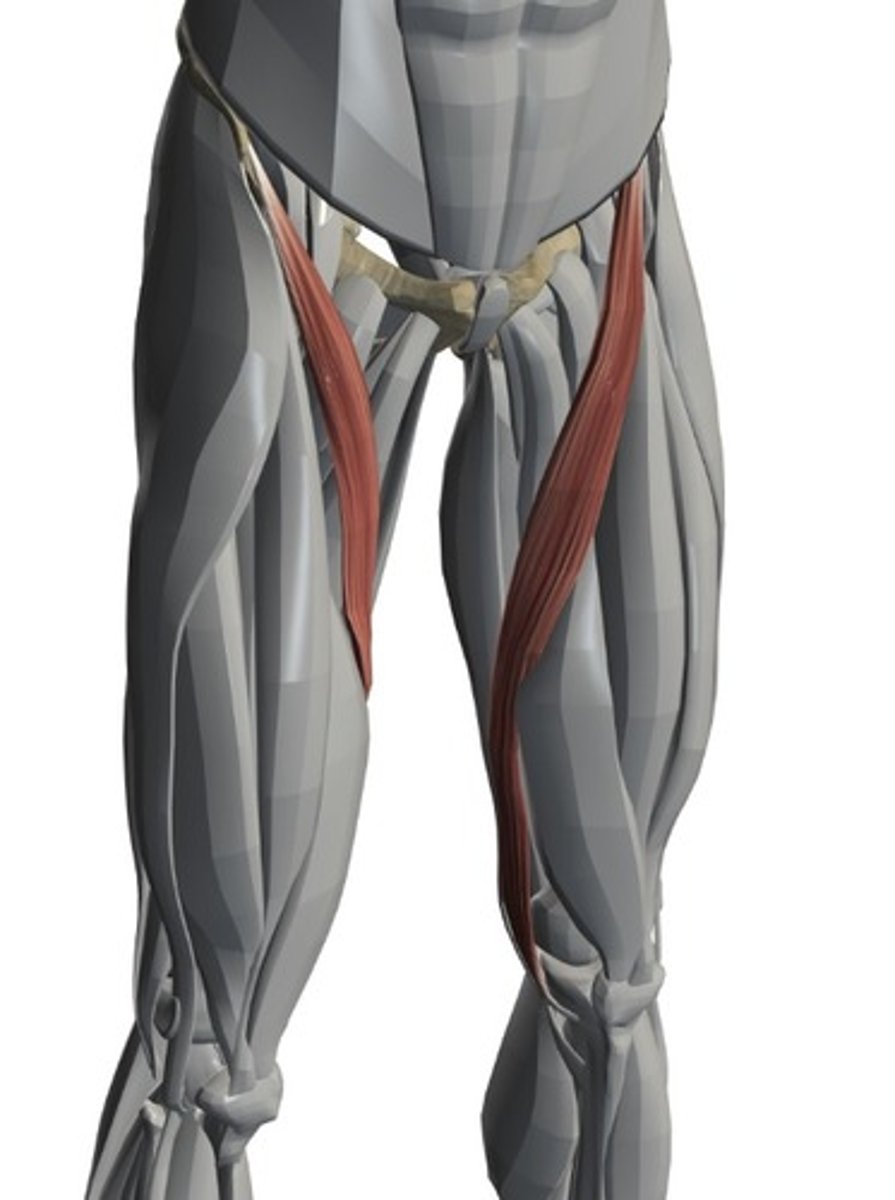
Adductor longus
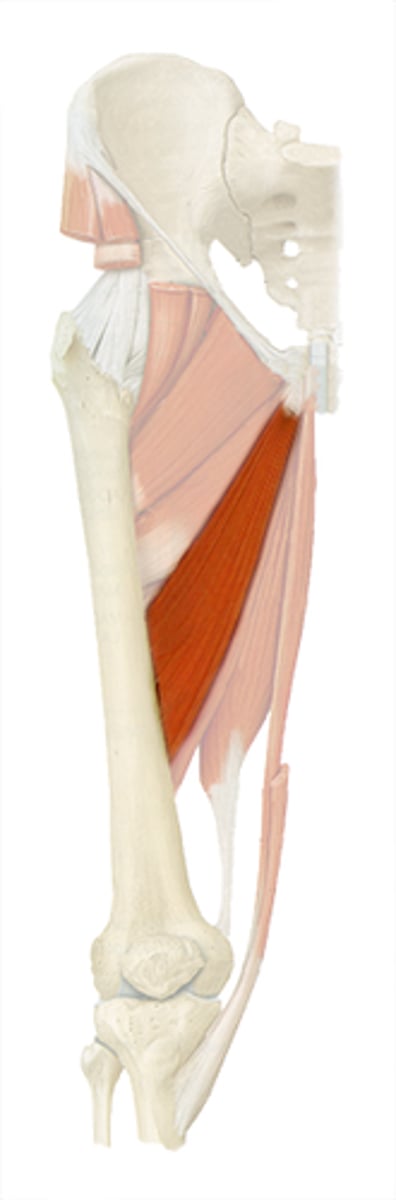
Gracilis
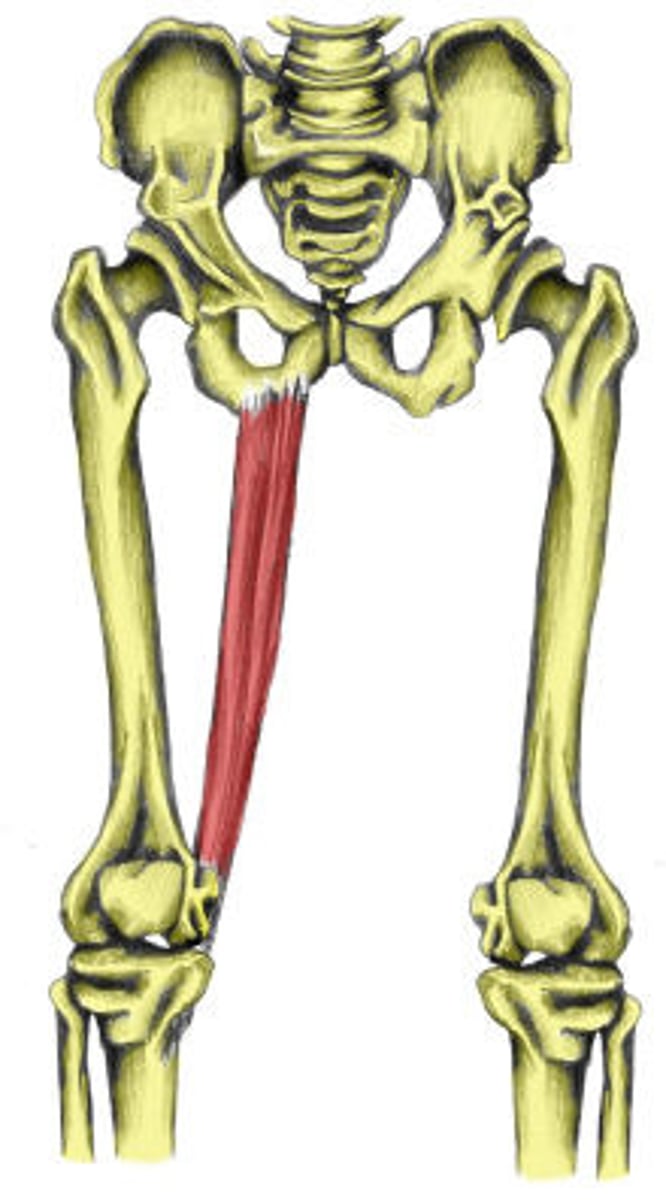
Vastus lateralis
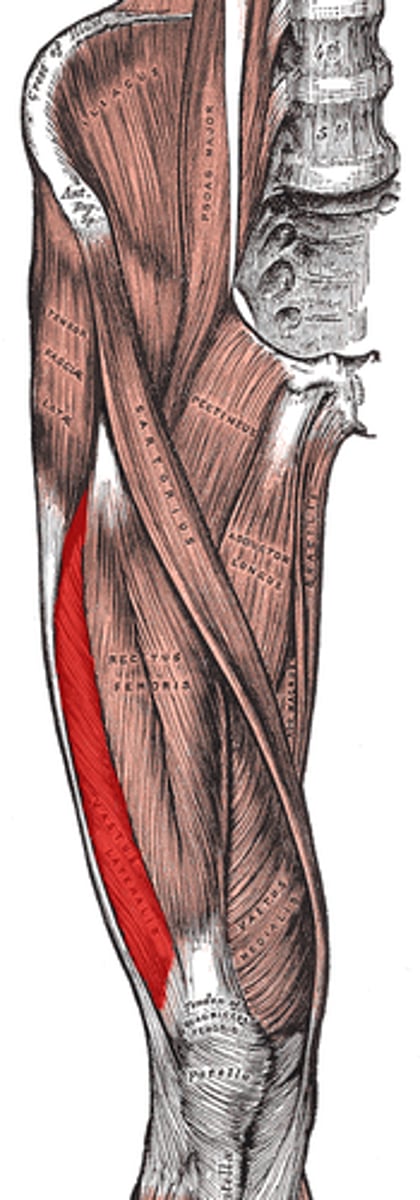
Vastus medialis
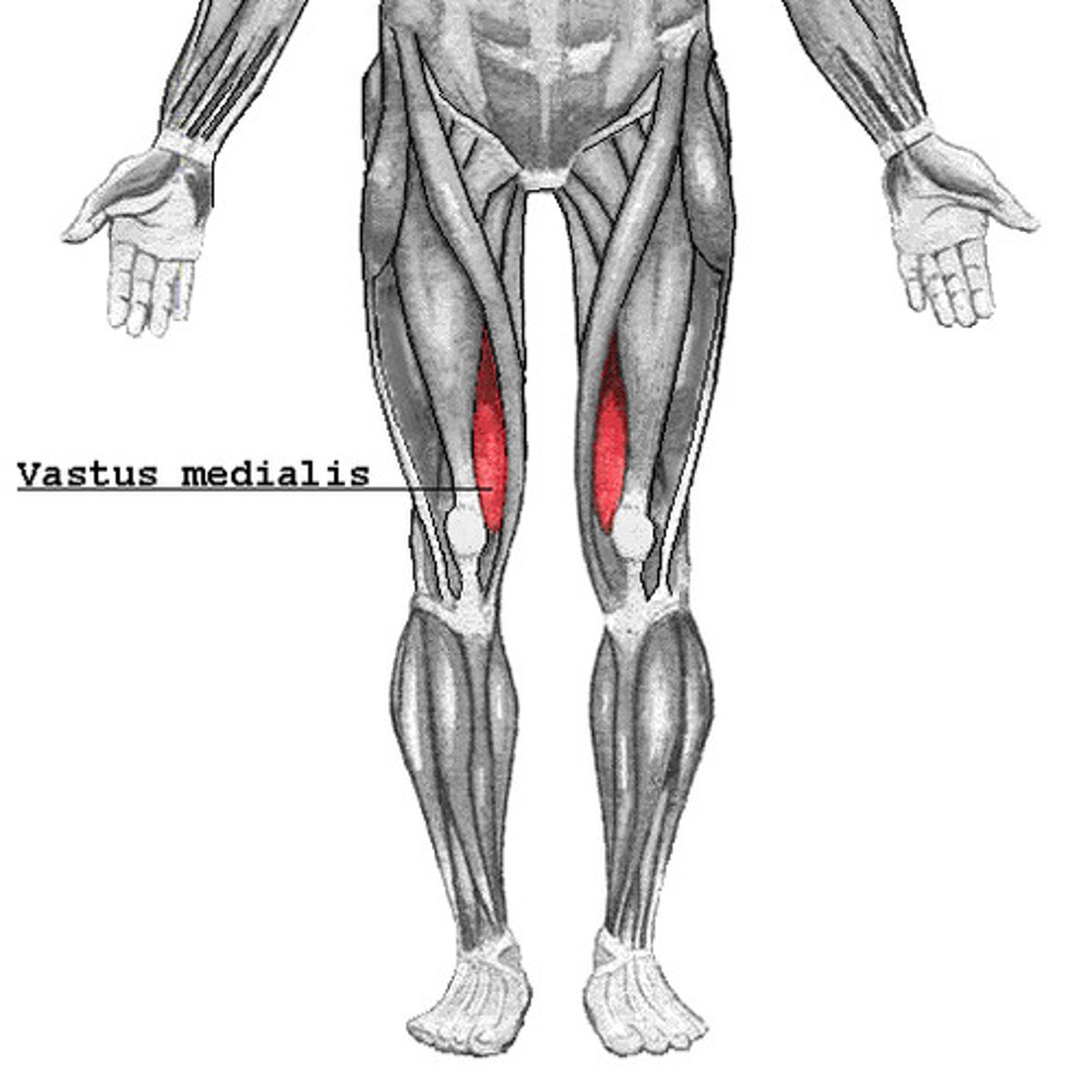
Vastus intermedius
Rectus femoris
Gastrocnemius
Soleus
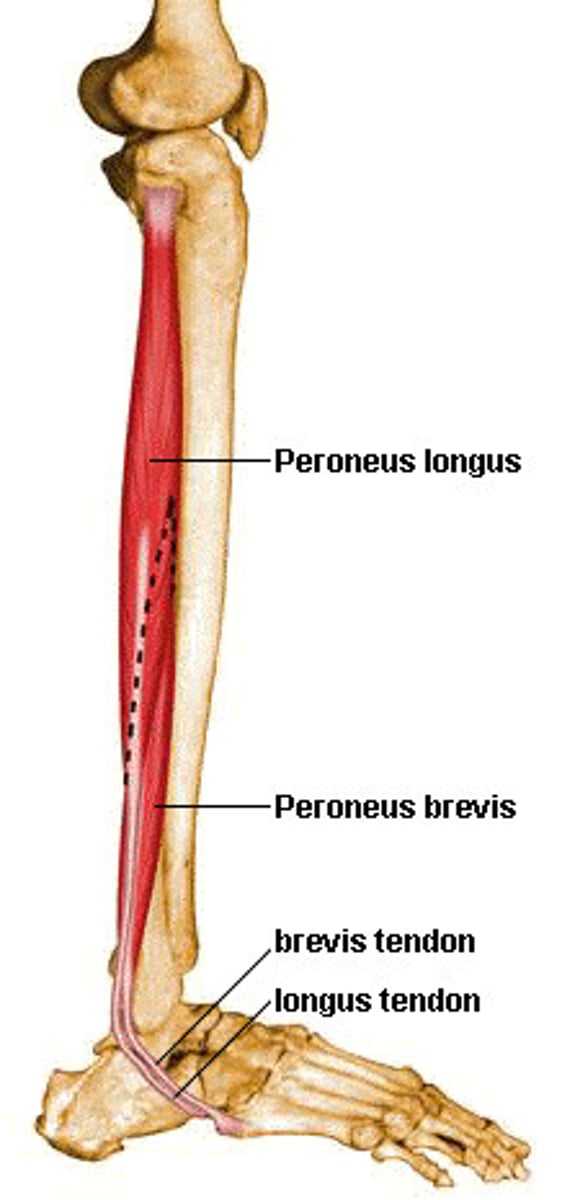
Peroneus
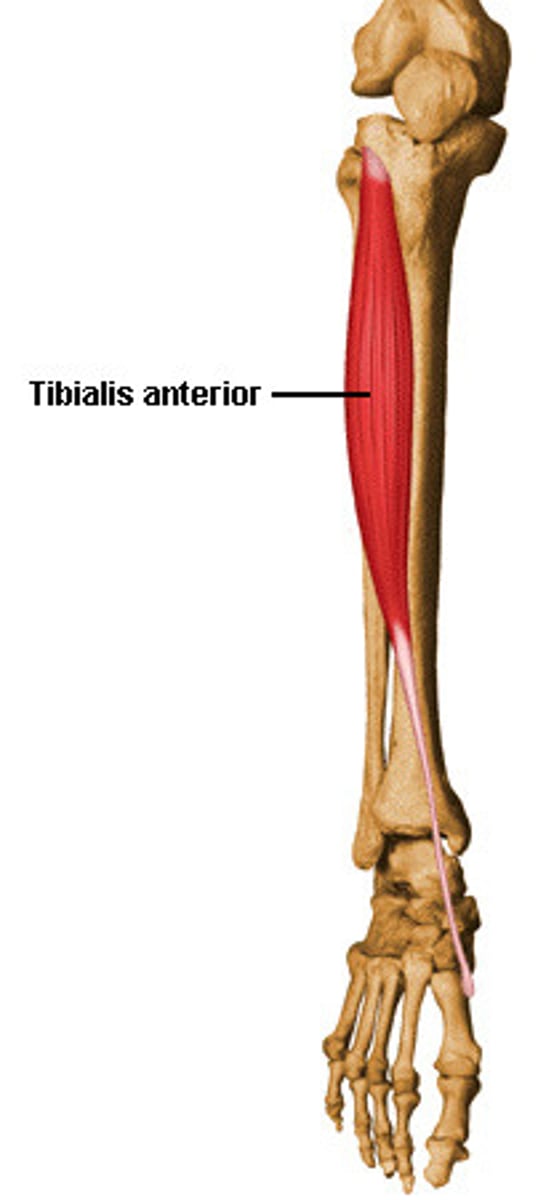
Tibialis anterior
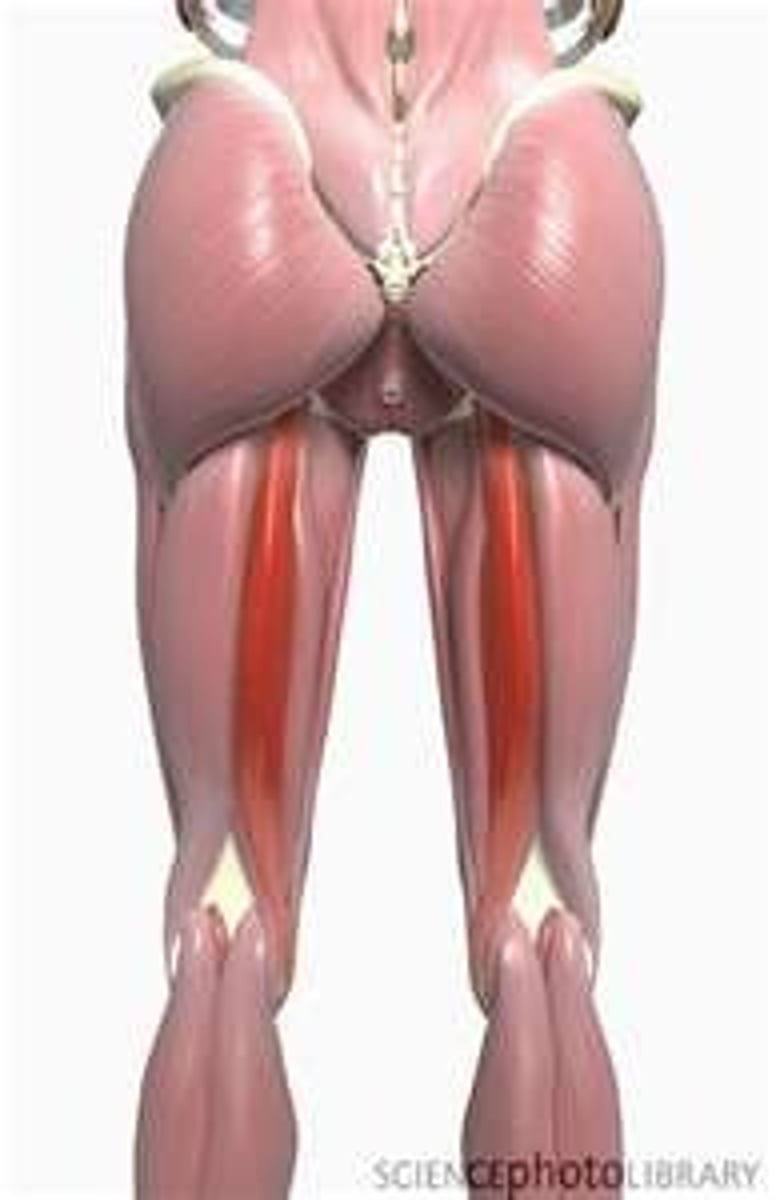
Semitendinosus
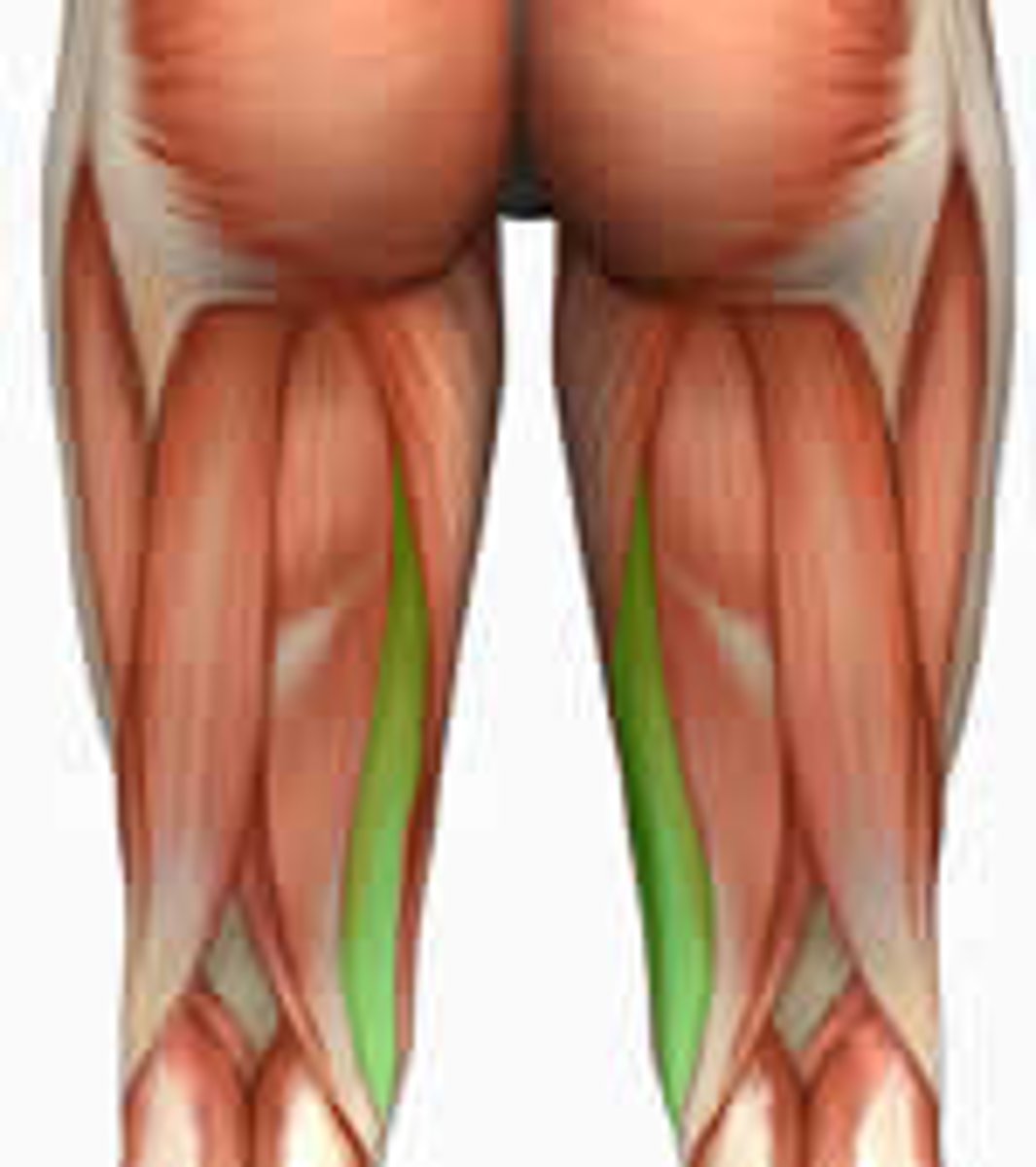
Semimembranosus
Biceps femoris
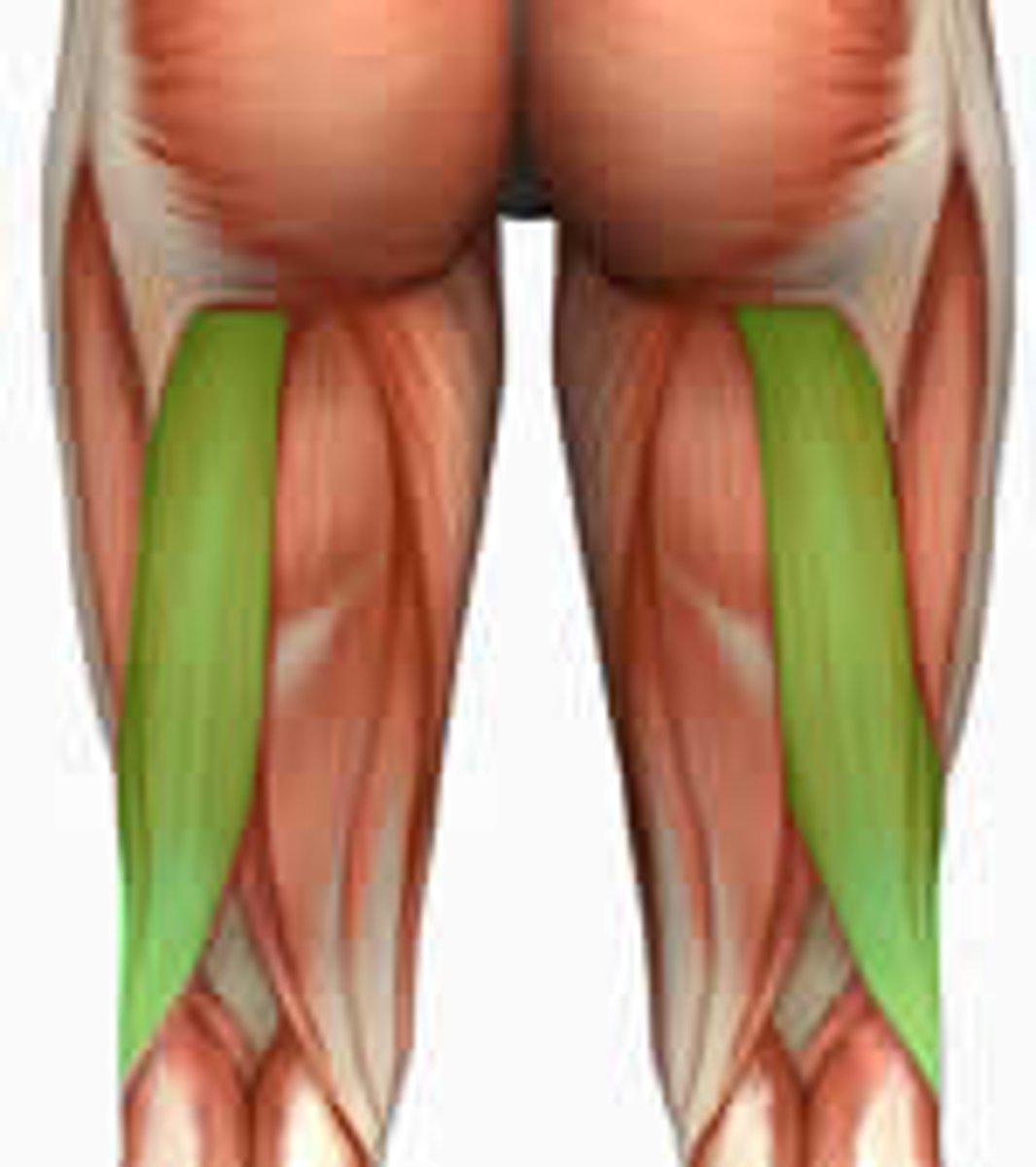
Tensor fasciae latae