NUR 3590 Exam 2: Conception and Fetal Development & Genetics
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
steps of fertilization
1. several sperm penetrate corona radiate
2. several sperm attempt to penetrate zona pellucida
3. one sperm enters egg and nuclei fuse, producing a zygote
-egg's plasma membrane and zona pellucida change to prevent polyspermy
zygote
when the ovum is fertilized by the sperm
polyspermy
-fertilization by more than one sperm
-incompatible with life
fertilization
the fusing of the ovum and sperm, which is the starting point of pregnancy
embryo
when a zygote begins dividing
implantation
developing embryo travels down oviduct and eventually implants in the endometrium
hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin)
-present by day 8-10 to maximal level usually by day 70 then decreases
-maintains corpus luteum
-causes positive pregnancy test
how many sperm are required to impregnate a woman?
20 million sperm in 1mL of Seminole fluid
male sperm
-light, fast, quick, and get to the target first but have no staying power
if a couple has intercourse when the egg is waiting in the right spot, odds are you are having a...
boy!
female sperm
-heavier, slower, and have more staying power
-can last 8 days
if sperm have to wait for the egg to show up, odds are you are having a...
girl!
where does the embryo usually implant?
posterior superior section of the uterus
embryonic period
-most critical part of the pregnancy
-begins at day 15 after conception and continues through week 8
-every organ is formed (organogenesis)
-most women don't know they are pregnant during this stage so a lot of damage can be done
placenta
-originates from maternal and fetal tissues
-produces HCG
corpus luteum
keeps pregnancy going until placenta takes over
physical signs of pregnancy
-no menstruation
-increased urination
-morning sickness
-increased size of breasts
-darkening of areolae
3 periods of prenatal development
1. Germinal
2. Embryonic
3. Fetal
germinal period
-first two weeks after conception
-"hanging out" and getting itself settled into the uterus
fetal period
-9th week after conception to birth
-only job is growth and refinement
estrogen
-promotes uterine growth and uteroplacental blood flow (increased blood volume by 50% by 20th week of pregnancy)
-promotes breast development (glands)
-stimulates uterine contractility
side effects of estrogen
-nose bleeds
-swollen feet
-increased vaginal mucus
progesterone
-maintains endometrium
-promotes breast development (alveoli)
-decreased uterine contractility
a drop in progesterone can lead to...
miscarriage
progesterone side effects
heart burn
hCG side effect
nausea
human placental lactogen (hPL)
-promotes glucose transport to fetus: if mom has low insulin levels to begin with, this can cause them to drop even lower ad lead to gestational diabetes
-stimulates breast development
relaxin
-increases pelvic flexibility
-causes women to waddle
cleavage
cell division without growth
morphogenesis
shaping of embryo
differentiation
cells take on specific structure and function
growth
increase in size of cells
morula
solid mass of cells resulting from cleavage
blastocyst
ball of cells formed from morula
embryonic disc
inner mass of cells of blastocyst
gastrula
-embryo composed of three tissues: ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm
-these are the foundation of the body systems (germ layer theory)
neural tube
-forms at 22 days
-becomes the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord)
neurula
-nervous system develops from ectoderm located just above notochord
-involves induction as one tissue influences the development of another tissue
-neural folds become brain
-somites become the body
ectoderm
-skin, epidermis, including hair, nails, and sweat glands
-nervous system, including brain, spinal cord, ganglia and nerves
-retina, lens, and cornea of eye
-inner ear
-lining of nose, mouth and anus
-tooth enamel
mesoderm
-all muscles
-dermis of skin
-all connective tissue including bone, cartilage, and blood
-blood vessels
-kidneys
-reproductive organs
endoderm
-lining of digestive tract, trachea, bronchi, lungs, gallbladder, and urethra
-liver
-pancreas
-thyroid, parathyroid, and thymus glands
-urinary bladder
embryo at 7 weeks
-legs, feet, and webbed toes have begun to develop
-a blood vessel that will become heart begins pulsating around this time
-can hear heartbeat (usually very fast, over 160 bpm)
-embryo is 2.5 cm long
-cannot feel baby move yet
embryo at 8 weeks
-now recognizable as human
-weighs 1 gram and is 1 inch long
-all basic organs and body parts of a human being
-tail is no longer visible (incorporated into lower spine)
-surrounded by amniotic fluid
extraembryonic membranes
Membranes that extend out beyond the embryo
- Amnion
- Yolk sac
- Chorion
amnion
provides fluid environment for developing embryo and fetus
yolk sac
first site of red blood cell formation
chorion
outermost membrane, develops from trophoblast, contributes to the placenta
placenta functions
-exchange of gases and nutrients between maternal and fetal blood takes place in the umbilical arteries
-umbilical vein carries blood and oxygen away from placenta to fetus
-produce hormones to maintain pregnancy (estrogen, progesterone, hCG)
ductus venosus
bypasses the liver
foramen ovale
-bypasses the lungs
-should close when the baby takes its first breath
PFO
persistent foramen ovale, can lead to CHF later in life
ductus ateriosus
-between aorta and pulmonary artery
-goes away when baby takes its first breath
placenta weight at end of pregnancy
1 pound
amniotic fluid
-initially diffused from maternal serum, later produced by fetal urine
-cushions fetus, allows for movement, prevents cord compression, provides oral fluid, maintains temperature
-volume varies: 800-1200 mL at term
-important assessment of fetal wellbeing
Polyhydraminos
-excessive amniotic fluid
-can be caused by gestational diabetes
-can lead to permanent conditions such as hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) and cerebral palsy
oligohydramnios
-low amniotic fluid levels
-usually due to placenta not functioning properly
-worry about kidney function
-put mom on bedrest so she can develop more fluid
-watch for fetal distress
umbilical cord
-contains two arteries and one vein in wharton's jelly
-provides connection between fetal circulation and maternal circulation
-at birth is 2cm in diameter and 30-90 cm in length
fetal development in third month
-at the beginning head growth begins to slow and body increases in length
-ossification center appears in bones
-sex can be determined
development of male and female sex organs
-sex of an individual is determined at the moment of fertilization
-Gonads arise from indifferent tissue that can develop into ovaries or testes depending on the action of hormones
-in absence of a Y chromosome and presence of X chromosome, ovaries develop instead of testes
1 lunar month is equal to...
4 weeks
pregnancy is how many lunar months?
10!
1st lunar month
-beginning of nervous and genitourinary systems, skin, bones, lungs, heart, eyes, ears, and nose form
-arm and leg buds form
2nd lunar month
-fetus is bent with large head
-sex differentiation begins
3rd lunar month
-fetal fingers and toes are distinct
-placental and fetal circulation are complete
4th lunar month
sex is differentiated, urine production begins, nasal septum and palate close (can see cleft palate here), fetal heartbeat detected by doppler
5th lunar month
-lanugo covers fetal body
-fetal movements felt by mother
6th lunar month
skin red and wrinkled, vernix caseosa present, fetal breathing movements begin, fetus responds to sound
7th lunar month
eyelids open, surfactant is produced, eyebrows and nails develop
8th lunar month
subcutaneous fat develops
9th and 10th lunar months
-skin pink and smooth, lanugo disappears
8th and 9th months
•Fetus usually rotates so head is pointed down toward cervix.
•Fetus is now about 530 mm in length and weighs about 3,400g
•Full-term babies have the best chance of survival.
fraternal twins
2 eggs, 2 sperm, 2 placentas
identical twins
sometimes have their own placenta, other times share one big placenta
how long should you take folic acid prior to getting pregnant?
3-6 months! helps prevent neural tube defects
genetics
the branch of biological science that deals with the transmission of characters from parents to offspring
genes
-a set of characteristics inherited from your parents
-found on chromosomes and contain DNA
heredity
the transfer of character or traits from parents to offspring
variations
the similarities and differences between the character or traits among individuals of the same species
autosomal dominant inheritance pattern
if dad has the condition and mom does not
-50% of children have the condition
-50% of children do not have the condition
autosomal recessive inheritance pattern
if dad is a carrier and mom is a carrier (neither have condition)
-75% of children don't have condition
-50% are carriers but don't have the condition
-25% have the condition
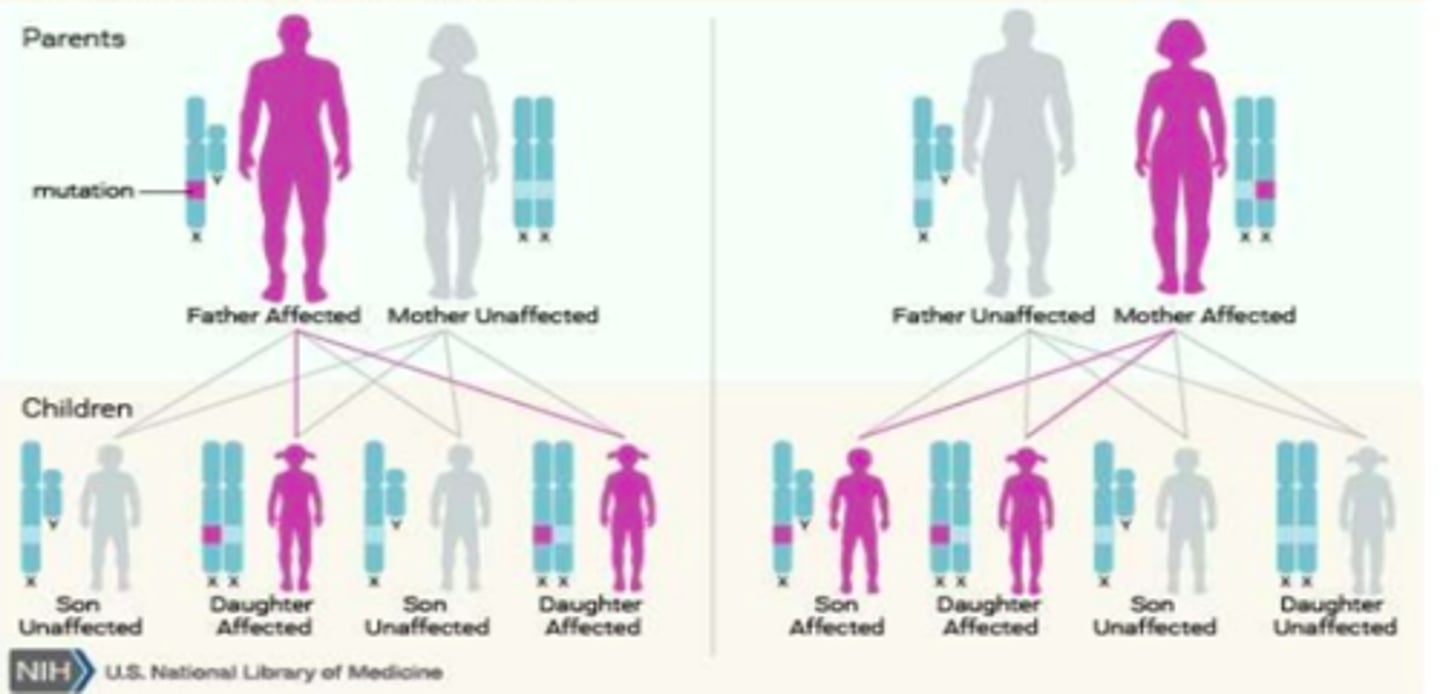
X-linked dominant
-if dad is affected and mom is not, the only way the x-linked gene is being passed on from dad is if he has daughters (if dominant, daughters will be affected)
-if mom is affected and dad is not, there is a 25% chance of son being affected, 25% chance of daughter being affected, and 50% chance neither is affected
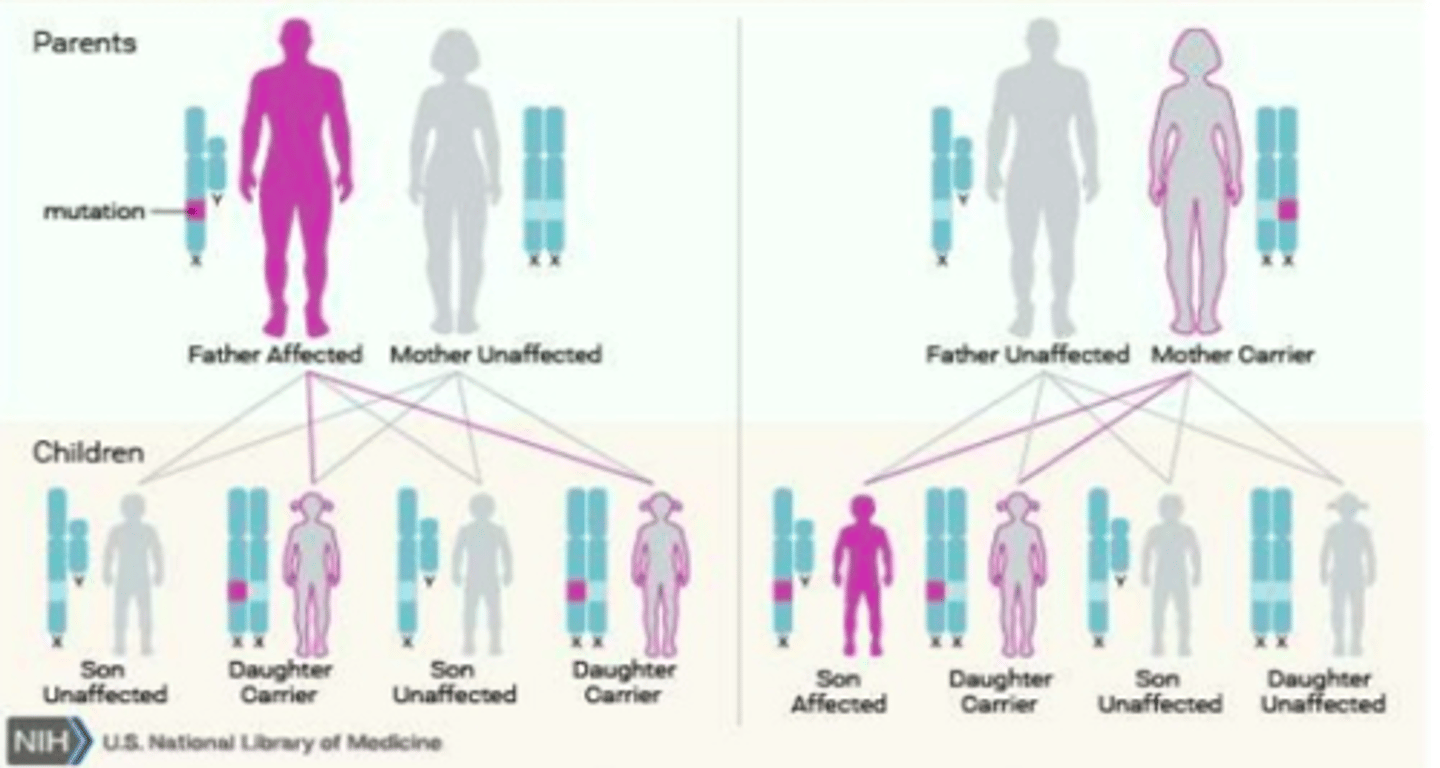
x-linked recessive
-if dad is affected and mom is not, the only way the gene is being passed down from dad is if he has daughters (daughters will be carriers and sons will not be affected)
-if mom is affected (carrier), she can give the condition to her son (25% chance), there is a 25% chance daughter is a carrier and 50% chance neither child will be affected
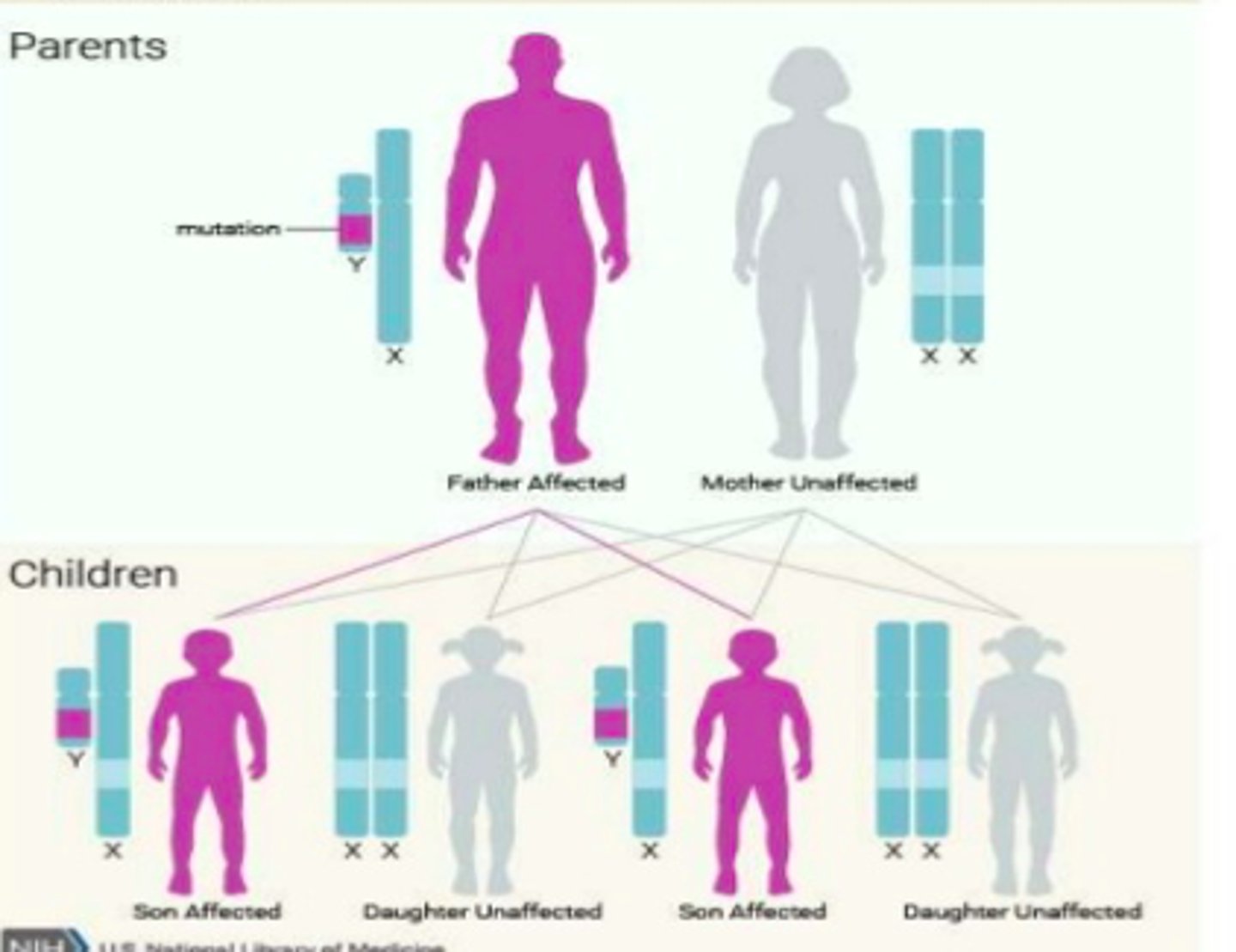
Y-linked
-only dad can pass it down
-if dad is affected, sons are affected
cytogenetics
-the study, structure, and function of the cell, especially the chromosomes
-concerned with the cytological and molecular basis of genetics
ex.
-Down syndrome (trisomy 21)
-Patau syndrome (trisomy 13)
-Edward syndrome (trisomy 18)
-Chronic myelogenous leukemia (has a small chromosomes in WBC)
biochemical genetics
-the study of fundamental relationships between genes, protein, and metabolism
-involves the study of the cause of many heritable diseases
ex.
-sickle cell anemia
-thalassemia
-phenylketonuria
-galactosemia
-depression and anxiety
developmental genetics
-attempts to understand the role of genes in development
-the process that gives rise to tissues, organs, and anatomy
-the process which brings about various changes in fertilized egg to make it into a complete adult
physiological genetics
-involves the use of knowledge of physiology to elucidate the effects produced by genetic factors on an individual
-relationship of hereditary disease and genetics
-what causes certain diseases to manifest in individuals
immunogenetics
branch of science which is concerned with the genetic aspects of immunity mechanisms
clinical genetics
helps to establish causative factors responsible for certain diseases like Diabetes Mellitus, Hemophilia, etc.
radiation genetics
studies the effects of various radiation on genes
ex. Chernobyl and Hiroshima
gametic mutations
are inherited and occur in the testes of males and ovaries of females
somatic mutations
-occur in body cells
-they are not inherited but may affect the person during their lifetime
eugenics
-a branch of science which deals with the application of principles of heredity to the improvement of mankind
-the study of all agencies under human control which can improve or impair the quality of future generations
positive eugenics
-aimed at encouraging reproduction among the genetically advantaged
approaches
-financial and political
-targeted demographic analysis
-in vitro fertilization
-egg transplants
-cloning
negative eugenics
-aimed to eliminate through sterilization or segregation
-physically, mentally, or morally undesirable
approaches
-abortions
-sterilization
-family planning
genomics
functions and interactions of all genes
DNA sequencing
-determining the exact order of the base pairs in a segment of DNA
-map-based (gene mapping): a method to produce the finished version of human genetic code
ethical, legal, and social issues of genetics
-fairness in use of genetic information
-physiological impact, stigmatization, and discrimination
-privacy and confidentiality
-reproductive issues
-clinical issues
Predictions for the future
-science will pinpoint what makes us Homo Sapiens
-Gene therapy will cure diseases
-personal genomes will spawn made-to-measure drugs
-personality will move from art to science
role of the nurse: genetics
-take detailed family history
-construct pedigree (genogram)
-assess hereditary and non-hereditary risk factors related to genetic diseases or having a genetic component
-provide genetic information to individuals and families
-interpret genetic tests and laboratory data
-manage and care for patients and families at risk for or affected by genetic diseases
-provide genetic counseling, genetic consultation, and case management for persons with complex genetic health care needs