Gausses Law and Electric Potential - ch 23-25
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
electric flux through the surface
amount of electric field that pierces the surface
area vector for a patch element on a surface (dA)
a vector that is perpendicular to the element and has a magnitude equal to the area dA of the element
how to calculate electric flux through a patch element
** dot product!
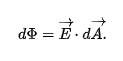
total flux through surface
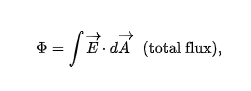
net flux through a closed surface
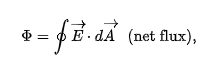
Gauss’s Law
Gauss’s Law states that the total electric flux through a closed surface is proportional to the total charge enclosed by the surface divided by the permittivity of free space.
piercing direction
inward: negative flux
outward: positive flux
skimming field: zero flux
how to find the piercing direction
draw the area vector that is perpendicular to a patch pointing outward from the surface
look at the field vector if it pierces outward/inward
if dot product = +, flux is also positive (vv)
Gauss’s Law (net flux penetrating a closed surface to the net charge enclose by surface)
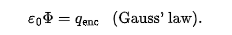
Gauss’s Law in terms of electric field piercing though the surface
substitute the definition of flux
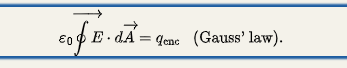
where are excess charge on an isolated conductor located?
entirely on the outer surface of the conductor
internal electric field of a charge isolated conductor is
zero
external field is
perpendicular to the surface
has a magnitude that depends on the surface charge density o
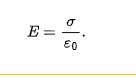
electric field at a point near an infinite line of charge with uniform linear charge denisty is
perpendicular to the line
has magnitude where r is the perpendicular distance from the line to the point

electric field due to an infinite non conducting sheet with uniform surface charge density
perpendicular to plane of the sheet
has magnitude of
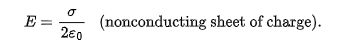
external electric field just outside the surface of an isolated charged conductor with surface charge density o
perpendicular to the surface and has magnitude

outside a spherical shell of uniform charge q, the electric field due to the shell is
radical (inward or outward depending on the sign of the charge)
r is the distance to the point of measurement from the center of the shell

inside the shell, the field due to the shell is
zero
inside the shphere with a uniform volume charge density, field is
radical
has magnitude of
R = radius of sphere
r = radial distance from the center of the sphere

electric potential energy at a point P in the electric field of a charged object
W(inf) = work that would be done by the electric foce on a positive test charge were it brought from an infinite distance to P
U = electric potential energy stored in
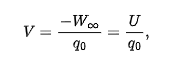
if a particle with charge q is placed at a point where the electric potential of a charged object is V, the electric potential energy of the particle object system is
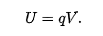
if the particle moves through a potential difference V, the chage in the electric PE is
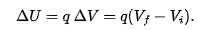
if a particle moves through a chage V in electric potential without an applied force acting on it, applying the conservation of mechanical energy gives the change in kinetic energy as
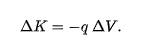
if an applied foce acts on the particle doing work W(app), the change in kinetic energy is
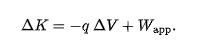
when K = 0, work of an applied force involves only the motion of the particle though a potential difference
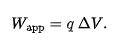
equipotential surface
adjacent points that have the same electric potential energy
electric potential difference betwen two points i and f is
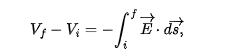
in a uniform field of magnitude E, the chage in potential from a higher equipotential surface to a lower one, spearated by distance x is
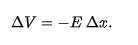
electric potential due to a single charged particle at a distance r from that charged particle is
V has the same sign as q
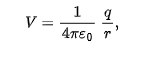
potential due to a collection of charged particles is
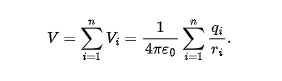
electric potential of the dipole is
at a distance r from an electric dipole with dipole moment magnitude p = qd
angle lies betwen the dipole moment vector and a line extending from the dipole midpoint to the point of measurement
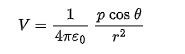
for a continuous distribution of charge over an extended object, potential energy can be found by
dividing the distribution into charge element dq that can be treated as particles
summing the potential due to each element by integrating over the full distribution
dq is replaced with the product of either a linear charge density and length element or a surface charge density o and area element
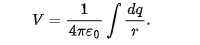
component of electric field potential is
negative of the rate at which potential changes with distance in that direction
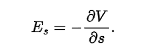
the x, y, z component may be found from
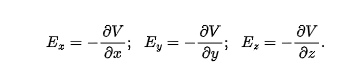
when E is uniform, it becomes
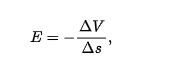
electric field is zero parallel to
equipotential surface
two particle at separation r, electric potential of a system of charged particles is
equal to work needed to assemble the system
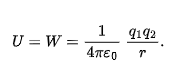
where is an excess charge placed on a conductor will, in the equilibrium state?
located entirely on the outer surface of the conductor
potential of the entire conductor, including the interior points?
uniform potential
if an isolated conductor is placed in an external field
then the electric field due to the conduction electrons cancels the external electric field that otherwise would have been there
net electric field at every point on the surface is ____ to the surface
perpendicular
capacitors
tow isolated plates with charges +q and -q
V is the potential difference between the plates
q = CV
when a circuit with a battery, an open switch, and an uncharged capacitor is completed by closing the switch
conduction electrons shift, leaving the capacitor plates with opposite charge
parallel- plate capacitors
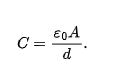
cylindrical capacitors
b = capacitance
a = radii
L = length
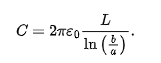
sphereical capacitors with conentric plates
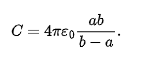
isolated sphere of radius R
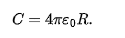
capacitors in parallel
Ceq = C1 + C2 + C3
capacitors in parallel
1/ Ceq = 1/C1 + 1/C2…
electric potential energy U of a charge capacitor
equal to the work requried to charge the capacitor.
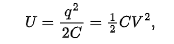
in a vacuum, the energy density u in a field of magnitude E is
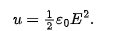
if the space between the plates of a capacitor is completely filled with a dielectric material, the capacitance C in the vacuum is
multiplied by the material’s dielectric constant K
in a region that is completely filled by a dielectric
all equation s containing E0 must be modified by KE0
when a dielectric material is placed in an external electric field
it develops an internal electric field that is oriented opposite the external fieldm thus reducing the magnitude of the electric field inside the material
when a dielectric material is placed in a capacitor with a fixed amount of charge on the surface
the net electric field betwen the plates decreased
when a dielectric is present Gauss’s law may become
q = free charge
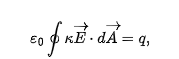
induced charge is ____ the free charge on the plates
less than
inserting a dilectric into a capacitor causes
induced charge to appear on the face of the dielectric and weakens the electric field between the plates