L1: Physiology of Cell Membranes
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What is the composition of extracellular fluid?
More Na+, Cl-, and HCO3-
what are characteristics of a bilayer?
-Impermeable to large molecules and charged ions.
-Permeable to small and uncharged molecules.
-Consists of membrane proteins to aide in structure and cell function.
-Contains cholesterol which adds stability to the membrane.
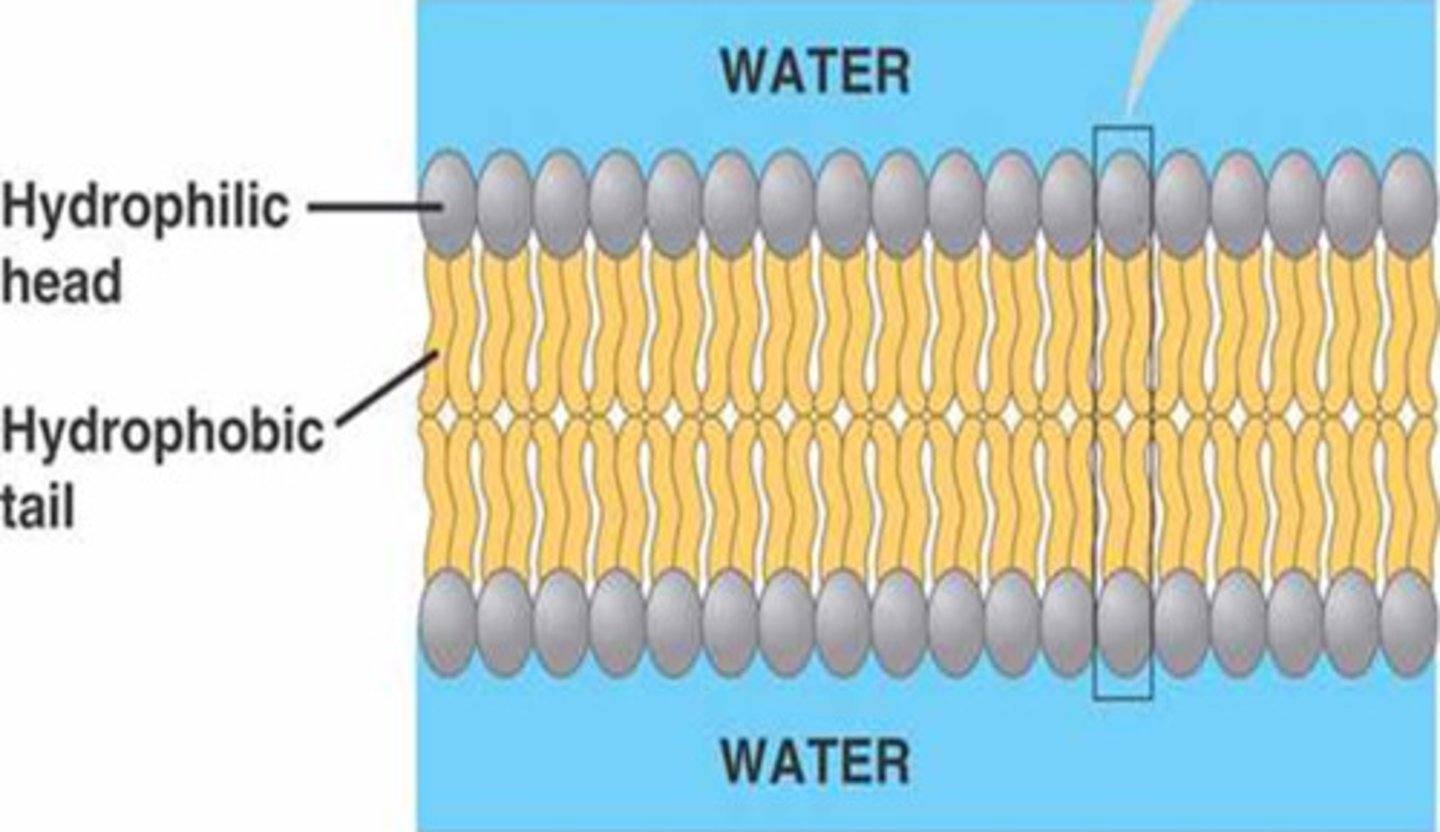
what are the three components that make up a cell membrane?
-Phospholipids
-Cholesterol (stability)
-Proteins (allows certain compounds to get into cell or leave the cell)
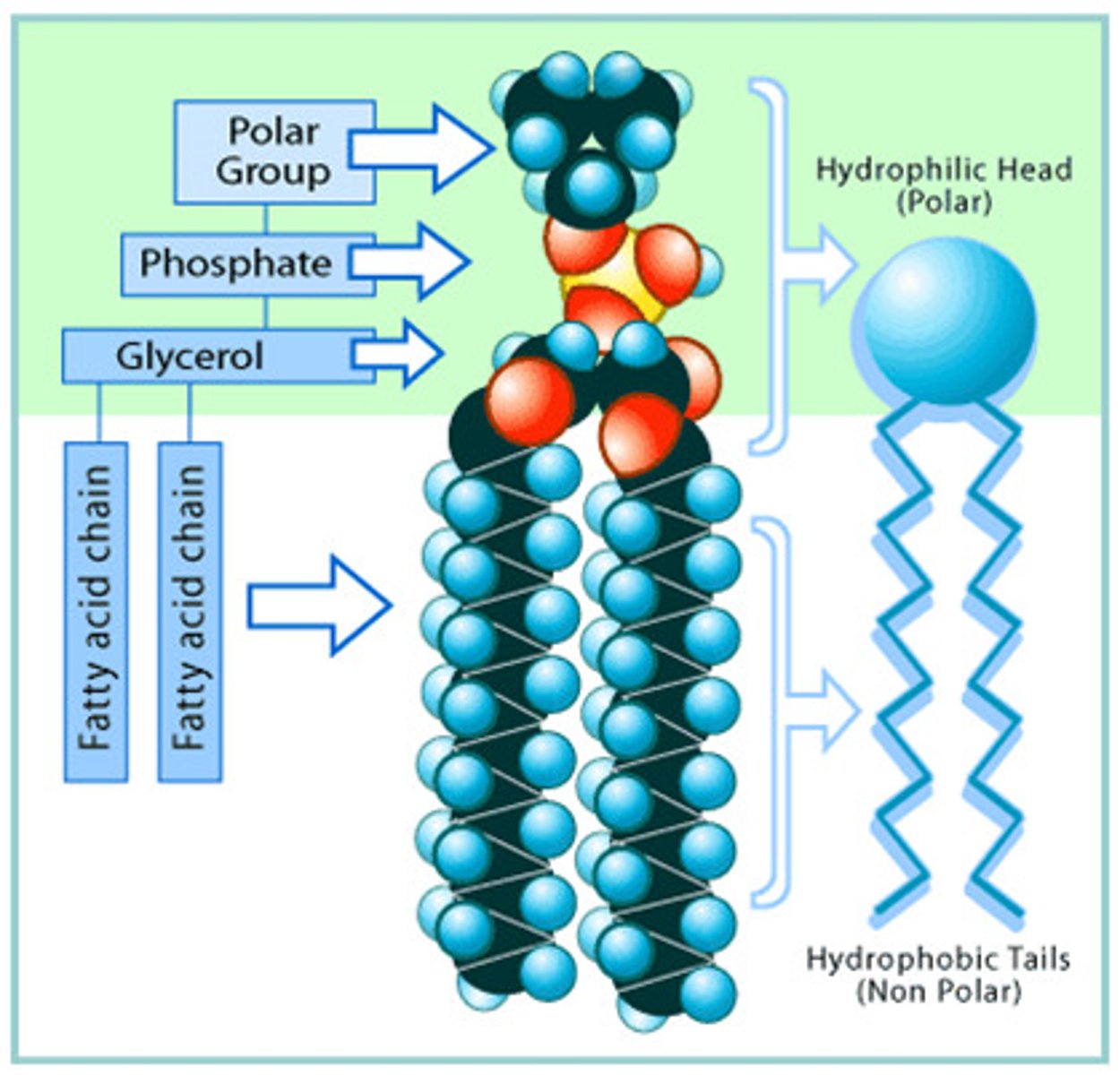
what is the structure of phospholipids?
-phosphate head group (polar, hydrophilic)
-fatty acid (2) and glycerol tail (non-polar, hydrophobic)
what does amphipathic mean?
having both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions
what are the effects of cholesterol on lipid bilayers?
-changes fluidity
-thickness
-compressibility
-water penetration
-intrinsic curvature of lipid bilayers
- induces phase separations in multicomponent lipid mixtures
- partitions selectively between different coexisting lipid phases
- causes integral membrane proteins to respond by changing conformation or redistribution in the membrane
what are the two types of membrane proteins?
integral proteins and peripheral proteins
what are peripheral membrane proteins?
not embedded in the cell membrane rather they tightly adhere to the cell surface.
what are integral proteins?
- embedded in the membrane and consist of three types:
- Transmembrane
- Partial
- Linked via covalent bonds
- Integral proteins can serve as enzymes or receptors.
what do membrane proteins often form?
- form α- helices leading to the formation of channels
- cell's cytoskeleton attaches to the cell membrane via the membrane proteins to give the cell a more defined shape.
- Problems with the proteins leads to disruption of the cytoskeleton and cell shape.
what makes up for half of the genetic causes of hereditary spherocytosis?
ANK1
what does the mutation in ANK1 cause?
- cause loss of proteins involved with attachment to the spectrin cytoskeleton.
- RBCs lose their discoid shape and become rigid. Thus, the RBCs cannot pass through small capillaries as easily and are prone to hemolysis.
what are the signs and symptoms of Hereditary Spherocytosis?
- Anemia
- Splenomegaly
- Jaundice, Icterus
- Fever, Infection
what are the treatments of Hereditary Spherocytosis?
- Folate Supplementation
- Blood Transfusions
- Definitive: Splenectomy
what is the role in power production of the smooth ER?
NO ribosomes, Lipid synthesis
what is the role in power production of the rough ER?
covered in ribosomes, participates in protein synthesis
What does the ER serve as in the production of power in a cell?
Intracellular Ca2+ store
What is the role of the Golgi Complex?
- Protein maturation
- Modifies proteins for their target destination.
what are ribosomes?
- Site of protein synthesis
- Consist of two subunits
what are lysosomes?
- Contain over 50 digestive enzymes
- Degrade excess material from cellular functions and material from outside the cell
After being synthesized in the rough endoplasmic reticulum, through which pathway do secretory and membrane proteins destined for the plasma membrane travel?
move through the Golgi stacks and secretory vesicles.
what happens in the constitutive pathway in the secretory pathway?
vesicles fuse spontaneously with the plasma membrane
what happens in the regulated pathway in the secretory pathway?
the vesicles fuse only when triggered by a signal such as a hormone
How do steroids work?
- Steroids diffuse across the cell membrane and bind to receptors on the nuclear membrane.
- The steroid inhibits genes responsible for production of proinflammatory factors
- Steroids are derived from cholesterol molecules
What kind of mutation is Tay Sachs?
-rare, autosomal recessive
-mutation in HEXA gene responsible for the formation of beta-hexosaminidase
-mutation on the X CHROMOSOME
what is the role of beta-hexosaminidase?
- responsible for removing the toxin GM2-ganglioside.
- In Tay-Sachs, this does not break down GM2 ganglioside leading to toxic levels and neuron death.
what are characteristics of Tay-Sachs?
- Seizures, vision/hearing loss, intellectual delay, weak muscles.
- Cherry Red spots (eyes)
- No cure, treatment is supportive/palliative.
- Typically fatal by age 5
What are the mutations involved in Gaucher Disease?
-rare, autosomal recessive
-mutation in GBA
- lack of enzyme glucocerebrosidase
- leads to the buildup of glucocerebroside
what are the distinct types of Gaucher disease?
-Type 1: No neuro S/Sx, onset in adolescence
•Type 2/3: Ataxia, Hypotonia, Spasticity, onset infancy or early childhood
what are the treatments for Gaucher disease?
enzyme replacement therapy, substrate reduction therapy
what are the symptoms of Gaucher disease?
- Anemia
- Fatigue
- Easy Bruising and Bleeding
- Nosebleeds
- Osteoporosis
- Bone pain and easily broken bones
- Swollen stomach due to enlarged liver and/or spleen
what is endocytosis?
process by which the cell takes in materials that are too large to pass through