Sodium Potassium Pump/Action Potential
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
Resting Membrane Potential
Channels closed but pump open to maintain resting potential, -70 mV
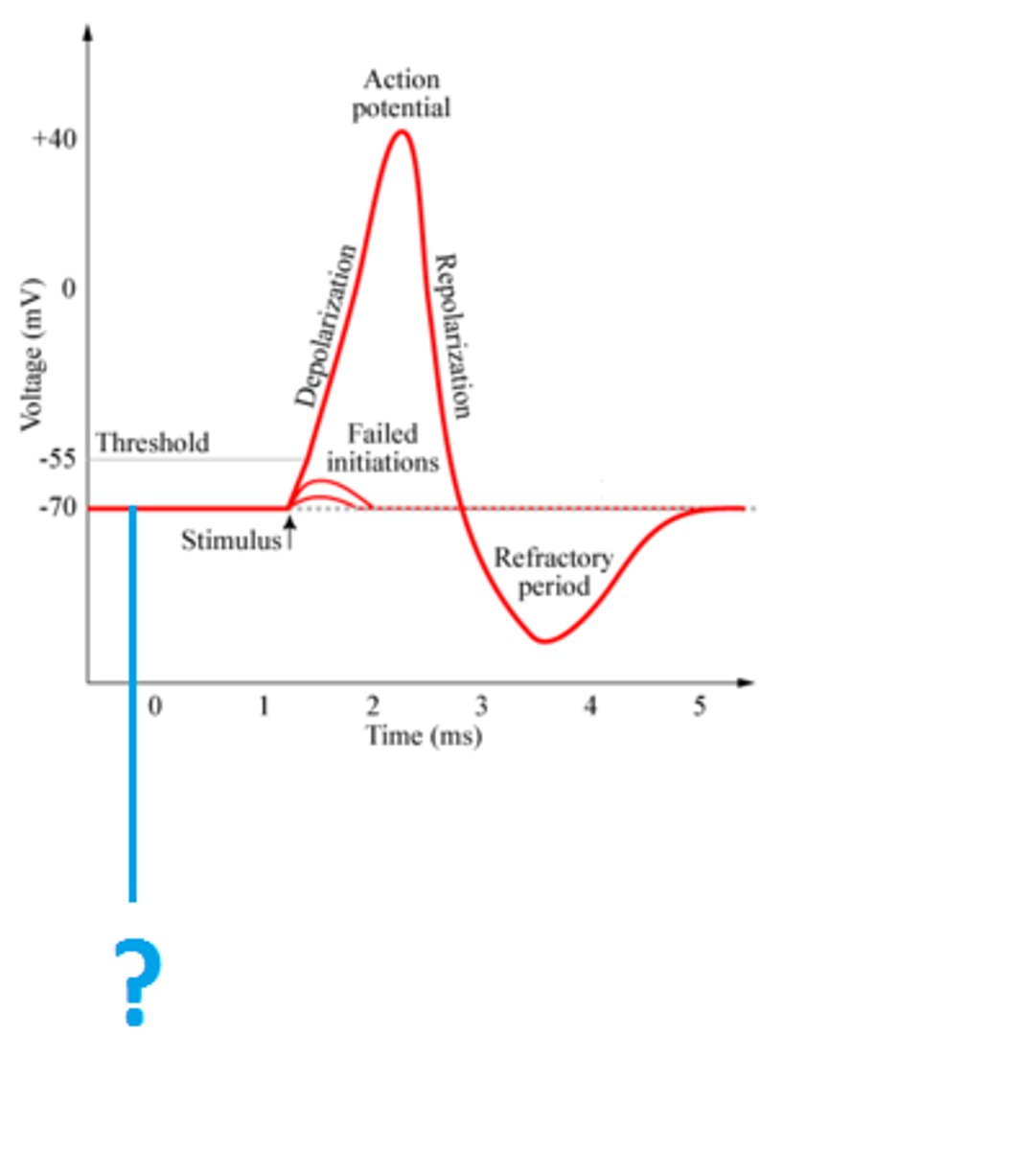
Depolarization
Na+ channel open and Na+ moves into cell, K+ channel closed, +40 mV, pump closed
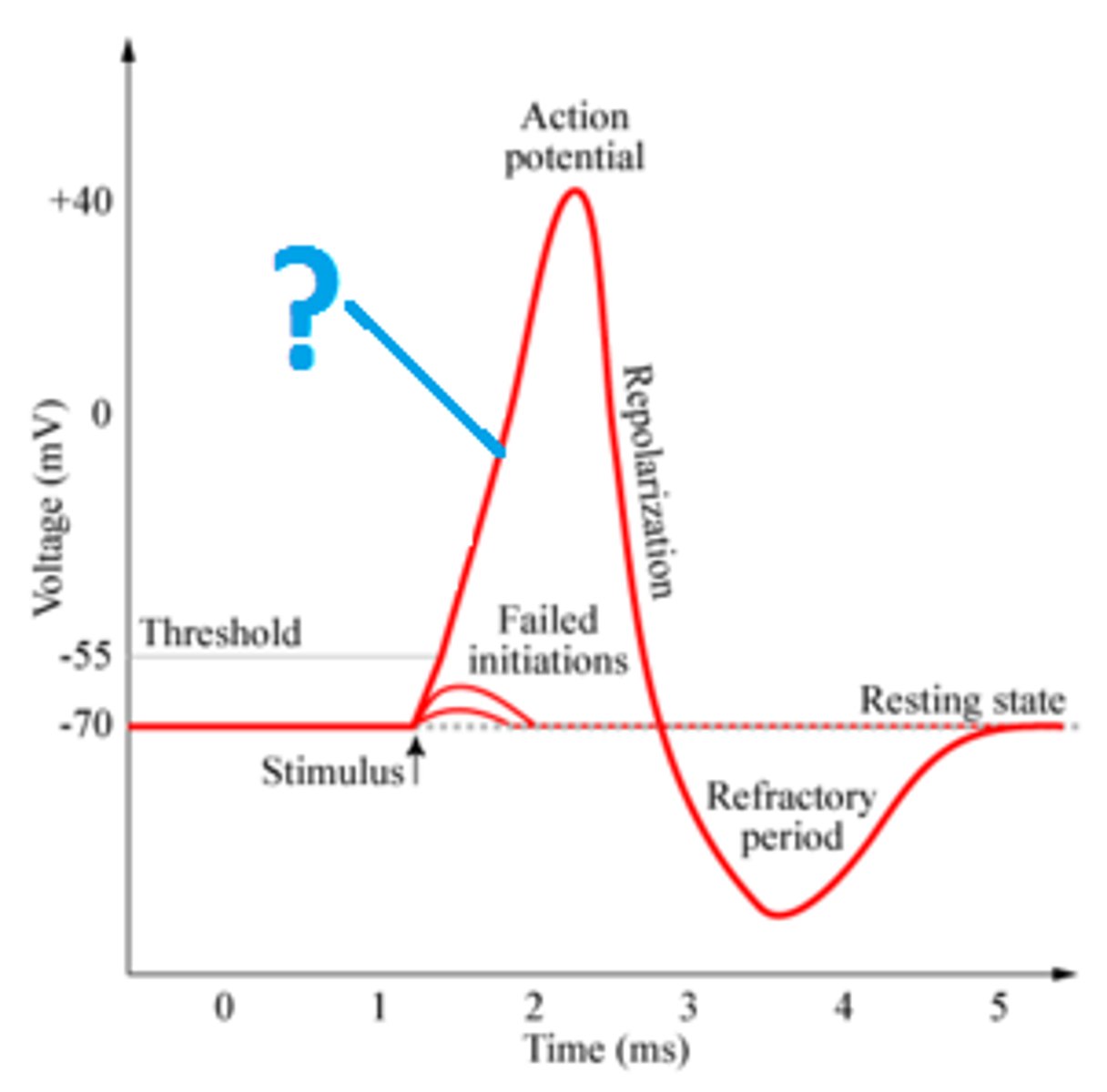
Repolarization
K+ channel open and K+ moves out of cell, Na+ channel closed, -70 mV, pump closed
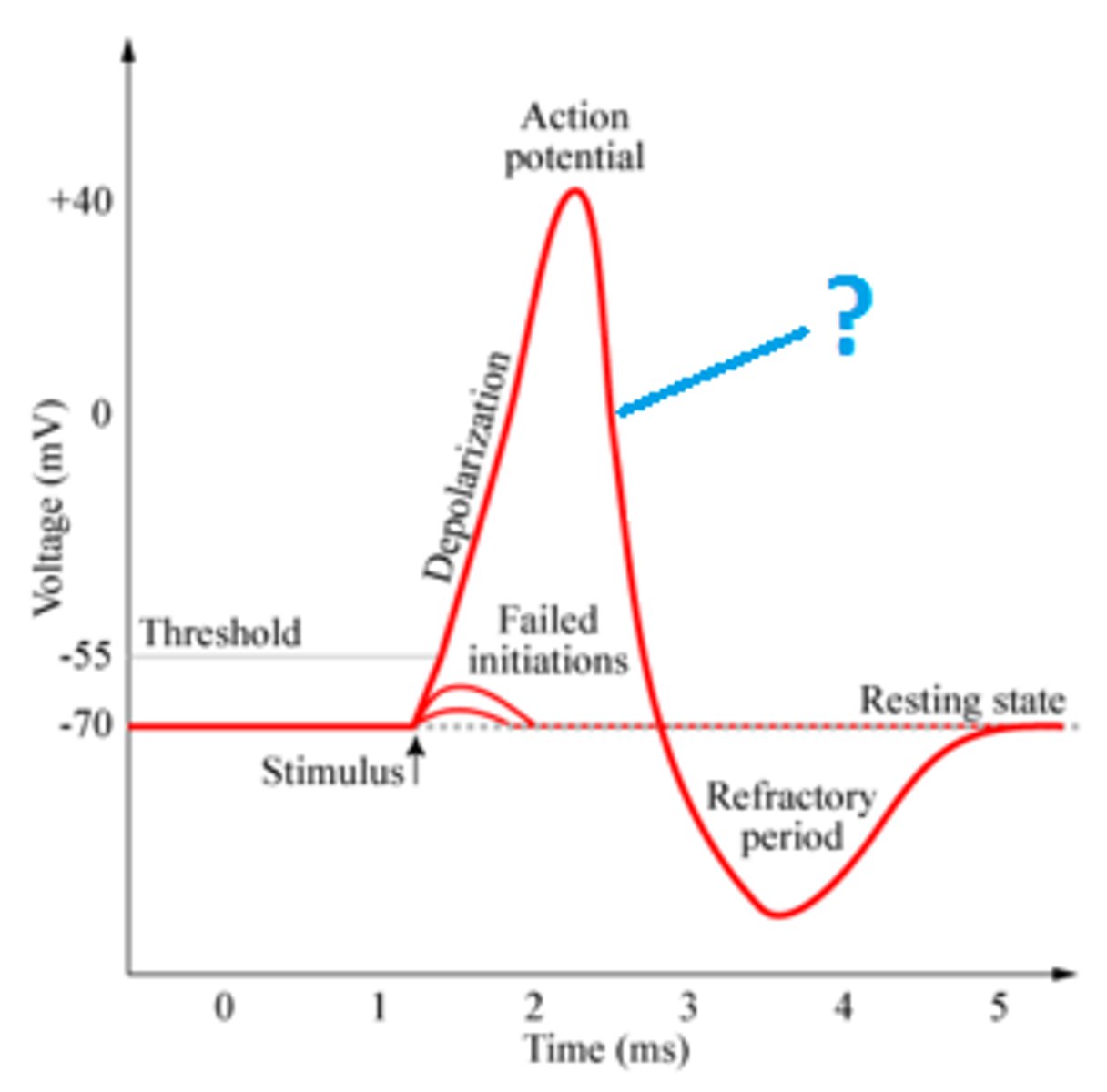
Hyperpolarization
K+ channel remains open and K+ continues to move out of cell, -75 mV, pump closed
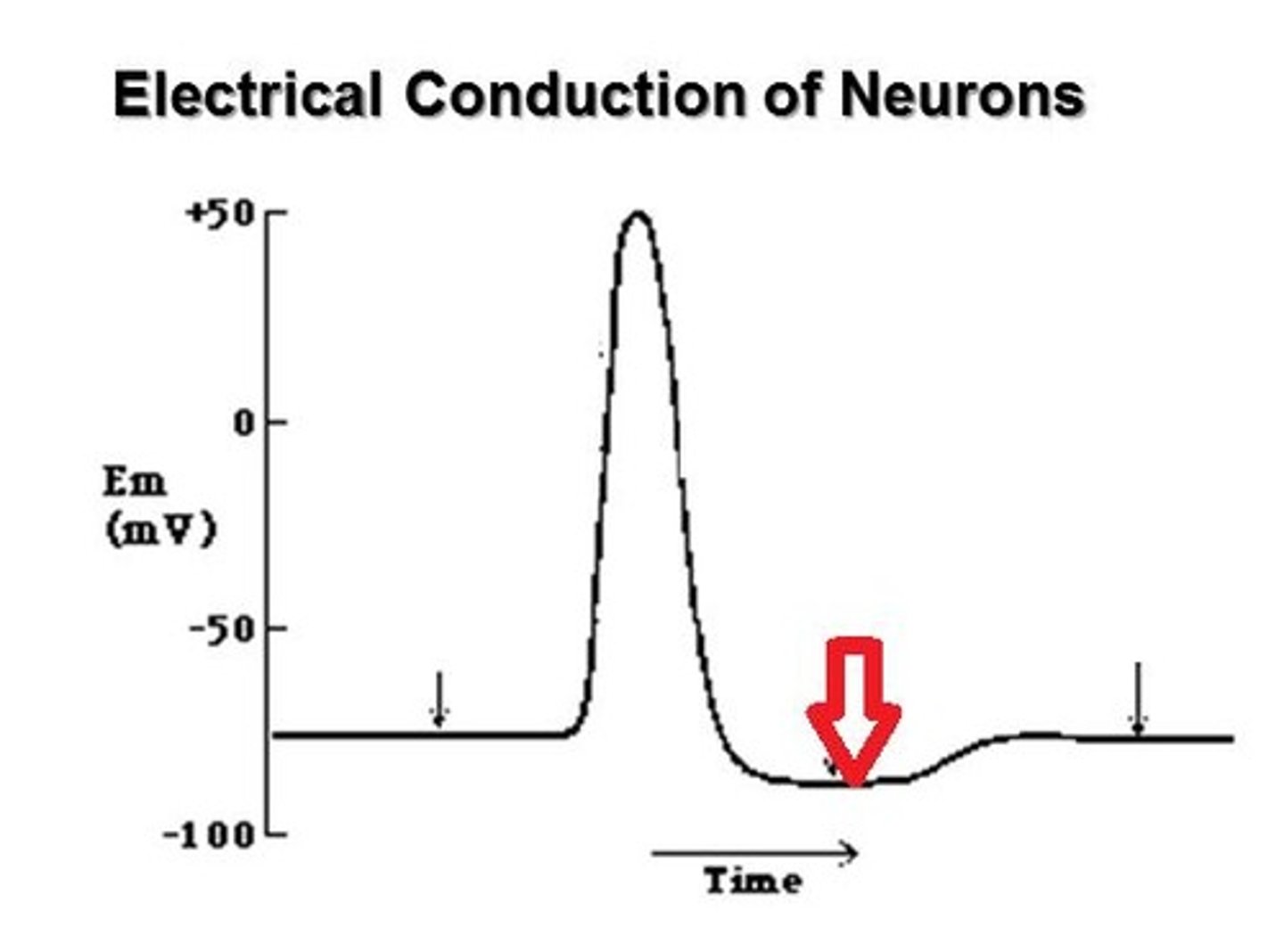
Types of ion channels
Mechanically gated, ligand gated, voltage gated, always open
Myelination
Allows for multiple action potentials to “skip” across an axon, increases propagation
Role of neurotransmitters
Carry signals between cells across the synapse
How neurotransmitters are stopped
Neurotransmitter degradation, reuptake, or diffusion