HRM 360 CH 5
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
Know that when leaders say “employee engagement,” they are talking about ______
employee motivation
Operant conditioning
What is it?
Positive and negative:
Reinforcement/punishment:
Positive Reinforcement
Negative Reinforcement
Positive Punishment
Negative Reinforcement
Extinction?
Conditioning human beings to like or not like things.
Positive and negative: Adding things or taking away
Reinforcement/punishment: behavior increases and behavior decreases
Behavior goes extinct, punishment or reward is no longer in place
What are the Social cognitive theory’s implications
Constantly observing actions from others and looking at rewards and consequences to learn ourselves
Intrinsic vs. Extrinsic motivation
Intrinsic motivation comes from within you
extrinsic when motivation comes from external things
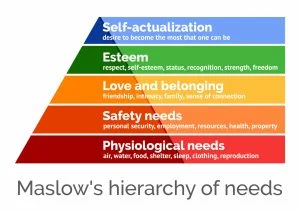
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs (what is at the top and bottom of the pyramid, what was this theory trying to claim that did not hold up to empirical tests? What did Maslow’s hierarchy give us that we didn’t have before?)
Self actualization (being your best self) top
physiological (hunger, water) bottom
The hierarchy doesn’t go from top and bottom it can be from everywehre
Maslow offers a holistic view of human needs (interconnected ways to see human needs)
What are the four drives? What should managers know about the four drive theory and how to help employees stay motivated?
Drive to acquire: seek, acquire, control, retain objects or experiences.
Drive to comprehend: satisfy our curiosity, know and understand ourselves and the environment
Drive to bond: form social relationships and develop mutual caring commitments with others.
Drive to defend: protect ourselves physically and socially.
Make sure all drives are met to motivate the employees.
Acquired Needs Theory-
a. How is it related to operant conditioning?
b. What is each of the following, and be able to recognize it in a person:
i. Need for achievement
ii. Need for power
iii. Need for affiliation
c. How are acquired needs different from the four drives?
d. What should managers know about acquired needs and how to help students stay motivated?
People are condition that they want something so much it turns into a need. Recognition.
Need for control
Drive to bond
how they are “shaped” or not
Continue to help with opportunities with students
Expectancy theory
a. What is it?
b. What is E-P
c. What is P-O
d. What is valence?
e. What does all of the above have to do with how management should motivate employees?
Motivated on what they expect.
E-P (effort to performance): my effort tied to performance
P-O (Performance to valued outcome): Is it going to get me somewhere I want
Valence: Positive and negative outcomes
They need to know if the emeployee will be able to get to that goal and that the outcome is worth it.
Equity theory
a. What is it? What are people comparing?
b. What are the implications for how equity theory says people are motivated?
c. Is it actual inequity or perceived inequity that influences whether or not people feel an injustice has occurred?
Comparing input and outcomes to other input and outcomes (monkey in cage).
Correct the justice, reduce input or show up late, complain
Perceive if something is not fair is when injustice can occur.