Radioactivity
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Antoine Henri Becquerel
nobel laureate
Antoine Henri Becquerel
first person to discover evidence of radioactivity (nuclear reactions)
Radioactivity
involves the spontaneous emission of particles or ionizing radiation by unstable nuclei
Unstable Nuclei
radioactive, referred to as radionuclides
Unstable Nuclei
tends to undergo radioactive decay into a more stable different nuclide
Alpha Particle
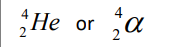
Electron
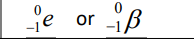
Positron
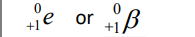
Proton
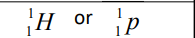
Neutron
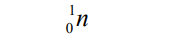
Types of Radioactive Decay
ALPHA EMISSION, BETA EMISSION, POSITRON EMISSION, ELECTRON CAPTURE, GAMMA EMISSION
Alpha Emission
Emission of an α–particle (a helium nucleus)
Beta Emission
Emission of a β–particle (a high-speed electron)
Positron Emission
Emission of a positron (a particle that has the same mass as an electron but positive charge)
Beta Emission
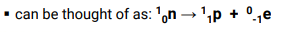
Positron Emission

Electron Capture
addition of an electron to a proton in the nucleus
Electron Capture
as a result, a proton is transformed into a neutron
Gamma Emission
emission of a γ–ray (high energy radiation)
Gamma Emission
almost always accompanies the loss of a nuclear particle
Nuclear Fission
splitting of a nucleus into smaller parts
Nuclear Fission
releases large amount of energy
Nuclear Fission
induced by bombarding a nuclide w/ n, e or etc
Nuclear Fusion
reactions in which two or more elements fuse together to form one larger element