d1.1 dna replication
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
what is the definition of dna?
dna is a polynucleotide consisting of 4 nucleotides that vary based on their nitrogenous base.
define dna replication.
dna replication is the production of exact copies of dna with identical base sequences.
what is dna replication required for?
reproduction: when asexual reproduction takes place, cells undergo a process called binary fission where the dna first replicates, followed by the mother cell dividing into two daughter cells.
growth and tissue replacement: when multicellular organisms produce new cells, this requires dna first followed by division of the nucleus via mitosis and cytokinesis. cells naturally age or get damaged/infected; when this happens, they repair and replace the tissue.
why is dna replication semi-conservation?
in dna replication, the parent strand acts as a template for the synthesis of the daughter strand from free nucleotides.
what are the complimentary base pairs?
The complementary base pairs in DNA are adenine paired with thymine (A-T) and cytosine paired with guanine (C-G). While errors are very rare, they can easily be checked, ensuring a high degree of accuracy.
what is the process of dna replication?
the enzyme helicase unwinds the double-helix structure of the dna by breaking hydrogen bonds between the strands using atp-hydrolysis energy.
the enzyme dna polymerase gathers free dna nucleotides and exposes them close to the bases of the template strand to form new strands.
the daughter dna molecules rewind into a double helix.
define PCR.
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is an artificial method of replicating regions of DNA by going through multiple cycles of synthesis. With every cycle, the DNA sample is doubled.
what is needed to conduct PCR?
5 things inside an eppendorf
target dna sample
free dna nucleotides
buffer solution: provides optimal conditions
taq polymerase: heat-resistant polymerase enzyme that synthesizes new DNA strands using free nucleotides. it is derived from thermus aquaticus— a hot springs bacterium that can withstand high temperatures and not denature.
dna primers: short, single-stranded sequences of dna that are specific to the target sample and bind complimentarily.
thermal cycler: automatically cycles between appropriate temperatures for the process.
what is the process of PCR?
DAE
denaturation: The temperature is set to 95 degrees to break hydrogen bonds between the two strands, unwinding the double helix and separating the two strands.
annealing: the temperature is set to 45-60 degrees for the DNA primers to complimentary bind to the target DNA strands. two primers are used—each for one strand.
elongation (72 degrees): taq polymerase synthesizes the strands using free nucleotides.
what is gel electrophoresis?
gel electrophoresis is a process of separating fragments of dna on polymer gel, based on size and overall change. in order for this to be done, samples must have
uniform charge
be small enough to move through gel
restriction endonuclease must take place to break the DNA sample into smaller proportions as it is very long
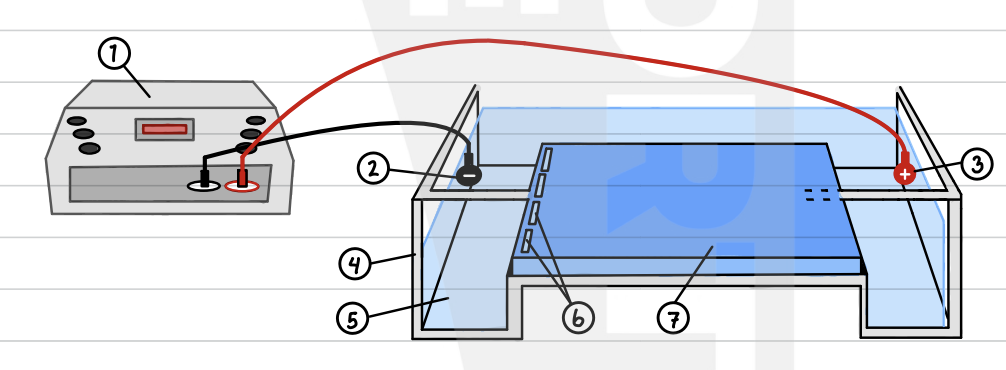
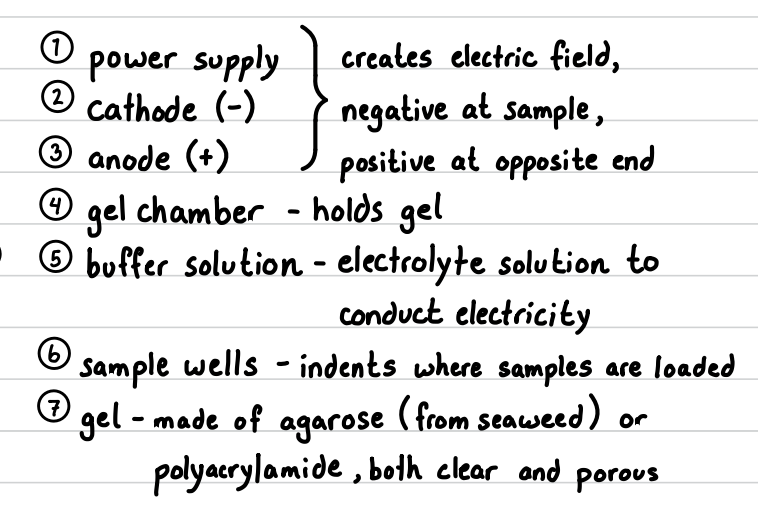
label the setup and what is it called?
what is the process of gel electrophoresis?
sample is injected on top of the gel using a micropipette.
molecules migrate down to the anode at different paces; smaller molecules will be faster, molecules of similar length and mass will transport in a group.
once the molecules reach the anode, voltage is turned off and gel is removed and stained with a dye. (in the case of dna, the dye can be seen under uv light) and bands are compared.
what is dna profiling and what is its process?
dna profiling is the process of identifying individuals based on DNA.
DNA sample is collected.
STR (short tandem repeats) sequences are then selected and amplified by PCR.
Gel electrophoresis takes place, producing a banding pattern and DNA profile—unique to the individual.
what are the applications of dna profiling?
forensic investigation
paternity test