Master List of All Fungal & Protozoal Diseases
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lu
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Ringworm (Tinea Infections)
fungal skin disease
cause: Tinea species (ex. Tinea corporis = ringworm of the body)
T. pedis may lead to a secondary bacterial infection
transmission: direct contact (person/animal to person); indirect (fomite)
treatment: antifungal drugs
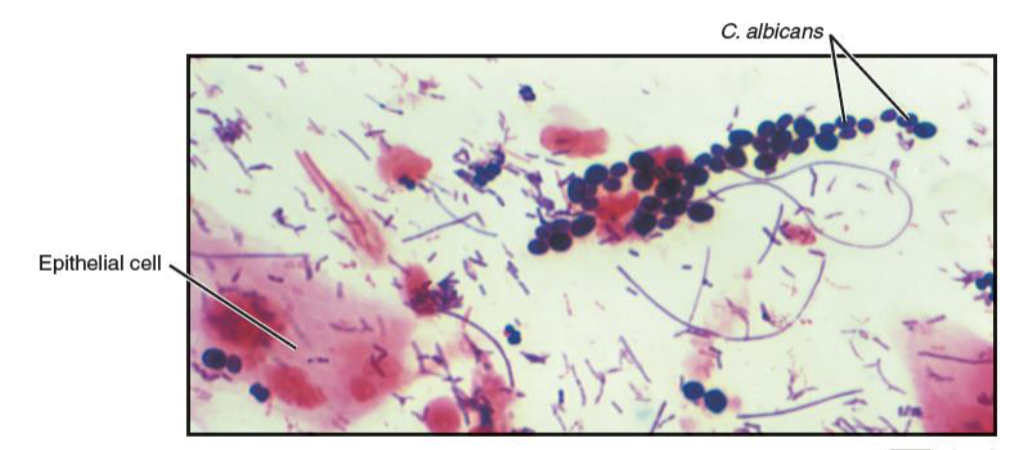
Candida albicans
fungal skin disease
cause: C. albicans
part of normal flora in mouth, GI, and vagina
virulence: opportunistic
transmission: direct or indirect contact in hospitals (nosocomial)
symptoms: oral thrush, cutaneous and vulvovaginal candidiasis
Candida auris
fungal skin disease
cause: C. auris
virulence: opportunistic, antifungal drug resistance
unique: requires special laboratory methods to identify
transmission: direct or indirect contact in hospitals (nosocomial)
will enter the BS and spread throughout the body
Cryptococcosis
nervous fungal disease
cause: Cryptococcus neoformans (C. gatti, C, grubii)
encapsulated, opportunistic
transmission: airborne spores; contaminated soil from bird poop
symptoms: pulmonary infection (alveoli); cryptococcal meningitis (after travel through BS to CNS)
African Trypanosomiasis
nervous protozoal disease
cause: Trypanosoma genus
virulence: antigenic variation of surface glycoproteins
transmission: infected tsetse fly bite
symptoms: from blood and lymph → all other organs
untreated → deteroriation of CNS → coma and death
treatment: NONE (too difficult due to antigenic variation)
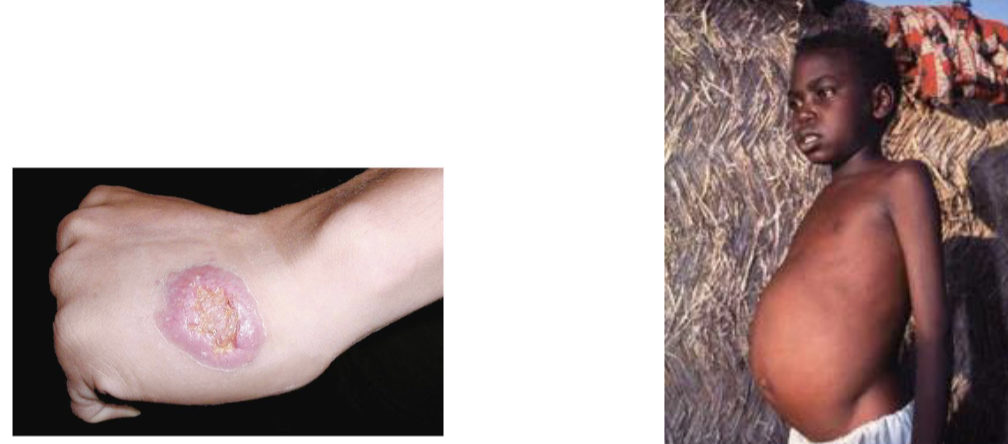
Visceral Leishmaniasis (Kala-azar)
cardiovascular/lymphatic protozoal disease
cause: Leishmania donovani
taken by macrophage → multiplies and circulates → systemic infection
virulence: opportunistic
transmission: sandfly bite
symptoms: fever, anemia, swelling due to enlargement of spleen and liver
other Leishmania species can cause cutaneous leishmaniasis
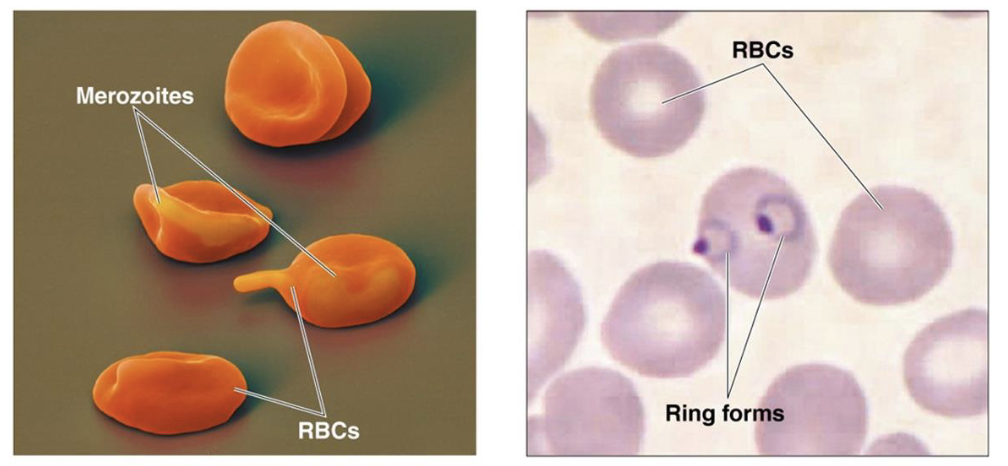
Malaria
cardiovascular/lymphatic protozoal disease
cause: Plasmodium protozoans
different stages:
sporozoite: carried by mosquito
merozoite: transforms in liver; ruptures RBCs
trophozoite: multiplies after RBC invasion → more merozoites
transmission: infected Anopheles mosquito bite
symptoms: fevers and chills because of infected RBC ruptures
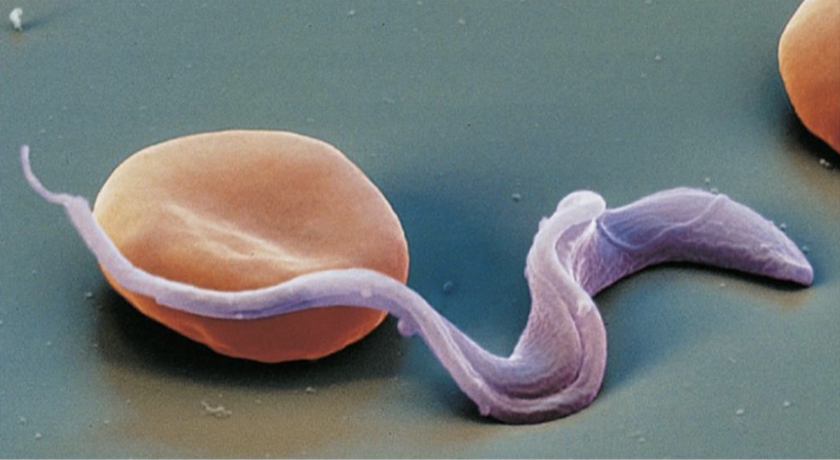
Plasmodium species
cardiovascular/lymphatic protozoal disease
cause: primarily P. falciparum
human parasite
virulence: obstructs blood vessels; antigenic variation; cholorquine resistance
treatment: Mosquirix; chemoprophylaxis; artemisinin-based combination therapies (ACTs)
Chagas disease (American Trypanosomiasis)
cardiovascular/lymphatic protozoal disease
cause: T. cruzi
found in Latin America (few in southern USA)
virulence: transplacental (chronic); multiples in host
transmission: reduviid (kissing) bug; contaminated feces
symptoms: fever, swollen glands, swelling at bite site; damaged nerves (chronic)
treatment: NONE (difficult)
Toxoplasmosis
cardiovascular/lymphatic protozoal disease
cause: Toxoplasma gondii
virulence: dormancy; transplacental; opportunistic
transmission: ingestion of oocysts from cat feces; tissue cysts of undercooked meat
symptoms: may appear asymptomatic; mild lymphadenopathy; acute infection (tachyzoites)
miscarriage or congenital disease
re-activation may lead to Toxoplasmic Encephalitis
Coccidioidomycosis
respiratory fungal disease
cause: Coccidioides immitis, C. posadasii
found in arid regions of southwestern USA
virulence: opportunistic; forms a thick-walled spherule filled with spores
transmission: inhalation of soil spores
symptoms: mild flu-like symptoms; may be asymptomatic
Histoplasmosis
respiratory fungal disease
cause: Histoplasma capsulatum
found in central and eastern US soil
virulence: replicate within macrophages, opportunistic
transmission: inhalation of soil spores
symptoms: mild and localized within lungs
immunocompromised → suffer severe disease
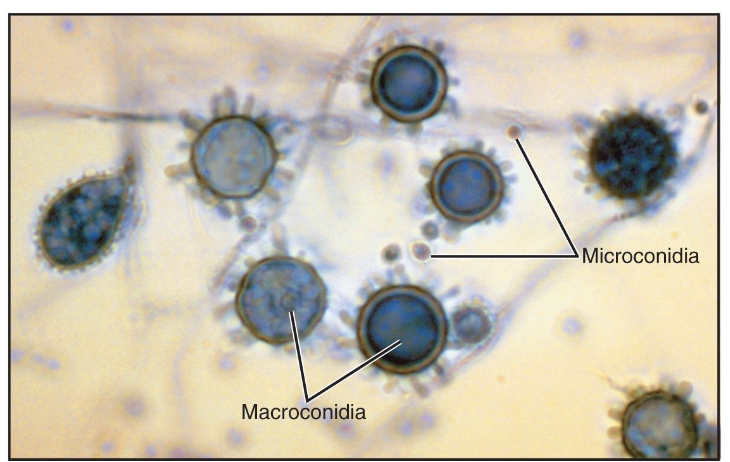
Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP)
respiratory fungal disease
cause: Pneumocystis jirovecii
virulence: opportunistic; antifungal drug resistance
symptoms: inflammation of lungs (alveoli)
treatment: specific antimicrobial drugs
Blastomycosis
respiratory fungal disease
cause: Blastomyces dermatitidis
thrives in moist soil rich in organic material
spores will mature into yeast cells
transmission: breathing spores into lungs; direct inoculation into wound (rare)
symptoms: pneumonia; extensive tissue damage (systemic)
Aspergillosis
respiratory fungal disease
cause: Aspergillus fumigatus
found in compost piles and decaying vegetation
virulence: opportunistic
transmission: inhalation
symptoms: triggers allergic reaction; infects lungs (invasive; immunocompromised)
Pulmonary cryptococcosis
respiratory fungal disease
cause: C. neoformans, C. gatti
found in environment (soil, brird droppings, tree debris)
virulence: opportunistic
transmission: inhalation of microscopic fungal spores
symptoms: pneumonia; may be asymptomatic
untreated = bloodstream → meningitis
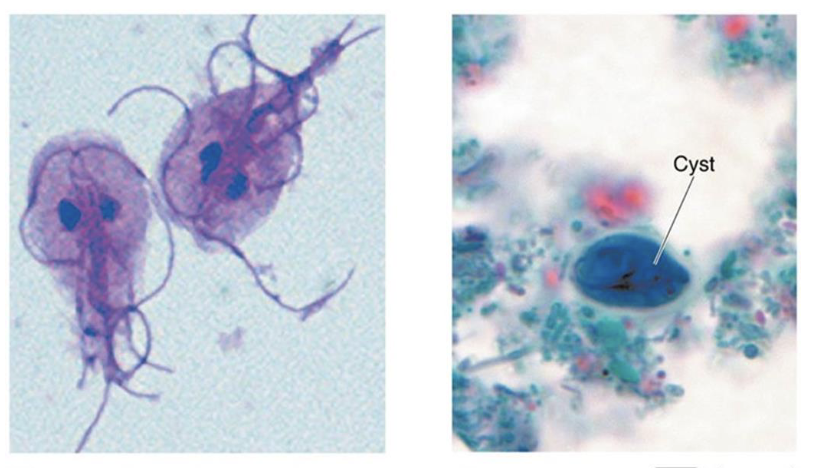
Giardiasis
digestive protozoal disease
cause: Giardia duodenalis
virulence: adherence to bowel walls (trophozoite); chlorination resistance
transmission: ingestion of cysts from contaminated water, food, or hands
symptoms: severe diarrhea (foul and greasy) → interrupts normal absorption
treatment/prevention: boiling, filtration, and good hygiene
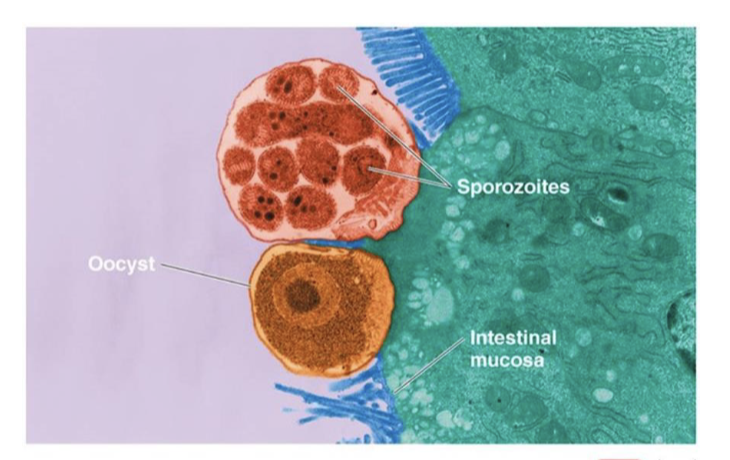
Cryptosporidosis
digestive protozoal disease
leading cause of recreational waterborne disease outbreaks
cause: Cryptosporidium hominis, C. parvum
virulence: opportunistic; chlorination resistance
transmission: ingestion of oocysts that mature into sporozoites
symptoms: mild, self-limited profuse diarrhea
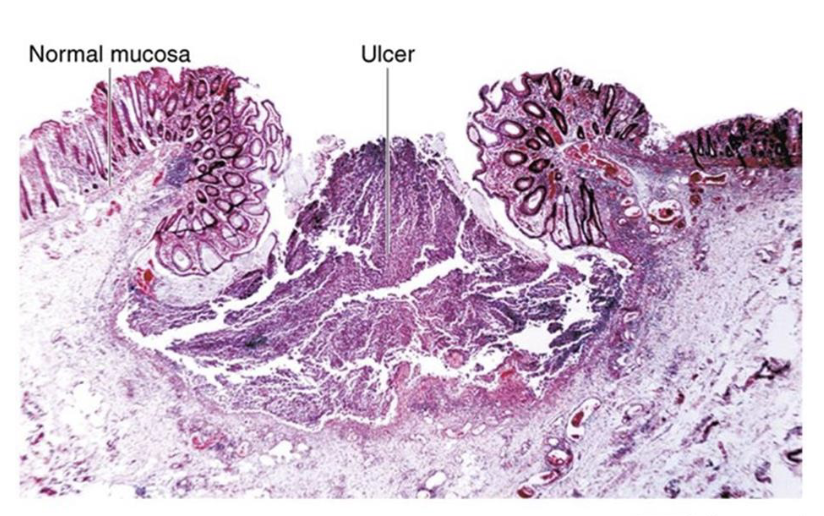
Amebiasis (Amoebic Dysentry)
digestive protozoal disease
cause: Entamoeba histolytica
virulence: mature into trophozoites to invade intestinal mucosa; chlorination resistance
transmission: ingestion of cysts from contaminated food or water
symptoms: dysentery and abdominal pain; peritonitis (severe)
Cyclosporiasis
digestive protozoal disease
cause: Cyclospora cayetanensis
found in tropical or subtropical regions
virulence: highly resistant to chlorination
transmission: ingestion of oocytes from imported fresh produce (cilantro, basil, raspberries, and leafy greens)
symptoms: watery diarrhea
Vulvovaginal Candidiasis
reproductive fungal disease
cause; C. albicans
virulence: opportunistic
transmission: overgrowth of C. albicans in vagina and vulva
symptoms: disrupts vaginal microbiota or immunity (such as uncontrolled diabetes, altered vaginal pH, hormone changes, and prolonged antibiotic therapy)
Trichomoniasis
reproductive protozoal disease
cause: Trichomonas vaginalis
transmission: sexually
symptoms: infects urogenital tract of both males and females
males: asymptomatic
female: irritation and profuse frothy, greenish-yellow, foul odor discharge
unique: other species of Trichomonas are normal commensals