Mod 03 - Stress, Mental Health & Sleep
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Fight or flight
The acute stress response. The nonspecific response to demands which are placed.
General Adaptation Syndrome
The three-stage response to stress: Alarm, Resistance, and Exhaustion.
Alarm Stage
First stage of General Adaptation Syndrome where cortisol is released.
Resistance Stage
Second stage where the body tries to counteract the physiological impact of the alarm stage.
Exhaustion Stage
Third stage reached in periods of extended stress, depleting the body's resources.
Central Nervous System
Comprises the brain and spinal cord.
Peripheral Nervous System
Connects the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body.
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
Controls organs and glands outside of voluntary control.
HPA Axis
Comprises the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and adrenal gland.
Hypothalamus
The command center of the brain that activates the sympathetic nervous system.
Sleep-Wake Homeostasis
Keeps track of your need to sleep.
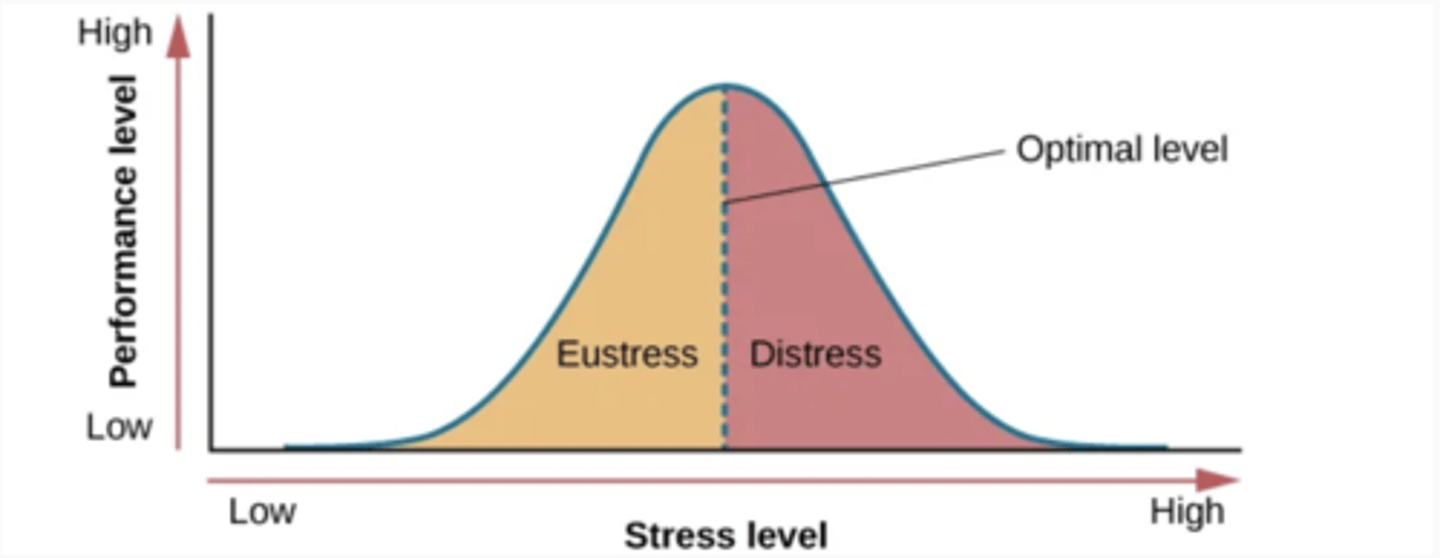
Eustress
Good stress.
Distress
Bad stress.
Relative Energy Deficiency in Sport (RED-S)
An imbalance in an athlete's energy intake and energy expended by exercise.
Karvonen Formula
Max HR = 220 - Age; HRR = Max HR - Resting HR; Upper limit = HRR x (0.85) + Resting HR; Lower limit = HRR x (0.6) + Resting HR.
Sleep recommendations
7-9 hours of sleep is recommended for health.
Effects of long-term stress
Includes difficulty sleeping, appetite changes, mood issues, and loss of interest in enjoyable activities.
Self-management Strategies
Include delegating work, establishing boundaries, and setting priorities.
Stressors
The stimuli that cause a response.
Unmanaged stress
Stress that is not effectively dealt with, leading to negative health outcomes.
Stress and sleep
Stress leads to lack of sleep, impacting overall health.
Things that increase the risk of having an eating disorder
Include biological, psychological, and social factors.
Characteristics of Stress Resilient People
Having a strong social network
Adapt and feed confident of what they can control
Open to change
Optimistic
Self-care
Stress
The response to the stimuli
Human Function Curve
What are the two major parts of the nervous system?
The central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system
A section of the peripheral nervous system is...
the Autonomic Nervous system (ANS)
The two systems that make up the Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) are...
the Sympathetic Nervous System and the Parasympathetic Nervous System
What are the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems involved in?
Initiating and regulating our stress response
If a stressor continues after the initial response, the hypothalamus...
Continues to respond by releasing a hormone to the pituitary gland. This causes a chain reaction of hormone release that ends in the adrenal gland
Common thinking traps
Always looking at a deadline as distress
Change
How many more minutes per night should Americans sleep to be happier, healthier, and safer?
60-90 minutes
What does lack of sleep cause?
Acute and chronic health problems including cardiovascular disease, diabetes and weakened immunity. Mental health can also be impacted.
What do neurotransmitters do?
Shape sleep and wakefulness. They can "switch off" the activity of cells that signal arousal or relaxation.
What is stress a risk factor for?
The development of drug addiction
Excess sugar consumption
Emotional eating
What type of risks are there that contribute to having an eating disorder?
Biological, Psychological, and Social
Biological risk (eating disorder)
Close relative with a mental health condition or eating disorder, history of dieting, type 1 diabetes
Psychological risk (eating disorder)
perfectionism, body image dissatisfaction, history of anxiety
Social risk (eating disorder)
weight stigma, teasing or bullying, appearance ideal internalization, acculturation (minority groups), limited social networks
What are ways to manage stress?
Keep things in perspective
Think positively
Improve Time Management
Mindfulness meditation
Cognitive behavior therapy
Physical activity
Spend time in nature
Nutrition
Resilience/social support
How long do you want to be between your upper and lower HR limit while working out?
20 minutes