Exam 2: Neuroscience and Sensory Systems: Neurons, Brain, and Cranial Nerves
1/253
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
254 Terms
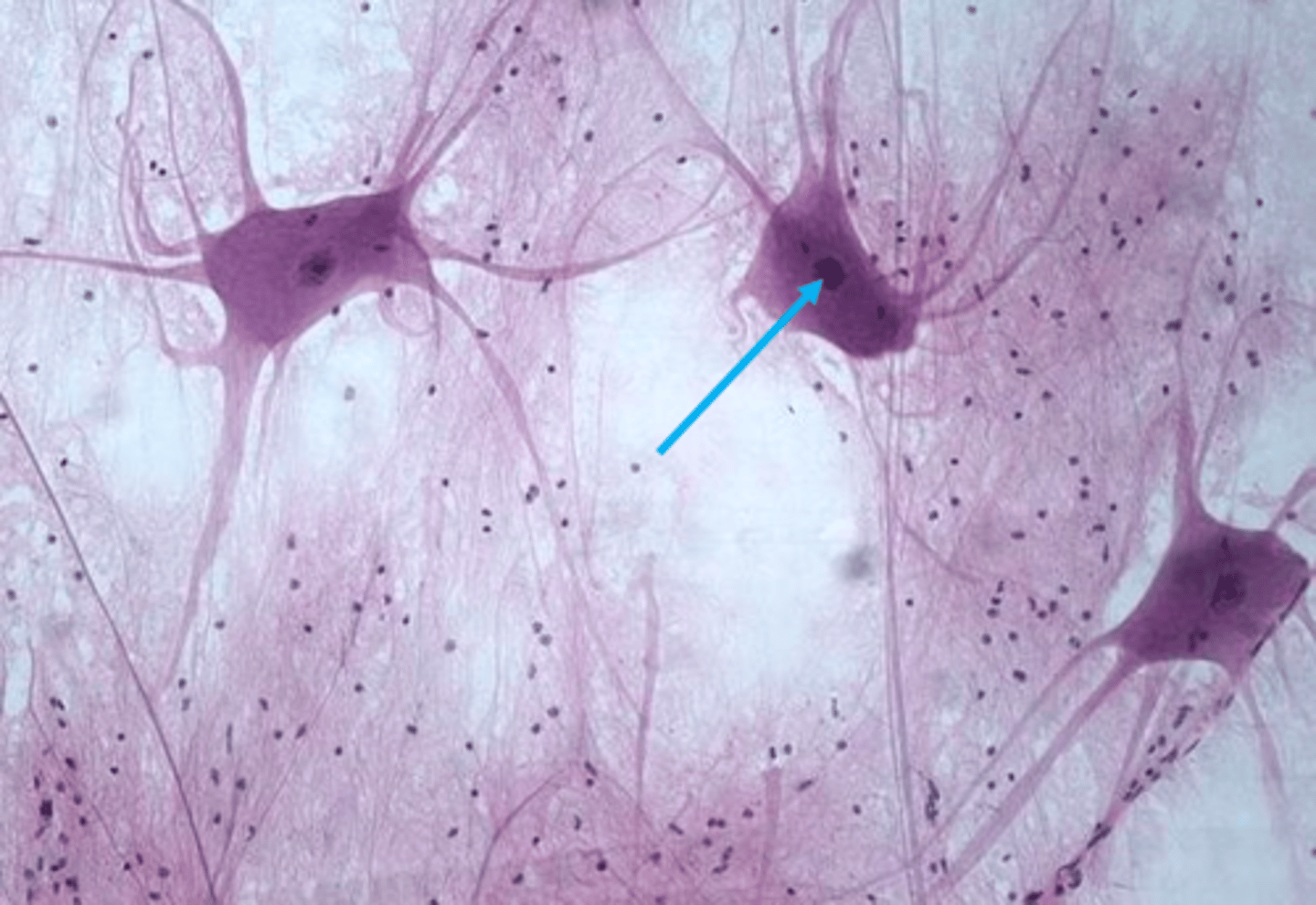
Cell Body
The part of the neuron that contains the nucleus and organelles.
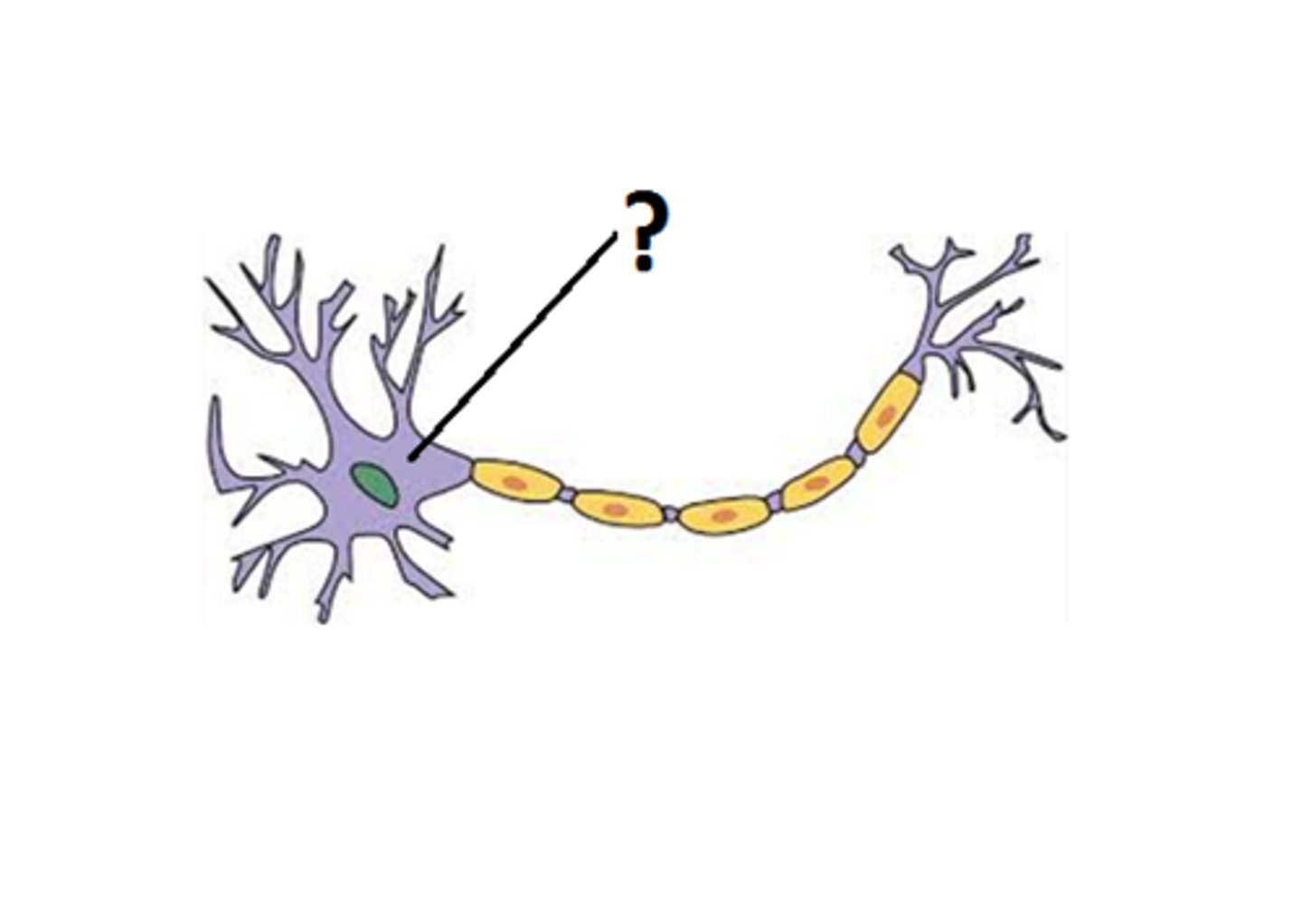
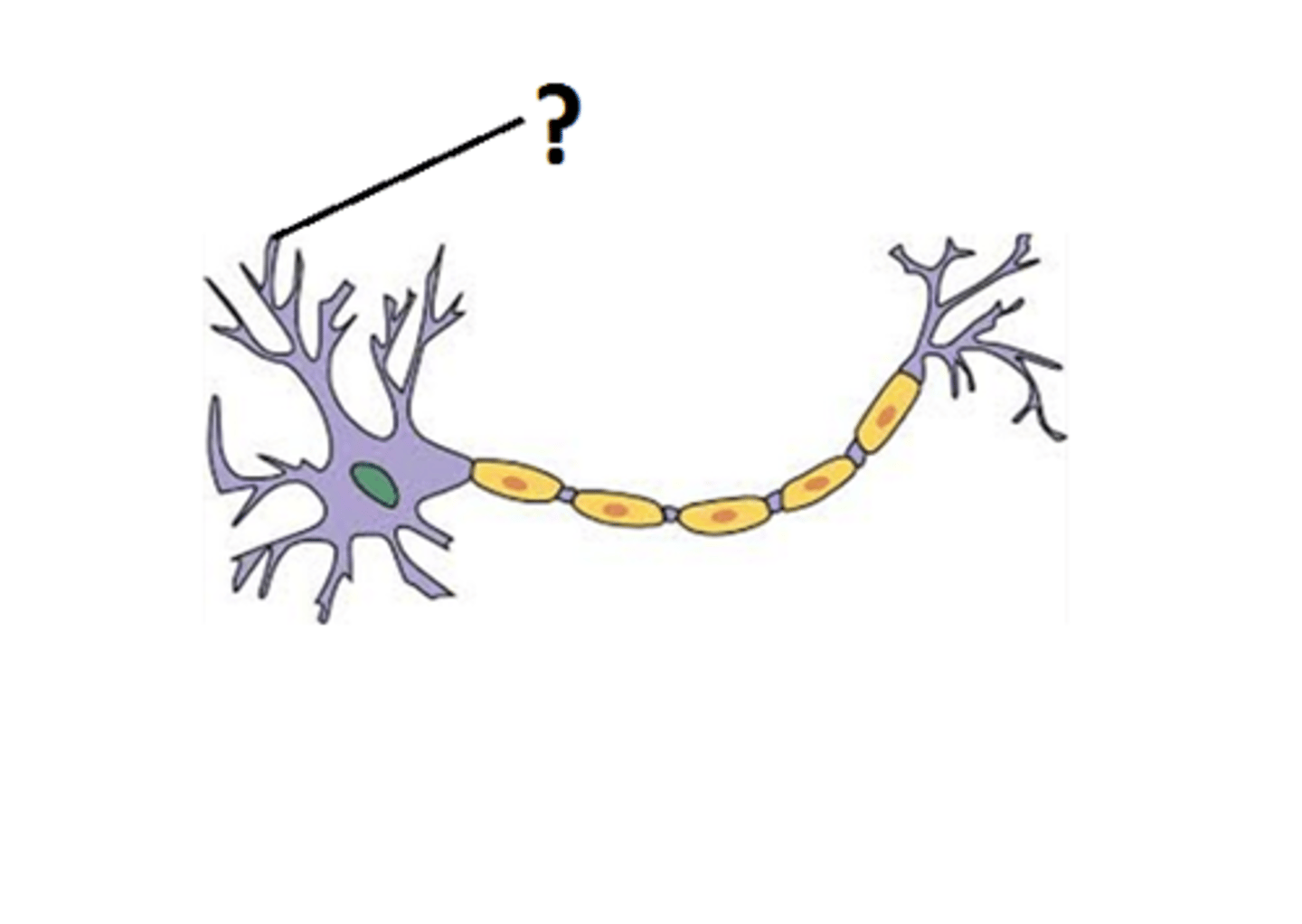
Dendrites
Branch-like structures that receive signals from other neurons.
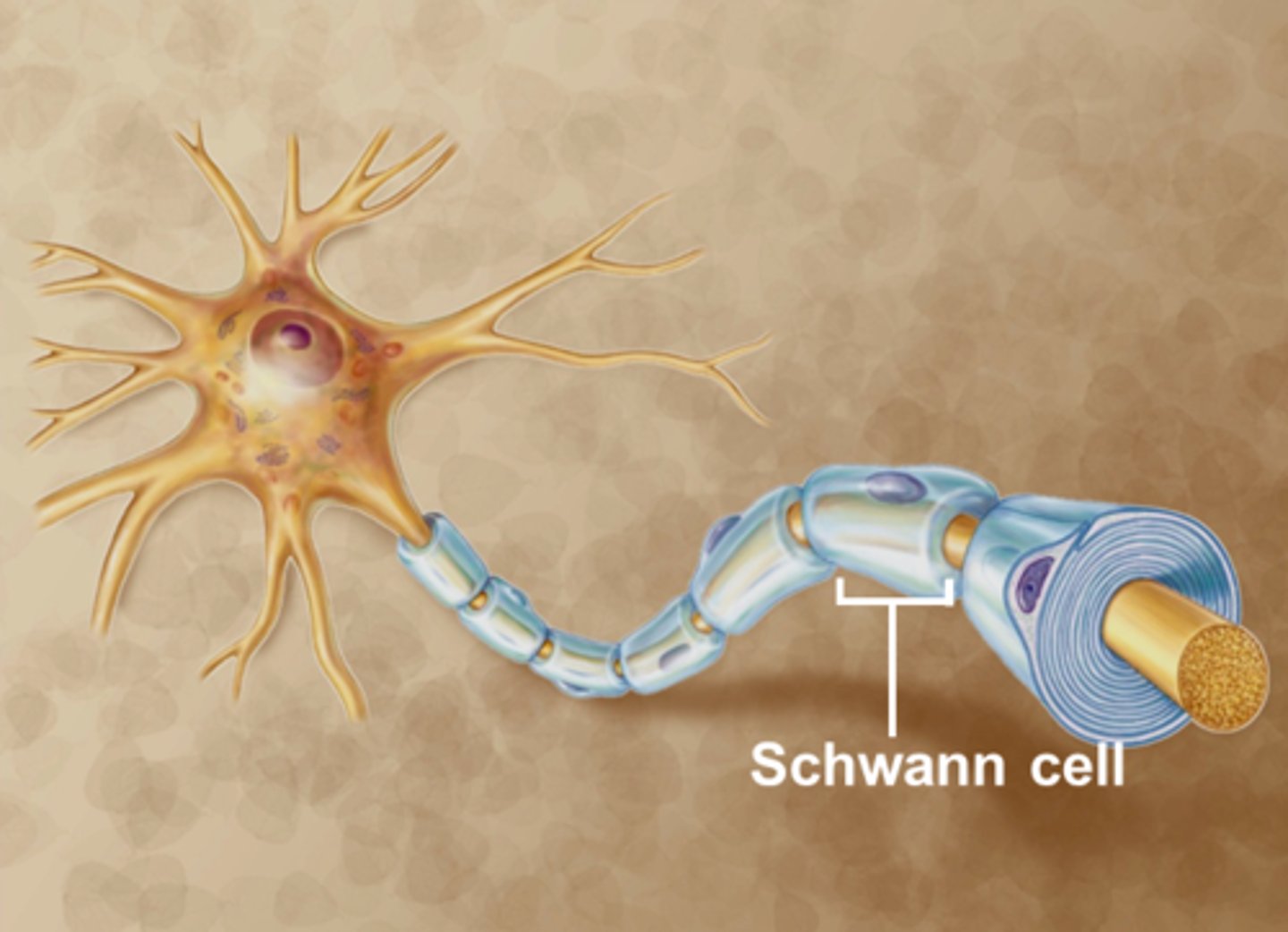
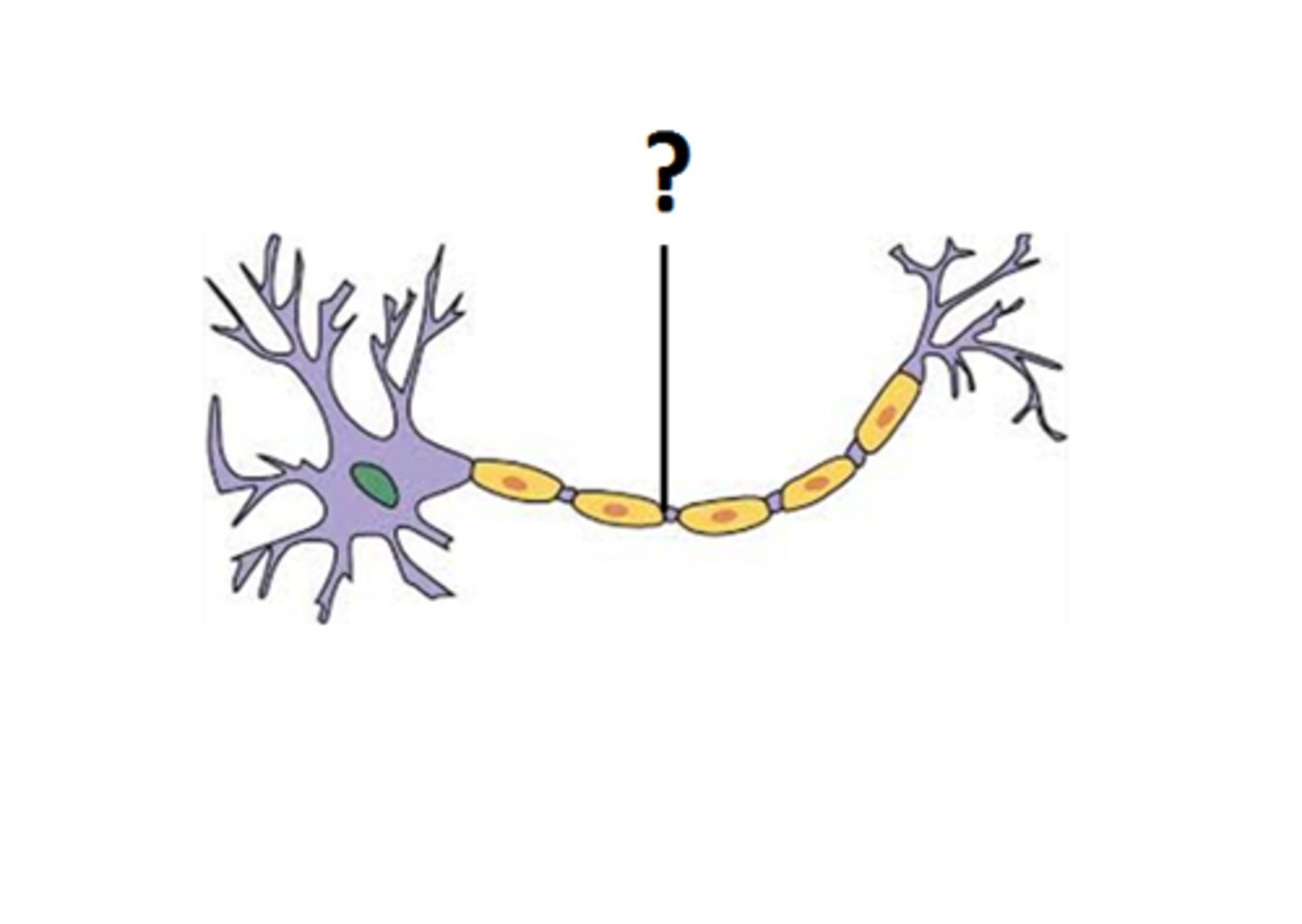
Schwann (PNS)
Cells that form the myelin sheath around axons in the peripheral nervous system.
Axon terminals
The endpoints of an axon where neurotransmitters are released.
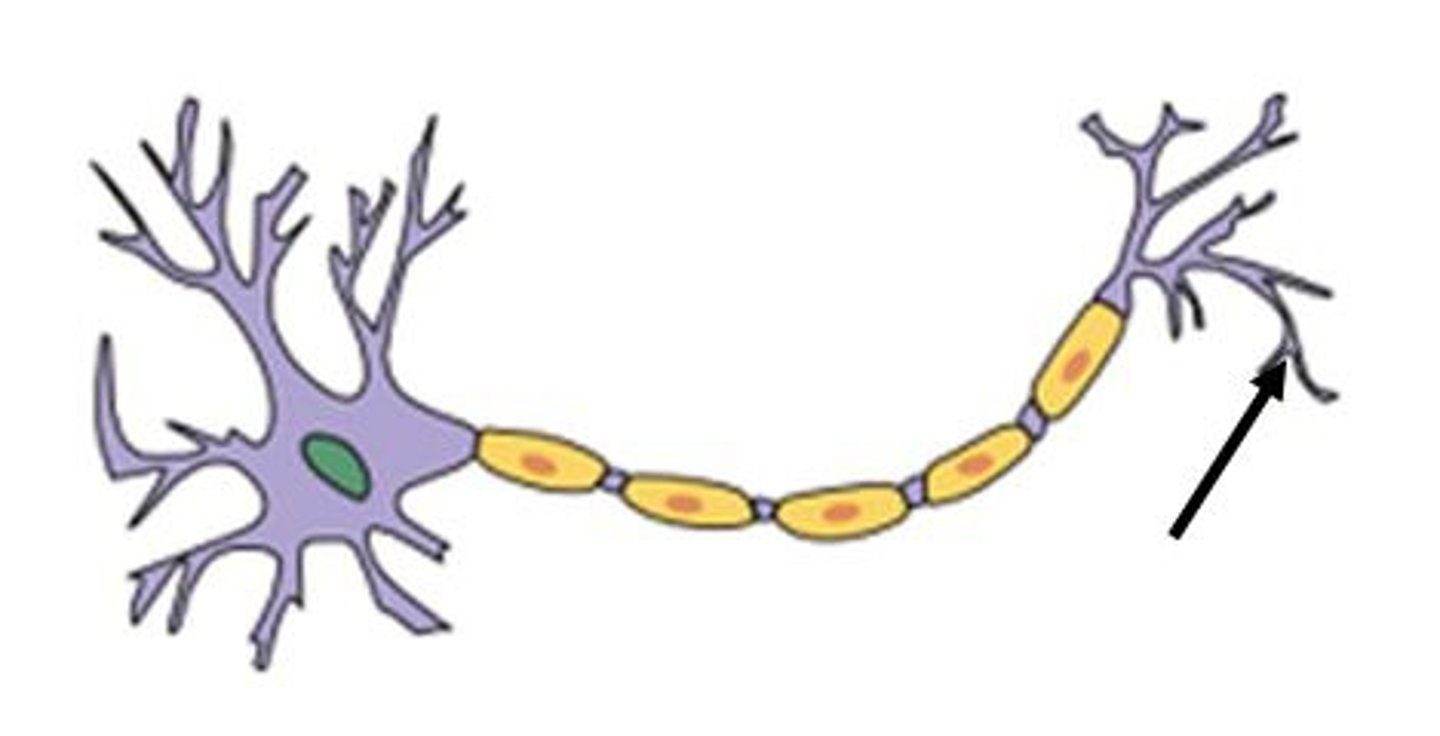
Axon
The long, slender projection of a neuron that conducts electrical impulses away from the cell body.
Nucleus
The organelle in the cell body that contains genetic material.
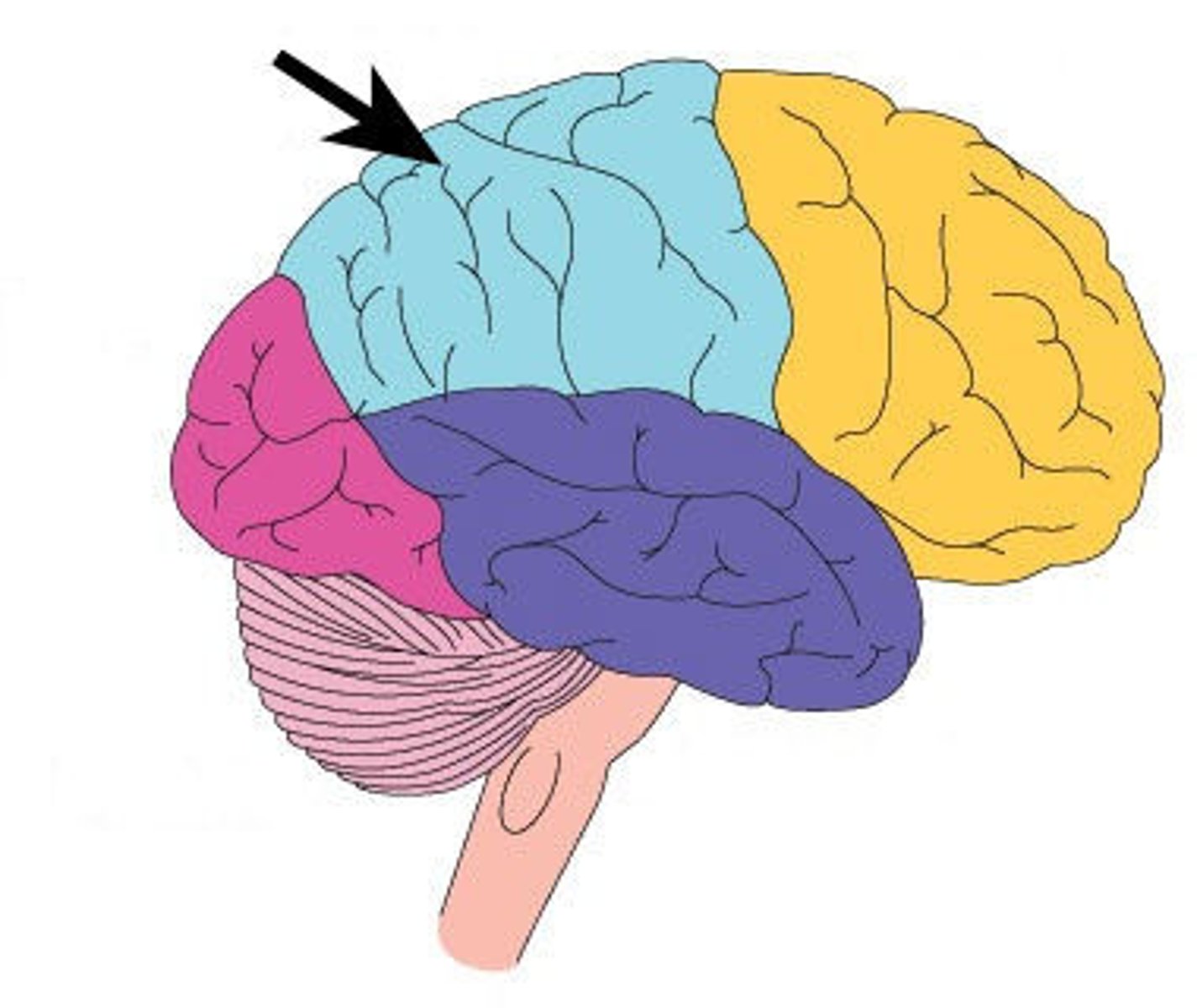
Frontal
The lobe of the brain associated with reasoning, planning, and problem-solving.
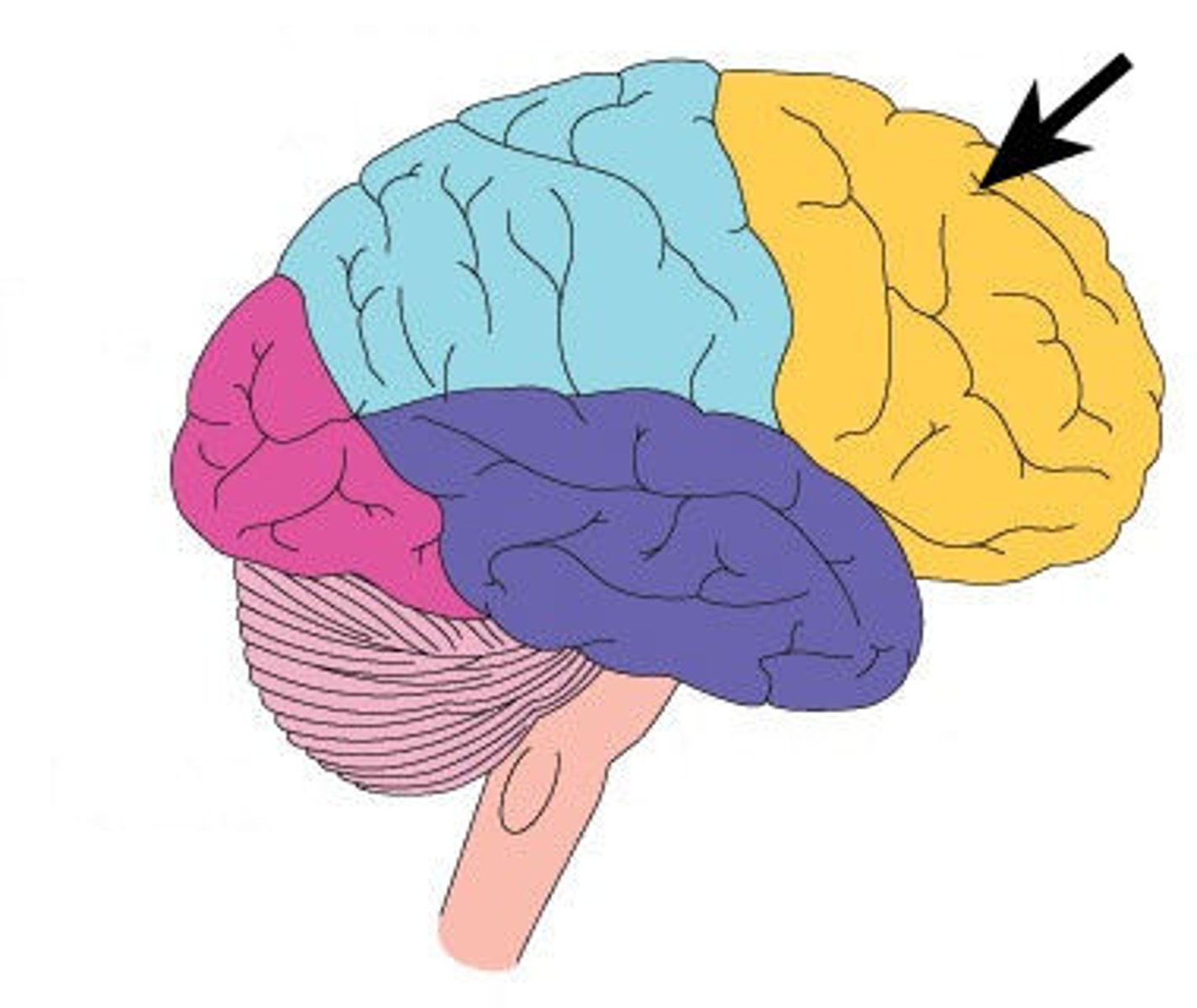
Temporal
The lobe of the brain associated with processing auditory information and memory.
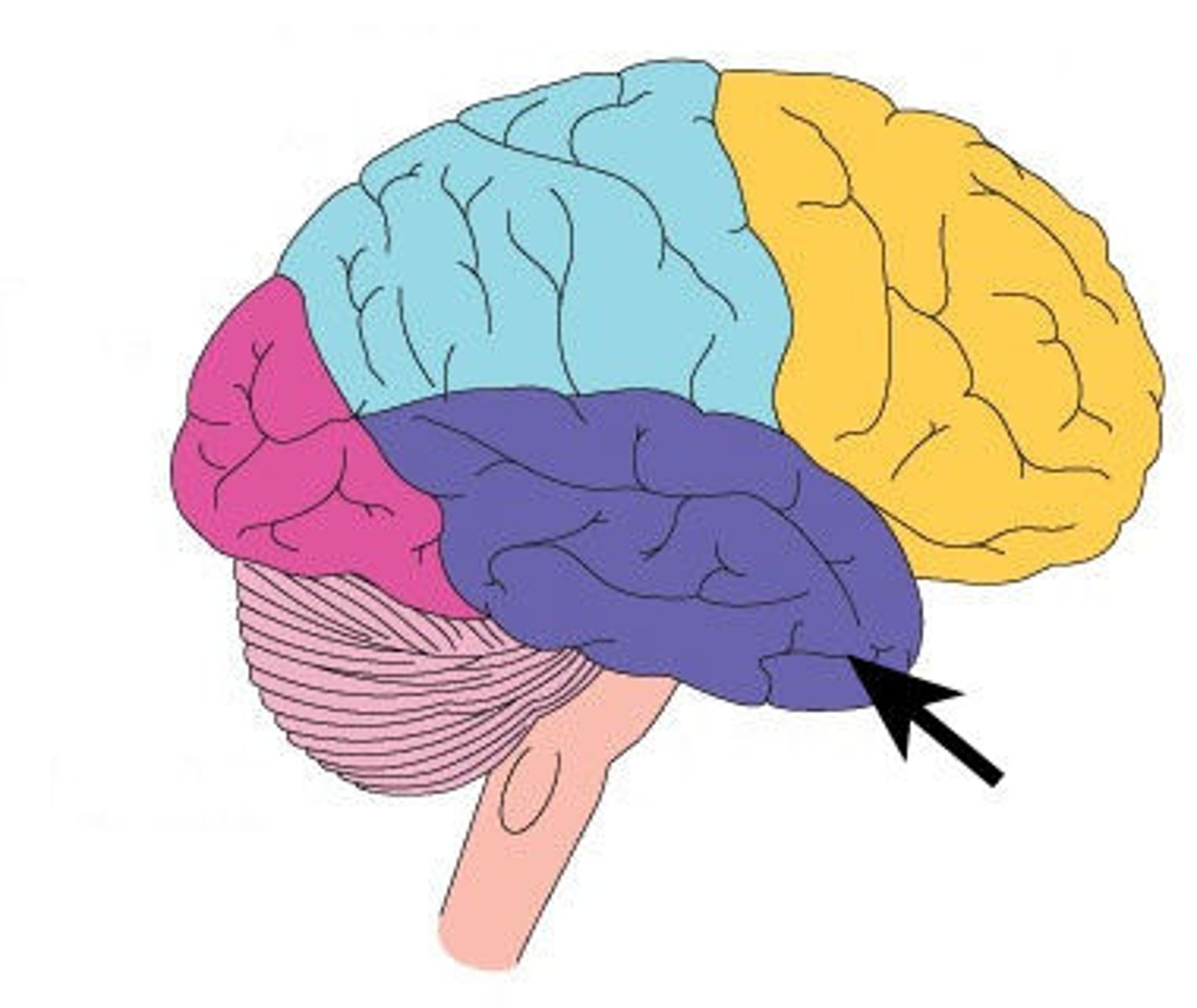
Occipital
The lobe of the brain primarily responsible for visual processing.
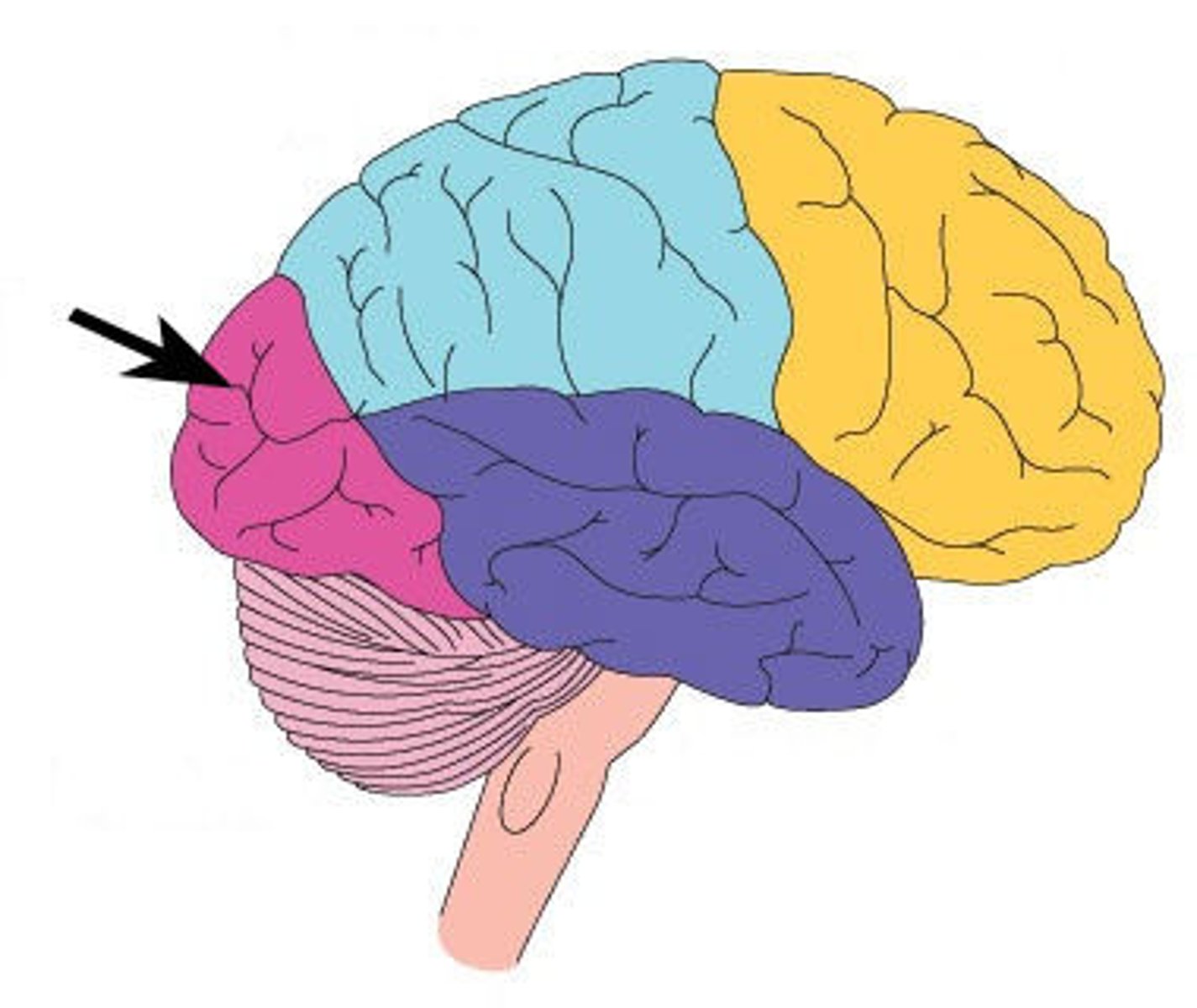
Parietal
The lobe of the brain that processes sensory information such as touch and temperature.
Resting Membrane Potential
-Neuron sits at about -70 mV
-Maintained by the Na+/K+ pump (3 Na+ out, 2 K+ in) and K+ leak channels
Depolarization
- A stimulus causes membrane potential to become less negative
- If it reaches threshold (~ -55 mV), voltage-gated Na+ channels open
- Na+ rushes into the cell - rapid depolarization
Rising Phase
- Membrane potential shoots up toward +30 mV as Na+ floods in
- Positive feedback: more depolarization - more Na+ channels open
Repolarization
- At peak (~+30 mV), Na+ channels inactivate
- Voltage-gated K+ channels open, K+ flows out of the cell
- Membrane potential moves back toward negative
Hyperpolarization (Undershoot)
- K+ channels close slowly - extra K+ leaves
- Membrane dips below resting potential (~ -80 mV)
Return to Resting Potential
- K+ channels fully close
- Na+/K+ pump restores -70 mV resting state
Absolute refractory period
The period during which no new action potential can be initiated due to inactivation of Na⁺ channels.
Relative refractory period
The period during which a stronger stimulus can trigger an action potential because the membrane is hyperpolarized.
Afferent
Refers to sensory input
Afferent fibers
Carry information from sensory receptors throughout the body toward the central nervous system
Efferent
Refers to motor output
Efferent fibers
Carry instructions from the central nervous system to effectors such as muscles and glands
Somatic
- Related to the body wall (skin, skeletal muscles, joints)
- Deals with voluntary control and conscious perception
Visceral
- Relates to the internal organs (smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, glands)
- Deals with involuntary control and unconscious regulation
Primary Function of the Nervous System
Performs 3 main tasks: Sensory Input, Integration, Motor Output
Sensory Input
Sensory (afferent) receptors detect and monitor changes inside and outside the body
Integration
The central nervous system processes and interprets sensory input, making decisions about what should happen next
Motor Output
The nervous system sends efferent signals to muscles, glands, or organs to produce a response
Central nervous system (CNS)
Brain and spinal cord; serves as the control center for processing and integration
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Cranial nerves and spinal nerves that connect the central nervous system to the rest of the body
Sensory (Afferent) Division
Carries instructions from sensory receptors to the central nervous system
Motor (Efferent) Division
Carries instructions from the central nervous system to effectors
Somatic nervous system (SNS)
Voluntary control of skeletal muscles
Autonomic nervous system (ANS)
Involuntary control of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands
Sympathetic Division
"Fight or flight" responses
Parasympathetic Division
"Rest and digest" responses
Sensory (afferent)
Transmits info from receptors to central nervous system
Motor (efferent) neurons
Transmits commands from central nervous system to effectors (muscles, glands)
Somatic motor
voluntary control of skeletal muscles
Autonomic motor
- Involuntary control (smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, glands)
- Sympathetic vs parasympathetic
Somatic sensory
from skin, skeletal muscles, joints
Visceral sensory
From internal organs (Ex: stretch, pain, chemical signals)
Nucleus
Collection of cell bodies in the central nervous system
Ganglion
Collection of cell bodies in the peripheral nervous system
Tract
Bundle of axons in the central nervous system
Nerve
Bundle of axons in the peripheral nervous system
Cell body (soma)
Contains nucleus, metabolic center
Dendrite function
Receive signals
Axon
Transmits impulses away
Axon hillock
Trigger zone for action potential
Axon terminals
Release neurotransmitters
Multipolar
Many dendrites, one axon; found in central nervous system and motor neurons
Bipolar neuron
One dendrite, one axon; found in sensory organs (eye, ear, olfactory)
(Pseudo)Unipolar
Single process splits into peripheral and central branches; most sensory neurons
Sensory neurons
Afferent, carry input into central nervous system
Interneurons
Association neurons in central nervous system, processes and integrate
Motor neurons
Efferent, carry commands to effectors
Six neuroglia
Astrocytes, microglia, ependymal, oligodendrocytes, satellite cells, schwann cells
Astrocytes (CNS)
Support, regulate chemical environment in the central nervous system
Microglia (CNS)
Immune defense, transform into macrophages
Ependymal cells (CNS)
Line ventricles, circulate cerebrospinal fluid
Oligodendrocytes (CNS)
Myelinate multiple axons in central nervous system
Satellite cells (PNS)
Support peripheral nervous system neuron cell bodies
Schwann cells (PNS)
Myelinate axons (one segment each) in peripheral nervous system
Myelination function
Wrapping axons with lipid-rich sheath for insulation; inccreases signal conduction
Myelination function
increases speed of impulse conduction
CNS myelination
oligodendrocytes wrap multiple axons
PNS myelination
schwann cells wrap only one axon segment
Large axon diameter
faster conduction (less resistance)
Myelination
faster conduction (saltatory vs continuous)
Major Ion Channels
Leak channels, ligand-gated, mechanically gated, voltage-gated
Leak channels
Na+ in, K+ out (constant)
Ligand-gated channels
open when neurotransmitter binds
Mechanically gated channels
open with pressure/tension
Voltage-gated channels
open/close at threshold voltages (Na+ fast, K+ slower)
Steps of an Action Potential
1. Local depolarization at axon hillock
2. Threshold reached (about -50 mV)
3. Na+ influx - rapid depolarization
4. Peak (+35-50 mV): Na+ channels close, K+ channels open
5. K+ efflux - repolarization
6. Excess K+ outflow - hyperpolarization
7. Return to resting potential (-70mV)
Depolarization
membrane potential becomes less negative
Repolarization
Membrane potential returns toward resting
Hyperpolarization
more negative than resting
Threshold
Critical voltage (about -50 mV) to trigger AP
Local (graded) potentials
short distance, graded, decremental, reversible, excitatory or inhibitory
Action potentials
long distance, all-or-none, non-decremental, irreversible
salatory conduction
the process by which action potentials are conducted in myelinated neurons
Role of myelin
action potentials jump node to node (nodes of ranvier)
Effect of salatory conduction
much faster than continuous conduction in unmyelinated axons
Neurotransmitters
Excitatory, inhibitory, biogenetic amines, acetylcholine, neuropeptides
excitatory neurotransmitters
- Ex: glutamate
- central nervous system
- stimulate depolarization
Inhibitory neurotransmitters description
- Ex: GABA, glycine
- central nervous system
- hyperpolarization
Biogenic amines
- Ex: dopamine, serotonin, norepinephrine
- mood, arousal, motor control
Acetylcholine neurotransmitters
- neuromuscular junction, parasympathetic synapses
Neuropeptides
- Ex: endorphins, substance P
- pain modulation, reward
Cerebrum
- Largest brain region
- two hemispheres
- responsible for higher functions
Diencephalon
- central core
- contains thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus
Brain stem
midbrain, pons, medulla
Cerebellum
coordination and timing of movement
white matter
myelinated neurons
grey matter
non-myelinated neurons
Major lobes
frontal, parietal, temporal, insula
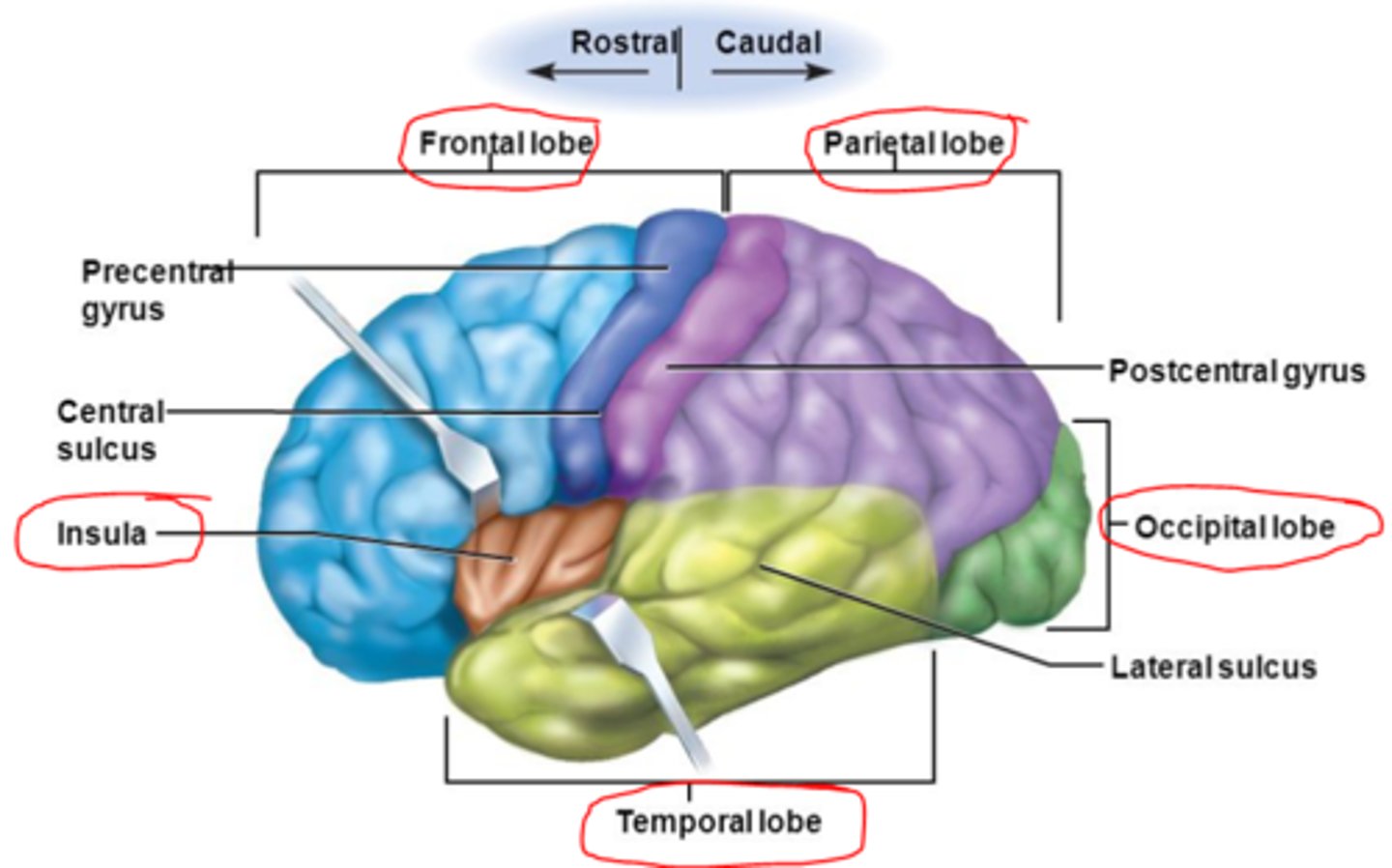
Major fissures/sulci
longitudinal fissure, lateral sulcus, central sulcus, transverse fissure
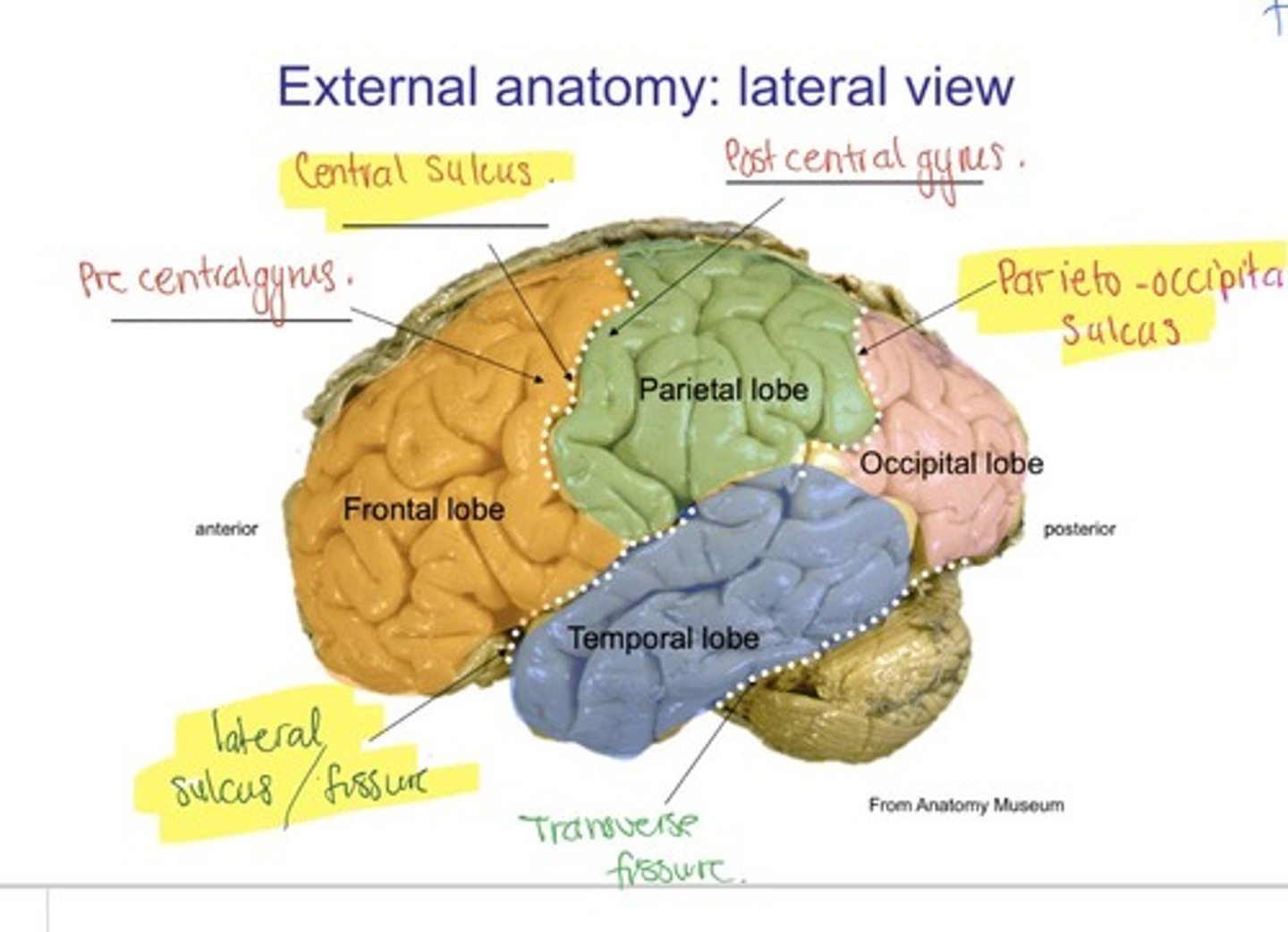
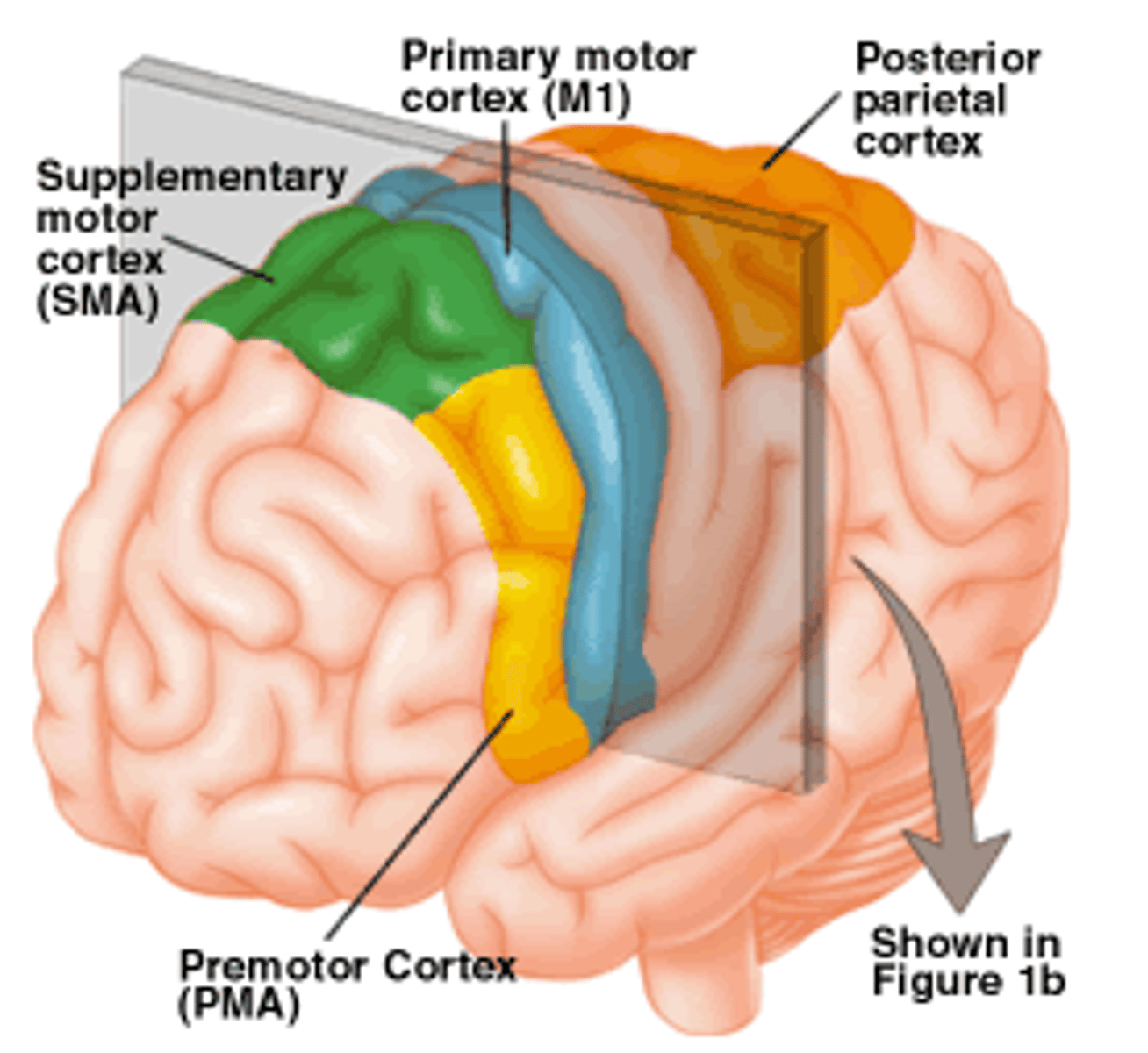
Motor areas
primary motor cortex (precentral gyrus), premotor cortex, broca's area, frontal eye field