2. Skeletal System (Osteology)
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
OSTEOLOGY
study of skeleton such as bones, joints, and connective
tissue.
1. Support
2. Locomotion
3. Protection
4. Storage
5. Haemopoiesis
functions of the skeletal system
Support
it acts as an internal ‘scaffold’ upon which the body is built
Locomotion
it provides attachment for muscles, which operate a
system of levers, i.e. the bones, to bring about movement
Protection
it protects the underlying soft parts of the body, e.g. the
brain is encased in the protective bony cranium of the skull
Storage
it acts as a store for the essential minerals calcium and
phosphate
Haemopoiesis
haemopoietic tissue forming the bone marrow
manufactures the blood cells.
Appendicular skeleton
Axial skeleton
Splanchnic skeleton
skeleton are considered to be made up of three parts:
Appendicular skeleton
bones of the thoracic limb and pelvic limbs.
Axial skeleton
it consists of skull, vertebral column, ribs, and sternum
Splanchnic skeleton
small bones seen in the tissues of an organs or other structures.
os penis/baculum
os clitoridis/ baubellum
os cordis
os rostrale
os phrenic
Examples of splanchnic skeleton
Bones
Cartilages
Tendons
Joints (articulation)
Components of skeleton
Bones
rigid organ that constitutes part of
the skeleton in most vertebrate animals.
Cartilages
non-vascular type of supporting
connective tissue that is found throughout the
body.
Tendons
fibrous connective tissue that
attaches muscle to bone.
Joints (articulation)
areas where two or
more bones meet
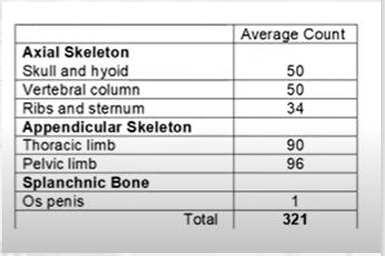
average count for the canine skeleton
Long bones
Short bones
Flat bones
Irregular bones
Bones are classified based on their general shape:
Long bones
are typical of the limb bones and also include bones of the metacarpus/metatarsus and phalanges
they have a shaft containing a medullary cavity filled with bone marrow
e.g., femur,humerus
Short bones
have an outer layer of compact bone with a core of cancellous bone and no medullary cavity
e.g., carpal and tarsal bones
Flat bones
have an outer layer of compact bone with a layer of cancellous or spongy bone inside
there is no medullary cavity
Irregular bones
have a similar structure to short bones but a less uniform shape and are unpaired
e.g., vertebrae
Sesamoid bones
Pneumatic bones
Splanchnic bones
Some specialized types of bones:
Sesamoid bones
are sesame seed-shaped bones that develop within a tendon that runs over an underlying bony prominence
e.g. patella associated with stifle joint
Pneumatic bones
contain air-filled spaces known as sinuses that have the effect of reducing the weight of the bones
e.g. maxillary and frontal bones
Splanchnic bone
bone that develops in a soft organ and is unattached to the rest of the skeleton
e.g. the os penis (bone within the penis of the dog and cat)
Ossification
process by which the bones is formed
Intramembranous ossification
Endochondral ossification
two types of ossification
Intramembranous ossification
is the process by which the flat bones of the skull are formed. The osteoblasts lay down bone between two layers of fibrous connective tissue. There is no cartilage template or ‘model’.
Endochondral ossification
involves the replacement of a hyaline cartilage model within the embryo by bone.
process starts in the developing embryo but is not completed fully until the animal has reached maturity and growth has ceased.
The long bones of the limb develop by this method.
Osteoblasts
cells responsible for laying down new bone.
Osteoclasts
cells that destroy or remodel bone
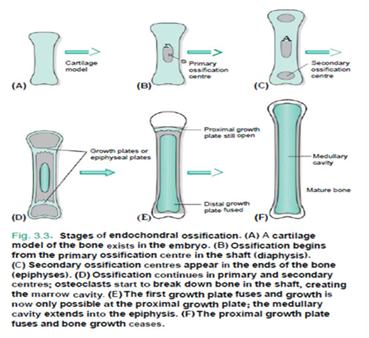
Stages of endochondral ossification
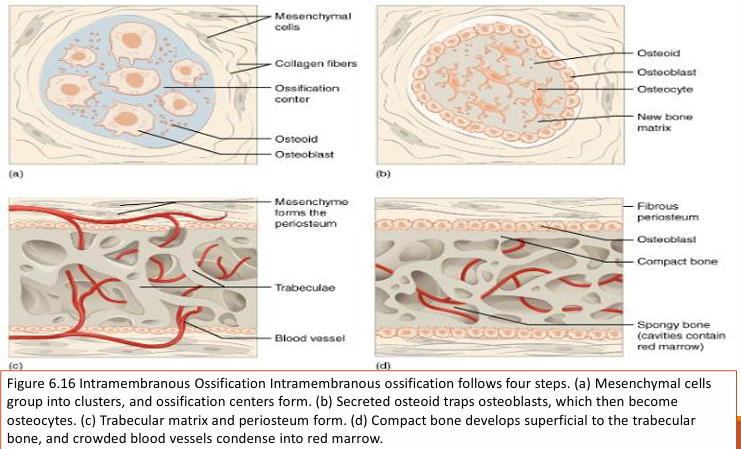
Steps of endochondral ossification
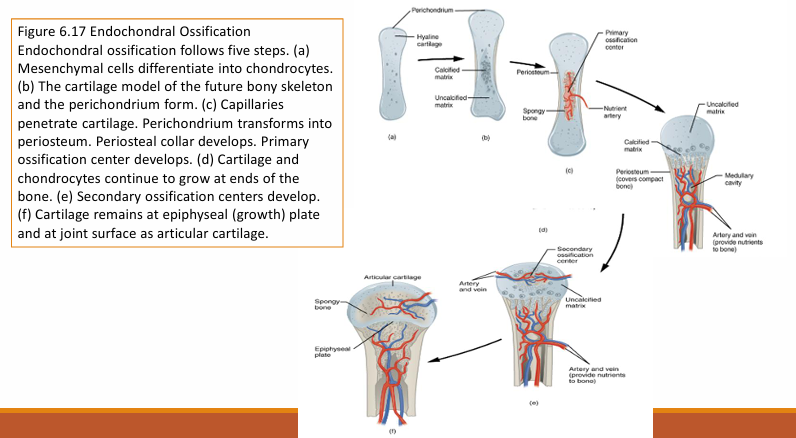
Steps of endochondral ossification
Compact bone
It is dense, white and hard and forms the outer shell of the bone
Bone is arranged in the form of concentric system called “Haversian system”
Cancellated or Spongy bone
It is made up of delicate plates, which intercrosses each other forming a meshwork with spaces containing marrow
Haversian systems are absent.
Medullary Cavity
Also known as bone marrow cavity, it is the space in the diaphysis containing the marrow
Epiphysis
Two enlarged ends of the long bone (proximal and distal extremities)
Metaphysis
The joining point of the diaphysis and epiphysis in a mature bone
Diaphysis
cylindrical shaft of a long bone between two epiphysis.
Epiphyseal cartilage
“growth plate” , is the cartilaginous plate between the diaphysis and epiphysis of immature long bones.
Periosteum
is the fibrous covering around the bone that is not covered by articular cartilage.
Endosteum
is the fibrous tissue lining the medullary cavity of the bone.
Cortex
compact bone surrounding the medullary cavity
Articular surface
are smooth layer of hyaline cartilage covering the epiphysis where one bone forms a joint with another bone
Apophysis
process/ any outgrowth of the bone
Nutrient foramen
a small opening in the bone that serves as a passageway for blood vessels, providing essential nutrients and oxygen to keep the bone healthy and promoting repair and growth.
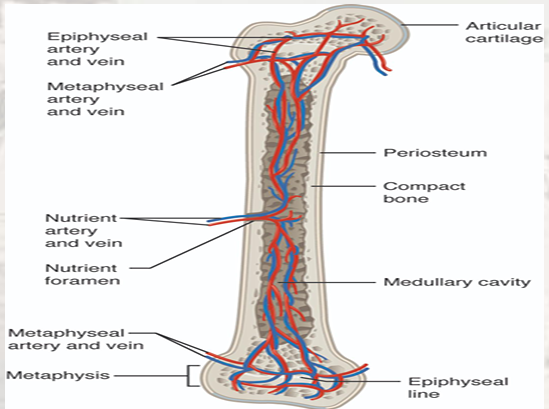
Diagram of Blood and Nerve Supply to Bone Blood vessels and nerves enter the bone through the nutrient foramen
BONY FEATURES
Bones have many external features depending on it’s specific function, it can either be a projection or depression.
Projection
is any bony feature that protrudes from the major bone part
Depression
is a shallow or deep concavity/depressed part of the bone
Articular projection
Non-articular projections
Articular depressions
Non-articular depressions
Types of Bony Features
Head
Condyles
Trochlea
Facets
What are the articular projections?
Head
rounded articular processes
(e.g head of the humerus/femur)
Condyles
large articular prominence
(e.g occipital condyles of the skull)
Trochlea
pulley-shaped structures
(e.gtrochlea of femur)
Facets
smooth, flat articular surfaces
(e.garticular facets of a thoracic vertebra for rib attachment)
Process
Tuberosity/tuber
Spine
Tubercle
What are the non-articular projections?
Process
general term for bony projections
(e.g zygomaticprocess of temporal bone)
Tuberosity/tuber
a large, usually roughened process
(e.g deltoid tuberosity of the humerus)
Spine
sharp, slender process
(e.g scapula)
Tubercle
small, rounded process
(e.g greater tubercle of humerus)
Cotyloid
Glenoidcavity
What are the articular depressions?
Cotyloid
deep articular depression
(e.g acetabulum of os coxae/hip joint)
Glenoid cavity
shallow articular concavity
Fovea
Fossa
Foramen
What are the non-articular depressions?
Fovea
a shallow, non-articular depression (e.gfovea capitison the head of the femur)
Fossa-
large, non-articular depression, usually they are wide in terms of area of attachment of muscles
Foramen
an opening through a bone
(e.g infraorbital foramen, obturator foramen, foramen magnum)