Chapter 22
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Five Rights
- Considered the “golden rules” of drug administration
- serve to reduce medication errors and harm to the patient
Five Rights of Drug Administration
- Right drug
- Right amount
- Right patient
- Right time
- Right route
Right Drug
– always read drug label; be careful of drugs whose names are similar.
- Retain container until after drug has been administered
Right Amount
measure drug carefully and accurately
Right Patient
- use patient identifiers before drug administration
- full name and date of birth usually
Right Time
follow physician's orders to administer drug at the right time, or timing between doses
Right Route
- the physician will specify route for administration
Health Care Providers
- are expected to chart any drug that they administered or helped to administer, to include drug, amount, route of administration, date and time
- Any adverse effects must be charted as well
common abbreviations
Healthcare providers who order, dispense, or administer drugs must be familiar with _________ to ensure safe and accurate administration of drugs
JCAHO (Joint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations)
has published a Do Not Use list of abbreviations
Institute for Safe Medication Practices
has published a list of error-prone abbreviations, symbols and dose designations
Standardized abbreviations
are used to reduce misunderstanding of orders and errors in medication administration
Metric System
is commonly used in the medical field; based on units of 10
Most common units a healthcare provider will encounter
liter, meter, gram
Drug Administration Routes
- Enteral
- Topical
- Parenteral
Enteral Route
Includes oral, sublingual, buccal and rectal
Oral Drug Administration Route
- an enteral route
- Termed PO, which means by mouth
- Absorbed by the GI tract
- Patient must be conscious and head elevated to aid in swallowing
- Absorption time is longer than other routes
- Do not handle tablets or capsules; use containers to transfer meds to patient
Sublingual Drug Administration Route
- an enteral route
- Drug is placed under the tongue and allowed to dissolve
- Should not be swallowed
- Example, nitroglycerin – given for angina
Buccal Drug Administration Route
- an enteral route
- Drug is placed against the mucous membranes of the cheek of upper or lower jaw and will dissolve and be absorbed
- Example, Vit B12 dissolvable
Rectal Drug Administration Route
- an enteral route
- Drug is administered through suppository into rectal canal
- Used when patient is not capable of taking the drug orally (such as from nausea and vomiting)
Topical Route
- Application of drug directly onto the skin
- Drug is diffused through skin and absorbed into bloodstream
- Can be applied as lotions or ointments
- Example, transdermal patch
- Healthcare provider should wear gloves when applying drug topically
Parenteral Route
- Drug is administered by a route other than GI tract
- All forms of parenteral require use of needle, syringe, and container
- Strict medical aseptic technique should be used
- can be administered in four different routes
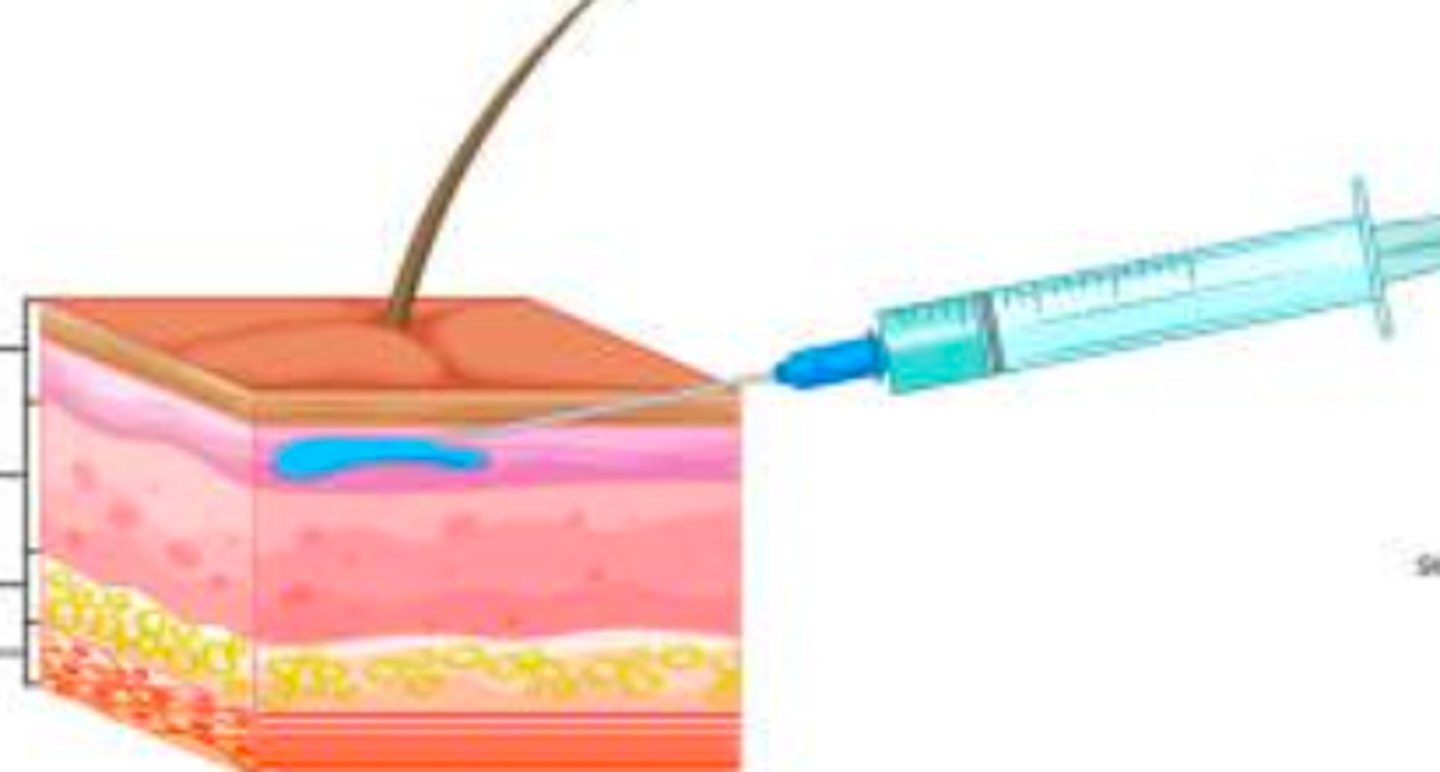
Intradermal (ID) route
- a parenteral route
- administered by injecting the drug between the layers of skin (second layer of skin)
- Sites are on the inside of lower arm for TB testing, on upper back for allergy testing
Intramuscular (IM) route
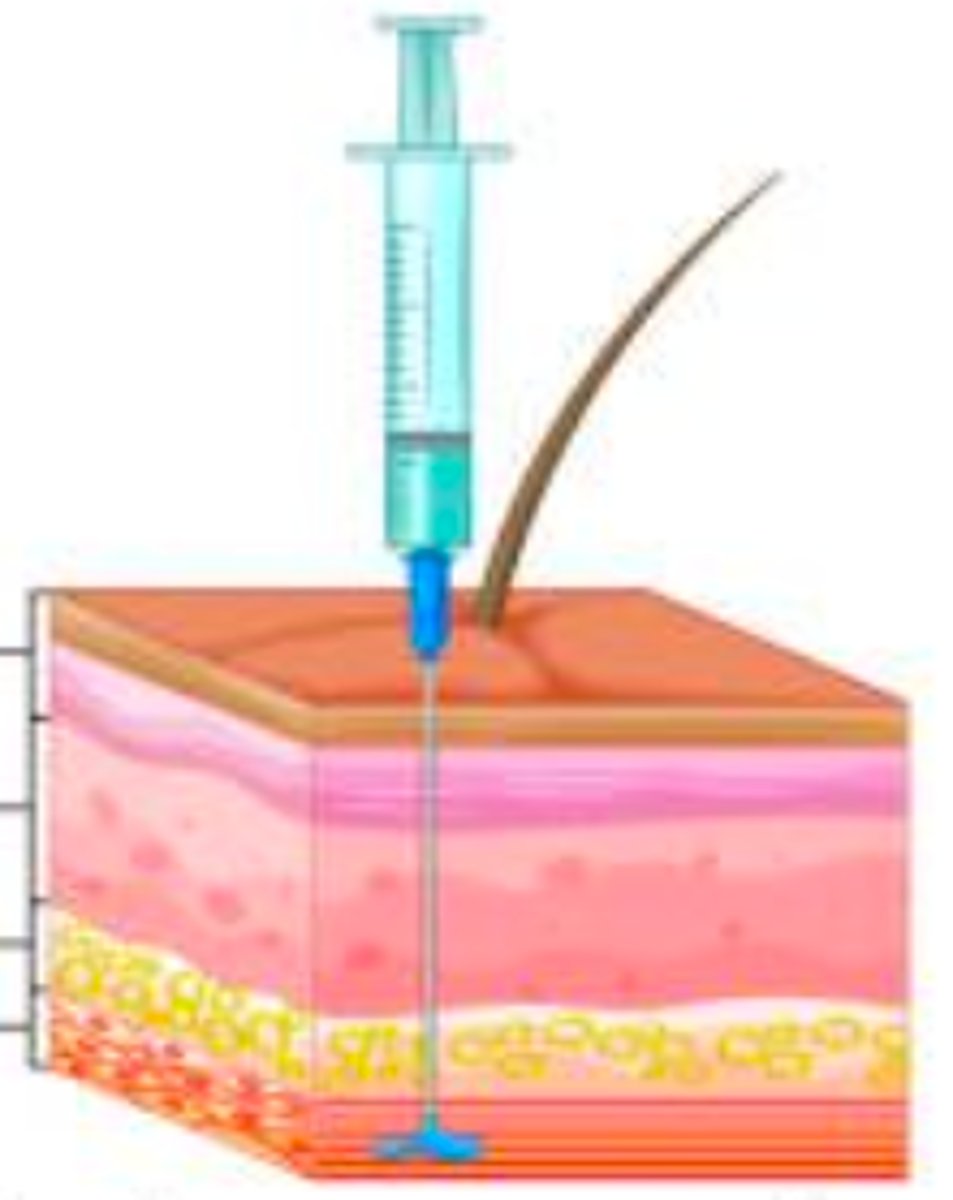
- drug is injected into muscle tissue that lies under subcutaneous layer
- rapid onset of action
- Can damage a blood vessel if injected too deeply into muscle
- Sites include deltoid muscle in upper arm and vastus lateralis muscle in the lateral thigh and gluteus maximus in the buttocks
- Needle length is 1"-3"
Subcutaneous (subQ) route
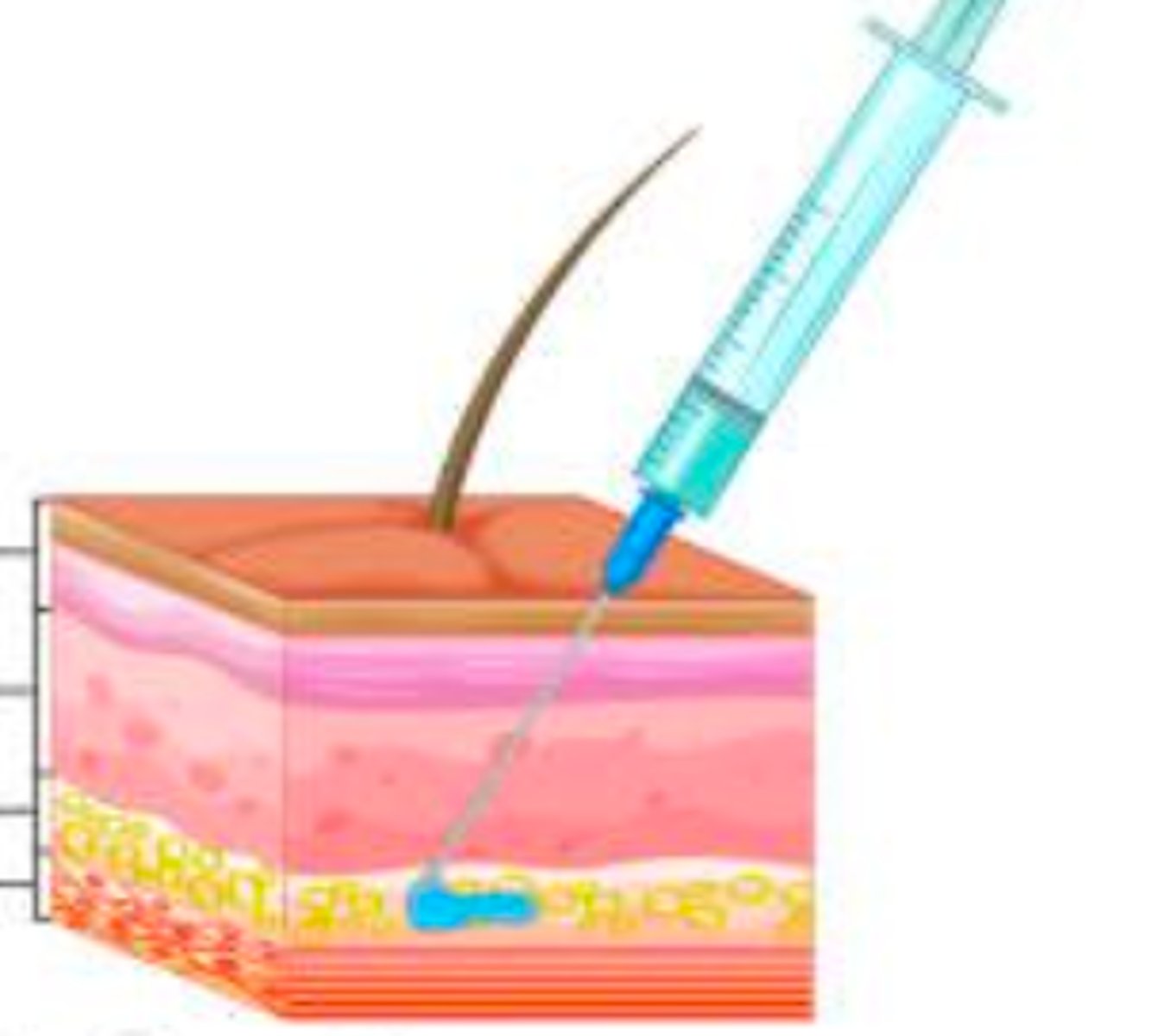
- drug injected under skin into subcutaneous tissue
- slow and constant absorption - below the first couple layers of skin
- Sites include anterior thigh, upper back, outer upper arms, and abdomen
- Example - insulin injection
Intravenous (IV) Route
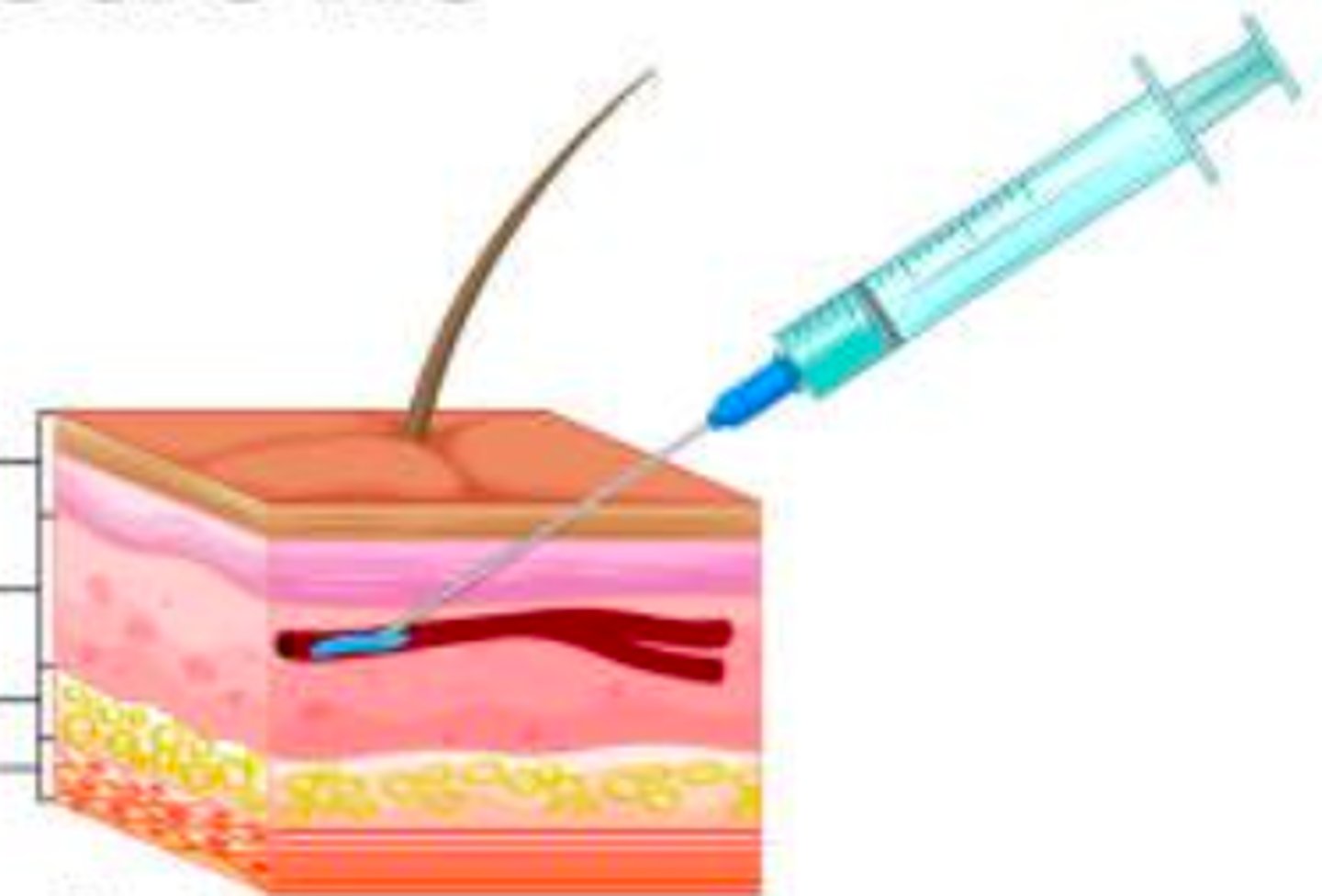
- drug is administered directly into the vein
- Rapid action
Needle and Syringe combinations used to administer parenteral drugs
Standard hypodermic syringe
Insulin syringe
Tuberculin syringe
Prefilled syringe
- these each come in a variety of sizes
Standard hypodermic syringe
used for a variety of medications
insulin syringe
used for insulin
Tuberculin Syringe
used for TB test or Heparin subQ injections
Prefilled Syringe
medication is pre-loaded with standard amount of a particular drug (such as an epipen)
Three parts of a syringe
- Tip
- Barrel
- Plunger
Tip of a syringe
where needle attaches
Barrel of a syringe
where calibration scales are printed and the part that holds the medication
Plunger of a syringe
inside part that fits into barrel and can be pushed or pulled in or out of barrel
needleless syringe systems
Many hospitals are utilizing ____________ for IV med administration to reduce needle sticks
Three Parts of the Needle
- Hub
- Cannula or shaft
- Bevel
Hub of a Needle
the part that attaches to the syringe
Cannula or Shaft of a Needle
length of the metal port
Bevel of a Needle
- slanted part at tip of needle.
- should always be positioned up before insertion into patient
Needles
- come in a plastic sheath for safety
- are sized according to length and gauge
Gauge of a Needle
- thickness or diameter or needle
- Varies from 14 - 28
- smaller diameter = larger
- larger diameter = smaller
The smaller diameter of the shaft
= larger number gauge needle
The larger the diameter of the shaft
= smaller number gauge needle
25g needle has a ________ diameter than a 16g needle
smaller
3 multiple choice options
Needles
- Length - measured in inches
- Varies from .25" - 5 "
- Shorter ones are used for subcut, longer ones are used for IM injections
Angiocath
- IV catheter
- needle within a sheath.
- Used for IV injections
Small drug amounts are packaged in two different packages
- ampules
- vials
Ampule
- Sealed glass containers designed to hold a single dose of the drug.
- Clear glass container with a scored constricted neck that breaks more easily than other parts of the glass structure.
- Tip of needle is inserted in ampule to draw out contents
Vial
- small glass or plastic bottle with a rubber top sealed with a metal ring.
- Contains multiple doses of a drug
- Drug can be drawn out with a needle and syringe or metal ring and rubber top can be removed and drug poured into container
Injection Safety
- Follow protocols for infection control and aseptic technique
- Do not administer drugs or medications from one syringe to multiple patients
- Use IV or drip infusion sets for one patient only
- Use single-dose vials whenever possible
- If multidose vials are used, both the needle and the syringe used must be sterile
IV Injection Methods
- Single Administration
- IV Bolus or IV Push
- IV Infusion
Single Administration IV Injection
drug is injected slowly
Administration by IV Bolus for IV Injection
refers to amount of fluid injected
Administration by IV Push for IV Injection
refers to a rapid injection
IV Infusion
- a large volume of fluid over an extended period of time.
- Also called drip infusion
- Drip infusion rates can be controlled by clamp, adjustable clamp, or IV pump and controller
Venipuncture
- a procedure in which a needle is used to take blood from a vein
- Means "cutting of the vein"
Veins
- divided into superficial and deep veins
- Most common for venipuncture is the medial cubital , superficial one in the cubital fossa of the arm
- Other sites – cephalic, basilic
Needles for Venipuncture
- Can use a straight one with safety cap or butterfly one with safety
Vacutainers
are used to collect blood once the venipuncture is complete