Bio 119 Lab Exam
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
Pinus Male Cone
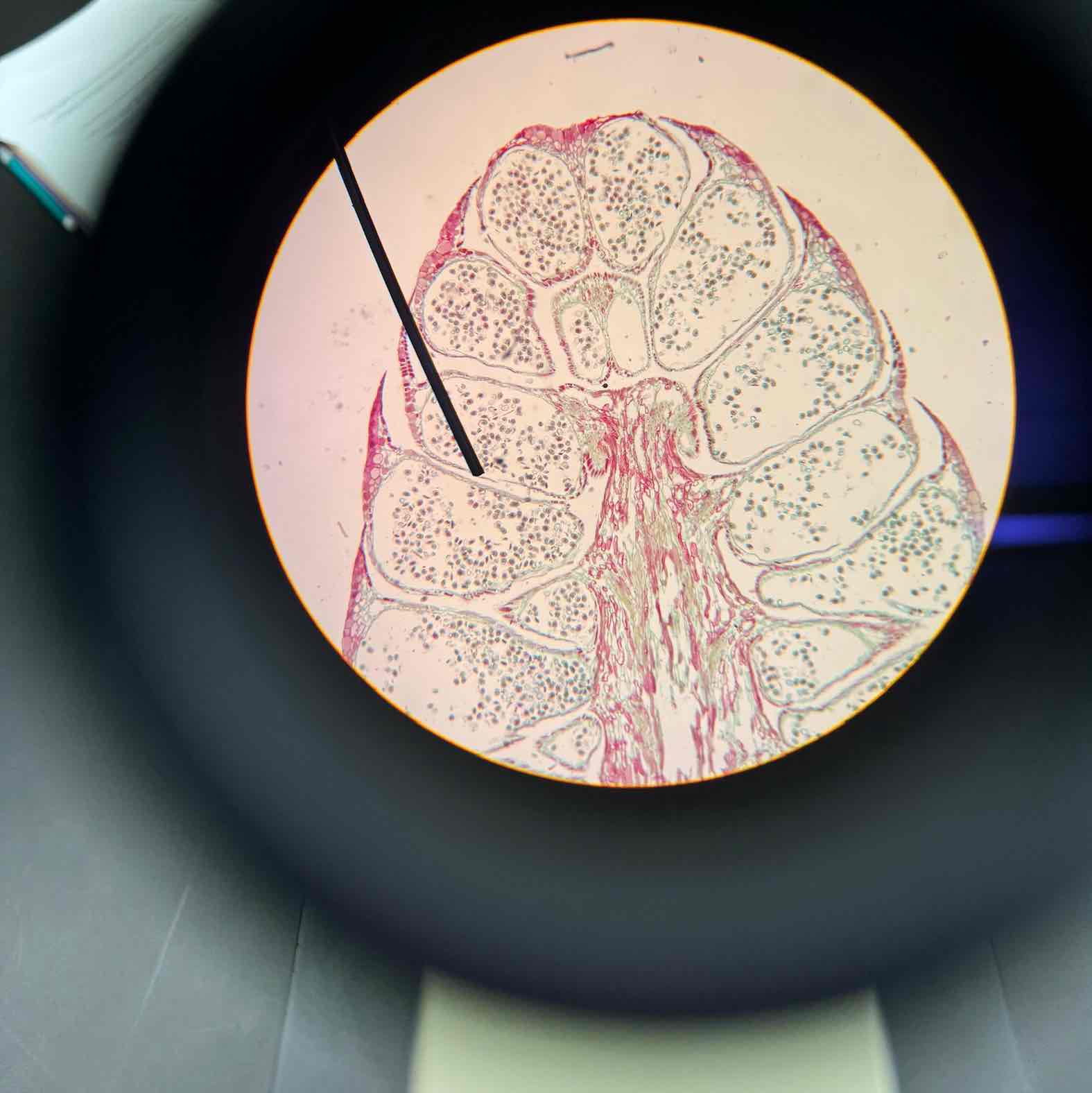
Pinus Female Cone
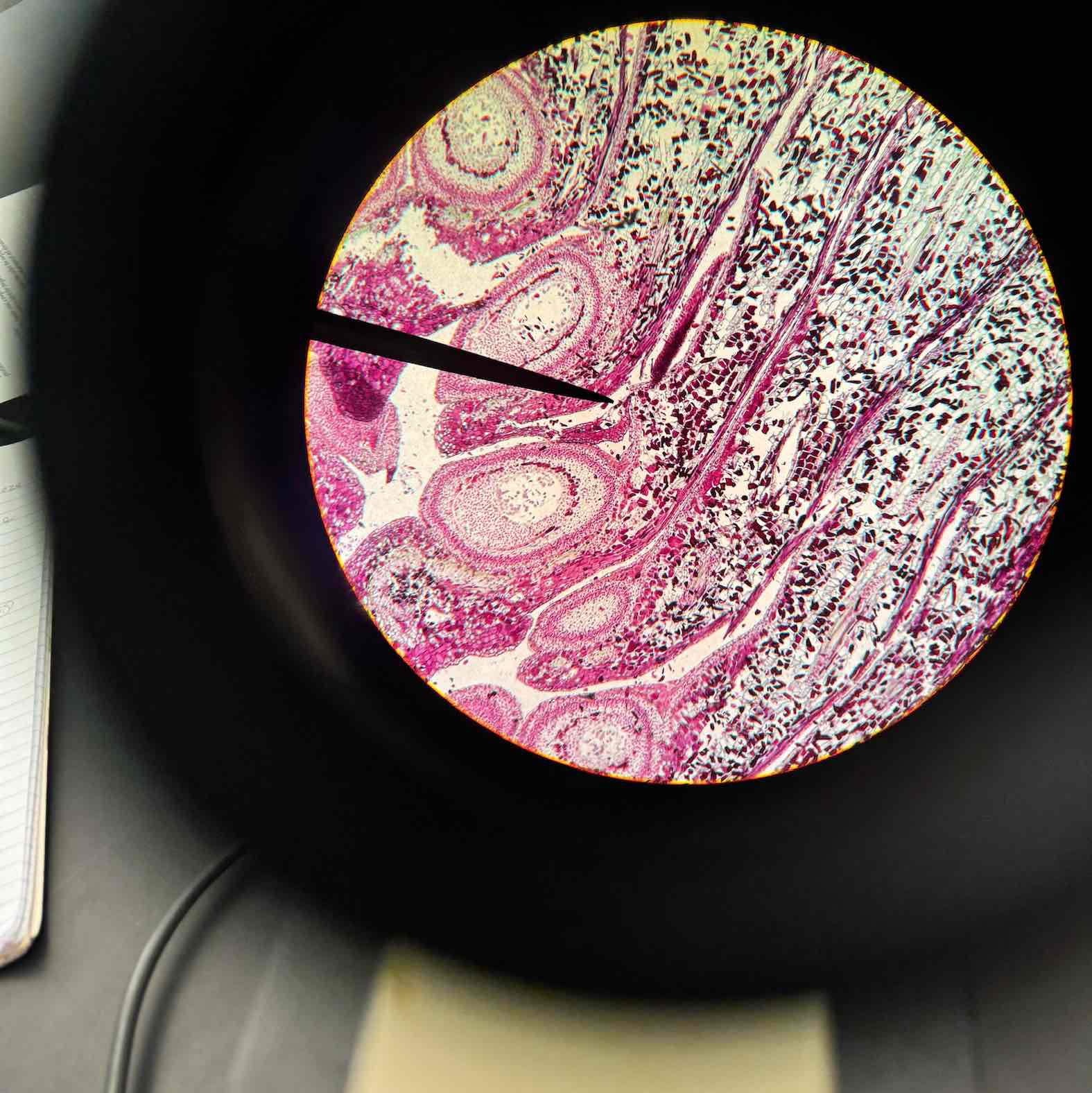
Pinus Mature Embryo
What do the pollen grains arise from and by what type of cell division
spores by mitosis
what will the megagametophyte of gymnosperms give rise to and by what type of cell division
eggs by mitosis
what serves as the nutrient source for the germinating seed of gymnosperms
ovule
are sporophytes diploid or haploid
diploid
What types of tissues are seen in stem of pteridophytes
dermal, vascular, ground
what generation is dominant in pteridophytes
sporophyte generation
what generation is dominant in gymnosperms
sporophyte generation
archegonium
female reproductive, produces eggs
antheridium
male reproductive, produces sperm
Pinus Young Embryo
Fern Gametophyte Antheridia
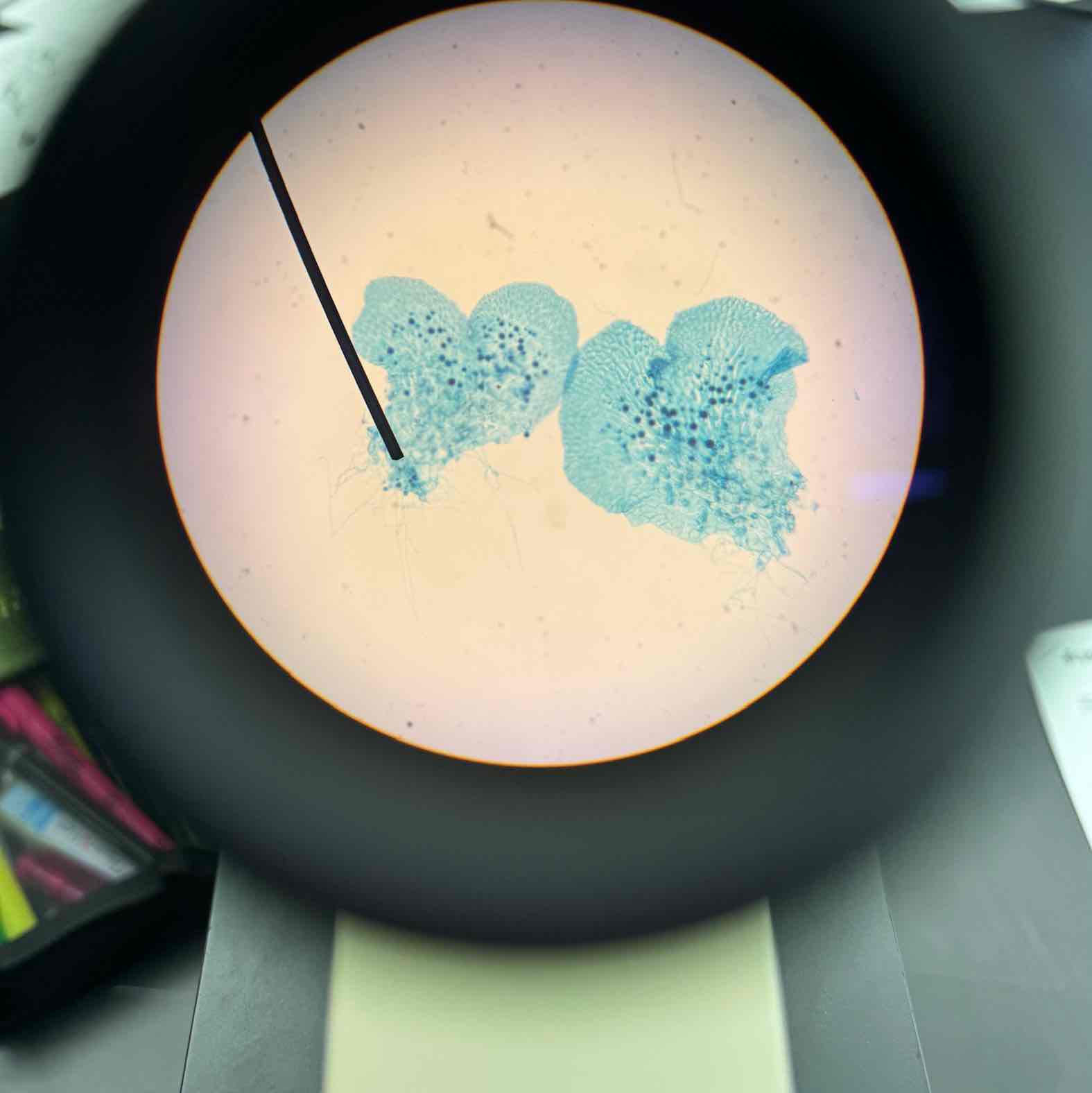
Psilotum Stem
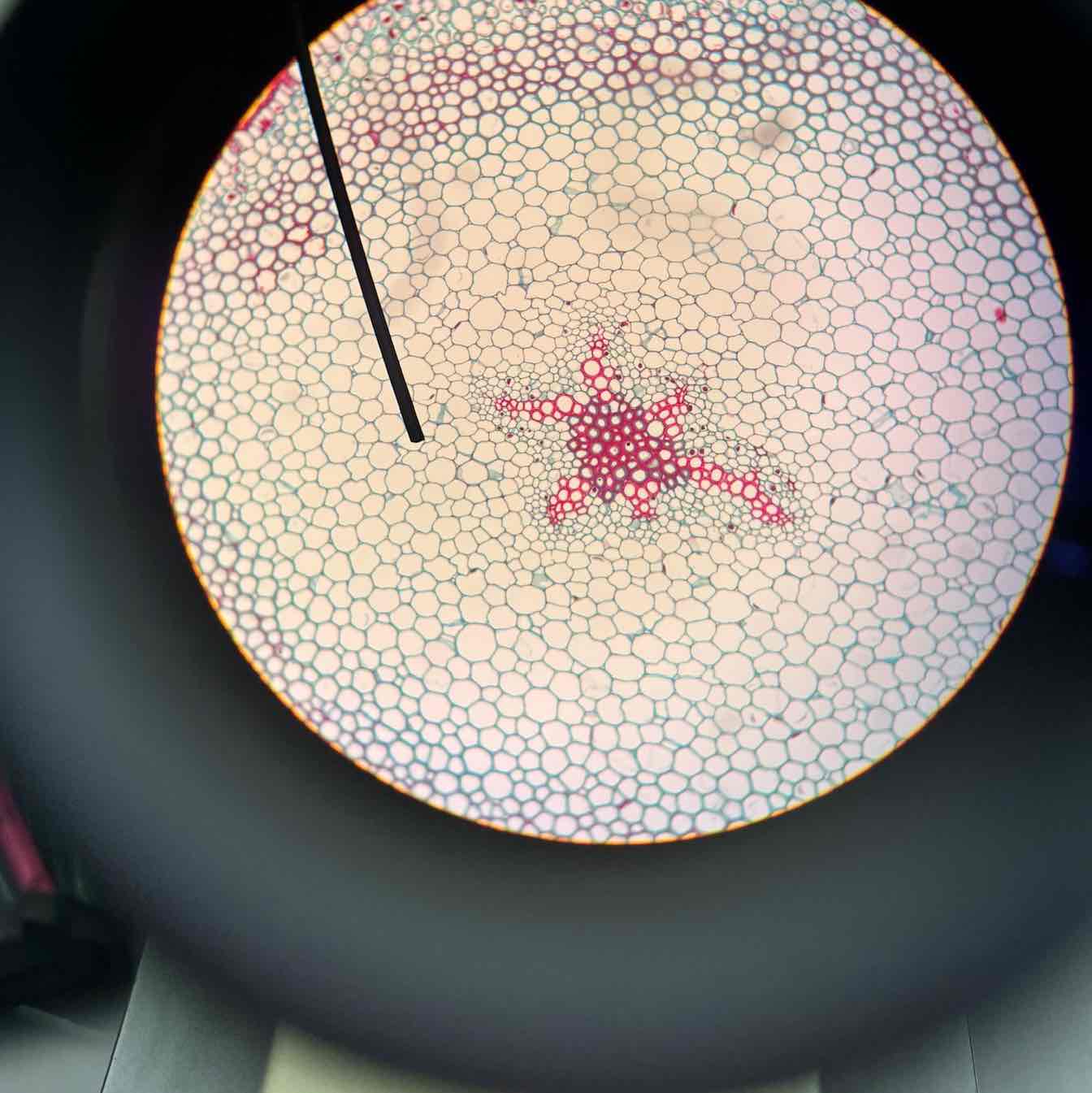
Fern Gametophyte Archegonia
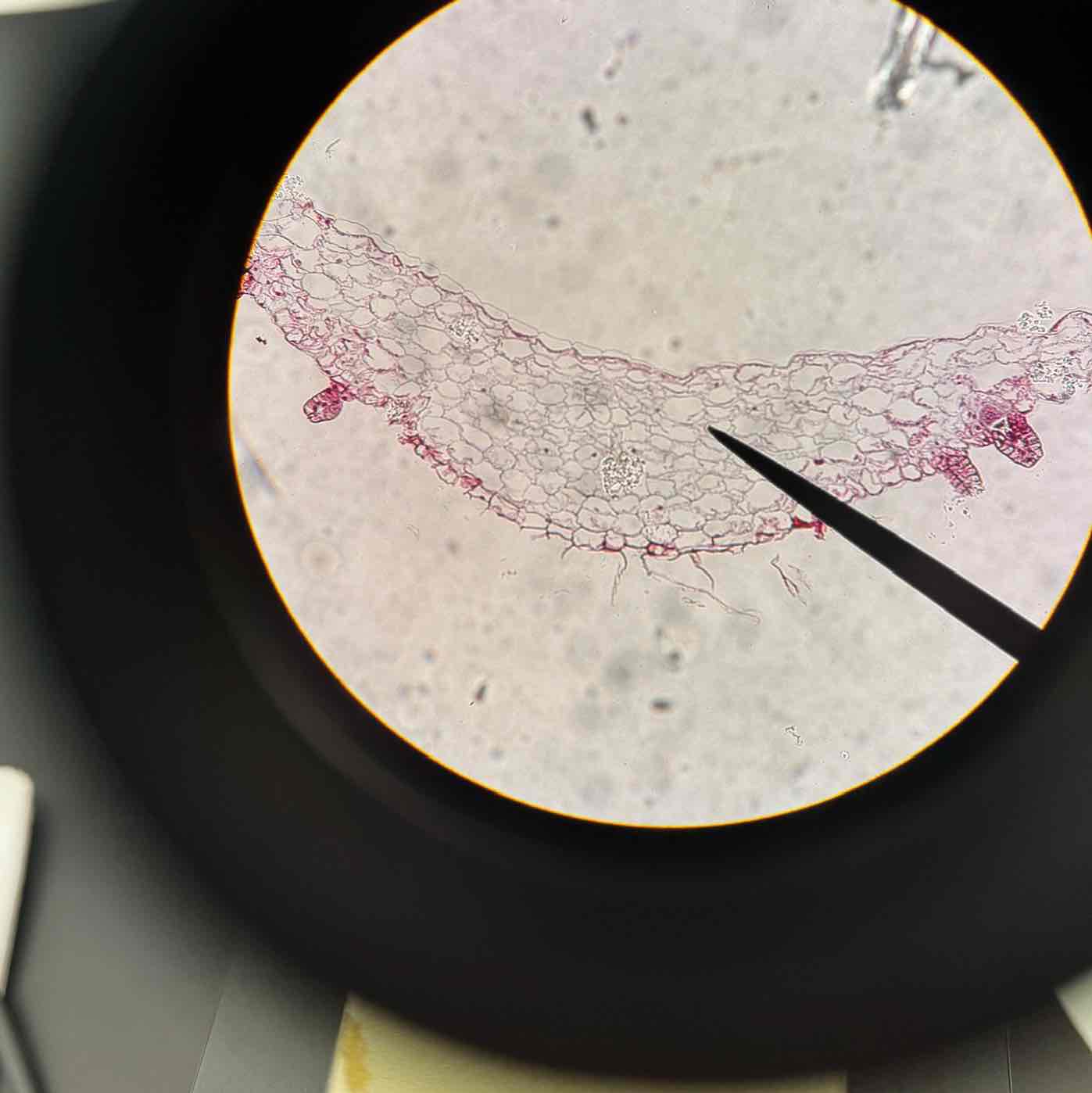
Fern Young Sporophyte example 1
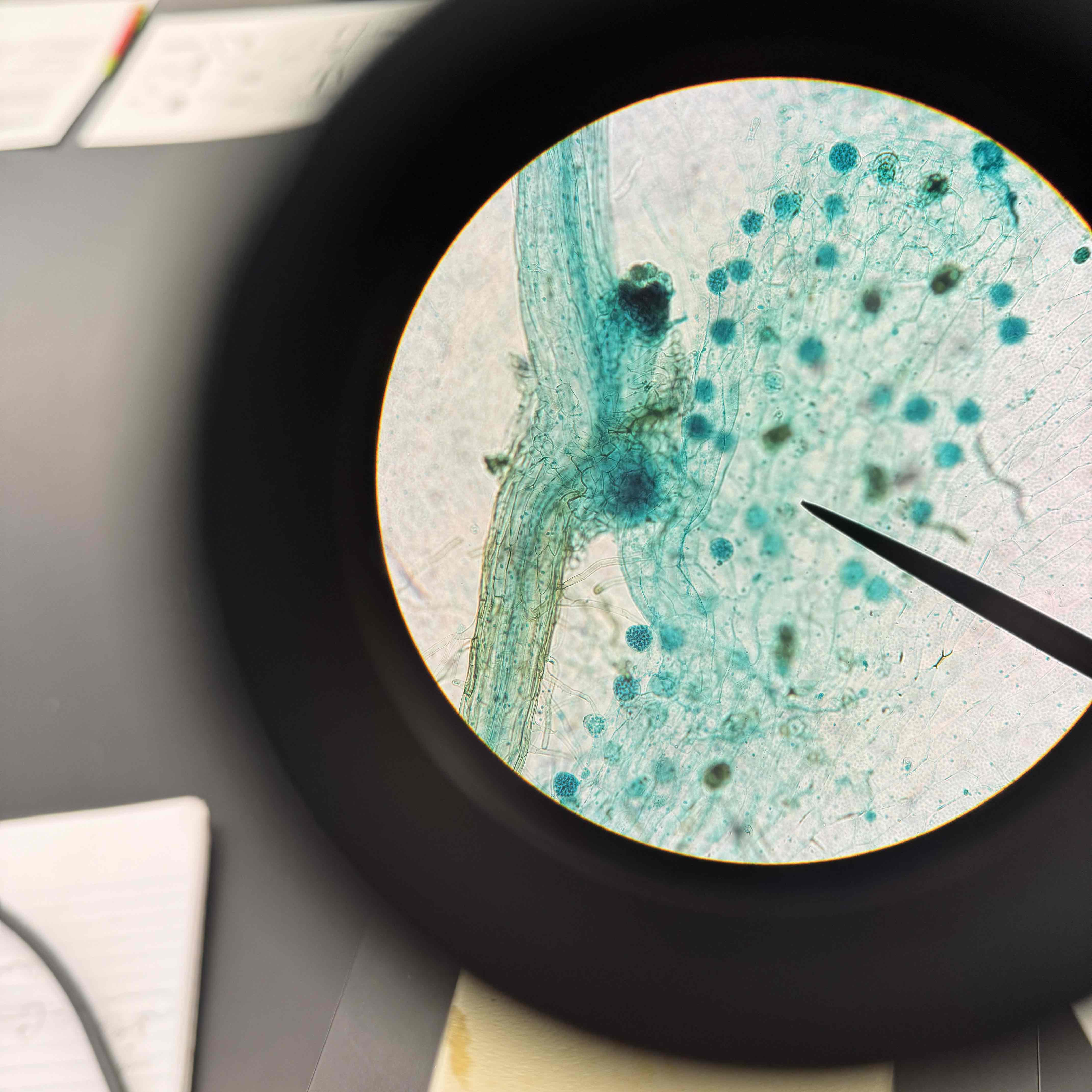
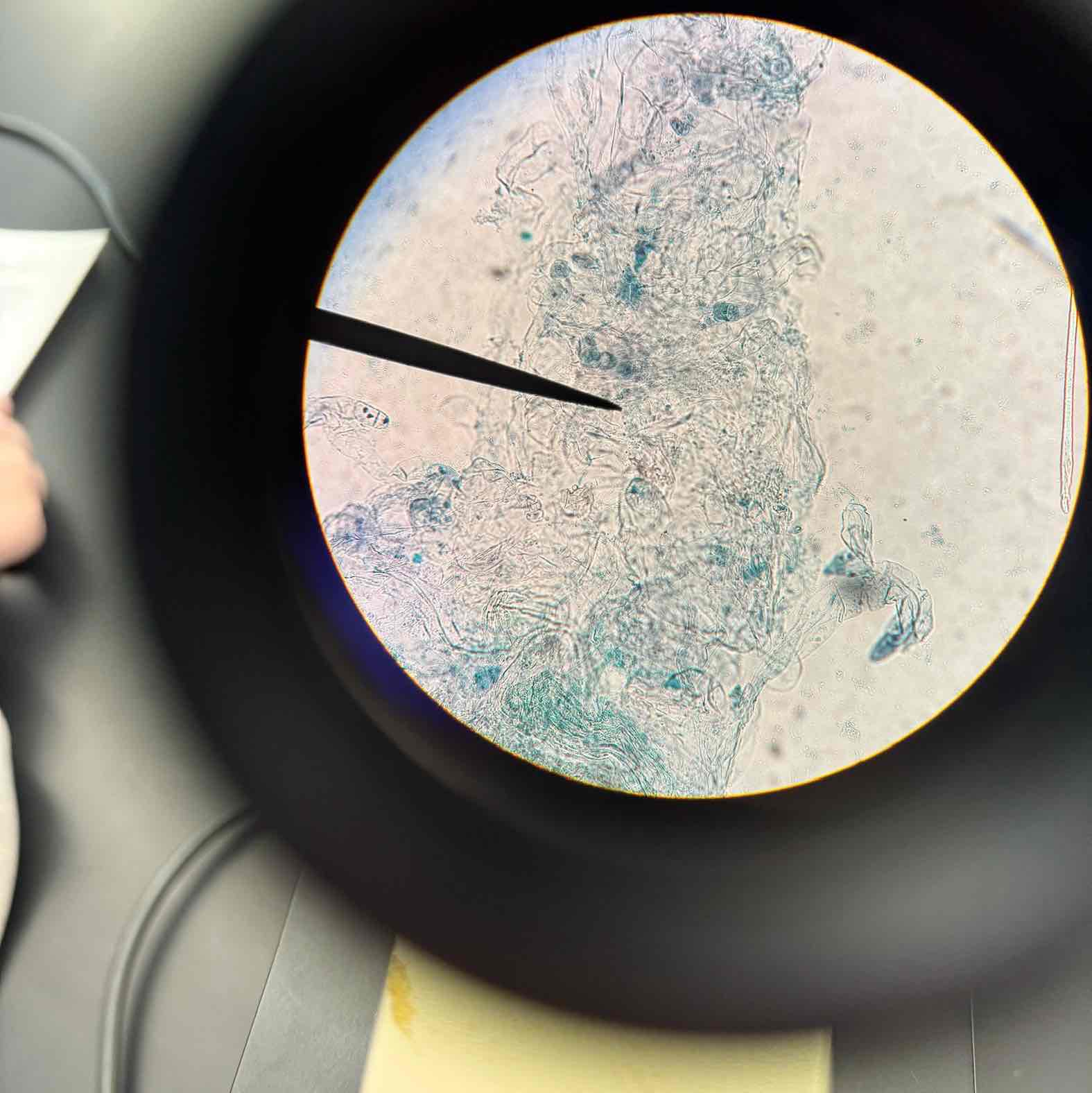
what does the gametophyte of the fern arise from?
germinating spore
is sporophyte or gametophyte generation dominant in seedless vascular plants
sporophyte generation
Fern Young Sporophyte ex 2
what advantage does vascular tissue provide to ferns over mosses?
the transportation of water and minerals (like a vacuum) and allows them to grow upwards away from the ground, towards the light
is the stem gametophyte or sporophyte generation
sporophyte gen.
is archegonia and antheridia gametophyte or sporophyte generation?
gametophyte generation
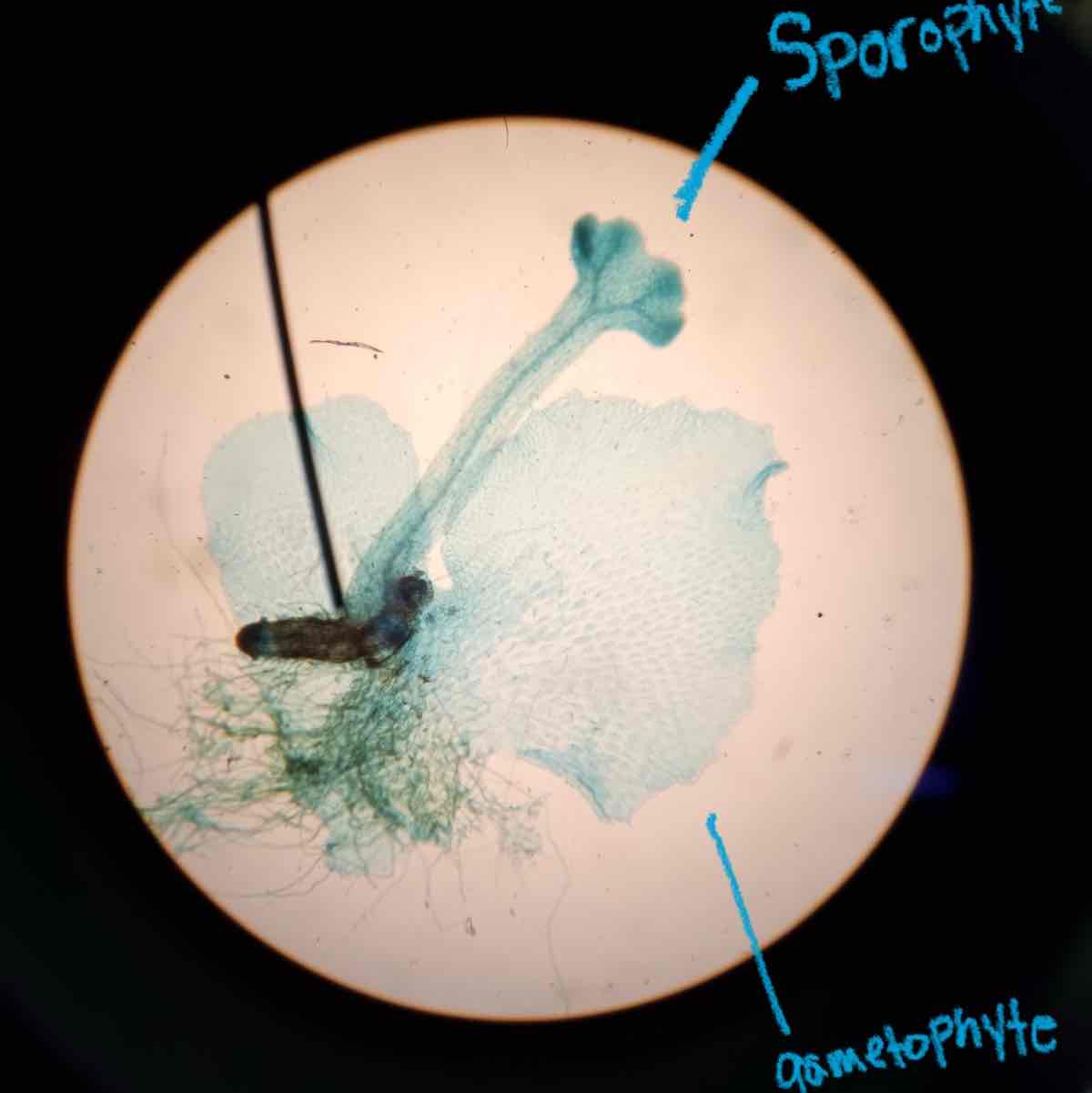
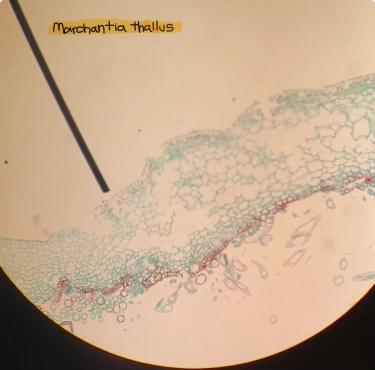
is the bryophyte thallus gametophyte or sporophyte generation?
gametophyte gen.
spores are created by what type of cell division?
meiosis
eggs and sperm are created by what type of cell division?
mitosis
Sperm Cells
antheridium
Egg cells
archegonium
Male mating patterns
want to mate with as many organisms as possible
Female mating patterns
picky with who they mate with because they want high quality offspring
If spores are produced by meiosis are they diploid or haploid
haploid
what cell division would produce multicellular, haploid gametophyte from a unicellular haploid spore
mitosis
Marchantia thallus
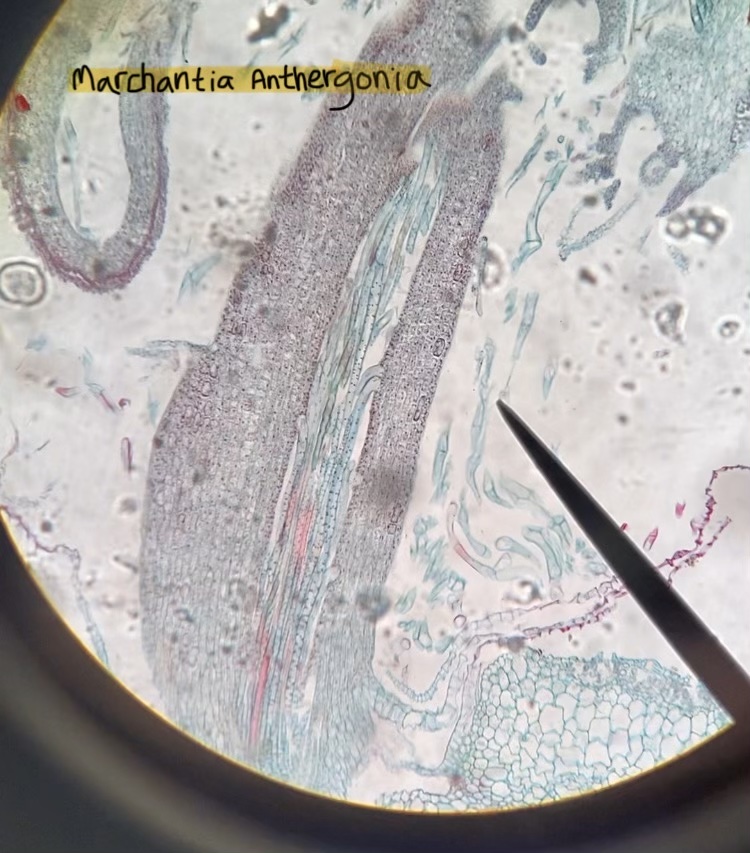
Marchantia archegonia
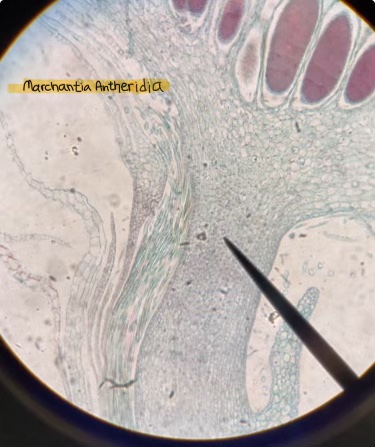
Marchantia antheridia
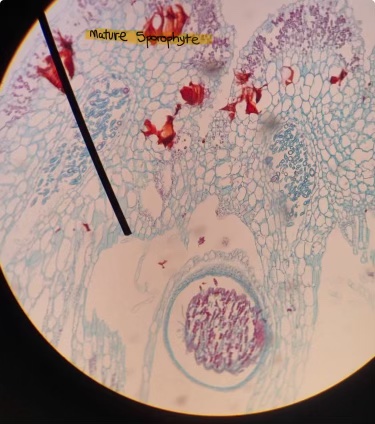
Marchantia mature sporophyte
Bryophytes
non-vascular plants
what structures are being produced in the archegonia and antheridia respectively
egg and sperm cells
what event leads to the production of the sporophyte
fertilization
Eudicot
vascular bundles in a ring, can have secondary growth
Vascular Cambium
meristem for secondary growth in woody plants
single tissue layer between xylem and phloem
produces new xylem and phloem
Monocot
scattered vascular bundles, no secondary growth
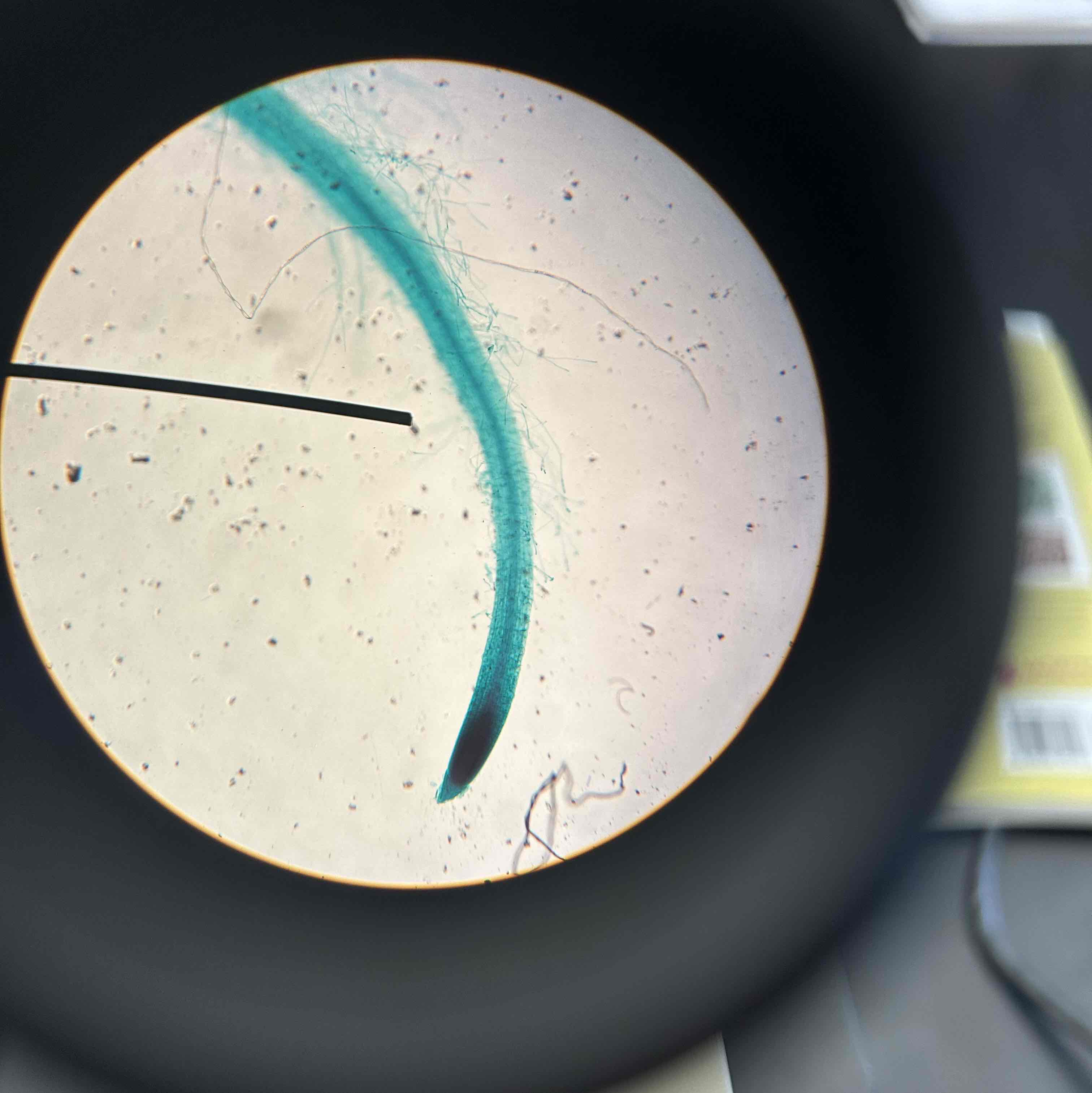
root hair
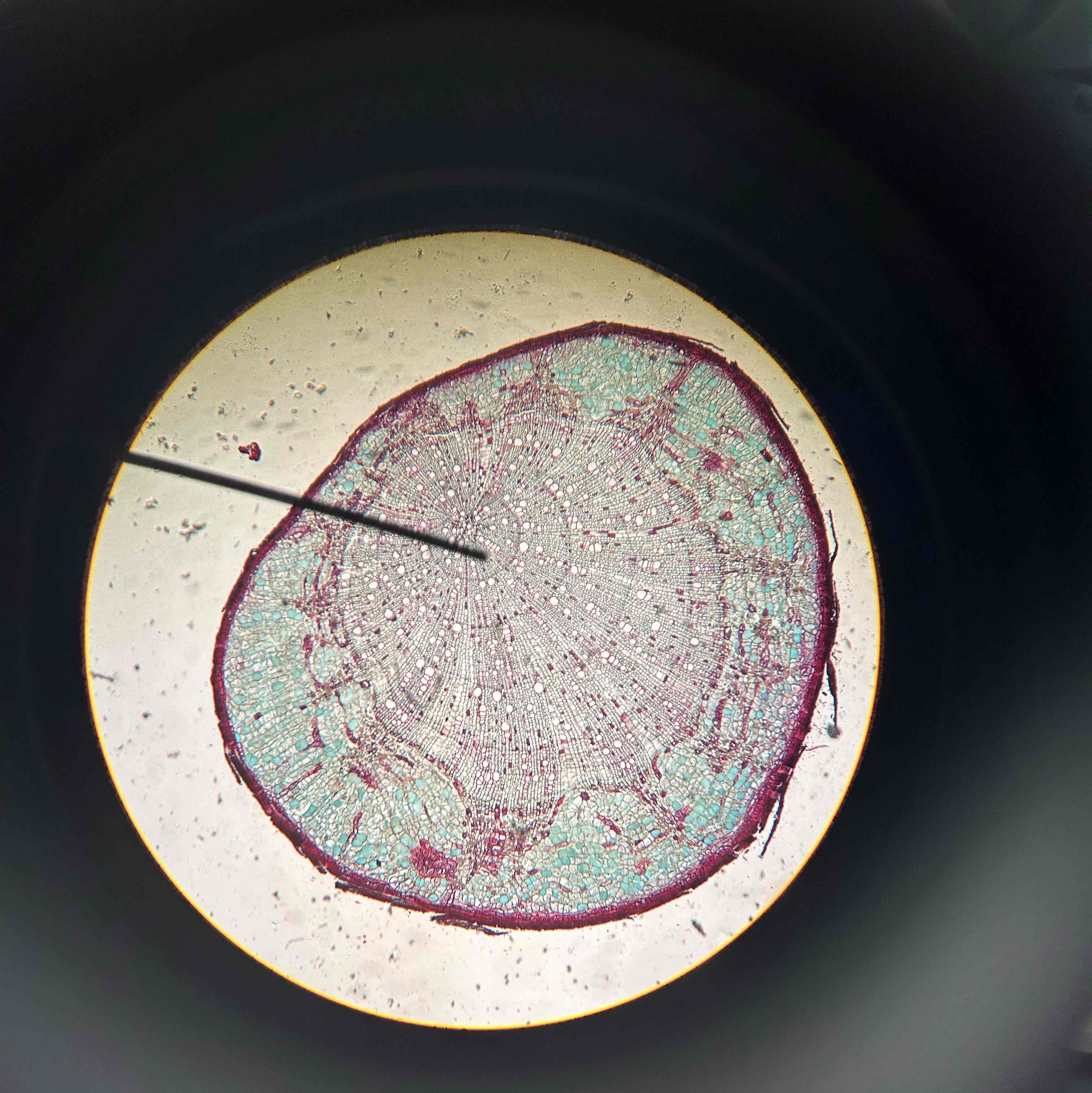
Root cross section
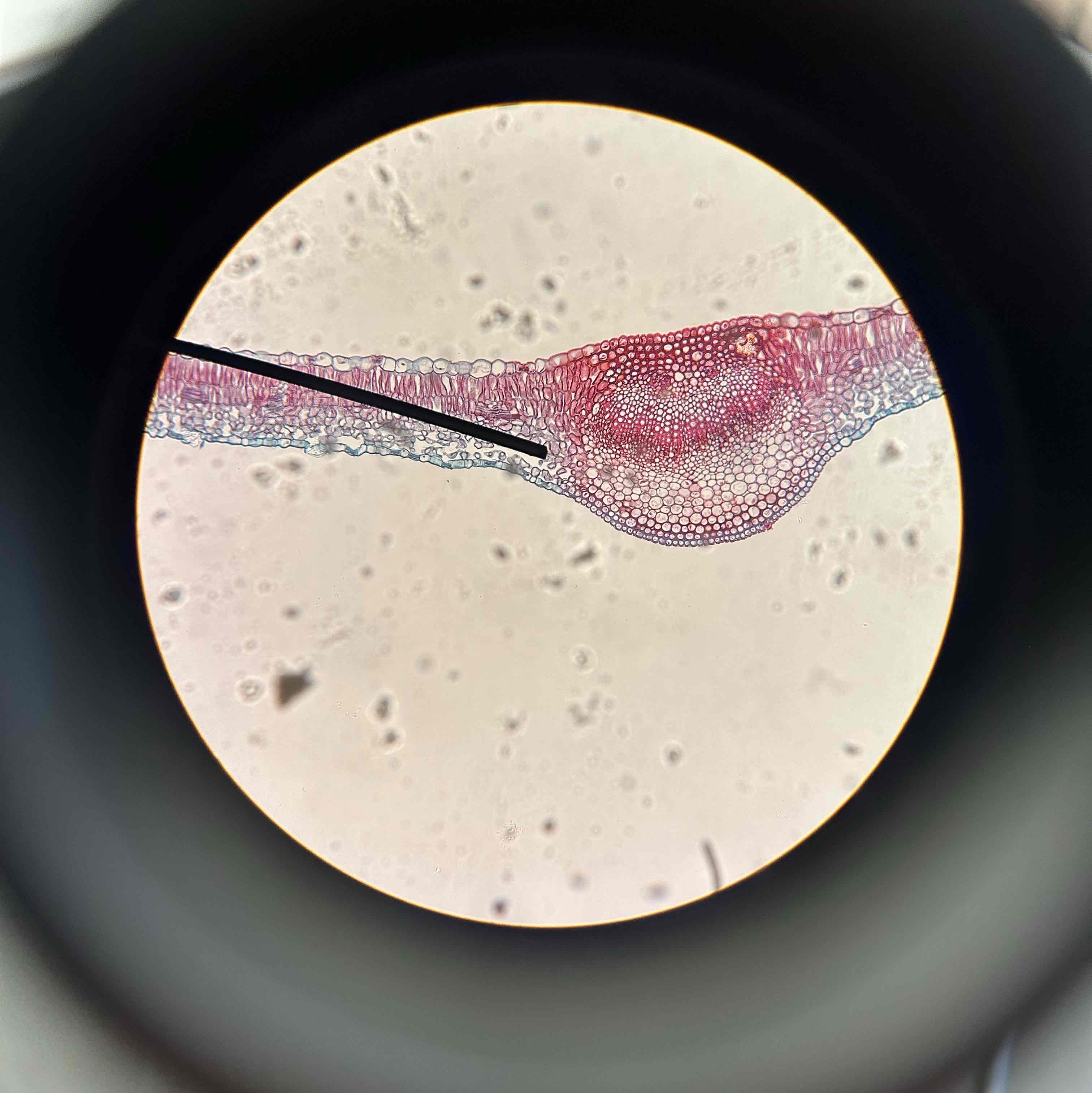
Lilac leaf
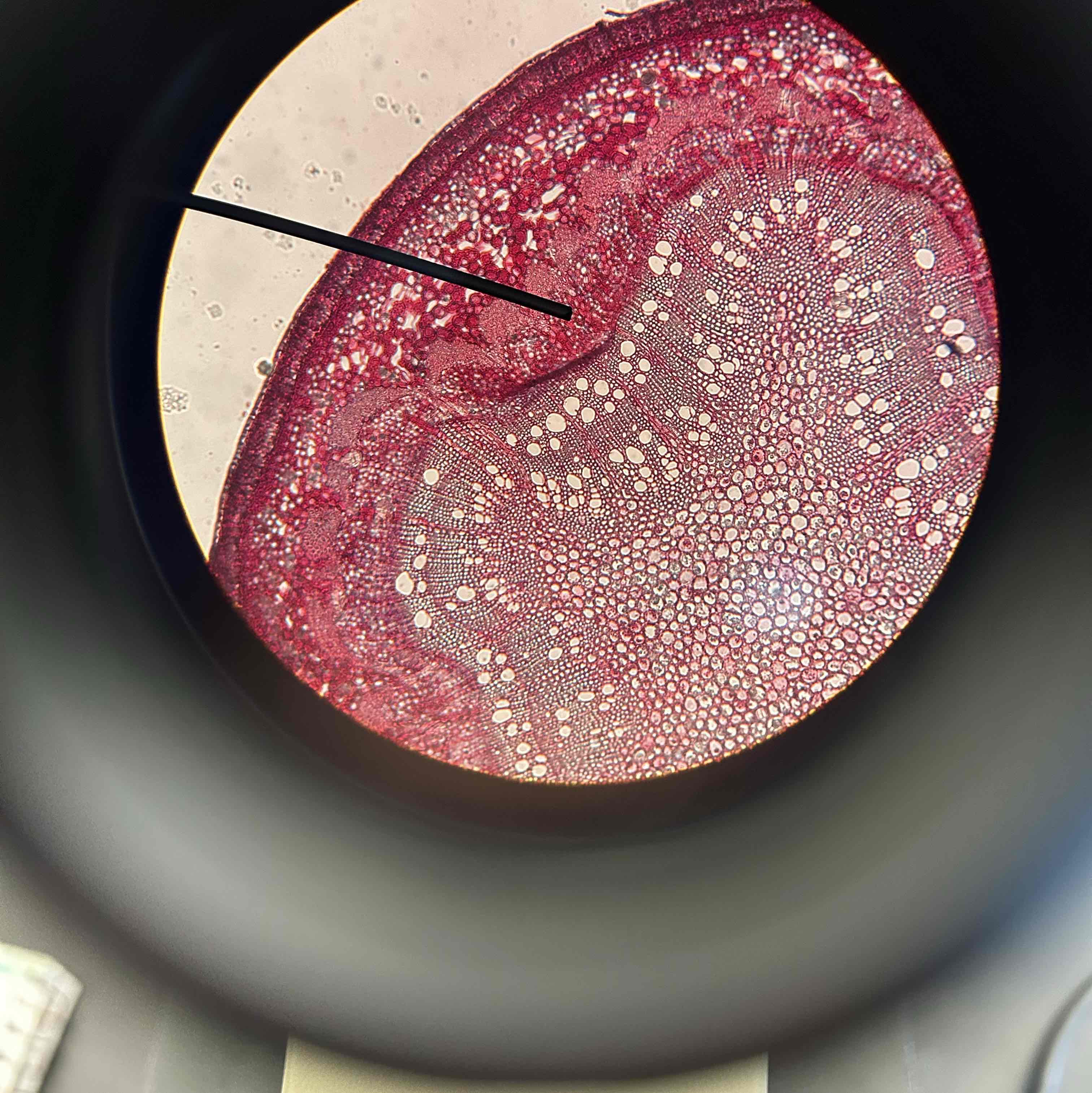
Woody stem
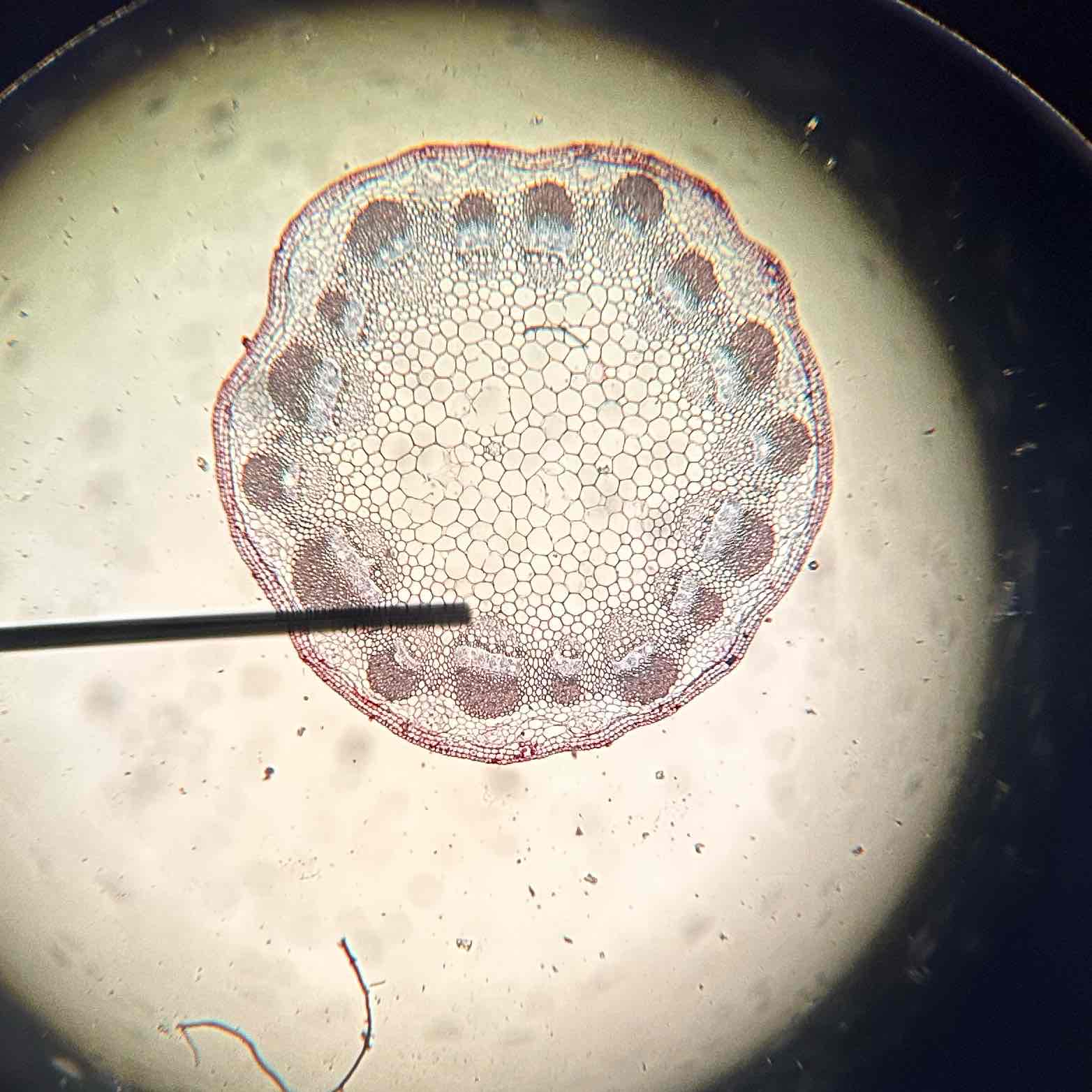
Herbacious stem/dicot stem
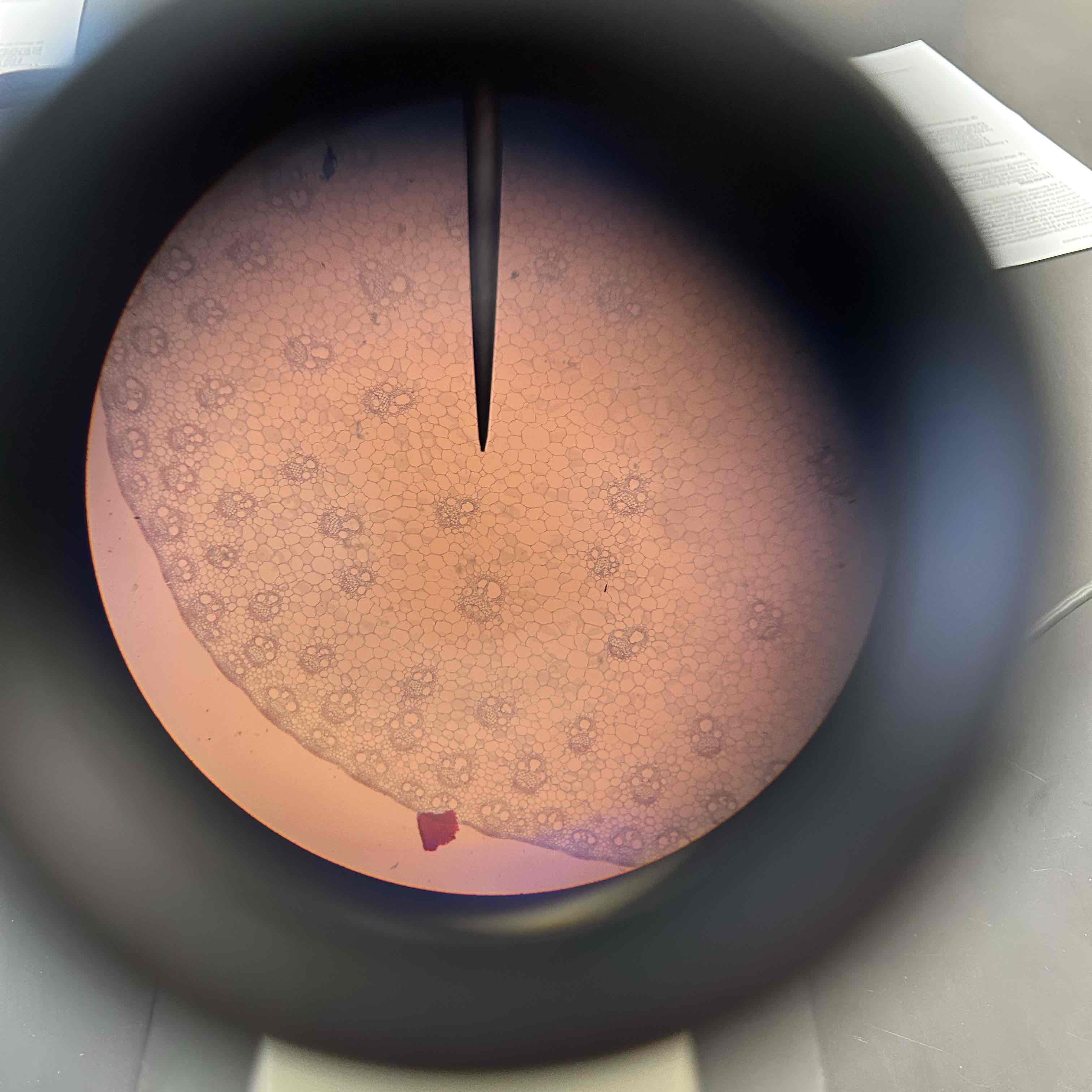
Monocot stem
Herbacious
No growth rings
Before secondary growth
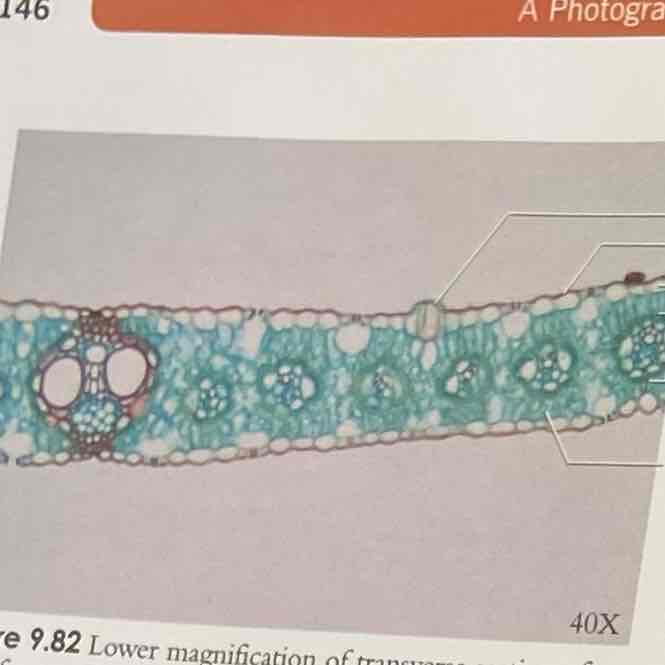
Corn Leaf
Endodermis
wraps around and protects vascular bundle in roots from pathogens, bacteria, etc.
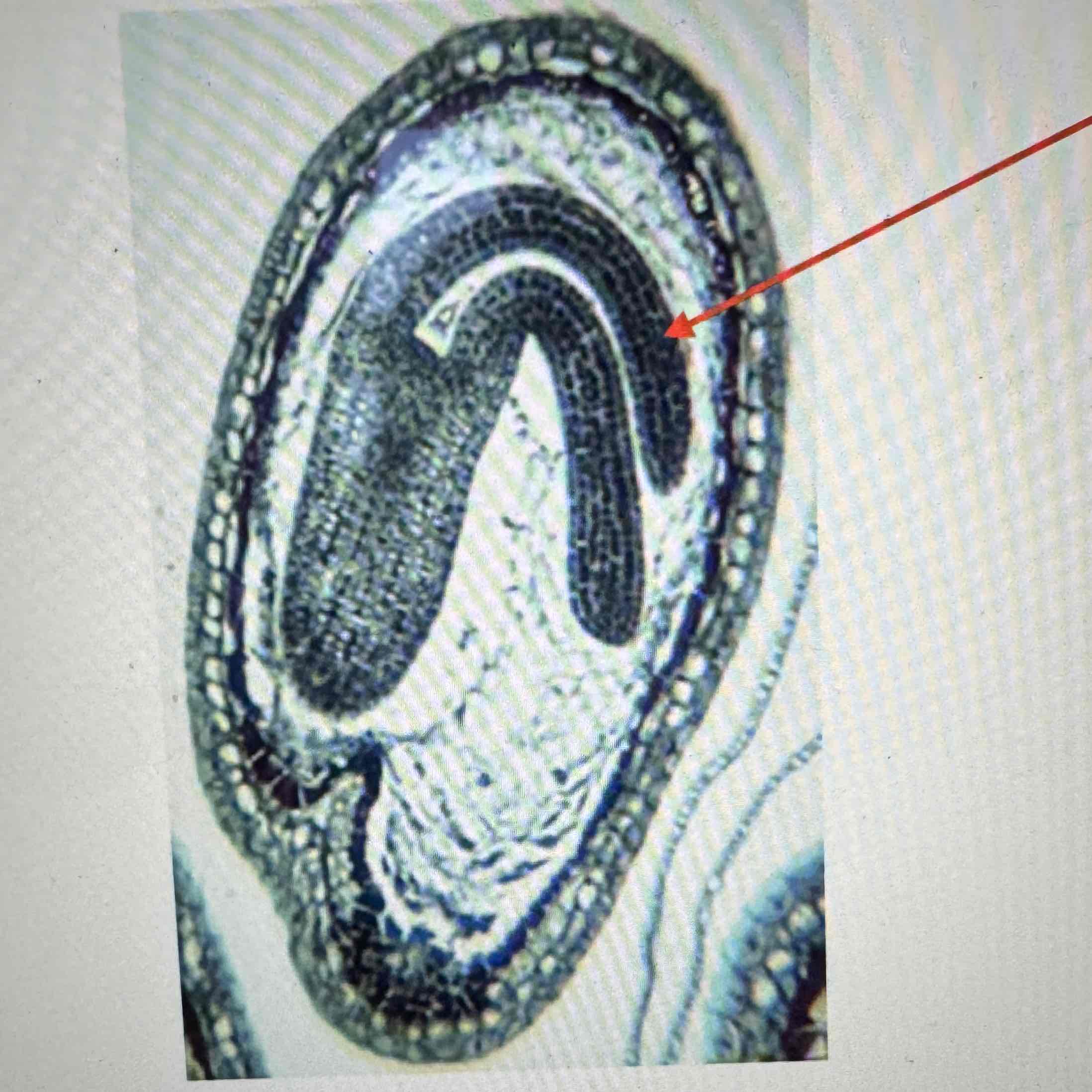
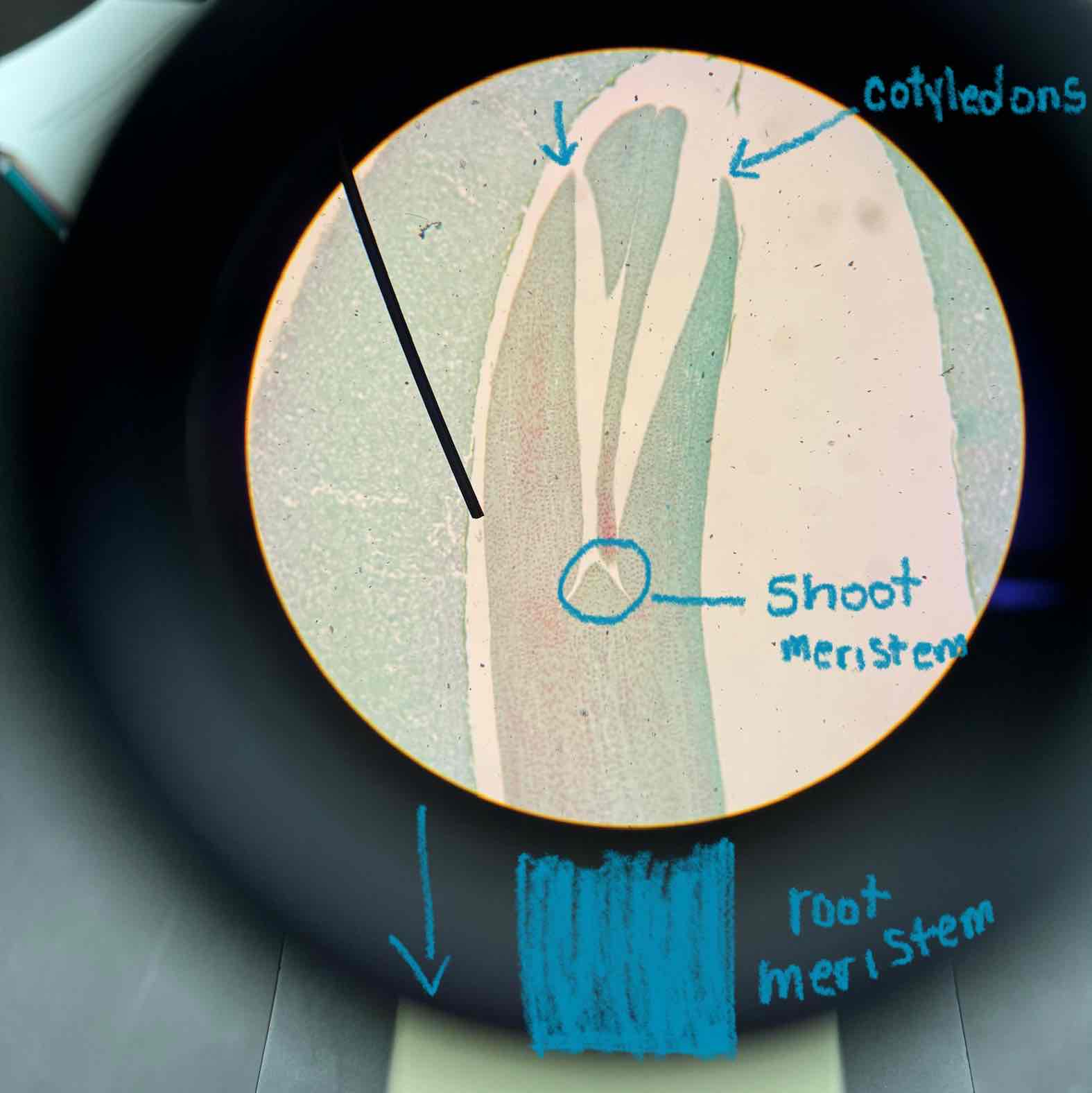
what part of this embryo is the arrow pointing to?
cotylodons
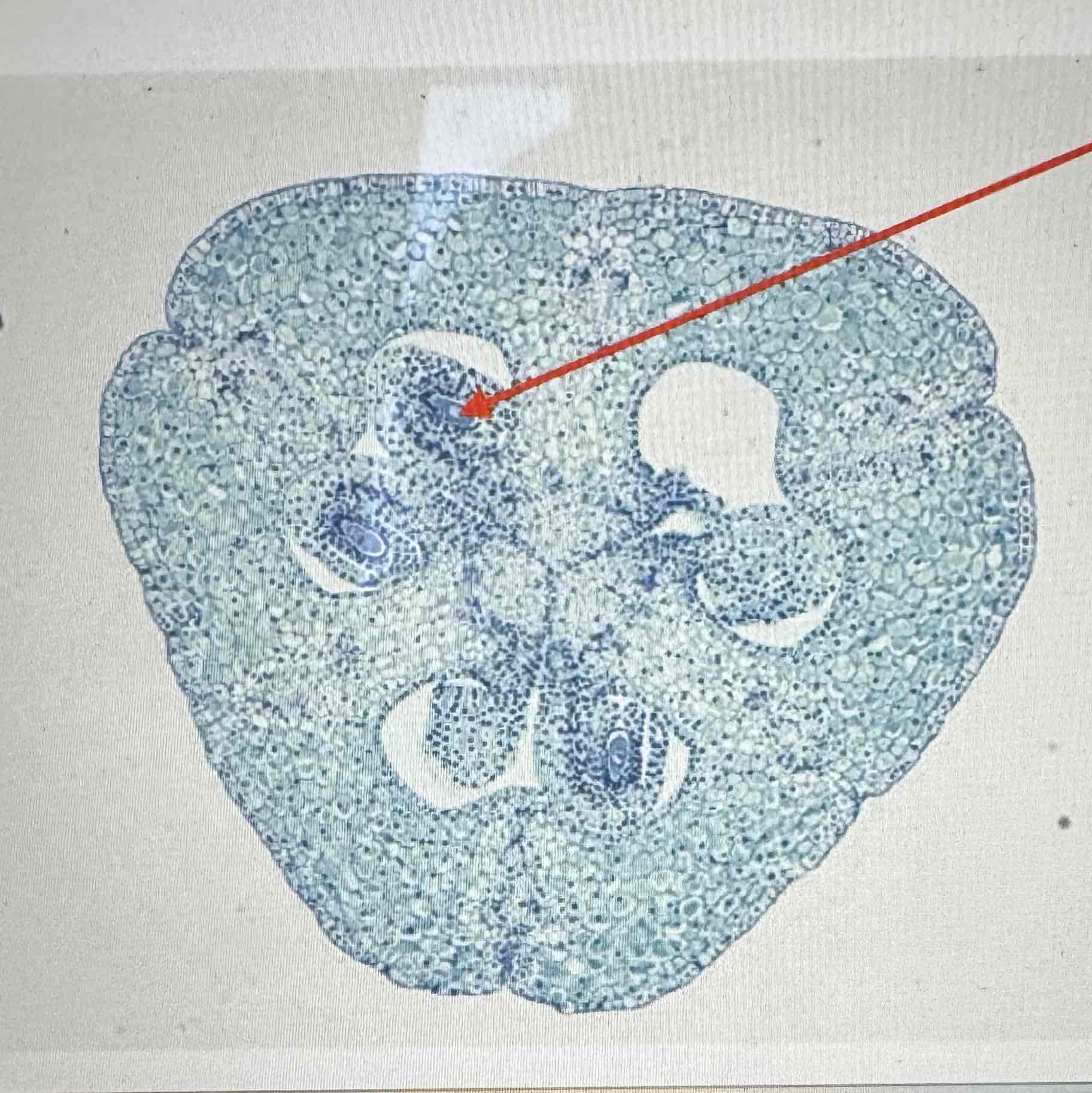
what part of the life cycle of the Angiosperm is this ovule?
gametophyte
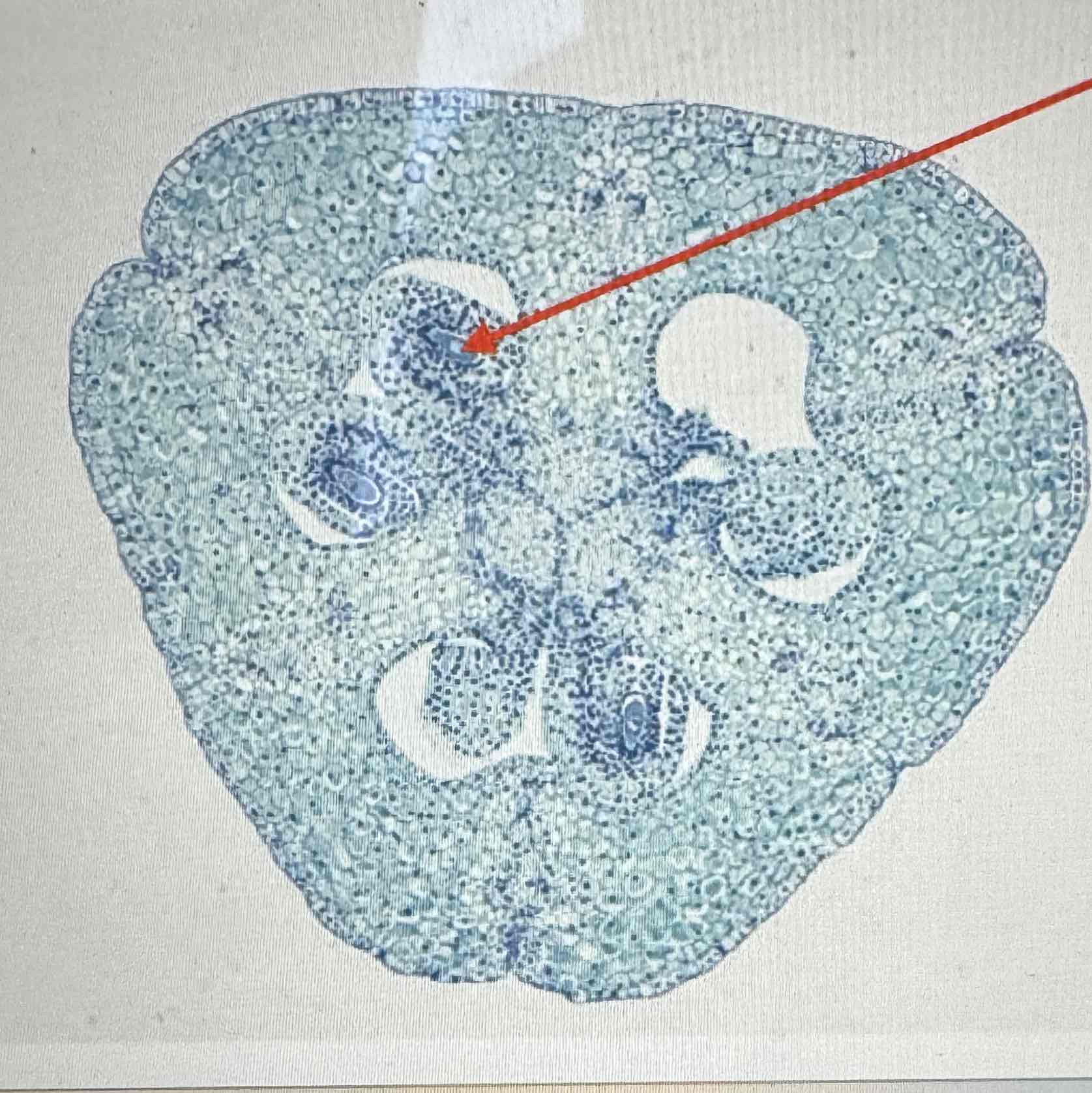
what is the ploidy of the Angiosperm ovule?
haploid
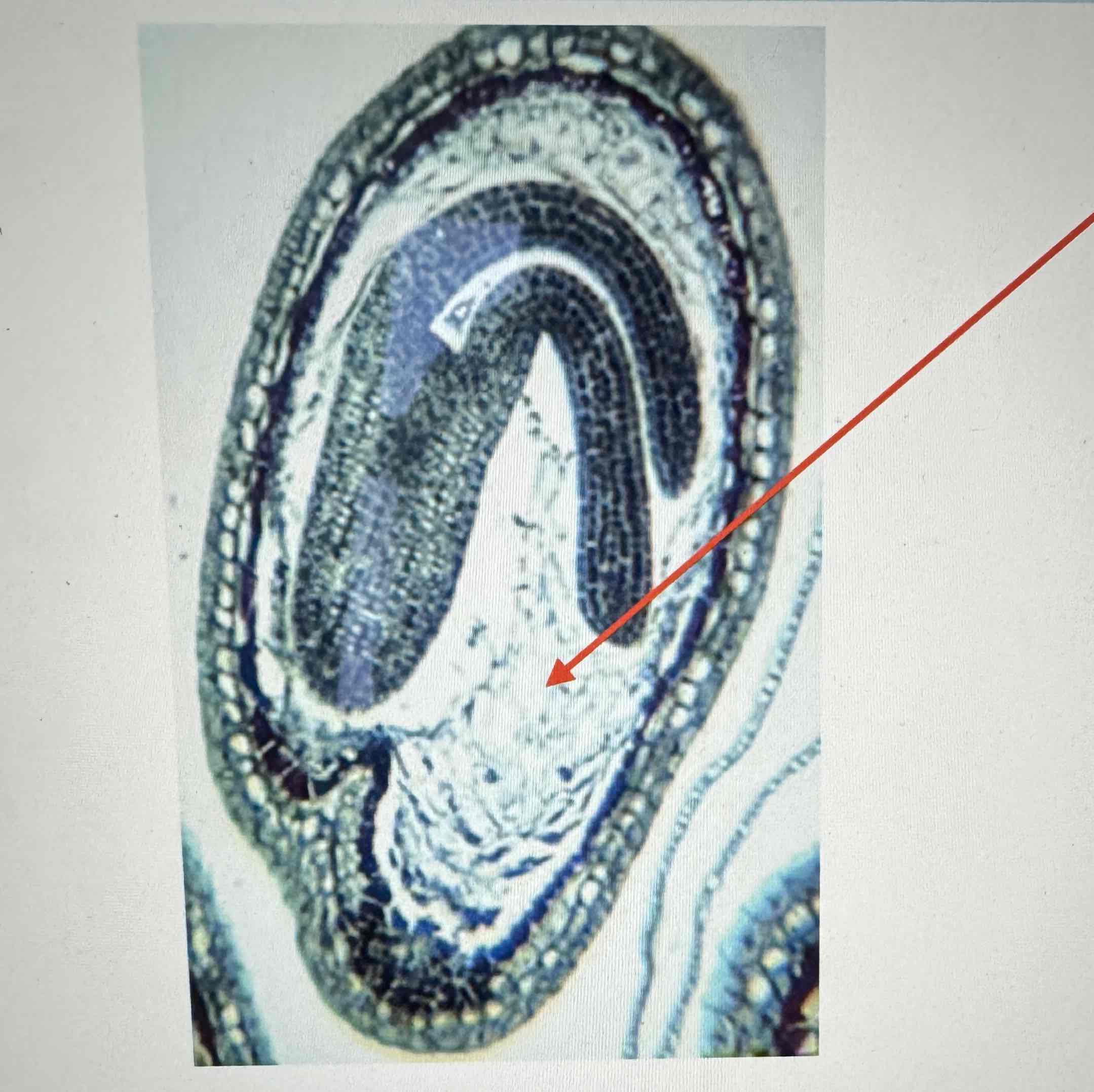
what is the arrow pointing to in this Angiosperm
endosperm
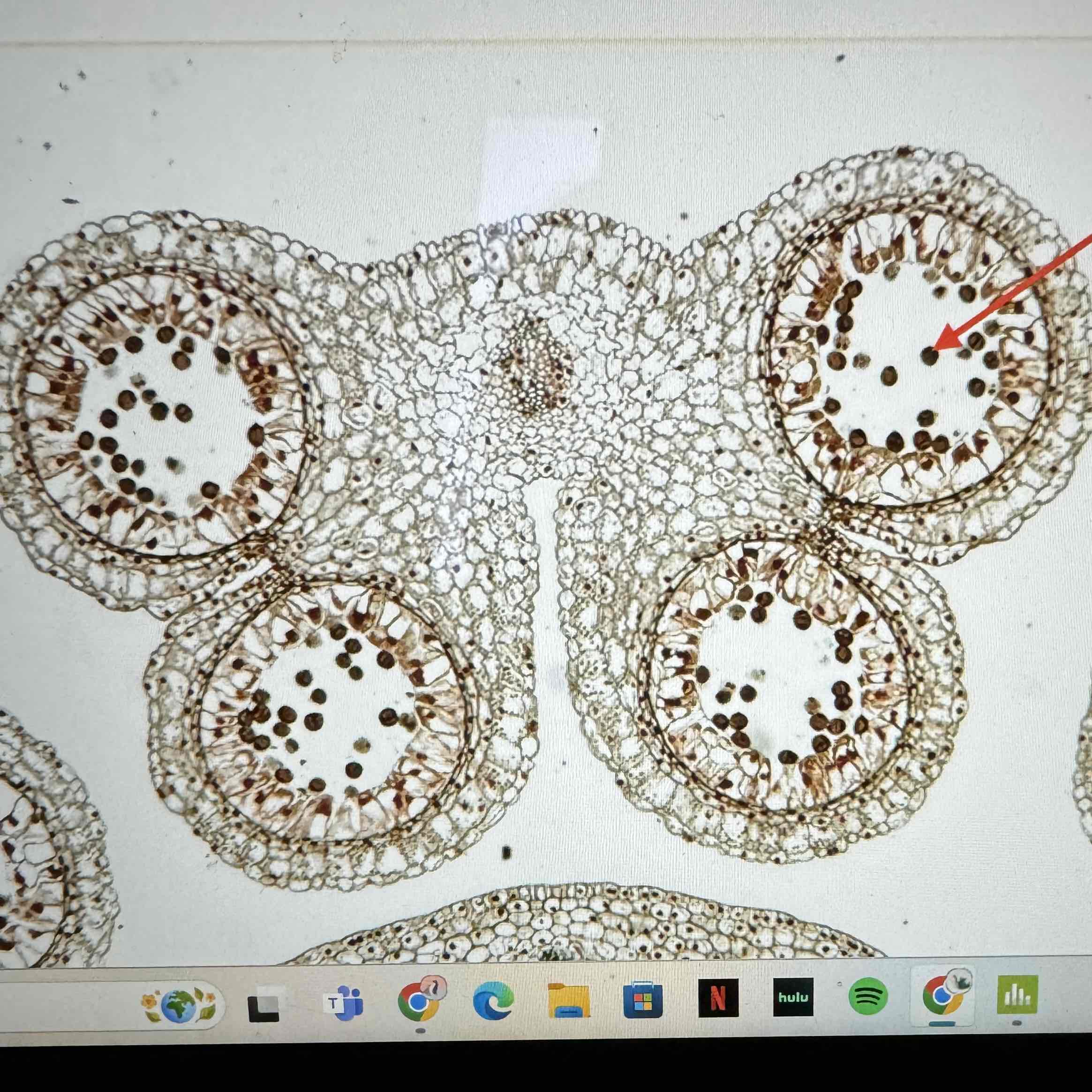
what is the ploidy of the pollen grains in this Angiosperm
haploid
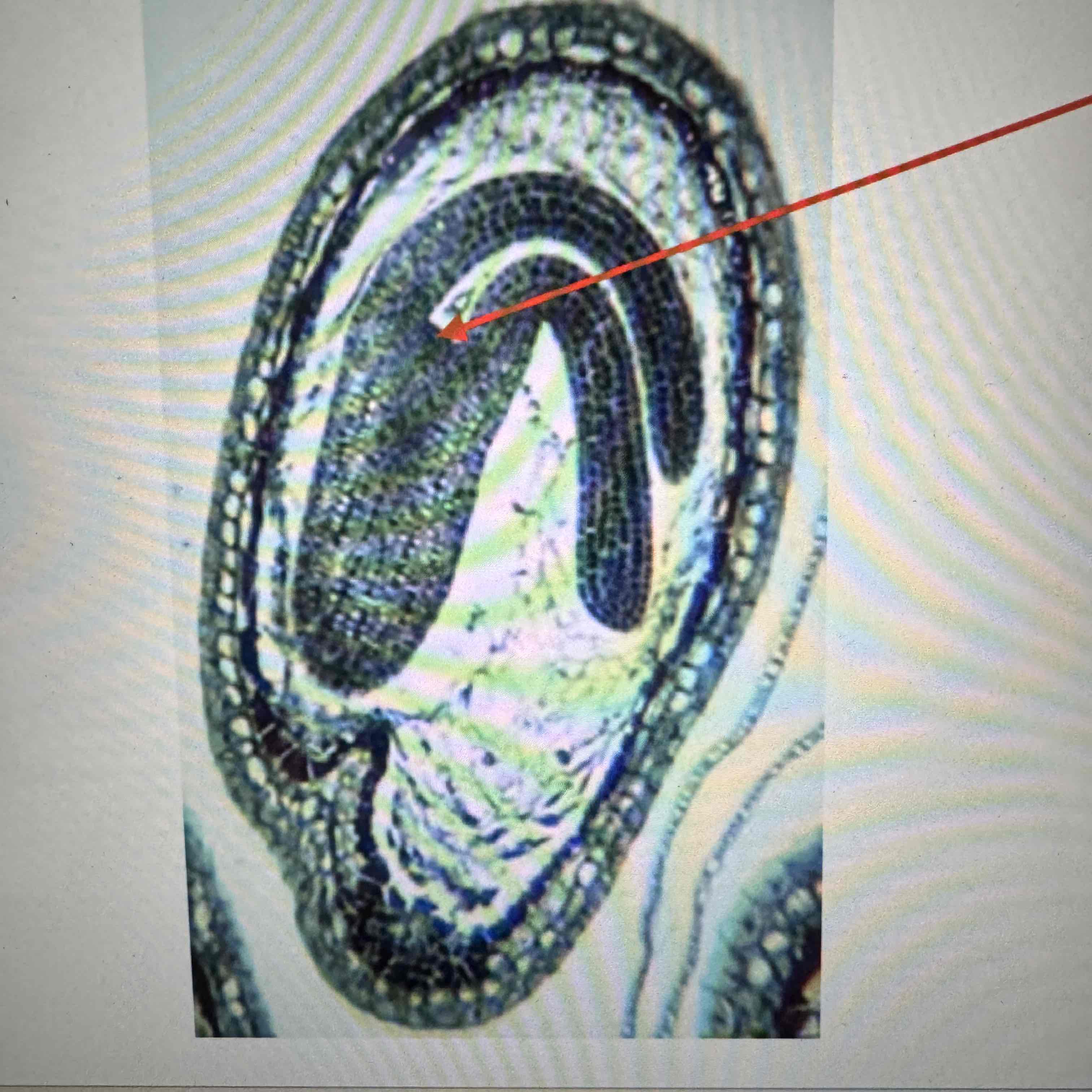
what part of the Angiosperm embryo is the arrow pointing to?
shoot meristem
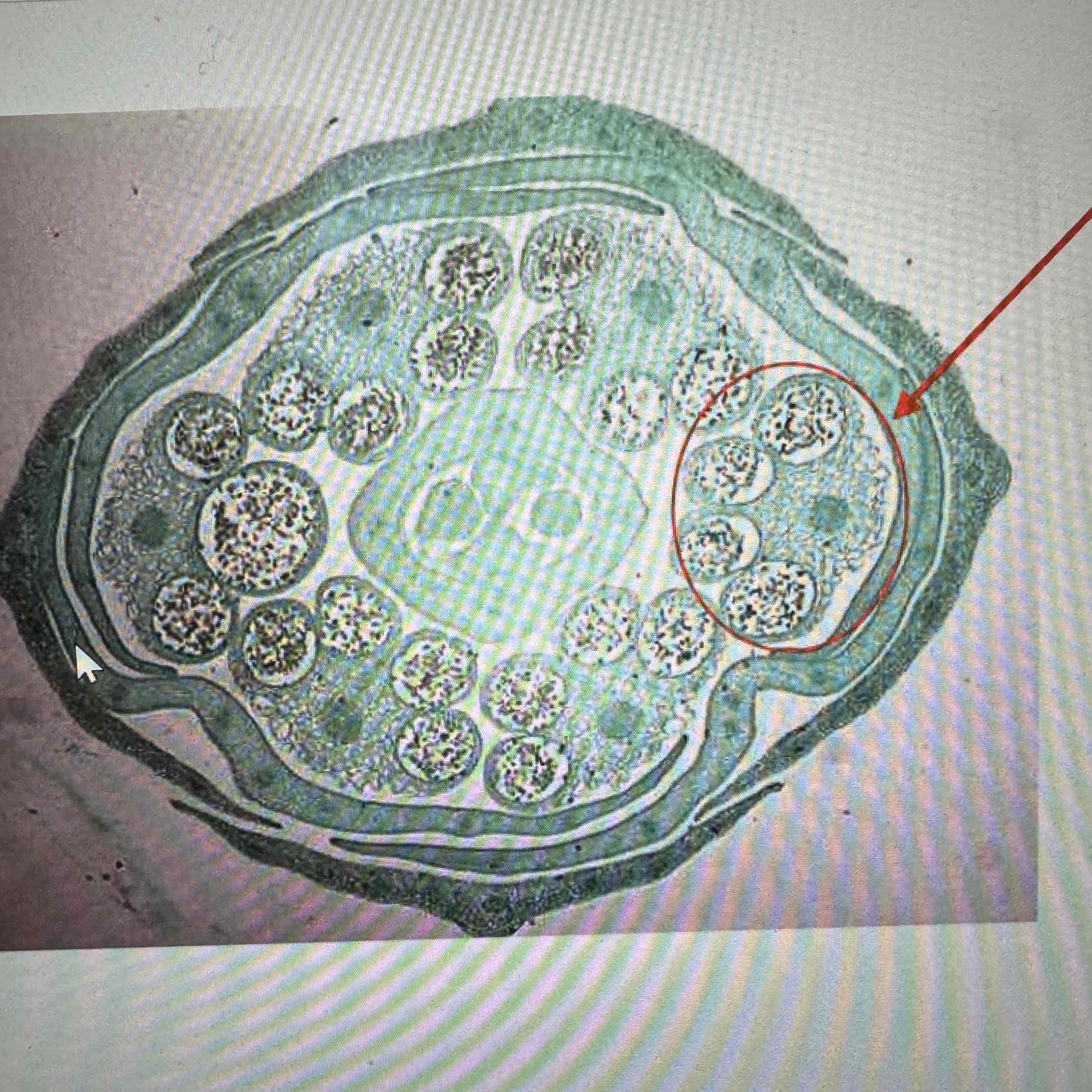
what part of the flower is circled
stamen
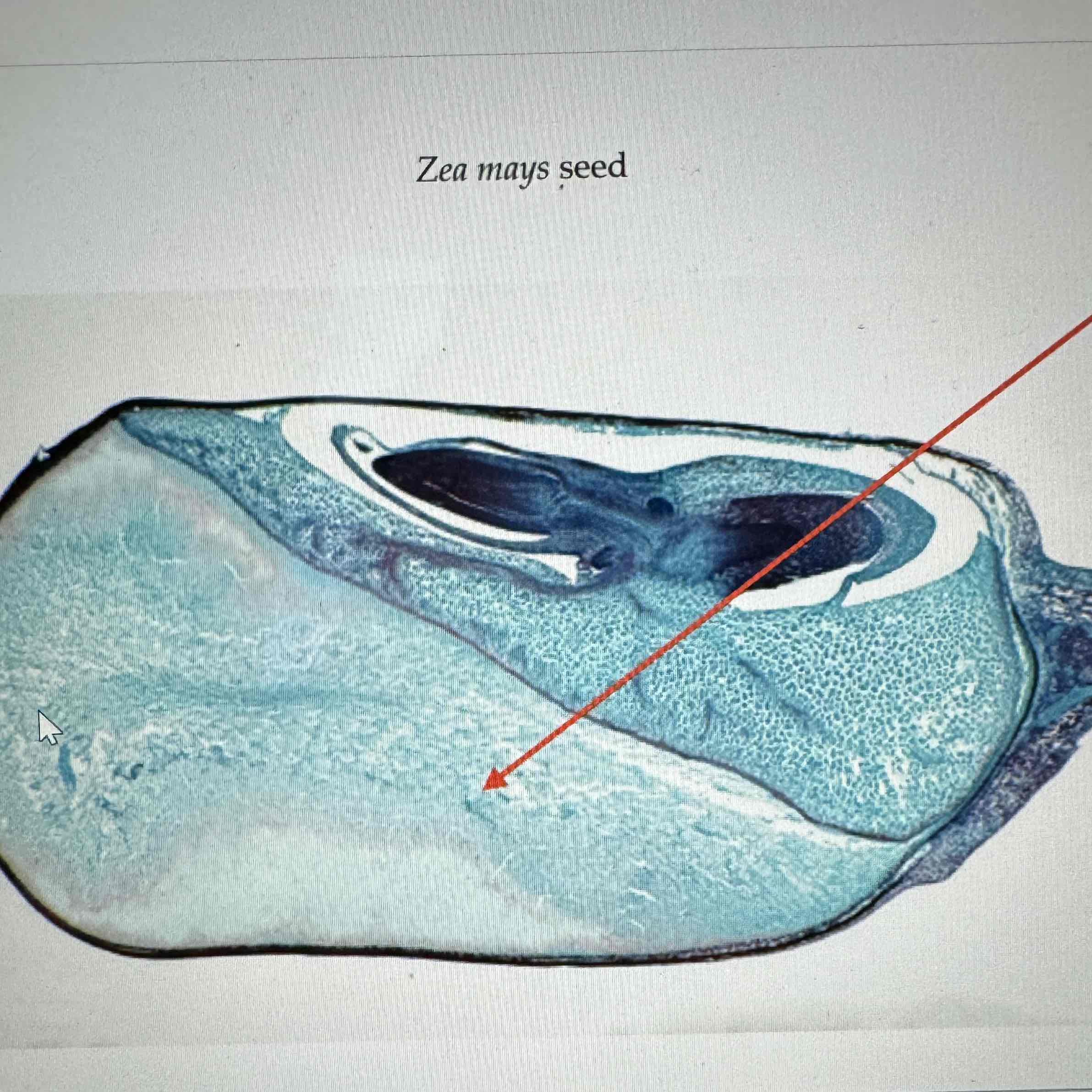
what is the ploidy of the cross section of the Angiosperm corn seed
triploid
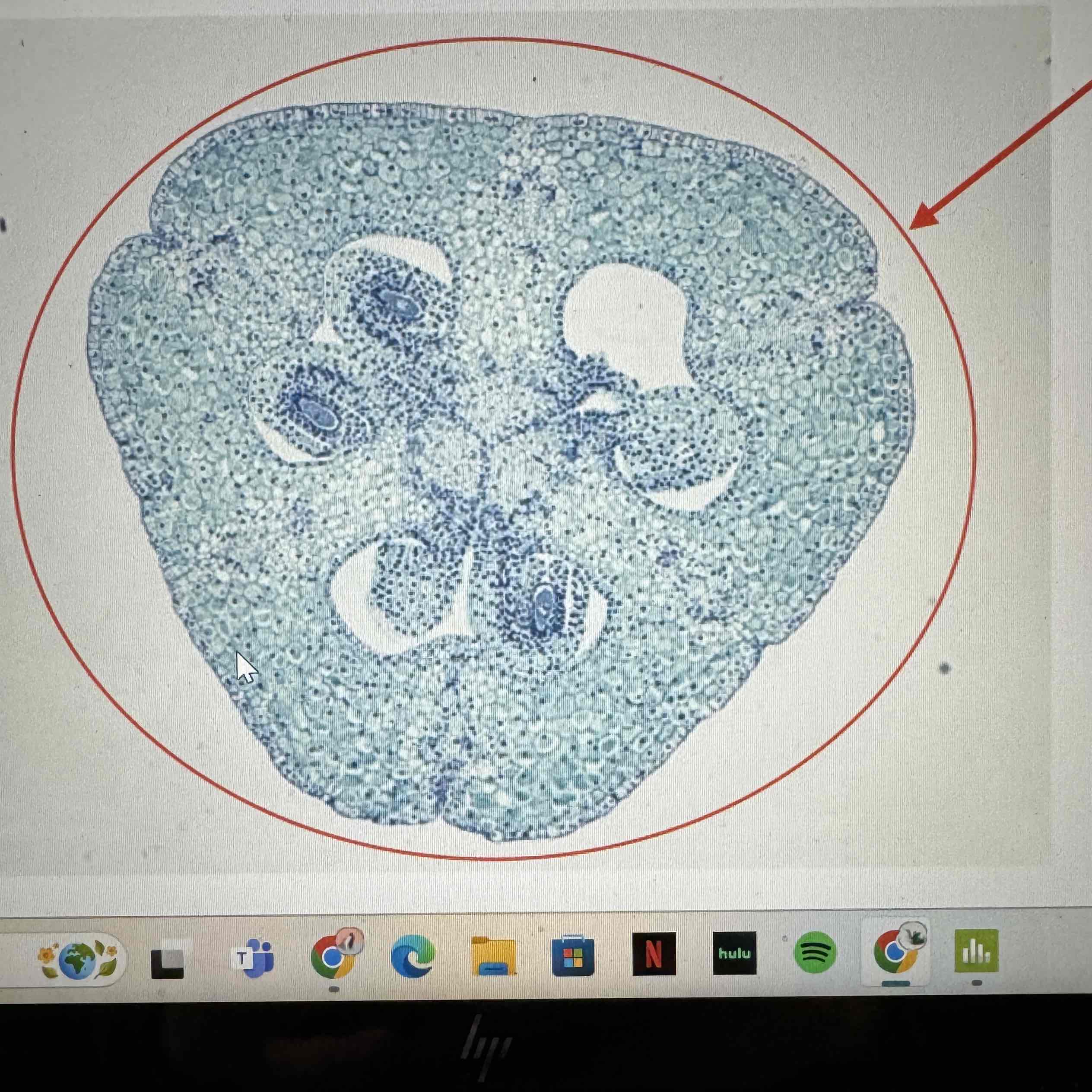
what is the ploidy of the ovary seen here
diploid
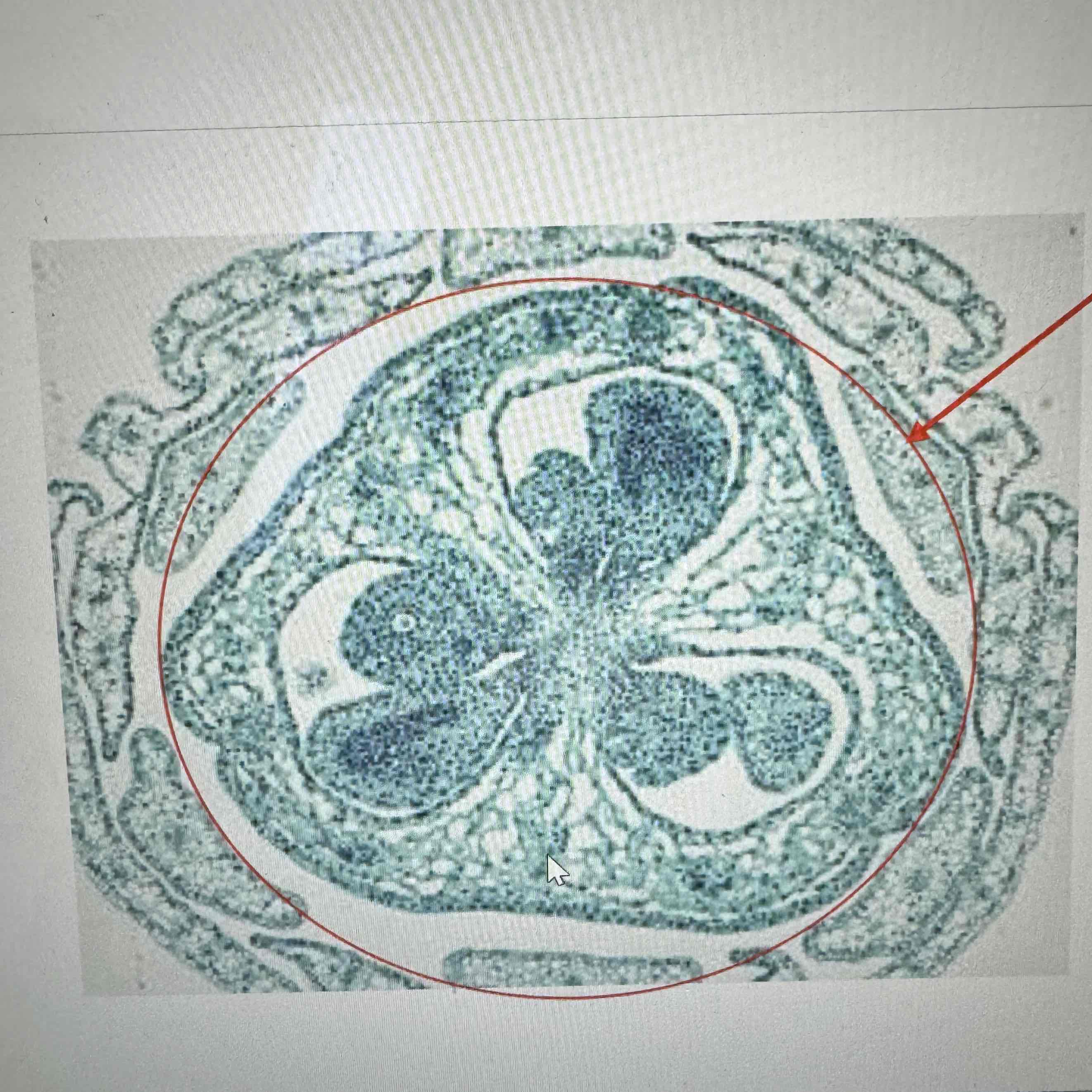
what part of the flower is seen here
carpel
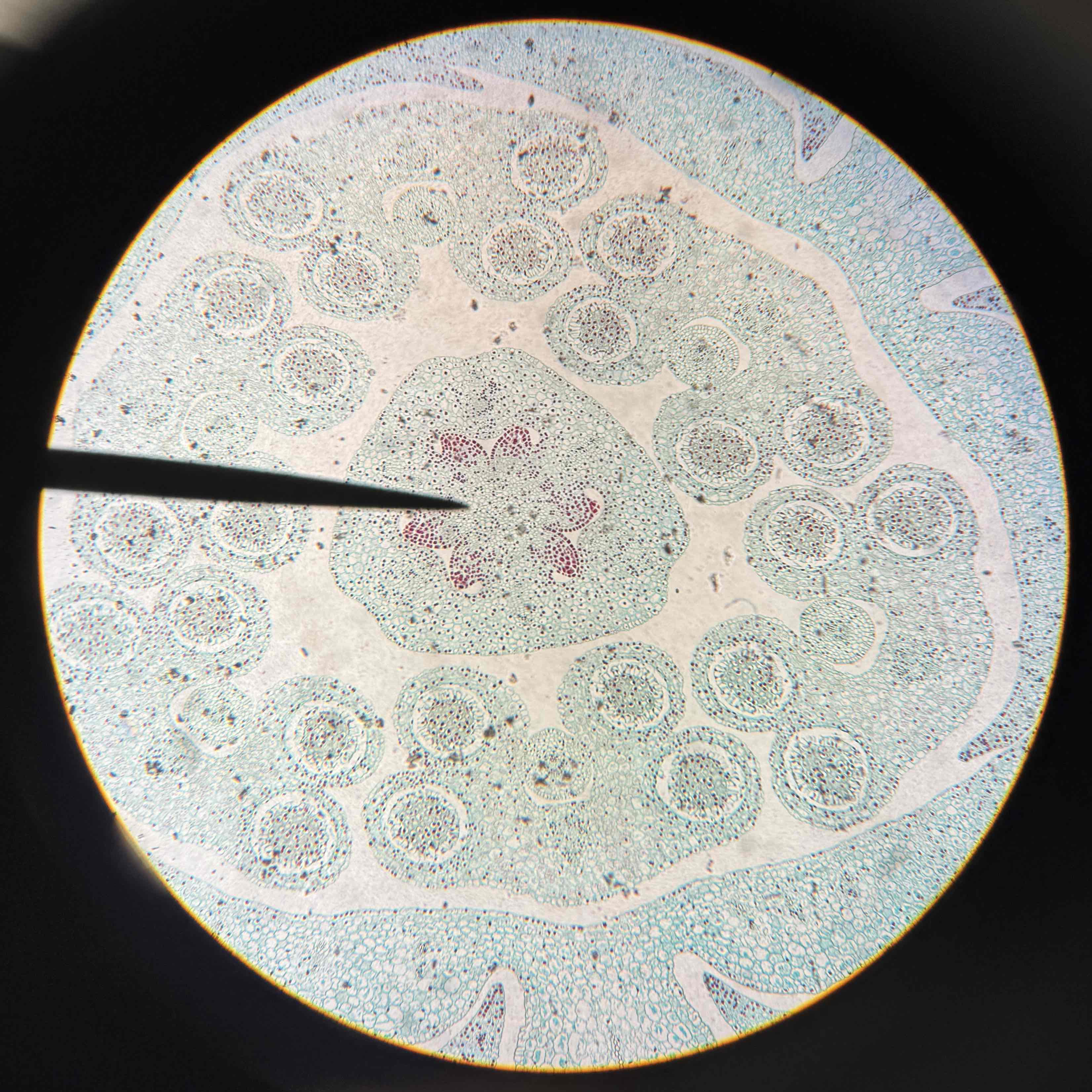
dicot flower bud (4 sepals)
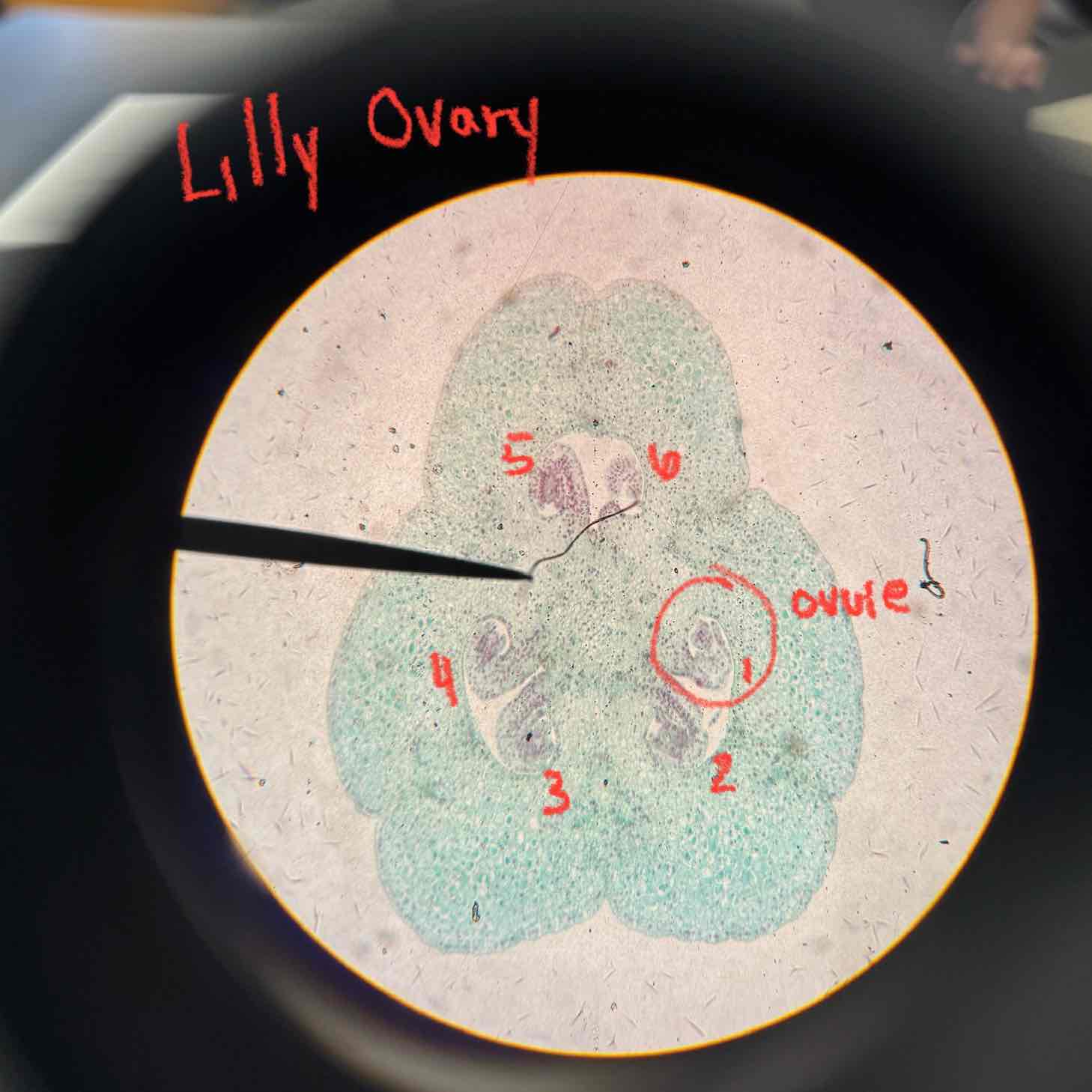
lilly ovary
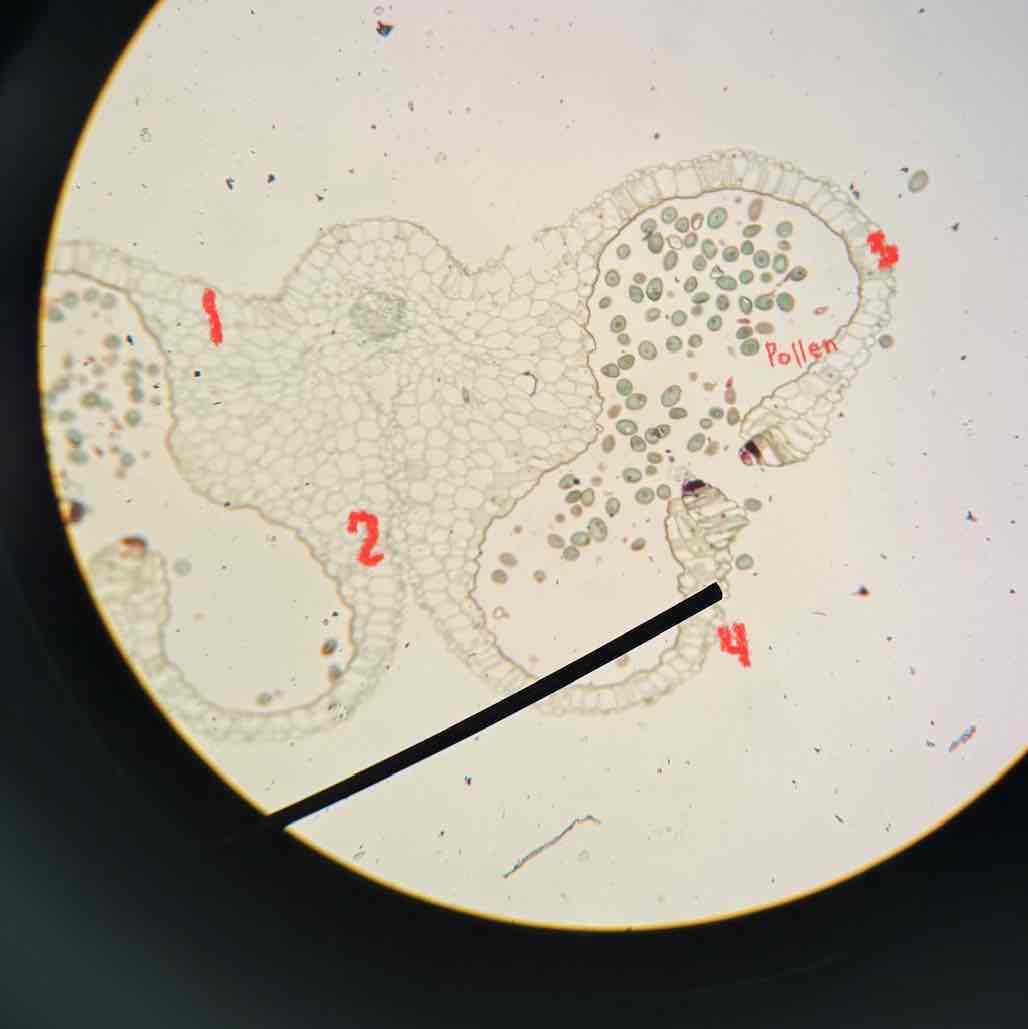
lilly anther