Quick & Easy Medical Terminology Ch. 10
1/129
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
130 Terms
urination
the act of voiding
erythr/o
red (c.f.)
-poietin
a substance that causes production (suffix)
urea
the final product of protein metabolism and the major nitrogenous waste product in urine
-ation
process (suffix)
urology
branch of medicine concerned with the male genital tract and the urinary tract of both genders
urologist
specialist concerned with the male genital tract and the urinary tract of both genders
ur/o
urine or urinary tract (cf)
-logy
science of (suffix)
-esis
action, process, or result of (suffix)
albumin/o
albumin (cf)
glycos/o
sugar (c.f.)
olig/o
few, scanty (c.f.)
-uria
urine or urination (suffix)
urinary
pertaining to urine or urine formation
ureters
urine leaves the kidneys by way of the _________
cyst/o
urinary bladder (or a cyst or a sac) (c.f.)
renal
pertaining to the kidney
ureteral
pertaining to the ureter
urethral
pertaining to the urethra
cystic
pertaining to the urinary bladder, the gallbladder, or a cyst
glomerul/o
glomerulus (kidney filter) (c.f.)
nephr/o, ren/o
kidney (c.f. x2)
pyel/o
renal pelvis (urine-collecting reservoir in the kidney) (c.f.)
ureter/o
ureter (cf)
urethr/o
urethra (cf)
fibr/o
fiber (cf)
-ous
characterized by (suffix)
urinary bladder
where urine is stored until urination
renal pelvis
funnel shaped structure located in the center of each kidney
ureter
tube through which urine passes from the kidney
urethra
tubular passage by which urine is discharged from the bladder
proxim/o
near (cf)
dist/o
far (cf)
nephrons
the functional unit of the kidneys
tubule
tubular section of a nephron
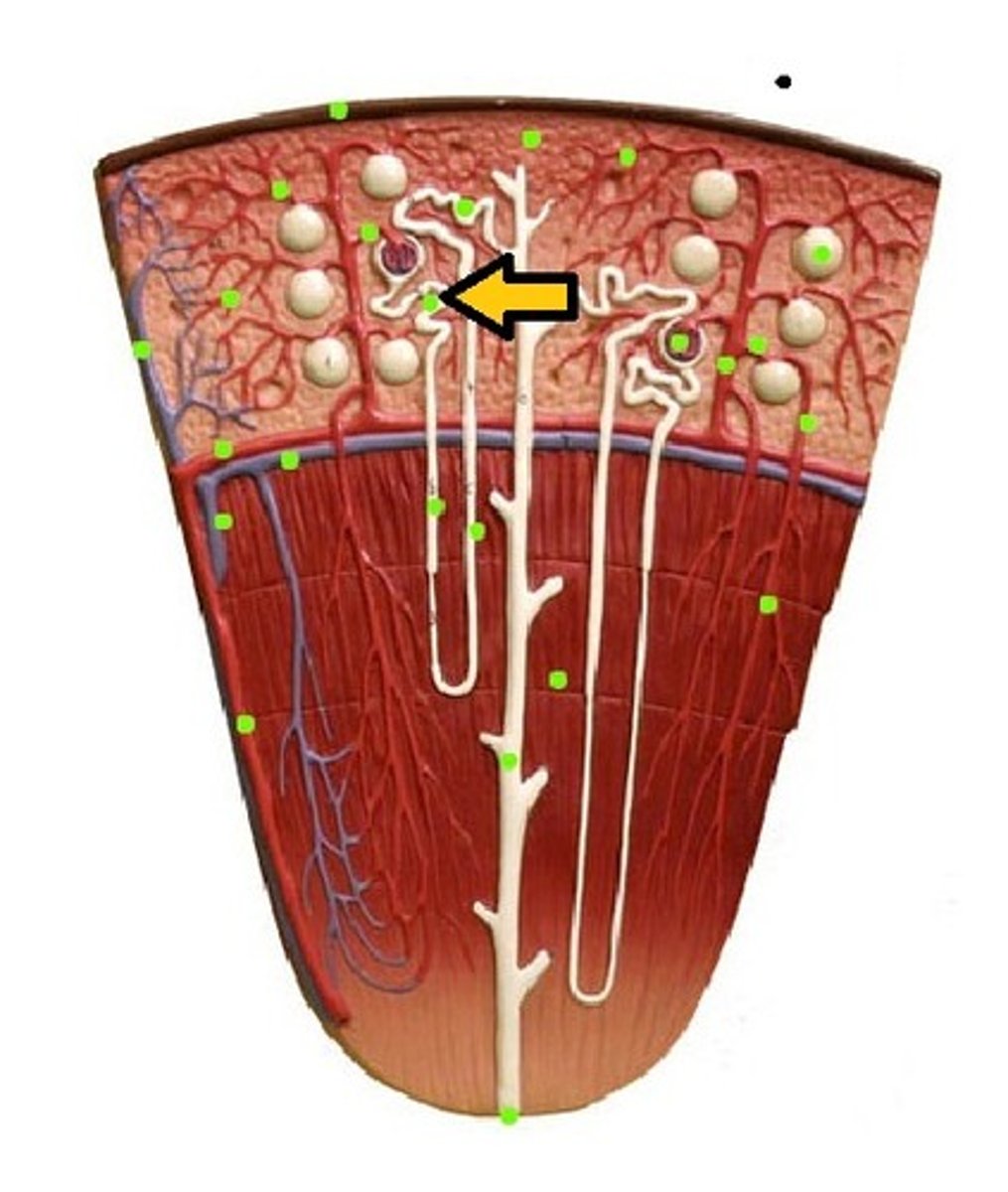
glomerulus
blood vessel cluster in a nephron surrounded by the "Bowman capsule"
glomerular filtration
initial process in formation of urine; filtering of blood in the kidneys
glomerulus
the _________ allows water, salts, wastes and most other substances except blood cells and proteins to pass through it's thin walls
tubular reabsorption
selective reabsorption of some substances in the kidneys; occurs after glomerular filtration
tubular secretion
secretion of substances into the urine; occurs after tubular reabsorption
antidiuretic hormone
increases the re-absorption of water by the renal tubules, thus decreasing the amount of urine produced.
glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption, tubular secretion
three processes in urine formation
urinalysis
test used to evaluate the status of the urinary system
sugar; protein; blood
substances which should not be found in the urine (x3)
glycosuria
sugar in urine
proteinuria
protein in the urine
albuminuria
high concentration of albumin in the urine
hematuria
blood in urine
pyuria
pus in urine
ketonuria
ketones in urine; can occur due to uncontrolled DM
diabetes mellitus (DM)
endocrine d/o characterized by glycosuria and hyperglycemia; results from inadequate production or use of insulin.
clean-catch
technique based on concept that the tissues adjacent to the urethral opening must be cleansed before collection to avoid contamination of the urine specimen, and only the middle portion of the urine stream is collected.
voided
a _____ specimen is one in which the patient voids (urinates) into a container supplied by the lab or doctor's office.
Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN)
a measure of the amount of urea in the blood; directly related to the metabolic function of the liver and the excretory function of the kidneys.
creatinine
measured in the blood and urine as an indicator of kidney function
tom/o
to cut (c.f.)
angi/o
vessel (c.f.)
renal angiography/arteriography
radiographic study to assess the arterial blood supply to the kidneys
renal arteriogram
record produced from a renal angiography
stenosis
constriction or narrowing of a renal artery
nephrotomography
sectional radiographic exam of the kidneys, generally using contrast dyes
nephrotomogram
images provided by nephrotomography
nephromegaly
enlargement of one or both kidneys
nephromalacia
softening of the kidney
bilateral nephromegaly
enlargement of both kidneys
nephrosonography
ultrasonic scanning of the kidneys
urolithiasis
presence of urinary stones found in the renal pelvis or the urinary bladder
cystolithiasis
presence of stones in the urinary bladder
nephrolithiasis
a condition marked by the presence of kidney stones
renal calculi
nephrolith is a word, but kidney stones are usually called ________
pyelitis
inflammation of the renal pelvis
nephritis
a.k.a. Bright disease; inflammation of the kidney
glomerulonephritis
glomeruli of kidney are inflammed
intravenous urography
radiographic technique for examining the urinary system
pyelography
intravenous urography was previously called _____
urogram
image produced in a urography
cystoscopy
examination of the urinary bladder
urethroscopy
visual examination of the urethra
cystitis
inflammation of the urinary bladder
dysuria
difficult or painful urination
polyuria; diuresis
excretion of an abnormally large quantity of urine (x2)
anuria
absence of urination (less than 100mL/day)
oliguria
diminished capacity to produce urine; excreting less than 500 mL/day
uremia
presence of nitrogen-containing wastes in the blood; a toxic condition associated with renal insufficiency or renal failure
nephroptosis
a prolapsed kidney
-ptosis
sagging or prolapse (suffix)
cystocele
urinary bladder hernia that protrudes into the vagina
nephrosis
degenerative changes in the kidneys w/o inflammation
nephrotoxic
destructive to kidney tissue
polycystic kidney disease
hereditary disorder characterized by hundreds of fluid-filled cysts throughout both kidneys
polyp
tumor found on a mucosal surface, such as the inner lining of the bladder
renal cell carcinoma
kidney cancer; malignant neoplasm (new, abnormal growth) of the kidney
renal failure
failure of the kidney to perform its essential functions
renal insufficiency
reduced ability of the kidney to perfrom its functions
retrograde urography
x-ray exam of the renal pelvis after injection of a contrast medium into the renal pelvis; alternative to intravenous urography (IVU)
urinary incontinence
inability to hold urine in the bladder
urinary retention
inability to empty the bladder
urinary tract infection
an infection of the urinary tract
urethral catheterization
a urinary catheter is inserted into a patient's bladder via the urethra.