Chapter 16 Practice Problems
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
C) Addition of the electrophile to the aromatic ring
1) What is the first step in the general mechanism for electrophilic aromatic substitution?
D) To rearomatize the ring system
What is the driving force for losing a proton as the last step in electrophilic aromatic
substitution?
B) NO2+
3) What is the electrophile in aromatic nitration?
D) HSO3+ or SO3 in acid
4) What is the electrophile in aromatic sulfonation?
B) To form the active electrophile NO2+
5) Why is sulfuric acid used in aromatic nitration?
A) The tert-butyl cation
6) What is the electrophile in the Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction with tert-butylchloride?
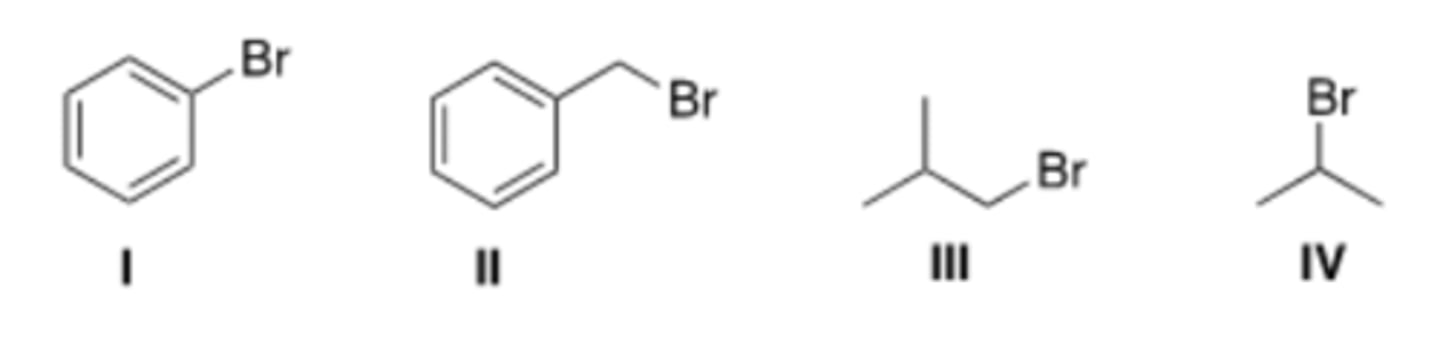
A) I
Which of the following halides will not work as an electrophile in a Friedel-Crafts
alkylation reaction?
C) Inductive and resonance
What are the two effects that have to be considered to determine the influence a substituent will have on electrophilic aromatic substitution?
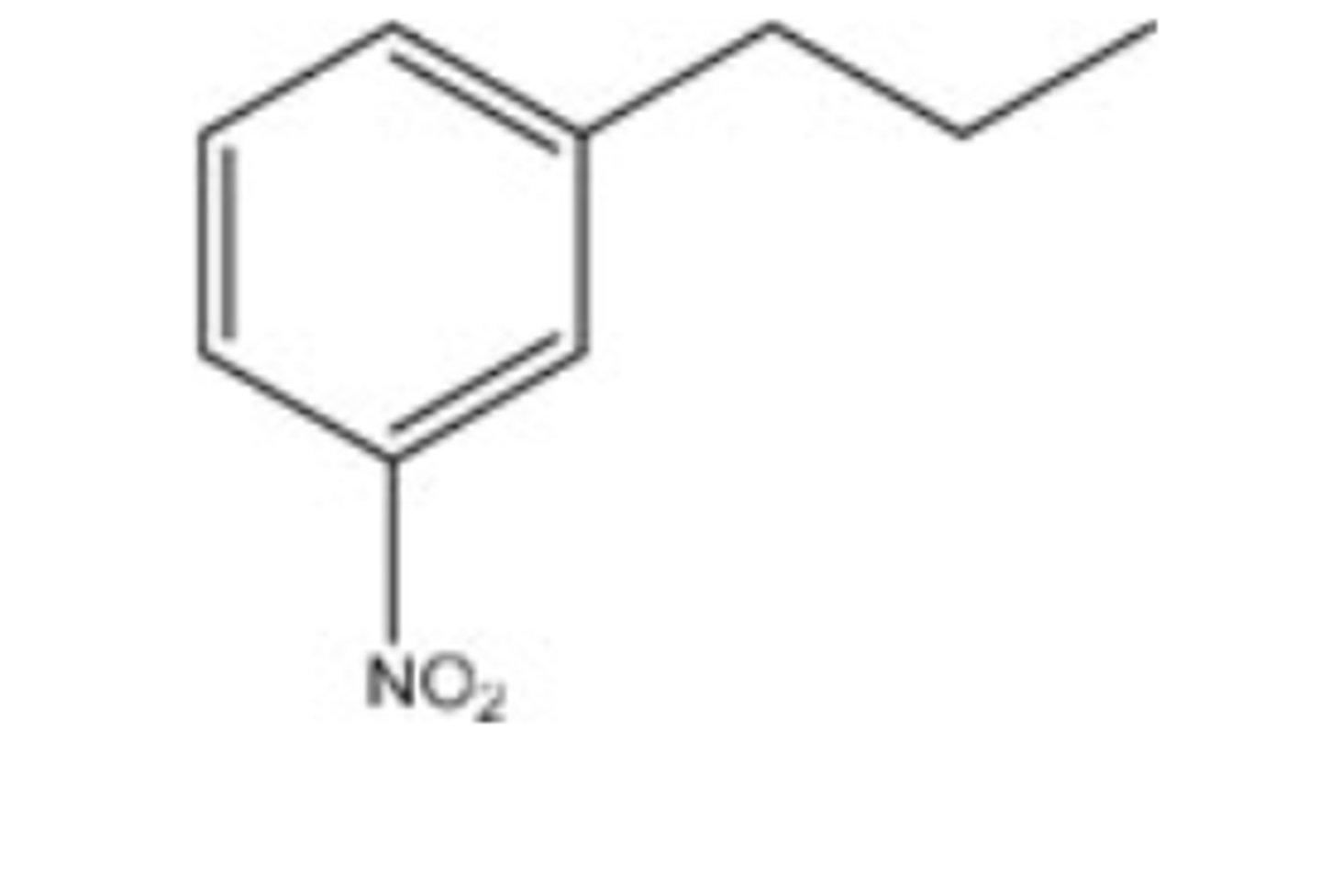
D) Because it removes more electron density from the
the meta position, thus deactivating the meta position less
9) Why is the nitro group a meta director?
C) The starting material is frequently over-alkylated.
10) What is a major problem with Friedel-Crafts alkylation?
B) The transition state of the first step is lower in energy.
Which of the following statements about the mechanism of electrophilic aromatic
substitution is not true?
D) IV
13) What is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction?
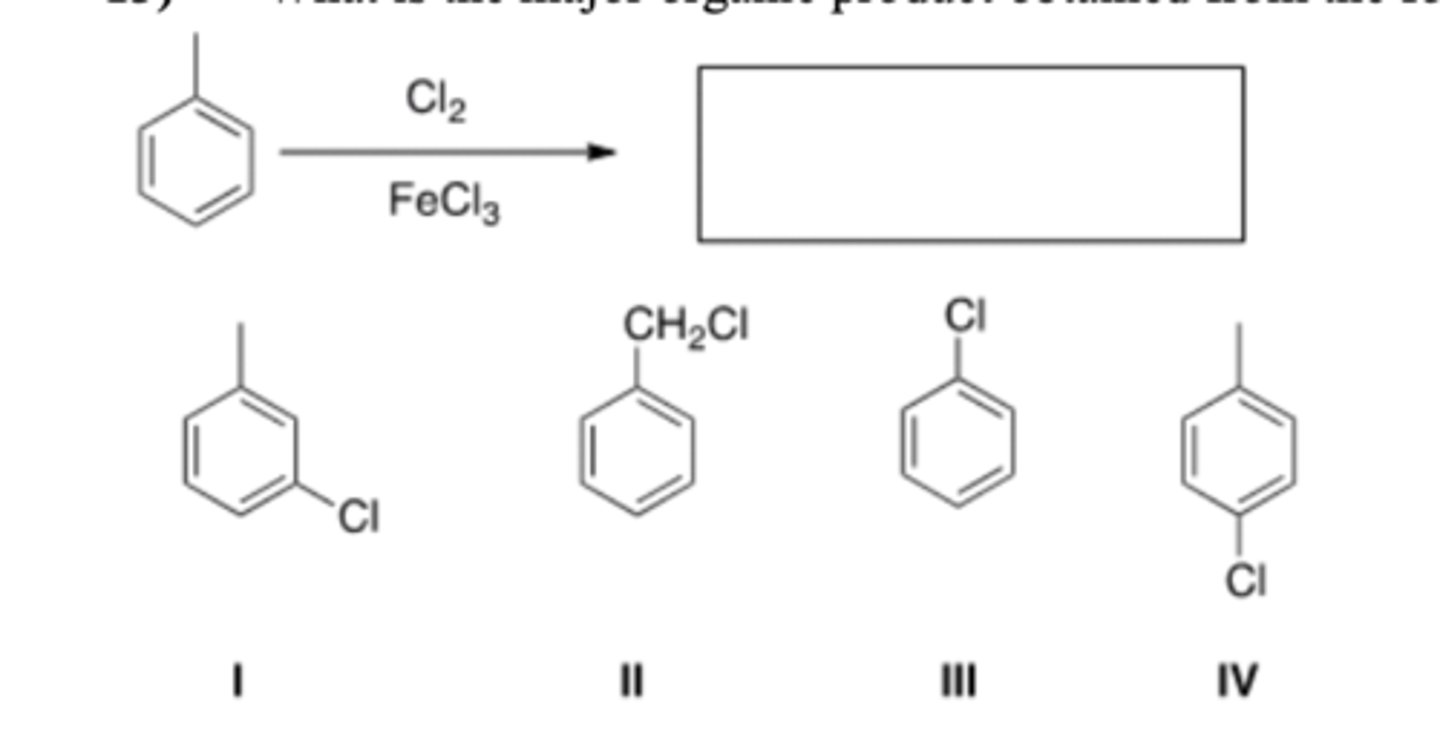
B) II
14) What is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction?
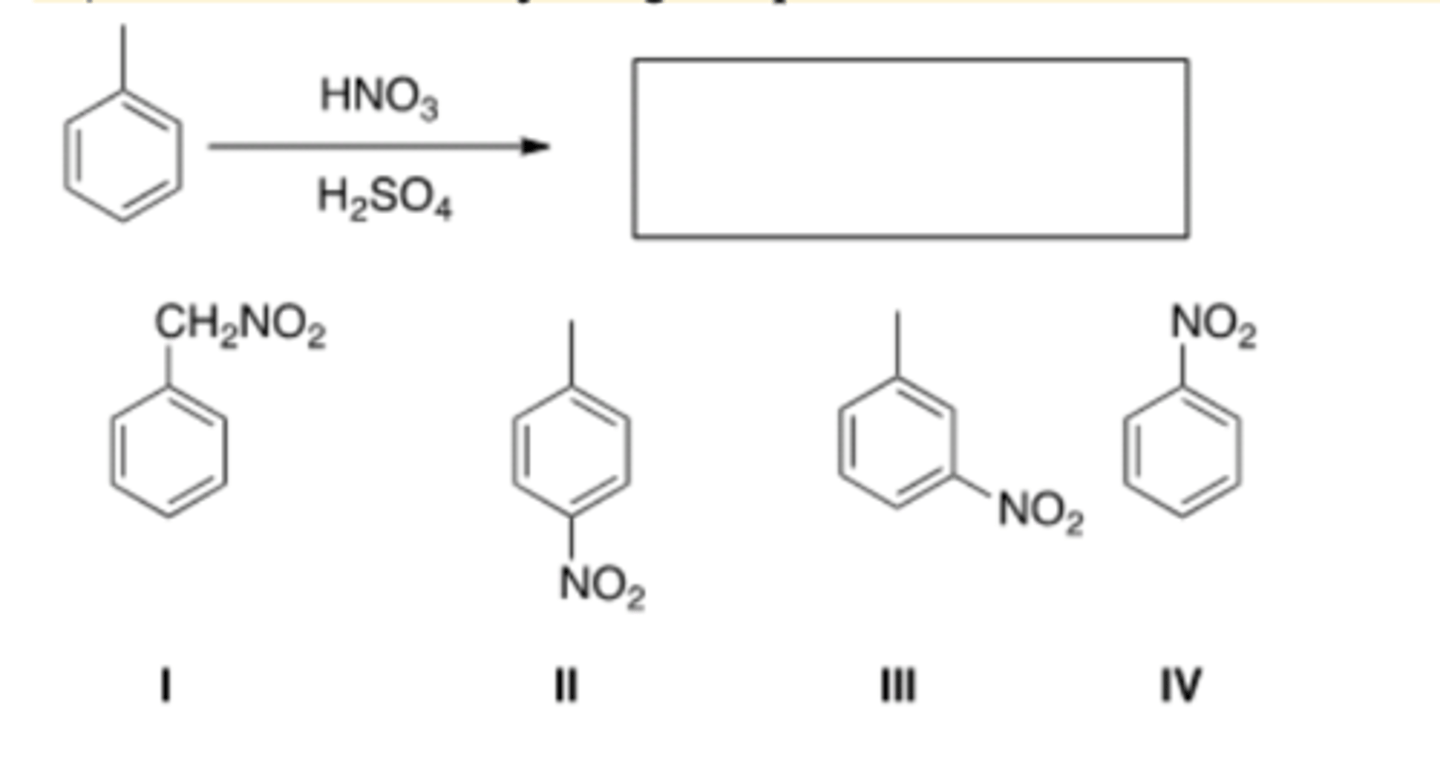
D) IV
15) What is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction?
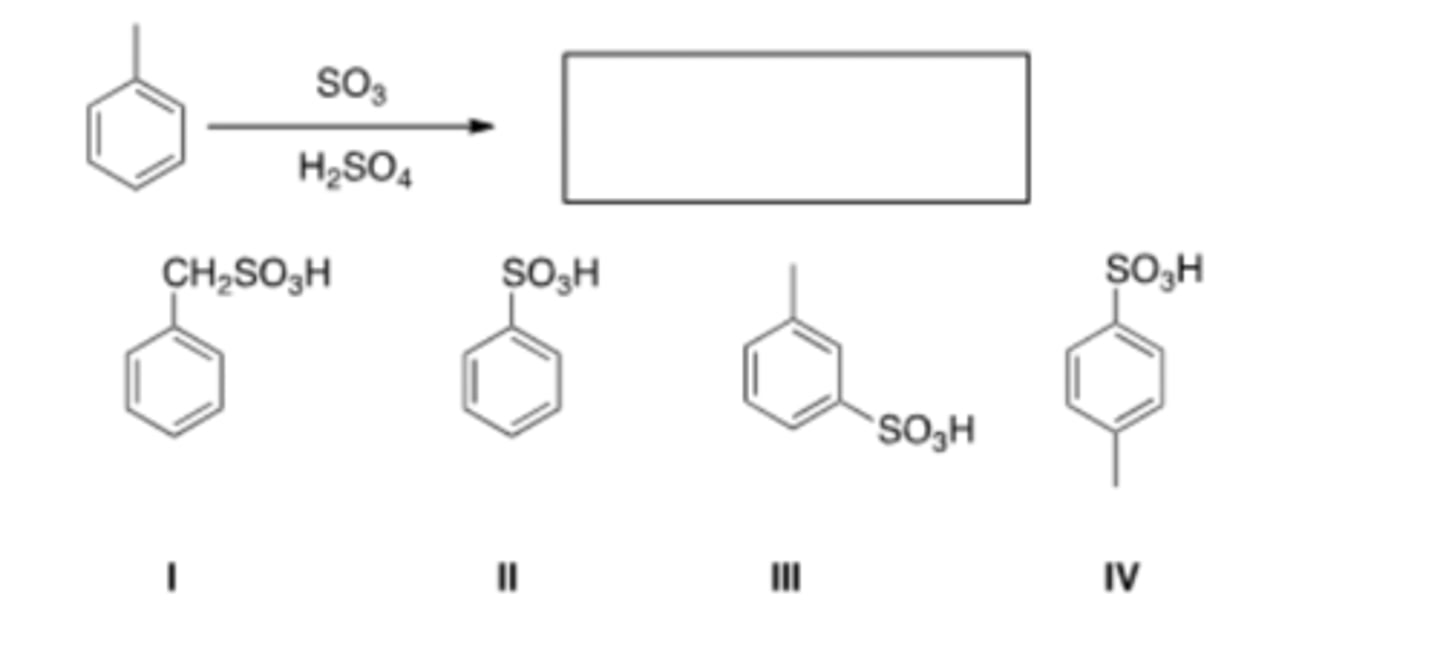
A) I
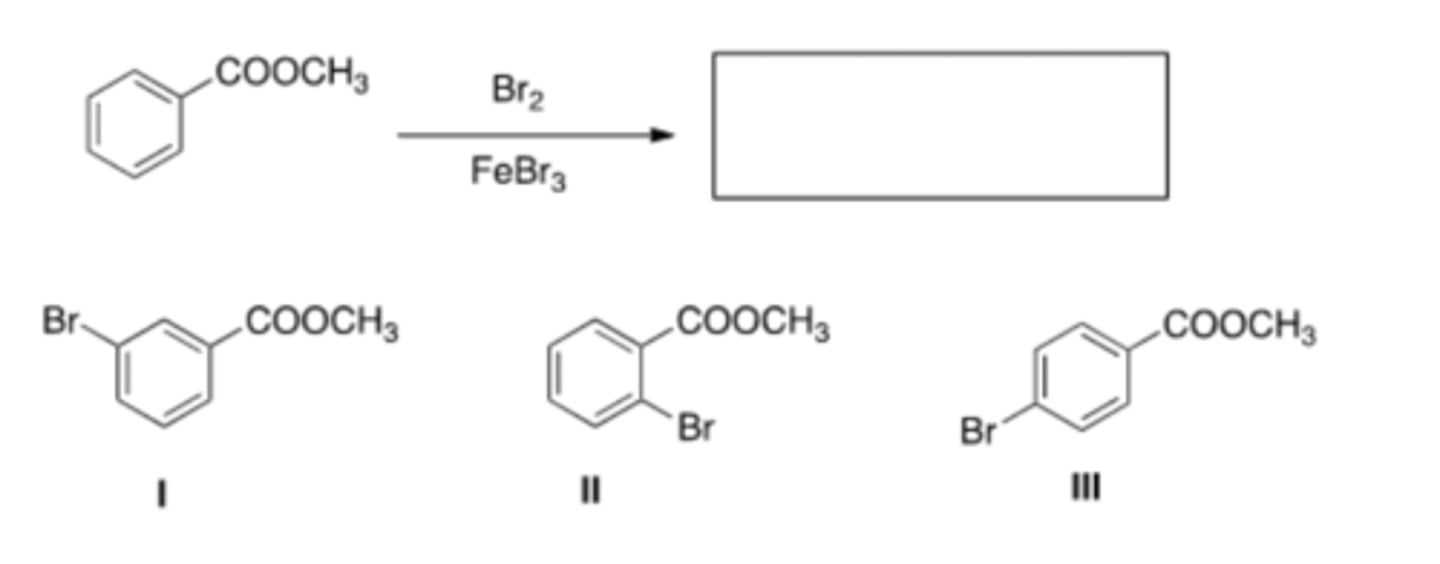
16) What is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction?
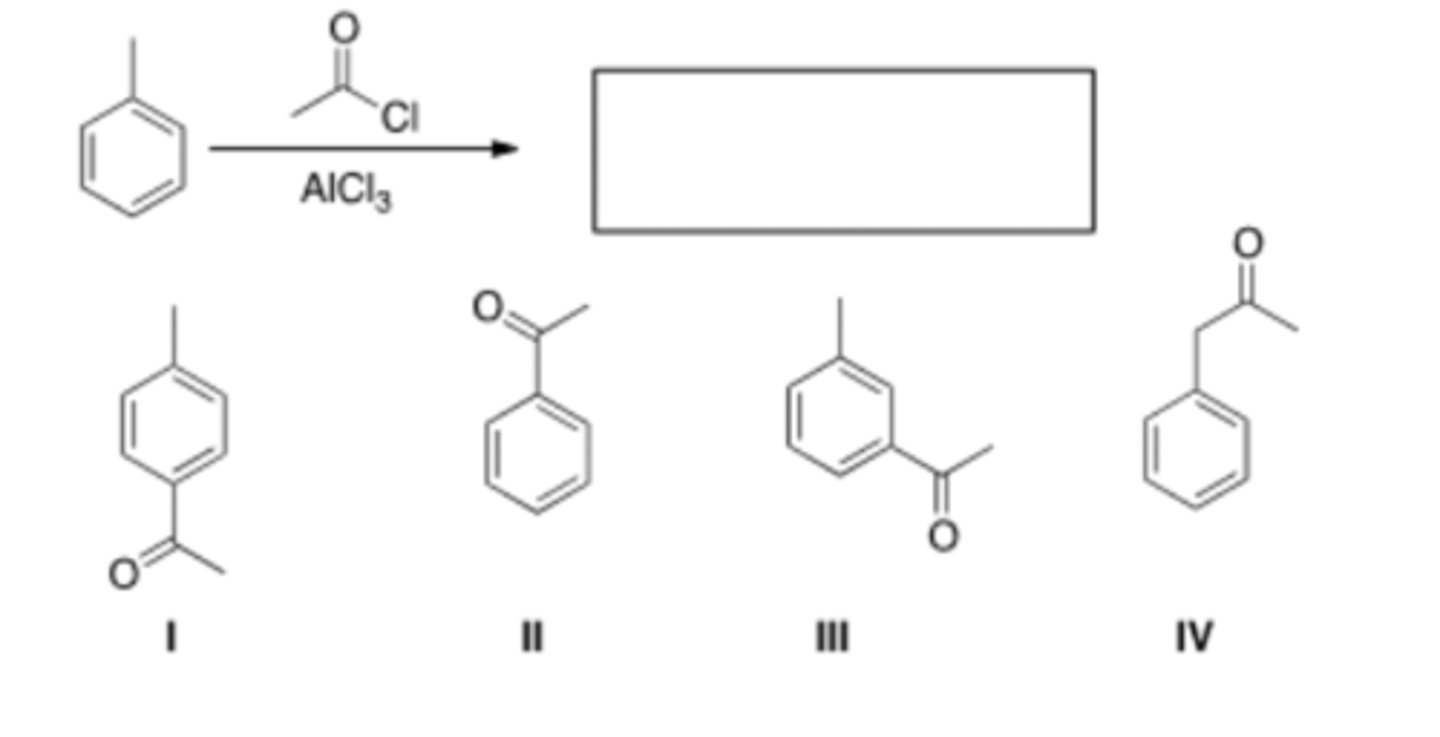
B) II
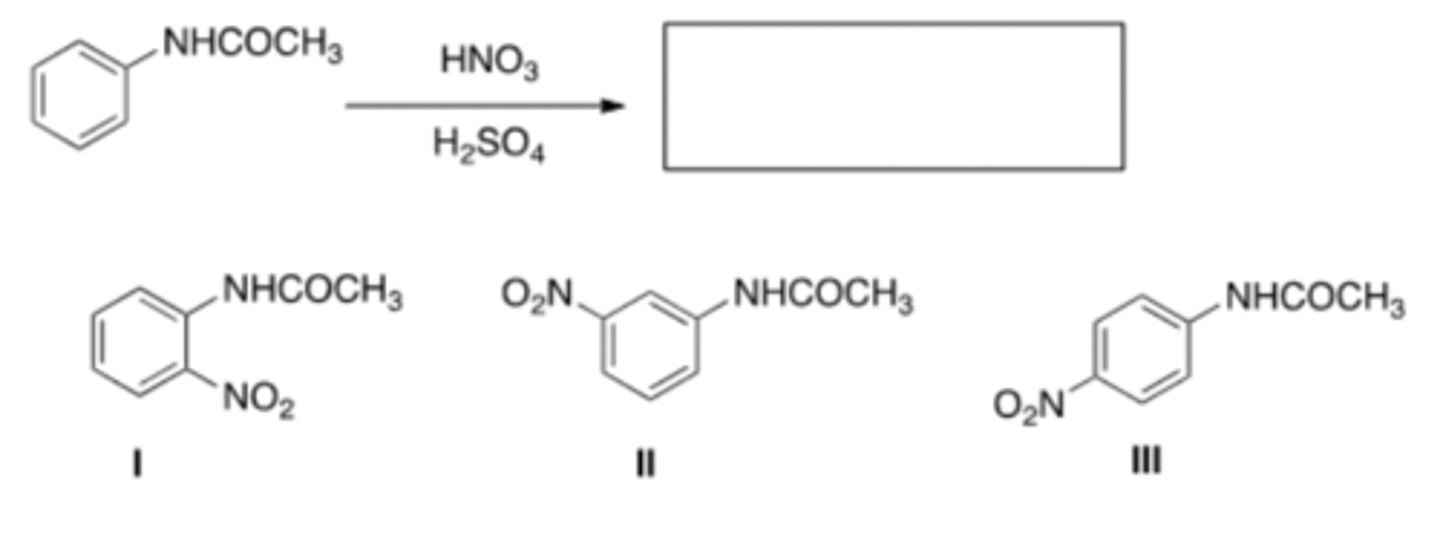
17) What is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction?
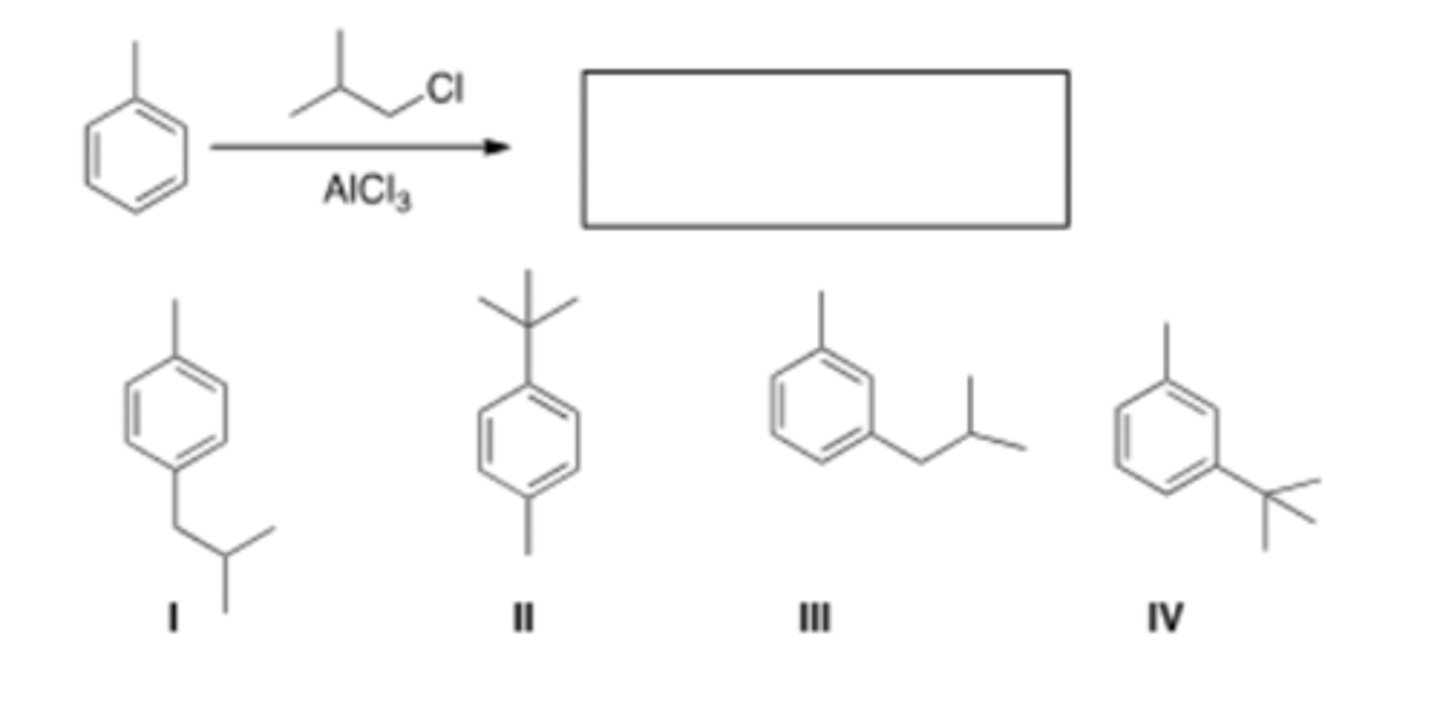
C) III
18) What is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction?
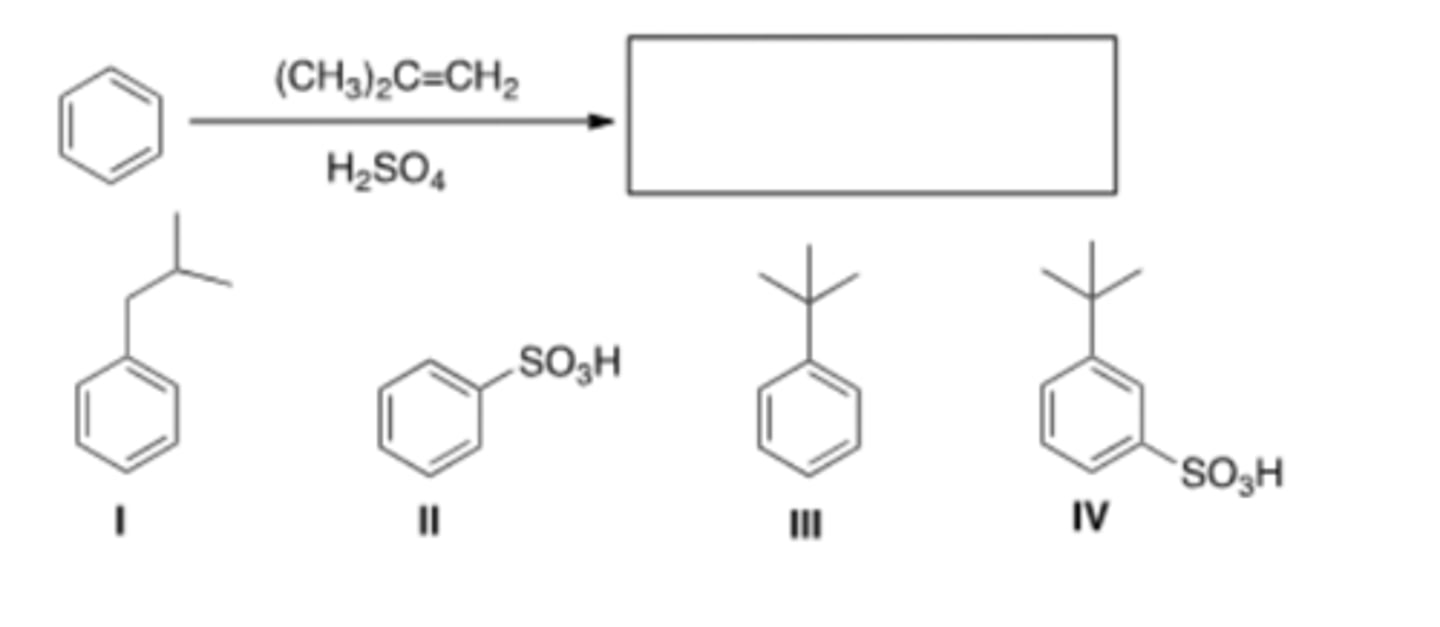
B) II
19) What is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction?
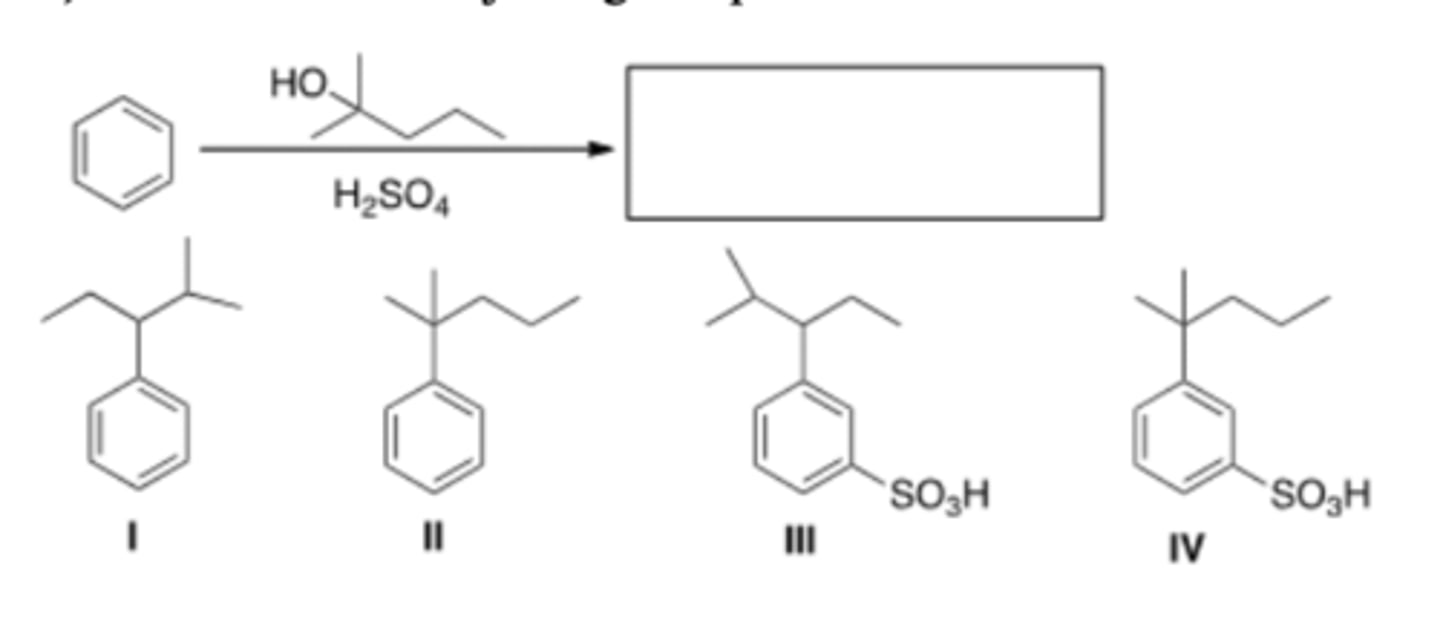
C) III
20) What is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction?
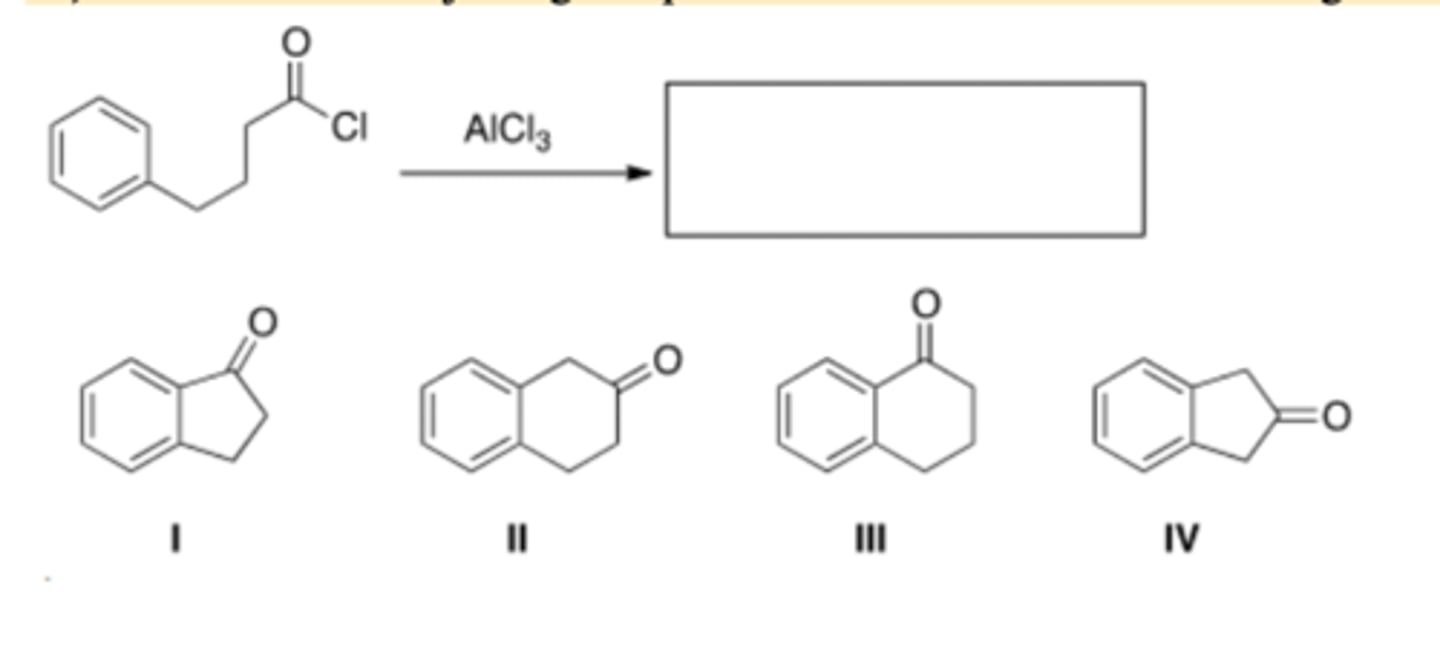
A) CH3O-
21) Which of the following substituents are activators in electrophilic aromatic substitution?
D) (CH3)3N-
22) Which of the following substituents are deactivators in electrophilic aromatic substitution?
C) -NHCOR
23) Which of the following substituents is an
D) -SO3H
24) Which of the following substituents is a meta director?
D) Only I and III
25) What is (are) the product(s) of the following reaction?
A) Only I
26) What is (are) the product(s) of the following reaction?
B) II < I < IV < III
27) Rank the following compounds in order of increasing reactivity in electrophilic aromatic substitution.

D) IV > I > II > III
28) Rank the following compounds in order of decreasing reactivity in electrophilic aromatic substitution.
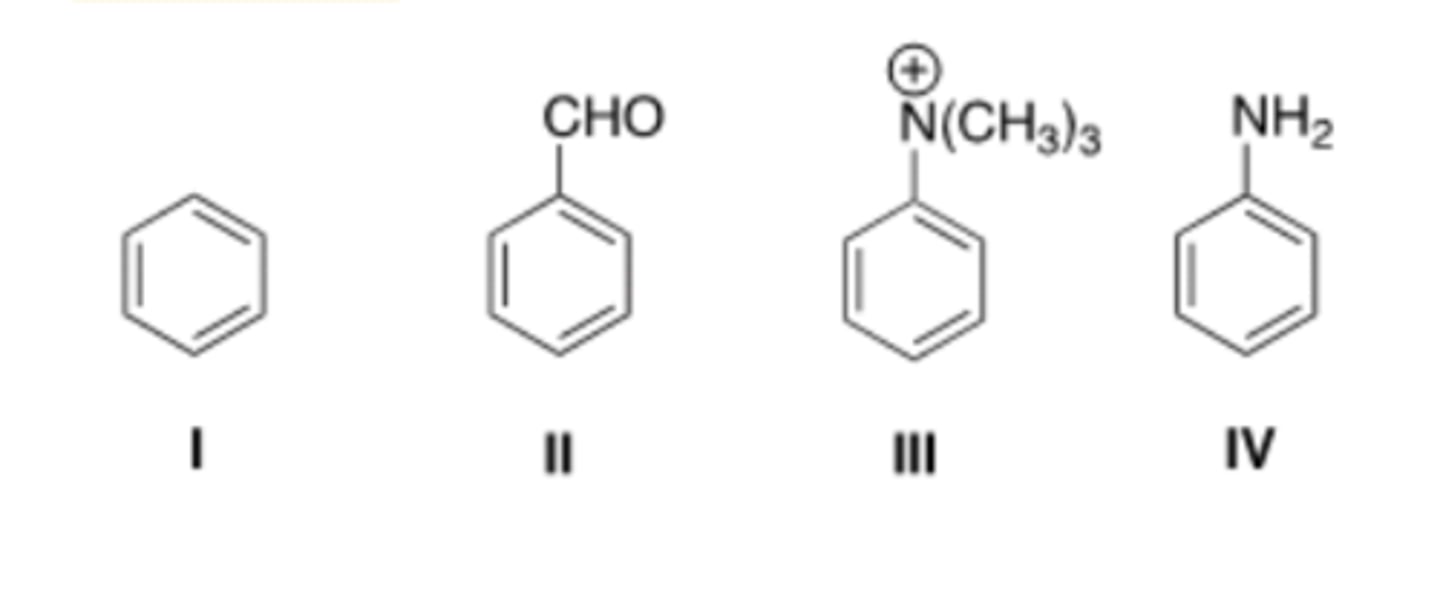
B) II > III > IV > I
29) Rank the following activating groups in order of decreasing strength of activation, listing the most activating first.

C) II < I < III < IV
30) Rank the following deactivating groups in order of increasing deactivating strength, listing the least deactivating first.
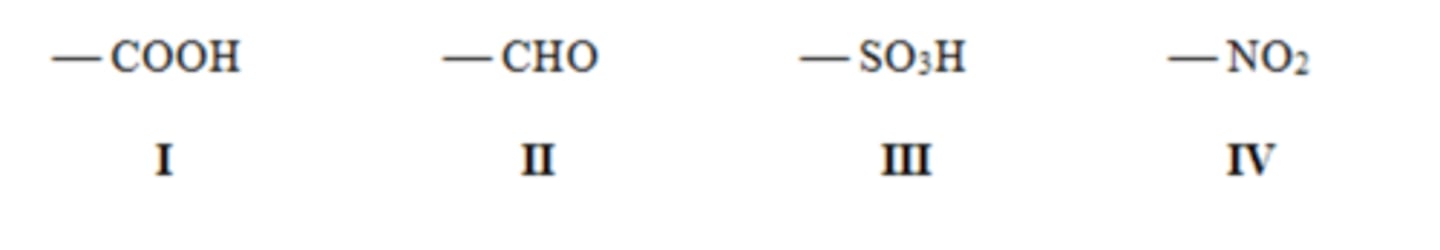
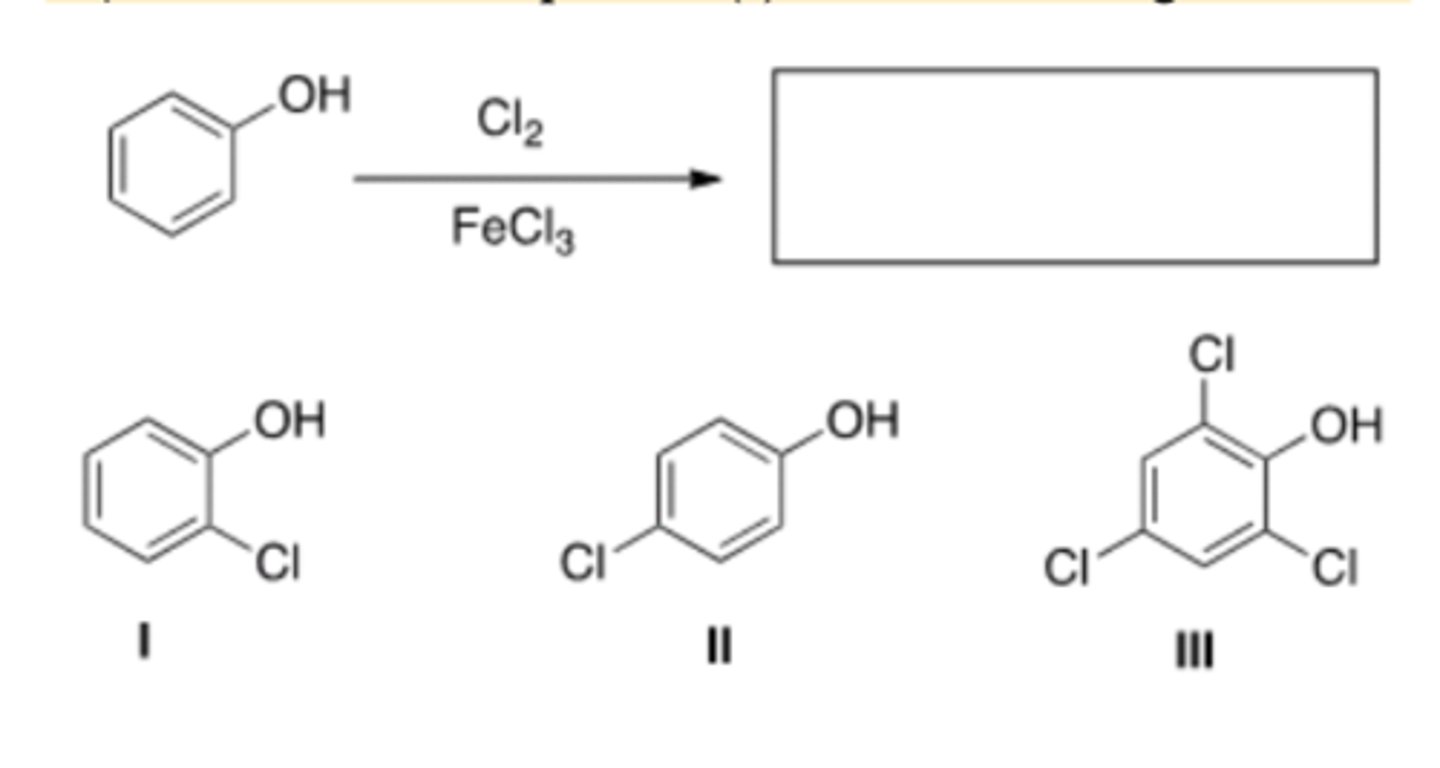
D) Only III
31) What are the product(s) of the following reaction?
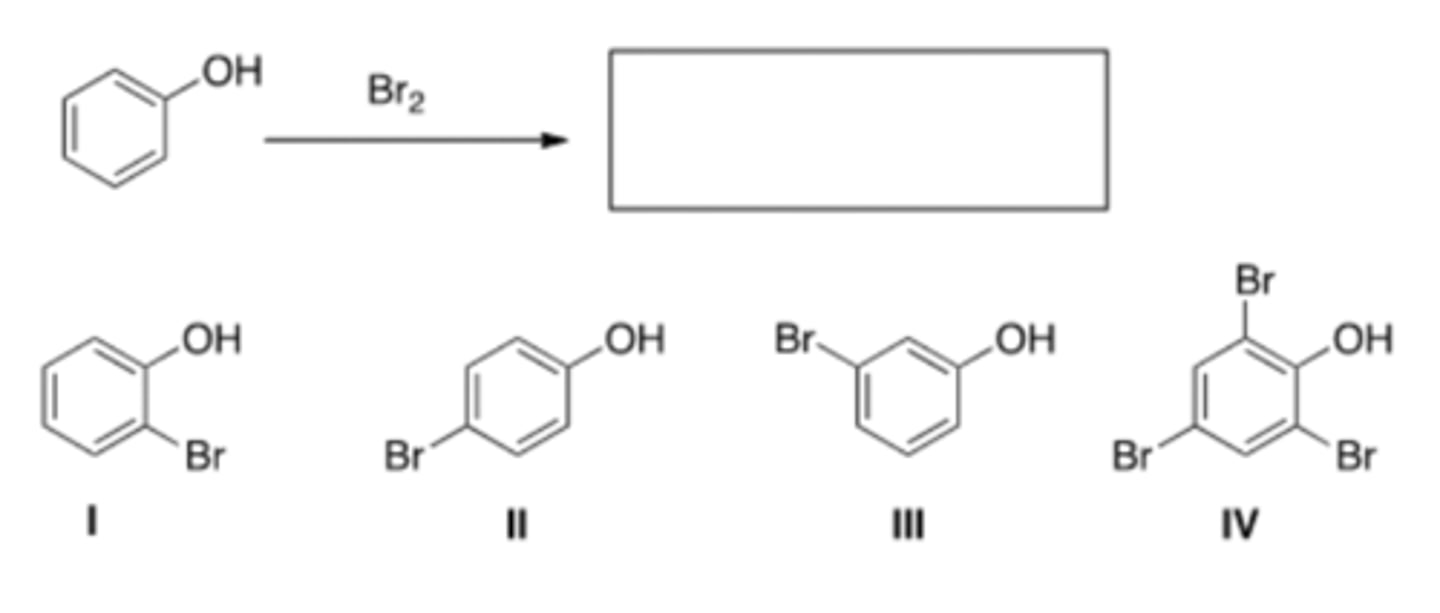
A) Only I and II
32) What are the product(s) of the following reaction?
B) Use a large excess of benzene relative to the alkyl halide.
33) How can polyalkylation be minimized in Friedel-Crafts alkylation?
A) I
34) What is the major product of the following reaction?
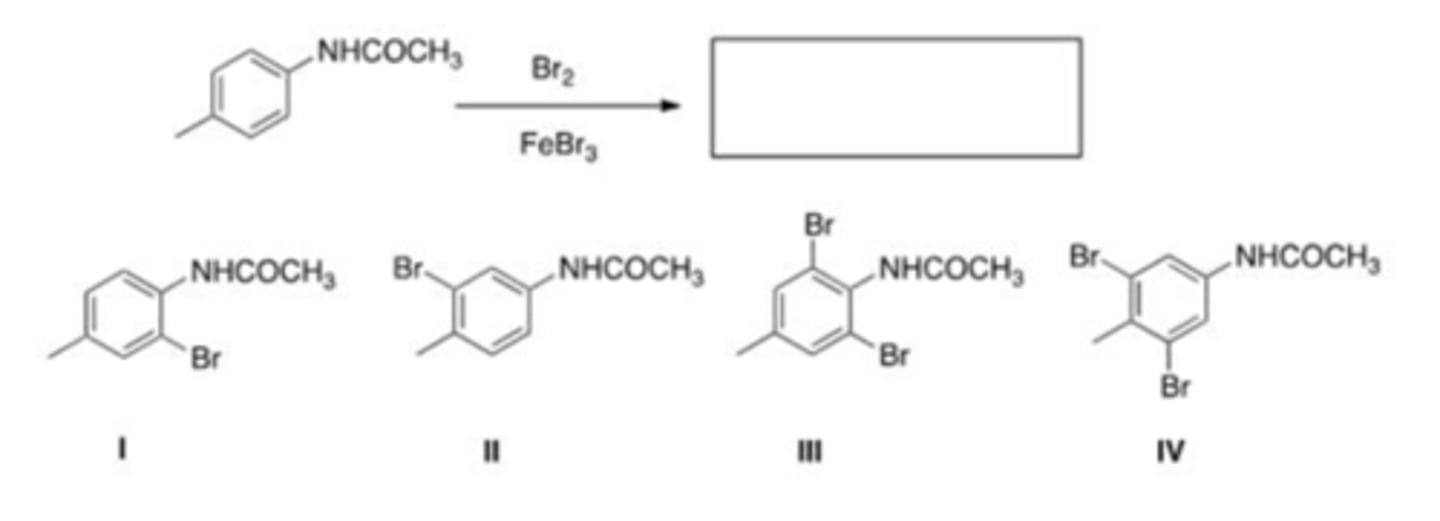
D) Only I and II
35) What is (are) the product(s) of the following reaction?
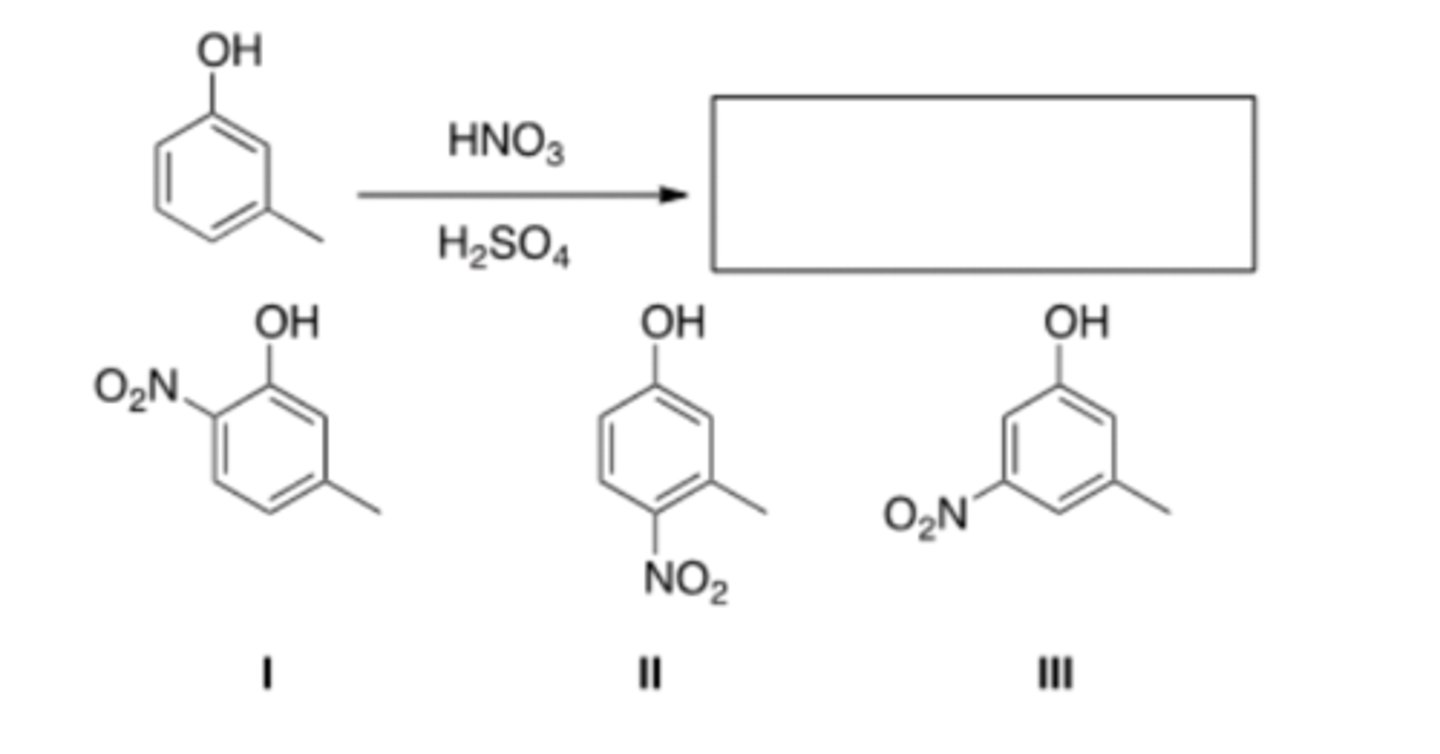
B) Addition-elimination and elimination-addition
36) What are the two distinct pathways for nucleophilic aromatic substitution?
D) Carbanion
37) What is the reactive intermediate formed in the addition-elimination mechanism of nucleophilic aromatic substitution?
C) Benzyne
38) What is the reactive intermediate formed in the elimination-addition mechanism of nucleophilic aromatic substitution?
D) When a nitro group is located meta to the halogen, the negative charge of the intermediate carbanion can be delocalized onto the NO2 group, thus stabilizing it.
39) Which of the following statements about nucleophilic aromatic substitution is not true?
C) The elimination-addition mechanism is not as common as the addition-elimination mechanism.
40) Which of the following statements about nucleophilic aromatic substitution is true?
B) I
41) Rank the following compounds in order of increasing reactivity in nucleophilic aromatic substitution.
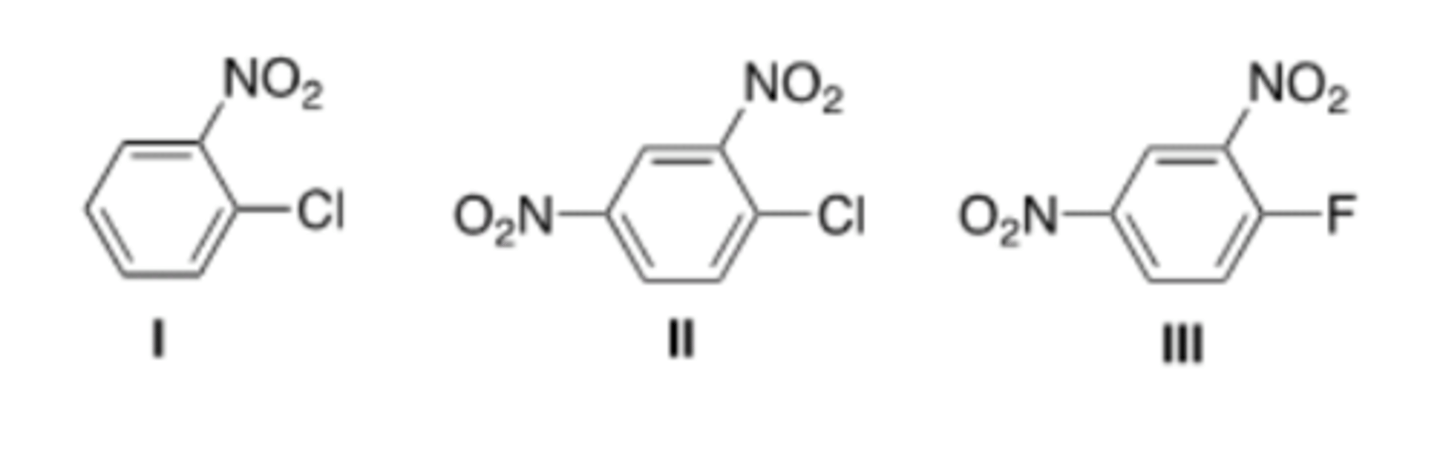
D) IV
42) What is the major product of the following reaction?
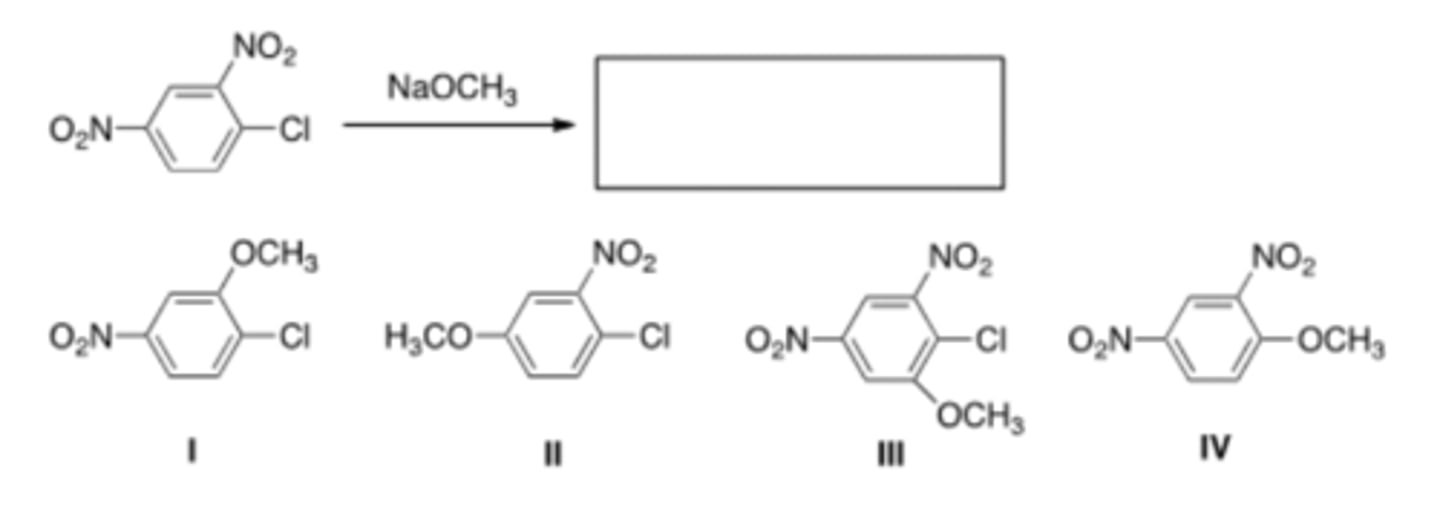
C) III
43) Which aryl fluoride reacts the fastest with NaOH?
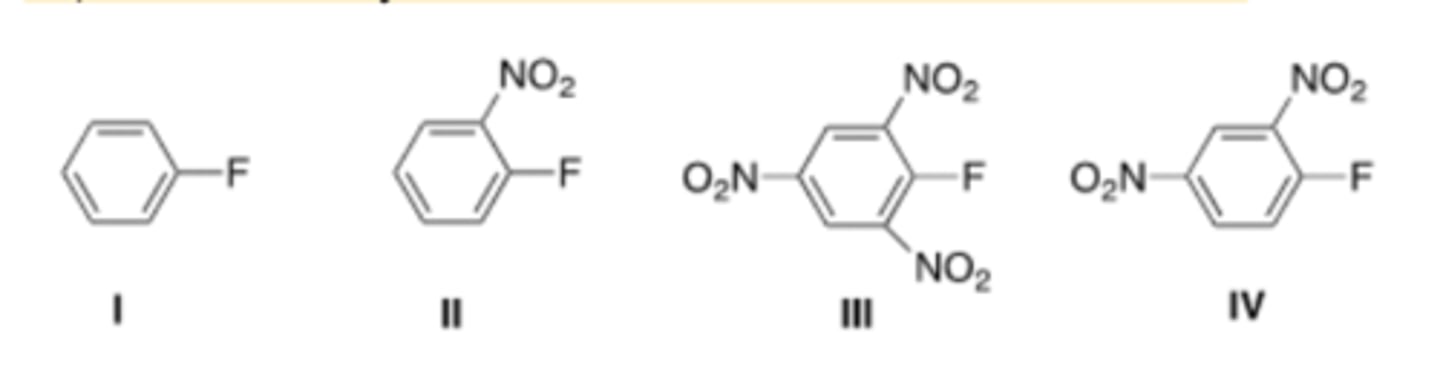
D) IV
44) In addition to the product shown, what other product is formed in the following reaction?
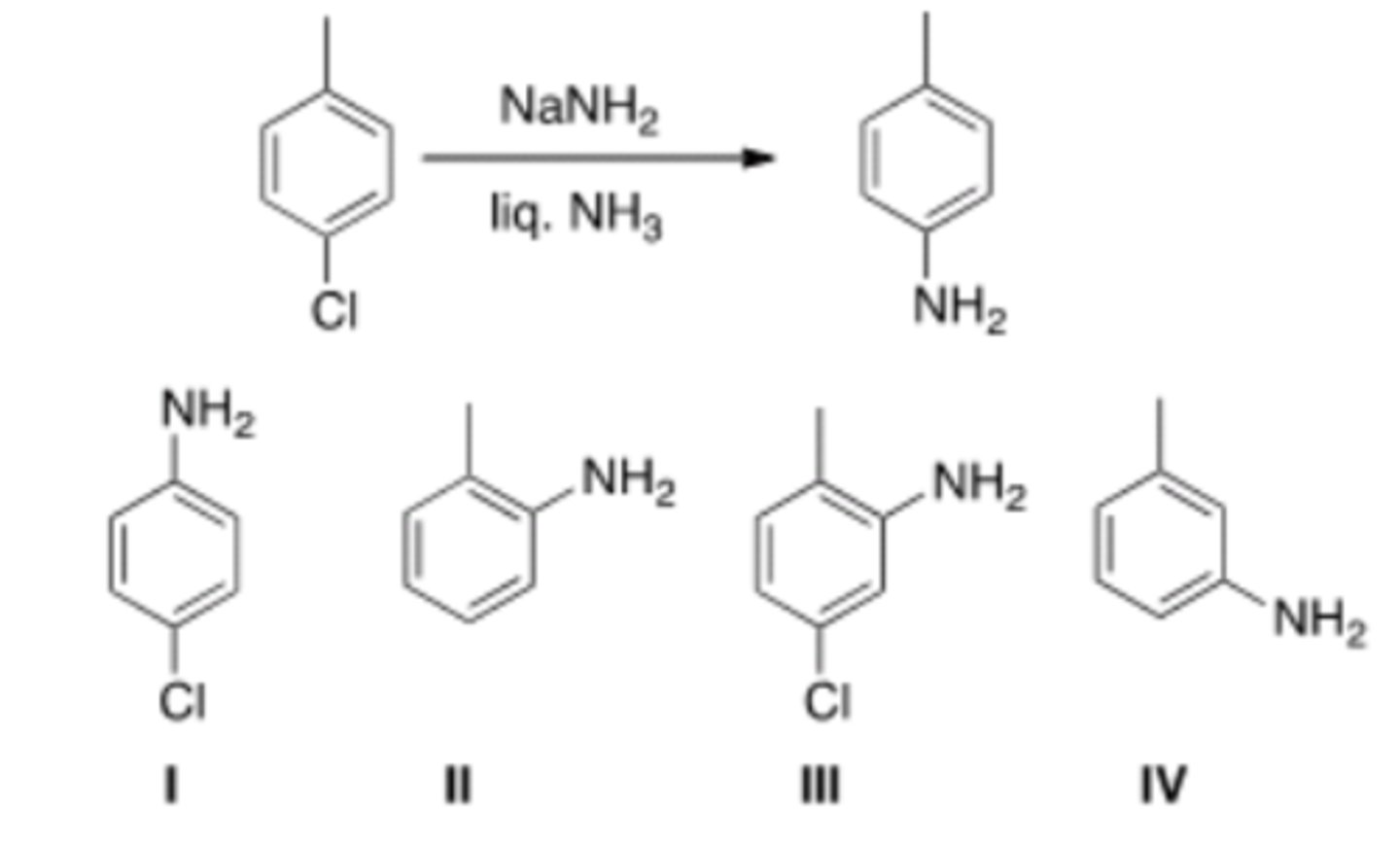
B) NBS and light
45) Which set of reagents would most likely bring about the following transformation?
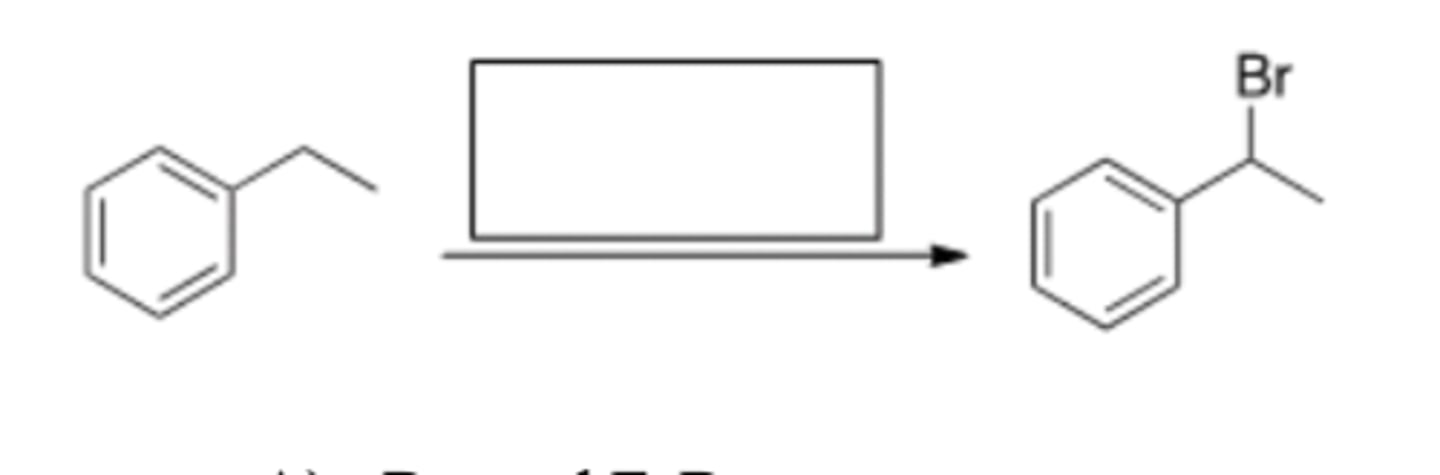
D) IV
46) What is the product of the following sequence of reactions?
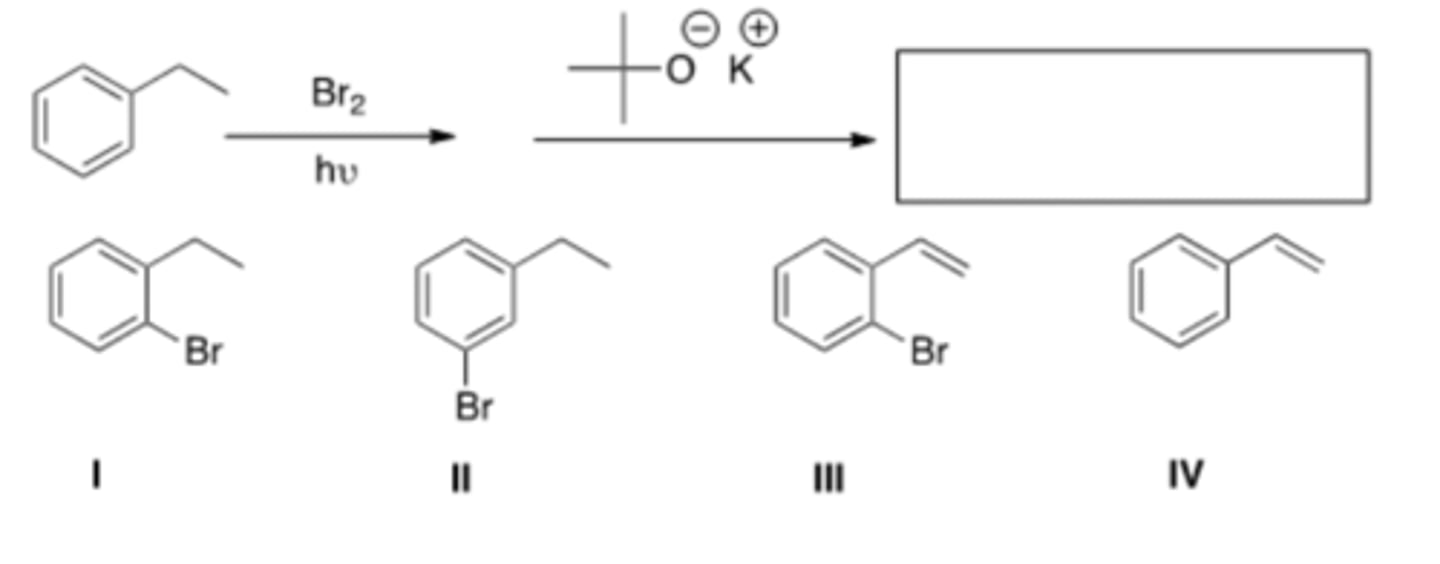
A) I
47) What is the product of the following reaction?
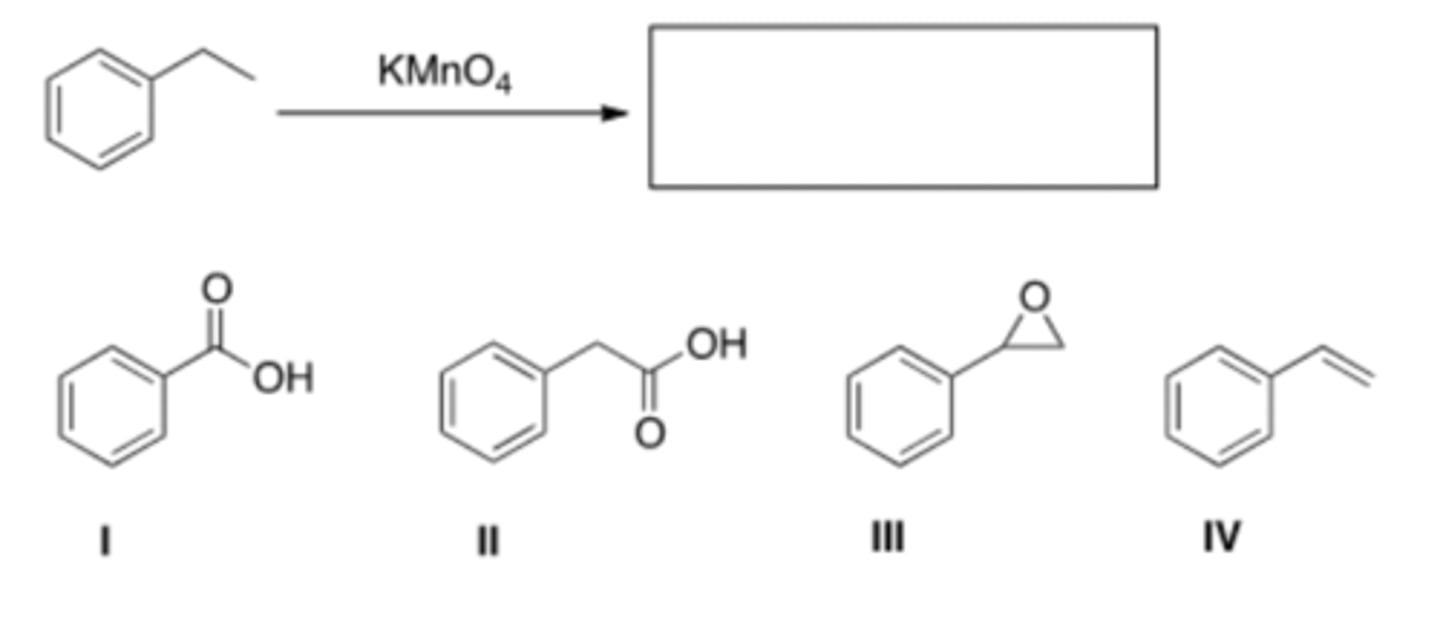
D) None of these
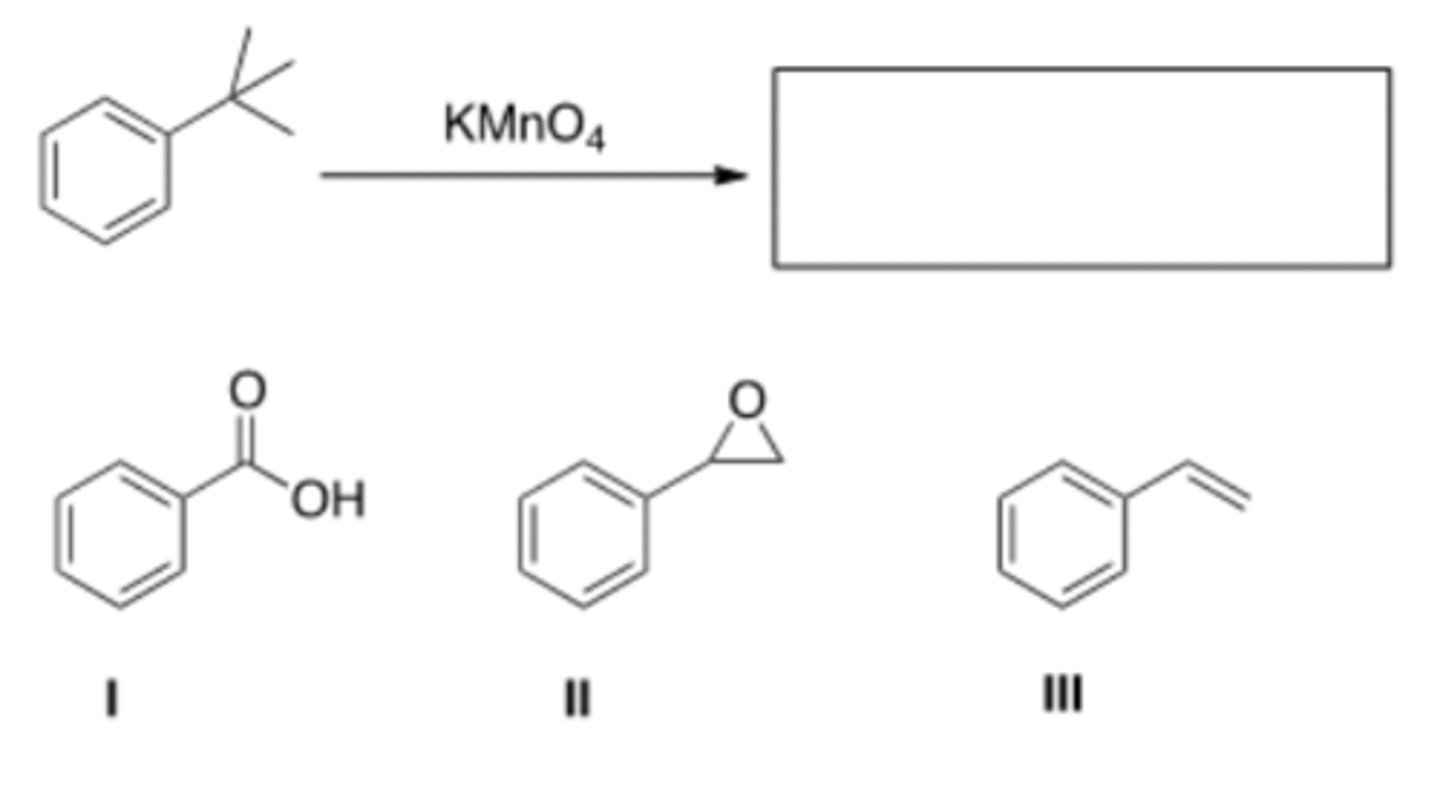
48) What is the product of the following reaction?
B) Zn (Hg), HCl
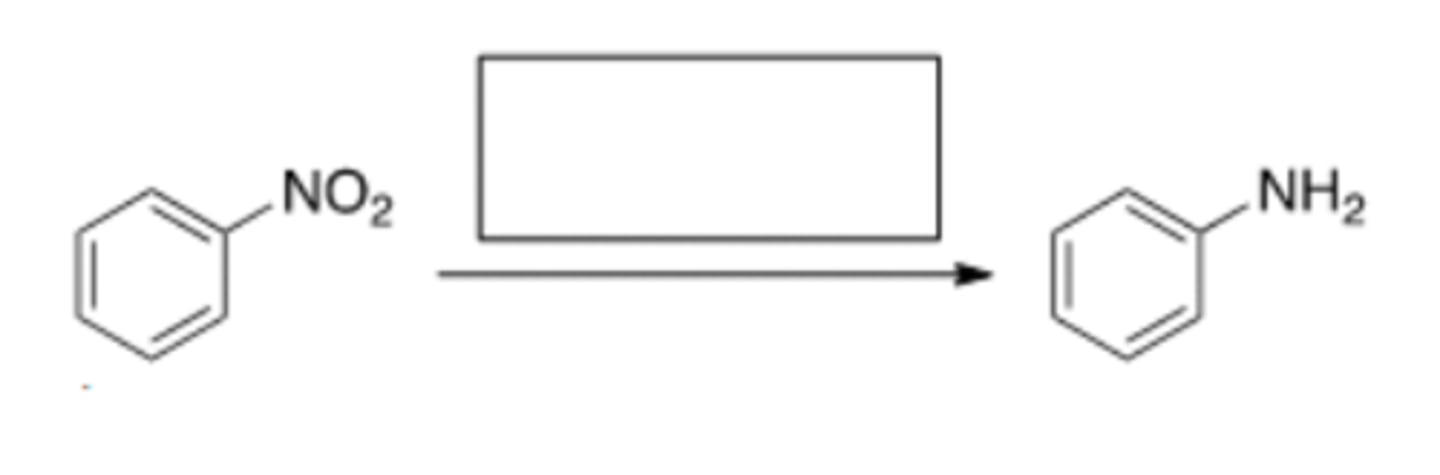
49) What is the best choice of reagent to bring about the following transformation?
D) H 2, Pd-C
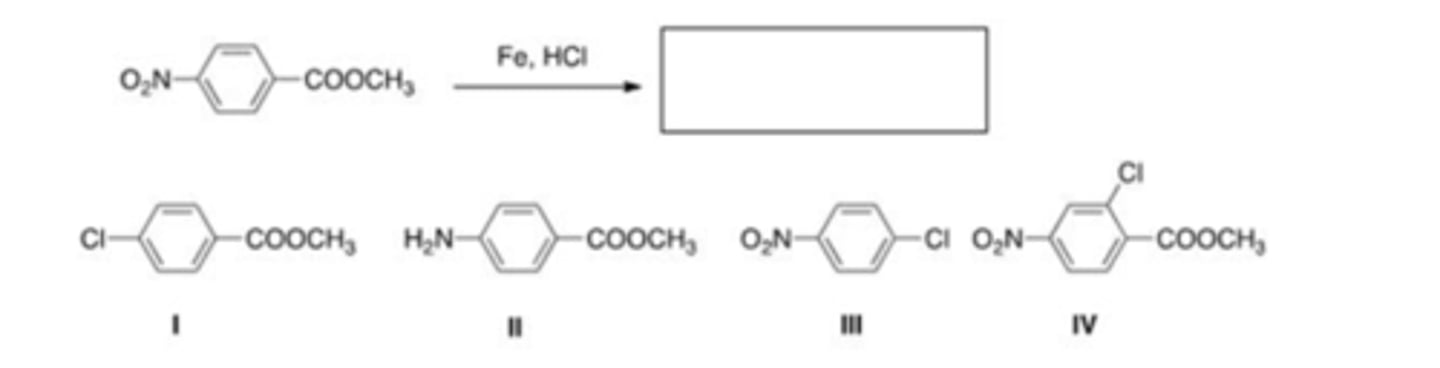
50) What is the best choice of reagent to bring about the following transformation?
B) II
51) What is the product of the following reaction?
B) II
52) What is the major product of electrophilic addition of HBr to the following alkene?
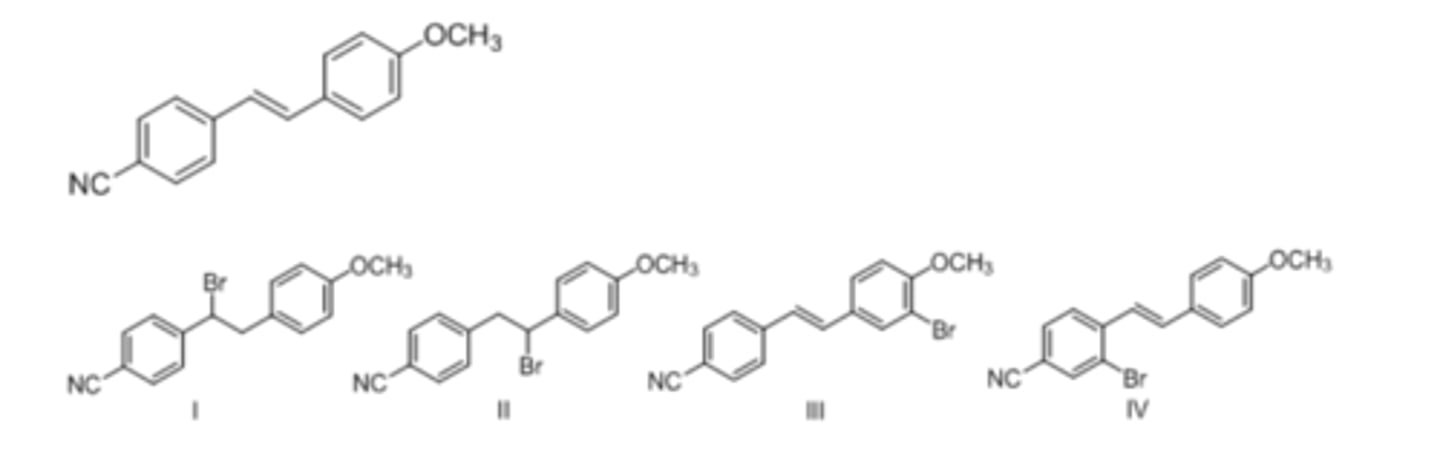
B) II
53) Consider the tetracyclic aromatic compound drawn below, with rings labelled as I, II, III, and IV. Which of the four rings is most reactive in electrophilic aromatic substitution?
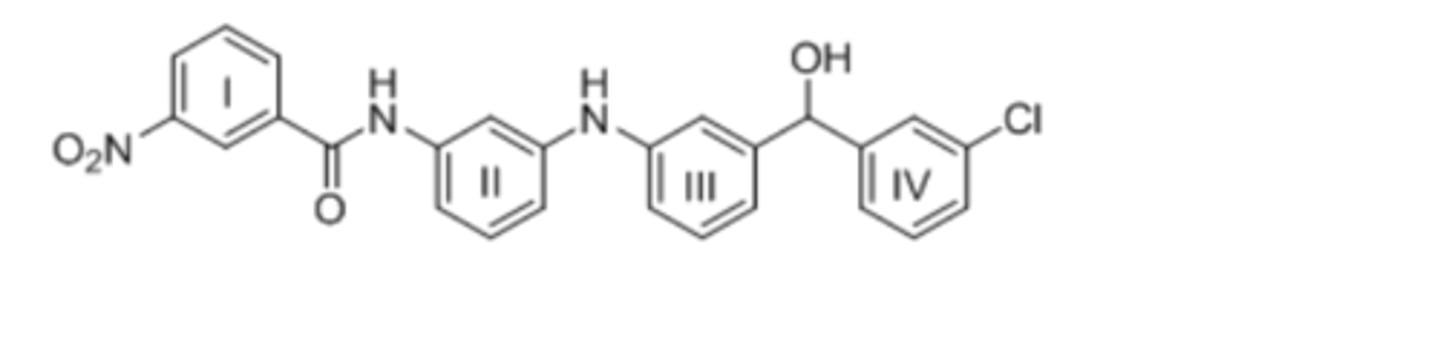
A) I
54) Consider the tetracyclic aromatic compound drawn below, with rings labelled as I, II, III, and IV. Which of the four rings is least reactive in electrophilic aromatic substitution?
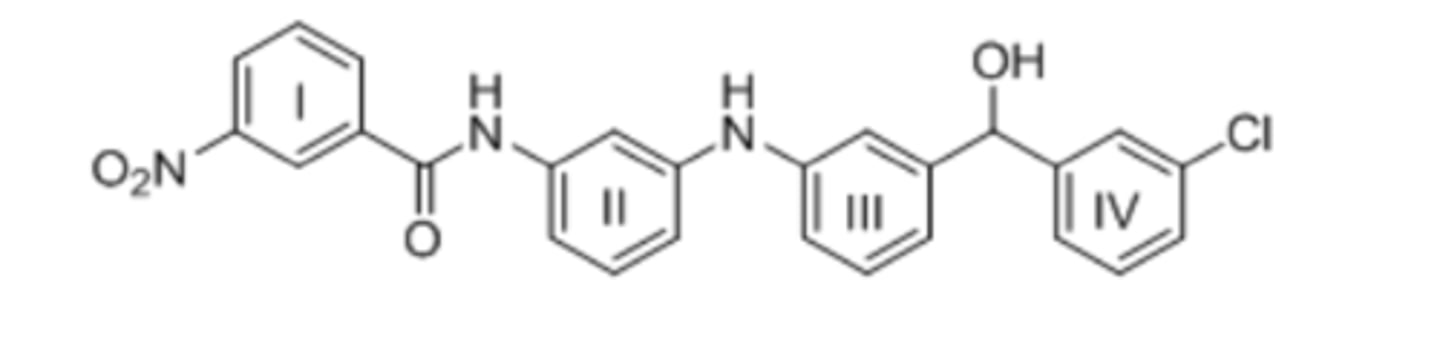
B) Only II
56) What is the product of the following monobromonation reaction?
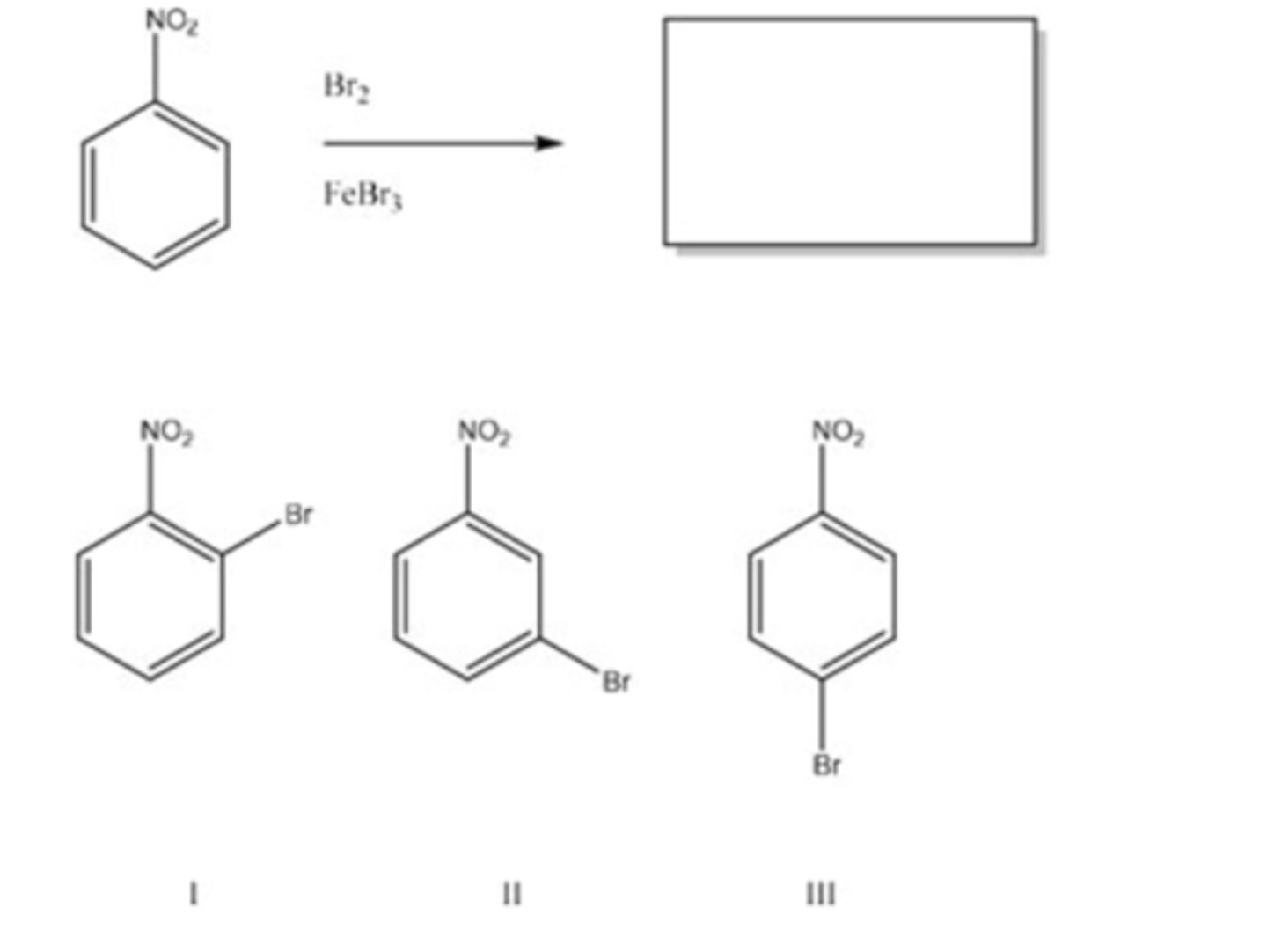
C) III
57) What is the major organic product of the following reaction?
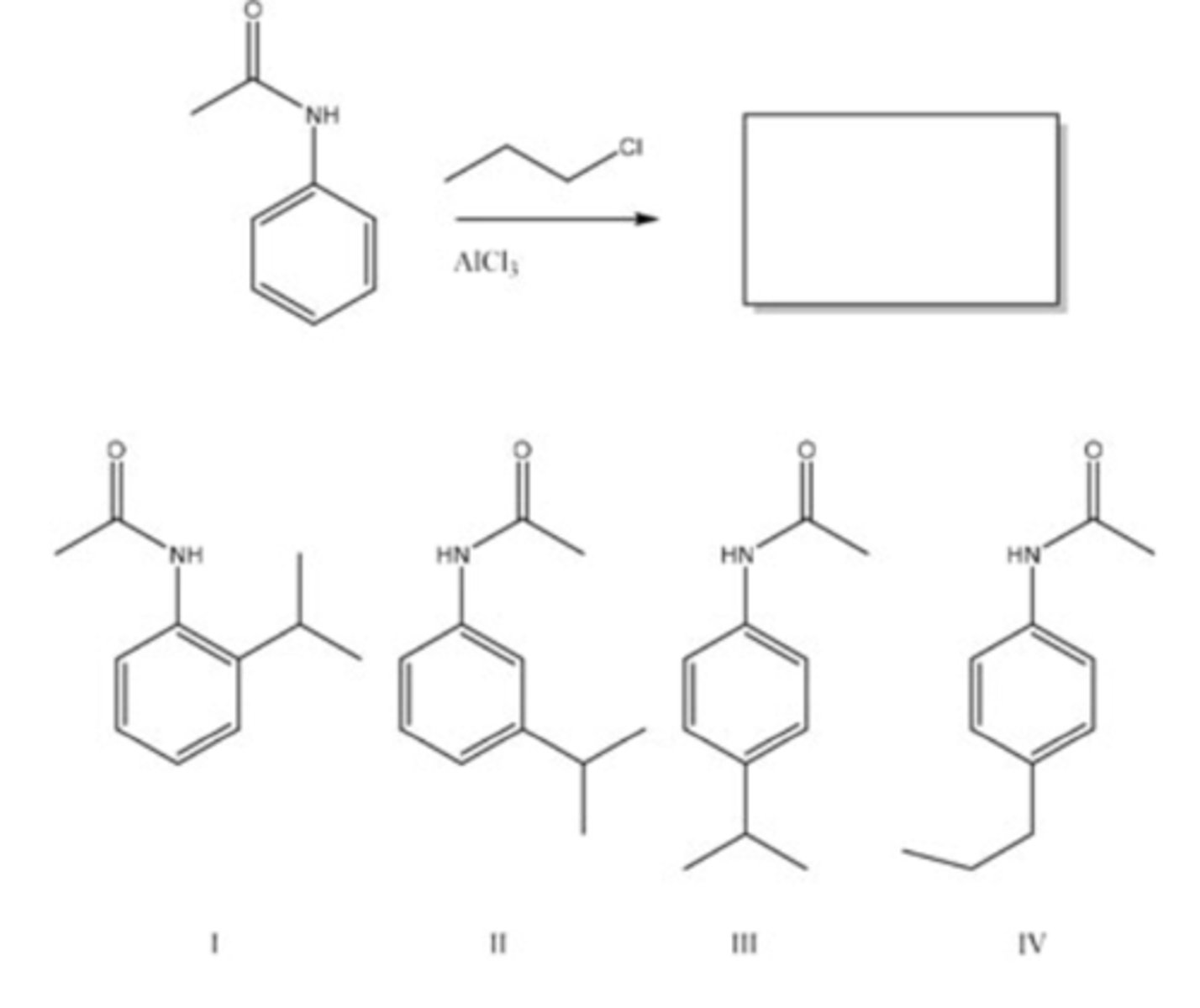
C) III
58) What is the major organic product of the following reaction?
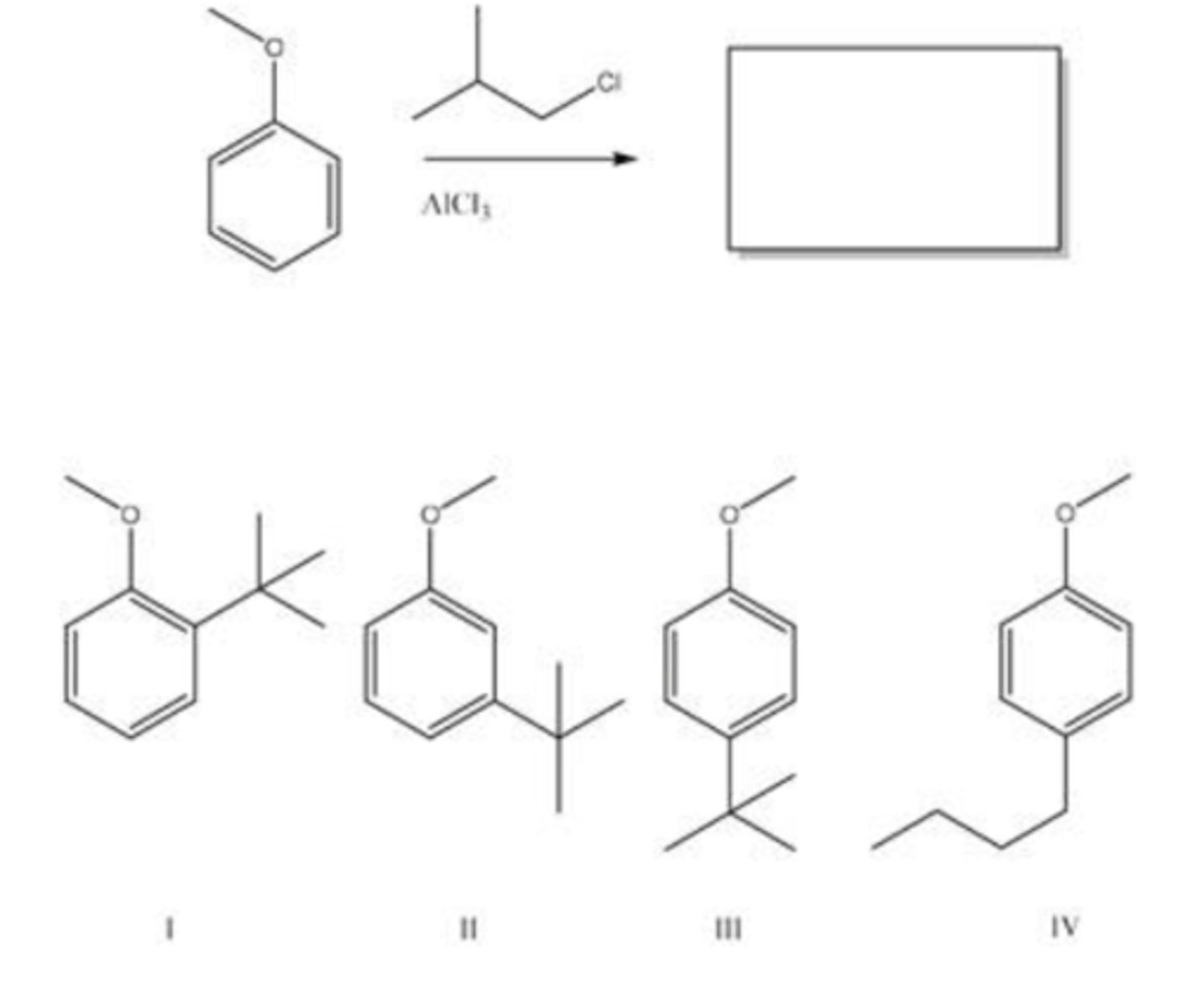
A) CH3Cl, AlCl3 2. HNO3, H2SO4 3. KMnO4
59) What reagents would be necessary to produce the following product from benzene?
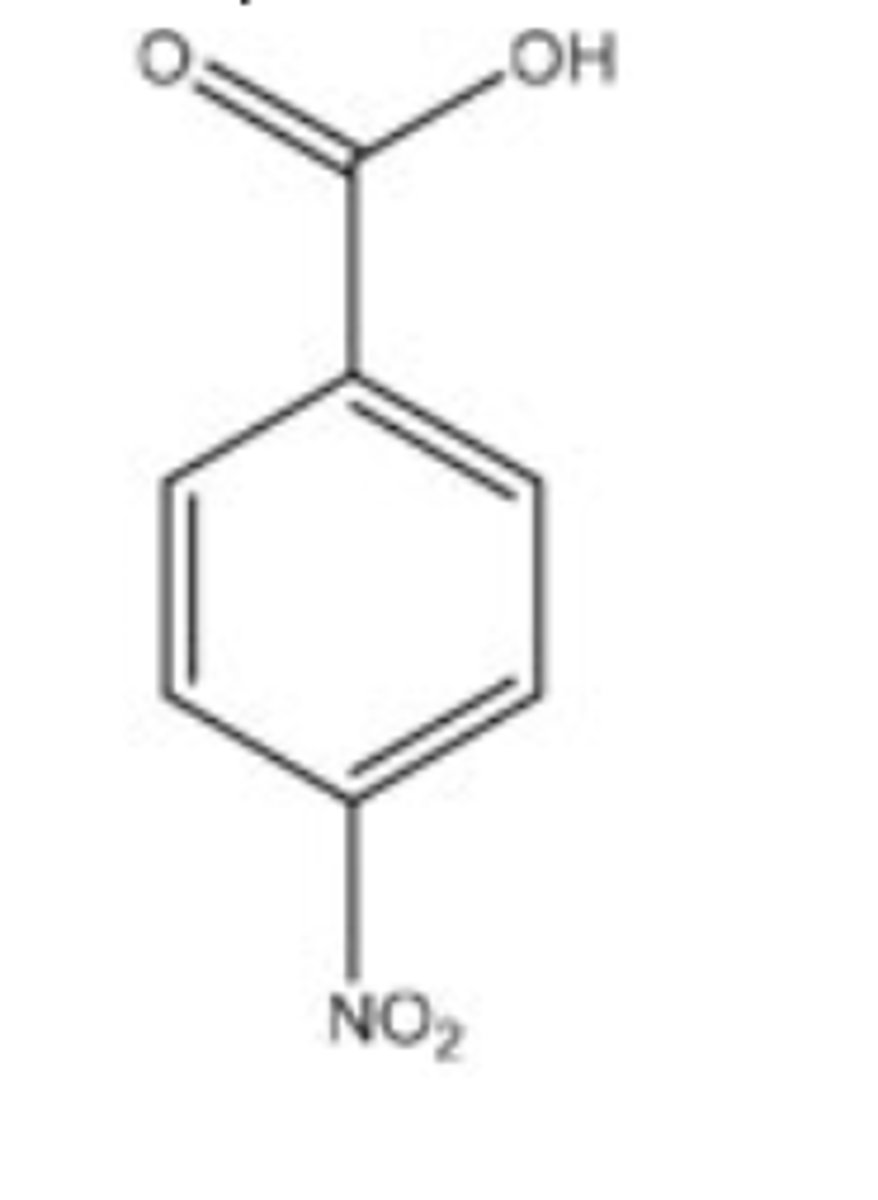
A) CH3CH2C(O)Cl, AlCl3 2. HNO3, H2SO4 3. Zn(Hg), HCl
60) What reagents would be necessary to produce the following product from benzene?