Measurements & Significant Figures
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Measurement Accuracy and Precision Significant Figures Significant figures in calculations Unit Conversions
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
standard
an unchanging body of each unit to serve as a primary reference
international system or si system
uses a different unit for each quantity
two types of SI units: fundamental and
derived
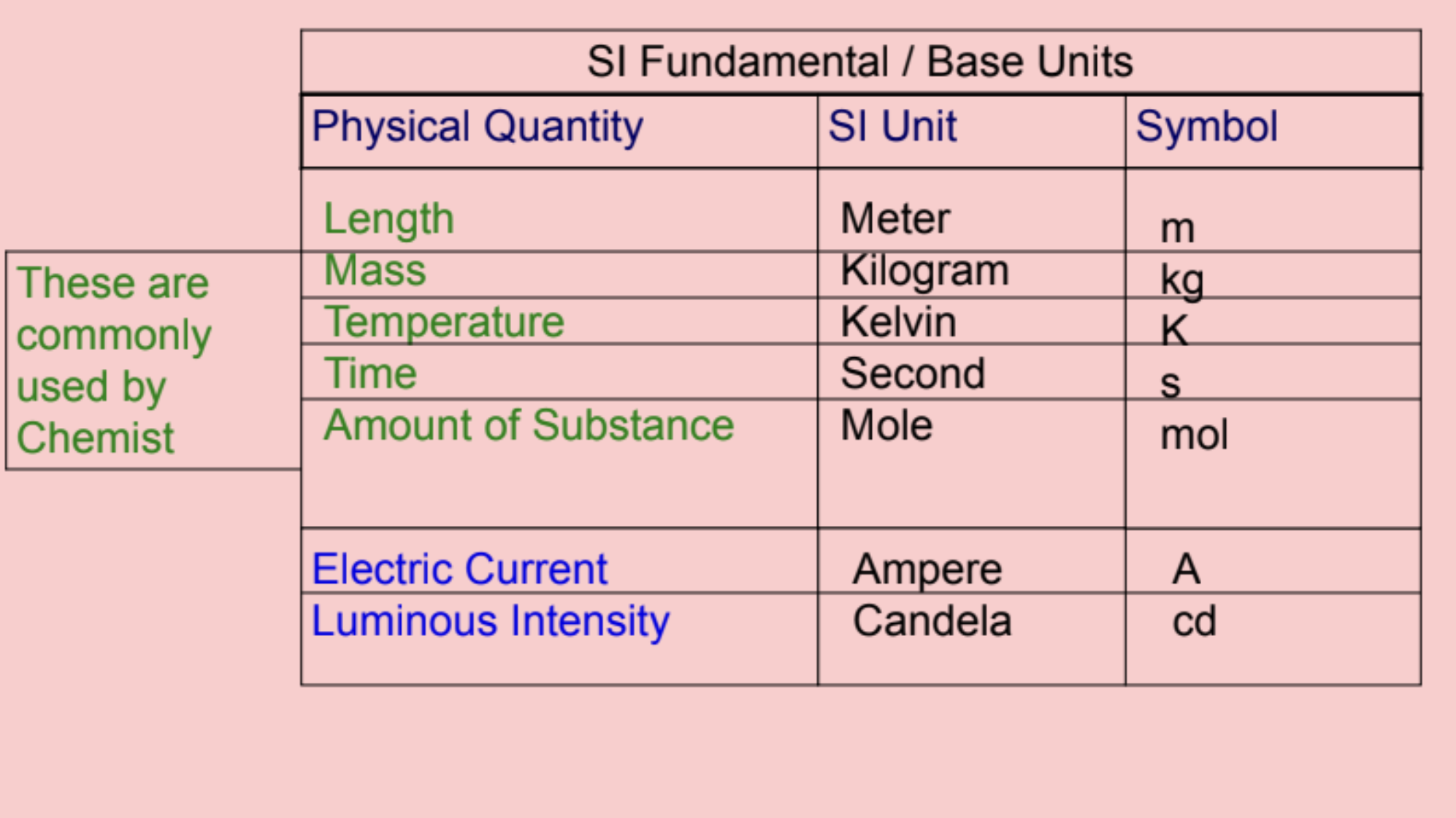
length
meter
(m)
mass
kilogram
(kg)
temperature
kelvin
(K)
time
second
(s)
amount of substance
mole
(mol)
electric current
ampere
(A)
luminous intensity
candela
(cd)
derived s.i. units
are composed of 2 or more base units
e.g) volume
• The volume of a regular-shaped solid can be found by using the volume formula of the shape
L x W x H
dimensional analysis steps
identify the given value: write down the quantity you are given, including its unit.
identify the desired unit: determine the unit you want to convert to
find conversion factors: Locate the relationship between the given unit and the desired unit
set up the conversion:
write the given value as a fraction (put it over 1 if it's a single number)
set up a conversion factor as a fraction with the unit you want to cancel in the denominator and the unit you want in the numerator
if needed, continue to add more conversion factors to complete the chain of conversions
cancel units: cross out units that appear in both the numerator and the denominator
perform the calculation: multiply the numbers in the numerator and divide by the numbers in the denominator
final answer: the remaining unit should be the desired unit, and the calculated number is your final answer
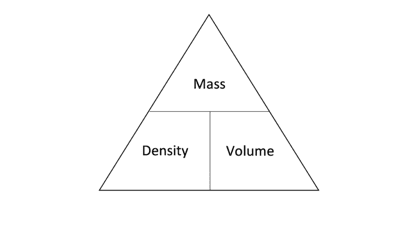
density
mass/volume
units raised to a power rule
raise both the number and the unit to the power
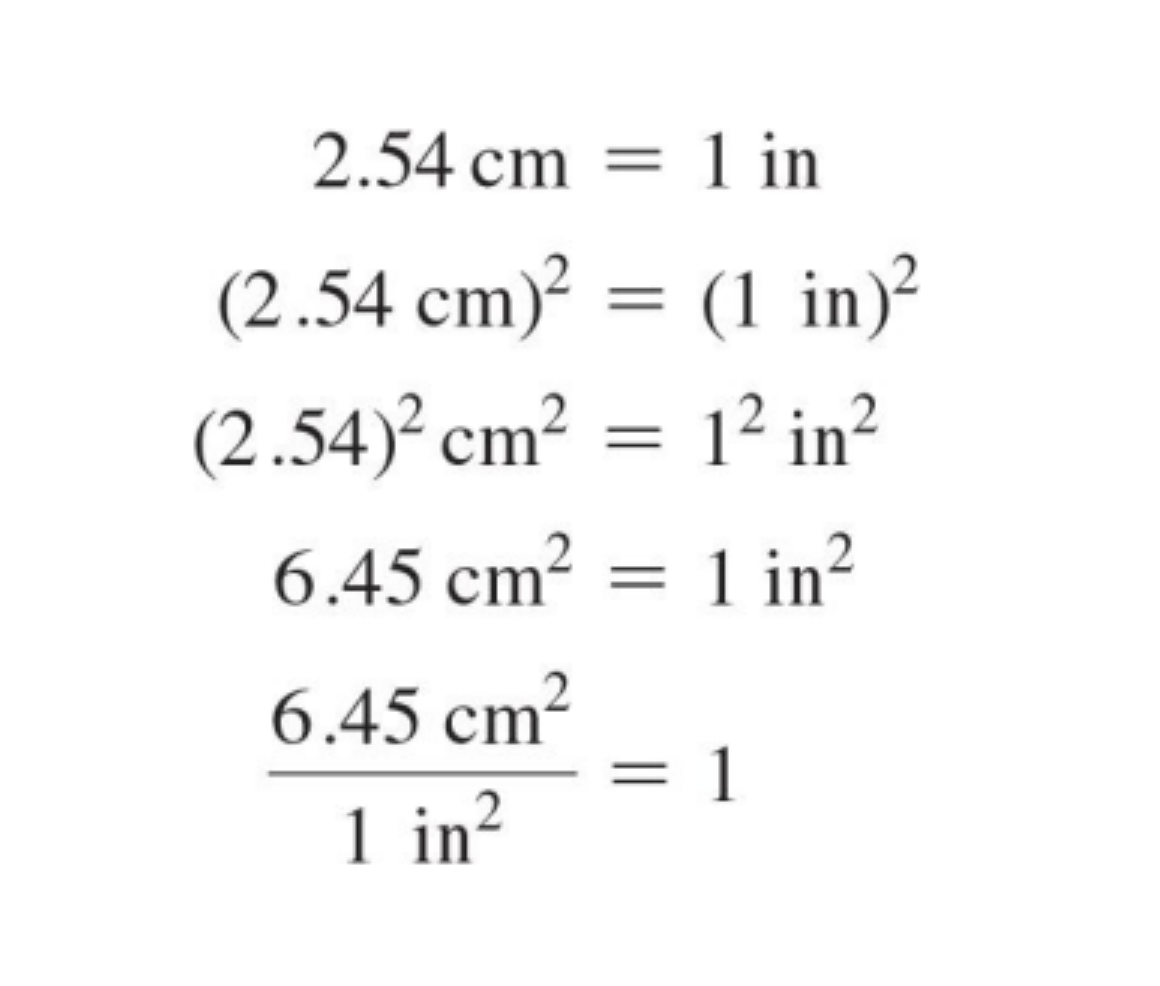
scientific notation
all scientific notation is based around a number multiplied by a power of ten
e.g) 0.000072 is 7.2 × 10⁻⁶
precision
refers to the degree of uncertainty in a measurement
is the ability of a measurement to be consistently reproduced
standard deviation is calculated to evaluate the precision of data
accuracy
accuracy refers to the proximity of a measurement to the true value of a quantity
percent error is calculated to evaluate the extent of deviation
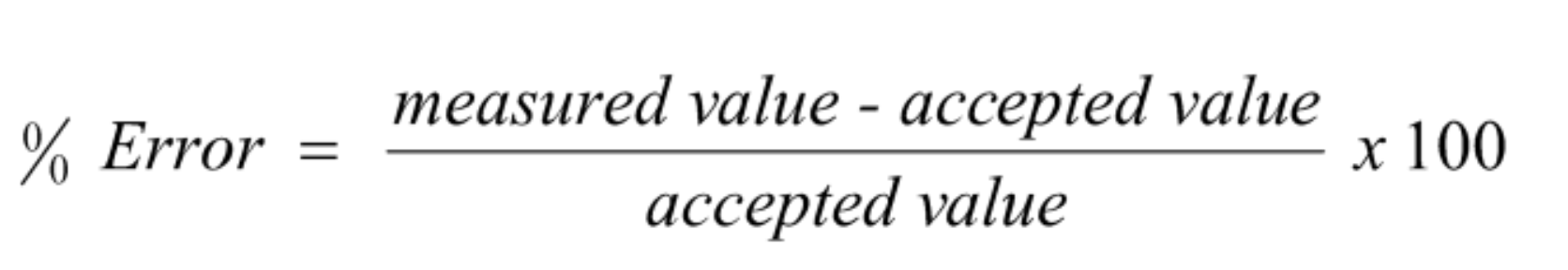
certain digits
values that are marked on the measuring device
uncertain digit
the last digit which is always estimated
significant figures
the number of digits used to express a measured or calculated quantity
significant figures rules
non-zero digits count (123 → 3 sig figs)
zeros between non-zeros count (101 → 3 sig figs)
leading zeros don’t count (0.004 → 1 sig fig)
trailing zeros count if decimal shown (12.00 → 4 sig figs)
Multiplication/division → round to least sig figs
Addition/subtraction → round to least precise decimal places
e.g) 12.11 + 18.0 = 30.1 (1 decimal place)
exact numbers
are assumed to have an infinite number of significant figures
e.g)
Counted quantities: quantities not measured
Defined numbers: a dozen = 12.00000000...
how does conversion between units affect number of significant figures?
converting units doesn’t change the certainty/uncertainty of the measurement → doesn’t change the number of significant figures