Lecture 22 - Dispersal, Metapopulations And Island Biogeography
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
True Or False: Real populations are closed systems
False, they’re not
Definition Of Dispersal
Individuals that can move from one population to another
3 Benefits Of Dispersal
Colonize New Areas
Escape Competition
Avoid Inbreeding
Post Glacial Colonization Depends On Plant & Animal _______
Dispersal
Definition: Metapopulation
Spacially separated populations connected by dispersal
True Or False: Metapopulations can survive even when individual populations are failing
True
What makes individual unstable groups globally stable?
Dispersal: individuals moving from patch to patch
How is patch dynamics different from population dynamics?
Patch dynamics track patch occupancy through time instead of an individual population
What is the constate rate e?
rate of extinction in a patch population
What is the constant P?
# of occupied patches
What does the expression 1-p refer to?
Fraction of empty patches
What is the constant c?
Colonization constant
What is the colonization rate expression?
cP(1-P)
What is the value of dP/dt @ equilibrium?
0
Say A always outcompetes B within a patch, what is required for global coexistence? (4 things)
A occasionally goes extinct OR new patches are created
B must be a better disperser than A
B must be a good colonizer
A= better competitor, B= better colonizer (tradeoff)
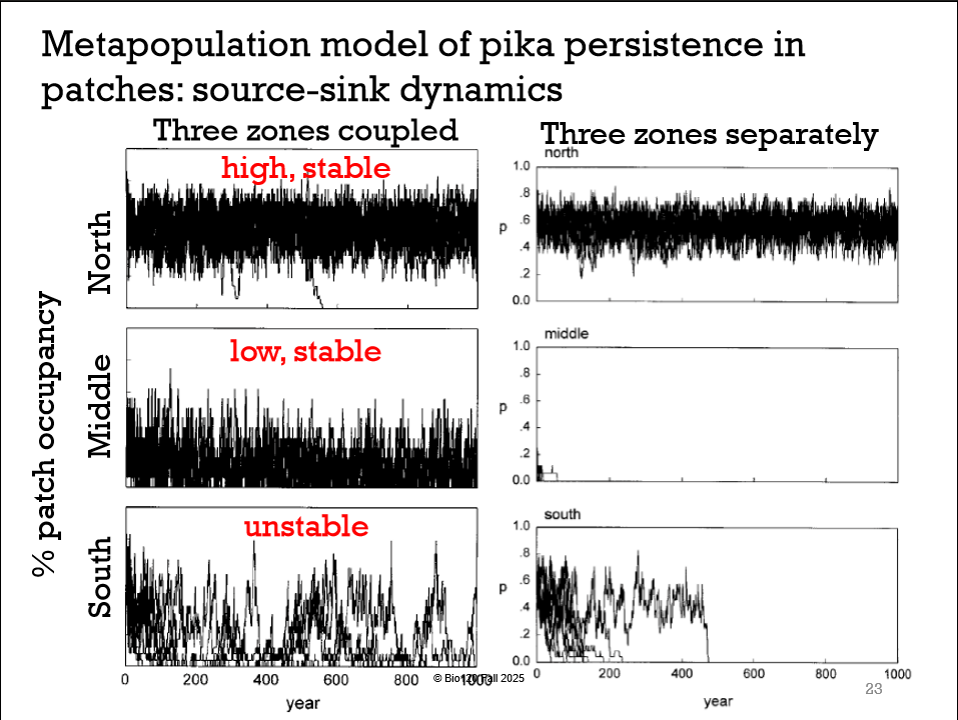
Explain the example of pikas being a metapopulation
Pika habitats are isolated but when they become vacant other pikas can relocate there (disperse)
That is what keeps the global population of pikas afloat.
Name 4 ways populations can be driven to extinction
Stochasticity: random fluctuations in population numbers
competitive exclusion
Predators/ parasites
extinction because of a very small population size
How Does Coexistence Keep Populations From Going Extinct?
Predation keeps dominant competitors from completely dominating
Non equilibrial conditions: patchy habits, migration, competition colonization trade off
Metapopulation Vs. Metacommunity
population -
Set of local populations connected by dispersal
Community -
Local communities connected by the dispersal of 1 or more other species
3 factors to determine # of species on an island
Colonization
Extinction
In-situ speciation
What Is The Goal Of MacArthur And Wilson’s Theory Of Island Biogeography?
Predict the # of species on an island based on the island’s size & distance from mainland
__________ speciation was ignored in the theory of island biogeography
In situ: New species formed from old ones
Will the extinction rate rise of fall as the # of species increases?
Rise
Near & Big Islands Have ______ Species, Small And Far Species Have ——————- Species
More, Less
According to Prof Muhler’s Research On Anolis Lizards He Concluded That
Large Islands have more species & Isolated islands have fewer species