Paper 1 Quiz Forces
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Data Booklet and calculators are allowed. Time how long you take to complete the quiz. 50% is a good start.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
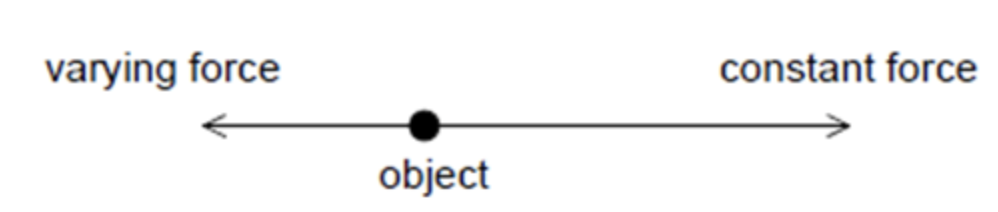
Two forces act along a straight line on an object that is initially at rest. One force is constant; the second force is in the opposite direction and proportional to the velocity of the object.
A. The acceleration increases from zero to a maximum.
B. The acceleration increases from zero to a maximum and then decreases.
C. The velocity increases from zero to a maximum.
D. The velocity increases from zero to a maximum and then decreases.
ANSWER: C
A climber of mass m slides down a vertical rope with an average acceleration a. What is the average frictional force exerted by the rope on the climber?
A. mg
B. m(g + a)
C. m(g – a)
D. ma
ANSWER: C
A cube slides down the surface of a ramp at a constant velocity. What is the magnitude of the frictional force that acts on the cube due to the surface?
A. The weight of the cube
B. The component of weight of the cube parallel to the plane
C. The component of weight of the cube perpendicular to the plane
D. The component of the normal reaction at the surface parallel to the plane
ANSWER: B
Two forces of magnitude 12 N and 24 N act at the same point. Which force cannot be the resultant of these forces?
A. 10 N
B. 16 N
C. 19 N
D. 36 N
ANSWER: A
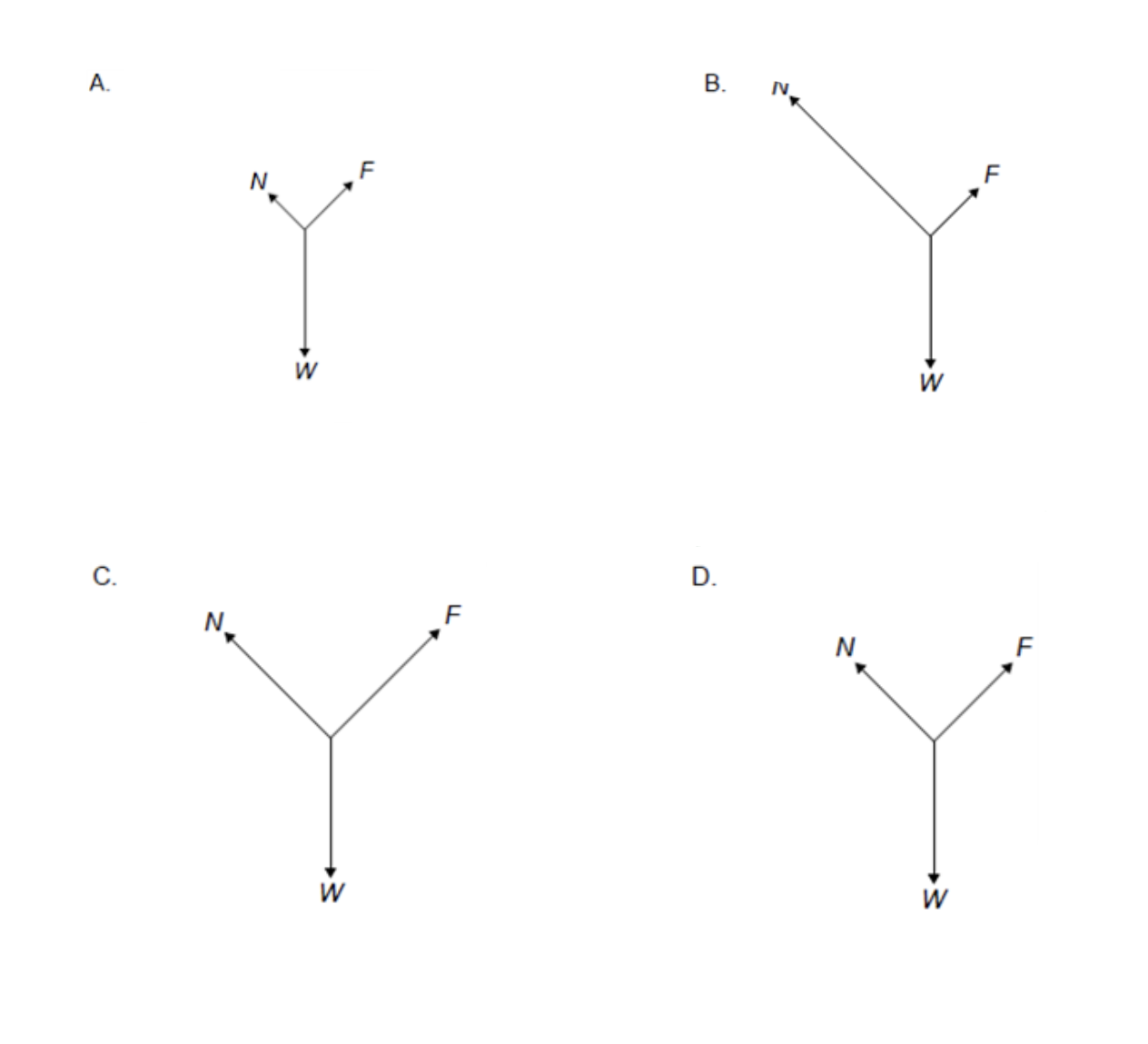
A block of weight W slides down a ramp at constant velocity. A friction force F acts between the bottom of the block and the surface of the ramp. A normal reaction N acts between the ramp and the block. What is the free-body diagram for the forces that act on the block?
ANSWER: D
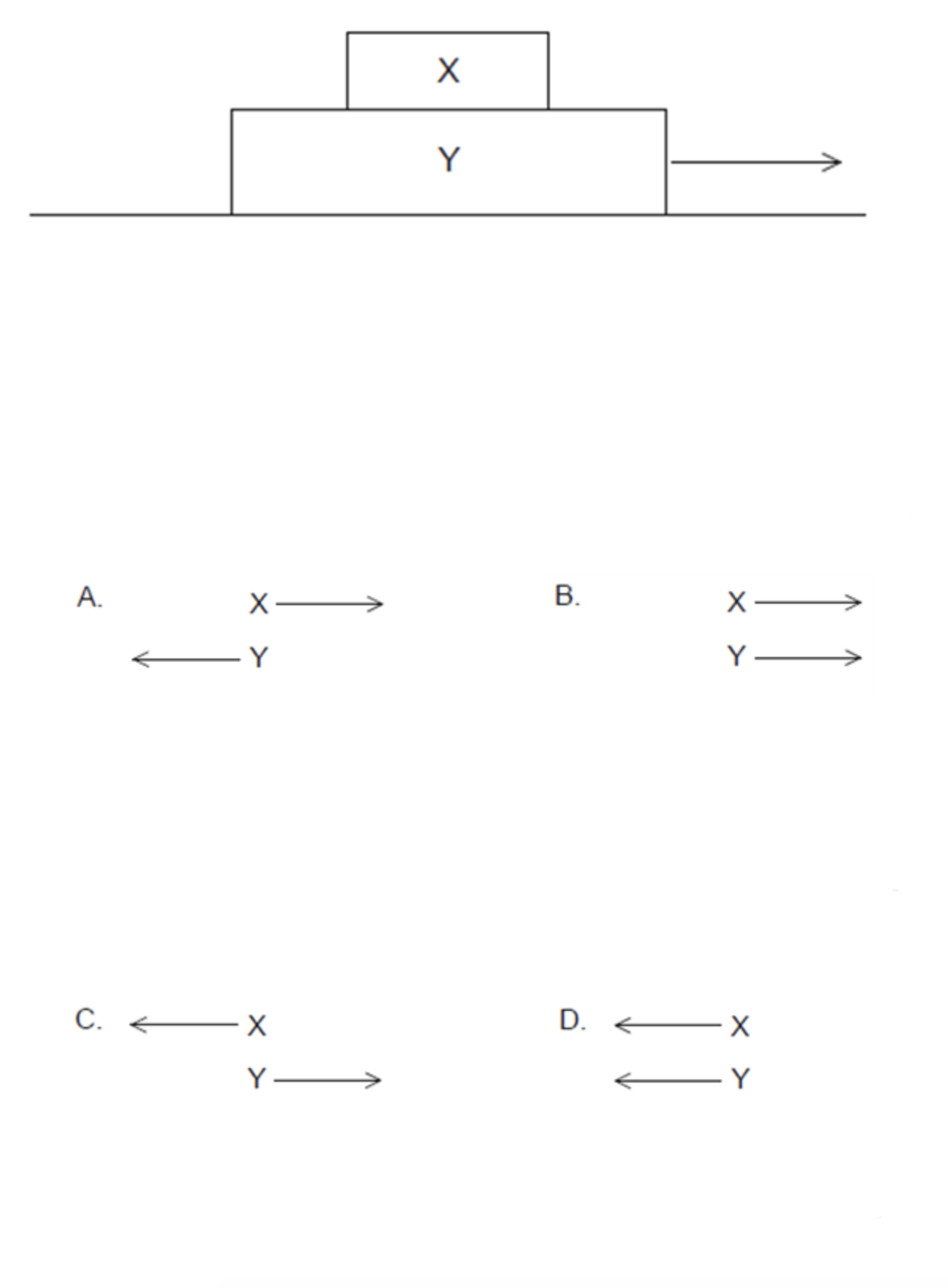
Two blocks X and Y rest on a frictionless horizontal surface as shown. A horizontal force is now applied to the larger block and the two blocks move together with the same speed and acceleration. Which free-body diagram shows the frictional forces between the two blocks?
ANSWER: A
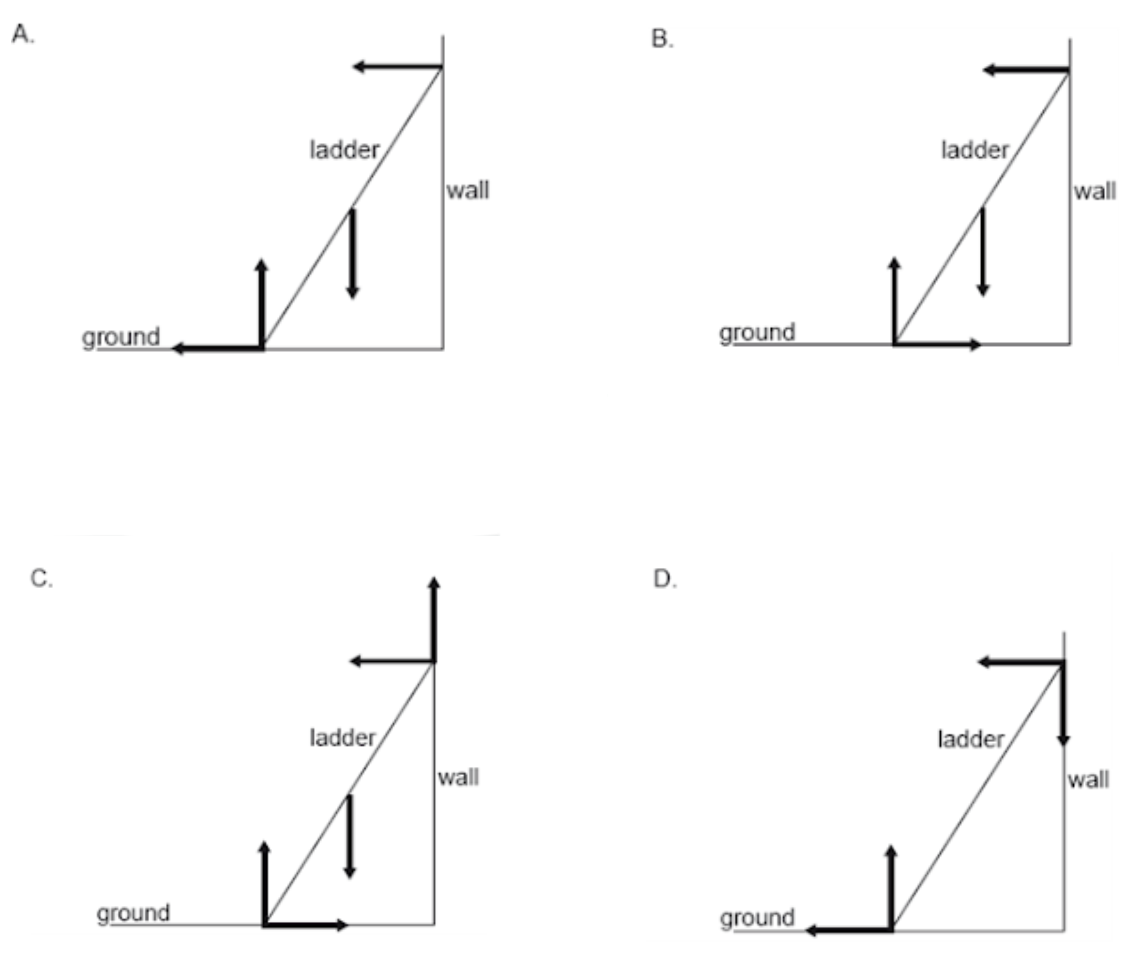
A uniform ladder resting in equilibrium on rough ground leans against a smooth wall. Which diagram correctly shows the forces acting on the ladder?
ANSWER: B
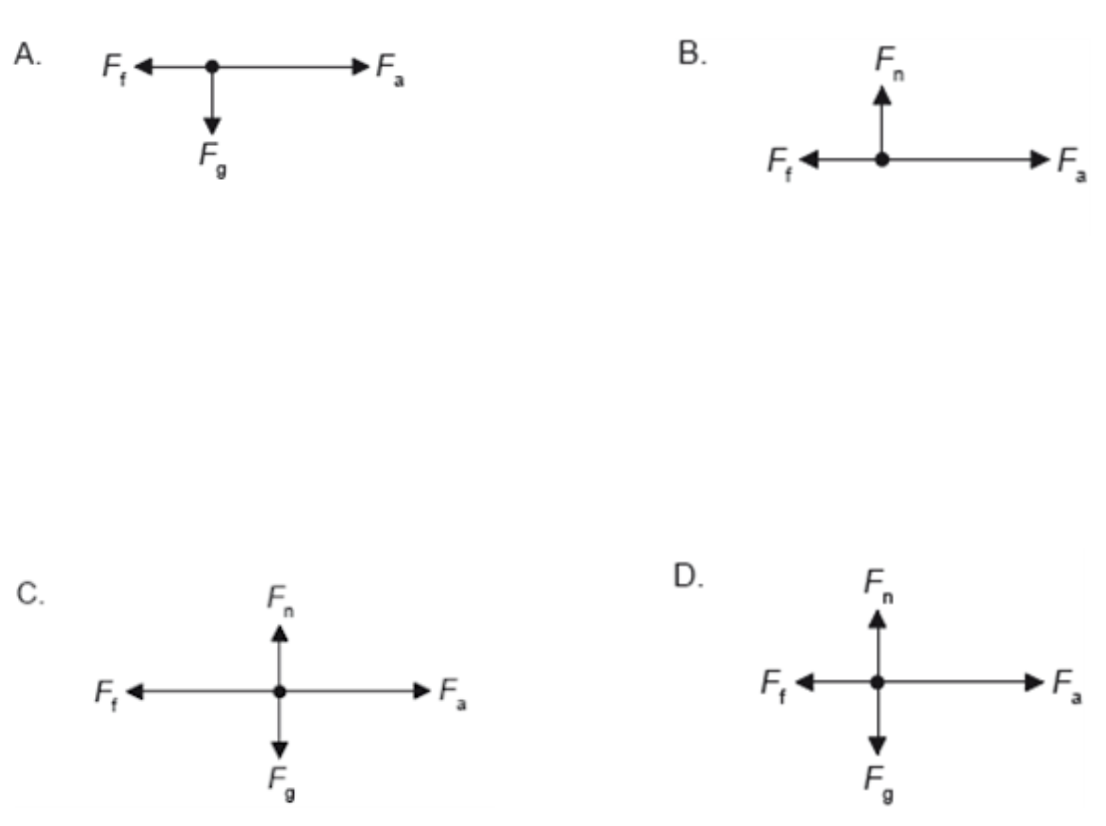
A box is accelerated to the right across rough ground by a horizontal force Fa. The force of friction is Ff. The weight of the box is Fg and the normal reaction is Fn. Which is the free-body diagram for this situation?
ANSWER: D
A weight W is tied to a trolley of mass M by a light string passing over a frictionless pulley. The trolley has an acceleration a on a frictionless table. The acceleration due to gravity is g. What is W?
ANSWER: A
The diagram shows the forces acting on a block resting on an inclined plane. The angle θ is adjusted until the block is just at the point of sliding. R is the normal reaction, W the weight of the block and F the maximum frictional force. What is the maximum coefficient of static friction between the block and the plane?
ANSWER: C
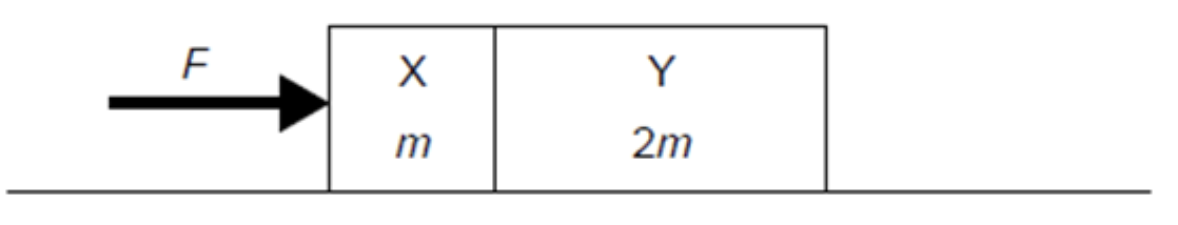
Two boxes in contact are pushed along a floor with a force F. The boxes move at a constant speed. Box X has a mass m and box Y has a mass 2m. What is the resultant force acting on Y?
A. 0
B. F/2
C. F
D. 2F
ANSWER: A
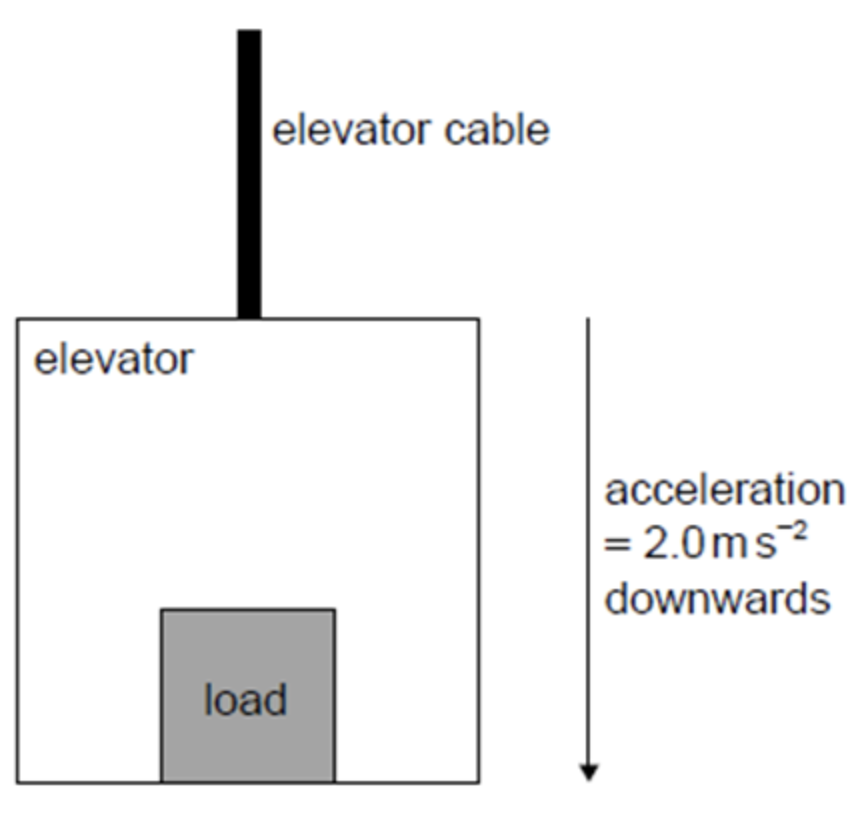
An elevator (lift) and its load have a total mass of 750 kg and accelerate vertically downwards at 2.0 m s^–2. What is the tension in the elevator cable?
A. 1.5 kN
B. 6.0 kN
C. 7.5 kN
D. 9.0 kN
ANSWER: B
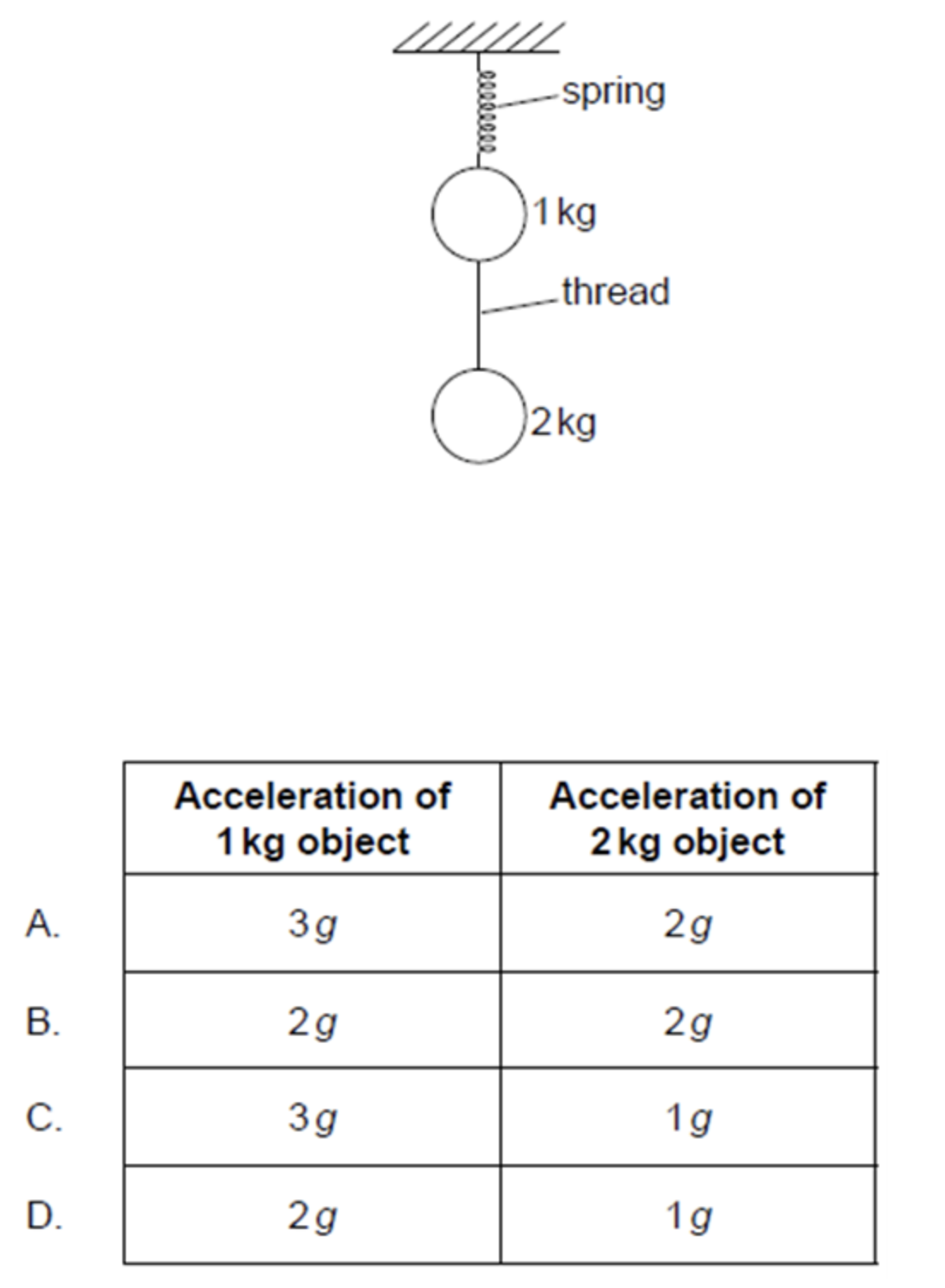
Two stationary objects of mass 1kg and 2kg are connected by a thread and suspended from a spring. The thread is cut. Immediately after the cut, what are the magnitudes of the accelerations of the objects in terms of the acceleration due to gravity g?
ANSWER: D
An object of mass m rests on a horizontal plane. The angle θ that the plane makes with the horizontal is slowly increased from zero. When θ=θo, the object begins to slide. What are the coefficient of static friction μs and the normal reaction force N of the plane at θ=θo?
ANSWER: D
An object of weight W is falling vertically at a constant speed in a fluid. What is the magnitude of the drag force acting on the object?
A. 0
B. W/2
C. W
D. 2W
ANSWER: C
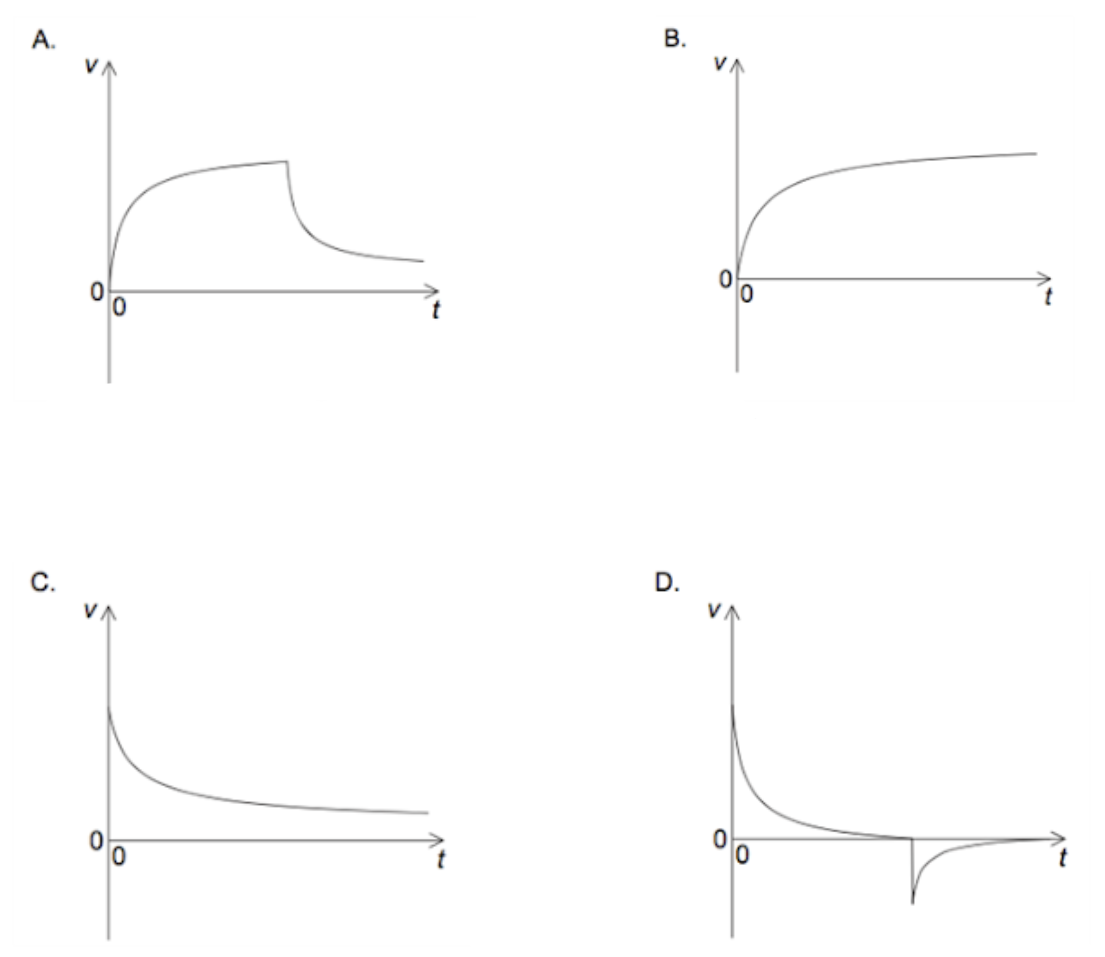
An aircraft is moving horizontally. A parachutist leaves the aircraft and a few seconds later opens her parachute. Which graph shows the variation of the vertical speed v with time t for the parachutist from the time she leaves the aircraft until just before landing?
ANSWER: A
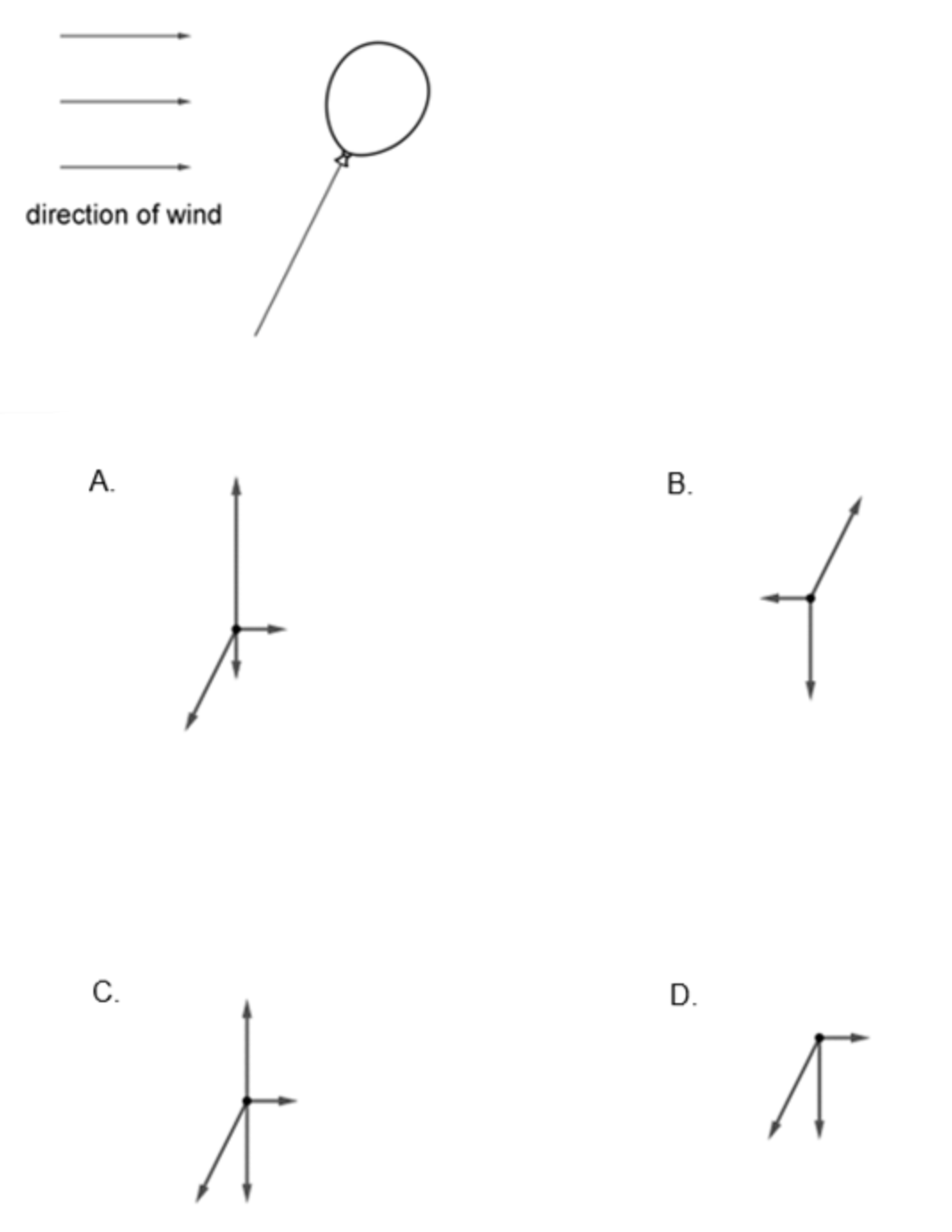
A toy balloon floats at the end of a string. A wind blows horizontally to the right. The balloon is in translational equilibrium. What is the free-body diagram of the forces acting on the balloon?
ANSWER: A
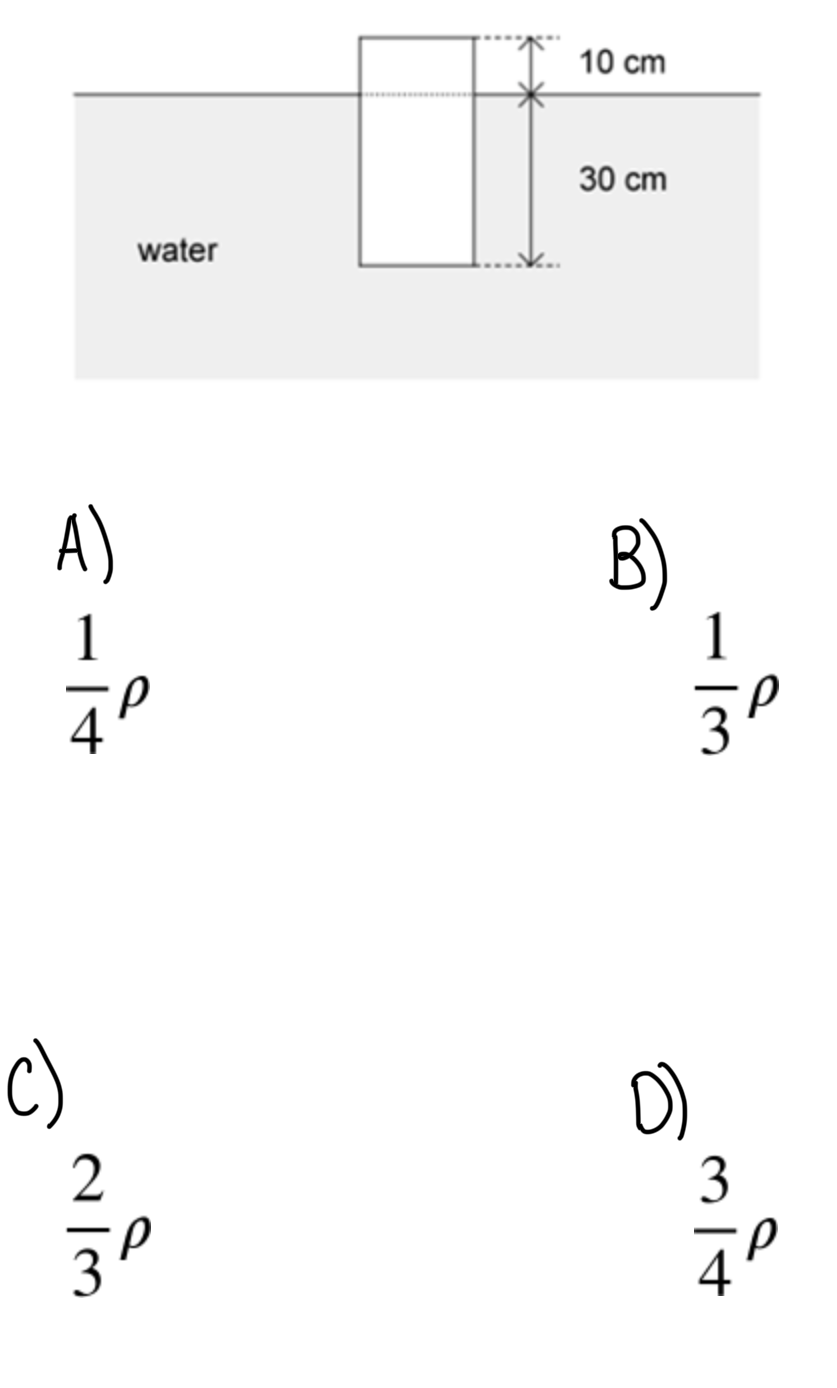
A body of height 40 cm and uniform cross-sectional area floats in water. 10 cm of the height of the body remains above the water line. The density of water is p . What is the density of the body?
ANSWER: D
An object is suspended from a spring balance. When the object is in air the spring balance reads 900 N. When the object is completely submerged in water the spring balance reads 400 N. The density of water is 1000 kg m−3. What is the volume of the object?
0.05 m³
An object is submerged in a fluid. Three quantities relating to this situation are:
The density of the object
The density of the fluid
The gravitational field strength
On which quantities does the buoyancy force acting on the object depend?
ANSWER: C