Human anatomy - week 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/106
Last updated 12:01 PM on 2/25/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
1
New cards
macroscopic anatomy
Structure and the parts of body that can be seen with unaided eyes
2
New cards
surface anatomy
The external body
3
New cards
Regional anatomy
Specific regions of the body
4
New cards
Systemic anatomy
Specific organ systems
5
New cards
Microscopic anatomy
Structure and parts of body that can only be seen through the aid of a microscope
6
New cards
Examples of microscopic anatomy
Histology and Cytology
7
New cards
Levels of structure organisation and body system
1. chemical
2. cellular
3. tissue
4. organ
5. organ system
6. organism
8
New cards
Chemical level
Basic structural and functional units of an organism that are composed of chemicals
9
New cards
Cellular level
Basic structural and functional units of an organism composed of chemicals
10
New cards
Tissue level
Groups of similar cells and materials surrounding them that work together to perform a particular function
11
New cards
4 primary tissues
1. Epithelial tissue
2. Nervous tissue
3. Muscle tissue
4. Connective
12
New cards
11 systems of the body
1. skeletal
2. reproductive
3. urinary
4. muscular
5. endocrine
6. nervous
7. integumentary
8. cardiovascular
9. respiratory
10. digestive
11. lymphatic
13
New cards
Directional terms
Used to describe the relative locations of the body parts
14
New cards
Connective tissue
Occurs throughout the body, supporting and binding tissues and are also found in between organs.
stores energy as fat
help provide the body with immunity to disease-causing organisms
support
transportation
stores energy as fat
help provide the body with immunity to disease-causing organisms
support
transportation
15
New cards
Epithelial tissue
Covers body surfaces and lines hollow organs, body cavities and ducts, also forms glands. The tissue allows the body to interact with its external and internal environment
16
New cards
Muscular tissue
Composed of cells specialised for contraction and generation of force - in the process muscular tissue generates heat that warms the body
17
New cards
Nervous tissue
Detects changes in a variety of conditions inside and outside the body and responds by generating electrical signals called nerve action potentials that activate muscular contractions and glandular secretions
18
New cards
Organ
A collection of two or more tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function
19
New cards
Organ system
A group of physiologically or anatomically complementary organs or parts
20
New cards
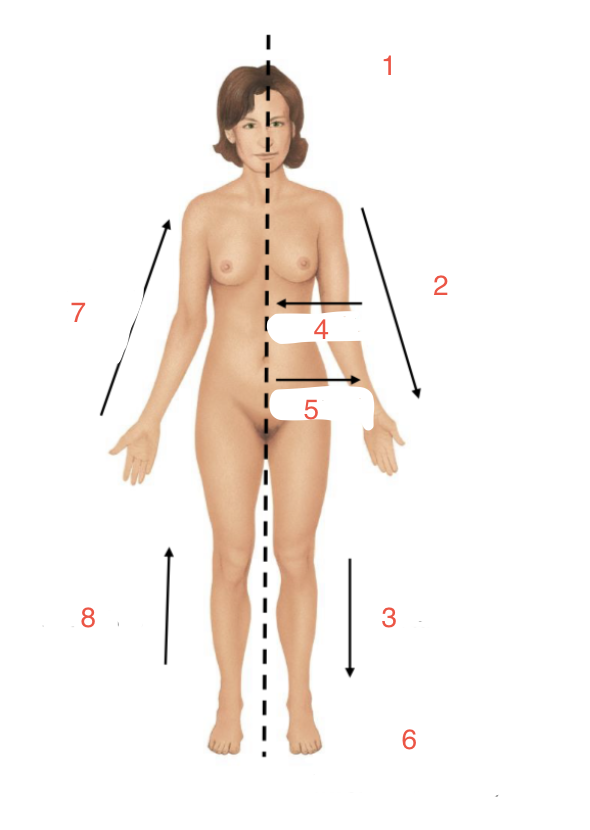
Identify 1
Superior - cranial
21
New cards
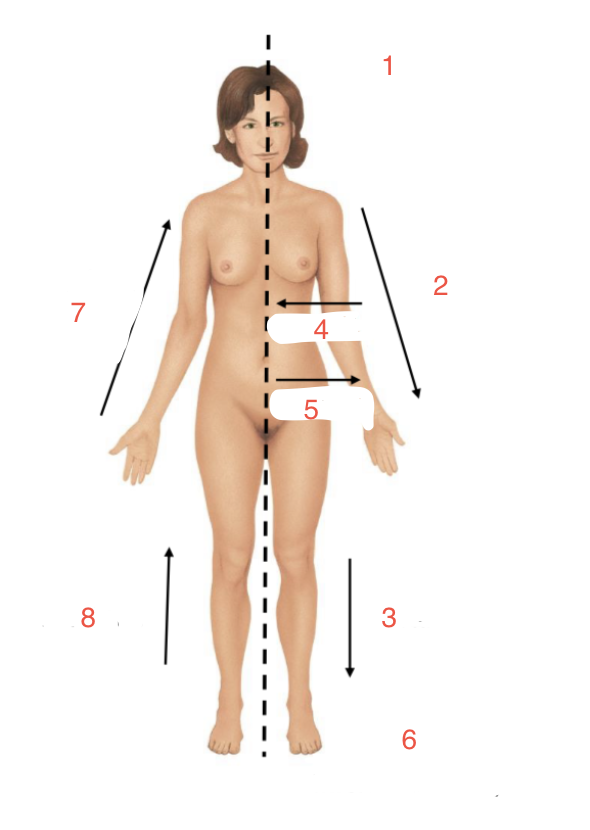
Identify 2
Distal
22
New cards
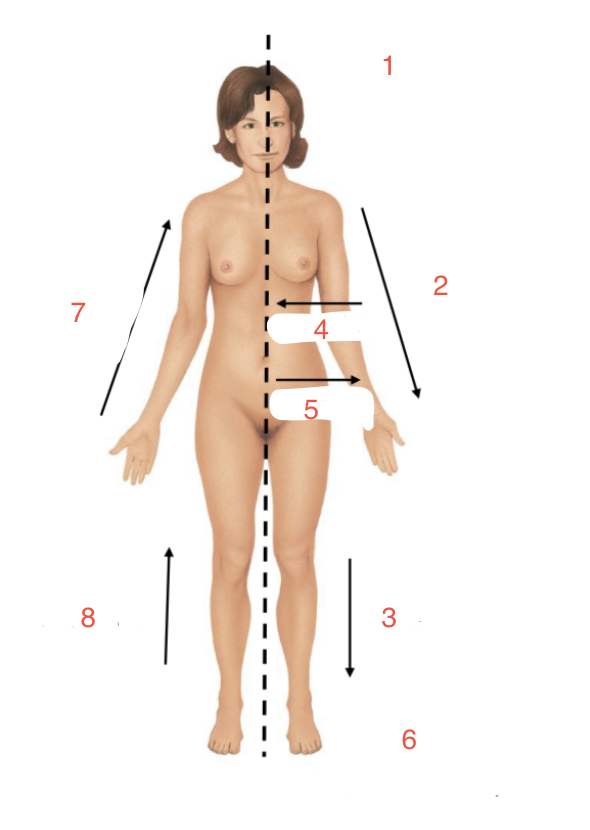
Identify 3
Distal
23
New cards
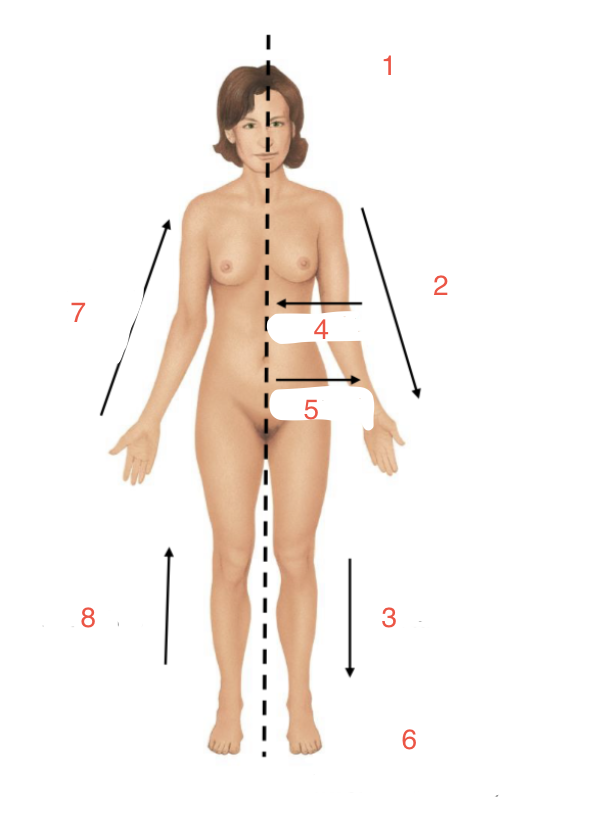
Identify 4
Medial
24
New cards
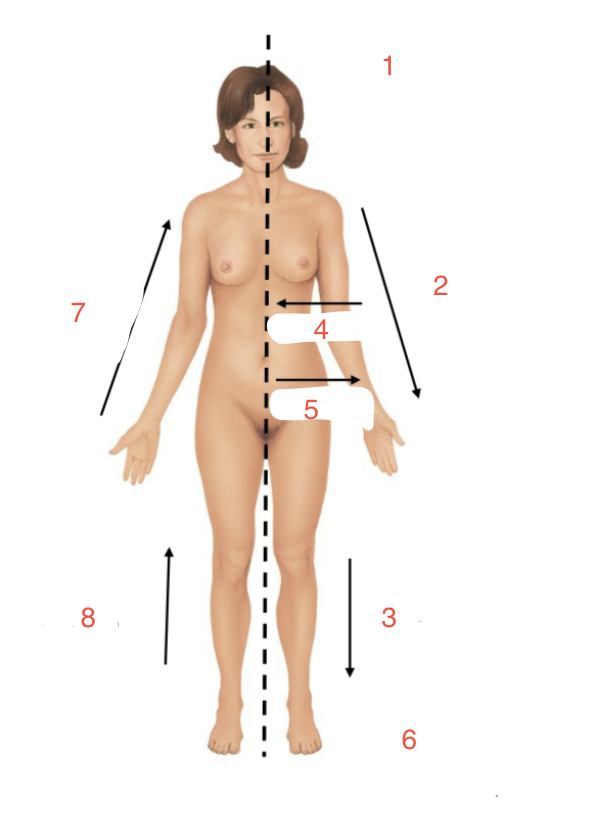
Identify 5
Lateral
25
New cards
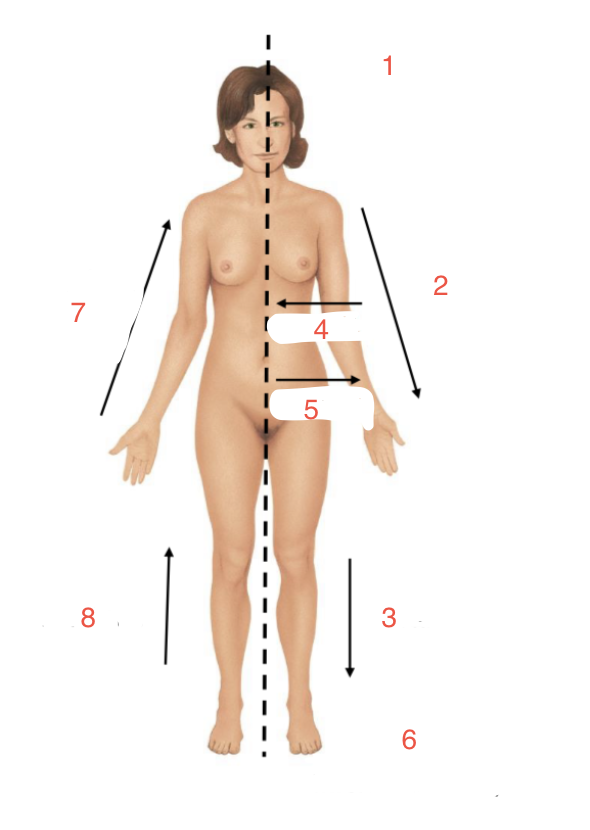
Identify 6
Inferior - caudal
26
New cards
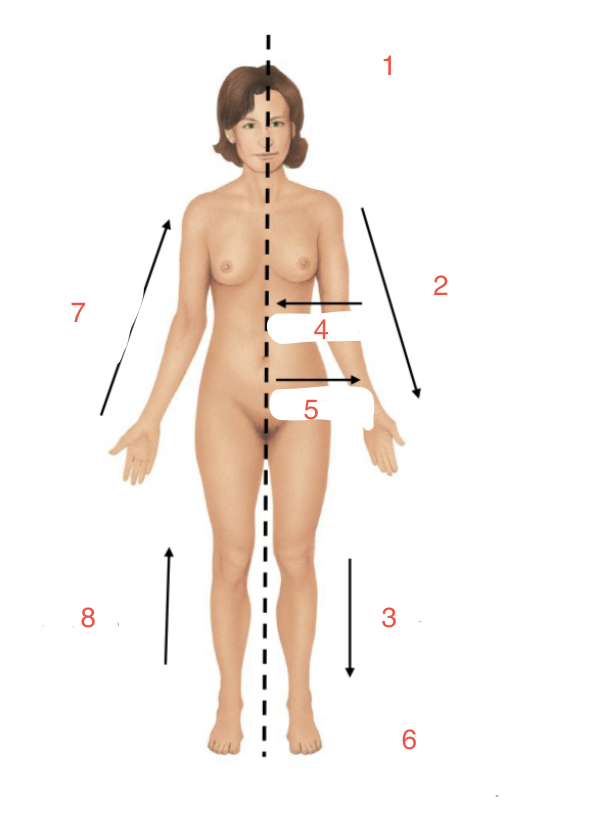
Identify 7
Proximal
27
New cards
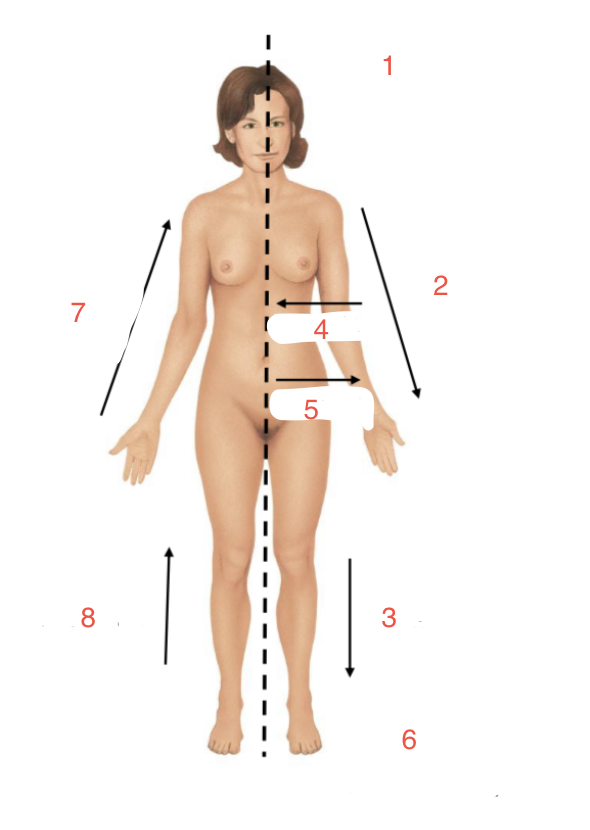
Identify 8
Proximal
28
New cards
Anterior
Front of body
29
New cards
Posterior
Back of body
30
New cards
Axial
Head, neck and trunk
31
New cards
Appendicular
Upper + lower limb
32
New cards
Body cavities
Spaces within the body that allows the body to move and expand and also protect internal organs
33
New cards
Posterior cavity
Cranial cavity and vertebral canal
34
New cards
Cranial cavity
Brain
35
New cards
Vertebral canal
spinal cord
36
New cards
Anterior body cavity
Thoracic cavity and abdominopelvic cavity
37
New cards
Thoracic cavity
Lungs
Mediastinum
pericardial cavity
Mediastinum
pericardial cavity
38
New cards
Mediastinum
Heart, oesophagus, major blood vessels
39
New cards
Pericardial cavity
Special cavity for the heart
40
New cards
Diaphragm
Separates thoracic cavity from the abdominal pelvic cavity
41
New cards
Abdominal cavity
Gastrointestinal tract, digestive organs, spleen, urinary organs
42
New cards
Digestive organs
Liver, pancreas, gallbladder
43
New cards
Urinary organs
Kidney and uterus
44
New cards
Pelvic cavity
Bladder and reproductive cavity
45
New cards
Cell
Fundamental unit of life of all organisms, cells work together to maintain homeostasis
46
New cards
3 basic components of the cell
1. plasma membrane (cell membrane)
2. nucleus
3. cytoplasm - cytosol + cytoskeleton + organelles
47
New cards
Plasma membrane function
Structural support
Controls the passage of materials between the inside and outside of the cell
Allows the cell to be identified to other cells
Allows the cell to communicate w/ other cells
Controls the passage of materials between the inside and outside of the cell
Allows the cell to be identified to other cells
Allows the cell to communicate w/ other cells
48
New cards
Plasma membrane - specialisation
Microvilli
Cilia
Flagellum
Cilia
Flagellum
49
New cards
Microvilli
Increase cell’s surface area for absorption
50
New cards
Cilia
Moves fluids along the cell’s surface
51
New cards
Flagellum
Moves the entire cell
52
New cards
Cell - cell adhesion
Process by which cells interact + attach to neighbouring cells
53
New cards
Cell - cell junctions
1. Adherens junctions
2. desmosomes
3. tight junction
4. gap junction
54
New cards
cell-matrix junction
hemidesmosomes
55
New cards
Nucleus function
Controls and coordinates the cells’ activities
56
New cards
3 components of nucleus
1. Nuclear envelope
2. Nucleolus
3. DNA and its associated proteins - histones
57
New cards
Function of nuclear envelope
Has nuclear pores allowing substance to move between the nucleus and cytoplasm
58
New cards
Function of nucleolus
The organelle containing RNA and proteins essential for protein synthesis
59
New cards
Function of DNA and histones
To form chromatin
60
New cards
Specific region of DNA
Gene
61
New cards
Gene
coding region used to produce protein
62
New cards
Gene expression
Process of the coding region producing proteins
63
New cards
2 components of gene expression
1. transcription
2. translation
64
New cards
transcription
DNA is copied into mRNA in the nucleus
65
New cards
translation
mRNA is translated into protein in the cytoplasm
66
New cards
Cytosol structure
Contains proteins and dissolved solutes
67
New cards
Function of cytosol
1. cellular process - protein synthesis and glycolysis
2. storage for nutrients
3. organelles perform specific functions in the cell
68
New cards
Cytoskeleton structure
Network of protein filaments
69
New cards
Function of cytoskeleton
1. Supports + maintains shape of cell
2. allows movement of substance within the cell
3. movement of external structures and can allow the cell to move, sperm cells
70
New cards
3 components of cytoplasm
1. cytosol
2. organelles
3. cytoskeleton
71
New cards
Organelles in cytoplasm
1. mitochondria
2. smooth endoplasmic reticulum
3. rough endoplasmic reticulum
4. ribosomes
5. Golgi apparatus
6. lysosomes
7. peroxisomes
72
New cards
rough endoplasmic reticulum structure and function
studded with ribosomes
ribosomes for protein synthesis to occur
folds protein into correct shape
discards proteins that are incorrectly folded
ribosomes for protein synthesis to occur
folds protein into correct shape
discards proteins that are incorrectly folded
73
New cards
ribosomes
made up from rRNA in nucleolus and is responsible for translation in protein synthesis
74
New cards
smooth endoplasmic reticulum structure and function
lacks ribosomes
carbohydrates/lipids/steroids synthesis
enzymatic degradation - detoxification for livers/hepatic cells
special role in nucleus
carbohydrates/lipids/steroids synthesis
enzymatic degradation - detoxification for livers/hepatic cells
special role in nucleus
75
New cards
Golgi apparatus structure and function
Flattened sacs of membrane and vesicles
Modifies, sorts, packages and transports protein received from the endoplasmic reticulum
forms small membrane bound vesicles into small membrane bounds secretory vesicles
Modifies, sorts, packages and transports protein received from the endoplasmic reticulum
forms small membrane bound vesicles into small membrane bounds secretory vesicles
76
New cards
Lysosomes
Formed from the Golgi apparatus
Contains powerful digestive enzymes
Autophagy - digestion of organelles
autolysis - destroys the cell
Contains powerful digestive enzymes
Autophagy - digestion of organelles
autolysis - destroys the cell
77
New cards
Peroxisomes
Similar to lysosomes - just smaller
contains enzymes for metabolism
contains enzymes for metabolism
78
New cards
Mitochondria
Tubular shape, double membrane, DNA and ribosomes
provides energy to the cell (ATP)
site of fatty acid oxidation, citric acid cycle, oxidative phosphorylation
provides energy to the cell (ATP)
site of fatty acid oxidation, citric acid cycle, oxidative phosphorylation
79
New cards
Epithelia tissue functions
selective barrier that limits or aids the transfer of substance into and out of the cell
protective surface that resists the abrasive influence of the environment
secretory surface that releases products produced by the cells onto its free surfaces, filtration, secretion, absorption and excretion
protective surface that resists the abrasive influence of the environment
secretory surface that releases products produced by the cells onto its free surfaces, filtration, secretion, absorption and excretion
80
New cards
Cell shapes
Squamous
Cuboidal
Columnar
Transitional
Cuboidal
Columnar
Transitional
81
New cards
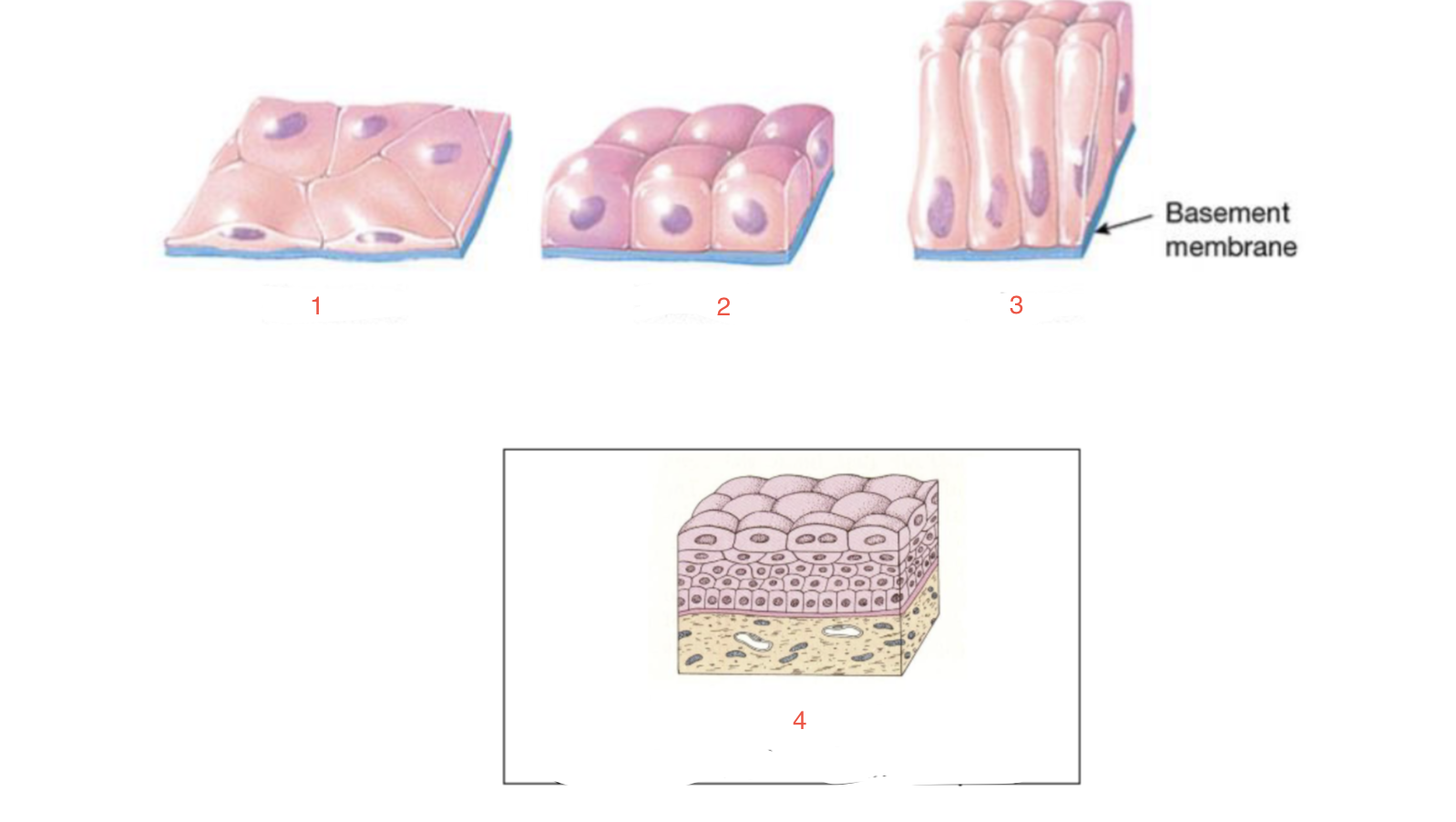
identify 1
Squamous
82
New cards
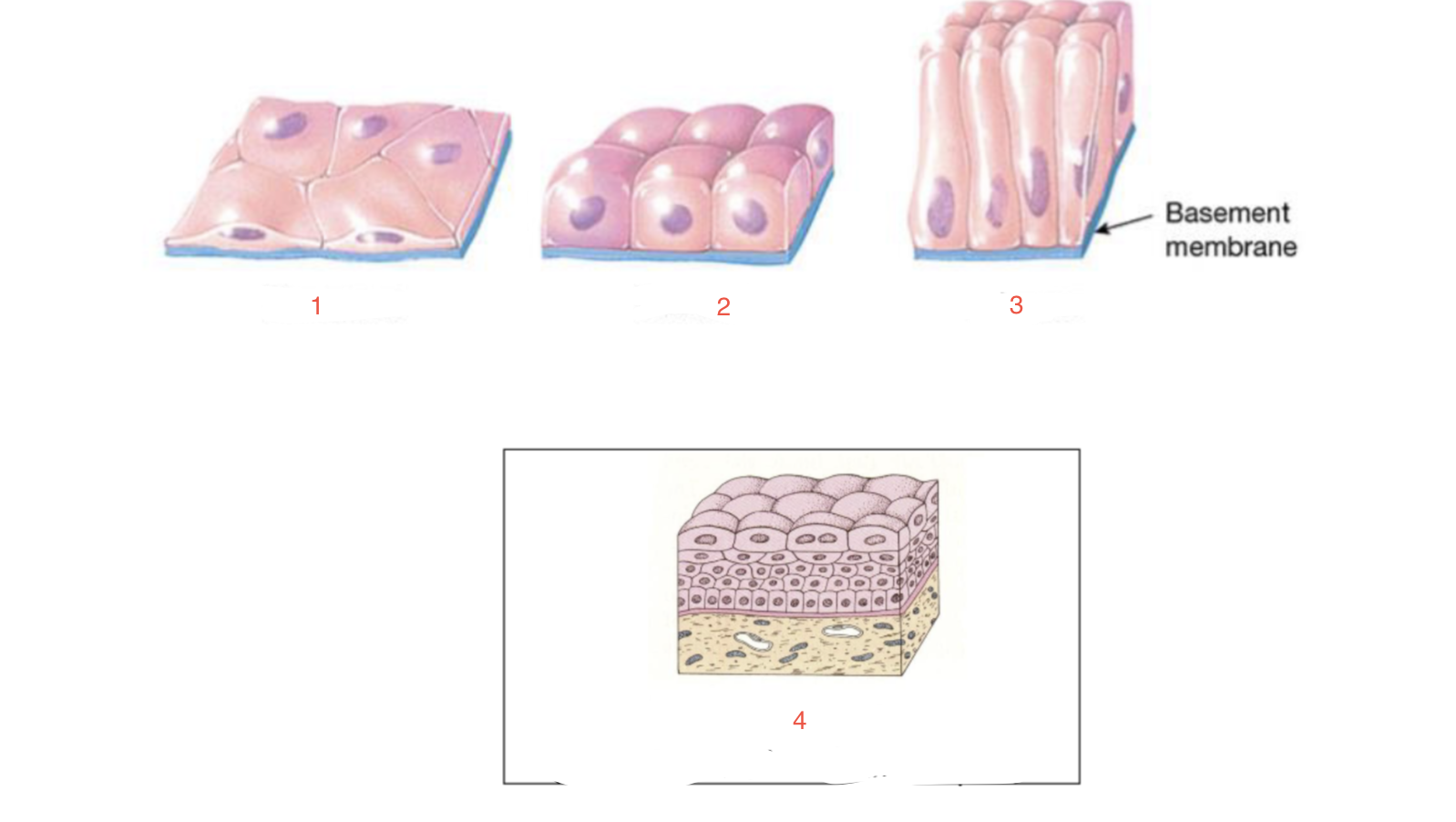
identify 2
cuboidal
83
New cards
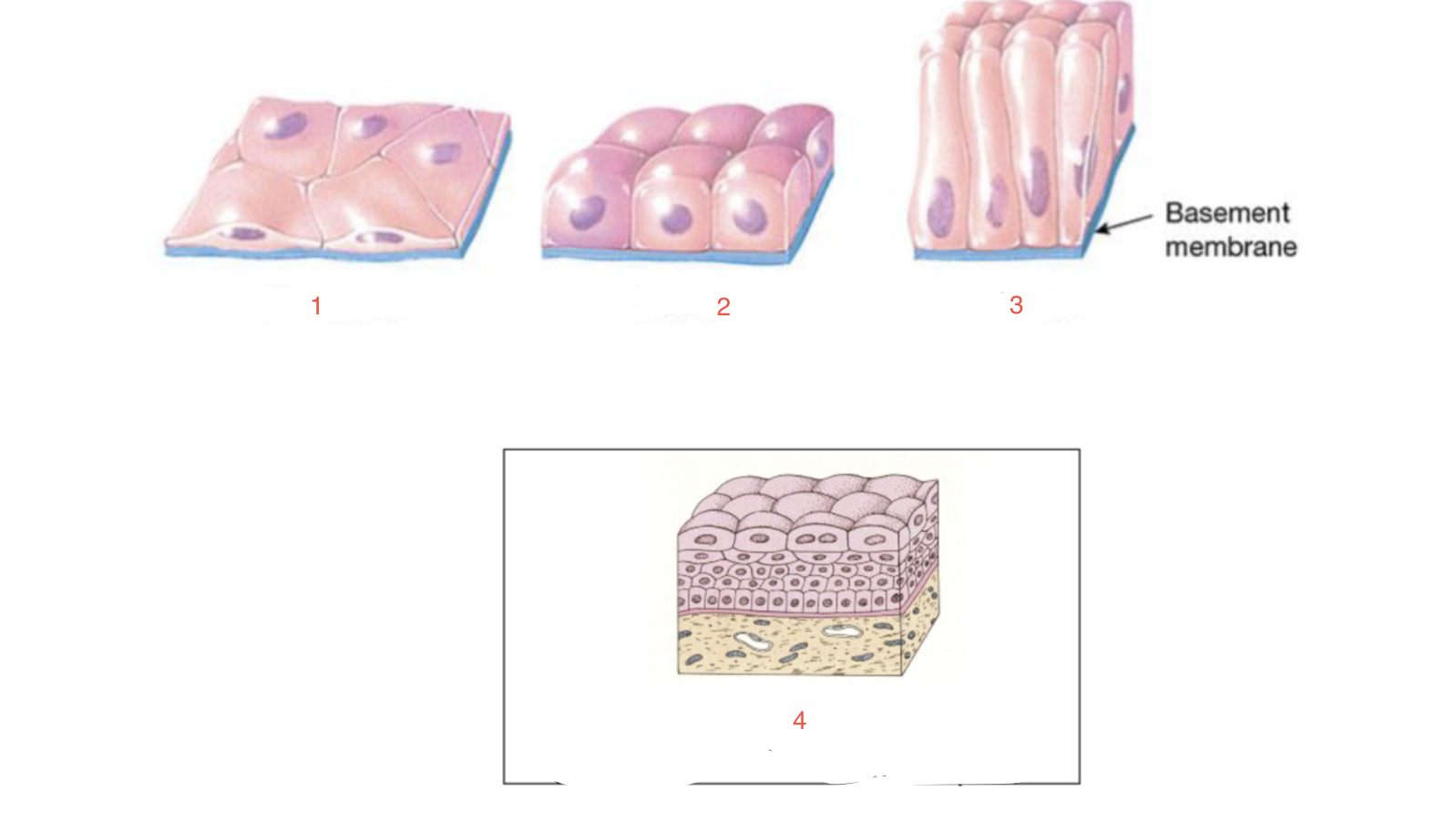
identify 3
columnar
84
New cards
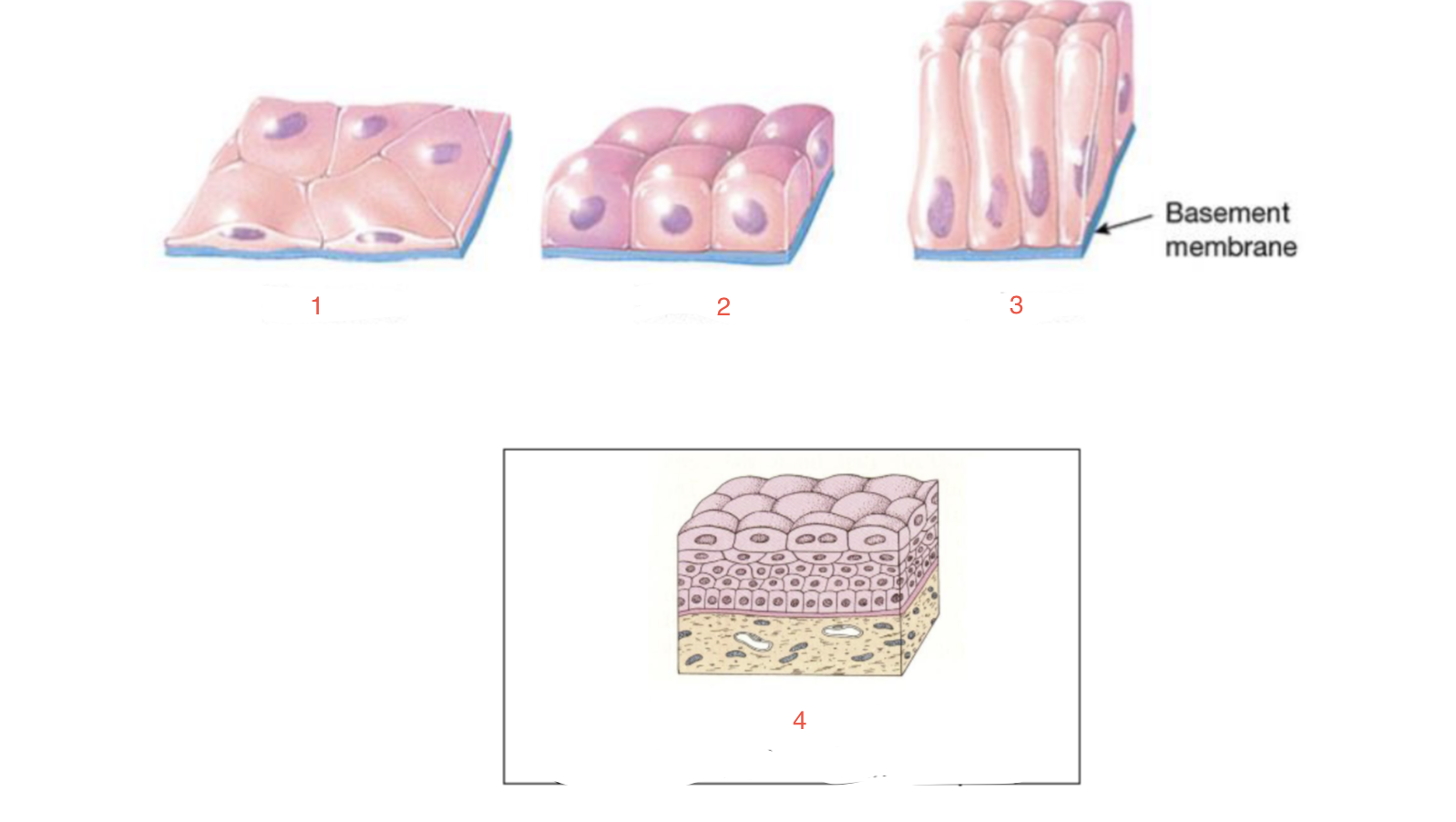
identify 4
transitional
85
New cards
Cell layers
simple
pseudostratified
stratified
pseudostratified
stratified
86
New cards
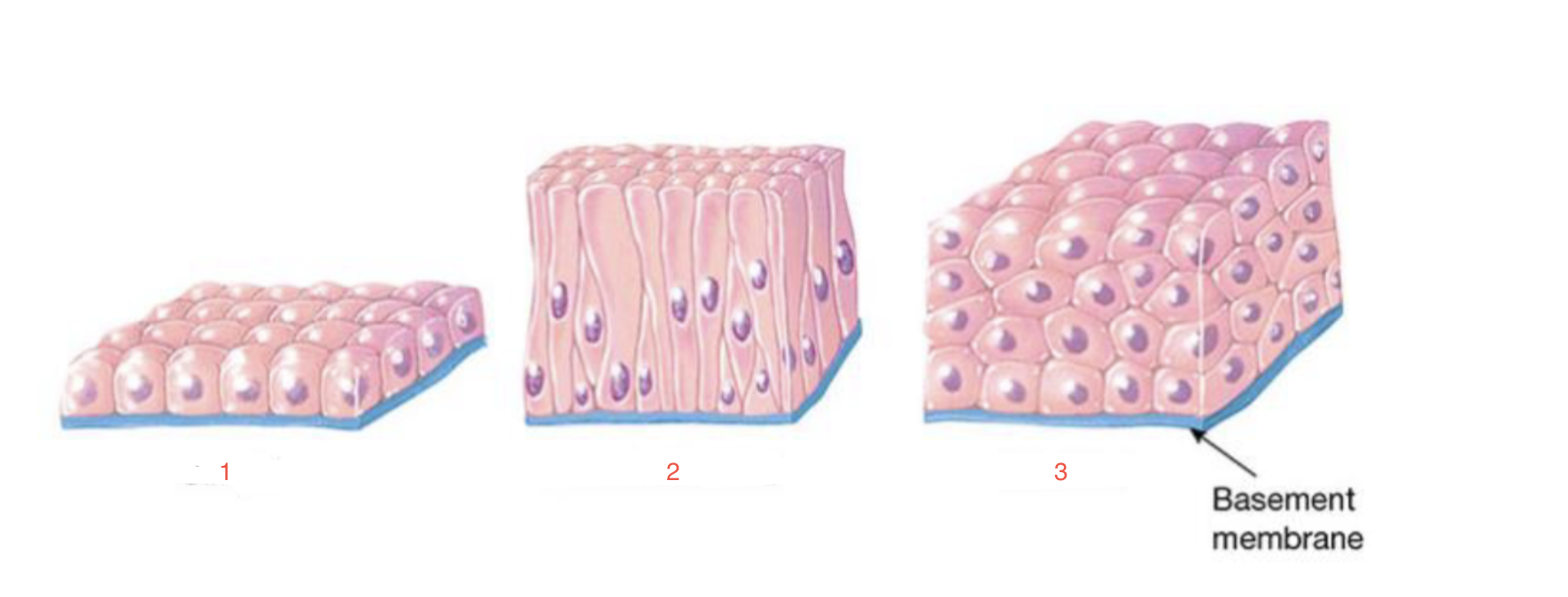
identify 1
simple
87
New cards
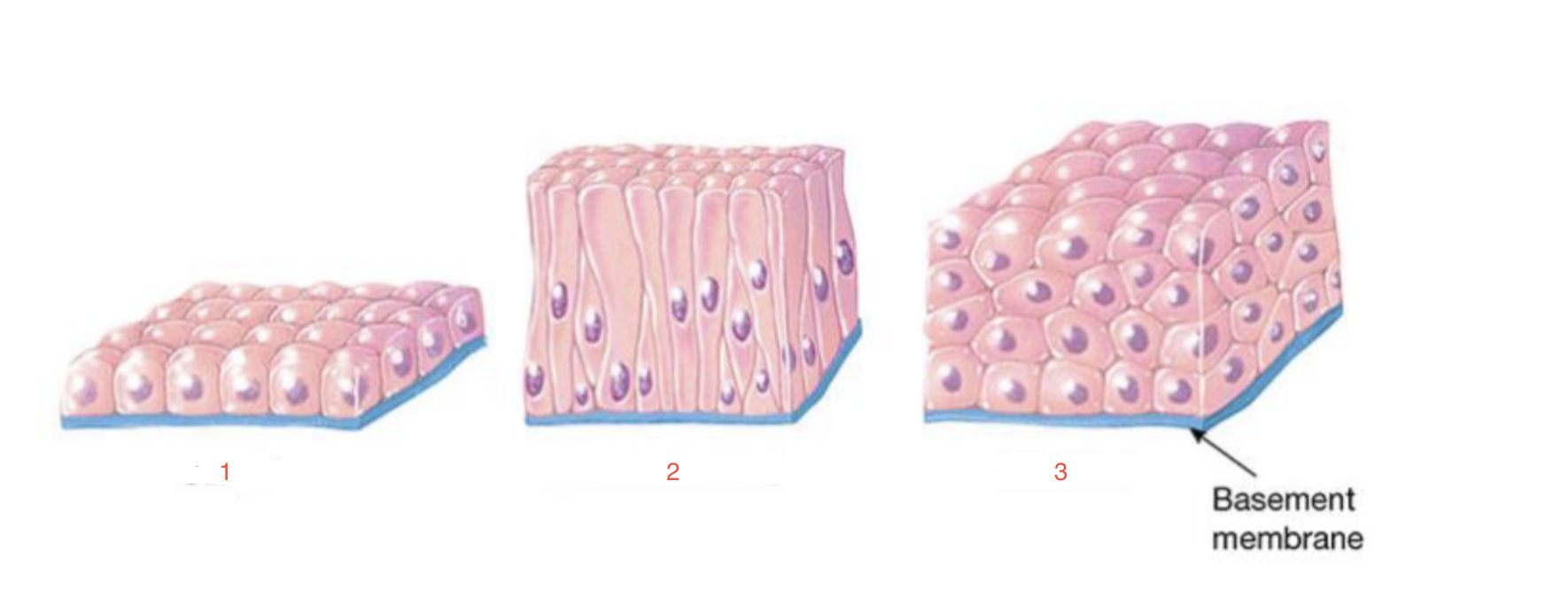
identify 2
pseudostratified
88
New cards
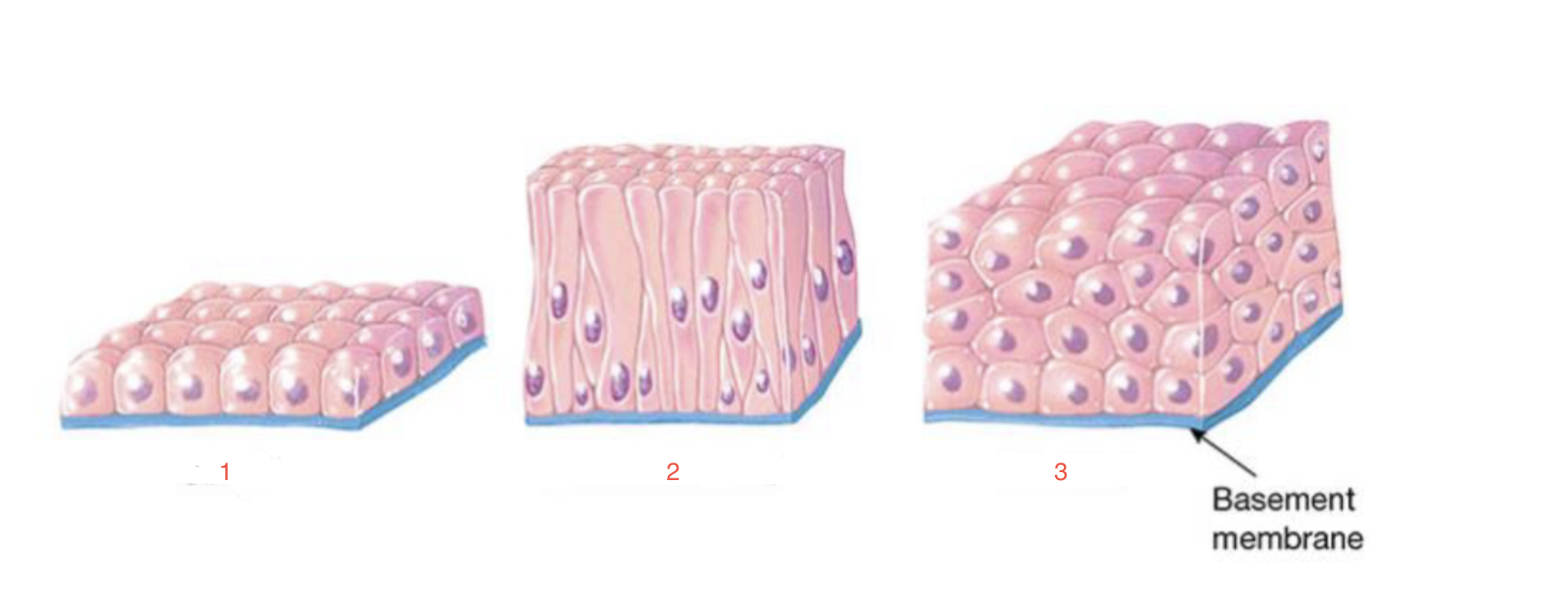
identify 3
stratified
89
New cards
Epithelia - surface specialisation
Keratin
Microvilli or cilia
goblet cells
Microvilli or cilia
goblet cells
90
New cards
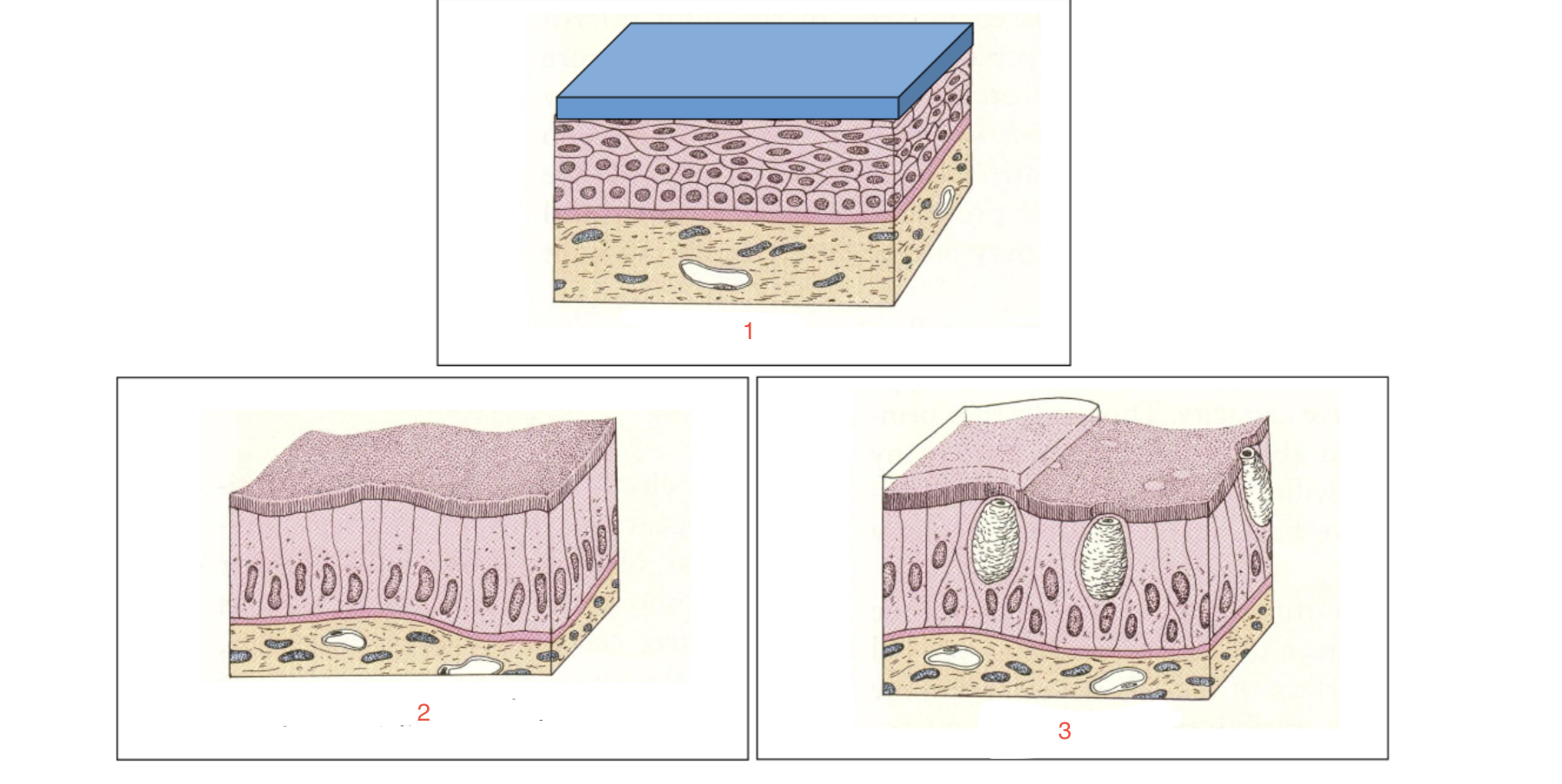
identify 1
keratin
91
New cards
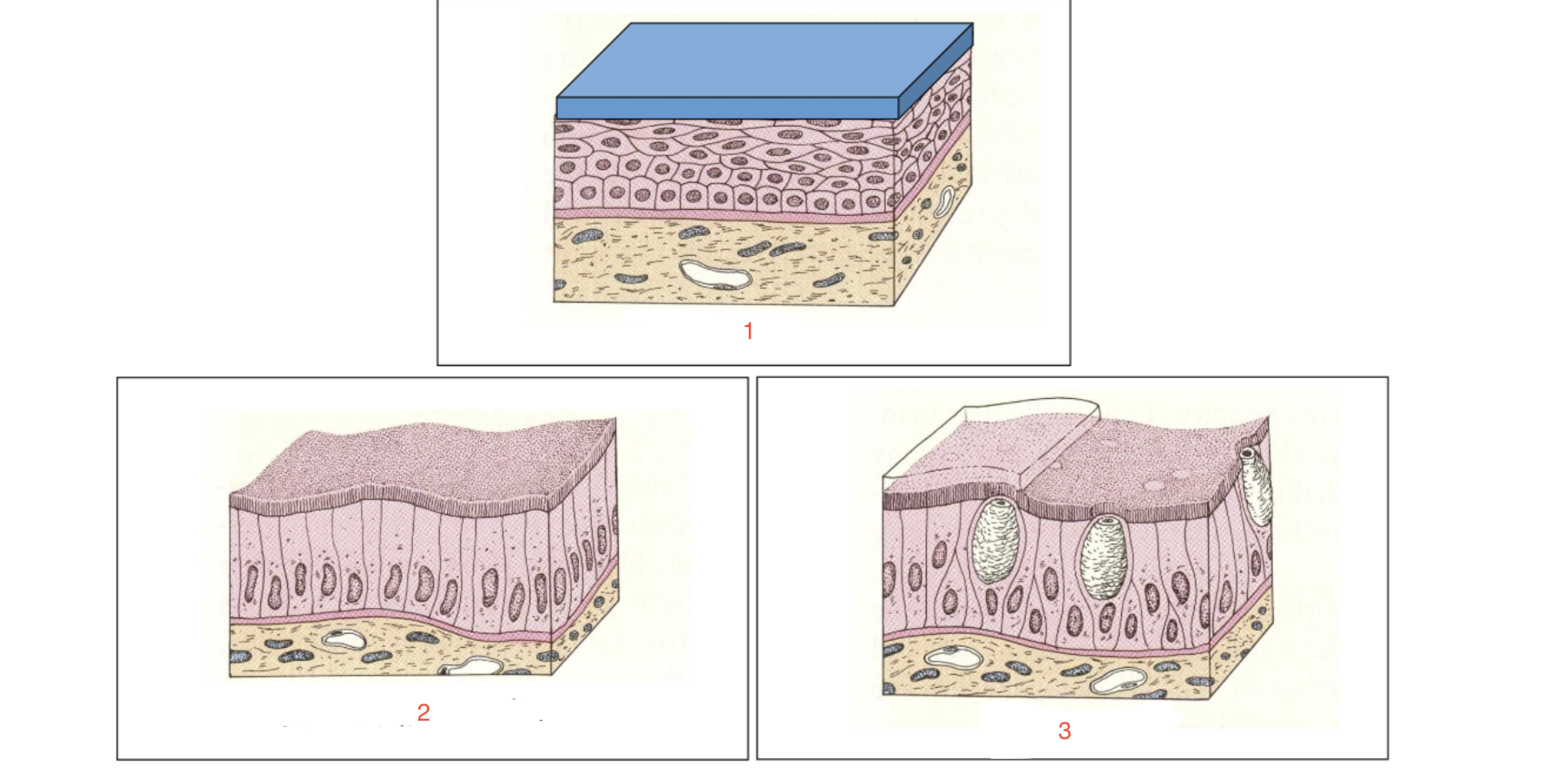
identify 2
microvilli or cilia
92
New cards
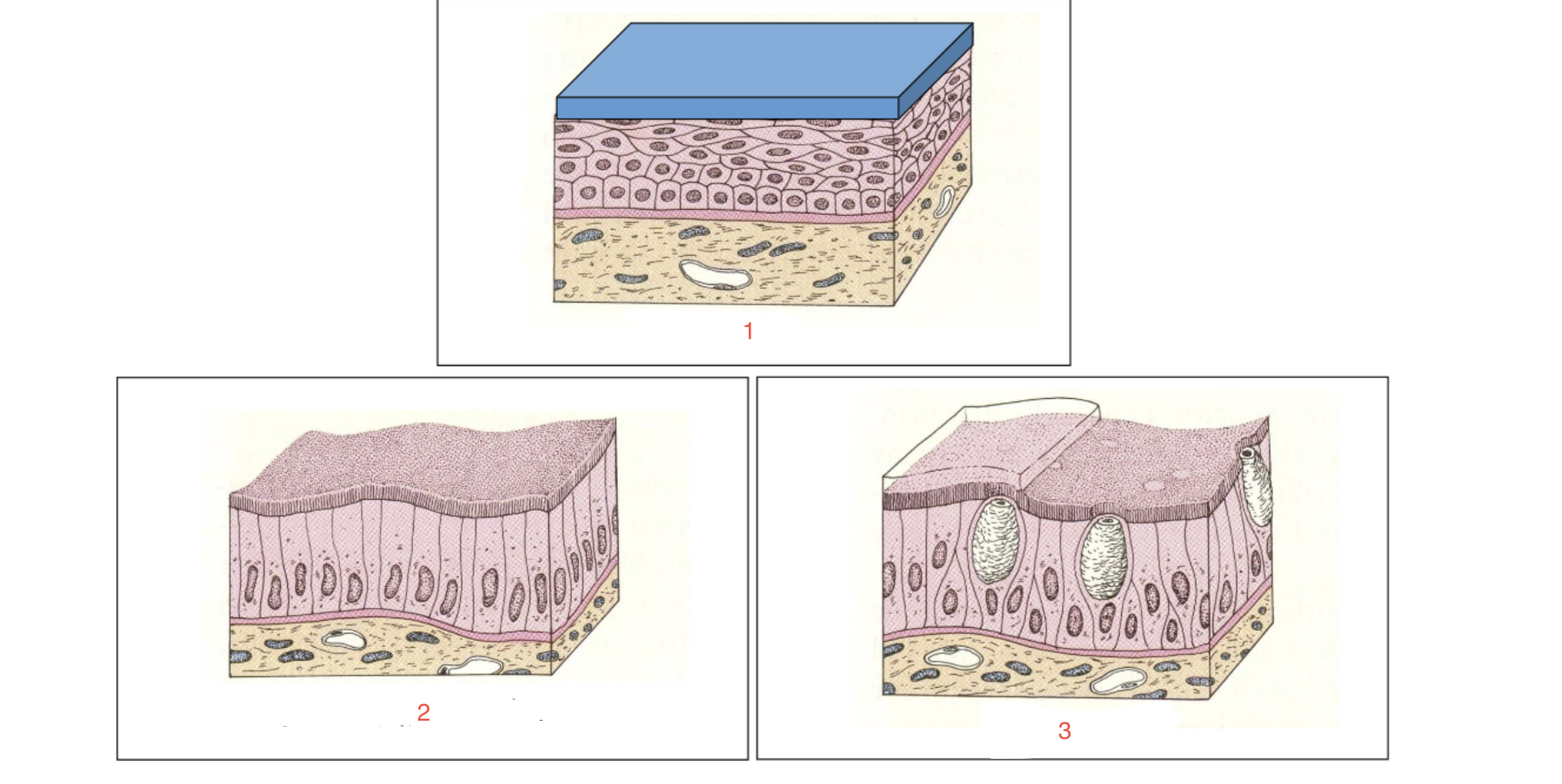
identify 3
goblet cells
93
New cards
Cell types for connective tissue
1. fibroblasts - dense, loose and reticular
2. adipocytes - fat
3. chondrocytes - cartilage
4. osteocytes - bone
5. red blood cells - blood
94
New cards
Extracellular matrix location and components
located between cells
protein fibres - collagen, elastic and reticular
ground substance - water and organic molecules
\
protein fibres - collagen, elastic and reticular
ground substance - water and organic molecules
\
95
New cards
Function of extracellular matrix
Supports the cells
allows substances to be exchanged
allows substances to be exchanged
96
New cards
proper connective tissues
connects tissue and organs together
loose, dense, reticular and adipose
loose, dense, reticular and adipose
97
New cards
Function of loose, dense and reticular cells
Stabilise
support
protect
support
protect
98
New cards
Function of adipose
Insulates
energy reserve
hormones
energy reserve
hormones
99
New cards
Specialised connective tissue
supportive tissues
cartilage - hyaline, elastic, fibrous
bone
cartilage - hyaline, elastic, fibrous
bone
100
New cards
Hyaline cartilage functions
Reduces friction at joints
Shock absorption at joints
flexible and strong support
Shock absorption at joints
flexible and strong support