Lecture 3 - Cellular Neurophysiology
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Membrane voltage
Ionic concentration gradients and membrane permeability determine
GHK Equation
Used to calculate the resting membrane potential
Generates signals
Voltage across the neuronal membranes
Passive voltage
Changes the membrane time constant and length constant.
The magnitude of change is proportional to current injected
Injected current changes (changes Q —> changes V) charge density on membrane by adding/taing change —> changes difference of + and -
Types of neuronal electrical signals
Passive and active
Membrane time constant
Passive voltage changes
Depolarization
Changes in membrane voltage towards a positive value
Hyperpolarization
Membrane voltage change that moves in the negative direction
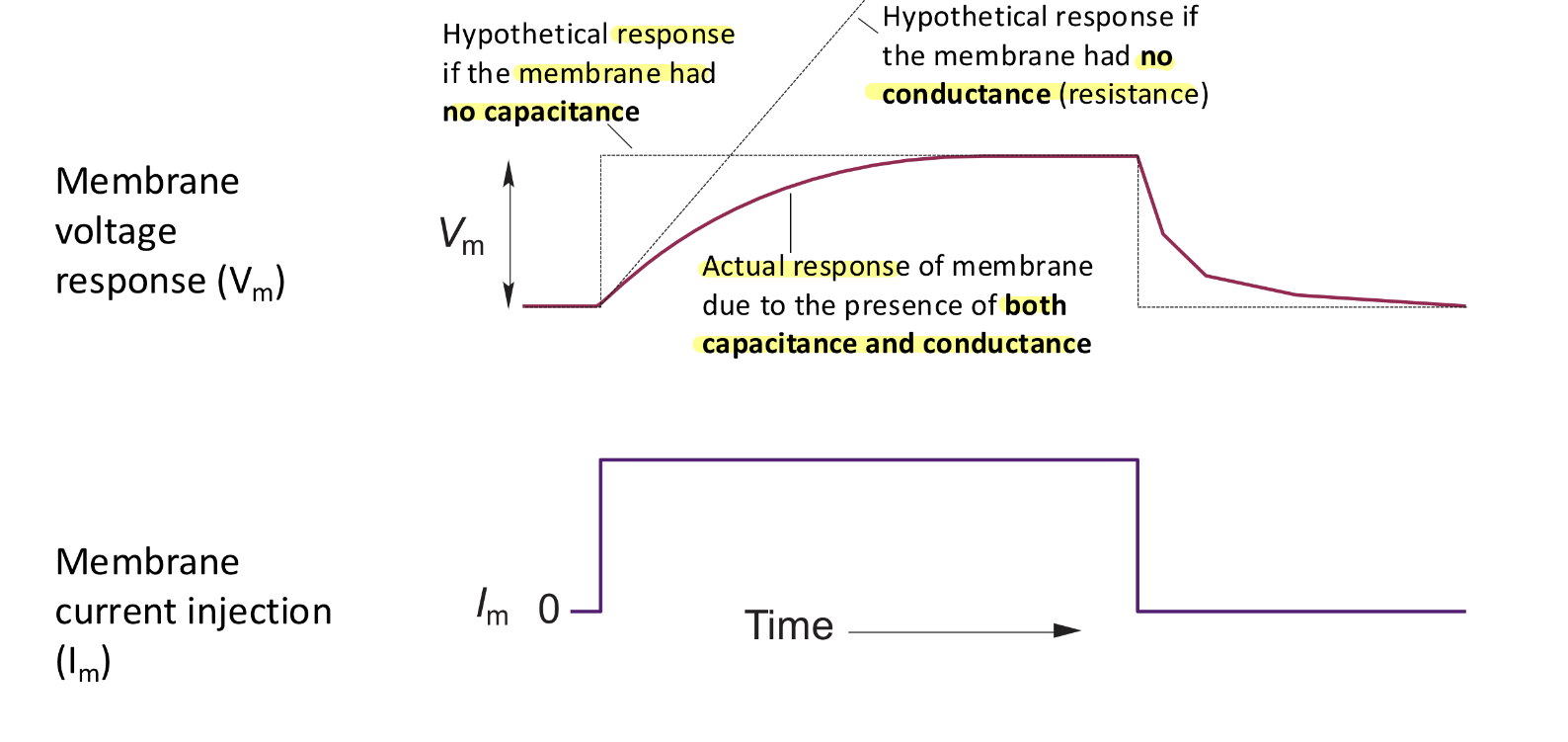
Membrane capacitance causes…
membrane voltage to take time to change
W/o conductance & only capacitance, Vm would keep going up in response to current injection as more and more change gets deposited on membrane
W/o capactitance and only conductance Vm would change instantly in response to current injection (no caapcitor to charge Vm is across conductor only)
Membrane time constant
Defines the rate of voltage change
Time it takes for Vm to change to 63% of max voltage change (Vmax)
Determined by membrane capacitance and resistance
τ = RC
Ic
Current that charges the membrane voltage (once charged, Ic stops flowing)
Ii
current through the membrane’s ion channels (is at max once the membrane is maximally charged)
Larger Vmax tells us about … and means…
resistance (conductance) of the membrane
larger membrane resistance
Passive voltage changes
Membrane length constant
Membrane ptl (Vm)
decays w/distance from site of current injection
Membrane length constant
Dependent on membrane resistance and axial resistance
Membbrane resistance decreases by (membrane condtance increased)—>
Having more ion channels, current will flow easier out thru membrane more easily —> decreasing λ (distance from site of current injection where Vm is 37% of Vmax)
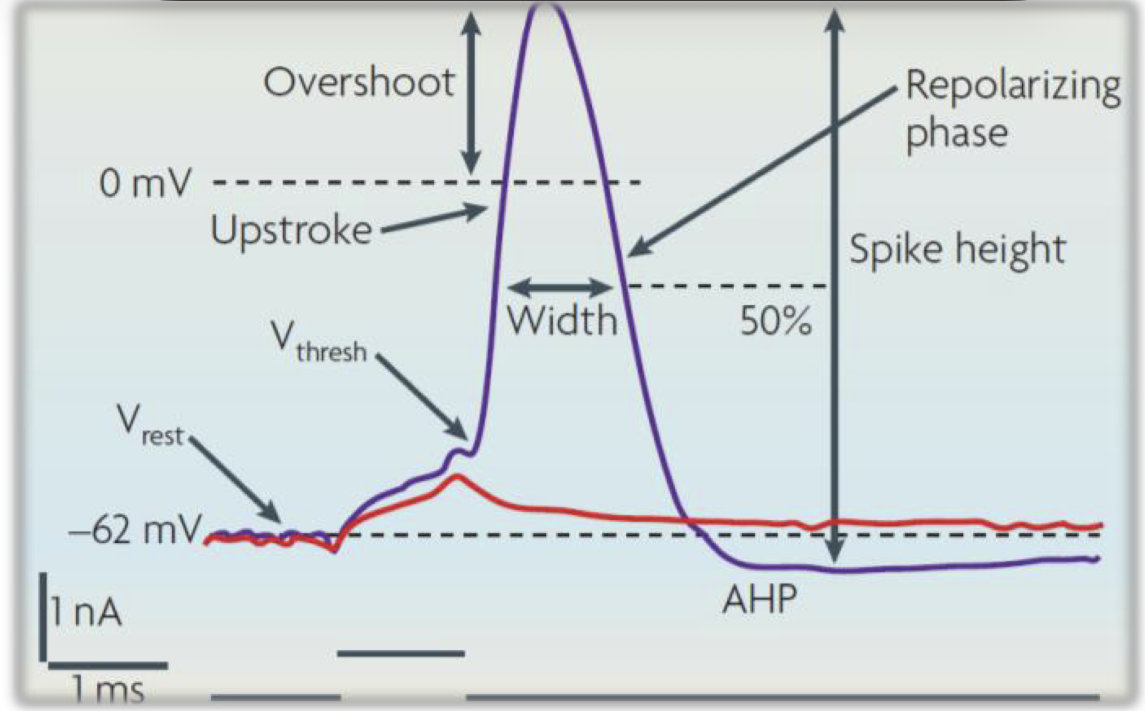
Action potentials
active voltage signals that are caused by passive voltage depolarization that reaches the AP threshold
Caused by a positive feedback loop
Regenerative signals —> don’t decay w/distance like passive voltage signals
AP propoagation
Each adjacent segment of an axon regenerates AP in the same way
Axon insulation
Speeds up passive voltage change and makes AP conduction velocity along the axon more reliable
From oligodendrocytes
Made of myelin
Nodes of ranvier
Exposed axon segments in between segments of myelin seath
Lowering capacitance speeds up
Changing voltage across a capacitor
Insulating axon does …
Decreases membrane capacitance
Increases membrane resistance by increasing membrane thickness
Increased Rm (define and effect)
Increased length constant in myelinated segments
Less charge lost across the membrane due to increased Rm—> allows voltage to remain above AP threshold for greater distances —> increases reliability
λ (length constant) equation
sqrt(rm/ra)
Rm = Membrane Resistance
Ra = Internal Resistance
Hodgkin and Huxley
discovered ionic currents and ion channels involved in generating AP
recorded action potentials and currents w/2-electrode voltage clamp method
found channel voltage dependence arose from charges in membrane that move under influence of electric field across membrane (gating currents)
Ion channels
Conductance of an ionic species across the membrane is same as membrane permeability
Ions pass through membranes via channels
Channels closed —> ions can’t pass through them —> conductance = 0
Some ion channels are gated by voltage
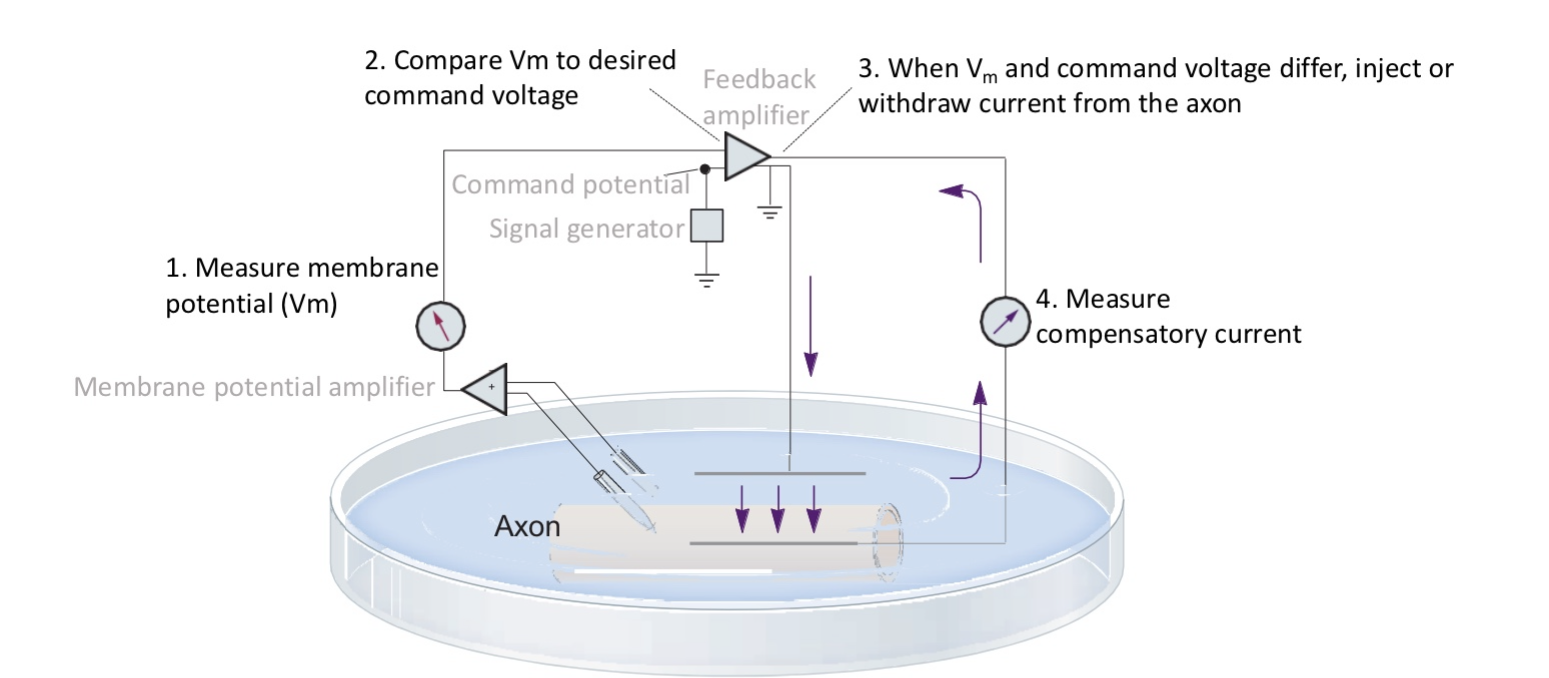
Voltage clamping squid giant axon used to…
Measure ionic currents
Current injected to maintain voltage at command voltage = & opp. to current flowing across membrane > can be used to measure ionic currents at diff. voltages
Allows you to set membrane voltage at whatever value>measure resulting flowing current
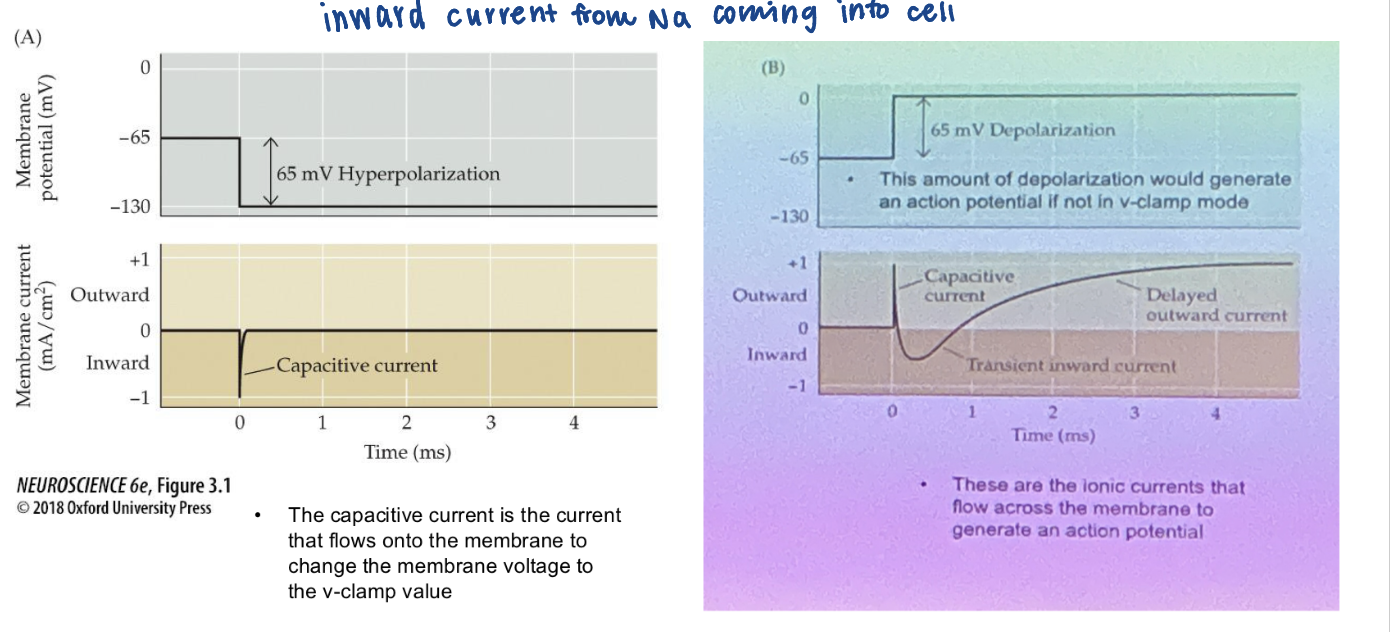
Drugs help block…
Specific ion channels to identify ionic currents responsible for action potential
Leaves just K+ current
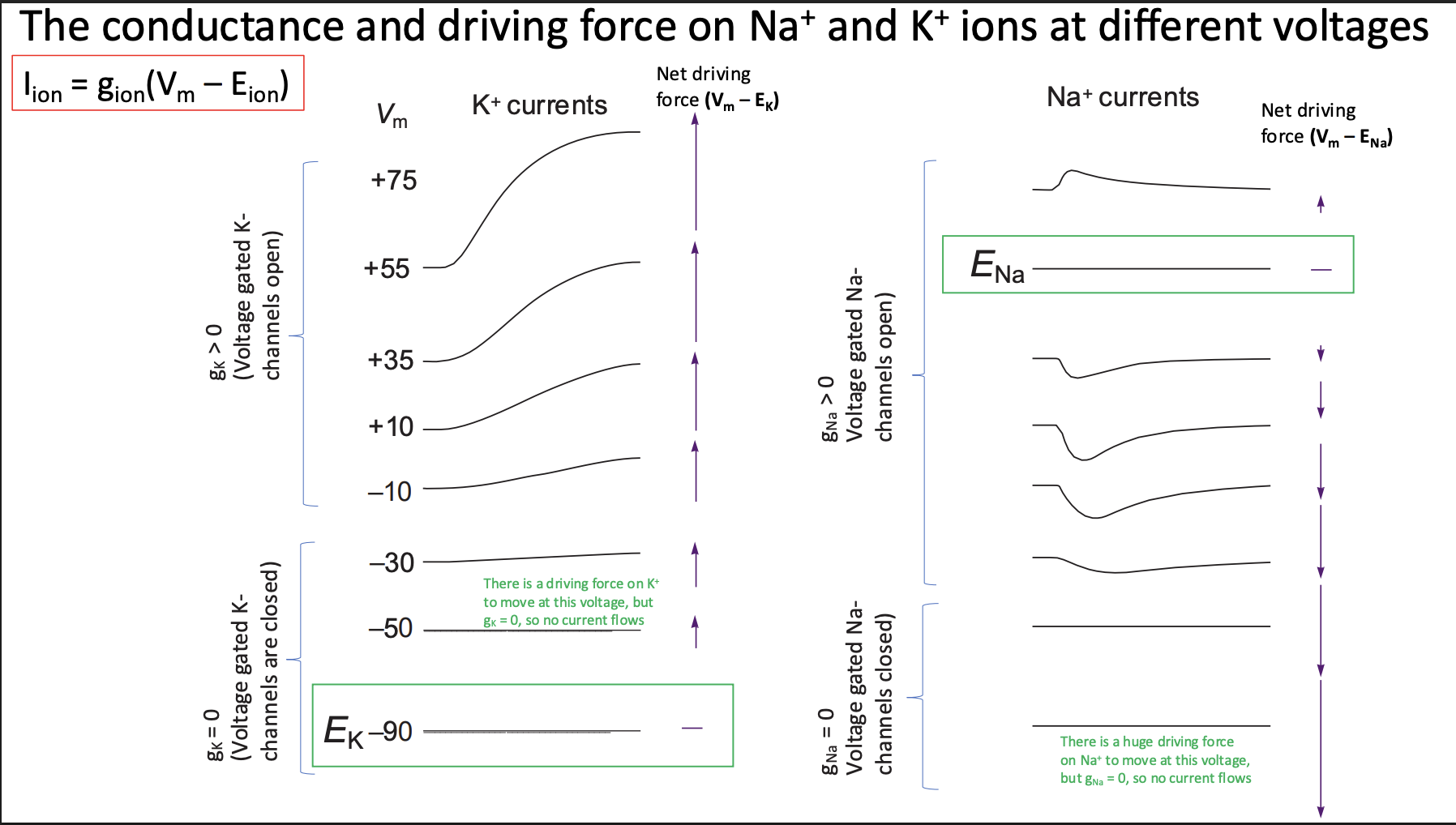
Na+ and K+ currents determined by…
Magnitude of Na+ and K+ conductance gna and gx (measure of # open Na+) and K+ channels in membrane
Electrochemical driving force on Na+ ions and K+ ions
Difference between membrane voltage & equilibrium ptl for that ion (Vm - Ena and Vm - Ek)
Ionic currents for each ion (at every membrane voltage) formula
Ik = gk(Vm - Ek)
gk = conductance
(Vm - Ek) = driving force