Chapter 8: The Role of Mental Illness in Court
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
actus reus
"guilty act"; the wrongful deed that constitutes the physical component of a crime

mens rea
criminal intent: "guilty mind"
the intention or knowledge of wrongdoing that constitutes part of a crime

unfit to stand trial
refers to an inability to conduct a defence at any stage of the proceedings on account of a person's mental disorder
the accused must have an understanding of the charges, proceedings, and potential consequences

lack intent/ ability to plead/ cognition
3 criteria delineated in the R vs. Prichard case of 1836
a key historical case for the fitness standard

understand proceedings/ understand consequences/ communicate with counsel
3 criteria for fitness standard under Bill C-30

fitness evaluation
can occur while the defendant
is in a detention, outpatient, or inpatient facility. 5 day limit but up to 60 days with extensions

medical practitioners
allowed to conduct court-ordered assessments of such aspects as fitness to stand trial and criminal responsibility in Canada
Fitness Interview Test Revised
semi-structured interview for assessing a person's competence to stand trial based on 3 psychological abilities stated in the code's fitness standard
each response rated on a 3 point scale 0-2 (severe impairment)
final decision based on 3 stages: determine mental disorder, capacity on 3 abilities, examine previous information

Competency Screening Test
A test to measure a person's competency to stand trial. The participant completes 22 sentence fragments to test their knowledge of legal proceedings, rated on 3 point scale. Measures 3 constructs: potential for constructive relationship with lawyer, understanding court proceedings, ability to emotionally cope with criminal process. A score below 20 indicates the need for further evaluation

Competency to Stand Trial Assessment Instrument
designed to accompany the CST in that the CAI is a semi-structured interview and constitutes a comprehensive competency evaluation. The CAI assesses 13 functions corresponding to a defendant's ability to participate in the criminal process on behalf of their best interests with 2-3 statements followed by questions for each with follow-up questions if the response is unclear
scores for each function are assessed overall

Interdisciplinary Fitness Interview Revised
semi-structured interview measuring 3 areas of competency: functional memory, appropriate relationship with attorney, and understanding of the justice system.
2 sections: Current Clinical Condition & Psycho-Legal abilities with subsections under each
ratings for each scale rank from 0-2

MacArthur Competence Assessment Tool- Criminal Adjudication
a structured interview containing 22 items that assess competencies in three areas:
• Factual understanding of the legal system and the adjudication process
• Reasoning ability
• Understanding of own legal situation and circumstances
scored from 0-2

single/ unemployed/ living alone
3 common characteristics of defendants referred for fitness evaluations

psychosis/ unemployment/ previous hospitalization
meta-analysis reviewing the competency to stand trial research, Pirelli, Gottdiener, and Zapf (2011)
3 qualities of defendants found unfit

medication
the most common form of treatment used to restore fitness

prima facie case
Case in which the Crown
prosecutor must prove there is
sufficient evidence to bring the
case to trial. Must be made every 2 years or whenever the defendant requests it when unfit cases are up for review

insanity
a legal term describing one's inability to be responsible for one's action due to the condition of the mind. Removes the responsibility for performing a particular act because of uncontrollable impulses or delusions, such as hearing voices.

McNaughton test
Five critical elements emerged from this historic case with 3 specific to the insanity defences of today
1. A defendant must be found to be suffering from a defect of reason/disease of the
mind.
2. A defendant must not know the nature and quality of the act they are performing.
3. A defendant must not know that what they were doing is wrong.

not criminally responsible on account of mental disorder
is a court verdict stating that a person has committed an illegal act but, at the time, was suffering from a serious mental illness that rendered him/her incapable of appreciating the nature, quality and consequences of the act.
Not guilty by reason of insanity was changed to this in 1992

review boards
legal bodies were mandated to oversee the care and disposition of defendants found unfit or NCRMD. They were required to review each unfit and NCRMD case every year.

Rogers Criminal Responsibility Assessment Scales
Measures designed to assess criminal responsibility and detect malingering in cases where the defendant is considering raising or has raised an insanity defense.

patient reliability/ organicity/ psychopathology/ cognitive control/ behavioural control
5 scales of R-CRAS
Each scale has 30 items scored from 0-6 (severe)
No cutoff score, interpreted by clinician. Used to standardize evaluations

absolute discharge
a release without conditions, with no criminal record

conditional discharge
releasing a convicted offender under certain terms, and erasing the criminal record after three years if the terms are met. Failure to meet the conditions imposed with a conditional discharge may result in the defendant being incarcerated or sent to a psychiatric facility.

capping
Notion introduced through Bill C-30 where there is a maximum period of time a person with a mental illness could be affected by their disposition
ex. 10 years for violent offence, same as maximum prison term
Can be involuntarily committed if still perceived to be dangerous

public safety/ mental state/ reintegration/ needs
4 main criteria considered when court/ review board is deciding on a disposition

dynamic risk factors
Attributes of the offender that can be altered through intervention, including level of education, employment skills, addiction issues, and cognitive thinking abilities, among others.
Stronger relationship to decision to detain and are considered by review boards

automatism
refers to unconscious, involuntary behaviour; that is, the person committing the act is not aware of what they are doing
two types: noninsane (external factor: not guilty) insane (mental disorder: NCRMD)

psychiatric assessments/ severity of trigger/ history
3 factors considered by a Judge re: automatism in the first step
Second step: insane/ noninsane automatism judgement

TBI/ stroke/ hypoglycemia/ Carbon monoxide poisoning/ sleepwalking/ involuntary intoxication/ dissociation
6 circumstances listed in the textbook where courts have recognized defences of noninsane automatism

substance use / ASPD/ anxiety
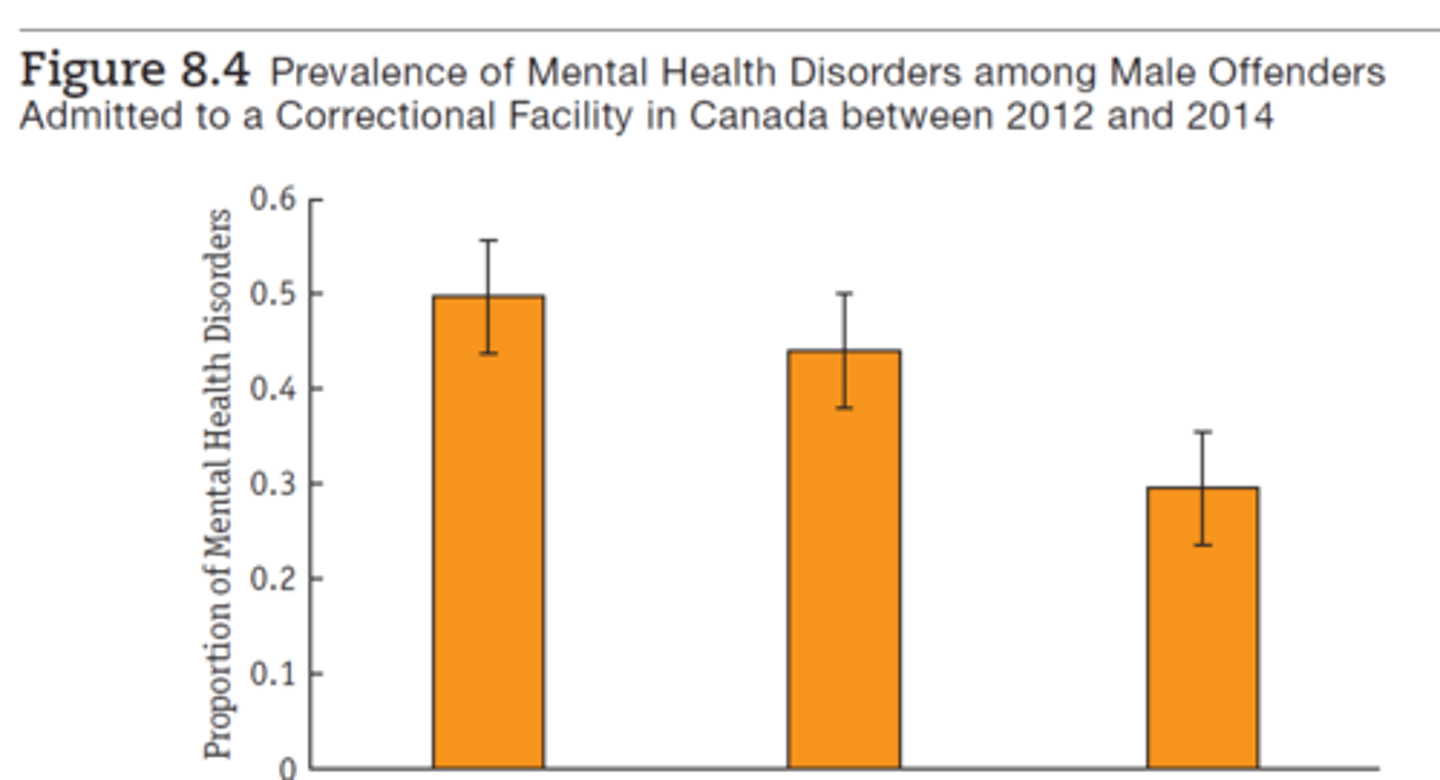
3 most common forms of mental health disorders found among Male Offenders Admitted to a Correctional Facility in Canada between 2012 and 2014
mandatory supervision
The release of an eligible inmate sentenced to the Correctional Institutions Division (CID) so that the inmate may serve the remainder of the inmate's sentence not on Parole but under the supervision of the Parole Division. Occurs after serving 2/3 of sentence
Offenders with mental disorders more likely to be conditionally released this way

wasn't
Bonta and colleagues (2014) found that having a mental disorder (was/ wasn't) predictive of recidivism.

wasn't
having psychosis (was/ wasn't) a useful predictor of recidivism

age/ days hospitalized/ previous offences
3 best predicting offending factors of reoffending (Phillips et al., 2005)
community treatment order
Sentence that allows the mentally ill offender to live in the community, with the stipulation that the person will agree to treatment or detention in the event that his or her condition deteriorates

diversion
A decision not to prosecute, but rather have an offender undergo an educational or community-service program. Also an option for the courts dealing with offenders with mental illness who are facing minor charges. The court can divert the offender directly into a treatment program rather than have them go through the court process

mental health court
court where the judges have special training and use non adversarial procedures that mandate treatment and rehabilitation rather than incarceration if a person with mental illness is found guilty of a crime
Main objectives:
offer alternative consequences
evaluate fitness
ensure treatment
decrease recidivism
Effectiveness:
more likely to connect to services
more satisfaction/ perceptions of fairness/ increased confidence in justice
Medium effect size for improving MH outcomes: access to services, reduced recidivism, decreased sentence length
completing treatment important

release plan
a plan setting out the residential, educational, and treatment arrangements (e.g., provide clothes, find housing, and select treatment options) once the accused is in
the community

mood/ personality disorders
Ennis and colleagues (2016) examined gender differences in mental illness and crime. Women had higher rates of these 2 types of disorders

psychotic disorders
Ennis and colleagues (2016) examined gender differences in mental illness and crime. Men had higher rates of these type of disorders

poverty
Inability to meet basic needs for food, clothing, and shelter.
Considered the leading cause of mental illness
23-67% homeless pop. have MI
70-90% those with SMI are unemployed

substance use
80% of inmates in provincial jails deal with this mental health problem

antisocial personality disorder
only diagnosis associated with general or violent recidivism
Public Safety Canada: Bonta et al. (2013)

drug treatment court
a problem-solving court with a specialized docket of drug offenses. The court incorporates intensive judicial supervision of drug offenders, mandatory drug treatment, and a rehabilitation program providing vocational, education, family, and medical services.
Focus on diversion from incarceration to treatment
non-custodial sentence
A sentence that does not involve imprisonment.
common outcome of mental health courts if charges are not dropped. In this case, adherence to treatment is a condition of release

high dropout
a major problem with drug treatment courts that impacts its effectiveness, especially when compared to mental health courts

mens rea
this necessary component of guilt is related to criminal responsibility
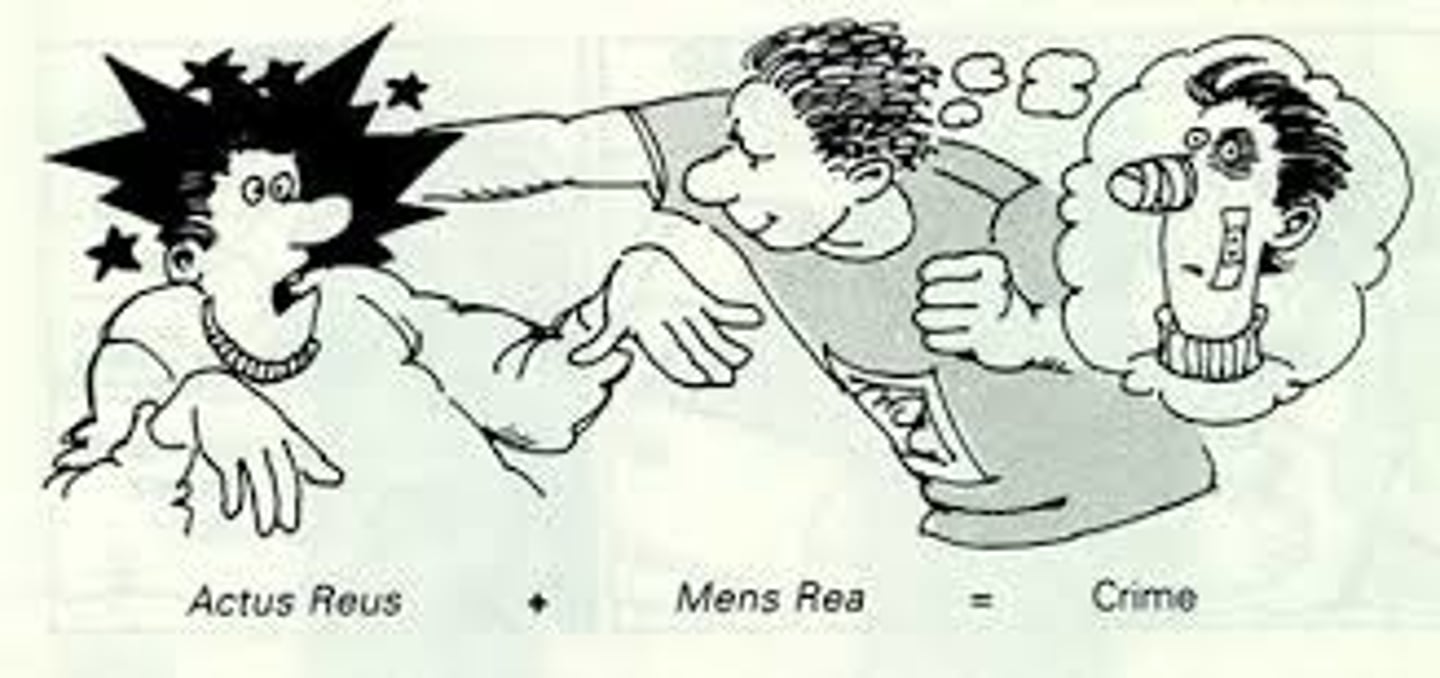

actus reus
this necessary component of guilt is associated with fitness to stand trial

at crime/ interrogation/ during statements/ represent self/ trial/ sentencing
times at which fitness to stand trial can be brought up as an issue

unfit to stand trial
Bisesar & Van Zuiden were found as this

respect for system/ fairness
2 reasons why defendants should be fit to stand trial in a Common Law system
waitlists/ time consuming/ ability to cooperate
3 reasons why fitness assessments are often delayed as discussed in lecture
Average wait: 3 weeks
88% conducted in inpatient facilities

male/ middle adulthood/ psychosis/ single/ unemployed/ minor offence
5 characteristics of offenders commonly found UST

stay of charges
case is put on hold with no conditions on the accused unless they commit another offence in the next year, then the charges return

45
If found unfit, reassessment occurs in ___-90 days (max)
If still unfit, review board is used for annual assessment & prima facie case every 2 years

civil commitment
a legal process by which an individual can be forced to undergo mental health treatment if seen as a risk to self/ others or they have a serious physical/ mental deterioration
aka involuntary hospitalization

criminal commitment
legal procedure by which a person found NCRMD and must be confined in a psychiatric hospital

Tim's law
proposed legislation to prevent a person found not criminally responsible of a crime from being released into the community (mandatory life sentence). Did not pass, violates Charter of Rights & Freedoms

annual review/ potentially held indefinitely
2 problems with NCRMD and why many defendants who could/should use this defiance are less likely to do so

trespassing
type of crimes typically associated with NCRMD absolute discharge

detention
most common outcome for NCRMD (51.7%)
schizophrenia/ affective
Approx 75% of those found NCRMD have one of these types of disorders

high risk
designation made under Bill C-54 that allows judges to determine if NCRMD offenders are likely to reoffend with no requirement for assessment
When this occurs, review boards only meet every 3 years, delaying reintegration by 3x

infrequent use/ lower recidivism/ weak link with violence/ low risk to public
4 points brought up in class that contest the necessity of Bill C-54's amendments to NCRMD re: high risk offenders

stigma/ deter from treatment/ diversion to incarceration
3 real dangers of the amendments to NCRMD
