BIO 142 - HEART
1/92
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
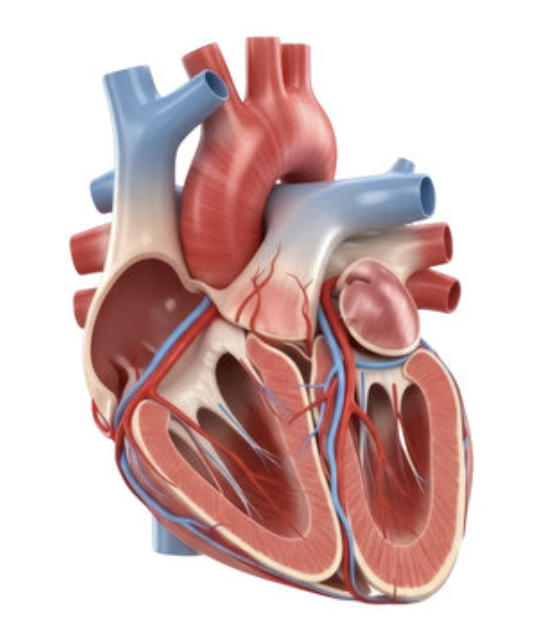
ascending aorta
what is outlined in pink? (largest artery in the body)
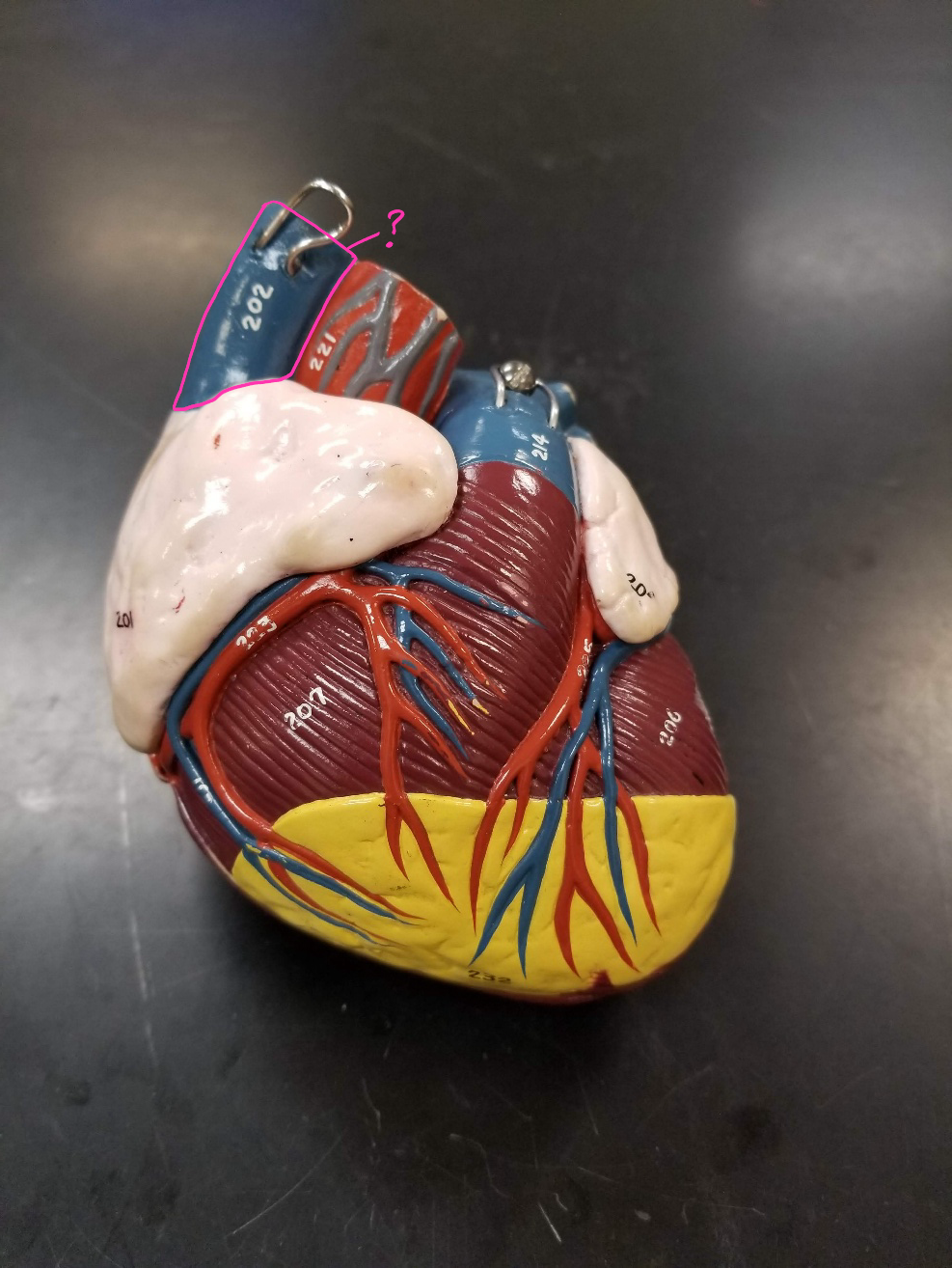
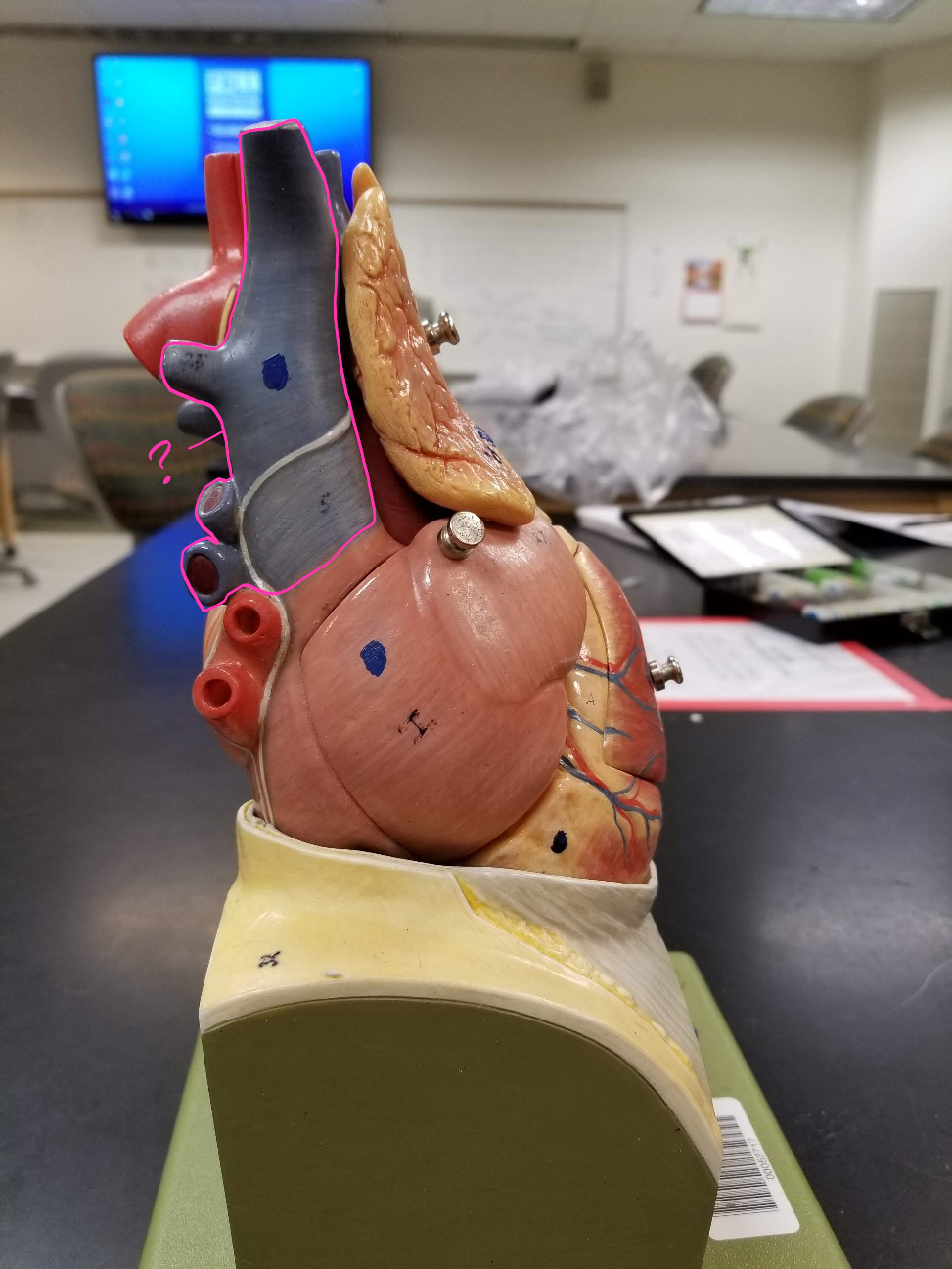
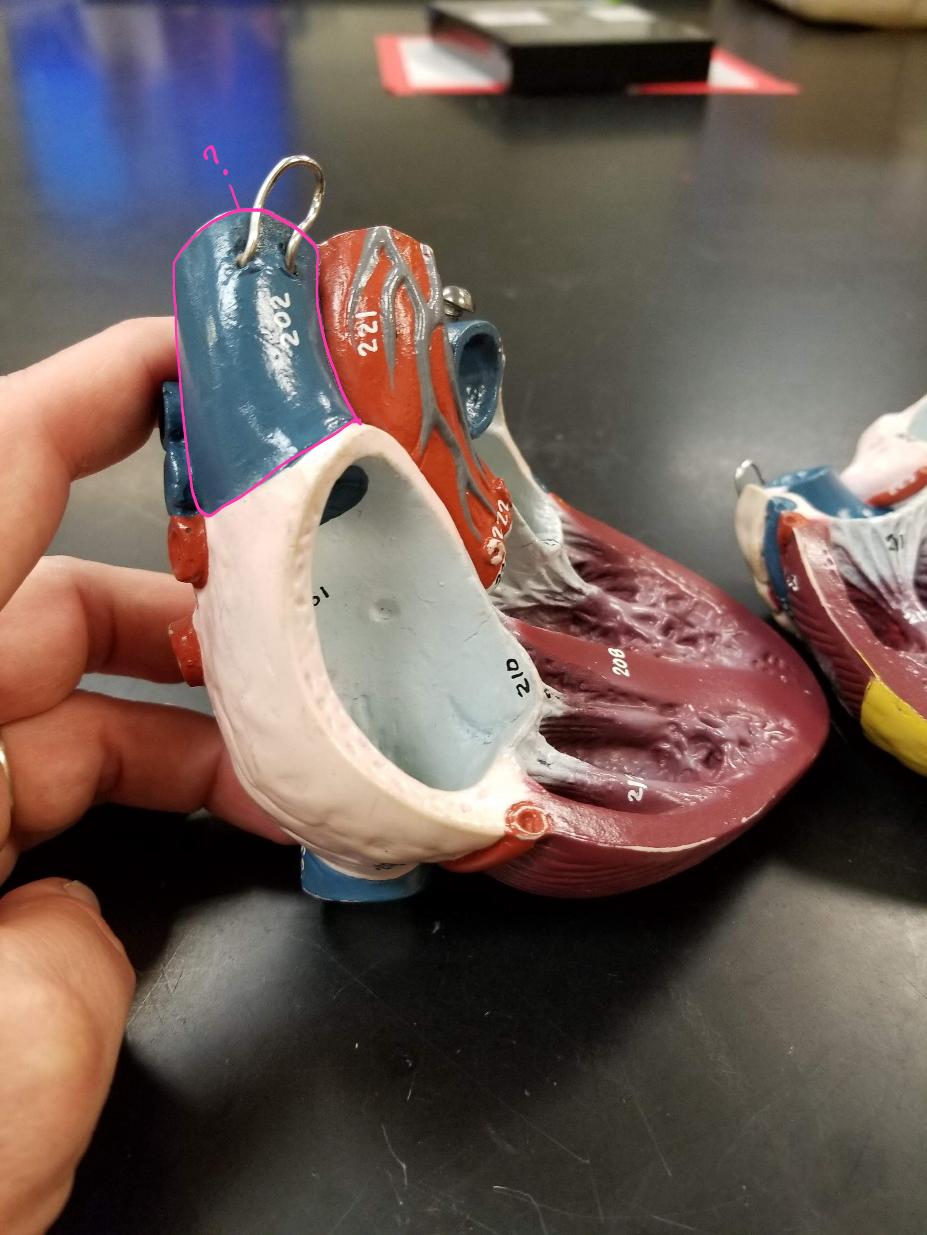
superior vena cava
what is outlined in pink? (transports blood from the upper portion of the body to the heart)
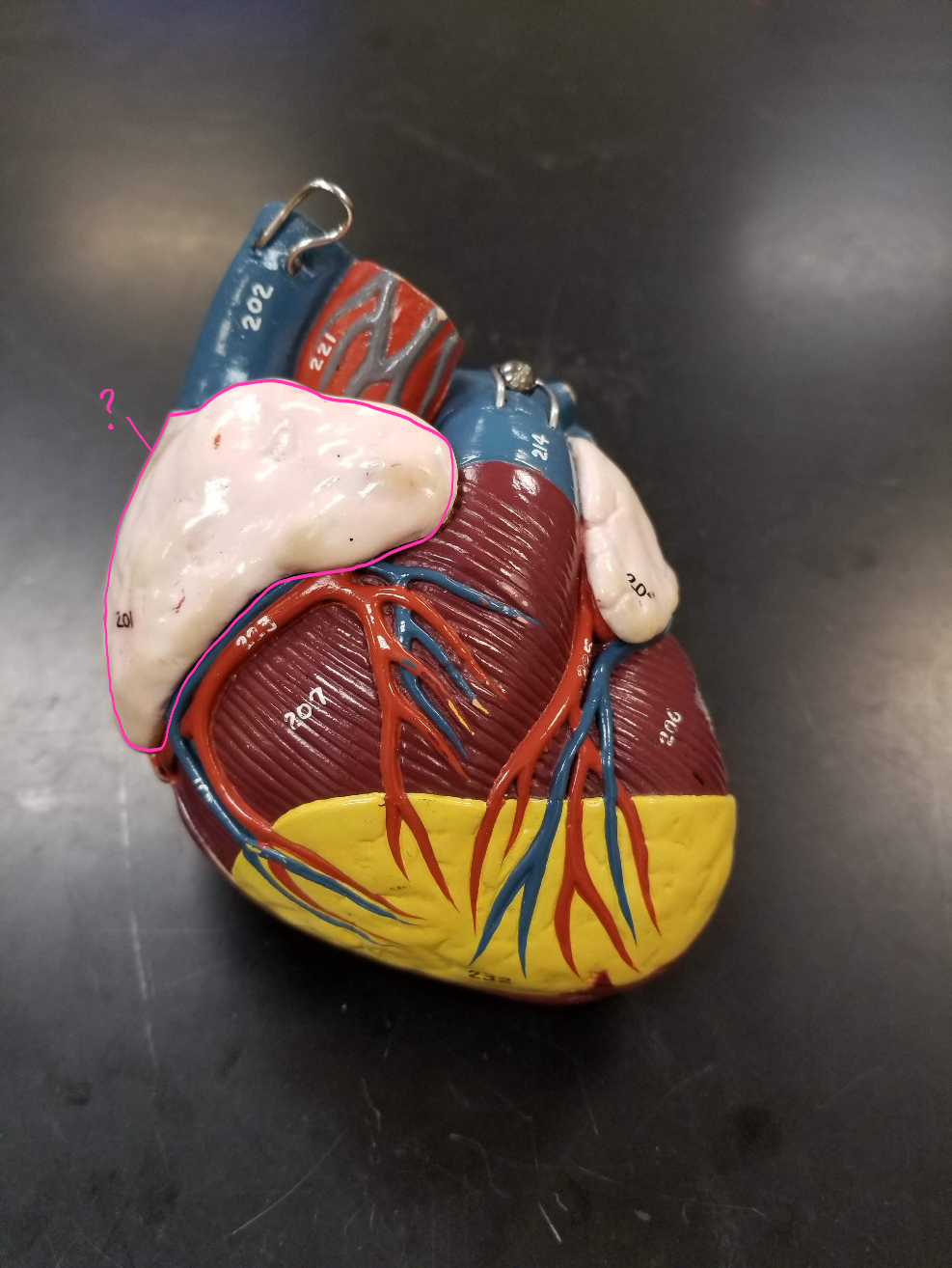
right atrium
what is outlined in pink? (receives deoxygenated blood from the body)
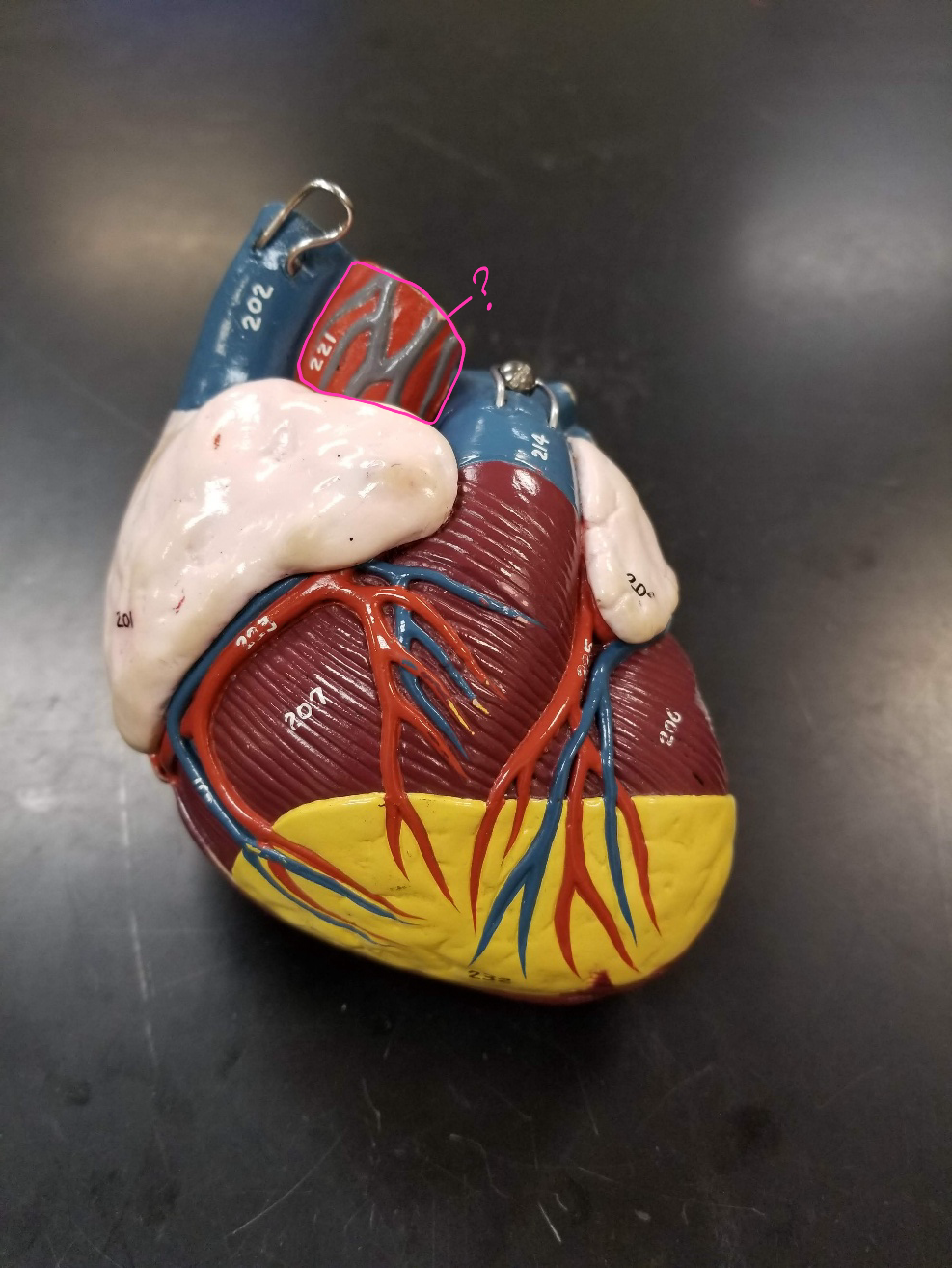
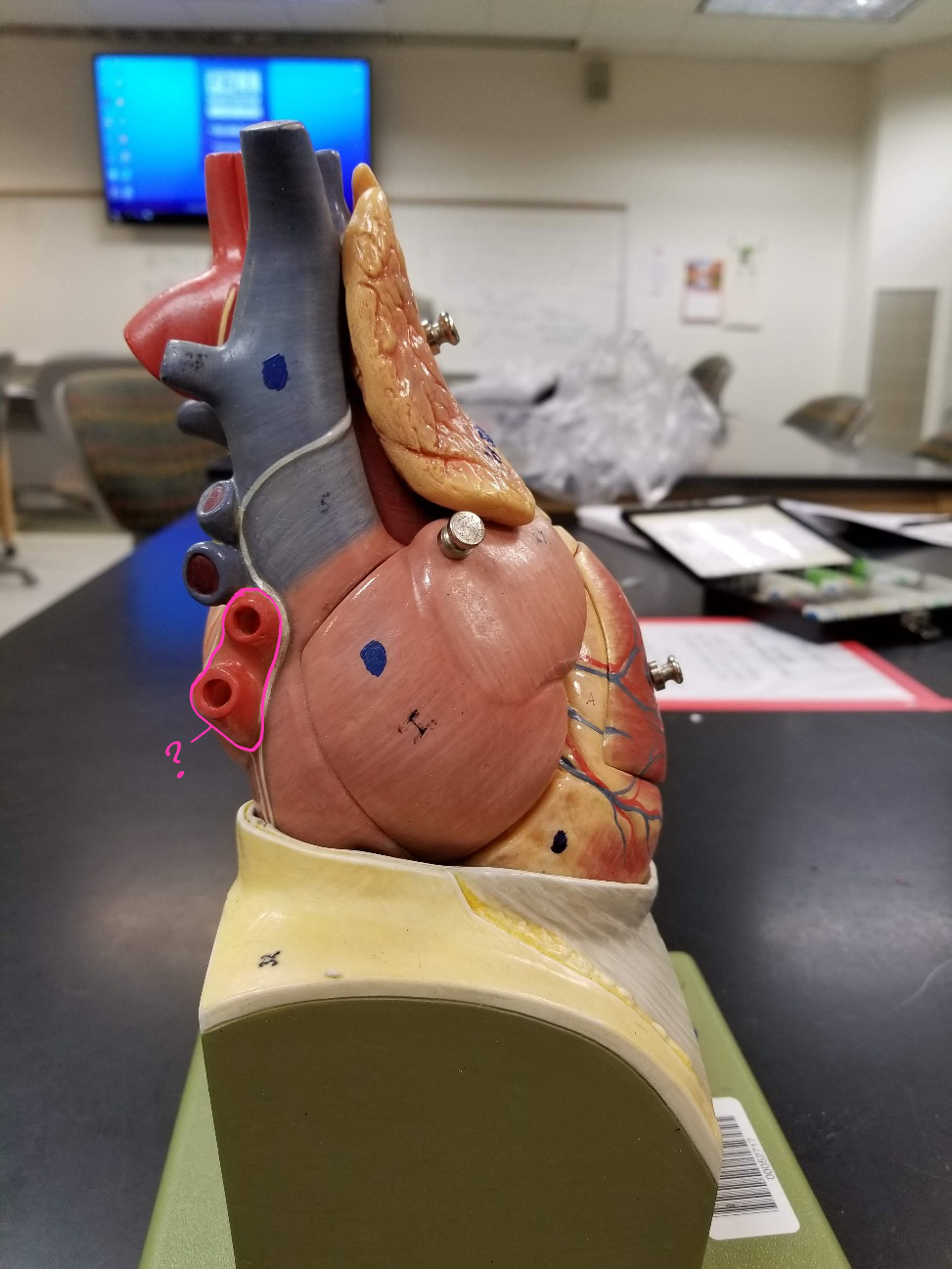
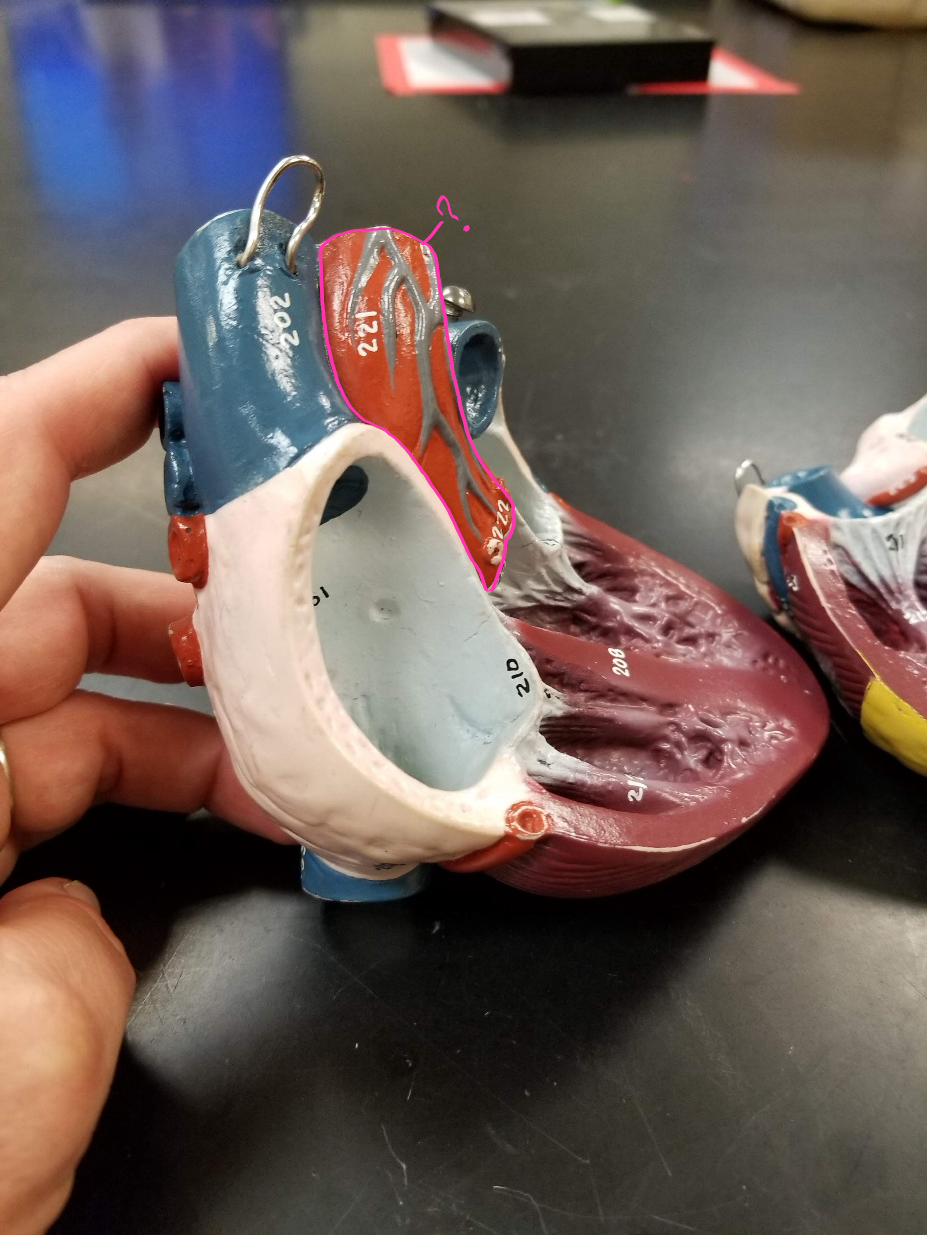
right coronary artery
what is outlined in pink?
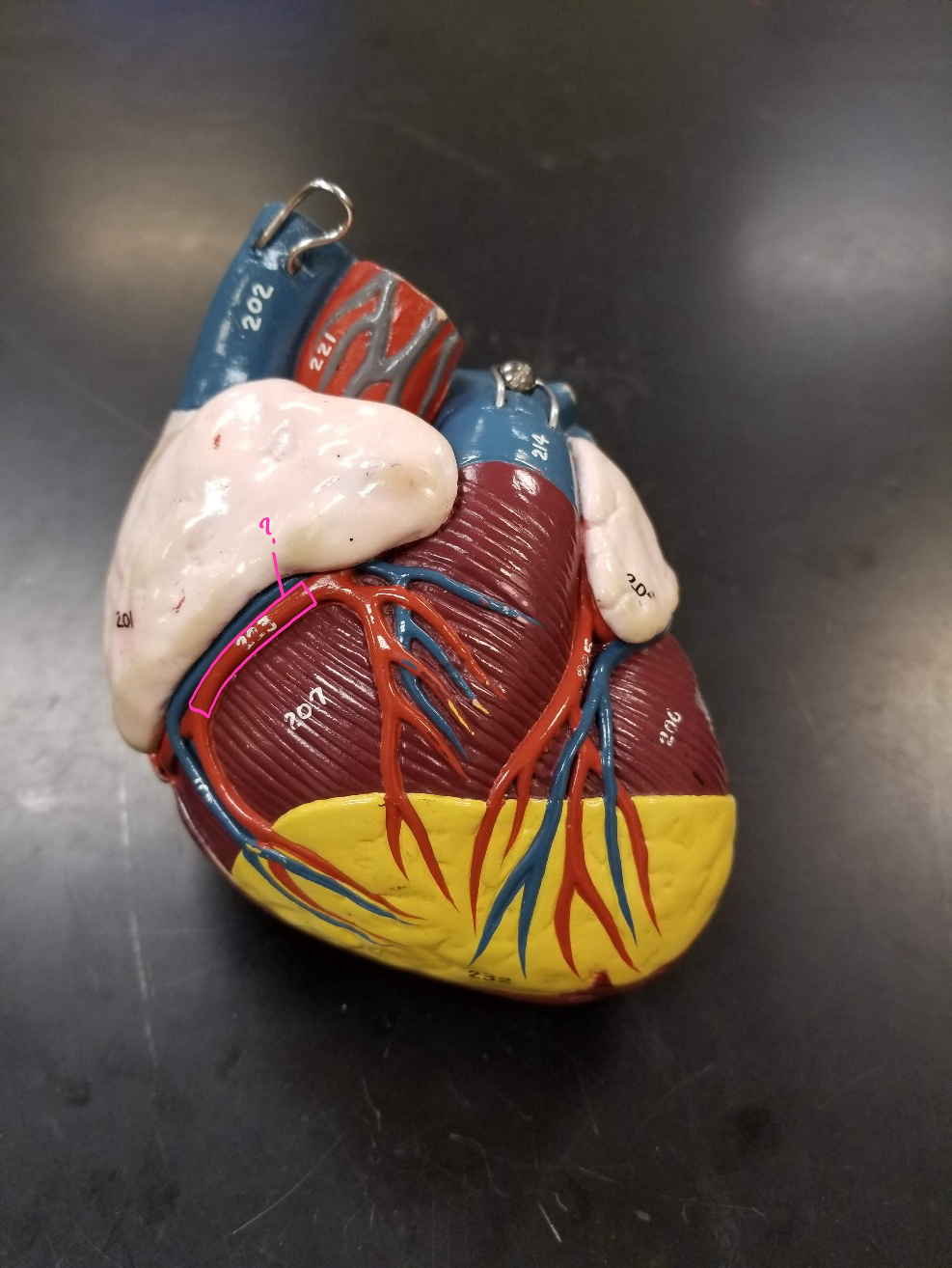
small cardiac vein
what is outlined in pink?
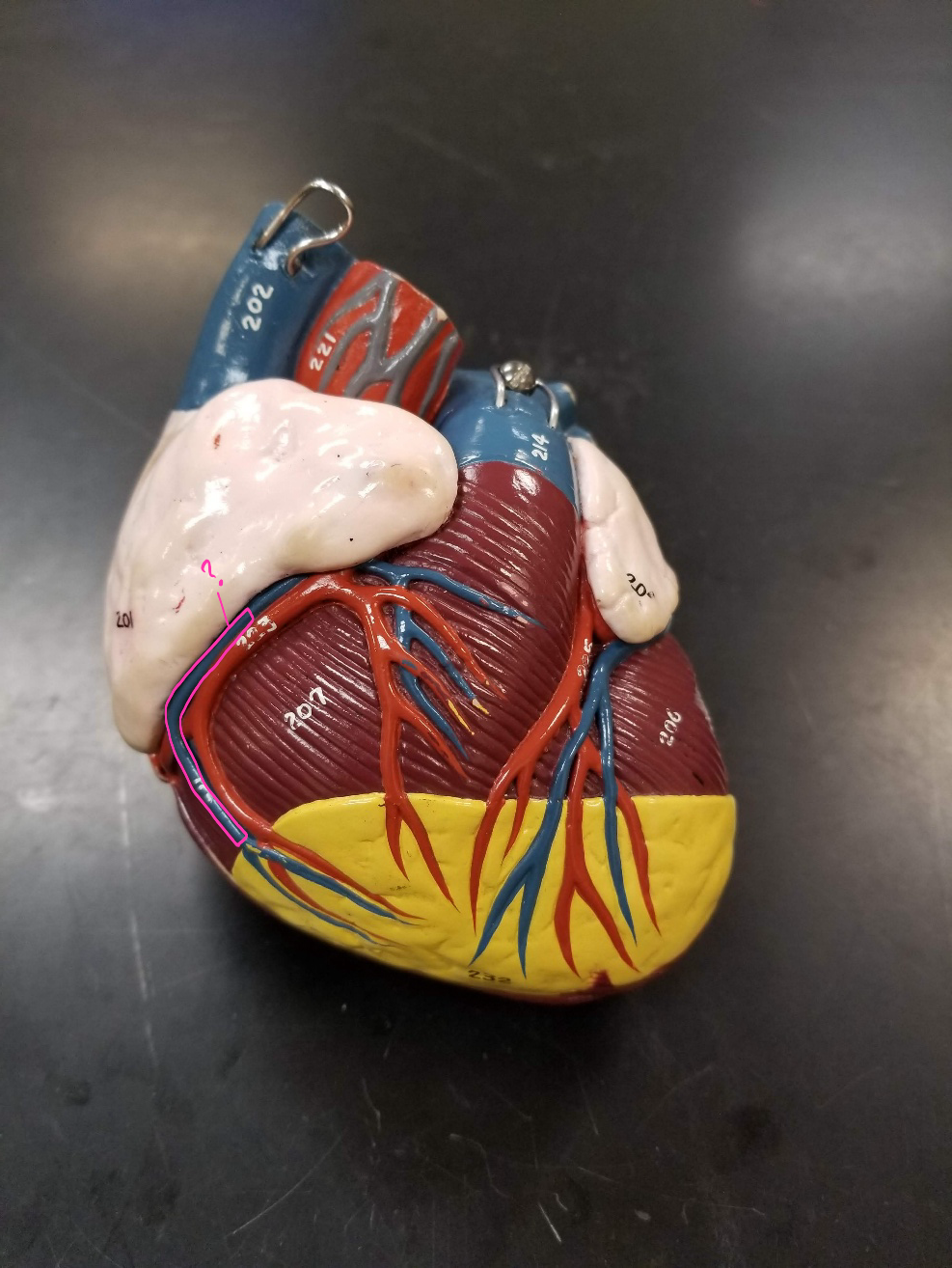
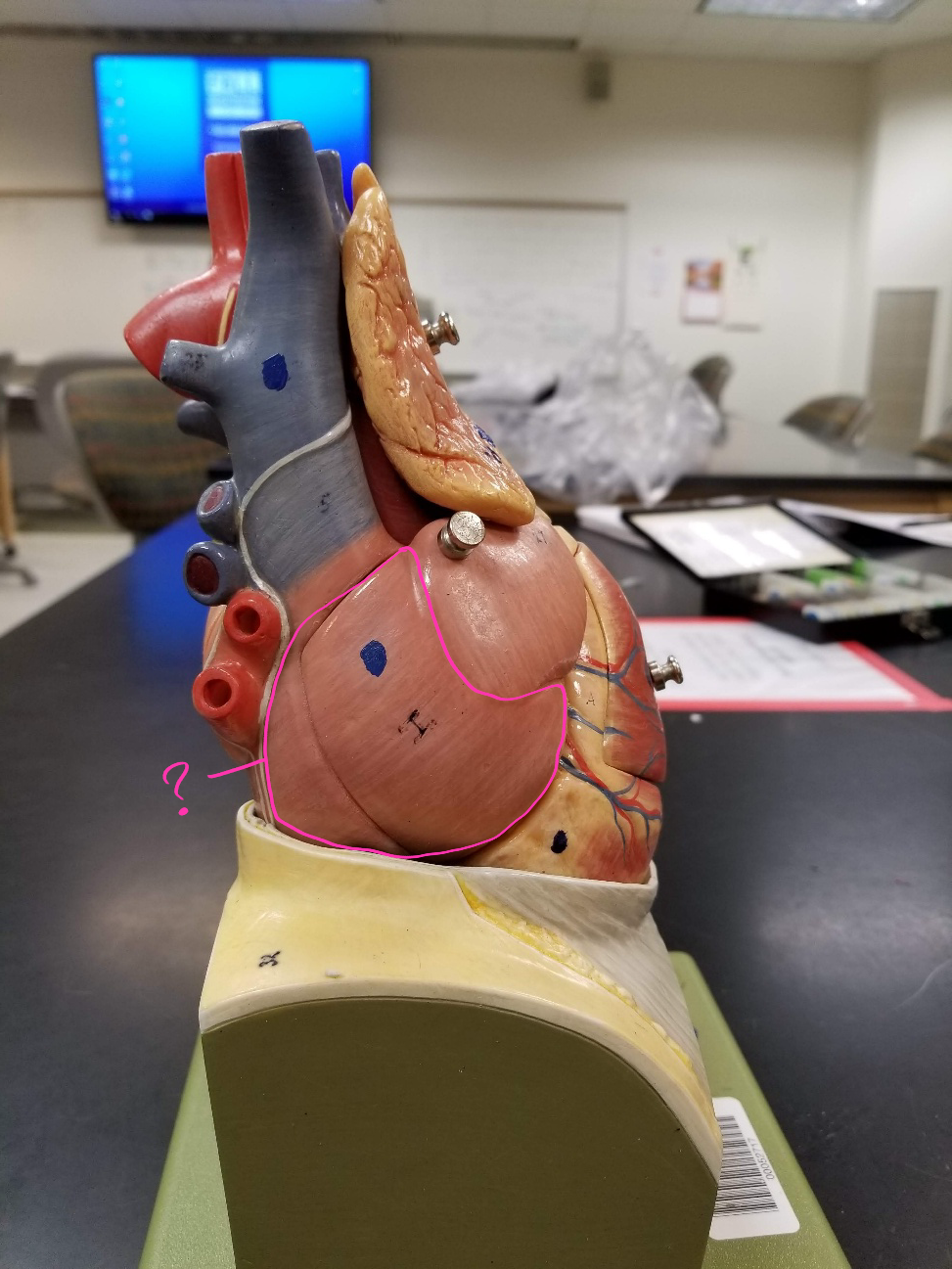
right ventricle
what is outlined in pink? (pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs)
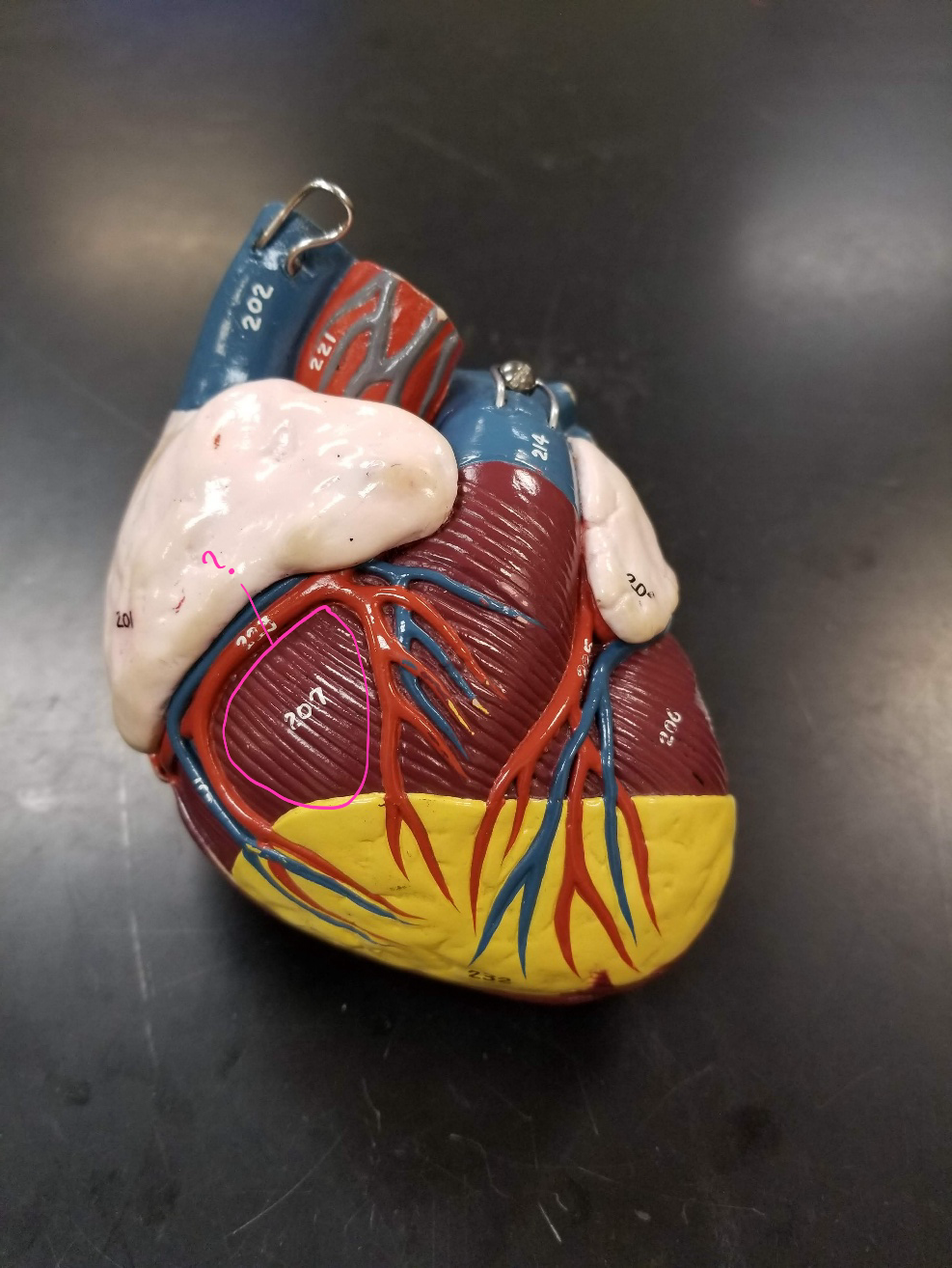
pulmonary trunk
what is outlined in pink? (carries blood from the right ventricle to the lungs)
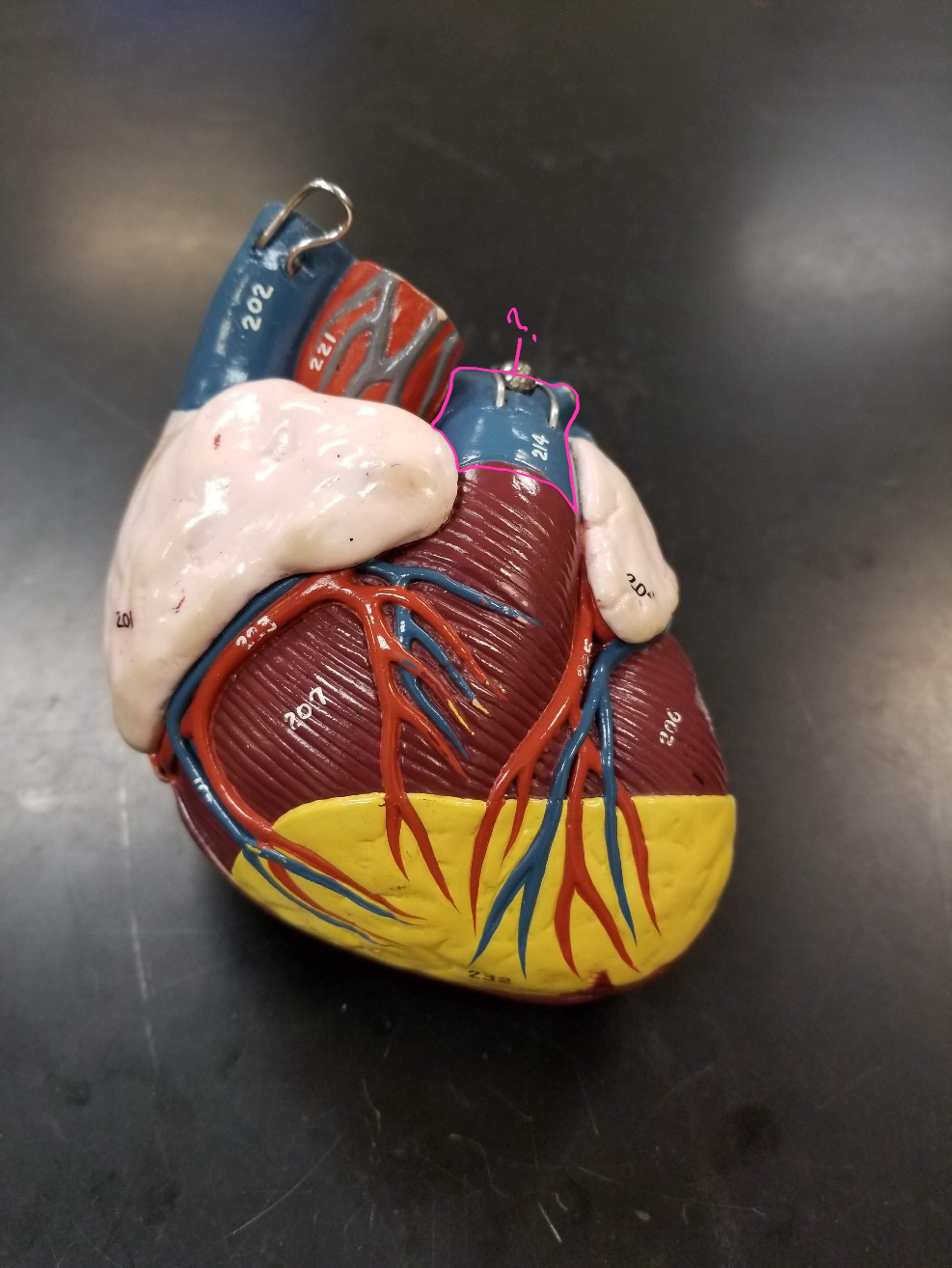
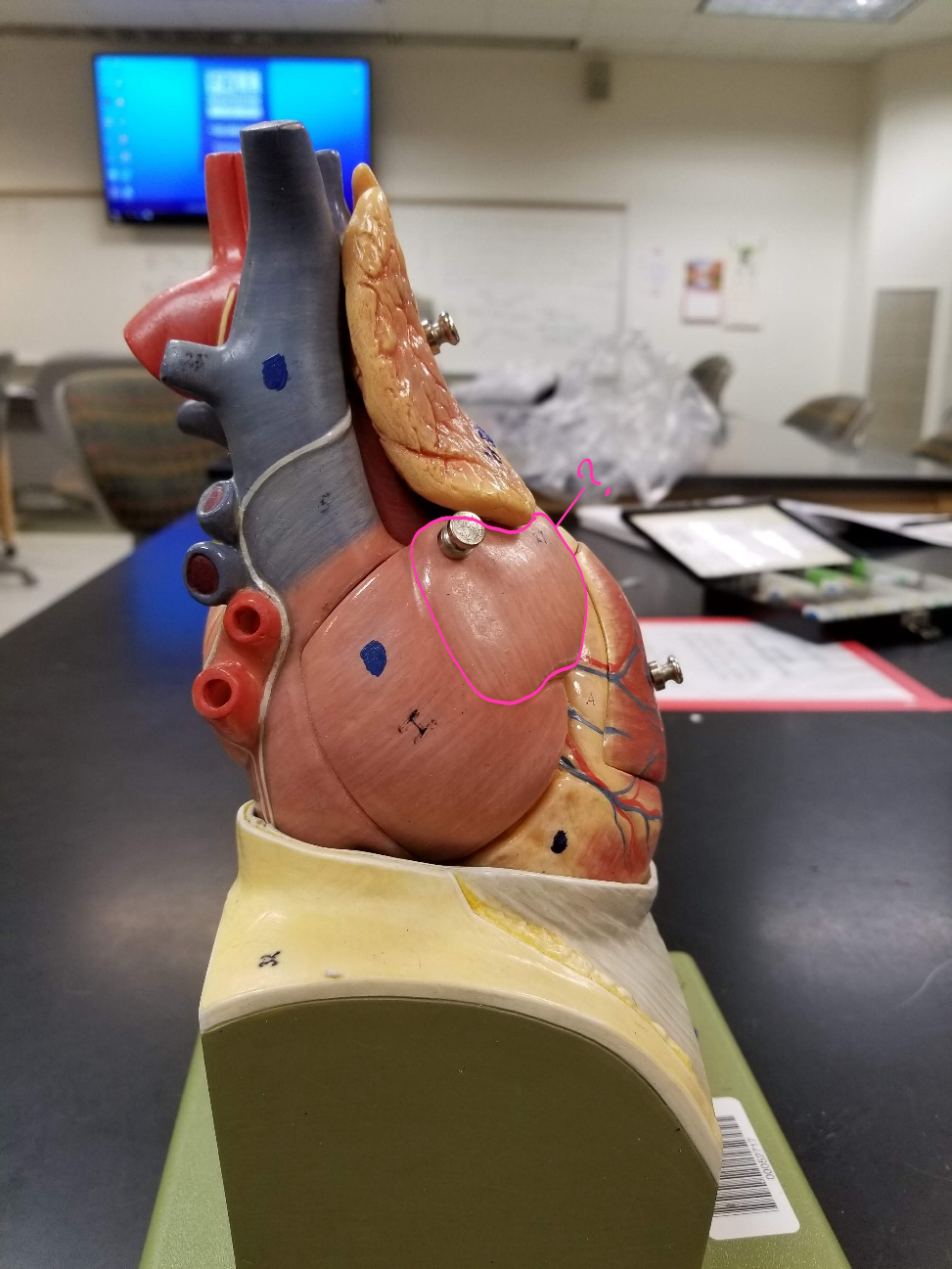
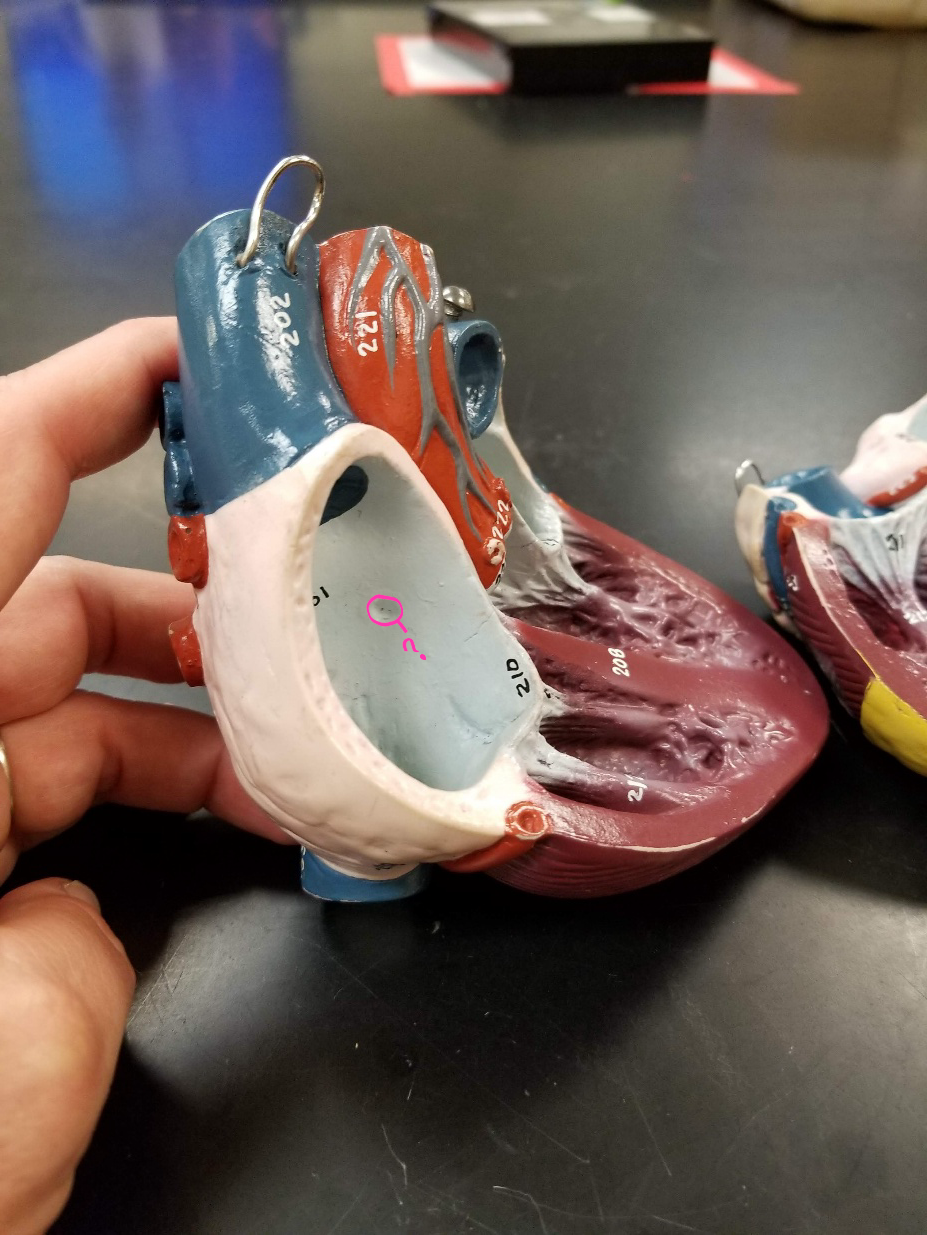
left atrium
what is outlined in pink?
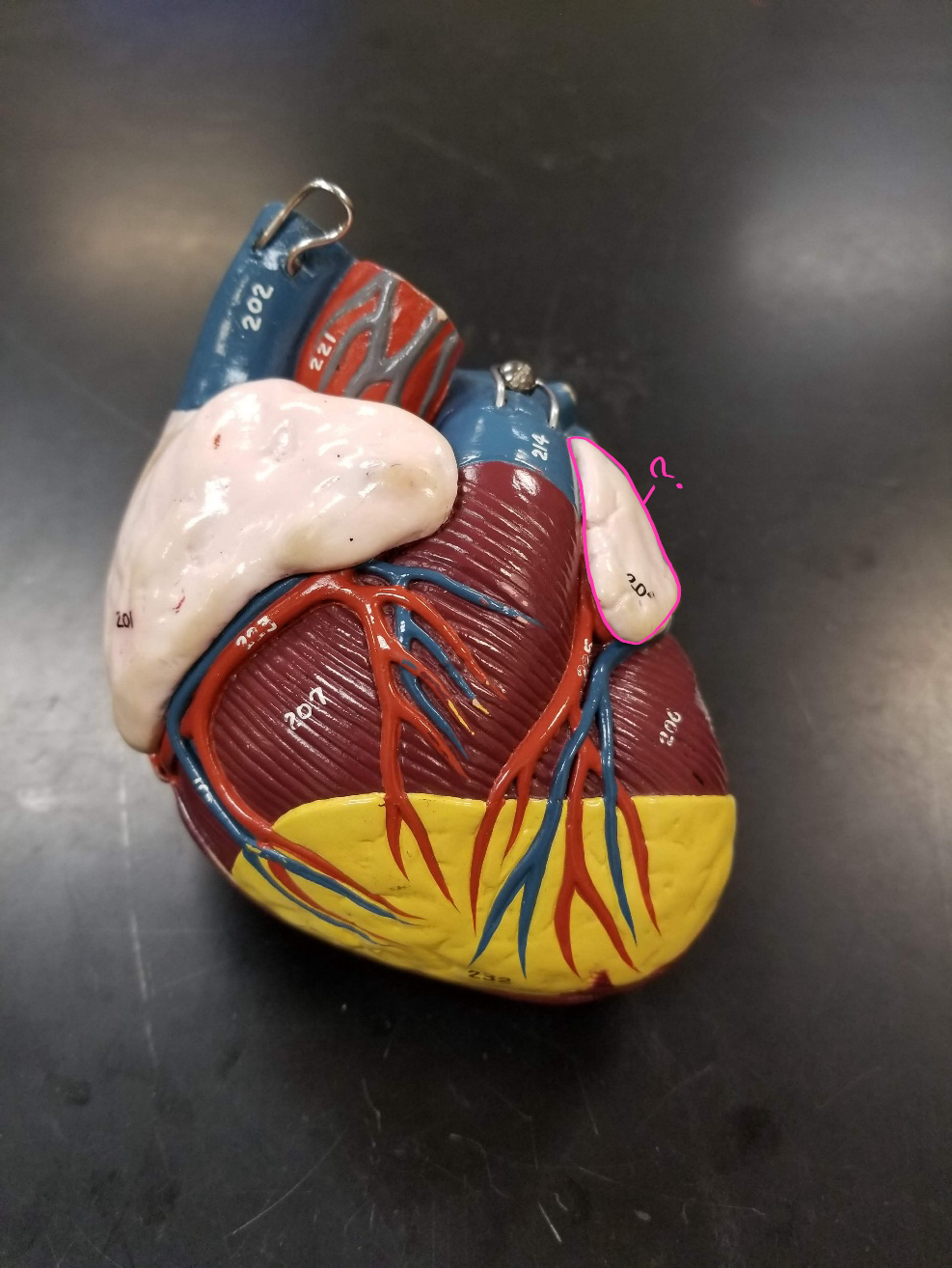
circumflex artery
what is outlined in pink?
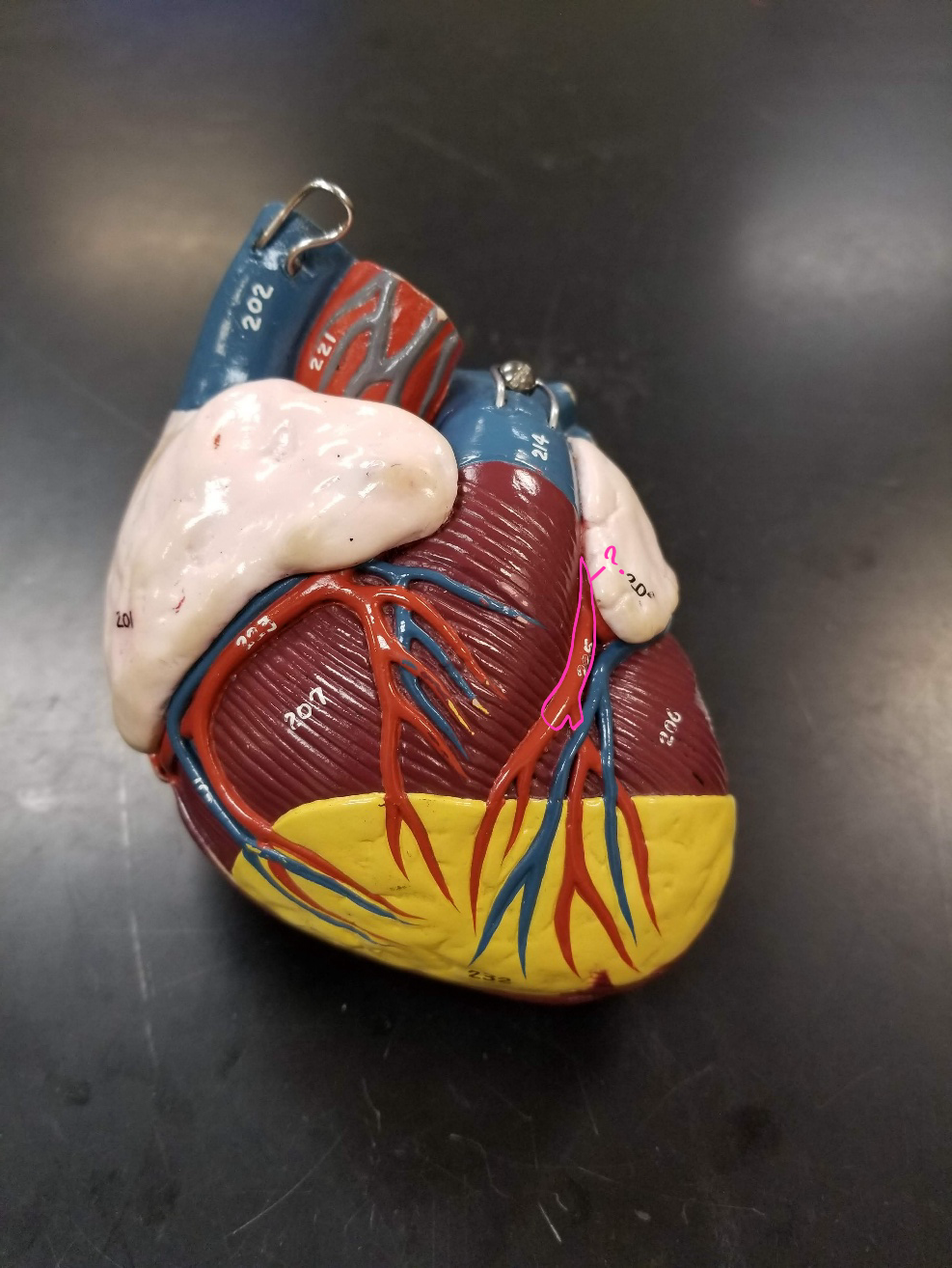
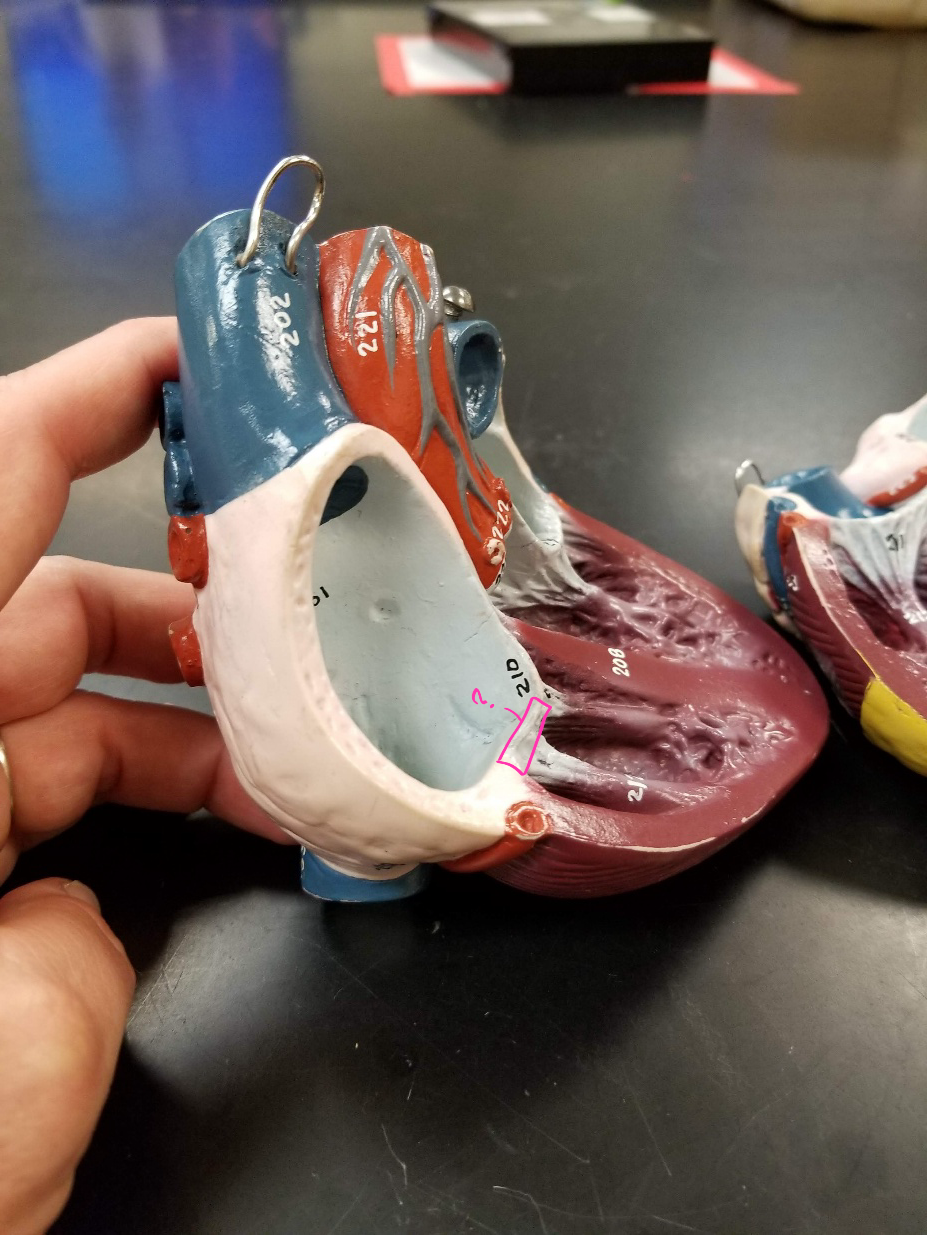
great cardiac vein
what is outlined in pink?
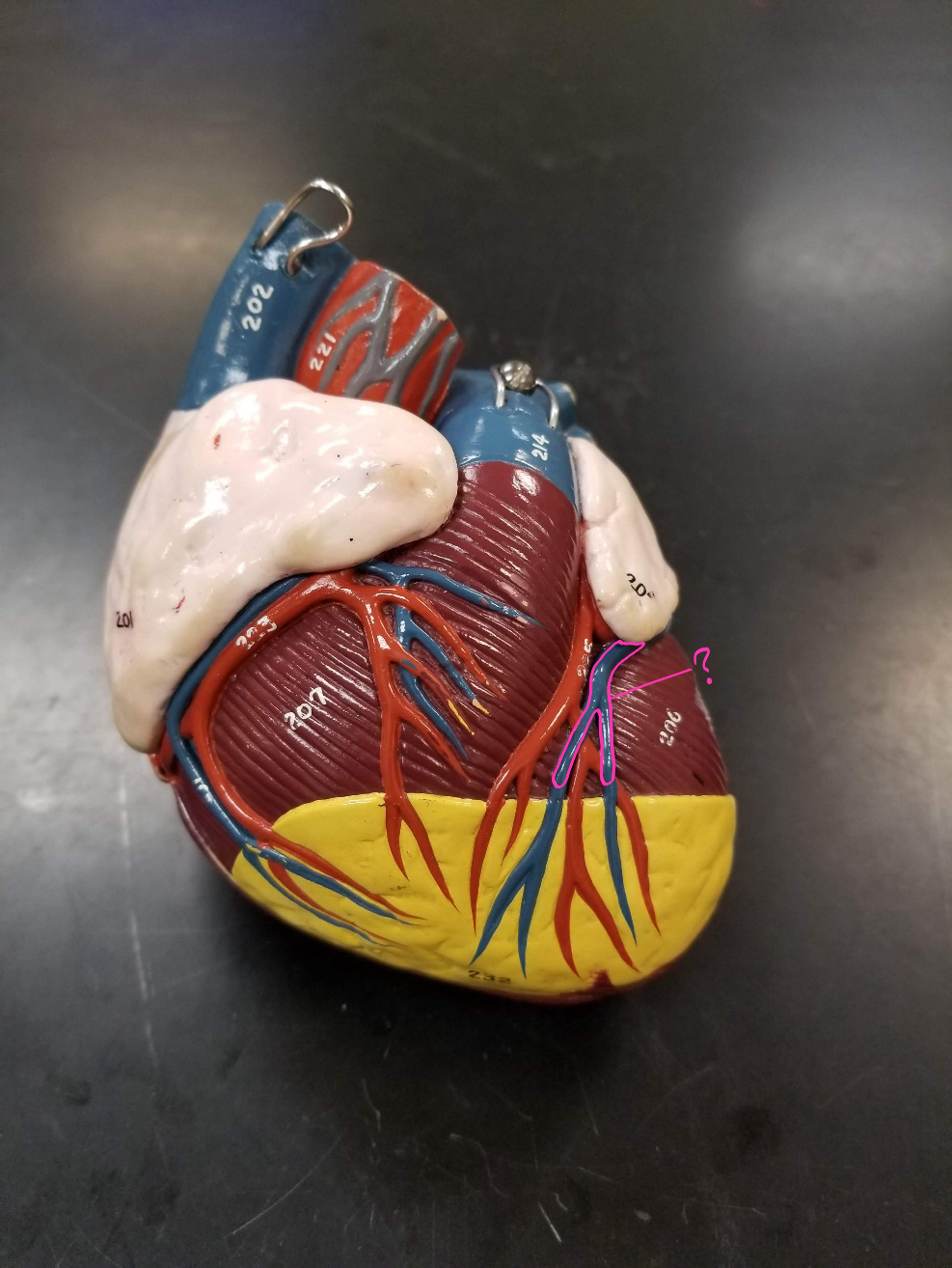
left ventricle
what is outlined in pink? (pumps oxygenated blood to the body)
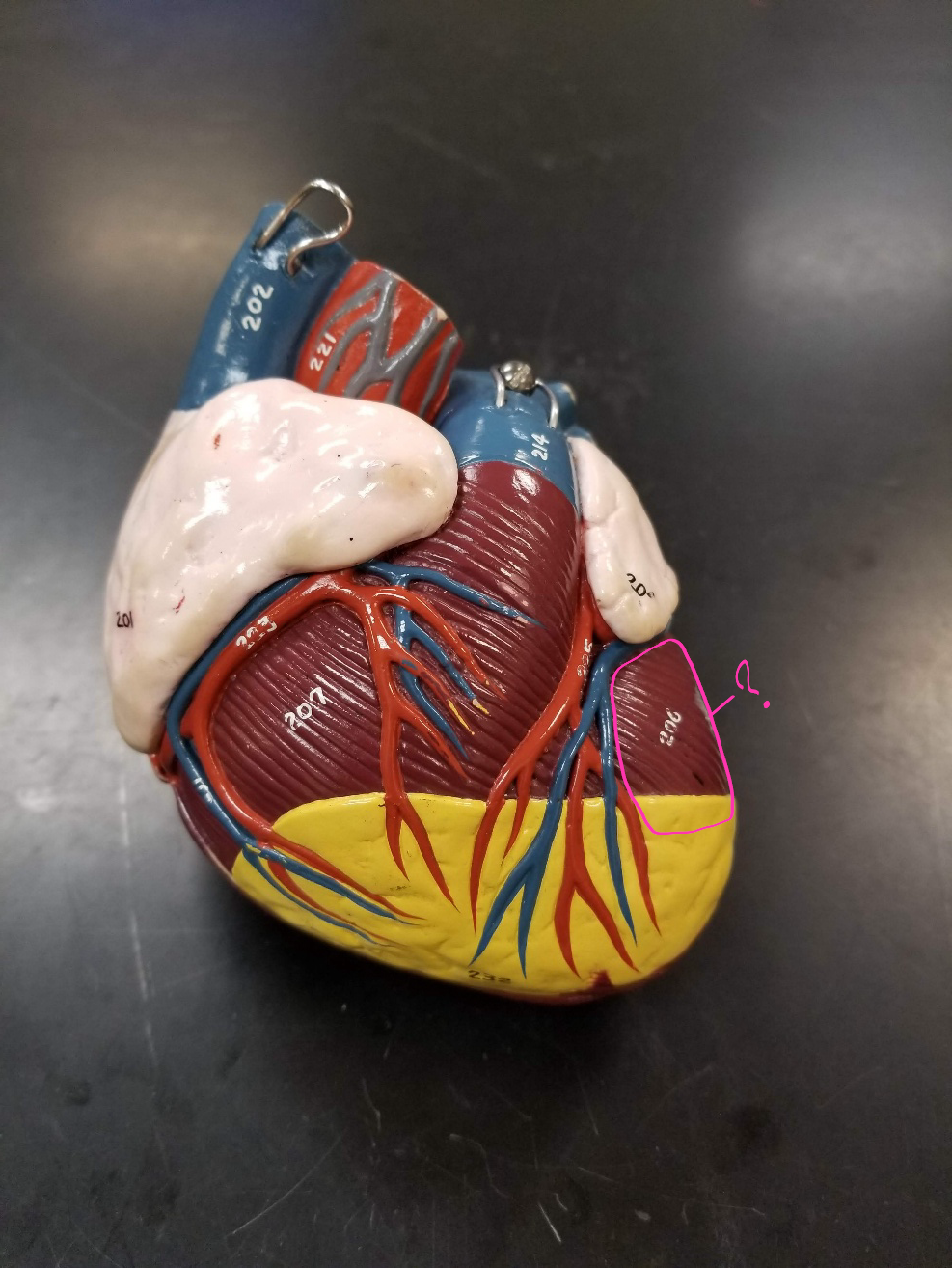
right ventricle
what is outlined in pink? (pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs)
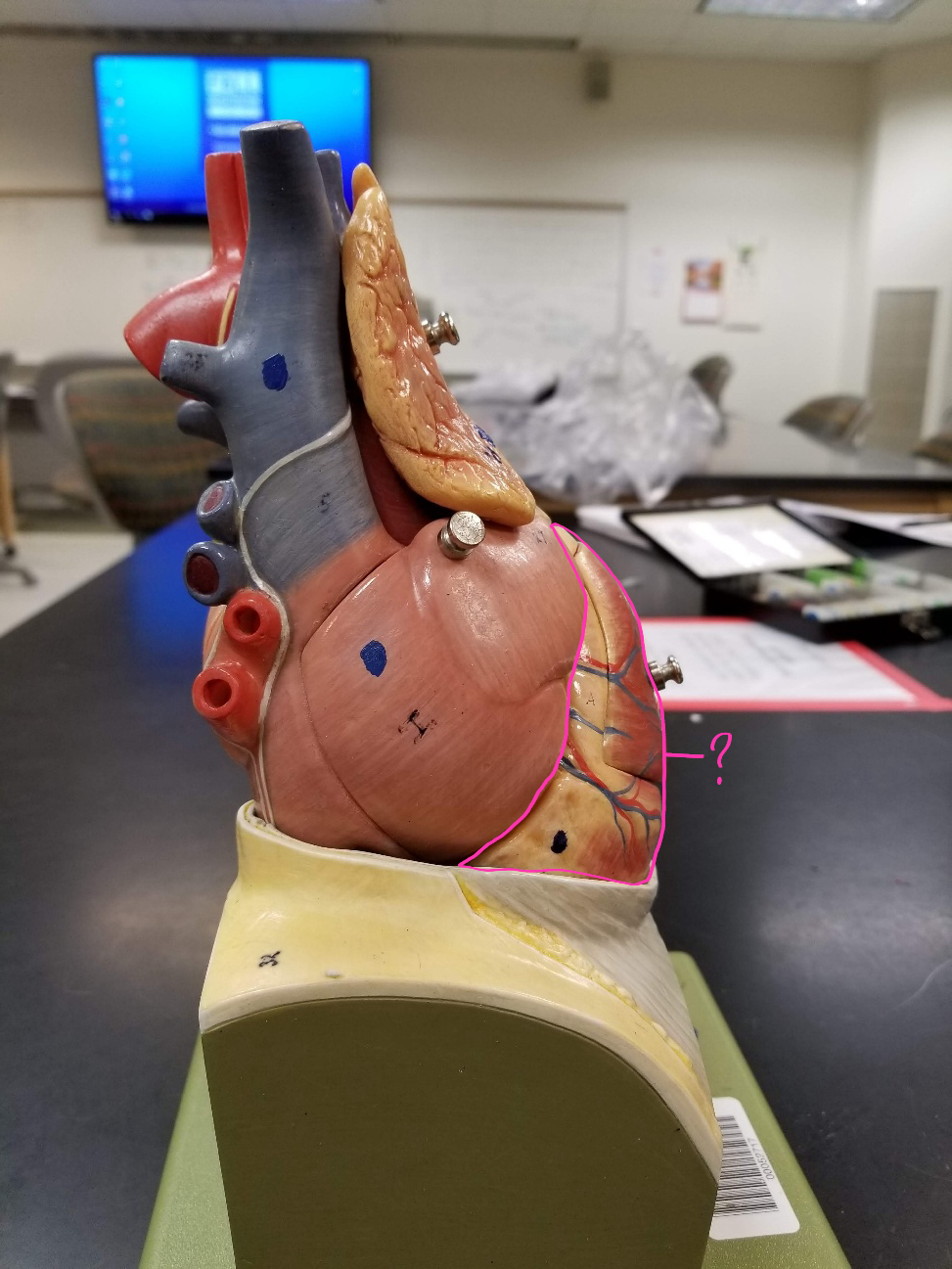
pulmonary veins
what is outlined in pink? (carry the oxygenated blood from the lungs into the left atrium of the heart)
superior vena cava
what is outlined in pink? (transports blood from the upper portion of the body to the heart)
right auricle
what is outlined in pink?
right atrium
what is outlined in pink? (receives deoxygenated blood from the body)
aorta
what is outlined in pink? (largest artery in the body)
superior vena cava
what is outlined in pink? (transports blood from the upper portion of the body to the heart)
fovea ovalis
what is outlined in pink?
tricuspid valve
what is outlined in pink?
chordae tendineae
what is outlined in pink?
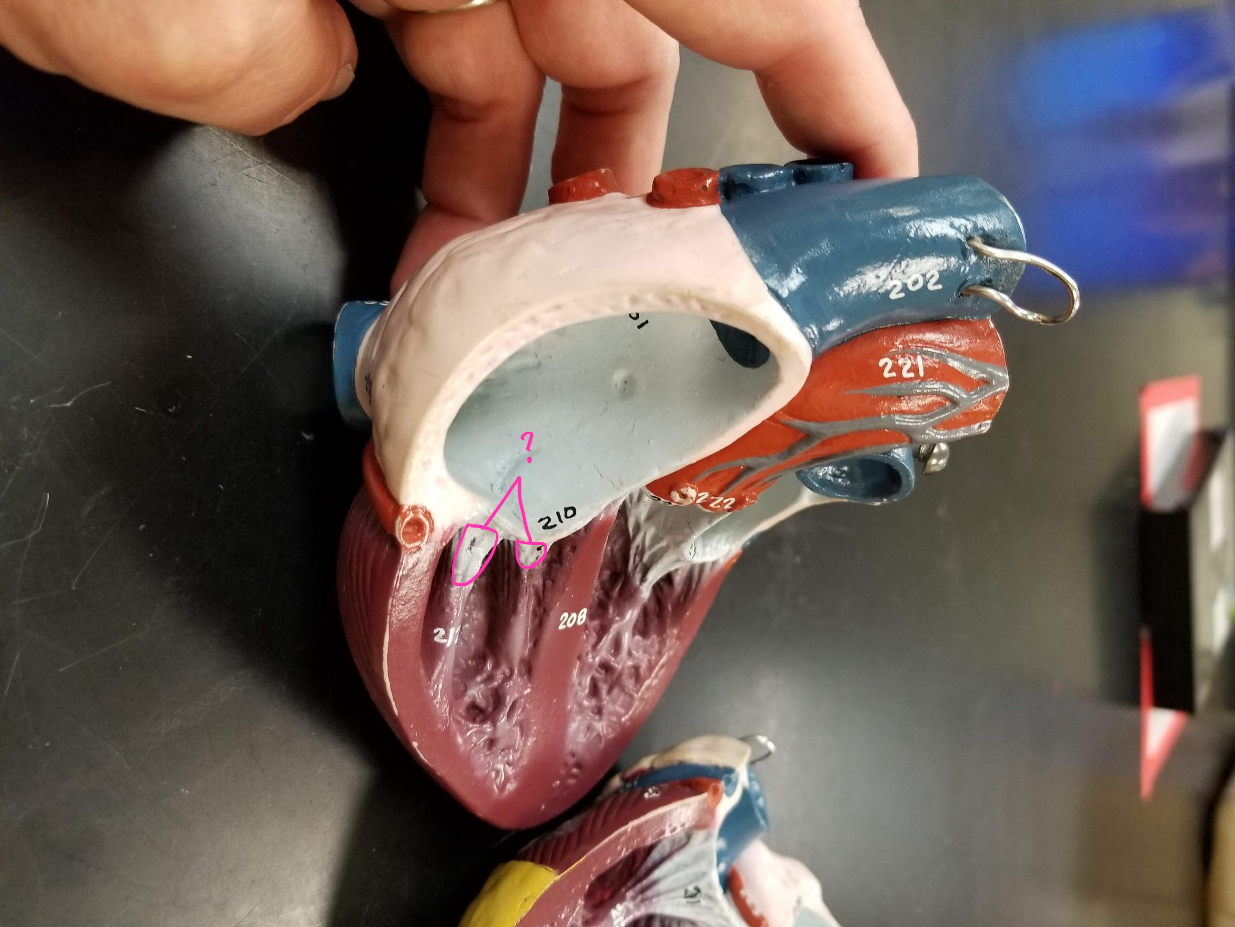
papillary muscles
what is outlined in pink?
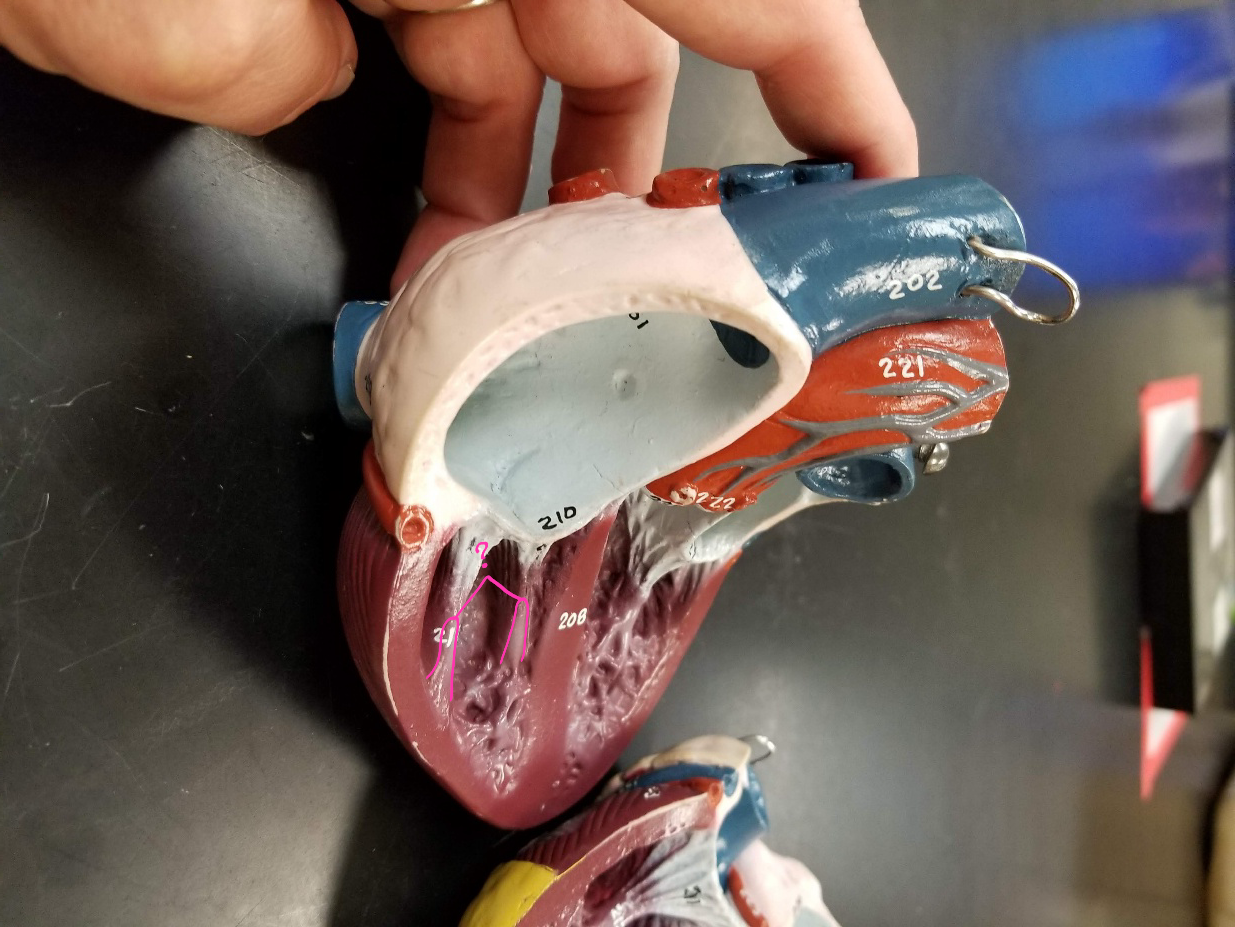
intraventricular septum
what is outlined in pink?
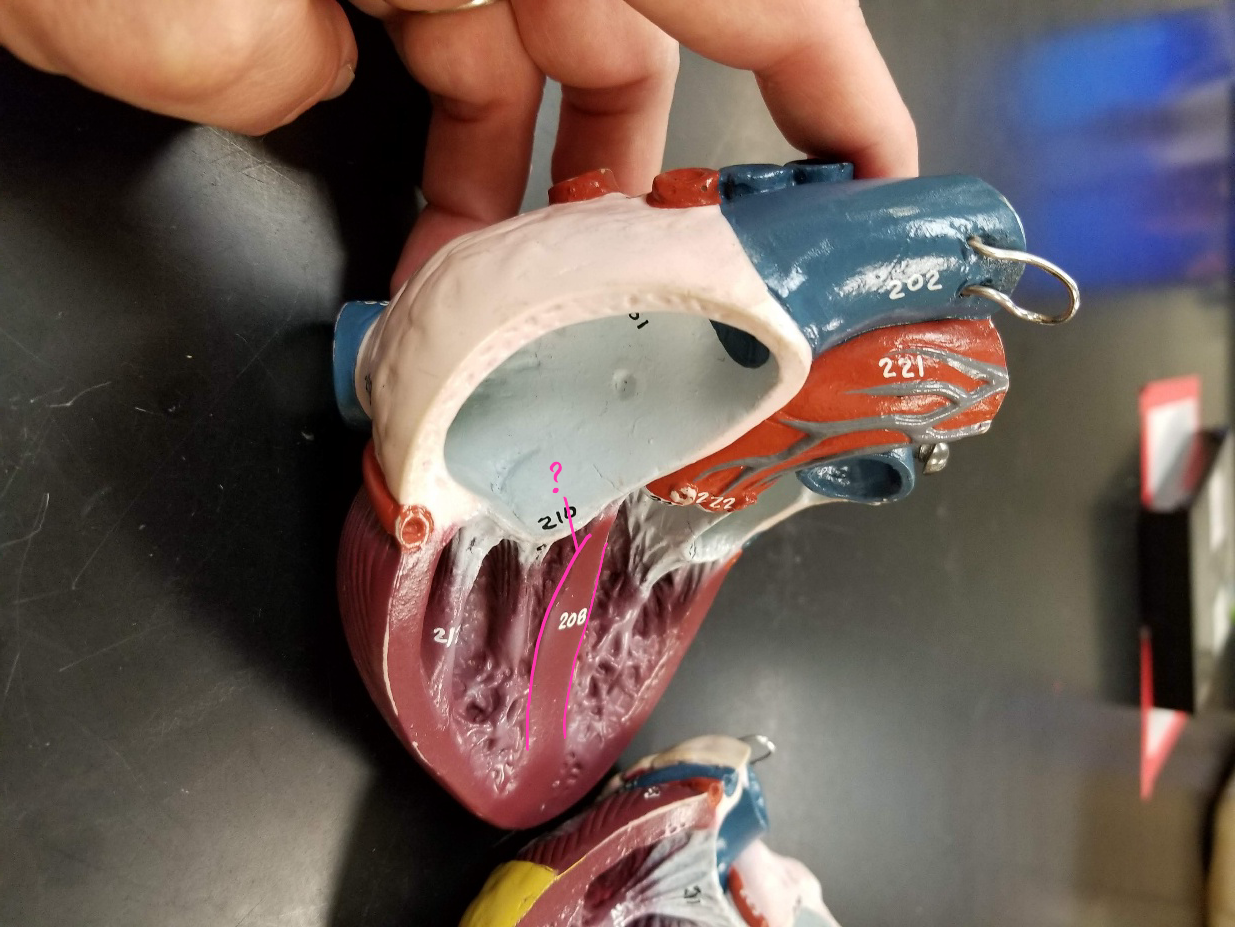
pulmonary trunk
what is outlined in pink? (carries blood from the right ventricle to the lungs)
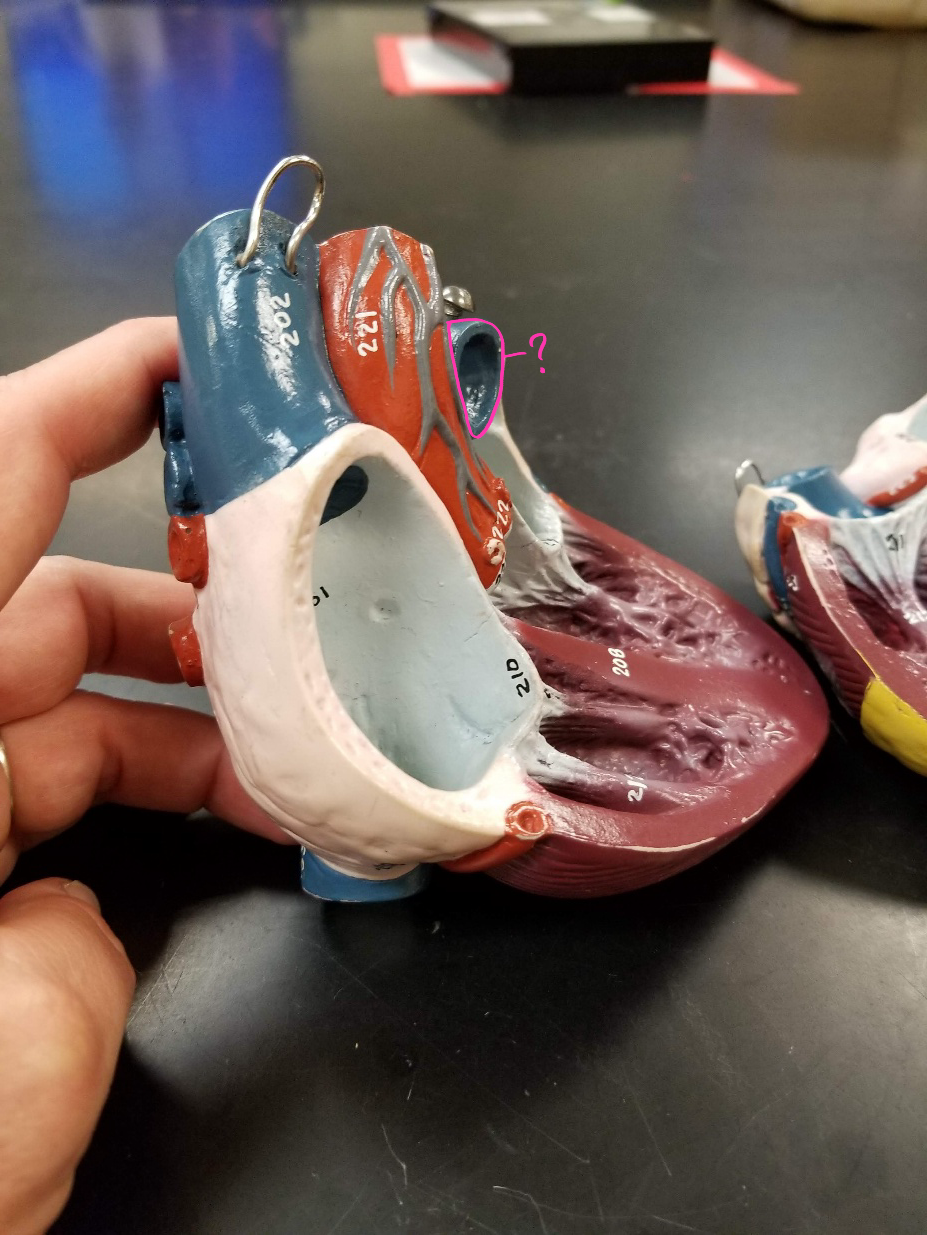
pulmonary arteries
what is outlined in pink?
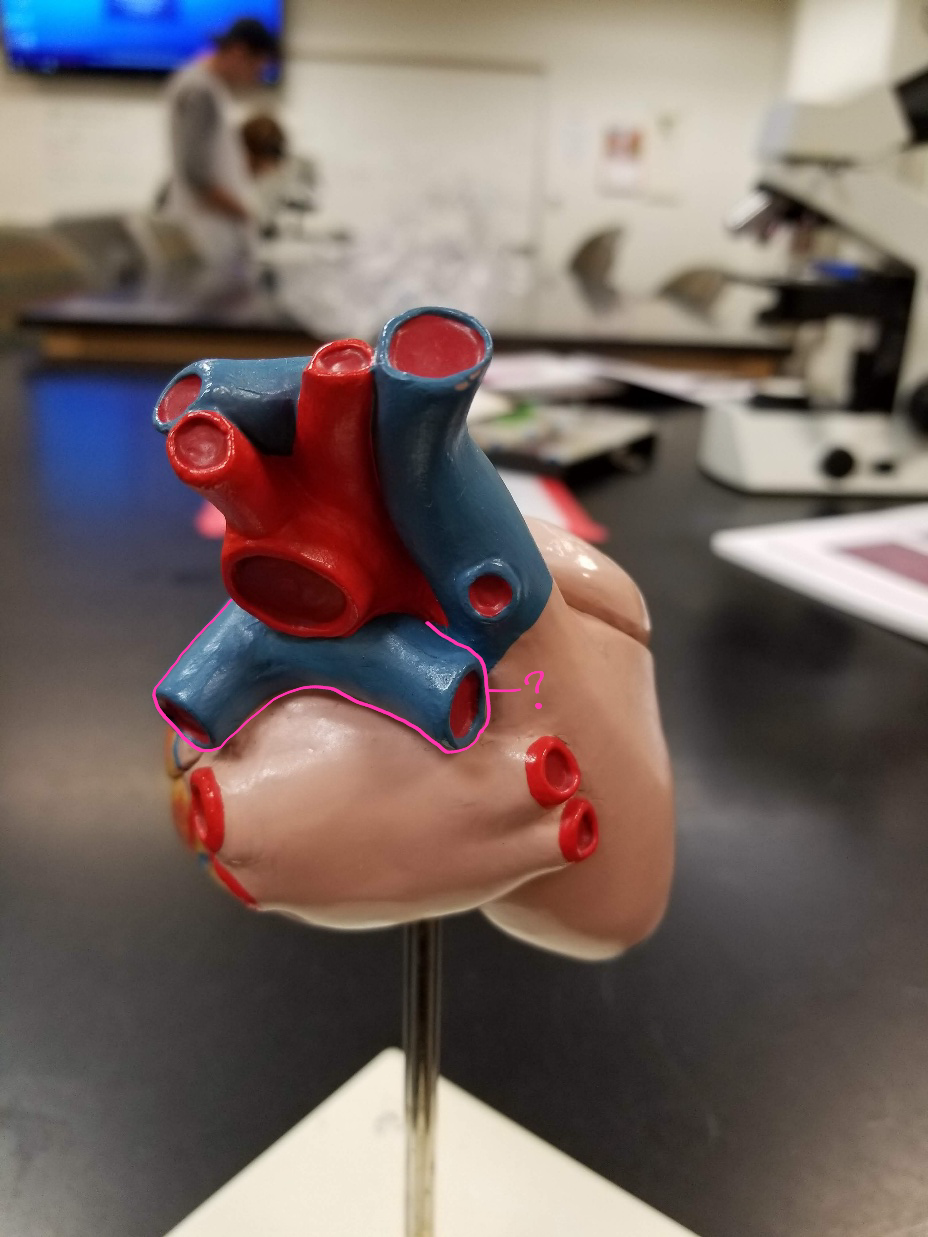

aorta
what is outlined in pink? (largest artery in the body)
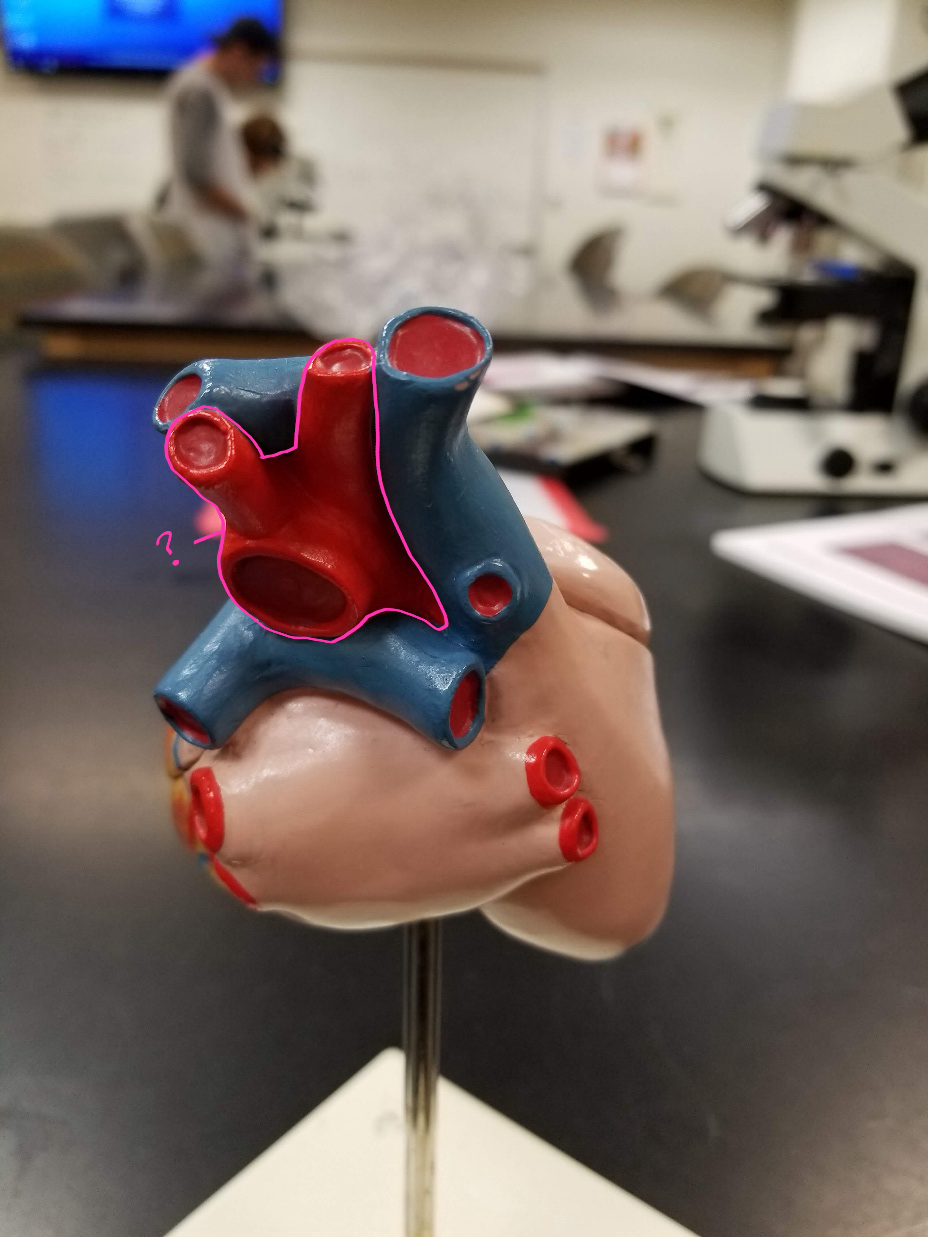

superior vena cava
what is outlined in pink? (transports blood from the upper portion of the body to the heart)
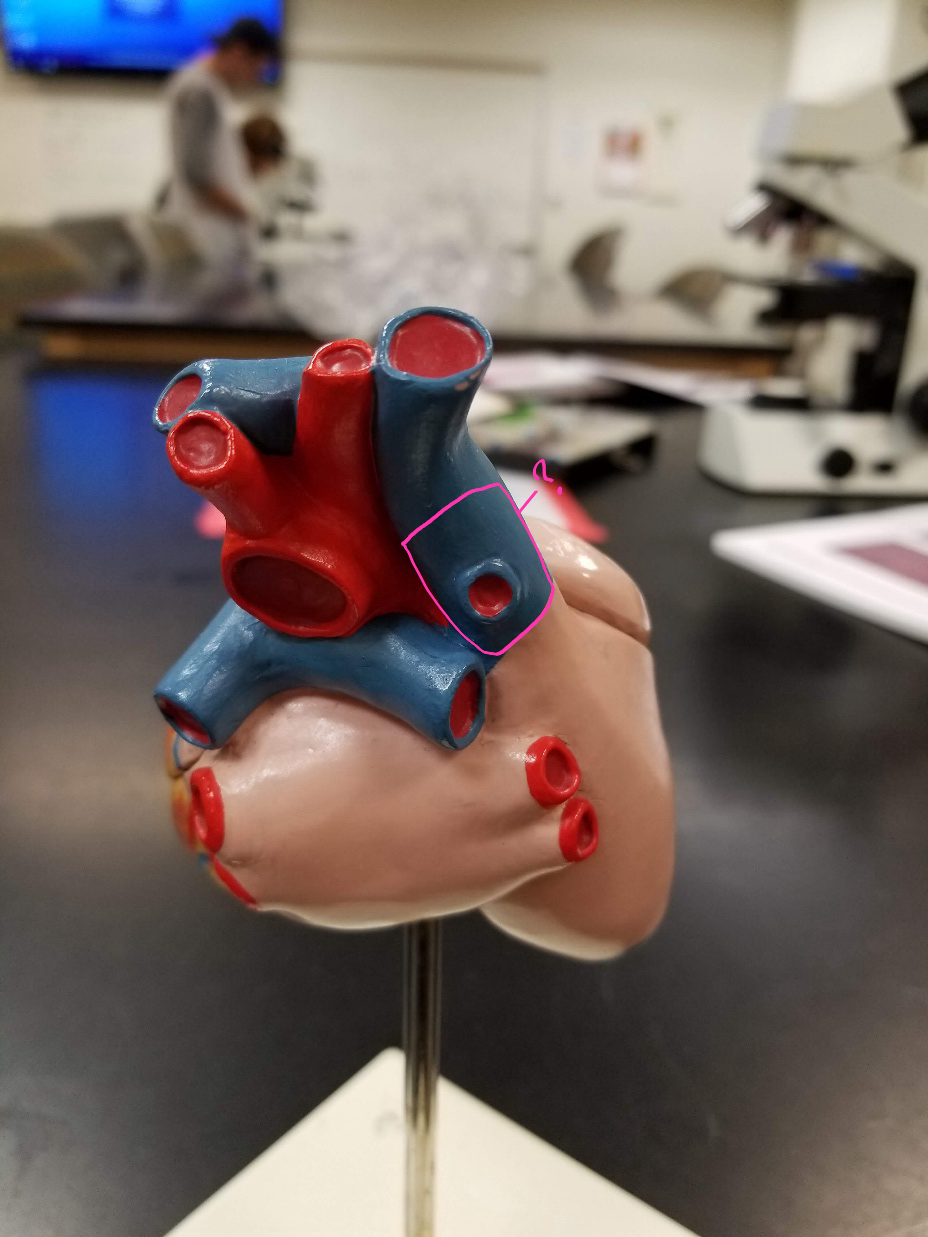
left atrium
what is outlined in pink?
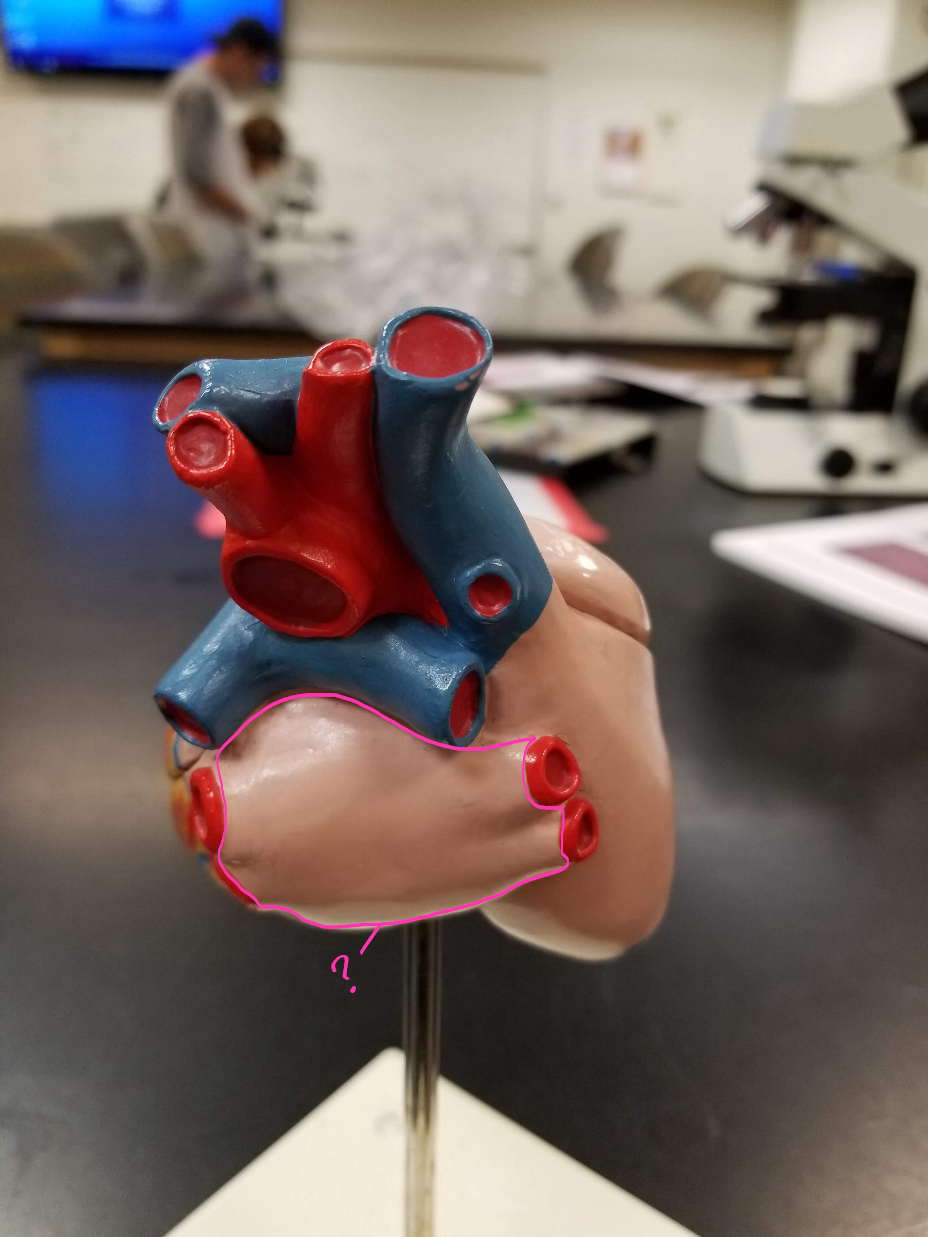
right atrium
what is outlined in pink? (receives deoxygenated blood from the body)
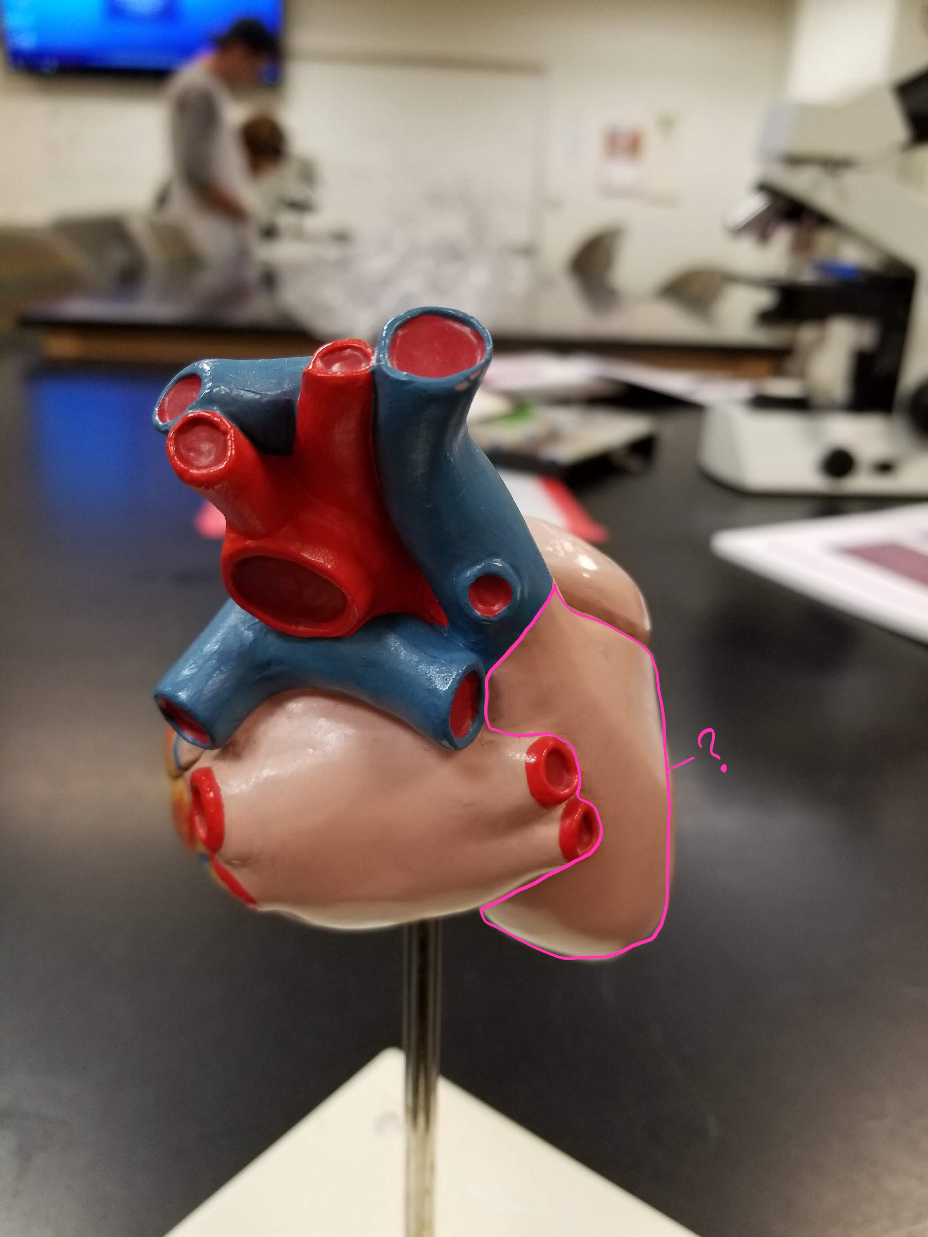
right coronary artery
what is outlined in pink?
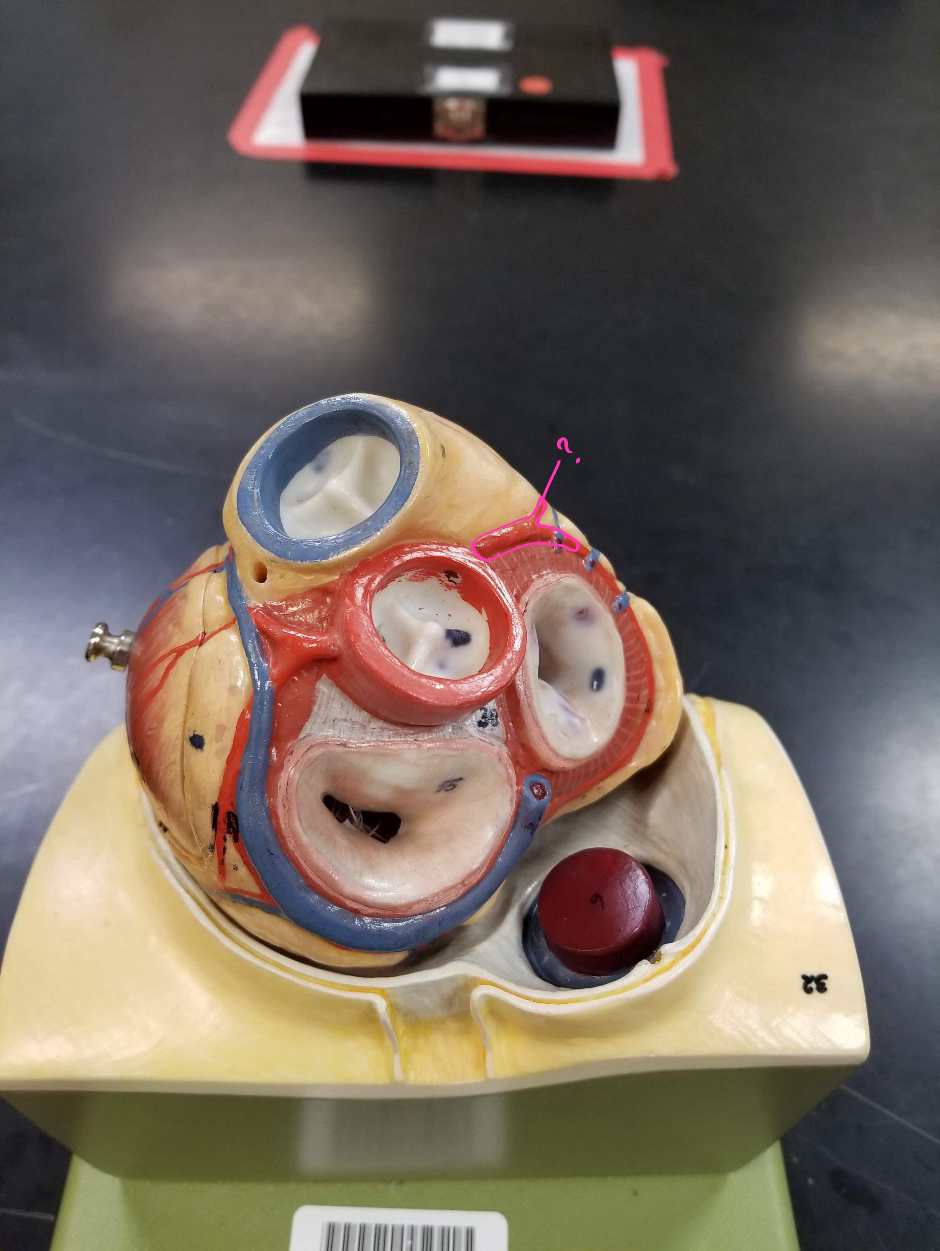
tricuspid valve
what is outlined in pink?
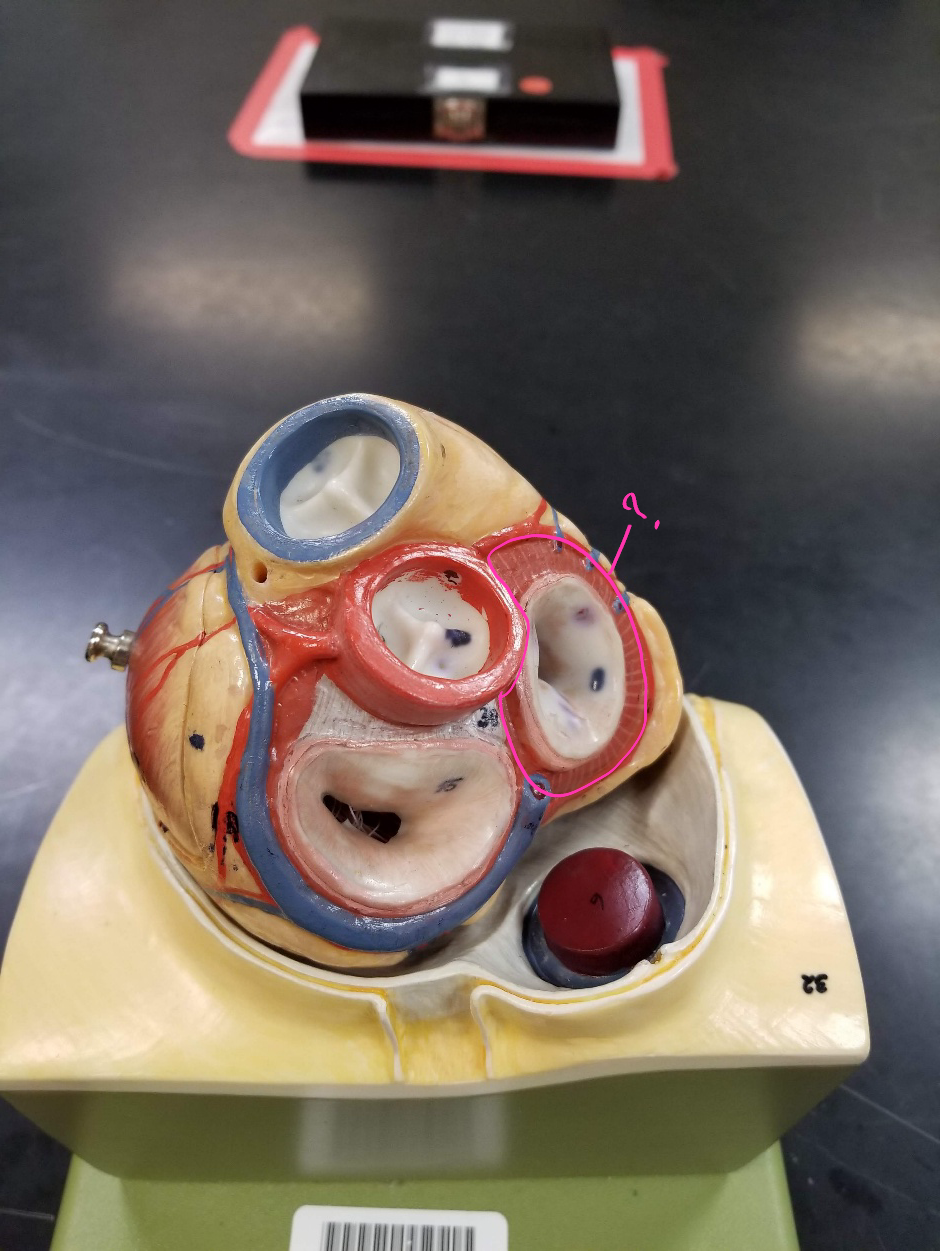
aortic valve
what is outlined in pink?
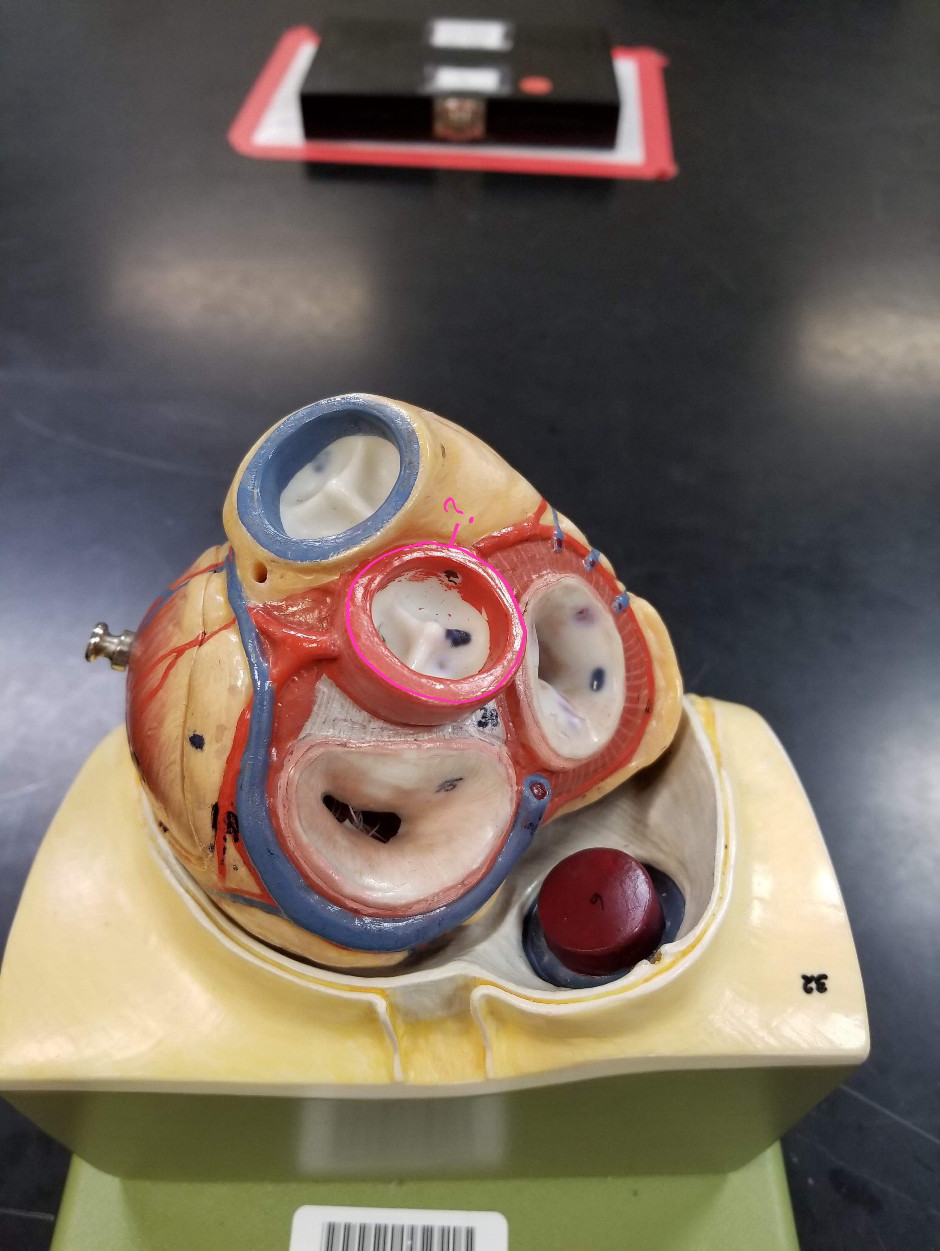
left coronary artery
what is outlined in pink?
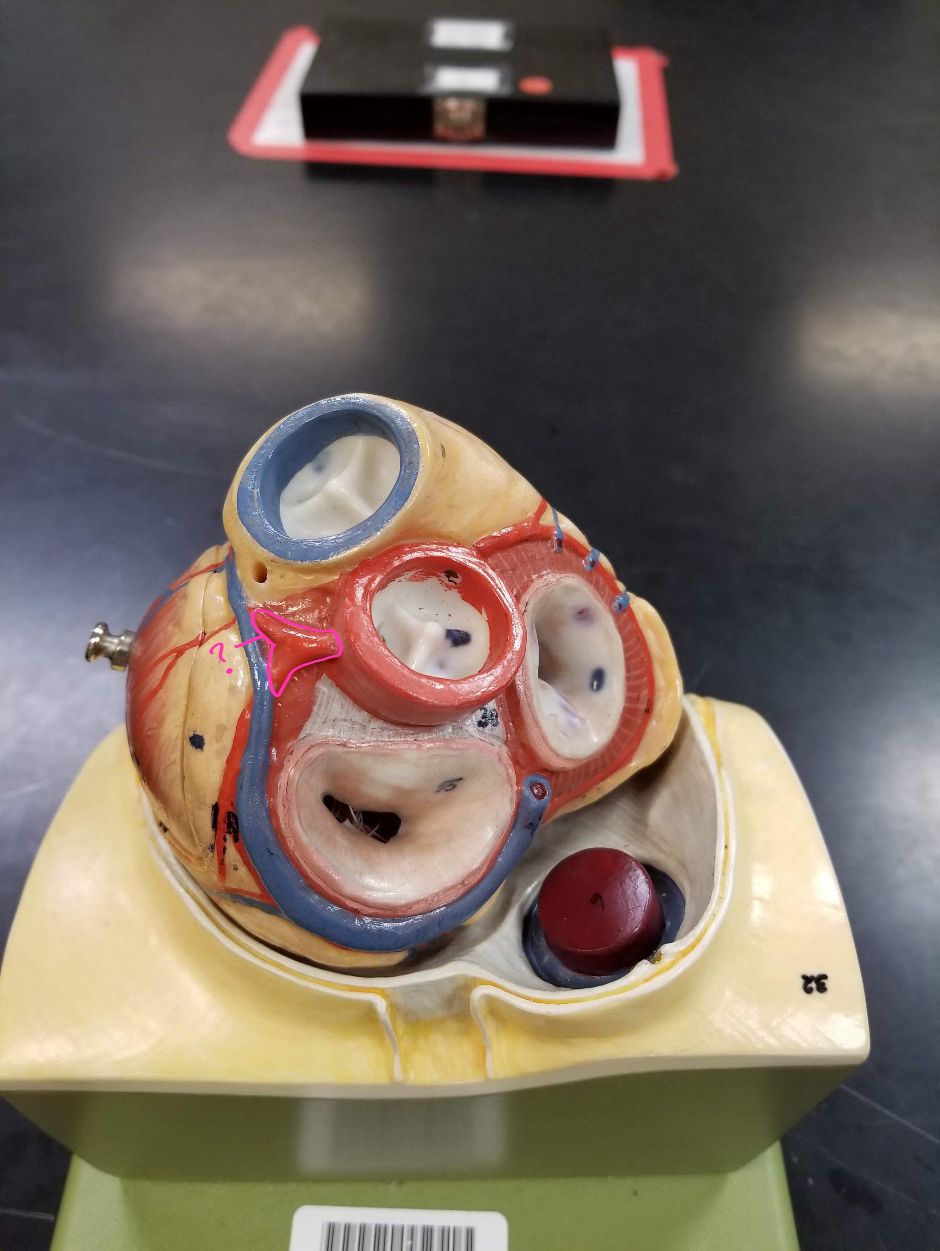
great cardiac vein
what is outlined in pink?
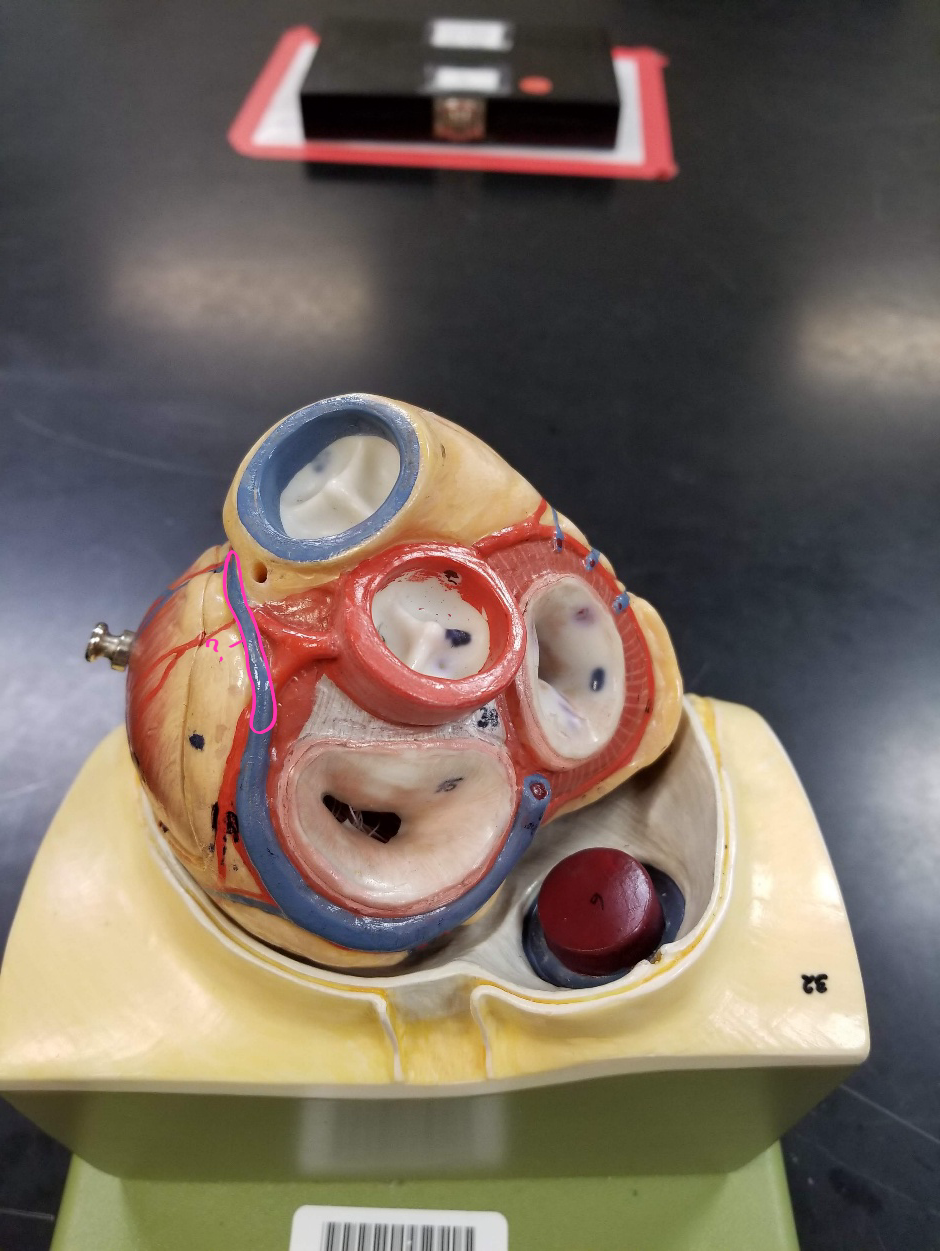
bicuspid valve
what is outlined in pink?
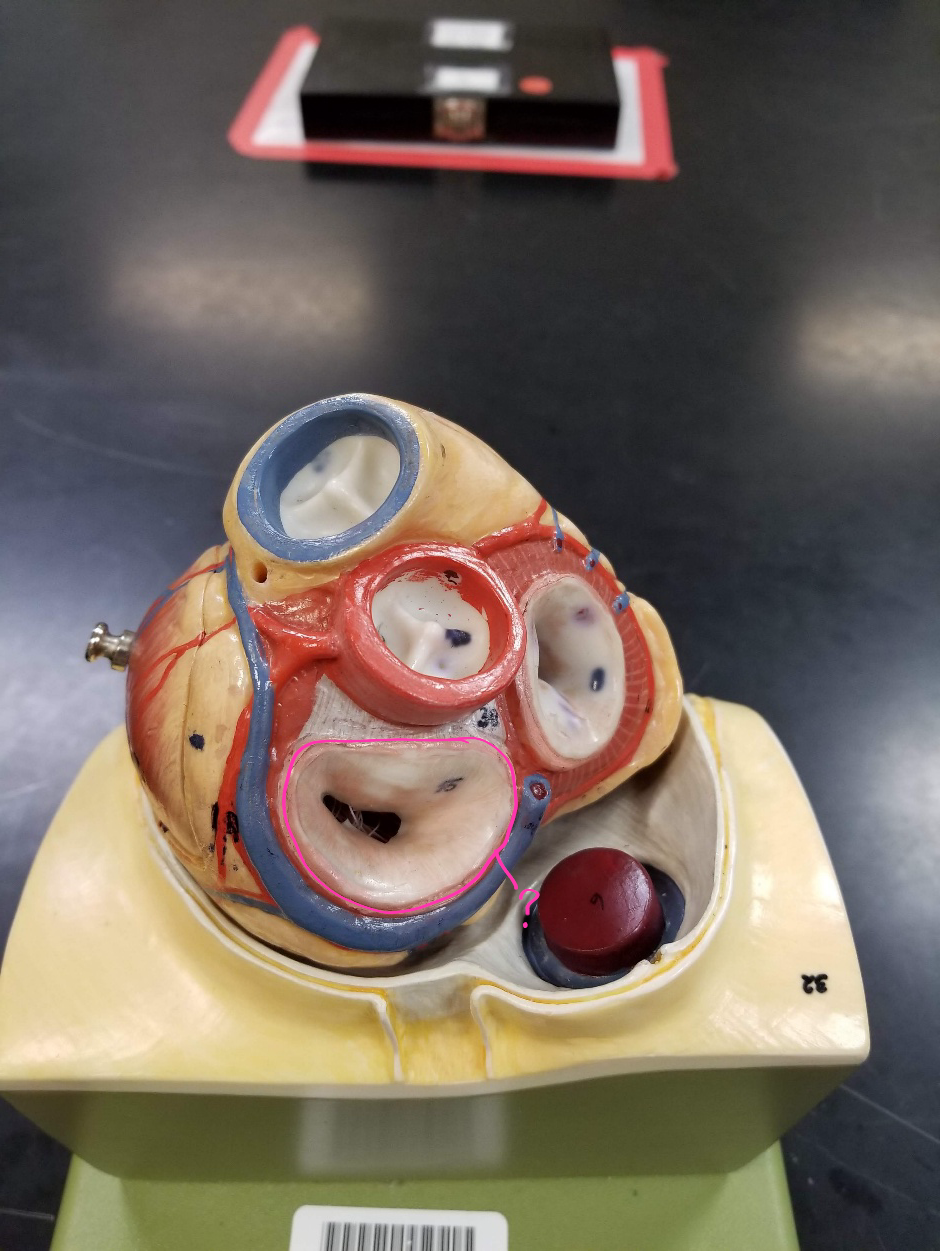
pulmonary valve
what is outlined in pink?
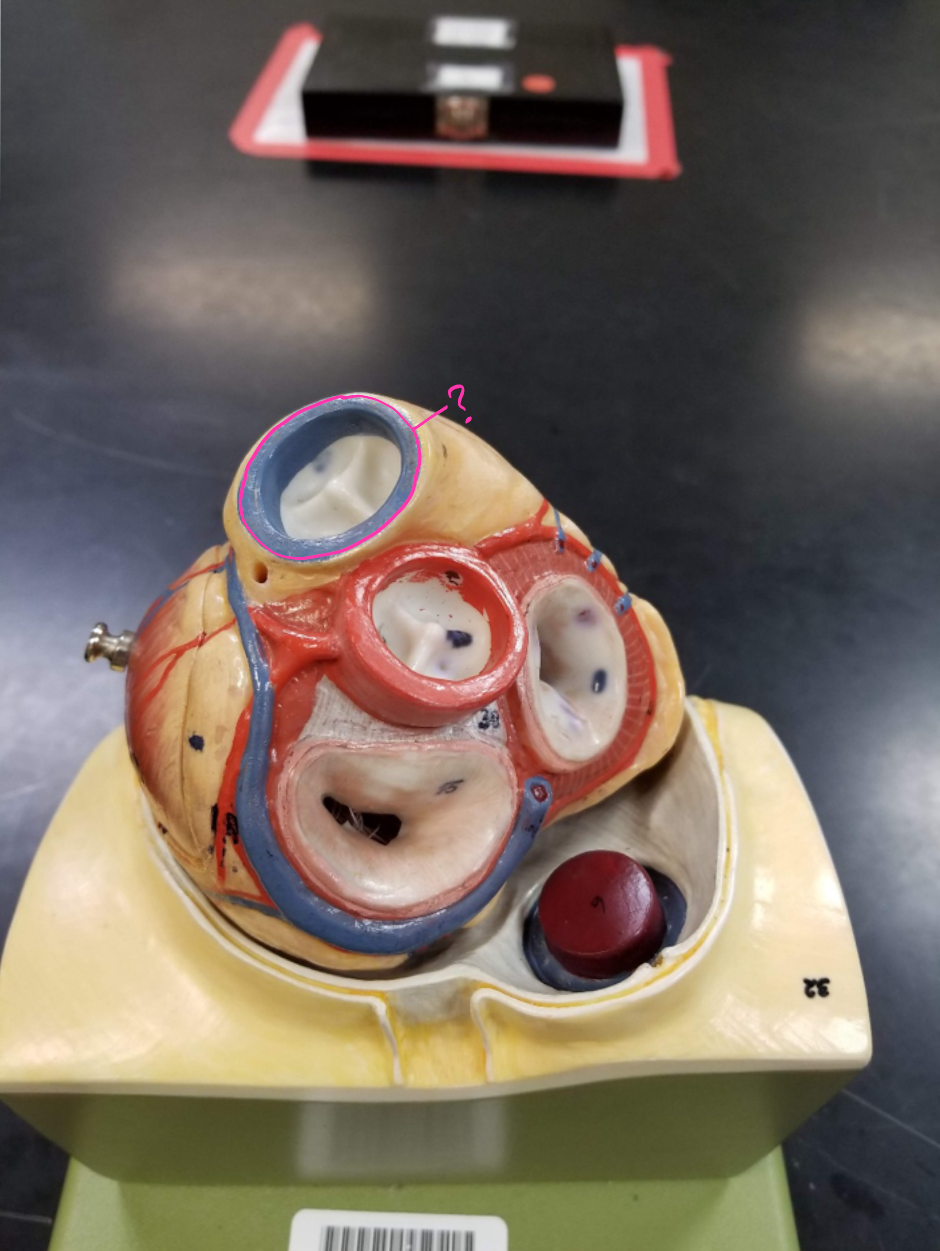
pericardium
what is outlined in pink?
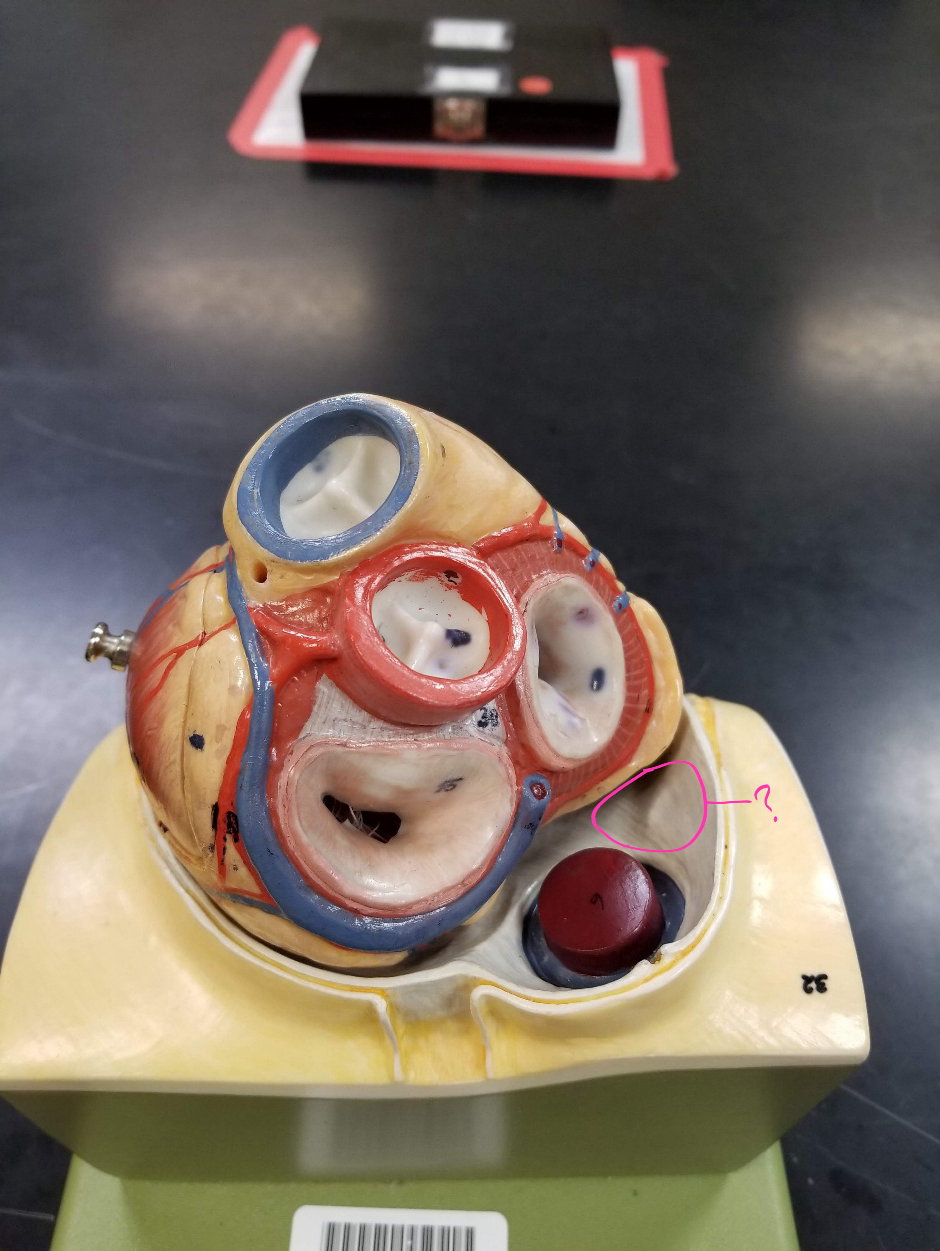
ascending aorta
what is #1 in the image? (largest artery in the body)
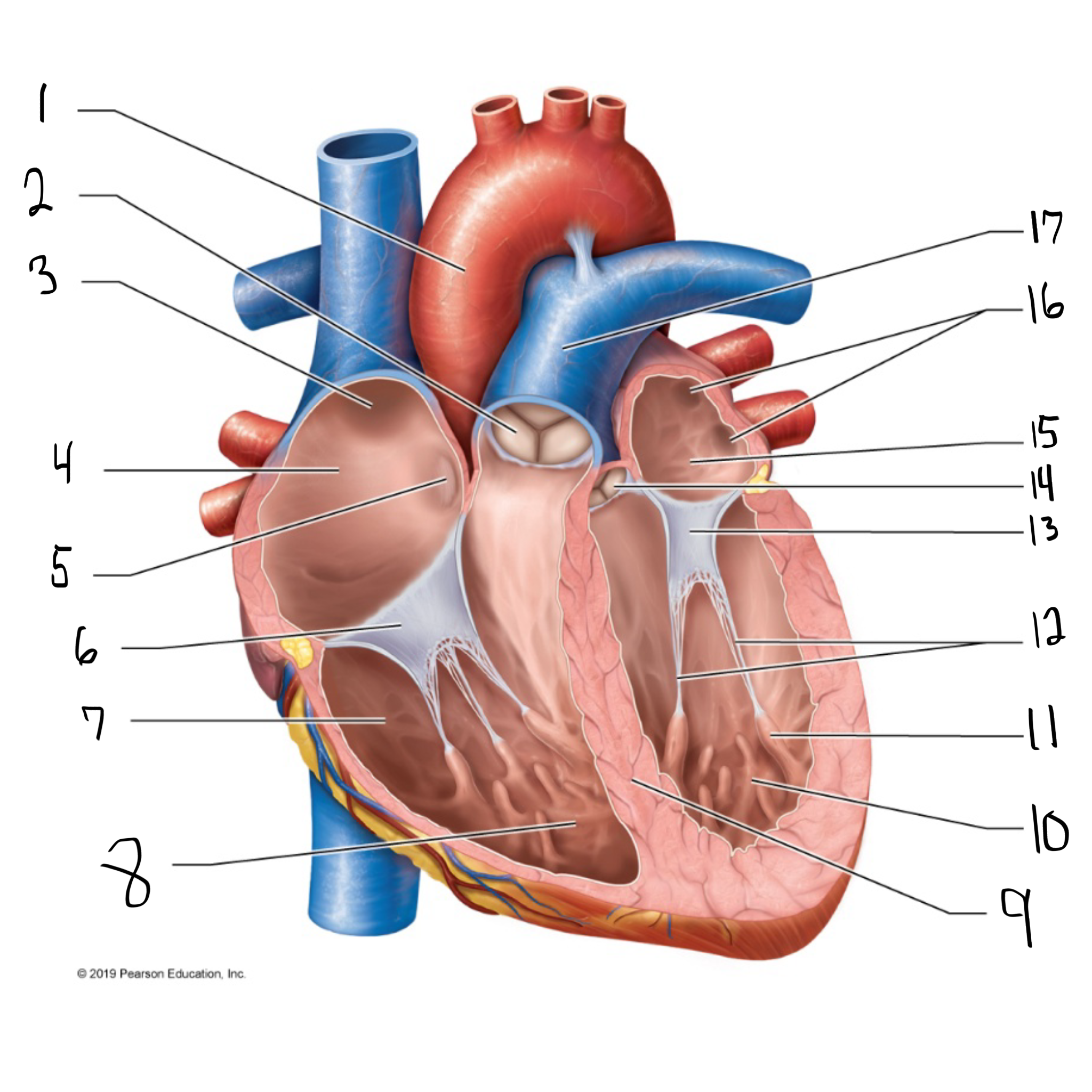
pulmonary valve
what is #2 in the image?
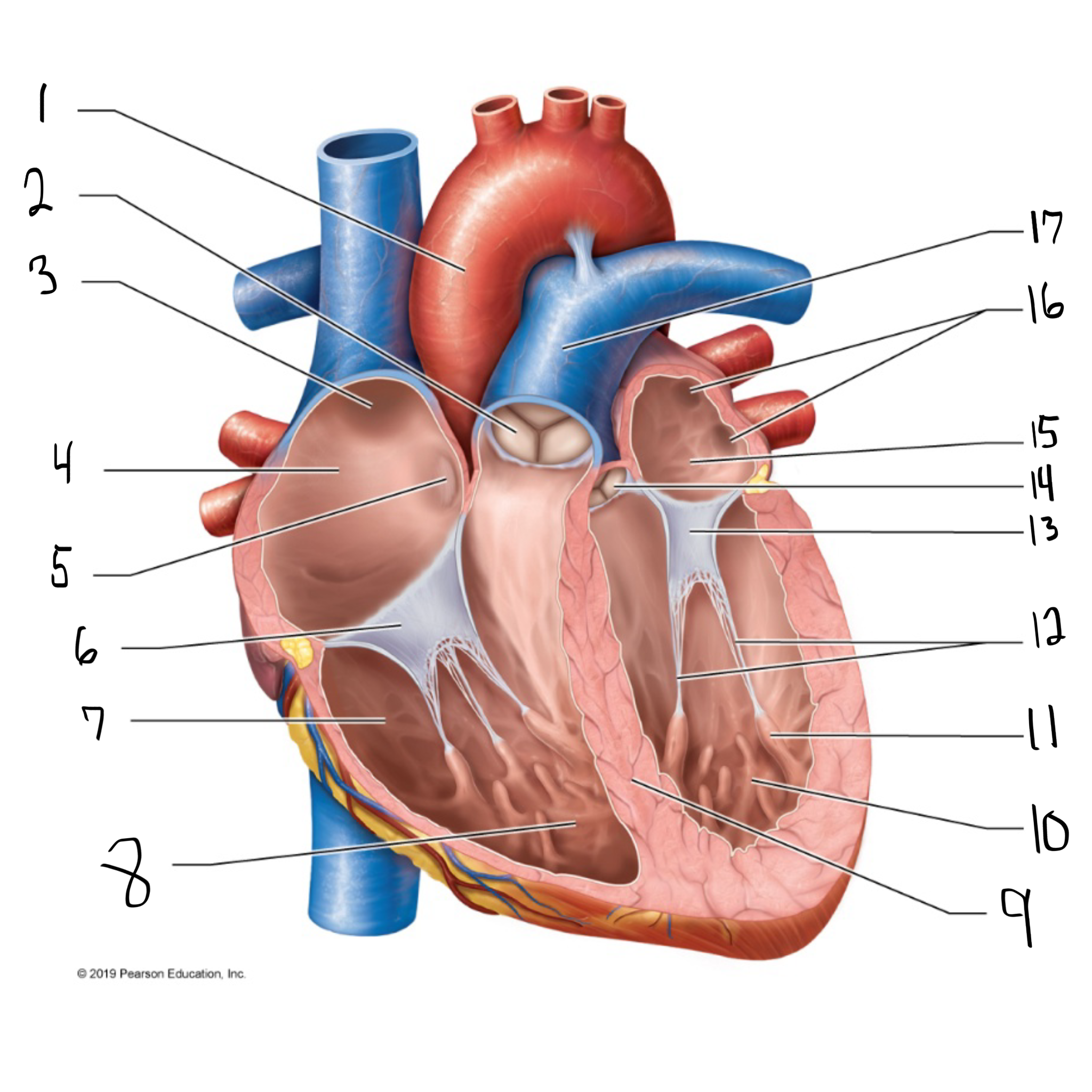
opening of superior vena cava
what is #3 in the image?
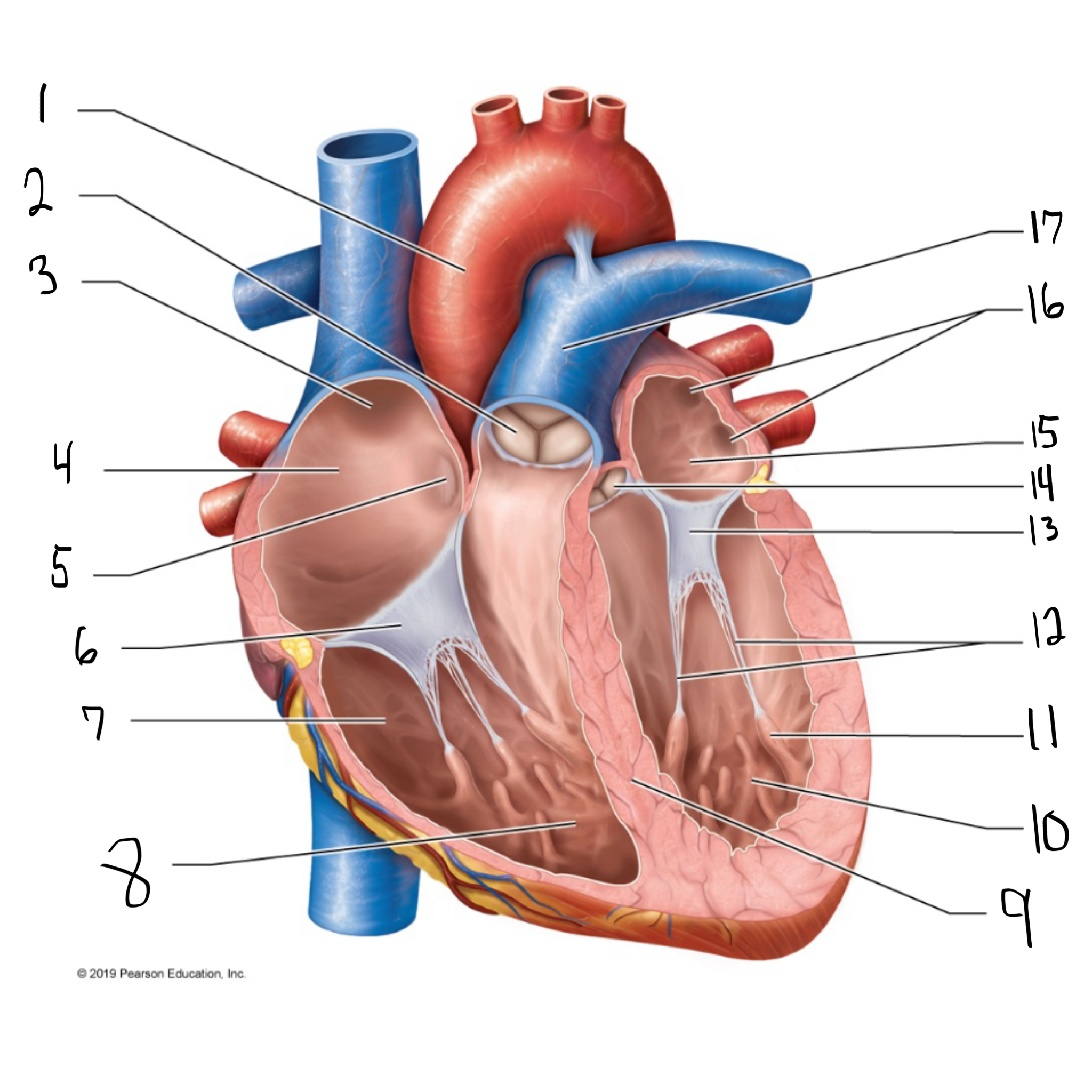
right atrium
what is #4 in the image? (receives deoxygenated blood from the body)
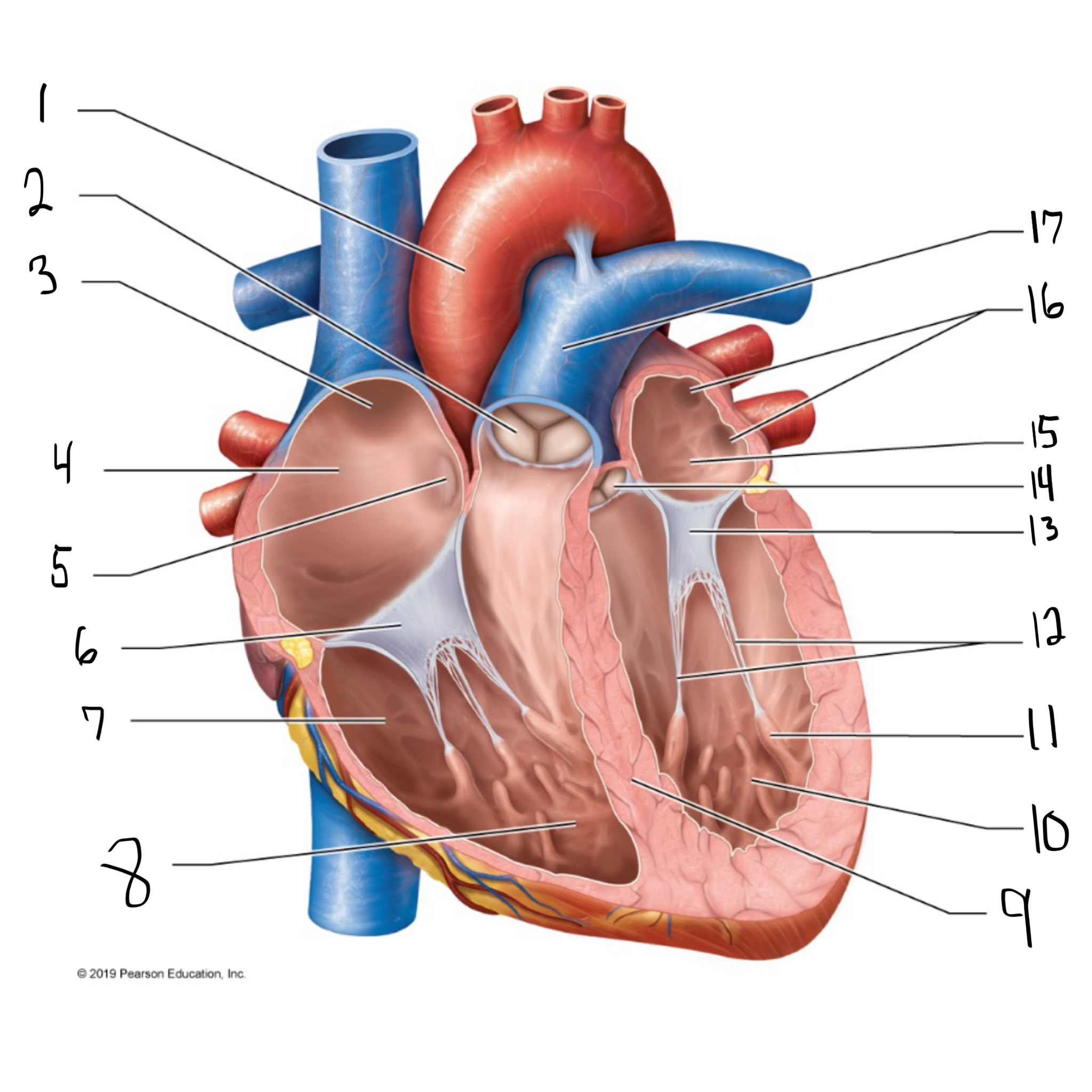
fossa ovalis
what is #5 in the image?
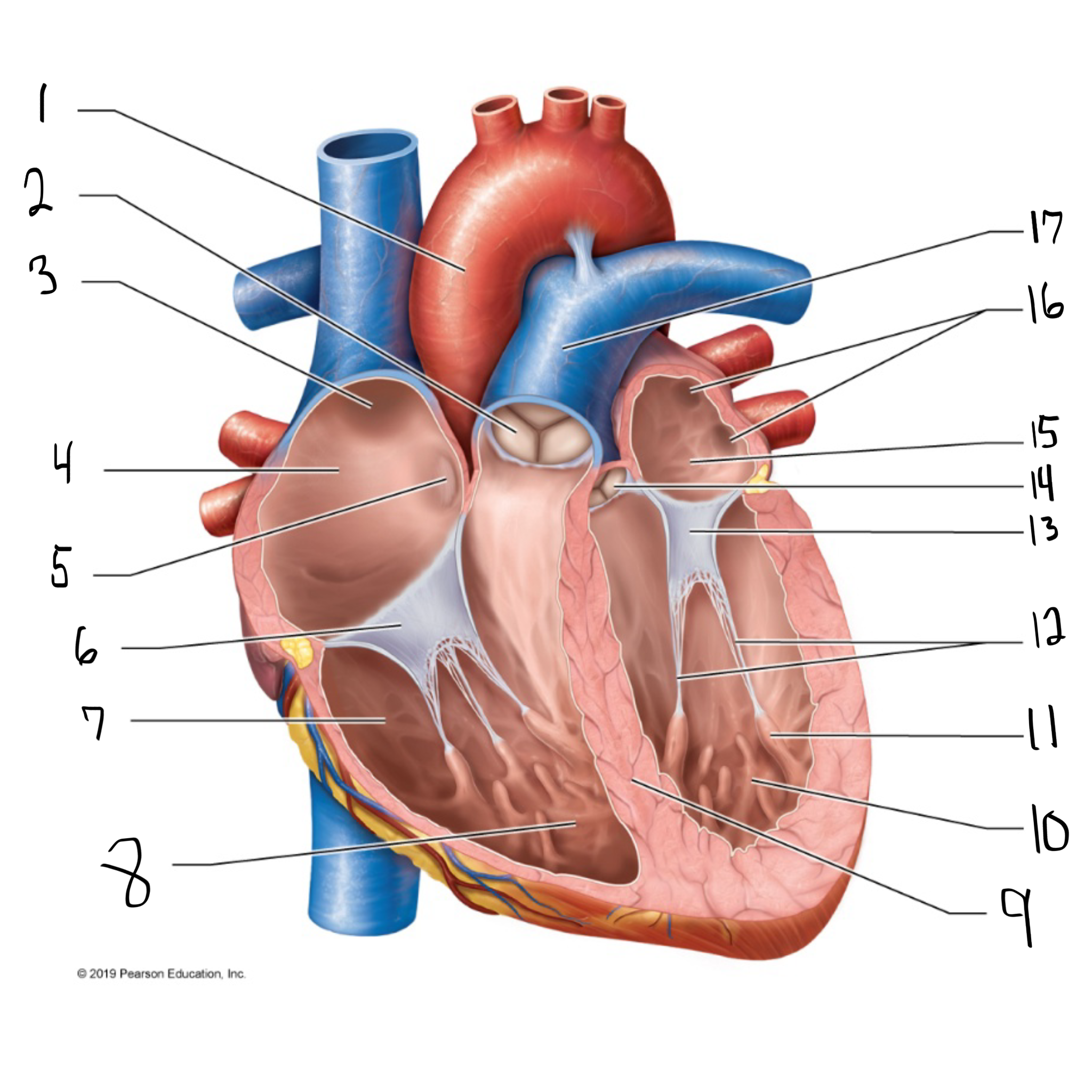
tricuspid valve
what is #6 in the image?
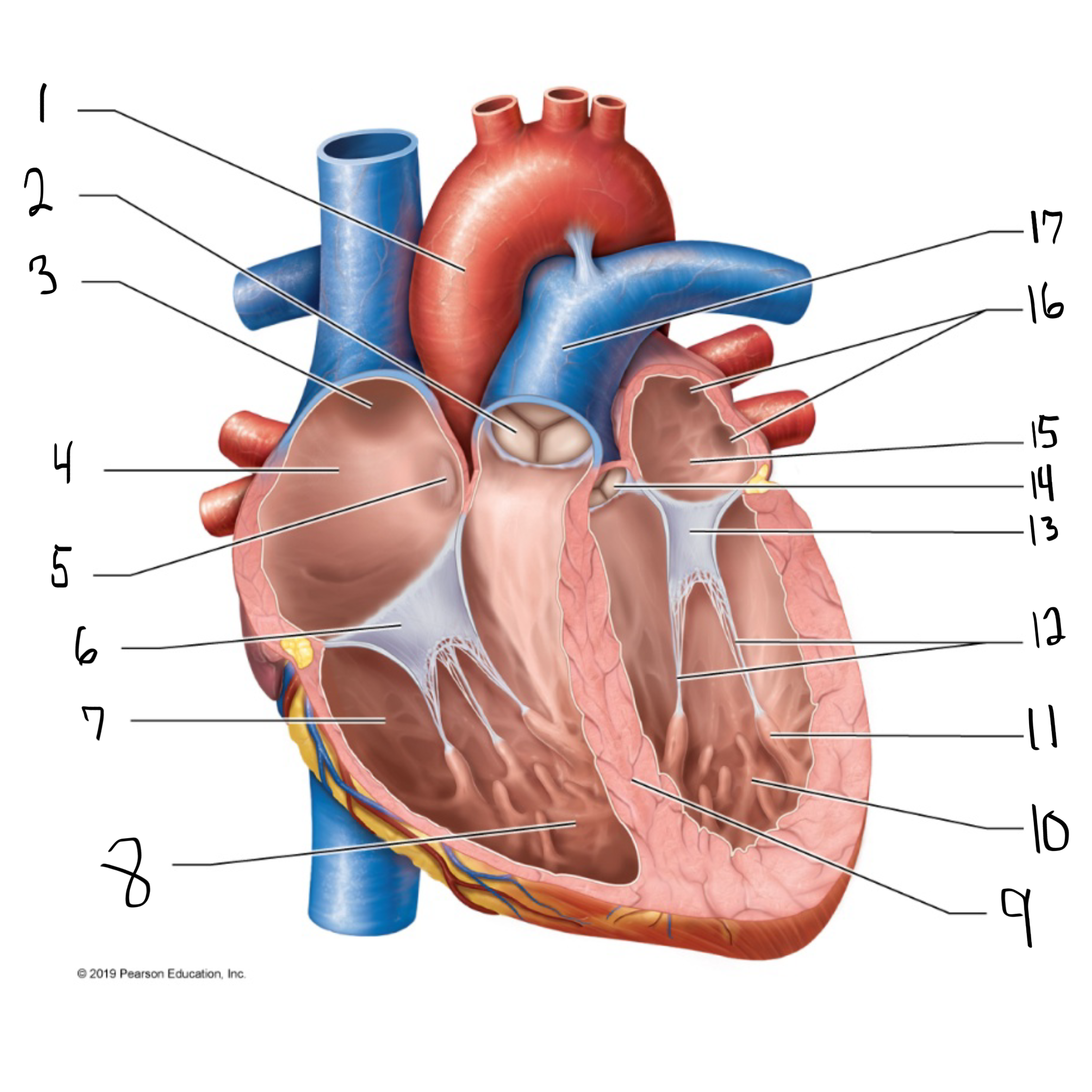
right ventricle
what is #7 in the image? (pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs)
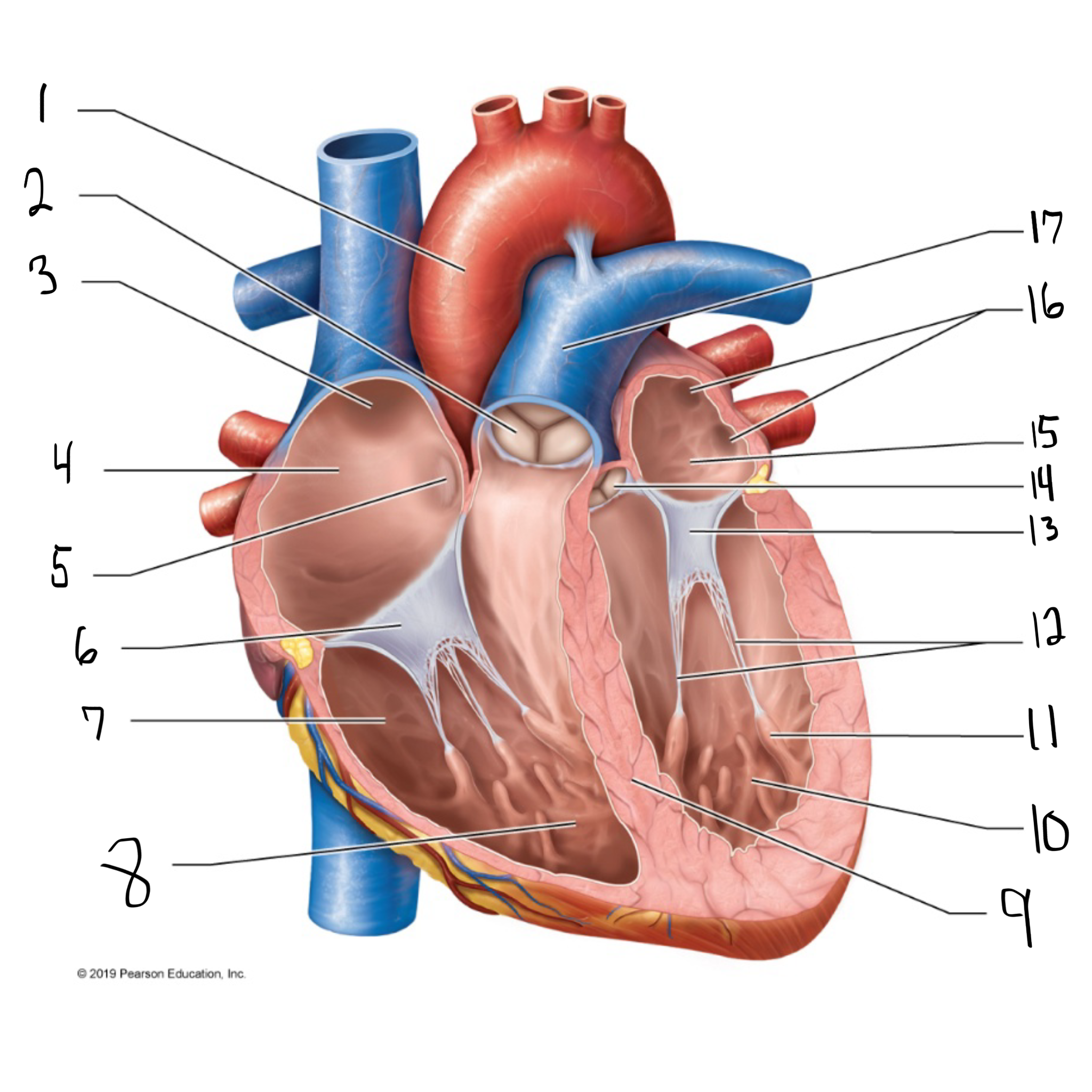
trabeculae carneae
what is #8 in the image?
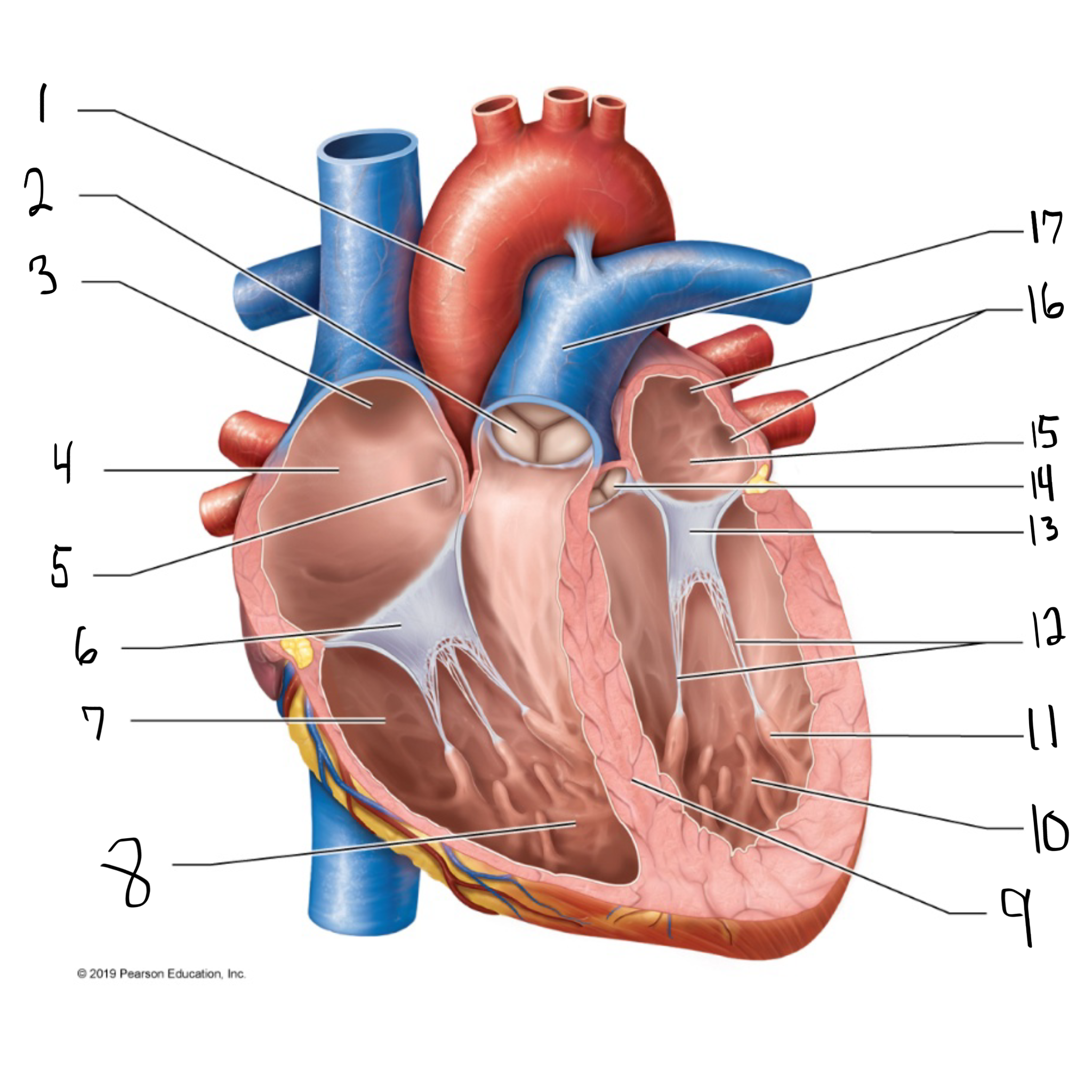
intraventricular septum
what is #9 in the image?
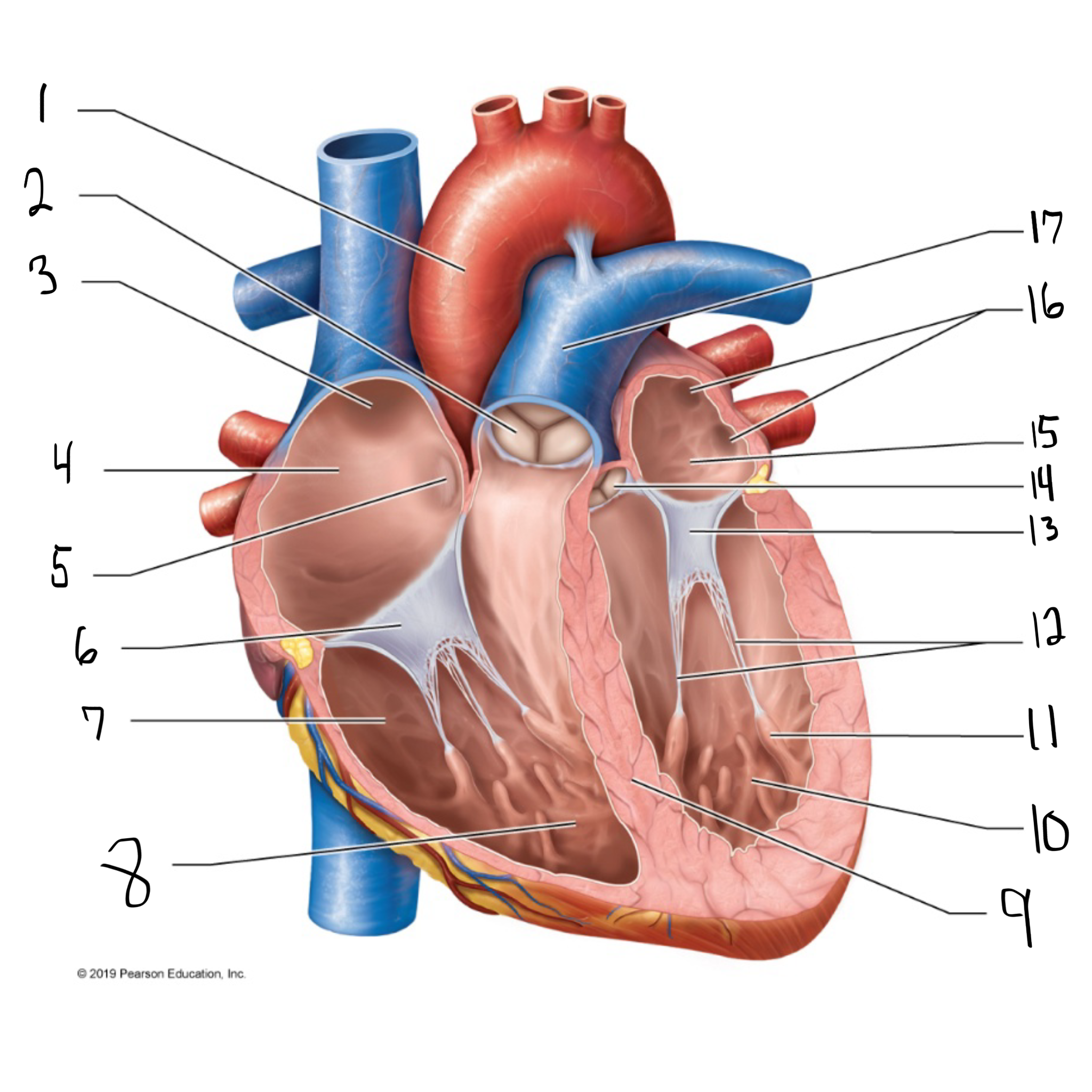
left ventricle
what is #10 in the image? (pumps oxygenated blood to the body)
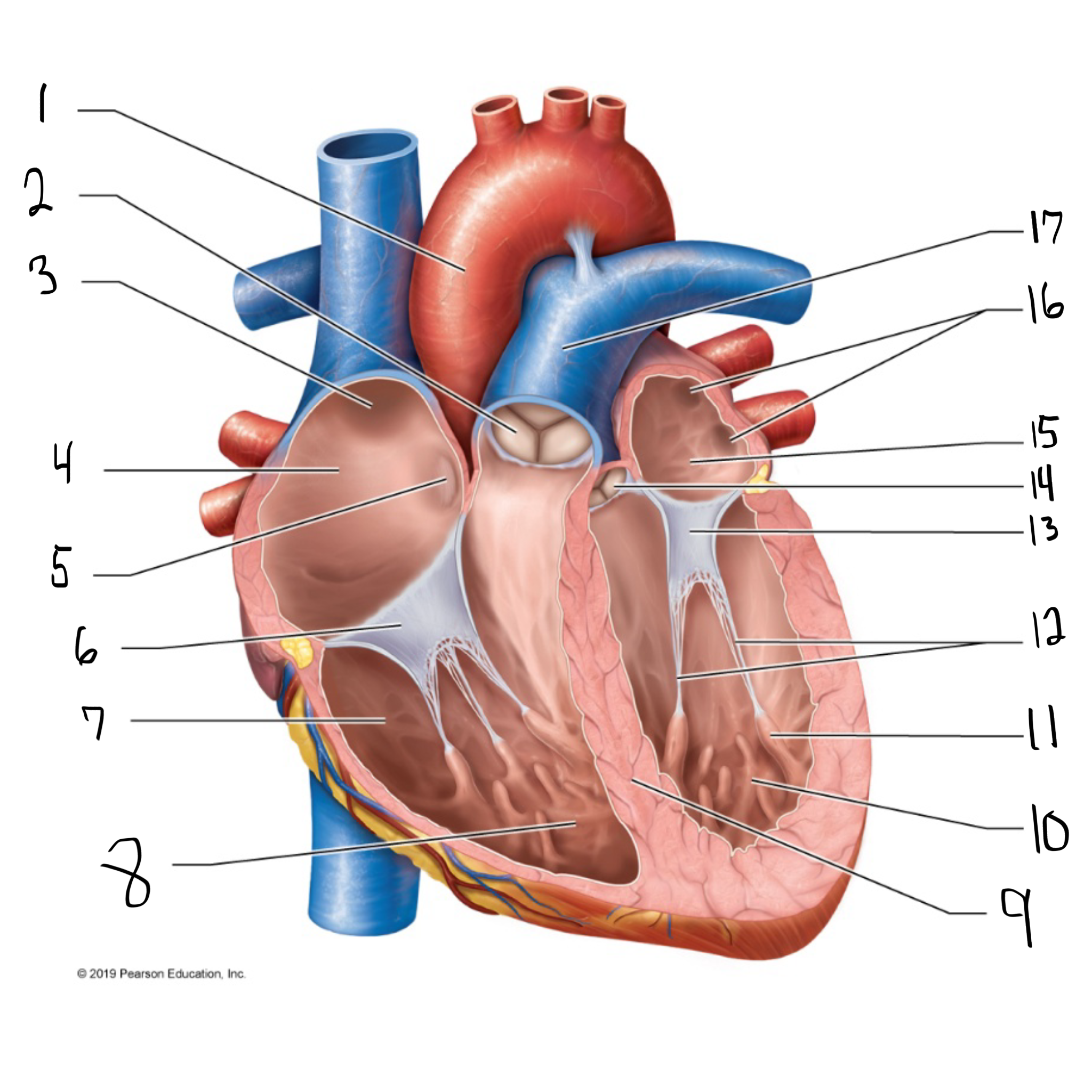
papillary muscle
what is #11 in the image?
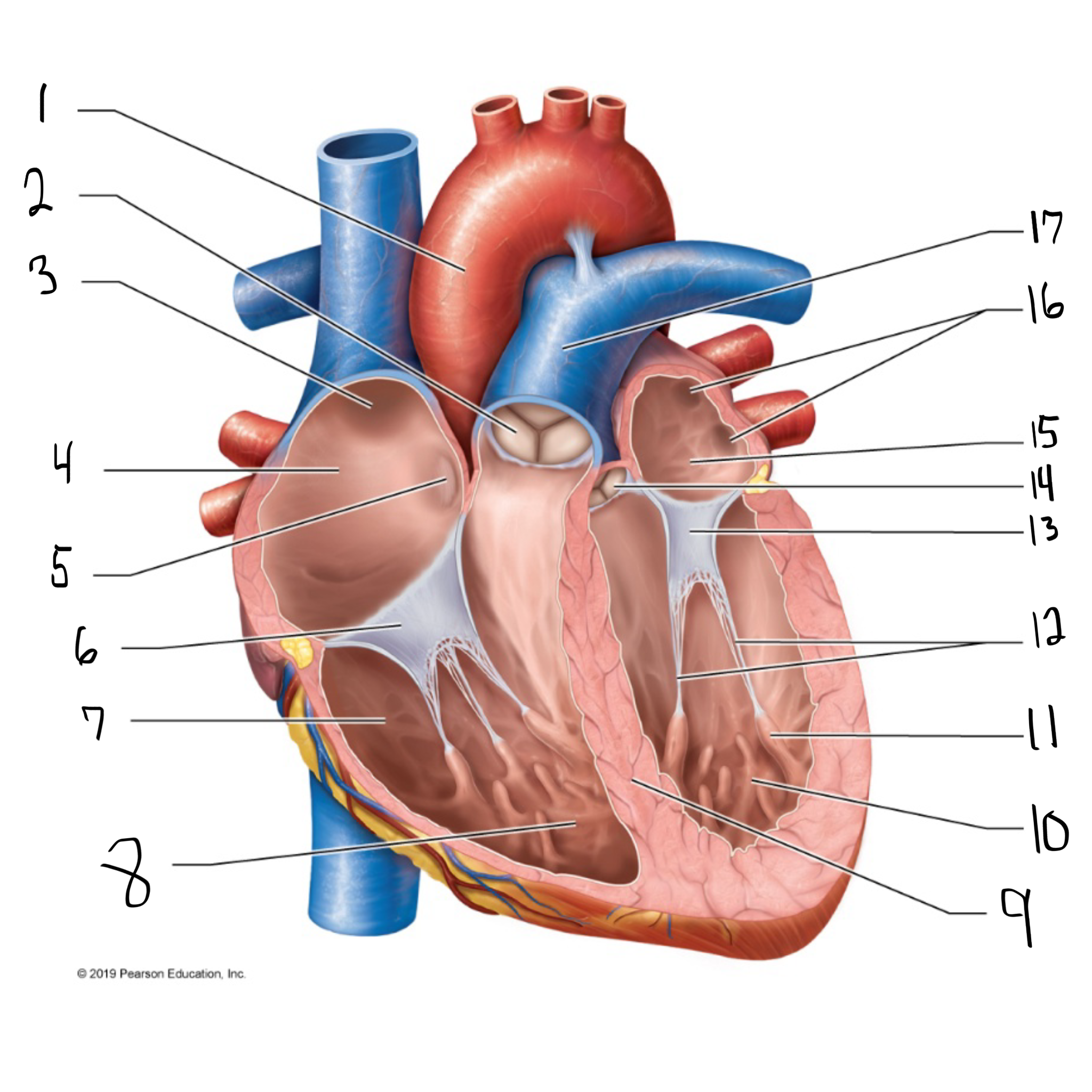
chordae tendineae
what is #12 in the image?
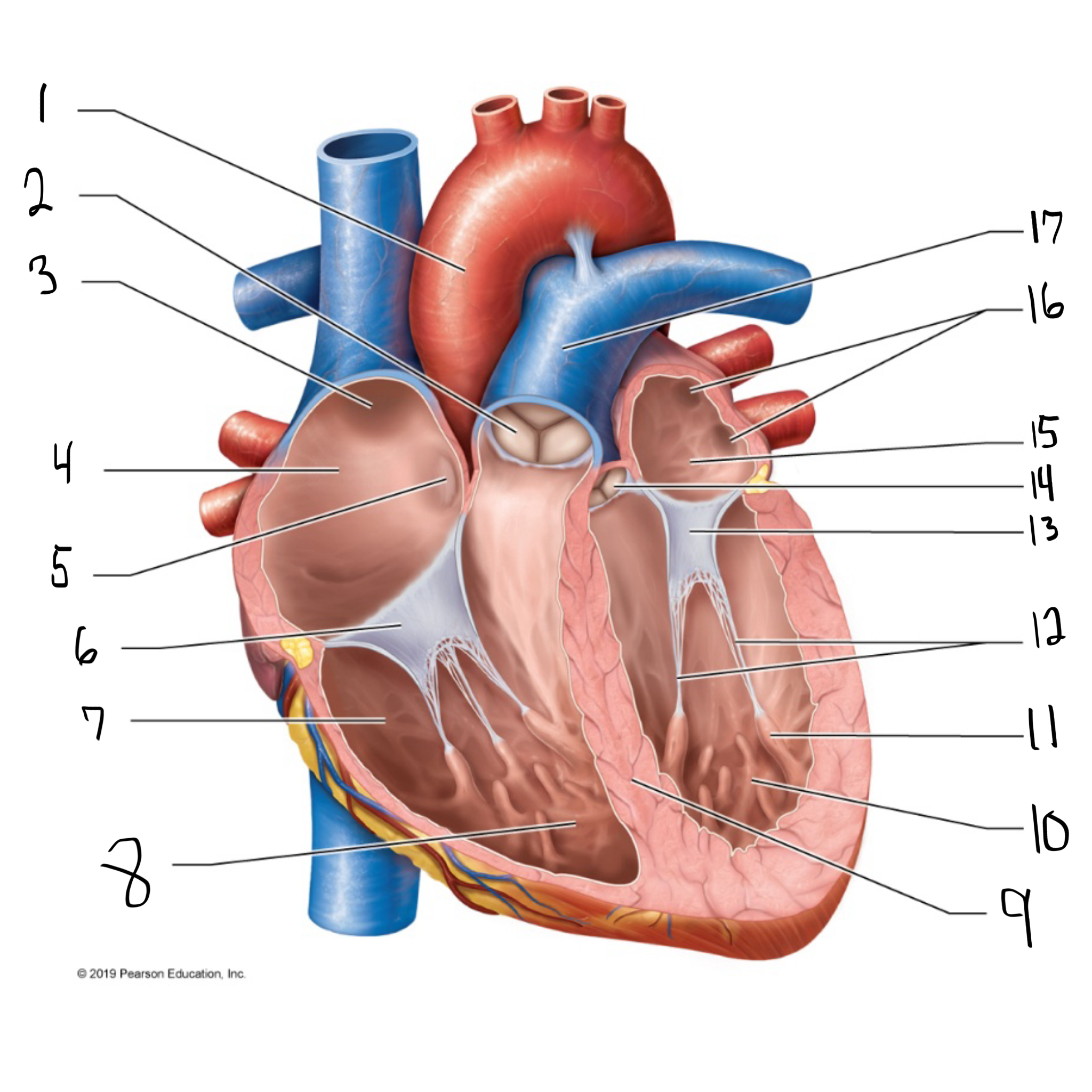
bicuspid valve
what is #13 in the image?
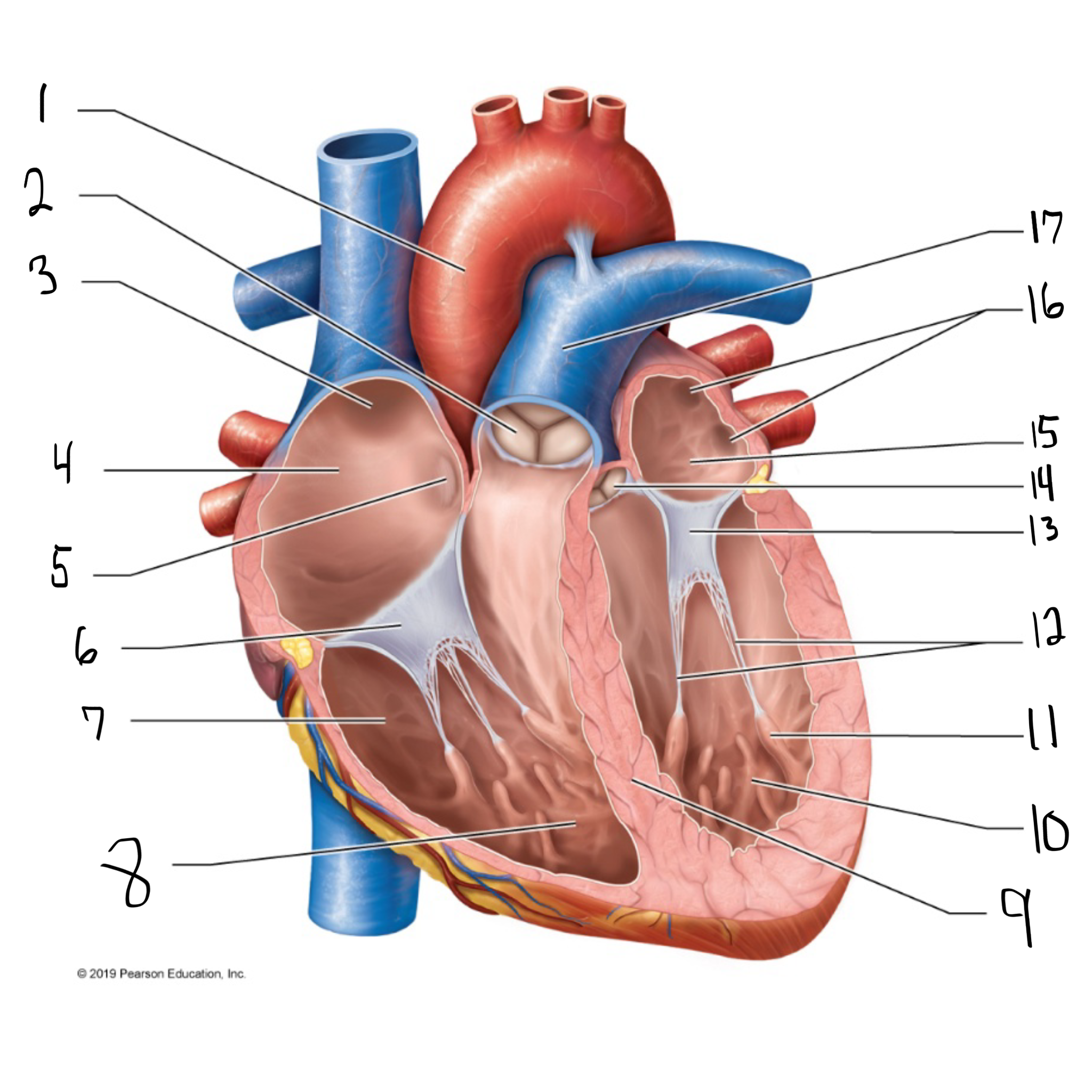
aortic valve
what is #14 in the image?
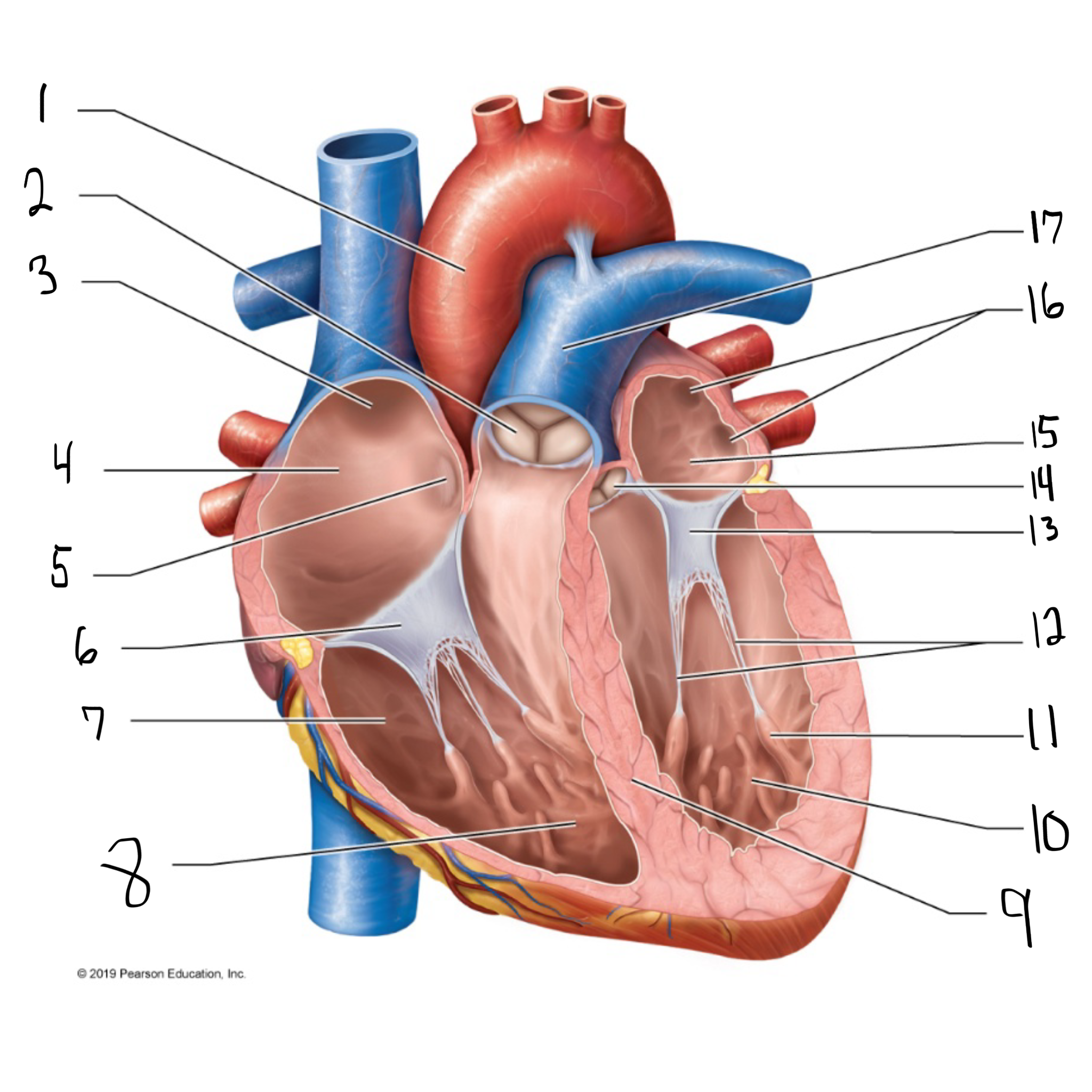
left atrium
what is #15 in the image?
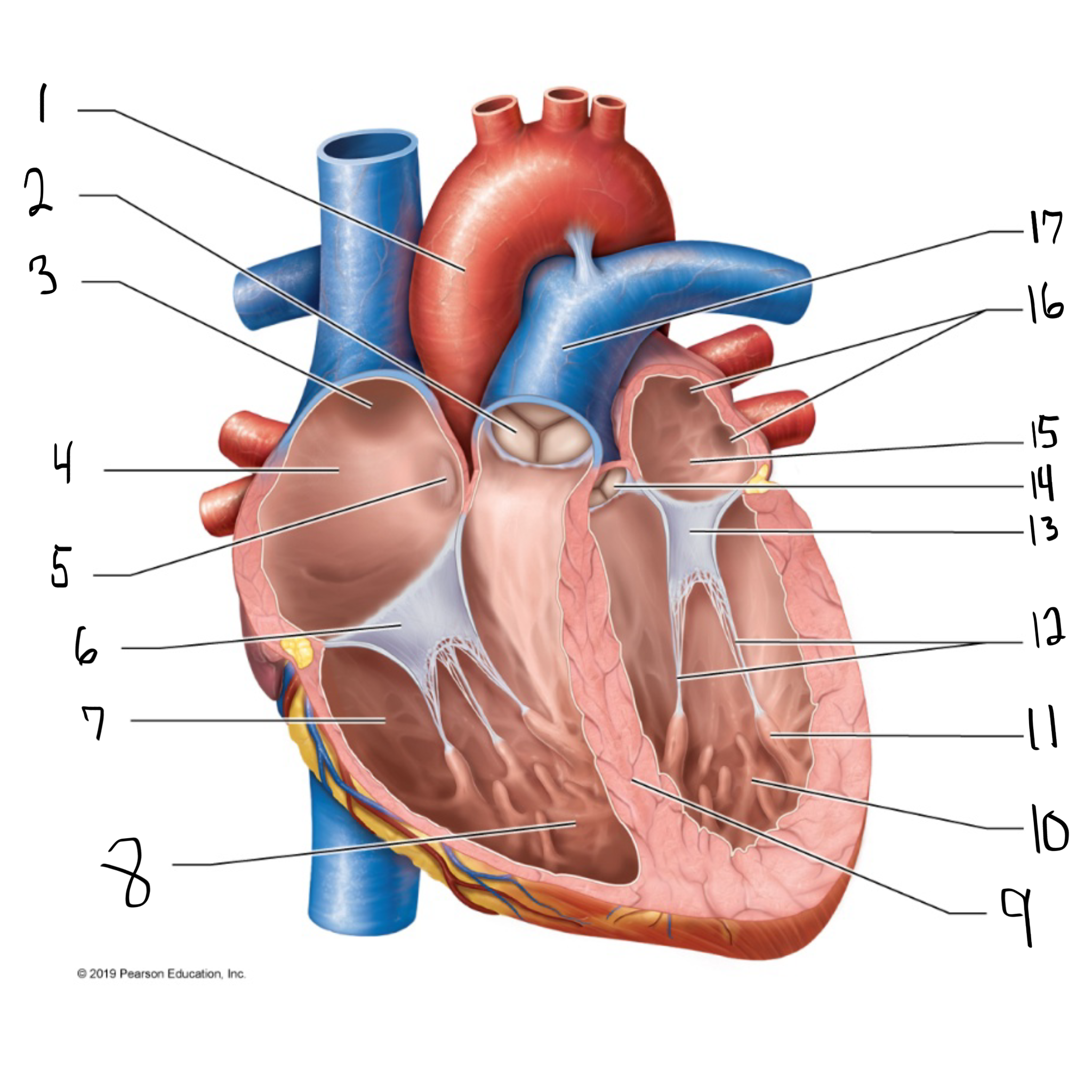
opening of left pulmonary veins
what is #16 in the image?
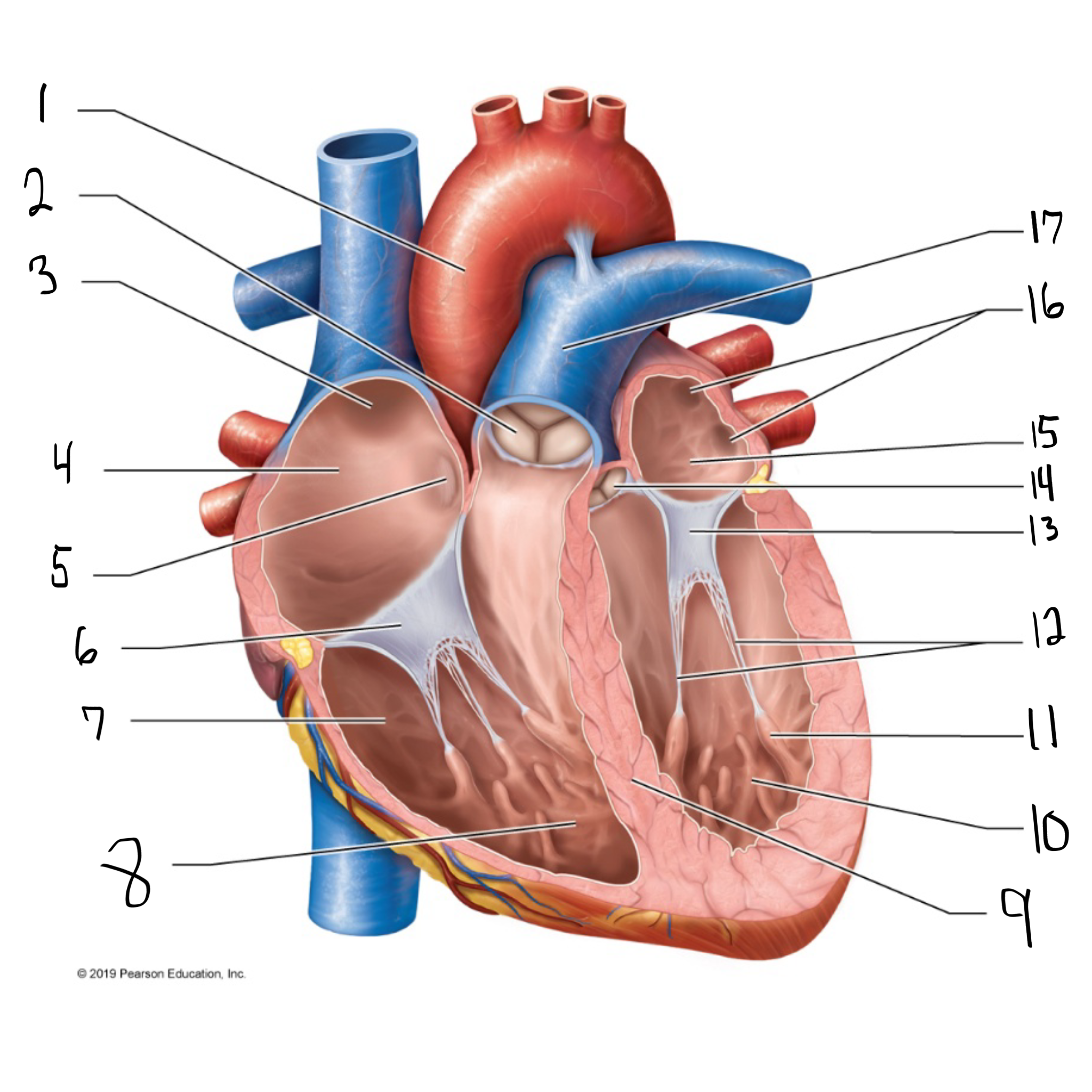
pulmonary trunk
what is #17 in the image? (carries blood from the right ventricle to the lungs)
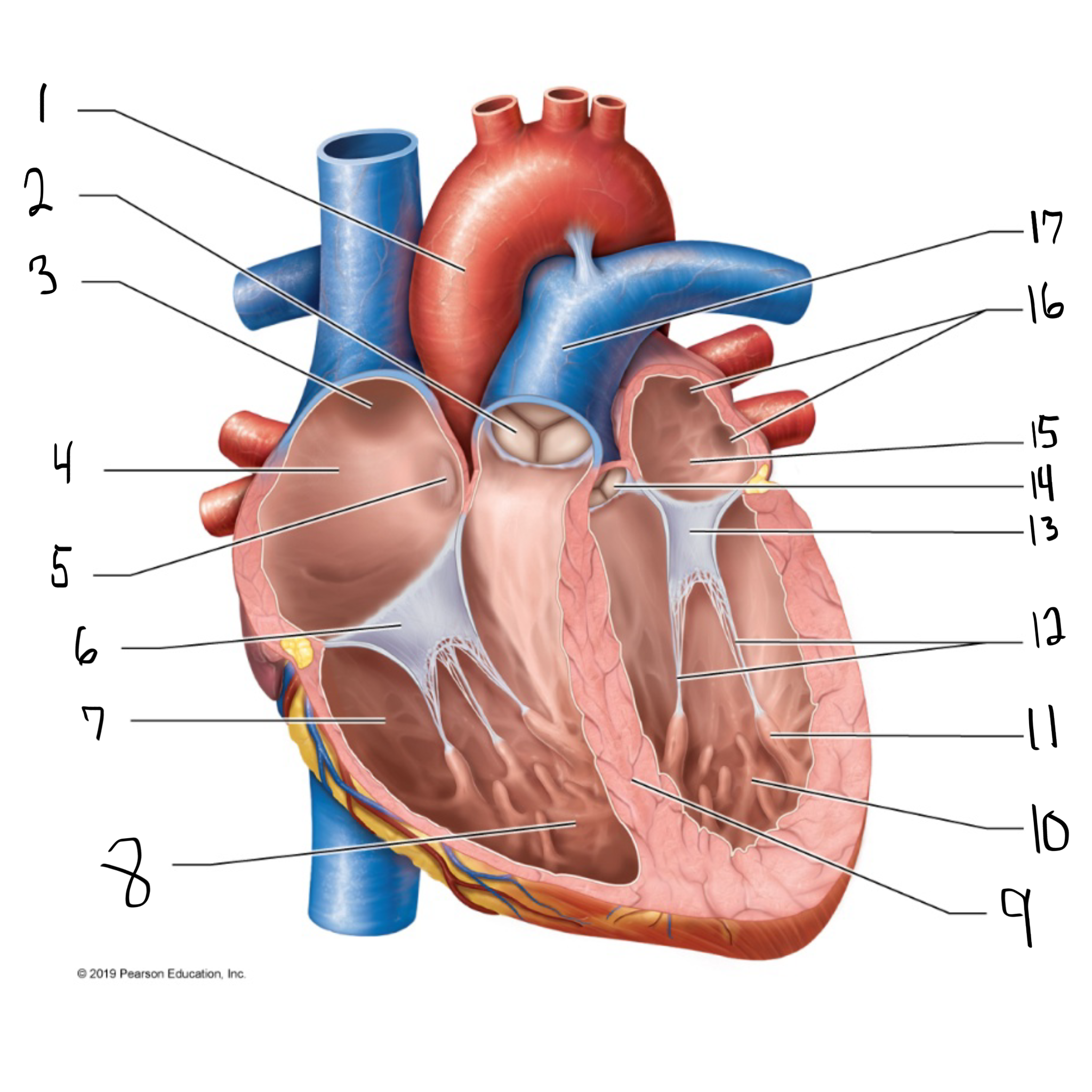
myocardium
muscular, middle layer of the heart
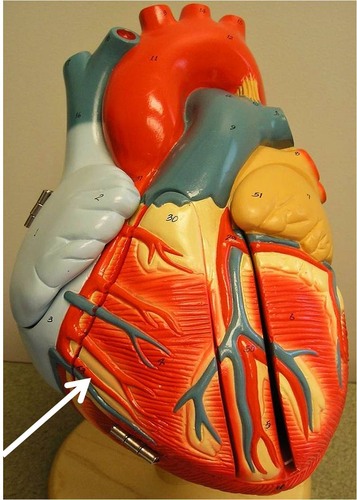
ligamentum arteriosum
what is in this image?
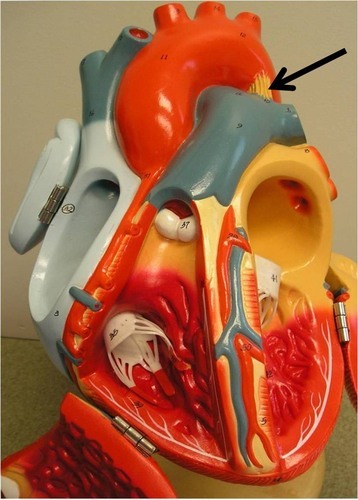
coronary sinus
what is in this image? (empties into right atrium)
marginal artery
what is in this image? (supplies the posterior surface of the left atrium and ventricle)
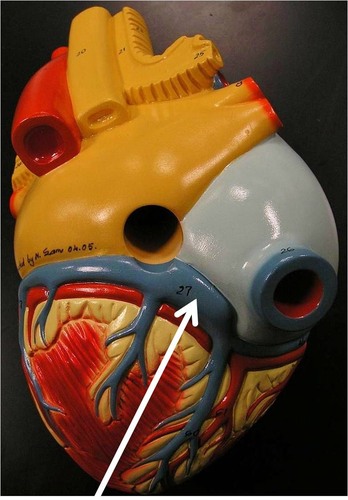
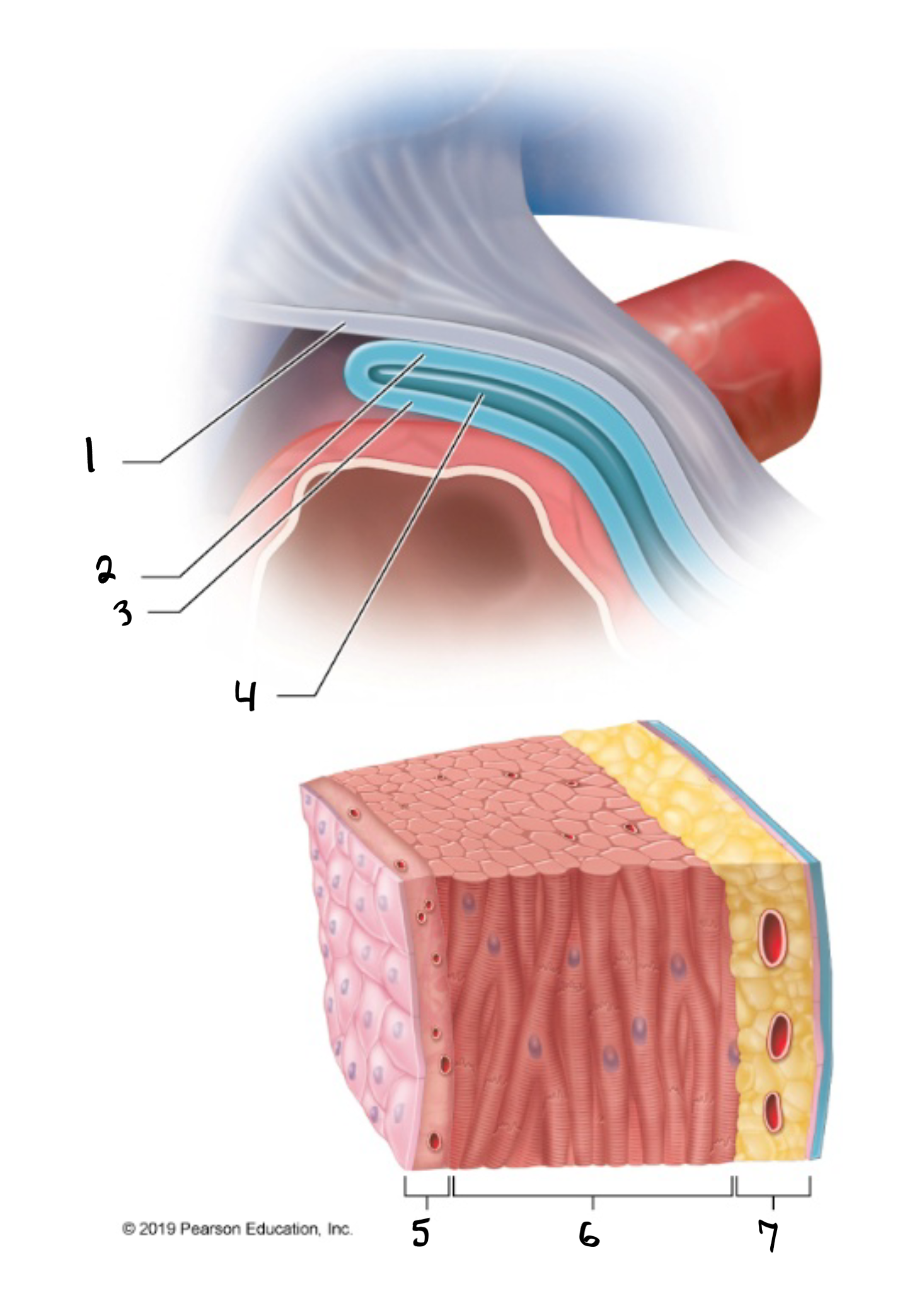
fibrous pericardium
what is #1 in the image?
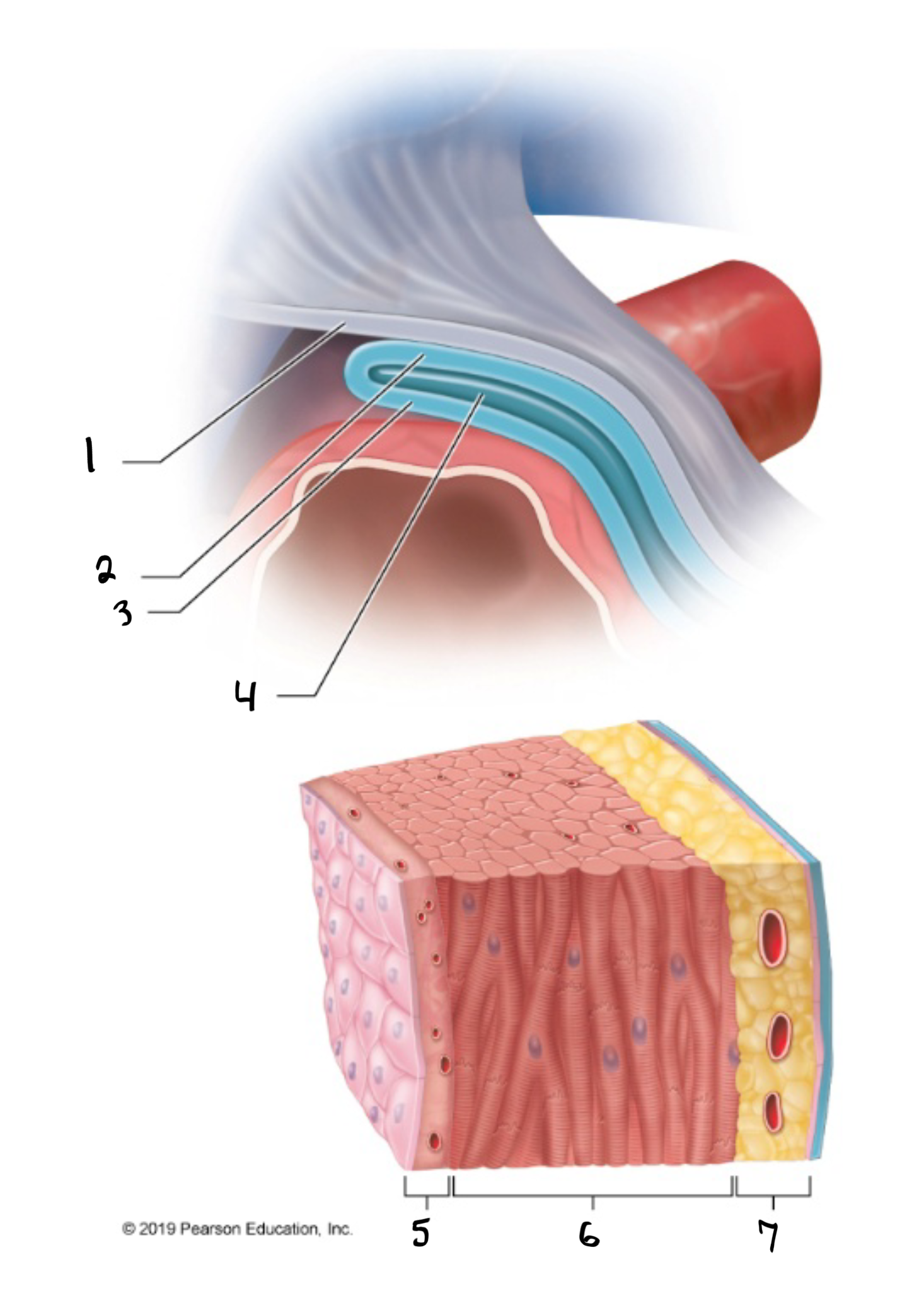
parietal pericardium
what is #2 in the image?
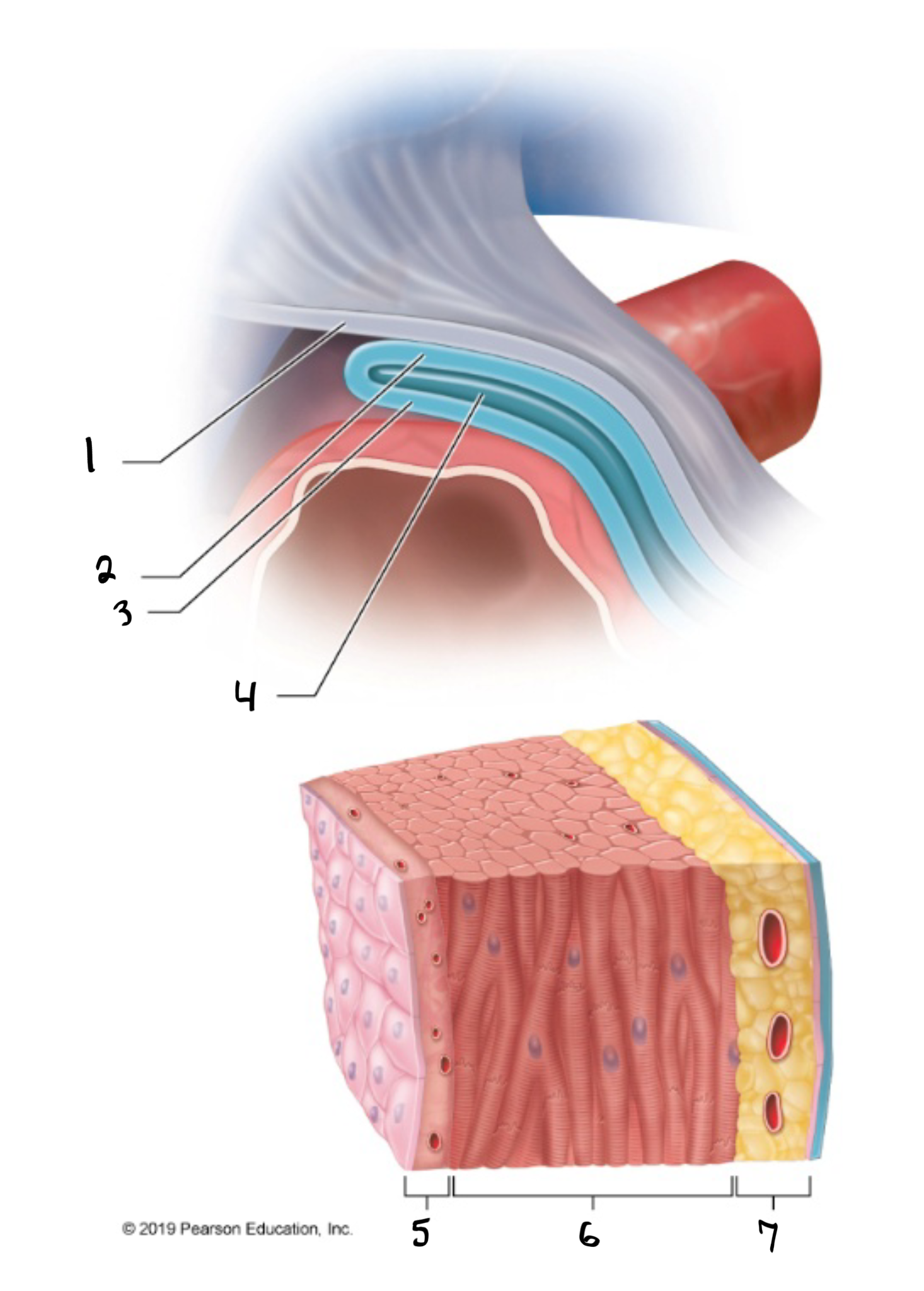
visceral pericardium
what is #3 in the image?
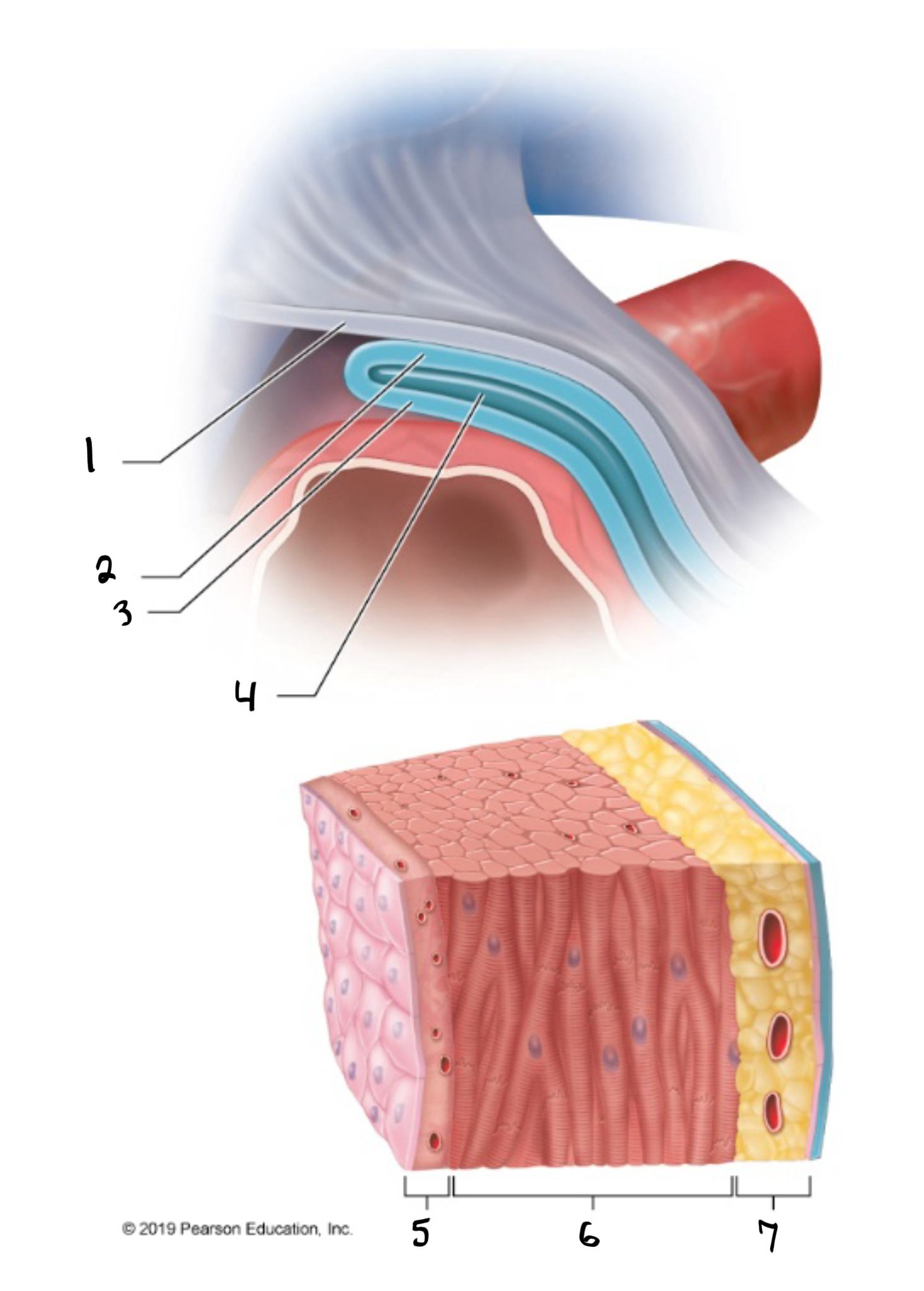
pericardial cavity
what is #4 in the image?
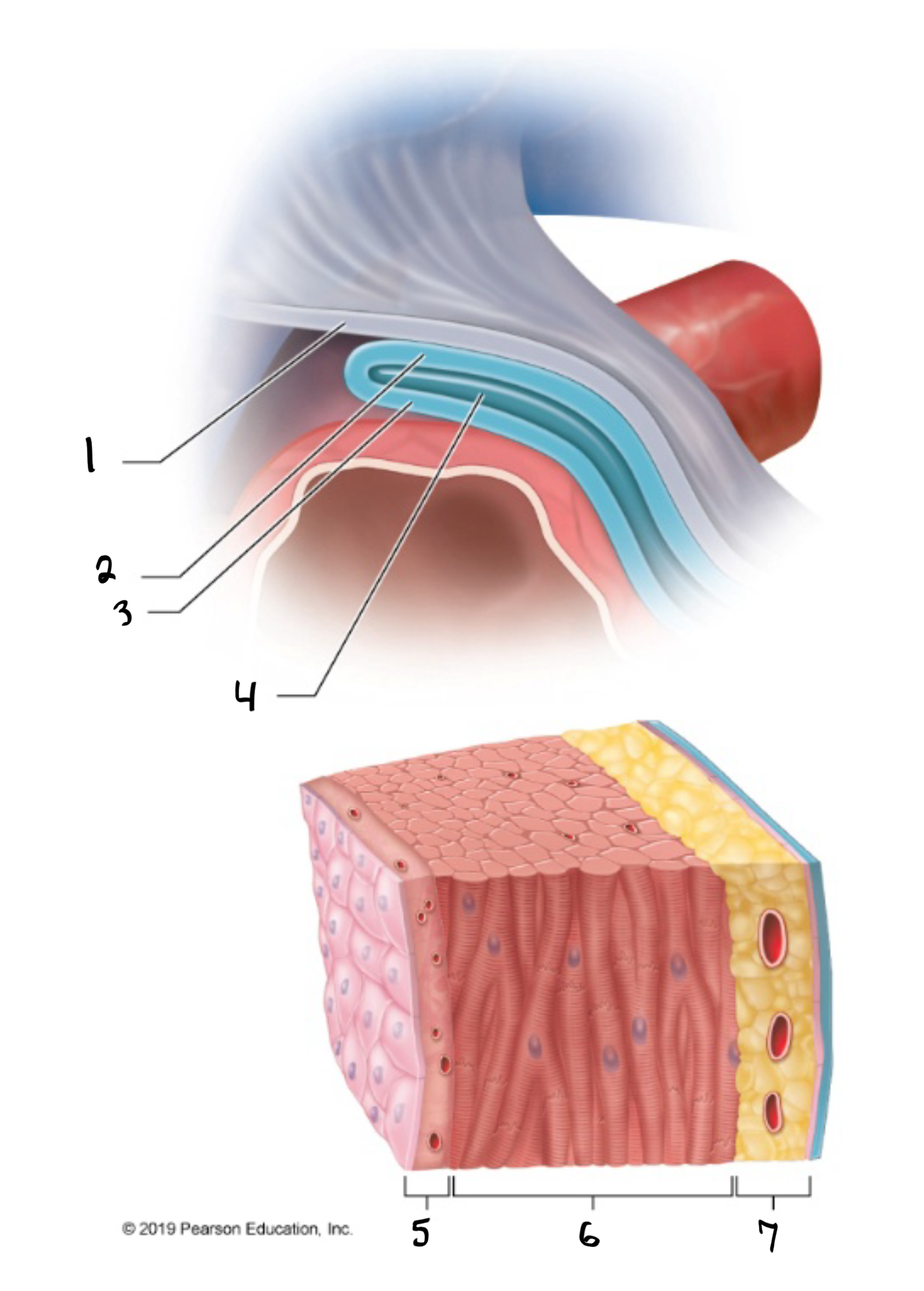
endocardium
what is #5 in the image?
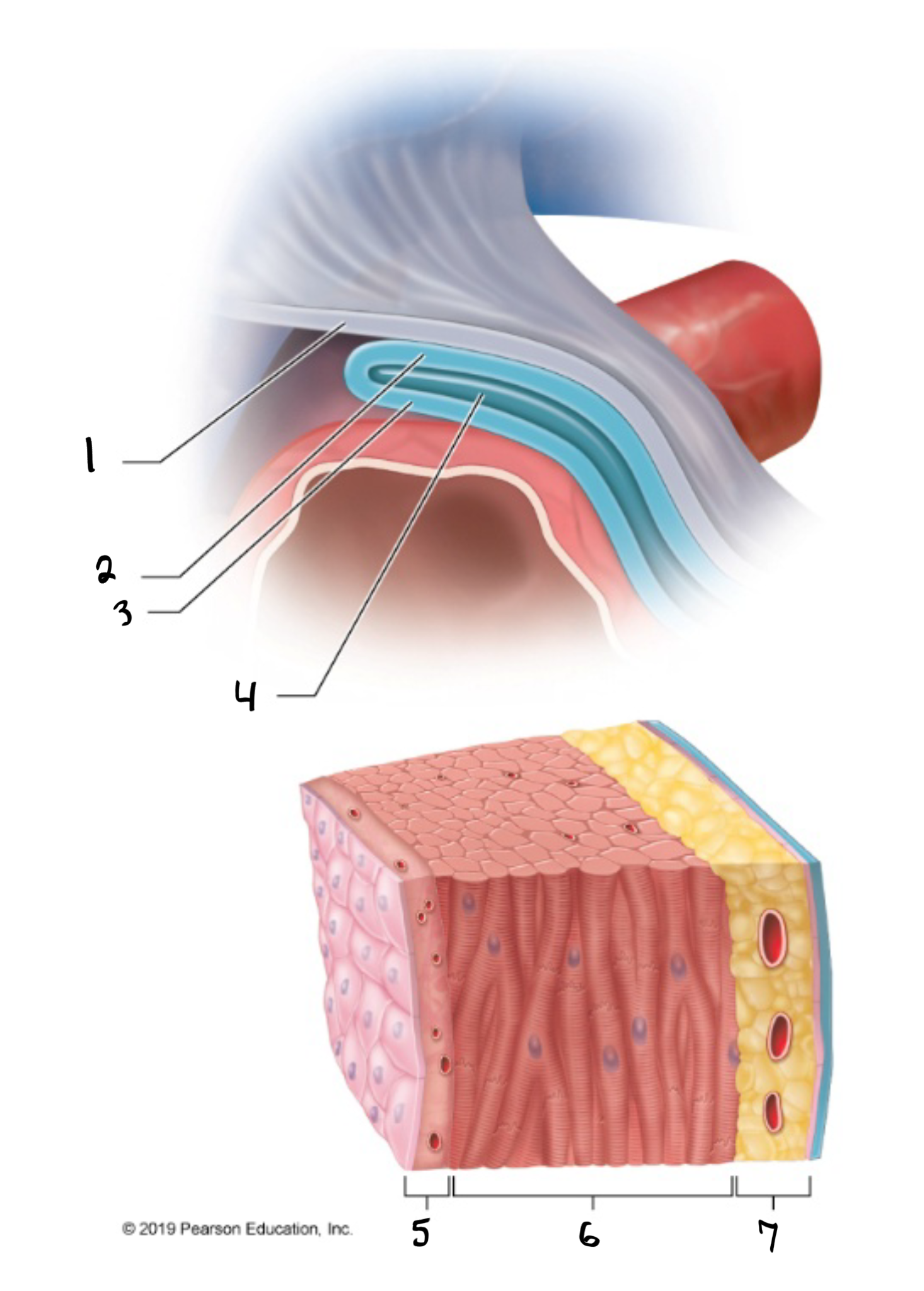
myocardium
what is #6 in the image?
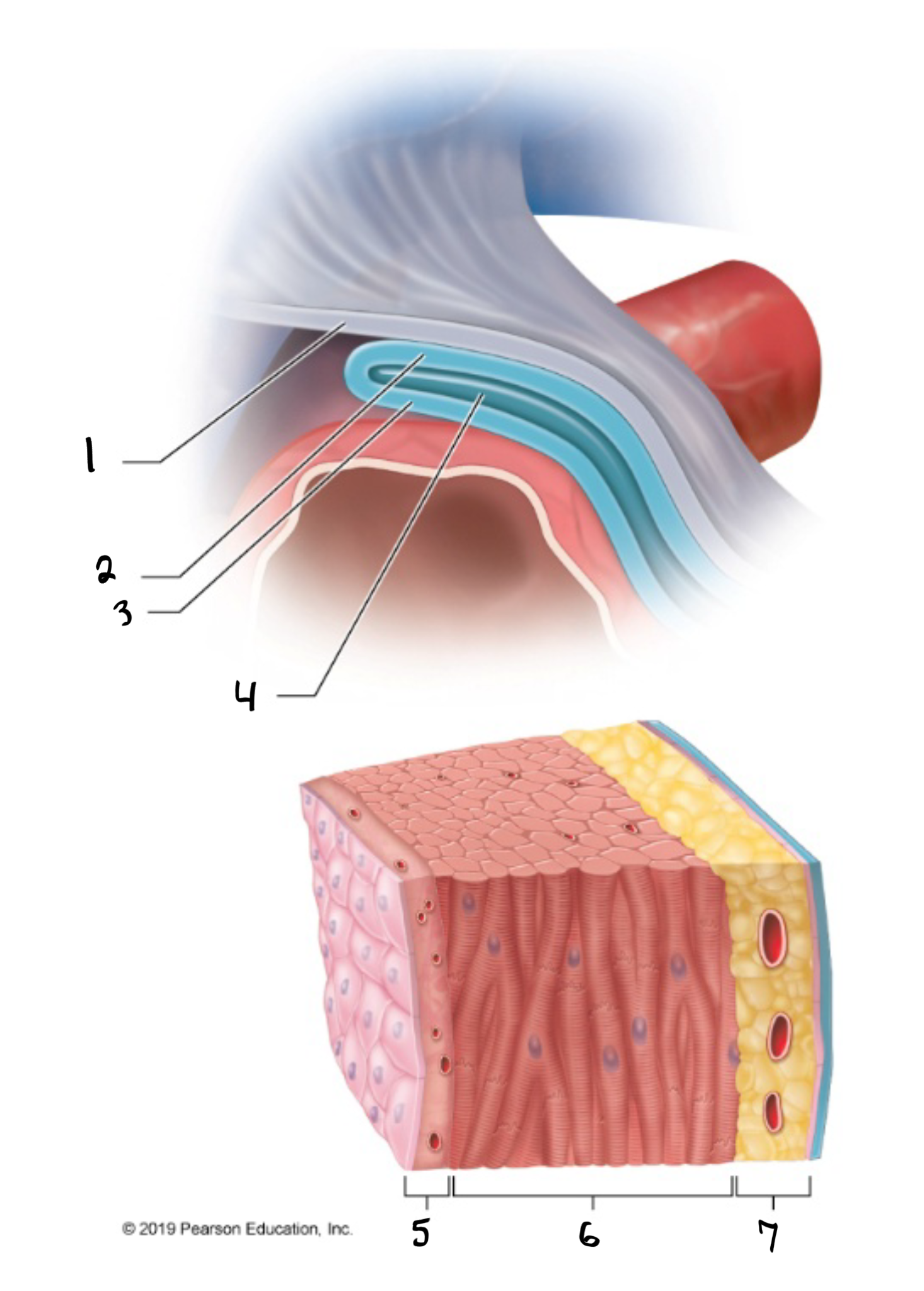
epicardium
what is #7 in the image?
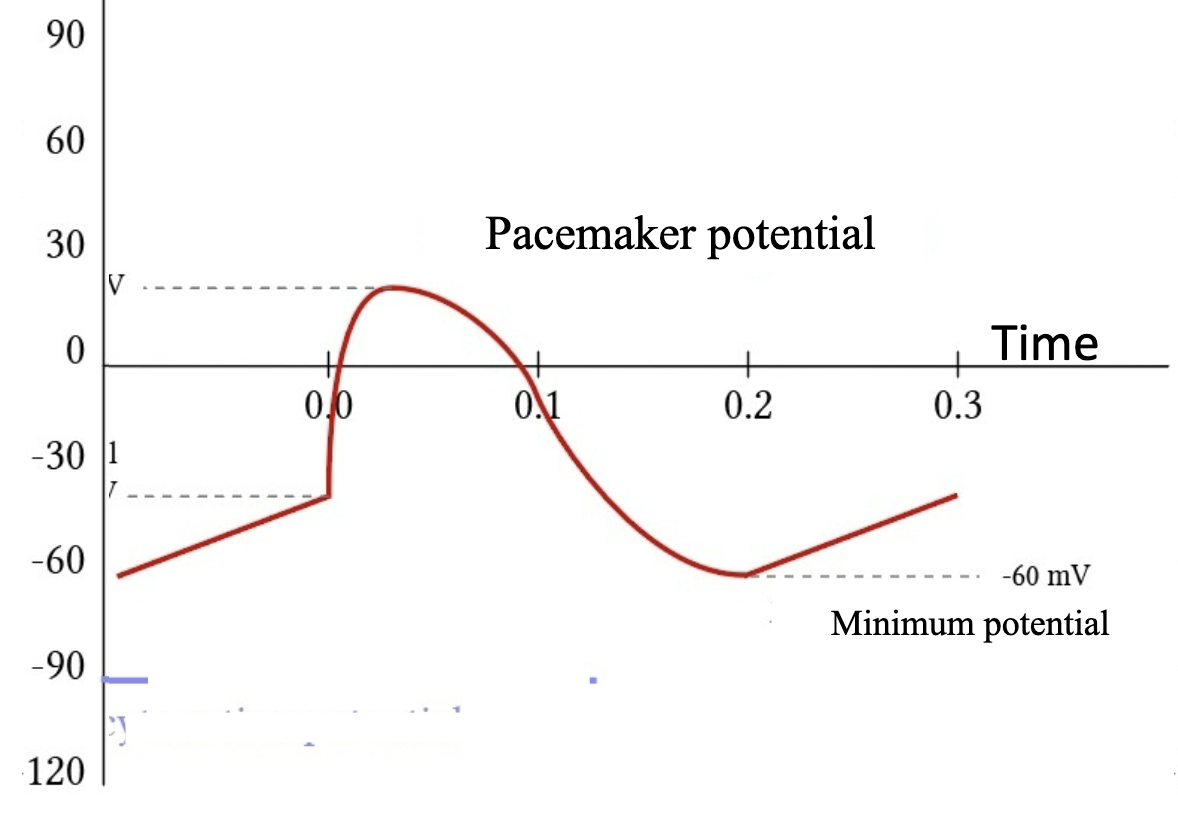
pacemaker cell
this image shows the action potential graph of what kind of cardiac cell?
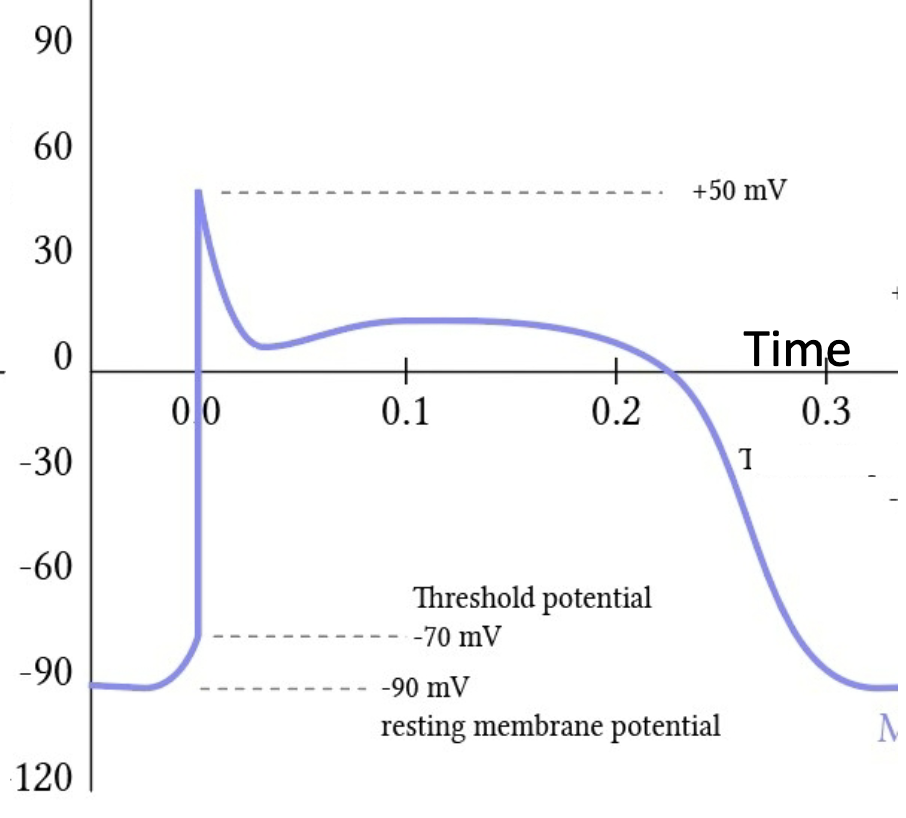
contractile cell
this image shows the action potential graph of what kind of cardiac cell?
atrioventricular node
after the sinoatrial node fires its action potential, what receives the action potential from there?
atrioventricular bundle
after the atrioventricular node receives the action potential, what does it pass it on to?
purkinje fibers
after the right and left bundle branches receive the action potential, what does it pass it onto?
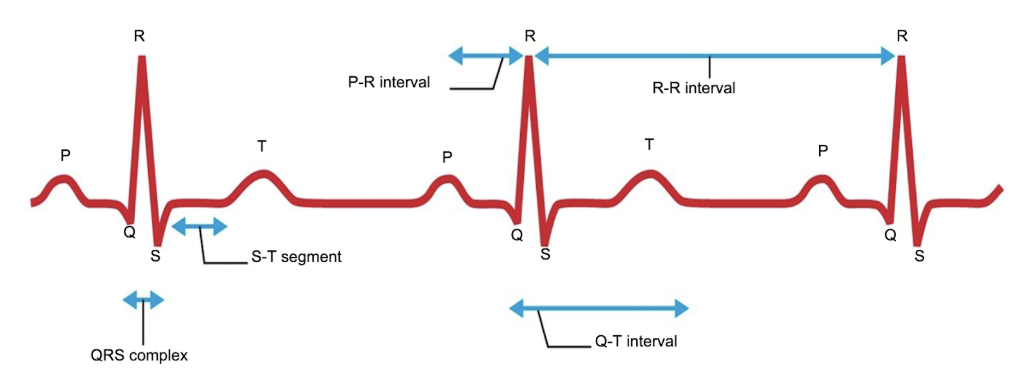
P wave
which wave demonstrates the atria depolarizing?
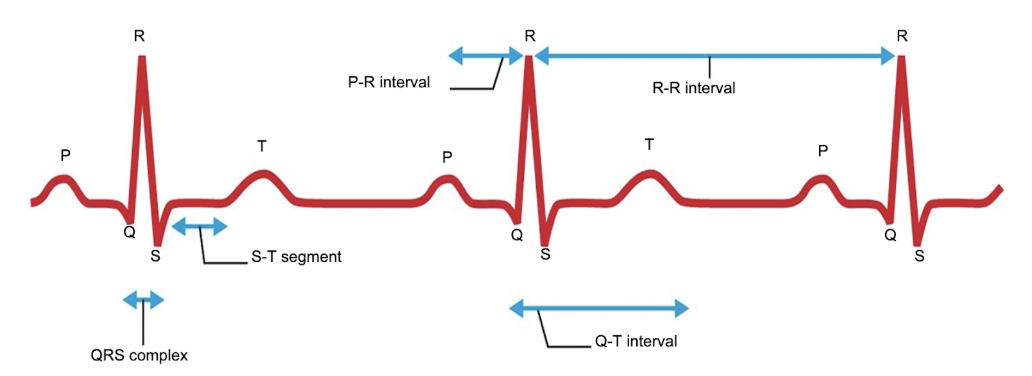
QRS complex
what demonstrates the ventricles depolarizing?
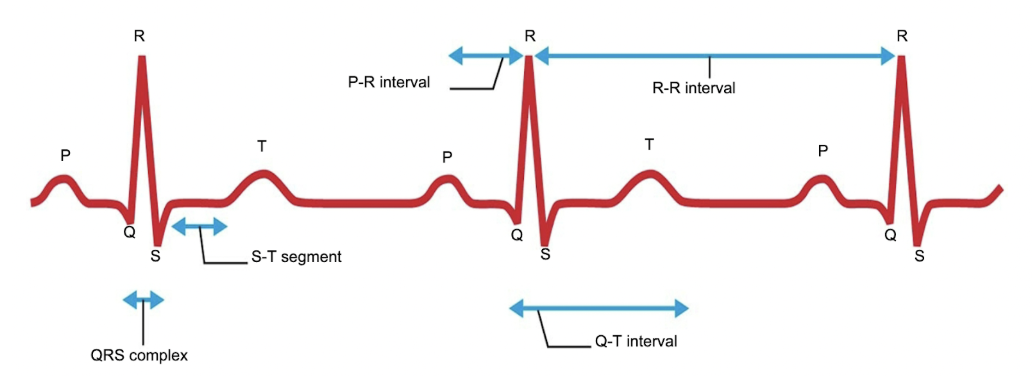
T wave
which wave demonstrates the ventricles repolarizing?
left ventricle
the myocardium of which ventricle are thicker?
weaker
the lesser the stretching of a ventricular contractile cell before contraction, the ______ the force of the contraction will be.
tricuspid valve
which valve is between the right atrium and right ventricle?
bicuspid valve
which valve is between the left atrium and left ventricle?
mitral valve
another name for the bicuspid valve is the
pulmonary veins
oxygenated blood is carried from the lungs to the left atrium by the?
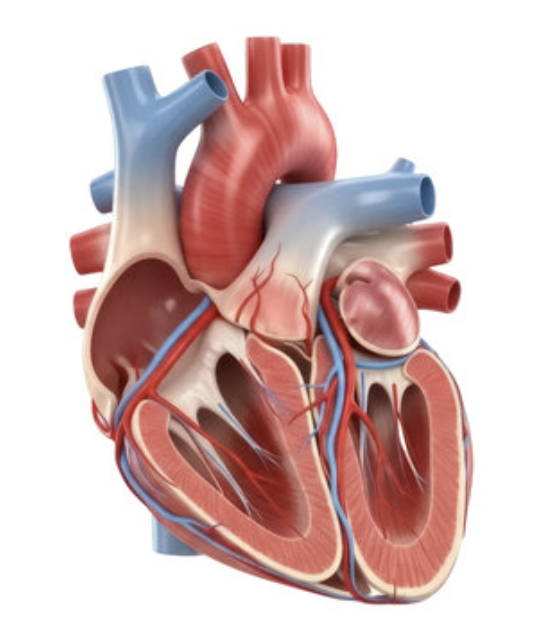
closed
When the ventricles are contracting and pumping blood out, the atrioventricular valves are?
open
When the ventricles are contracting and pumping blood out, the semilunar valves are?
pulmonary trunk
Blood is pumped from the right ventricle directly into the?
from
Does the aorta sends blood to or from the heart?
chronotropic agents
what agents (no matter positive or negative) change the heart rate?
positive chronotropic
a ____ agent will cause an increase in heart rate
negative chronotropic
a ____ agent will cause an decrease in heart rate
diastolic
end _____ volume is the volume of blood in a ventricle before the ventricle contracts
systolic
end _____ volume is the volume of blood in a ventricle after ventricular ejection
ANP
Which hormone can decrease cardiac output by decreasing blood volume and preload?
aldosterone and ADH
Which two hormones can increase cardiac output by increasing fluid retention and preload?
pacemaker cell
“A hyperpolarization triggers a slow depolarization to a threshold voltage.” This describes what cardiac cell?
contractile cell
“Calcium ions enter the cell at the same time potassium ions exit the cell, prolonging the length of time the cell experiences the action potential.” This describes what cardiac cell?
contraction
inotropic agents influence…?