MATE 210 Lecture 15-18
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Ceramics- properties, composition, performance, structure
Structure- ceramics tend to have more complex structures than metals

Types of ceramics
Glasses, clay products, refractories, abrasives, cements, ceramic bio materials, carbons, advanced ceramics
Refractories
Clay
R- withstand high T without melting or decomposing, resistance to thermal shock, basically good in extreme temps
C- one of most used ceramics, cheap, abundant, layered crystal structures, drying and firing
How cement works
Chemical reactions between water and cement particles
Mix cement and water, cement grains dissolve in water, hydrates precipitate (new solids with higher volume)
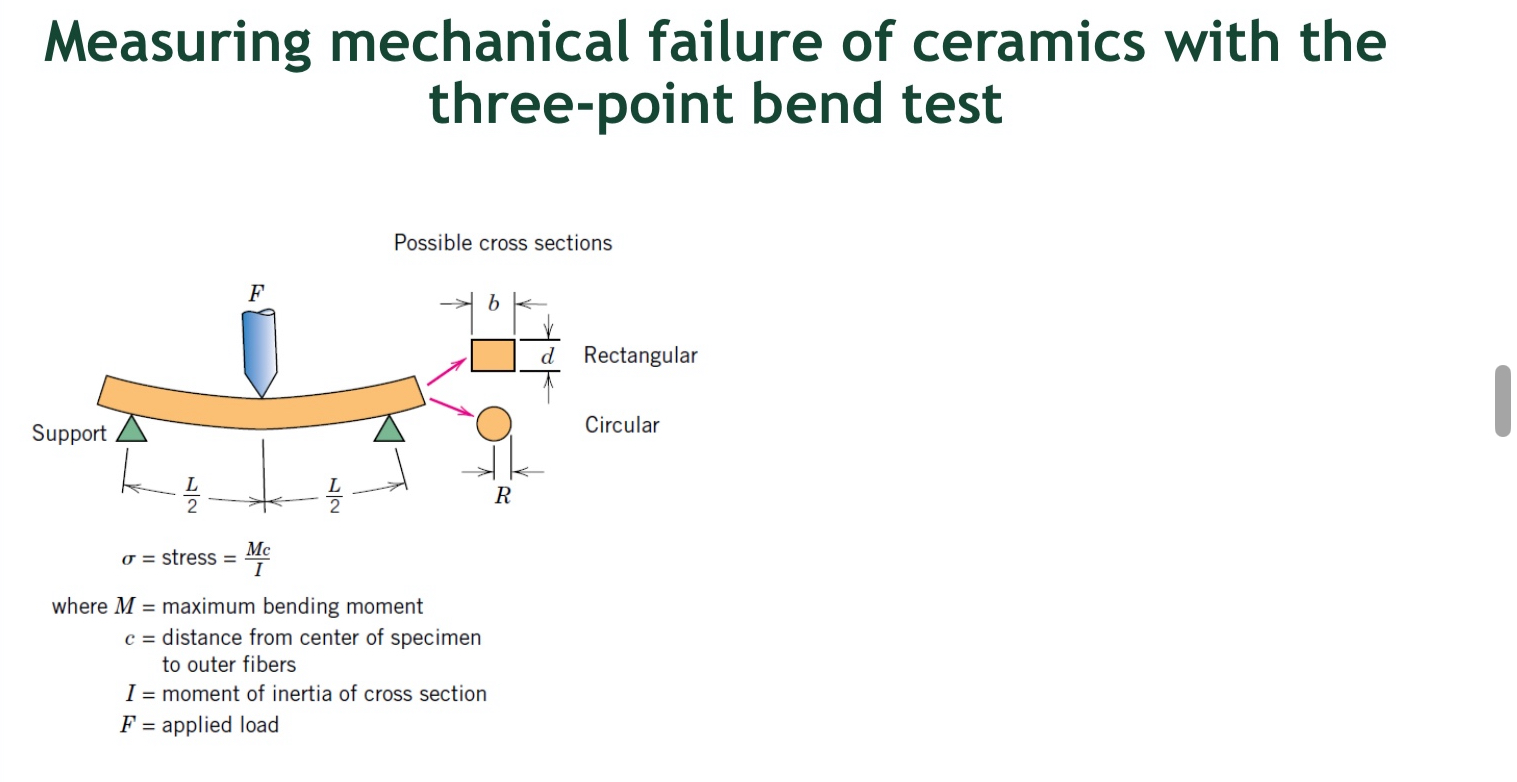
Describe 3 point bend test
What is the 3 point bend test used for
Used for measuring mechanical failure in ceramics
Glasses
Non-crystalline silicates containing other oxides
Properties change drastically at glass transition temperature
Tempering improves properties by inducing compression on glass surface
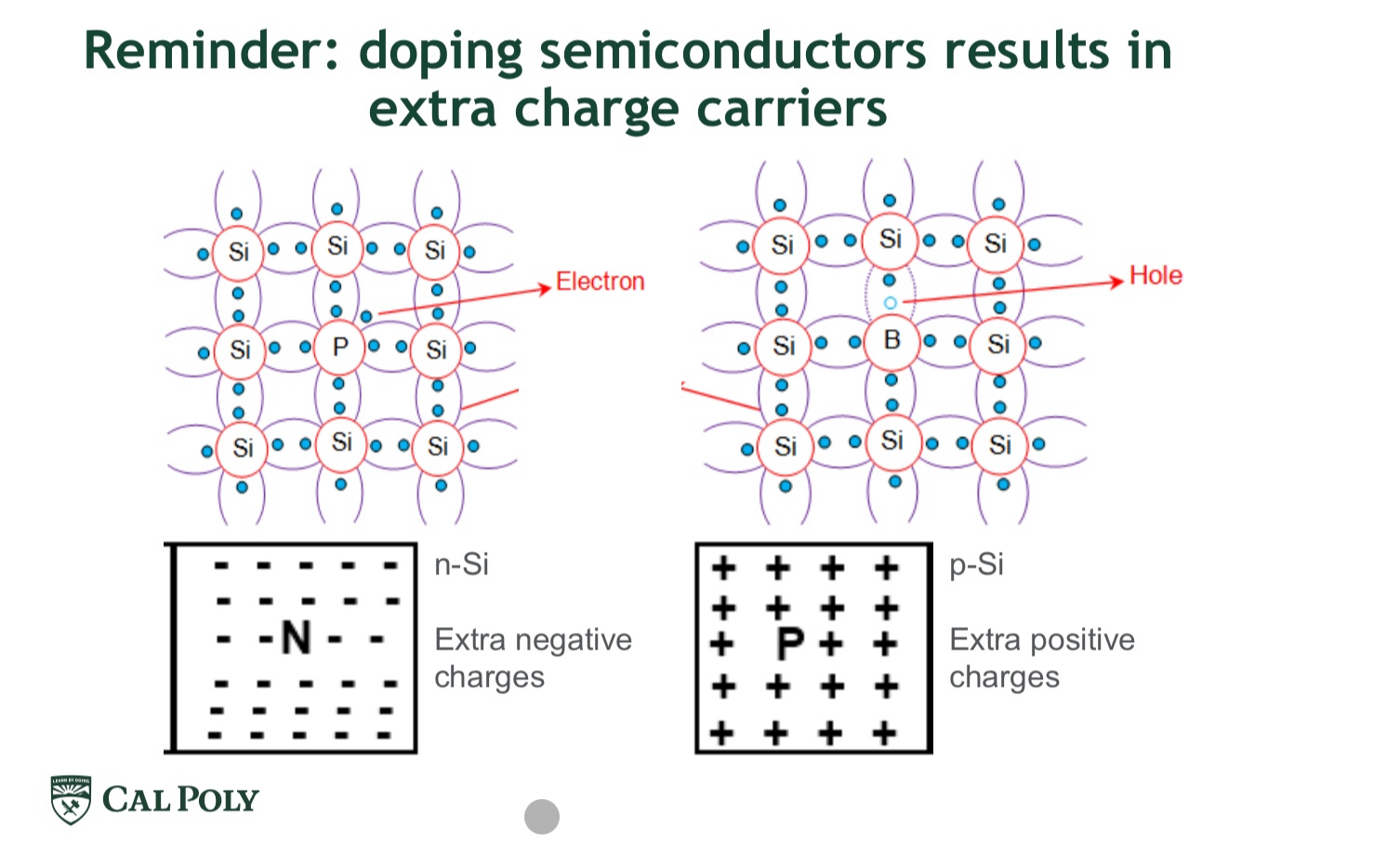
Semi conductors
Materials with low to moderate conductivity due to Their electronic structures (0 eV < Band Gap < 2 eV)
Intrinsic Semiconductors: materials with band gaps in the correct range as pure materials (only Si and
Ge)
Extrinsic Semiconductors: materials with band gaps in the correct range when doped with specific Atoms
N vs p type doping
Polymers (composition, properties, structure, performance)
Polymers are made up of repeating units bonded together through polymerization

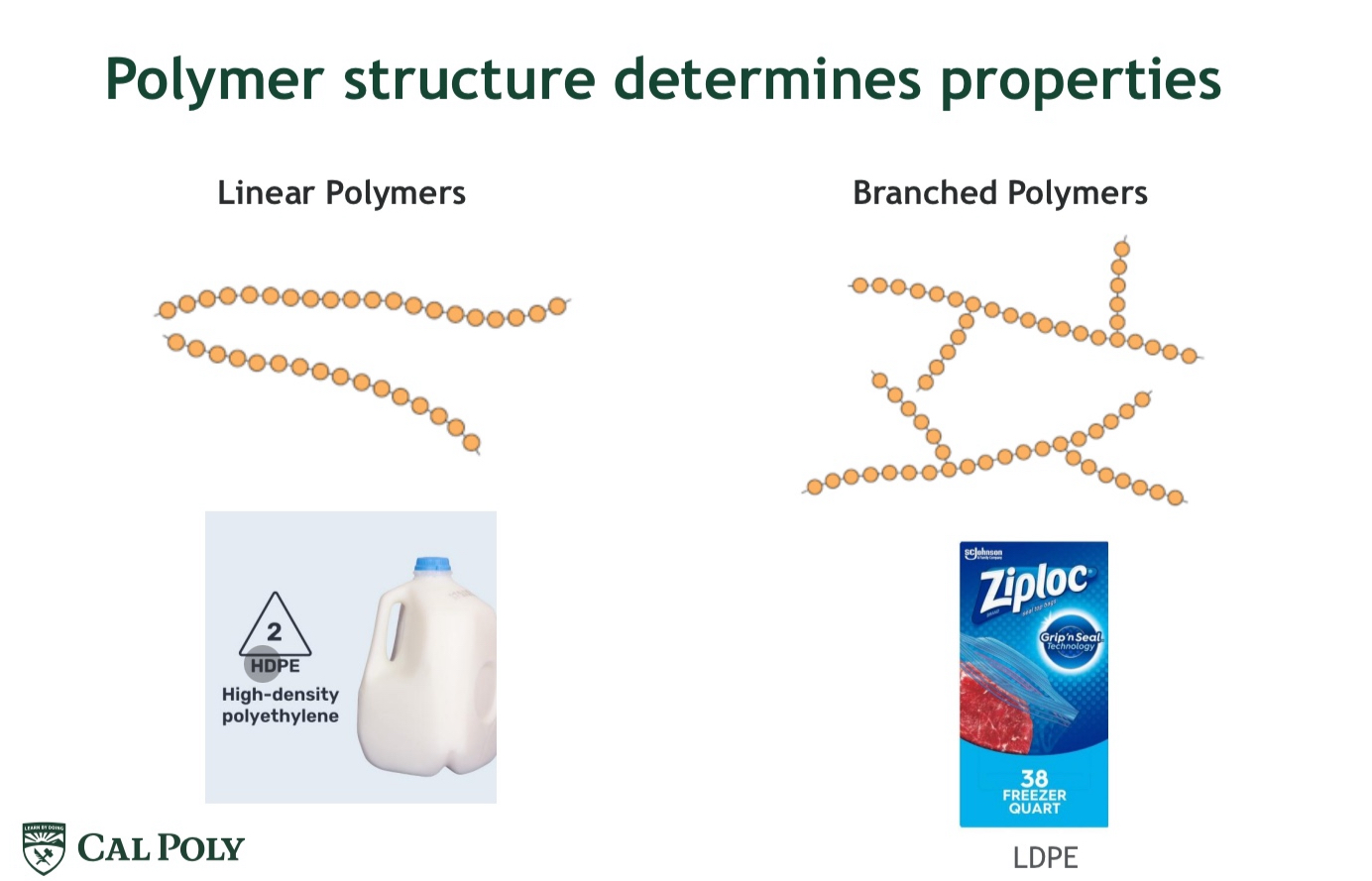
Polymer Structure
Repeating units
Linear vs branched polymers
Copolymers- polymers with different repeating units in their chains types of copolymers: Random, Alternating, Block, Graft
Cross linked polymers- separate chains covalently bonded together
Chemical reactions, light, and temperature Influence cross-linking and properties
What do plasticizers do
How to control crystallinity and density
Use additives called plasticizers to change
glass transition temperature
Extrusion of the material controls density and crystallinity
What is a composite, , what phases are there,
Composite is a combination of two or more materials
Dispersed phase and matrix phase
Dispersed phase
Dispersed phase influences properties of composites- concentration size, shape, orientation, distribution
3 types of composites and things to think about for each
Particle reinforced- how many particles to put in the matrix
fiber reinforced- direction of fibers, length of fibers, random or aligned
structural- laminating sheets with different fiber orientations yields in plane isotropy
Steps in material selection process
Translation- express design requirements as constraints and objectives
Screening- eliminate materials that fail constraints
Ranking- find materials that do job the best
Supporting information- explore top ranked candidates
Impacts on environment
What is impacting the environment? Is it the materials, manufacturing, use, or disposal?
Are you designing for it to be good for environment now or for it to be sustainable for a long time?