Geology Midterm 2
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Foliation degrees and draw out chart kinda
Shale-thin dull layers
Shiest-shiny with observable layers
Gniess-thick with obervarble crystals
migmatitic-thick with very observable crystals
3 tidal zones and schedules
Weaters law
Weaters-weather. enviornemtents beside each other eventually land ontop each other
3 types of longshore deposits
2 types of pressures
think of box being squished into small space,confining, direct
4 types of river styles
4 types of allochems
fossils
oolites-small spherical sand sized grains, each with laters,
intraclasts-eroded peices of preexisting rock
pellets-lithified poop
wilson cycle
rift occurs causing ocean to form, ocran eventually sloses up causing 2 plates to converge and mountains to form, mountains get eroded and cycle continues
types of siesmic waves
appalation mountain origin
mountains in convergent and rift
4 physical traits for transported sediments
roundness, sphericity, sorting, grain size
types of sedimentary enviornments
3 examples of parent rock
biotite to amphibolite sandstone to quartz shale to slate
4 types of sedimentary structure
ripples, crossbed, graded bedding, mudcracks
3 main types of sedemintary rocks
4 sediment types and rocks affiliated w each one
4 things tide depend on
Foliation stress types
where does metamorophism happen and what kinda rocks r present
stress vs strain
joints, dipslip + strike slip faults
ductile deformation, plunging fold, basin dome + connection to syncline vs anti cyncline
archbishop ussher
used bibliological geneologies to fix time of earth
william smith
first map of england
james hutton
charles lyell unformitasnisms and 3 elements
nicholas steno and 3 principles
know all 4 eons
explain the roundness/ spericity for supermature, mature, submature and immature sedimentary rocks
supermature-rounded quartz
mature-subrounded
submature-subangular
immature-angular
the more mature it is the more weathered it is
A foraminifera
Stromataporoids
A bivalves
Byozoans
crinoids
open water
bottom dwelling
freshwater and saltwater
attached to hard surfaces
attached to sea floor
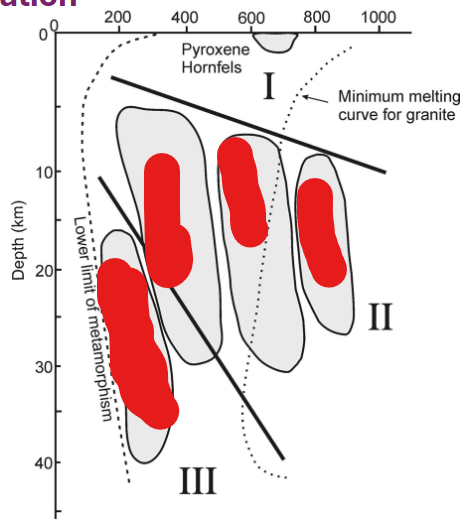
label this and describe the facies