Principles of Biology Exam 1 (Uark Shadwick)
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
Strengths of Science
-publicly understandable
- self correcting
- predictive
Qualities of Life
- organized
- acquire material and energy
- reproduce
- respond to stimuli
- homeostatic
- grow and develop
- capacity to adapt
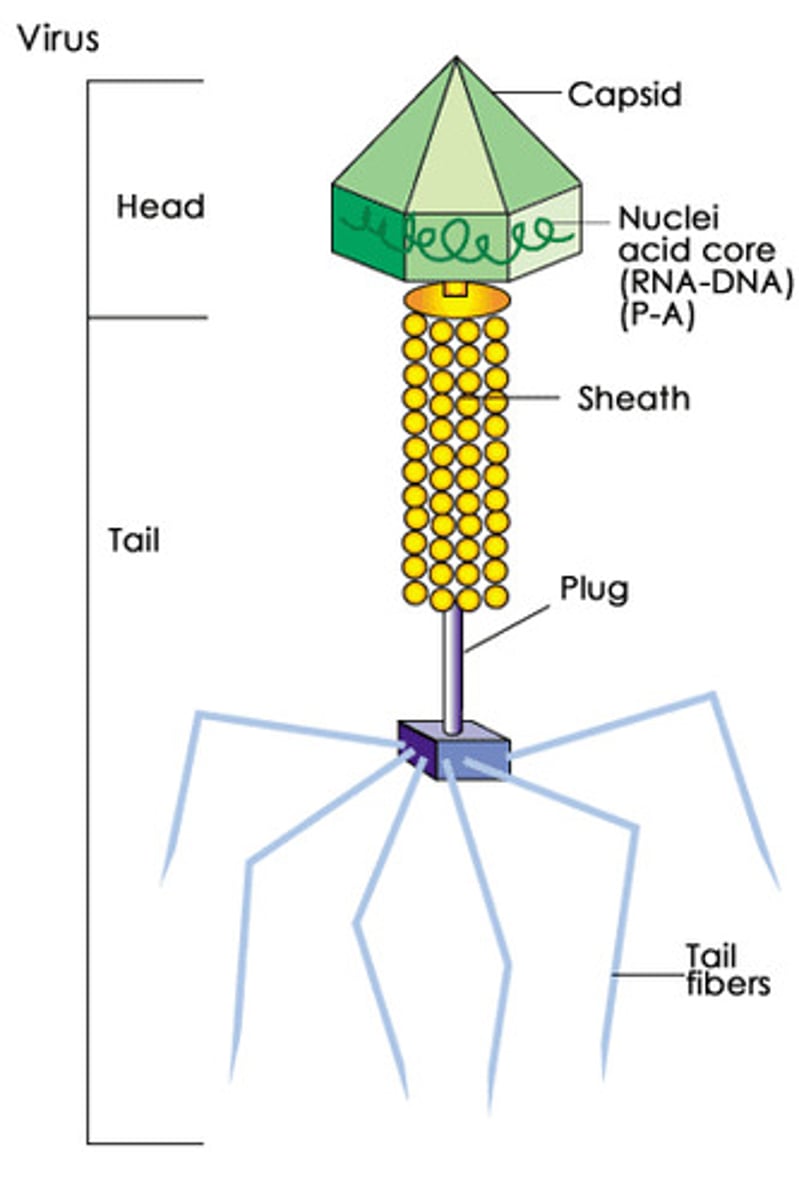
2 main components of viruses
-capsid
- nucleic acid core (DNA or RNA)
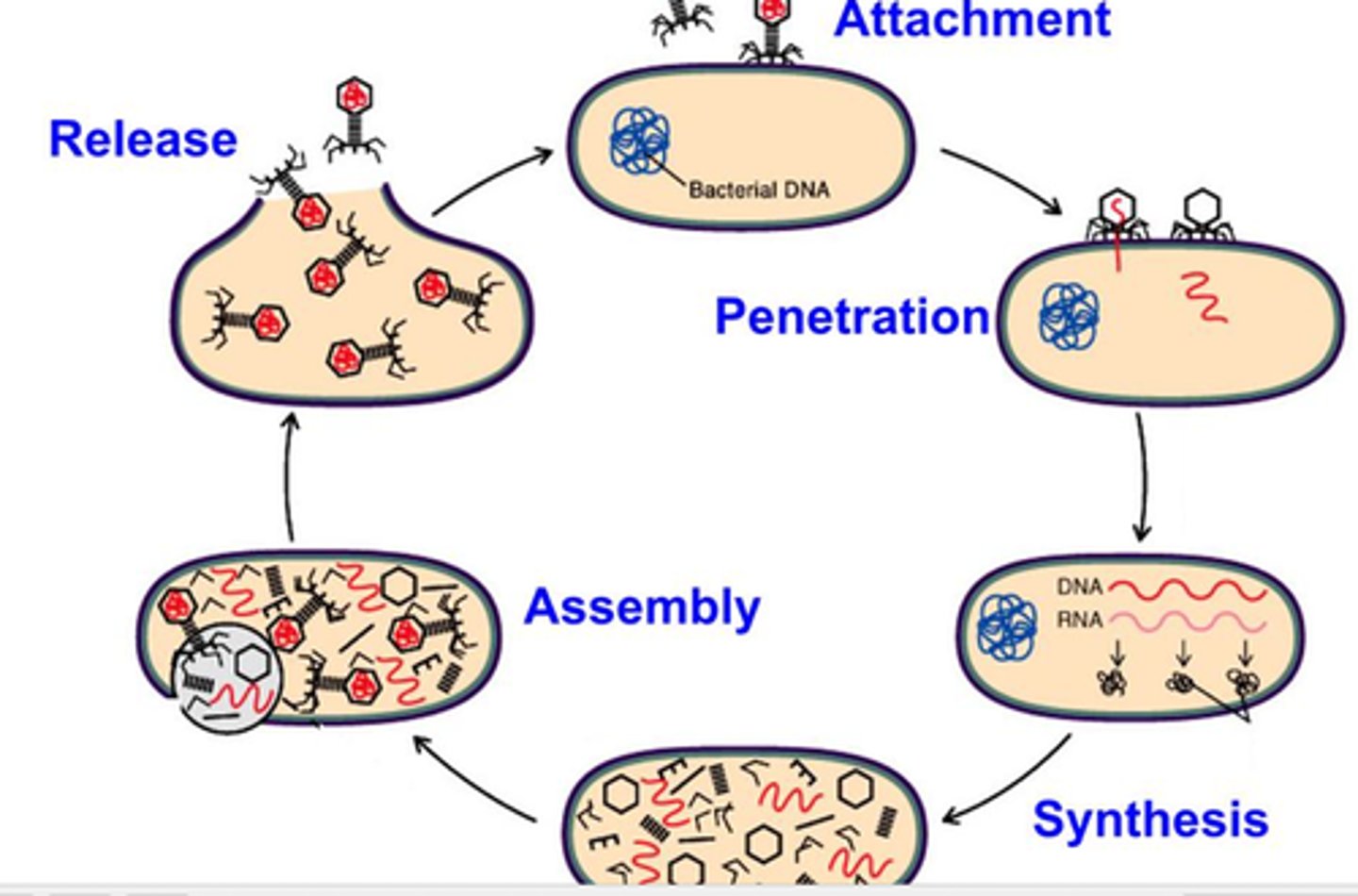
Virus life cycle
Attachment
Entry
Replication
Biosynthesis
Assemble
Budding/Emergence
Repeat/Release?
Life on earth has changed
Law (describes)
Things fall due to orbit
Theory (explains)
All mammals have mammary glands, therefore humans are mammals...
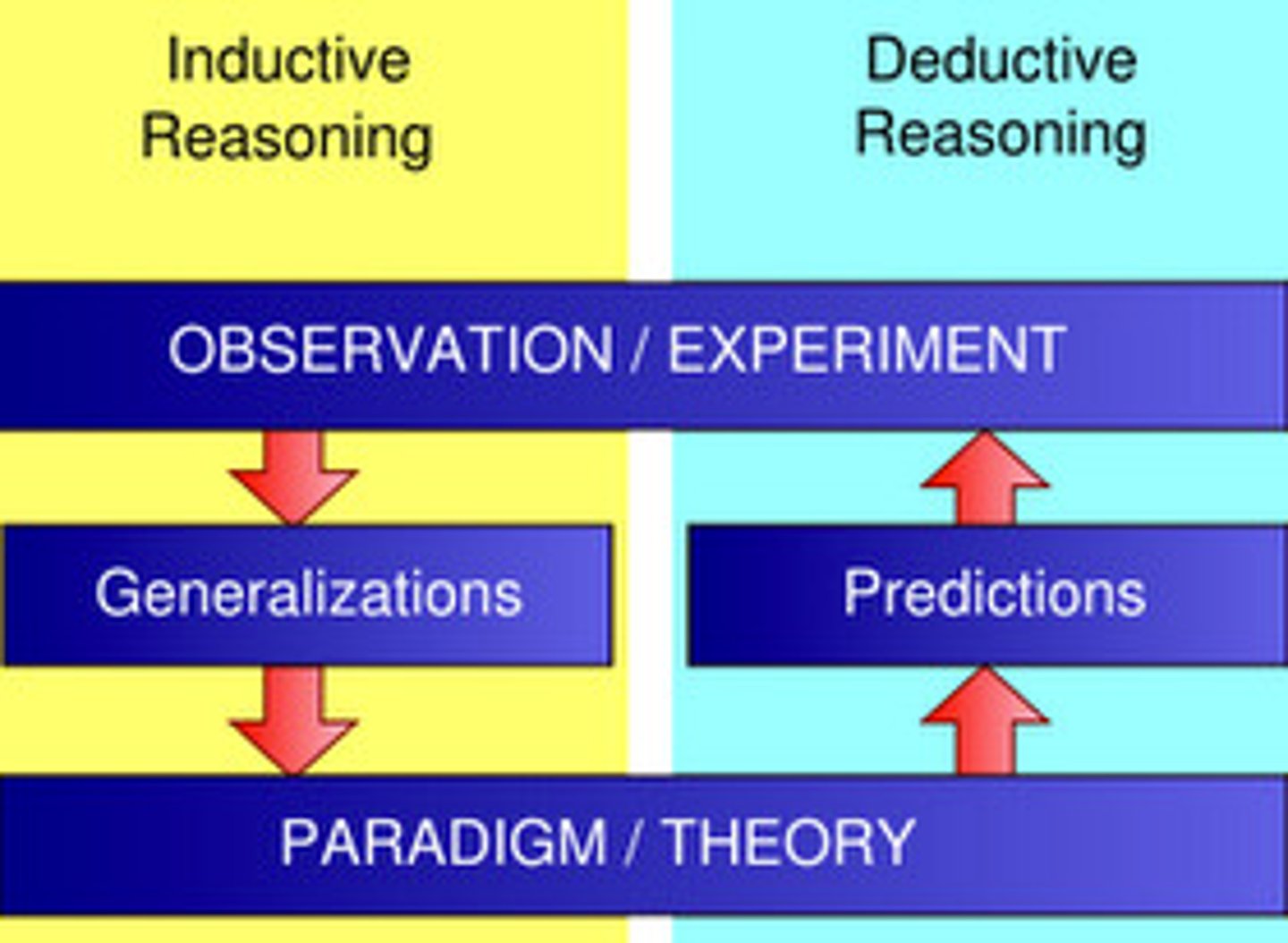
Deductive reasoning
Inductive reasoning
specific to general
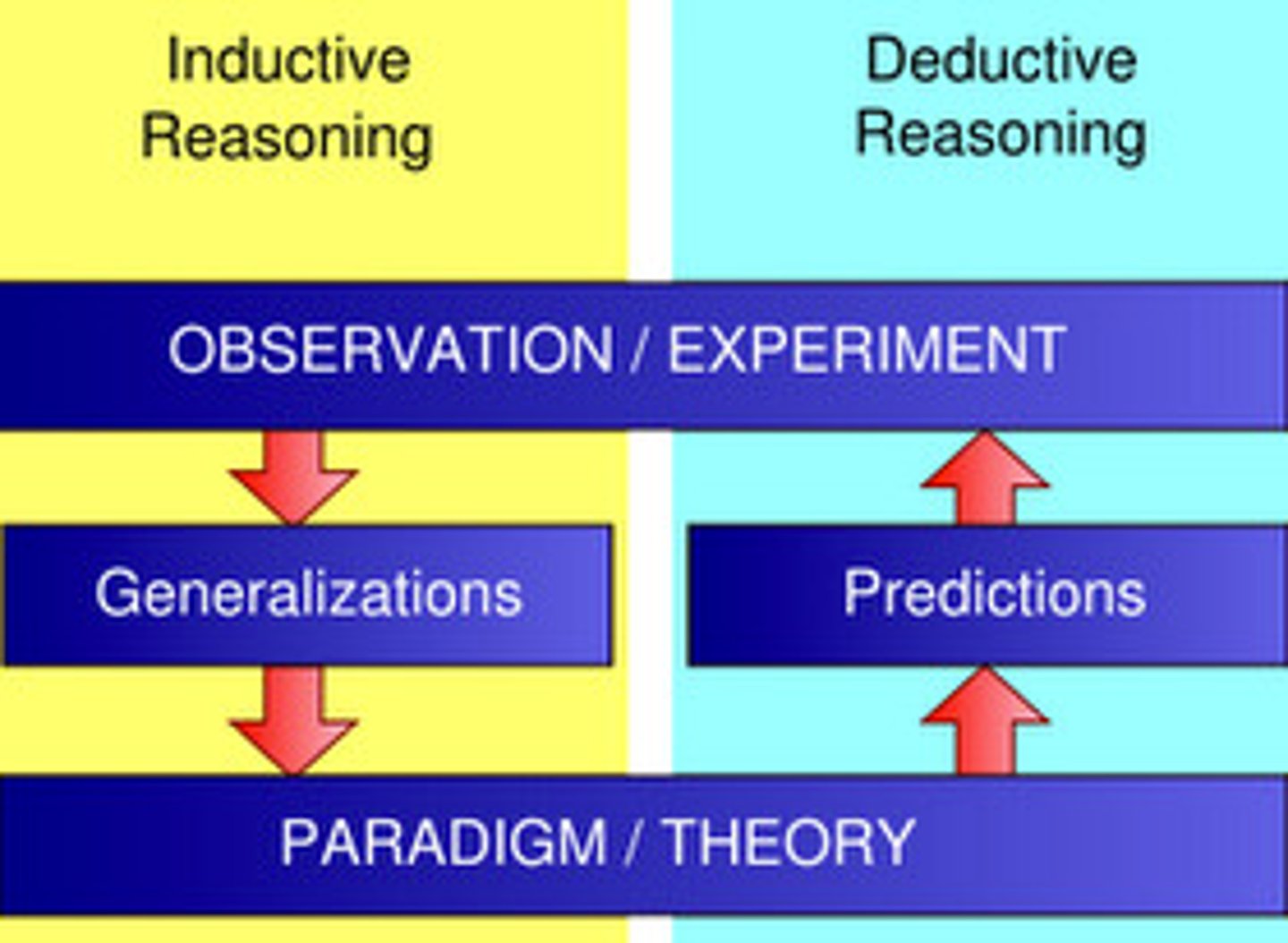
Deductive reasoning
general to specific
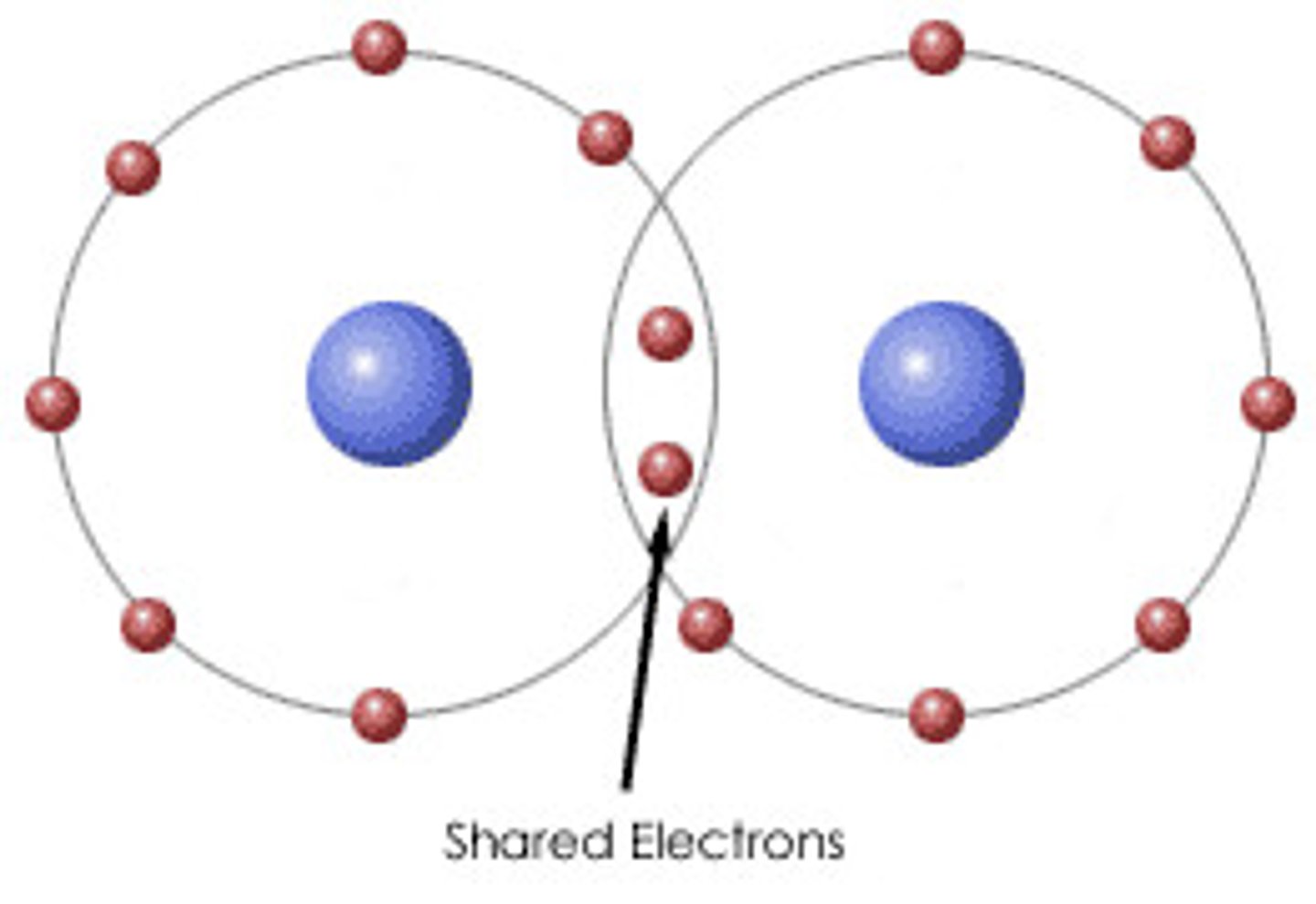
Covalent bonding
SHARING of Electrons!
polar= unequal
non-polar= equal
Ionic bonds
transfer electrons
Na- donor
Cl- acceptor
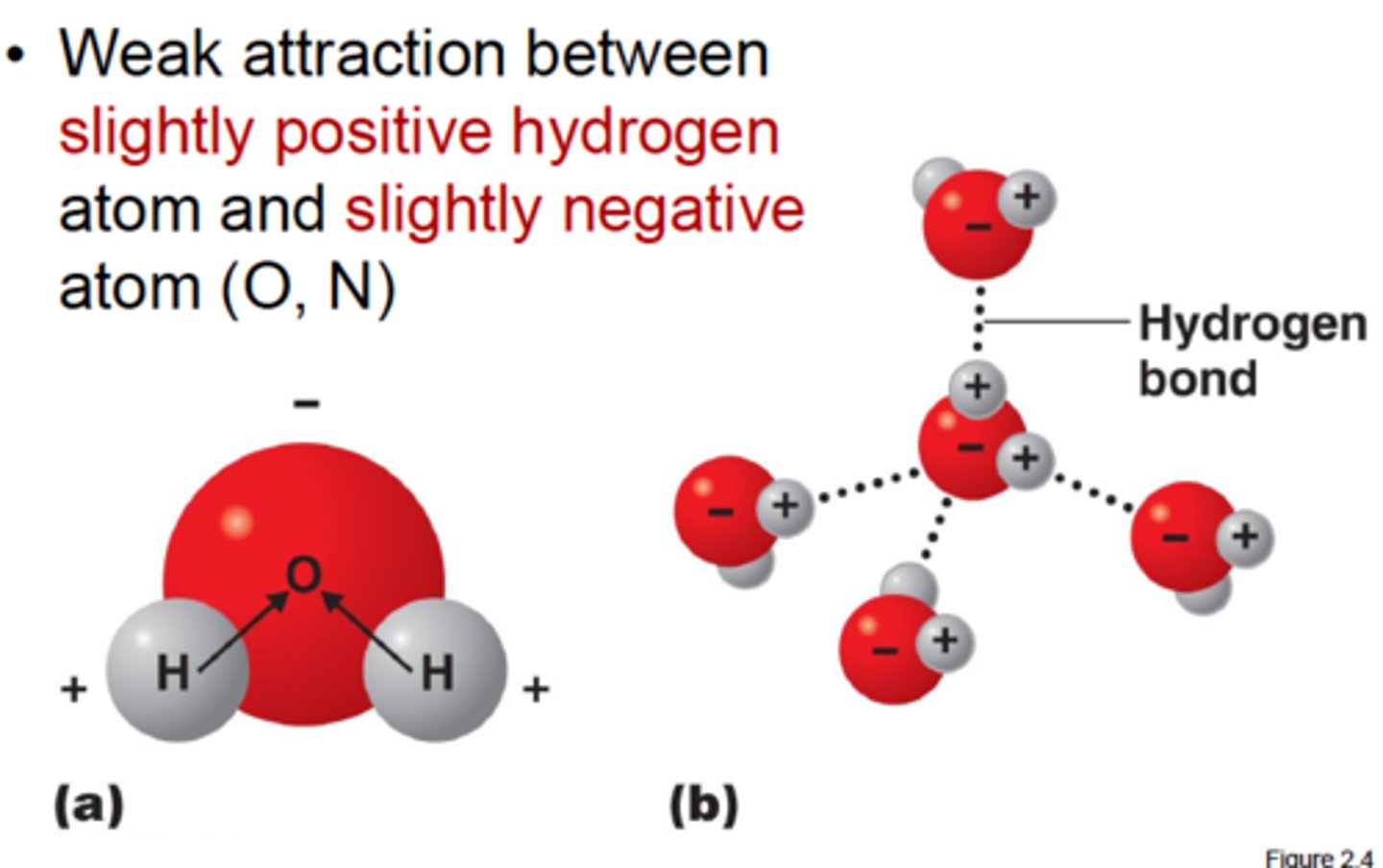
Hydrogen bonds
Weak individually, but strong together
(F) (O) (N)
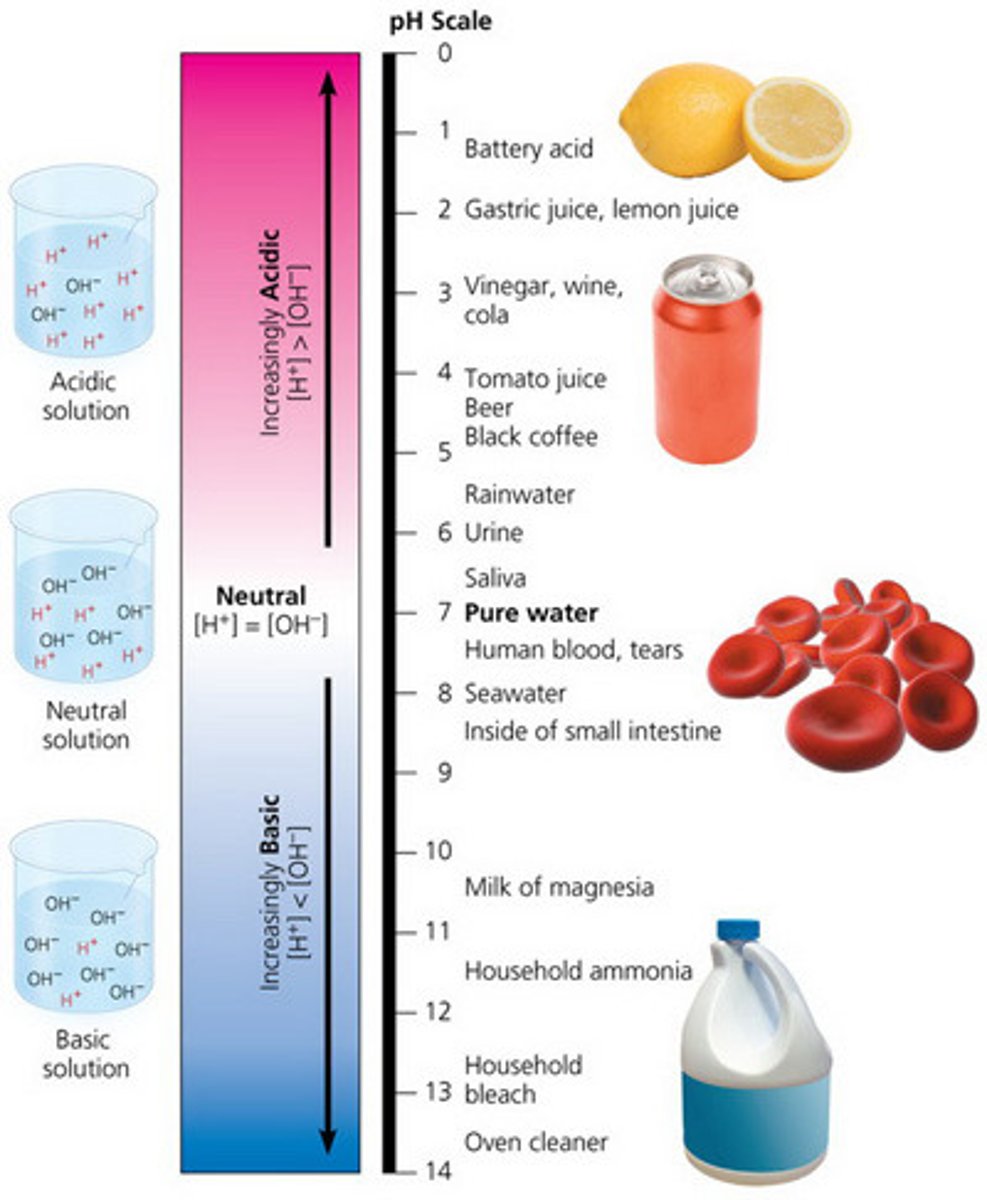
Acid solutions
high concentration of Hydrogen ions
-pH of 0-6
X-axis
experimental variable (time)
Y-axis
dependent (result)
Challenges for Science
-Loss of Diversity
-Emerging/Reemerging Diseases
-Climate Change
Properties of H2O due to Hydrogen Bonds
- high heat capacity (doesn't change temp. easy)
- High heat vaporization (cooling)
-dissolves in many molecules (hydrophobic/phillic)
Cohesion
water molecules cling together.
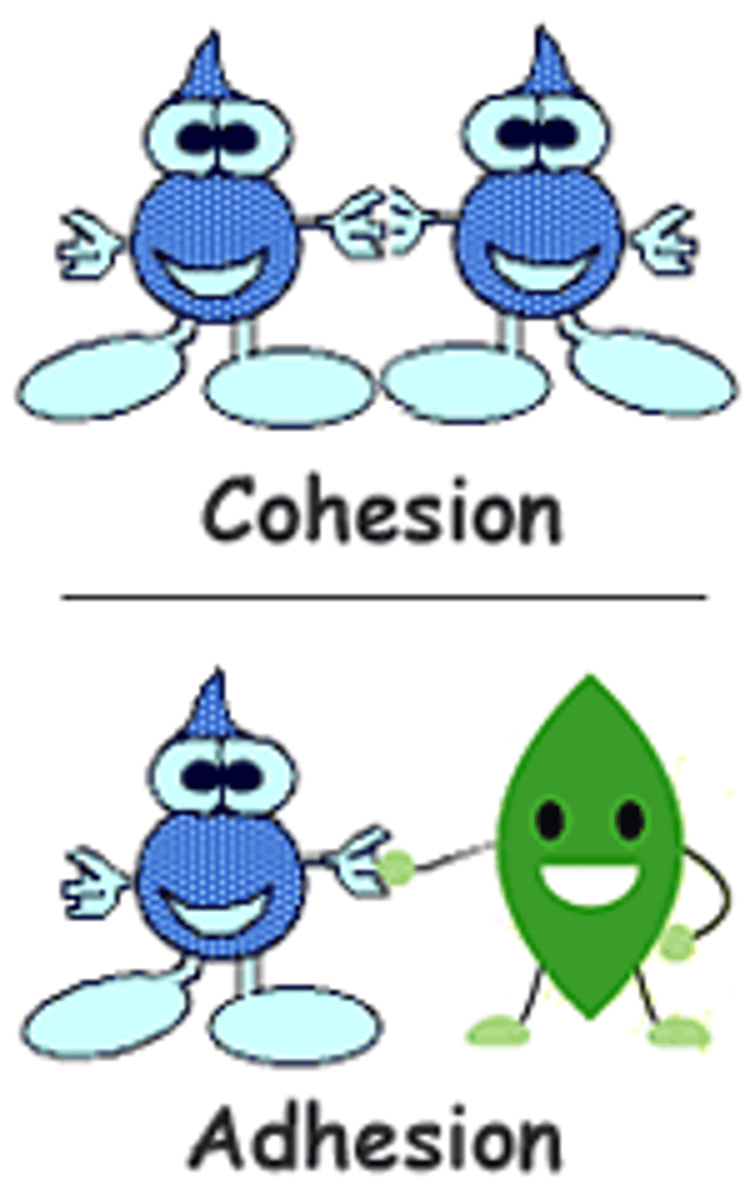
Adhesion
water adheres to polar surfaces b/c of - & + poles

Basic solutions
Low concentration of H+
- pH of 8-14
Functional groups
specific combination of bonded atoms that REACT the SAME
-Hydroxyl
-Amino
- Methyl
Organic molecules always have:
Carbon and Hydrogen
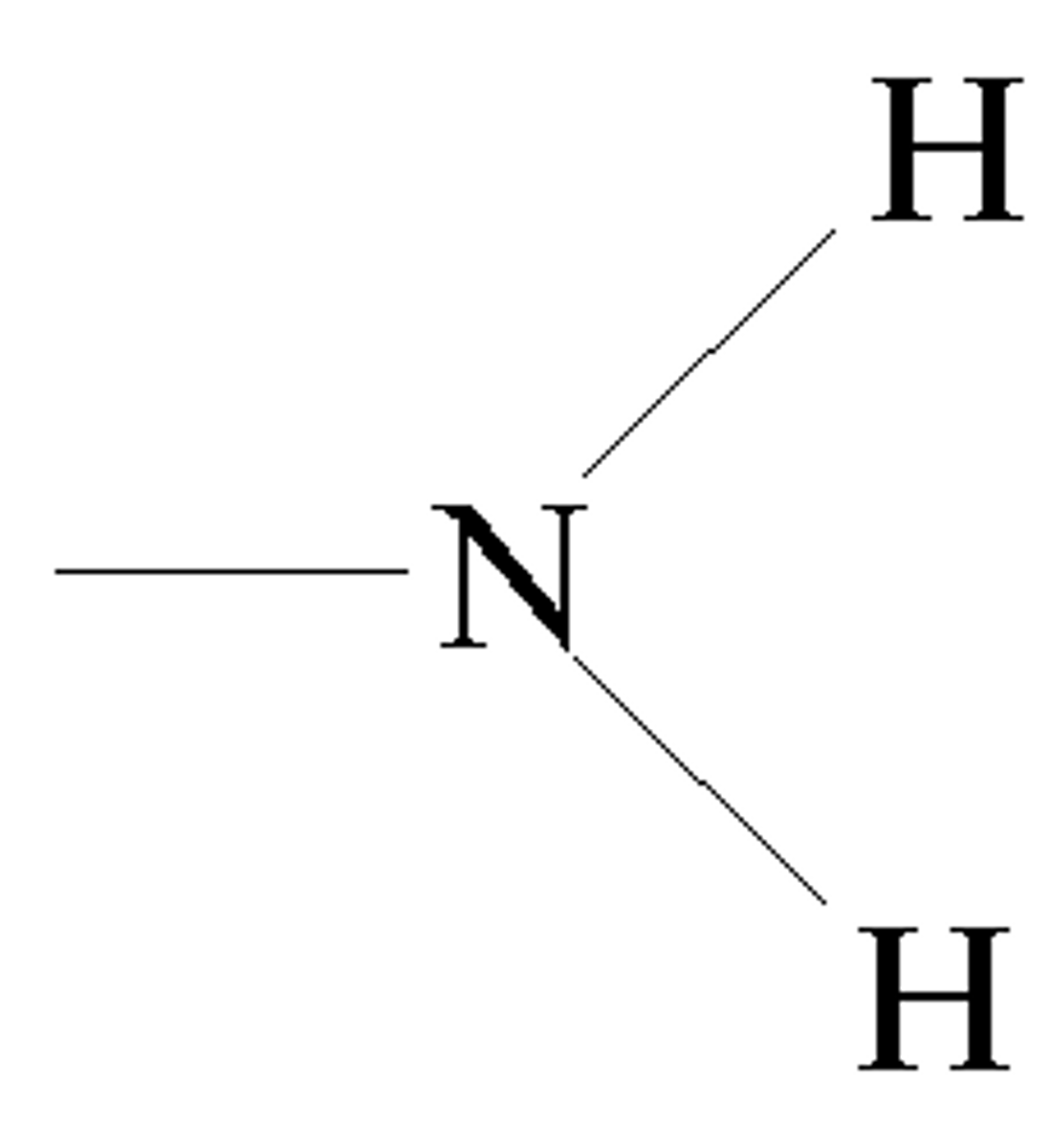
Amino group
-NH2 (Amine)
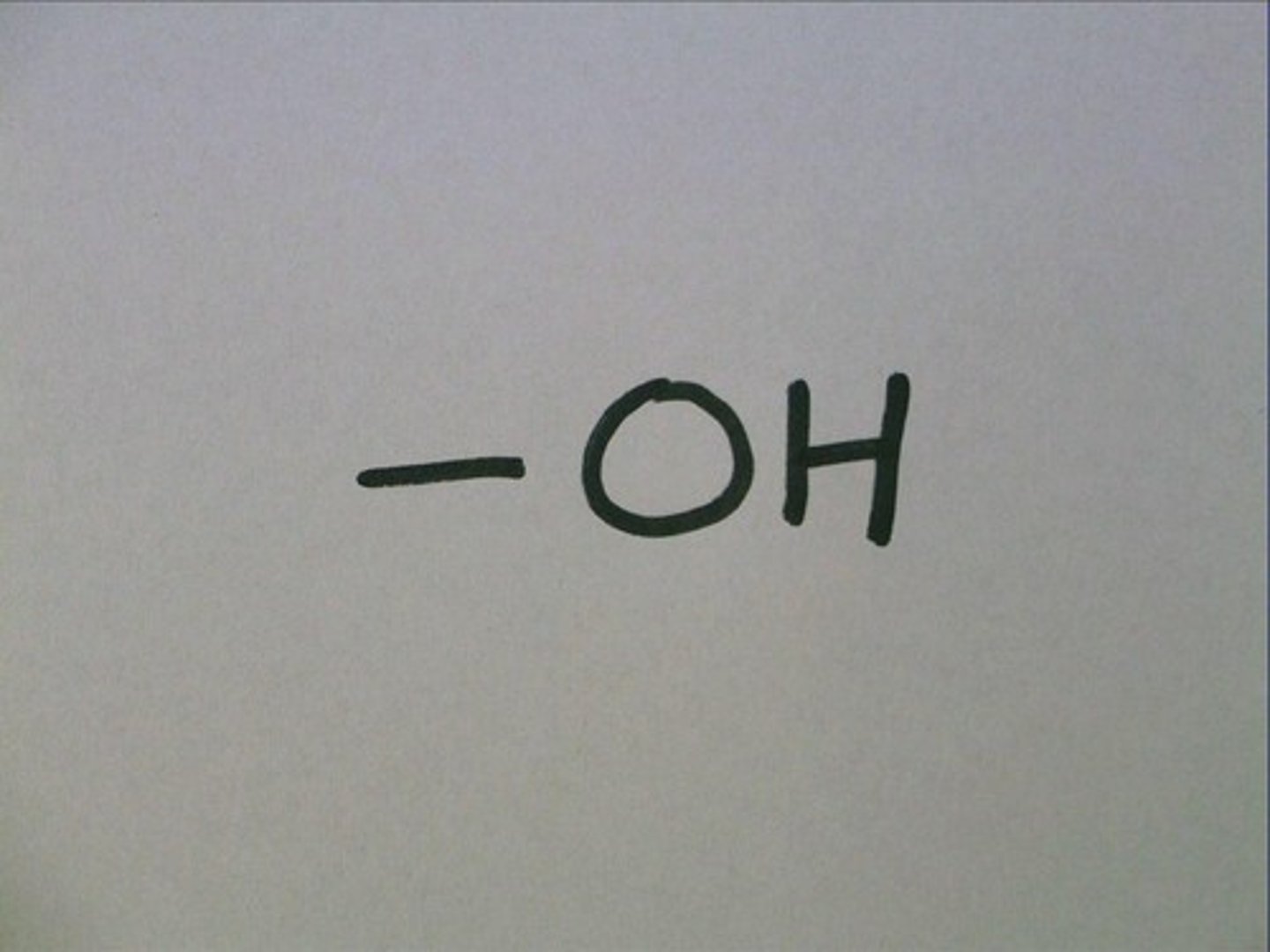
Hydroxyl group
-OH (Alcohol)
Methyl group
Methylated group
Hydrolysis
Breaking of water, water added
-reaction to degrade polymers
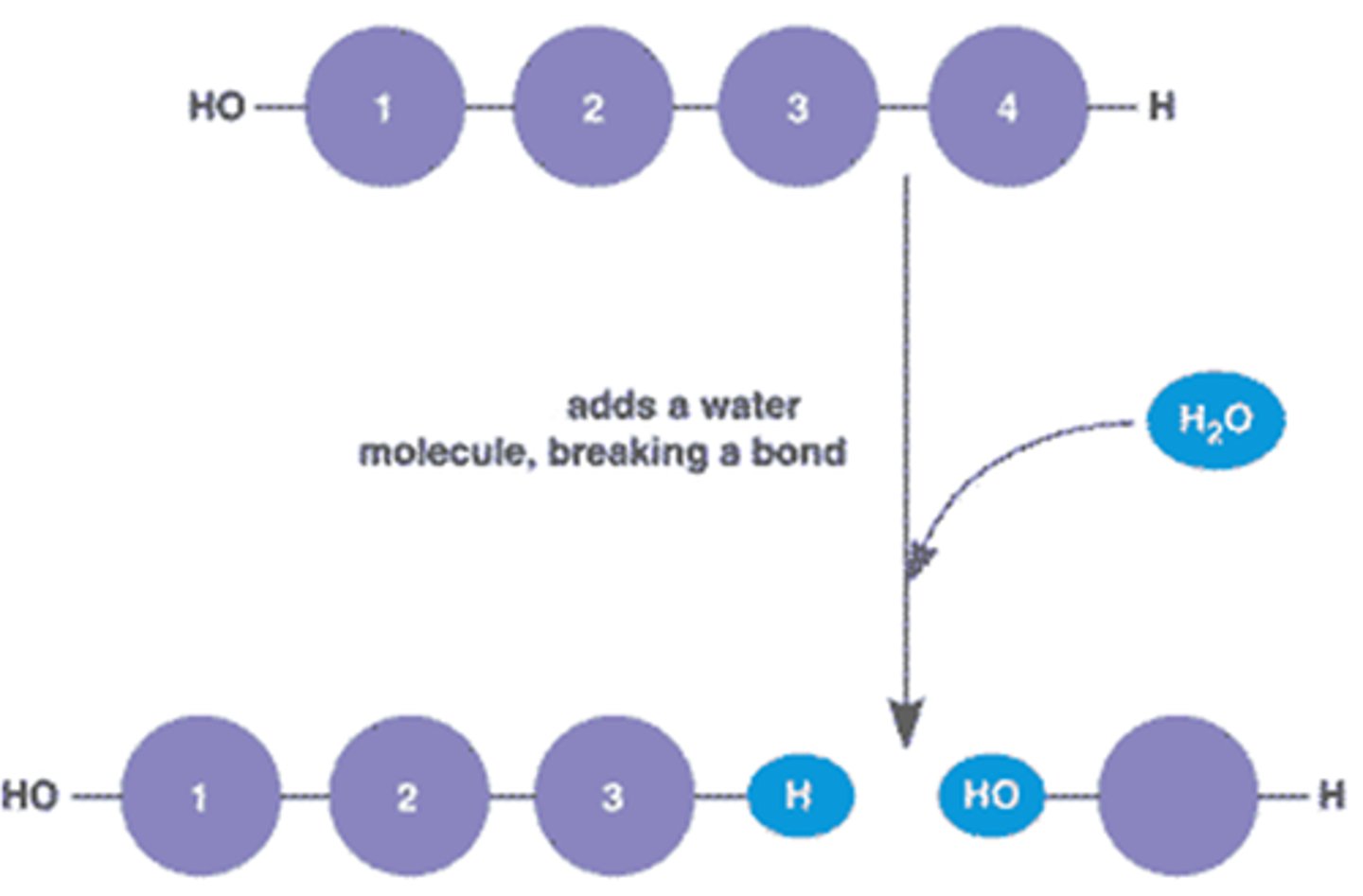
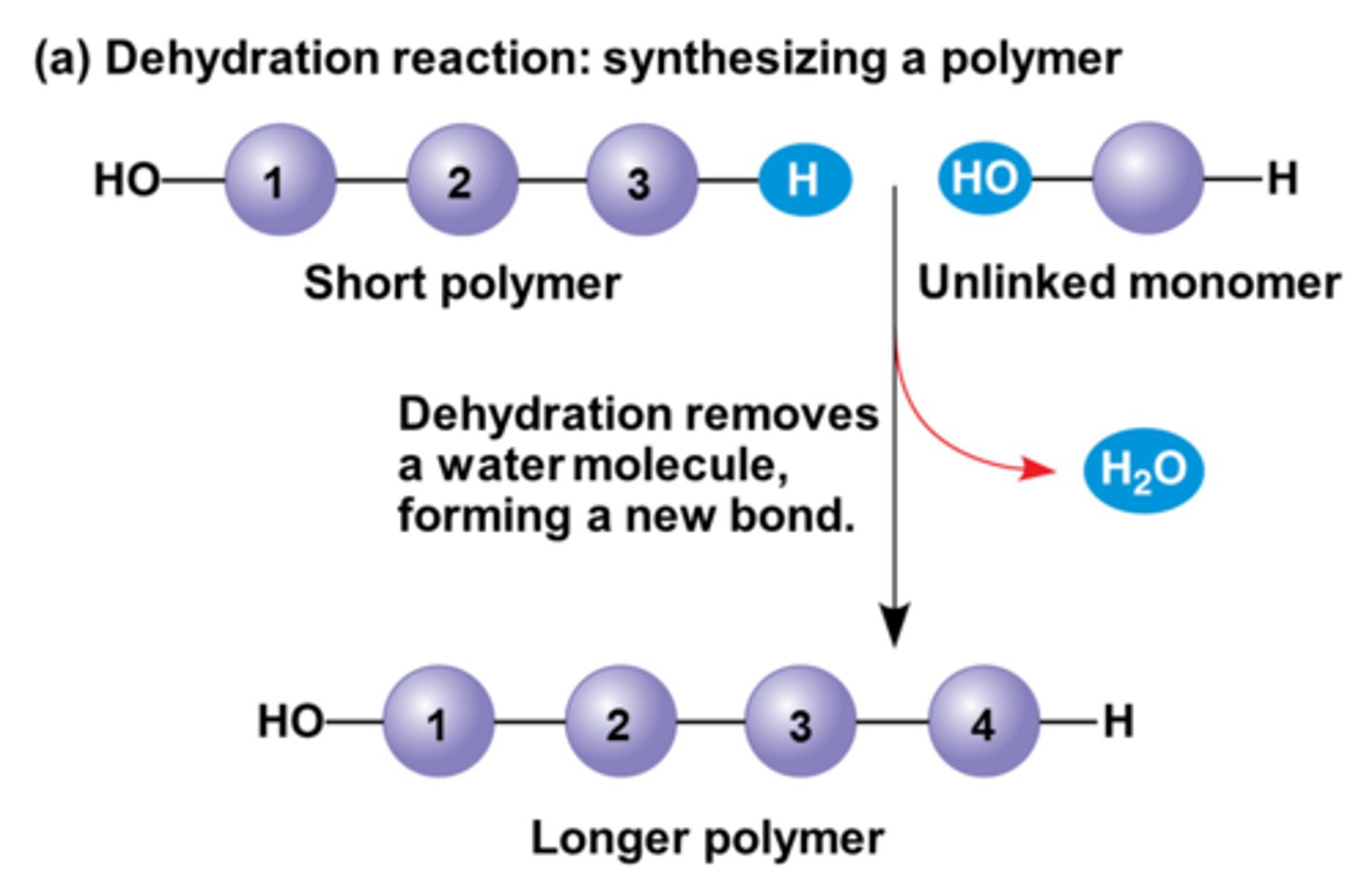
Dehydration reaction
an -OH and -H removed as a water molecule
Carbohydrates
short term energy storage, fuel.
-structural in plants (cell wall)
---monosachharides and polysachharides

Monosacharrides
simple sugars.
-fructose
-glucose
MONO-FRU-GLU :)
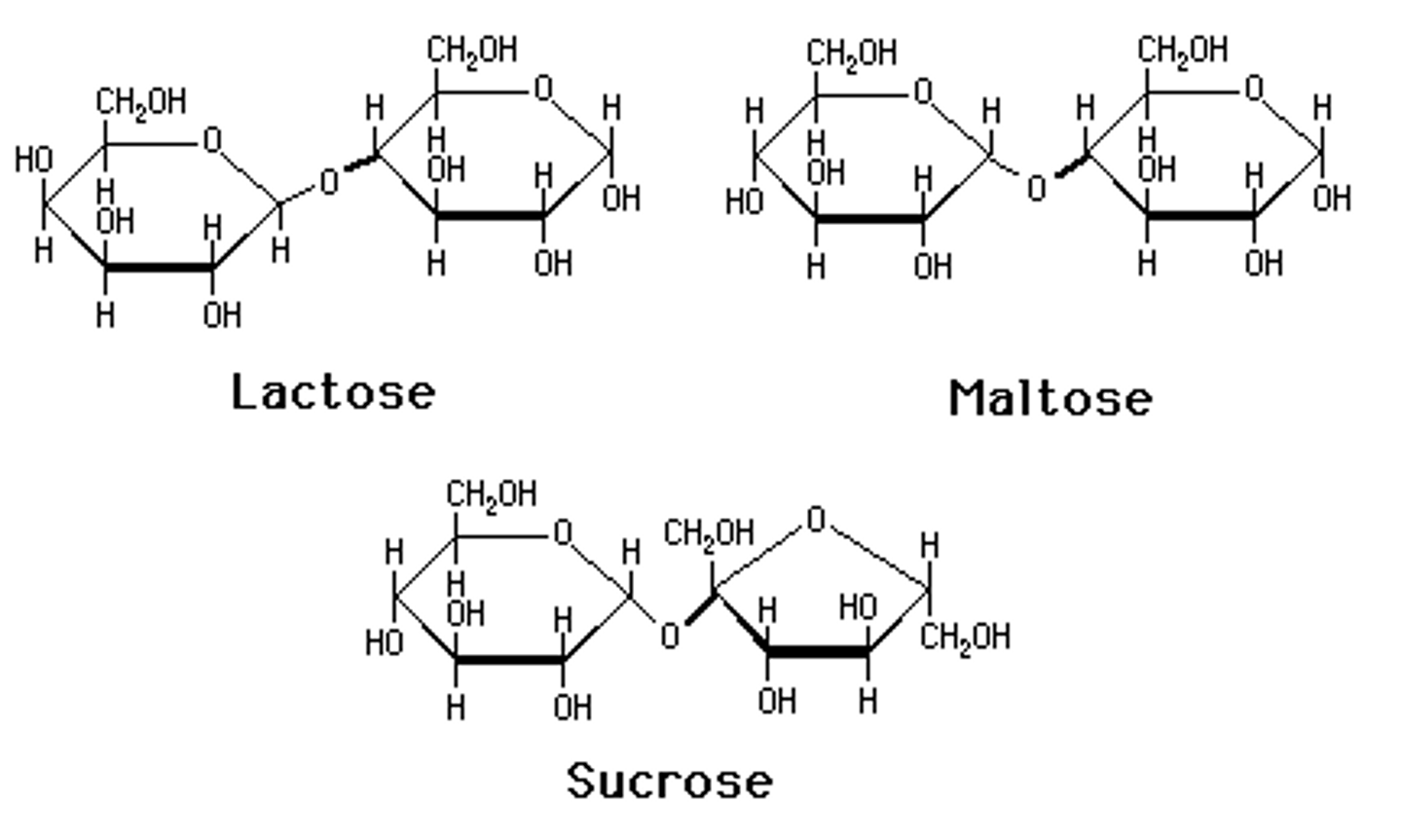
Disacharides
-maltose
-sucrose
-lactose
DI-MA-LAC-SU
4 Macromolecules?
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Proteins
Nucleic Acids

Lipids
don't dissolve in water - HYDROPHOBIC
fats n oils for storage
steroids->sex hormones
DON'T have MONOMERS OR POLYMERS

Oils
liquid at room temp.
Plant origin
store energy in seeds

Fats and lipids have:
1 glycerol backbonde (hydroxyl)
3 fatty acids (tryglyceride)
Act as LONG TERM ENERGY STORAGE
Unsaturated fats
double bonds
plants (oils)
fewer hydrogen atoms
NOT PACKED TIGHTLY

Saturated fats
max # of hydrogens
animal origin
health risks
tail bends
Packed tightly

How is an unsaturated fat made saturated?
By adding hydrogen, duh.
Partially Hydrogenated Oils?
Trans Fats
-high shelf storage
-reheat/ frying
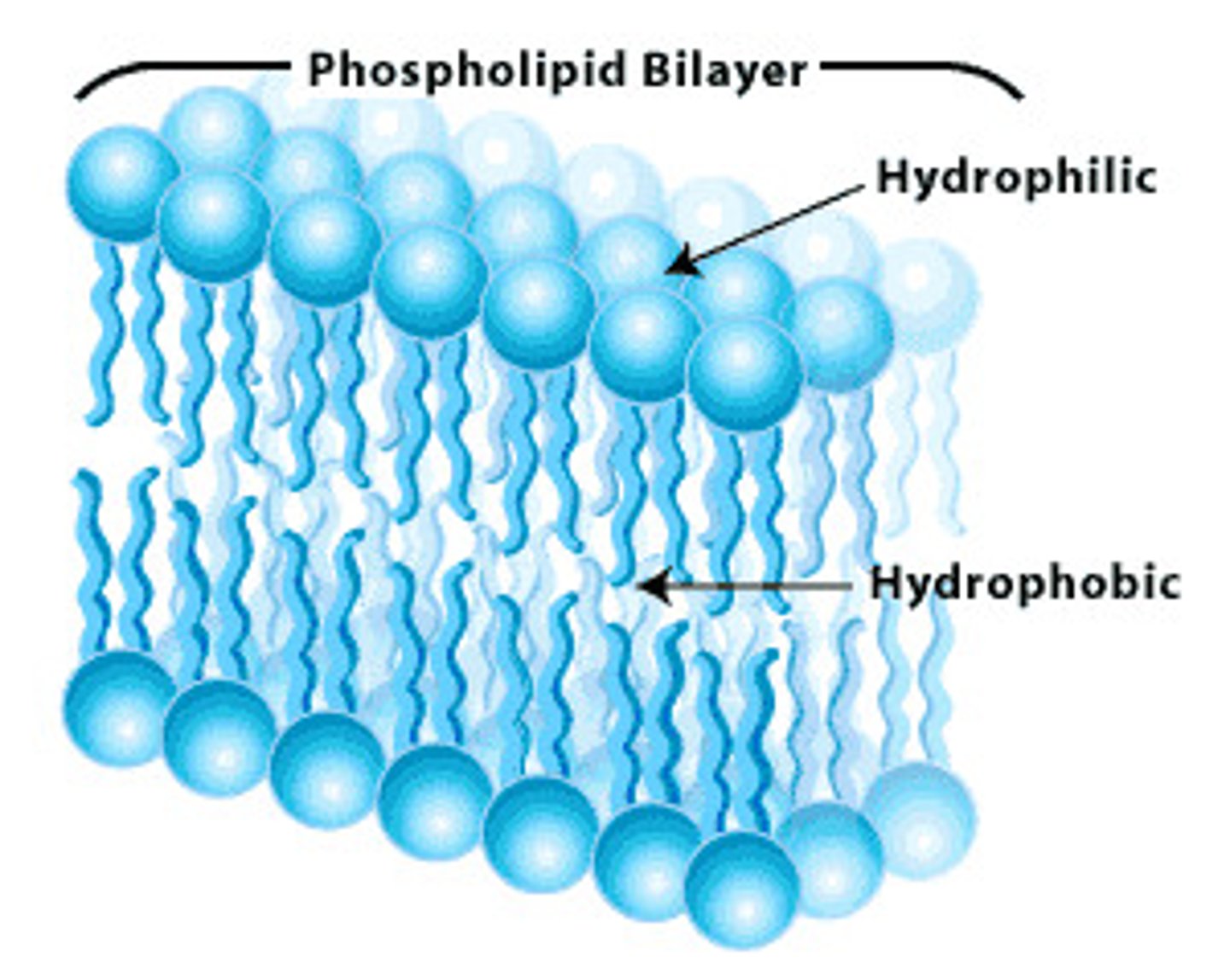
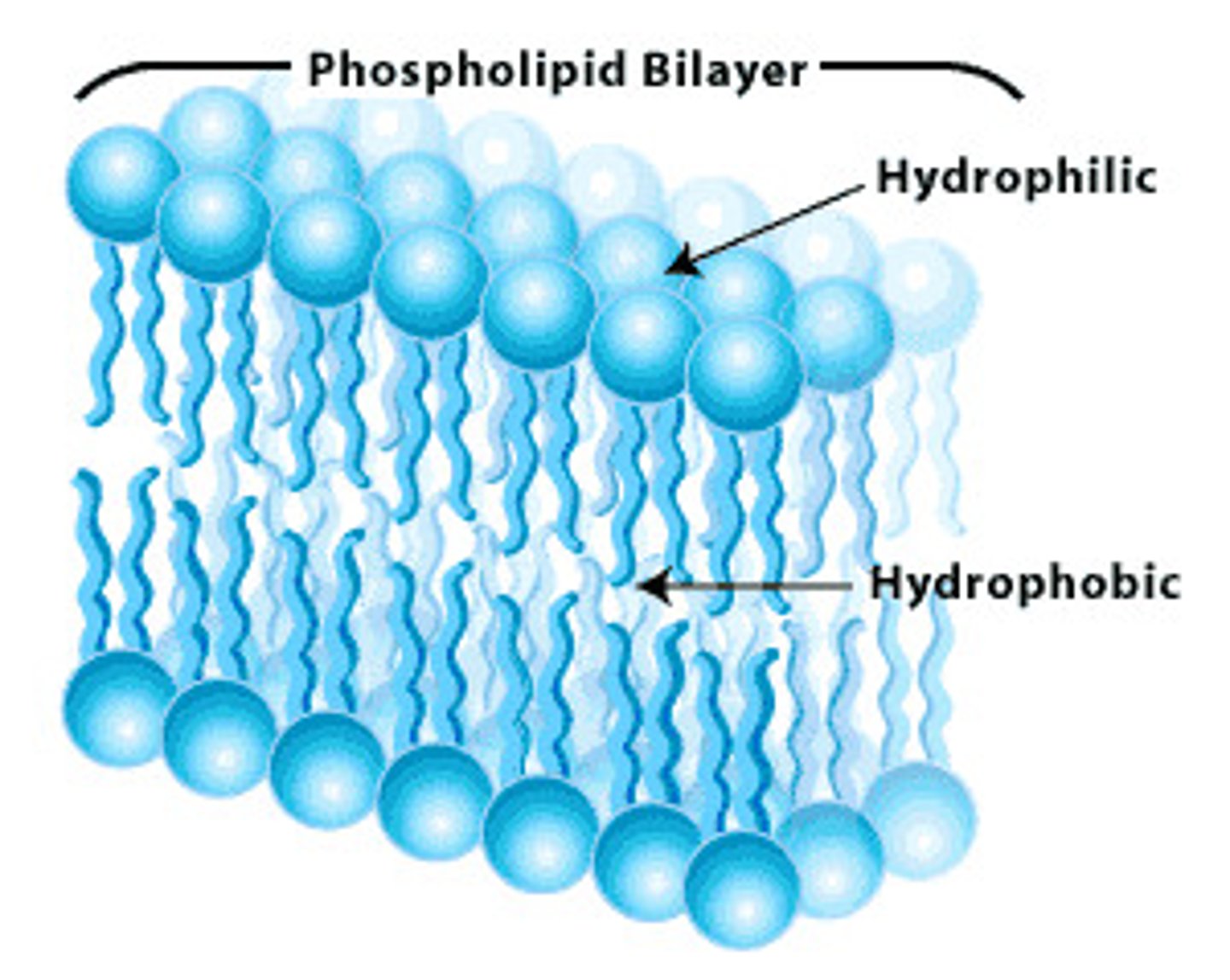
Phospholipids
2 fatty acids and phosphate group
polar head is hydrophillic, tails are hydrophobic
-forms bilayer. head faces outward, tails- interior.
Steroids
Backbone of 4 fused carbon rings
ex: Cholesterol, Testosterone, Estrogen

Hormone analogs
chemicals that act like hormones in body
ex: estrogen in animals
-changes in behavior and development of animals exposed to them.
-PLASTICS
Proteins
polymers of amino acids monomers
-structure in keratin and collagen
Enzymes speed up chemical reactions
-Amino acids, peptides
Amino acids (CAR)
-amino group -NH2
-acidic group -COOH (CARBOXYL)
-R group
Peptides
single chain of amino acids
Peptide bond- joins 2
Levels of Protein Organization
-Primary- linear structure of amino acids
-Secondary- protein makes certain types of structures in different places. ALPHA HELIX or PLEATED SHEET shape.
-Tertiary- final 3D shape. Maintained by bonds b/w R groups.
-Quartenary- found in proteins with multiple polypeptide chains. Arrranged to highest structure. Lactase - 4 same polypeptides to gain final structure.
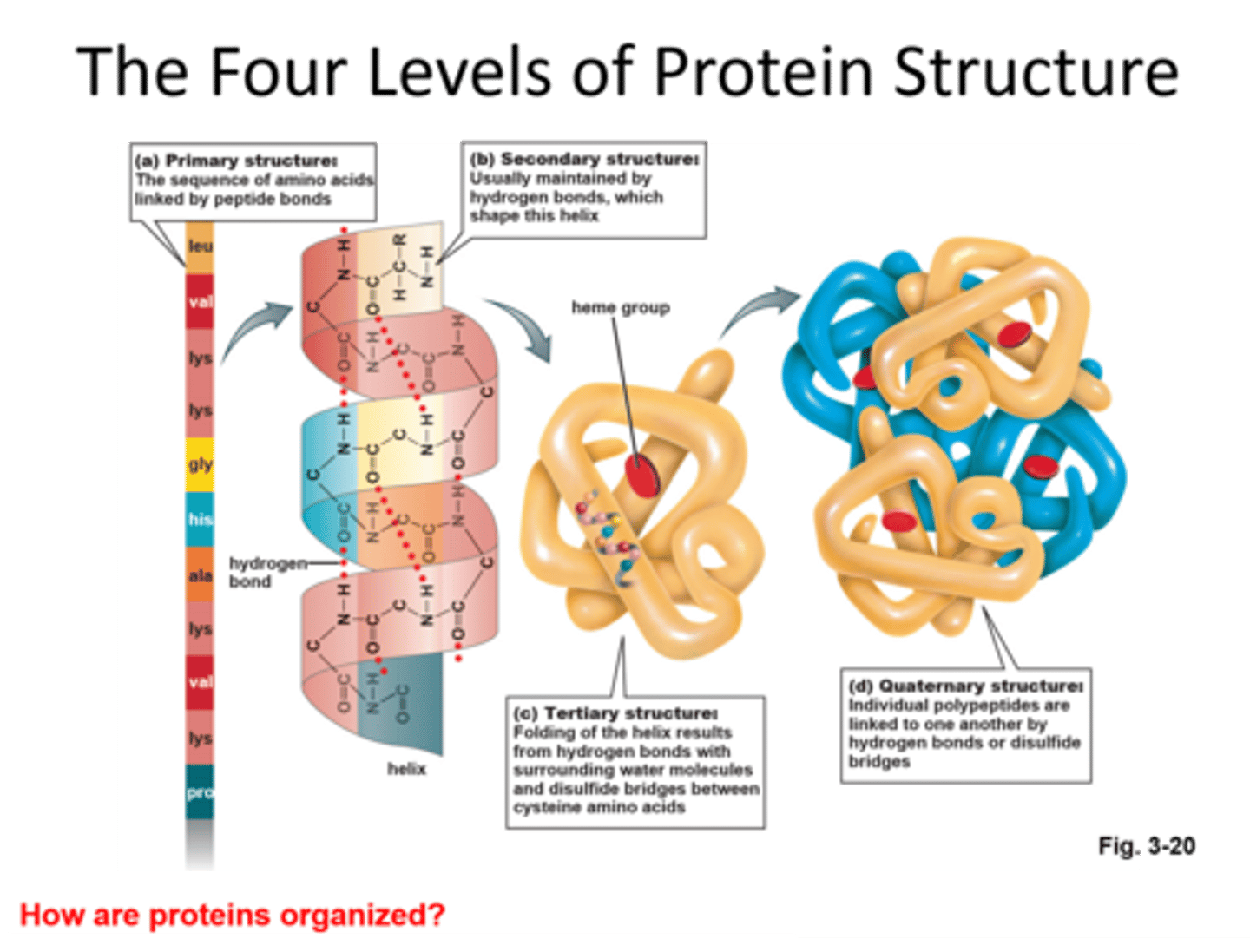
A protein that lost structure b/c of extreme heat or pH is:
Denatured
Nucleic Acids
2 polymers - DNA and RNA
-ATP
monomer of nucleotide
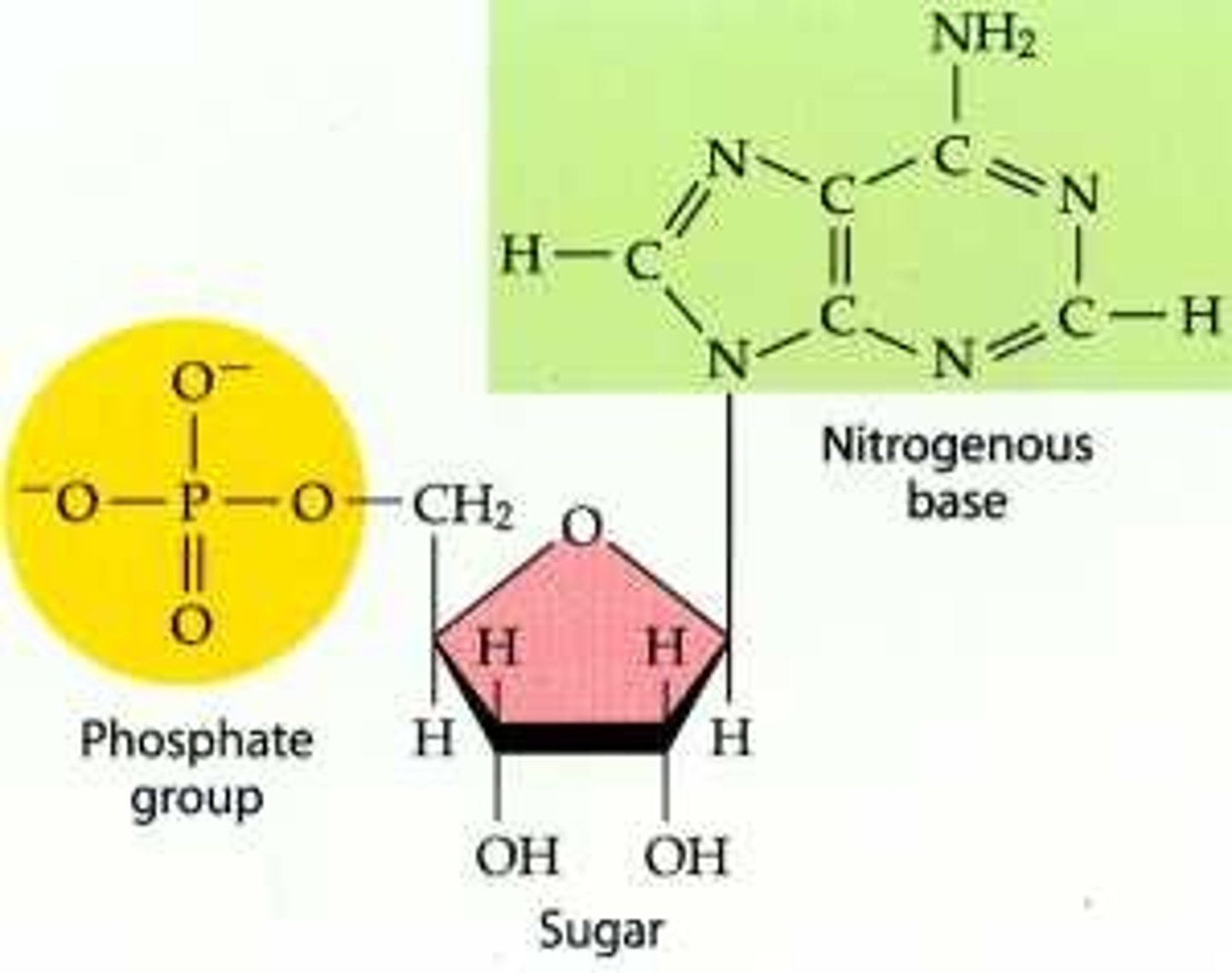
DNA
polymer of nucleotides
genetic info
replicate to transmit info
-double helix
held by hydrogen bonds
rung of ladders with complementary bases
A-T, C-G
Nucleotide
has: -phosphate, -pentose deoxyribose (SUGAR), -nitrogenon-containing base.
ATP
Adenine Triphosphate
-high energy molecule
- goes thru HYDROLYSIS and energy is RELEASED!
ENERGY CURRENCY
IS a NUCLEIC ACID
Macromolecules that need nitrogen?
Protein and Nucleic Acids
Microscope
revolutionary and made by Robert Hooke
Light Microscope
visible light passes through specimen, then lens, then ur eyes.
1,000
Cell Theory
All organisms are made up of one or more cells
Cells are the basic unit/structure
Cells come from other cells
Magnification and Resolution of Microscope
Mag- objects size
Res- clarity
Scanning Electron Microscope
study detailed external architecture of cell surfaces
Black and White
Transmission Electron Microscope
internal structure of cells
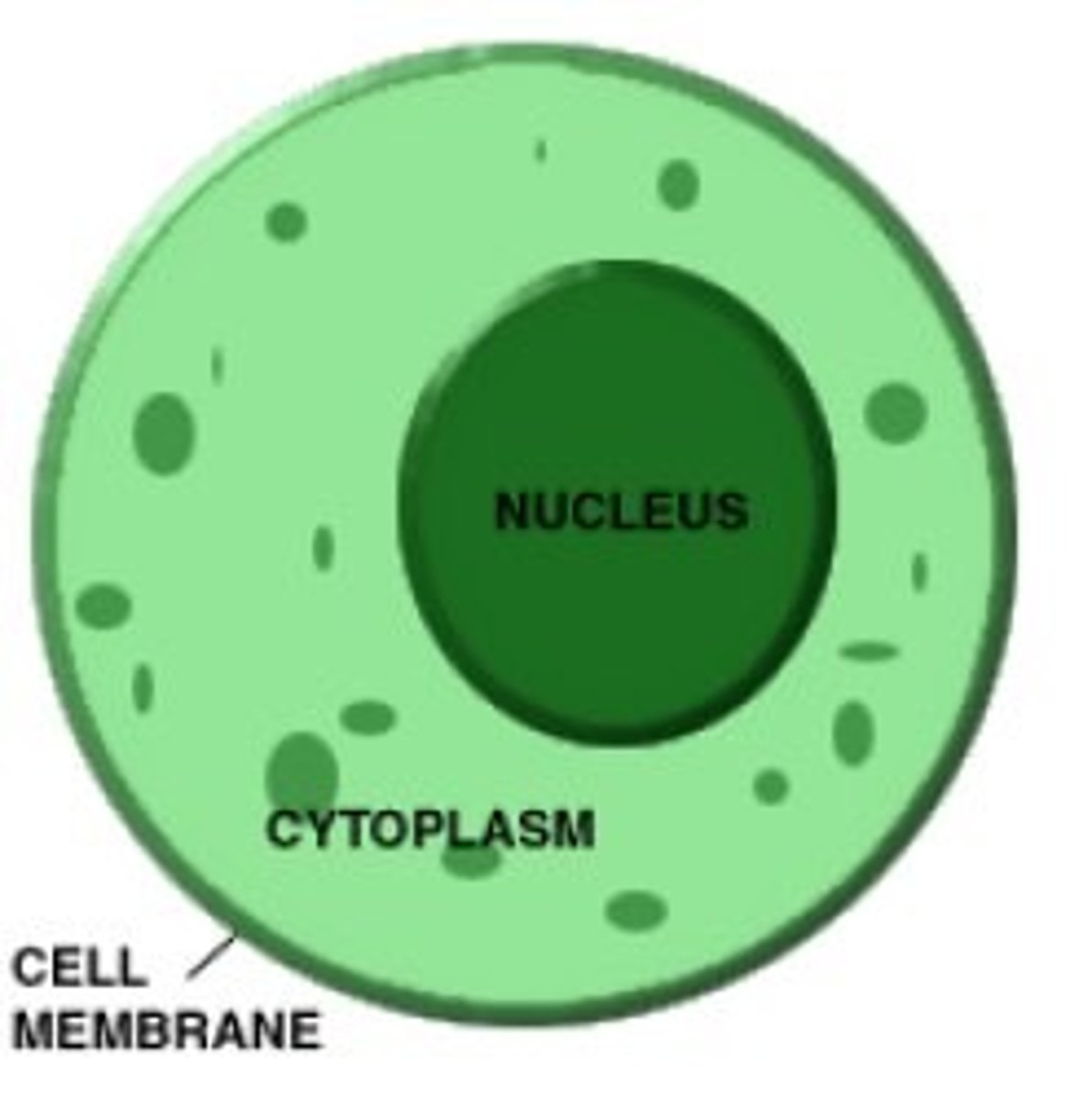
Plasma membrane
-surrounds cells
-boundary and gatekeeper
-has cytoplasm semifluid
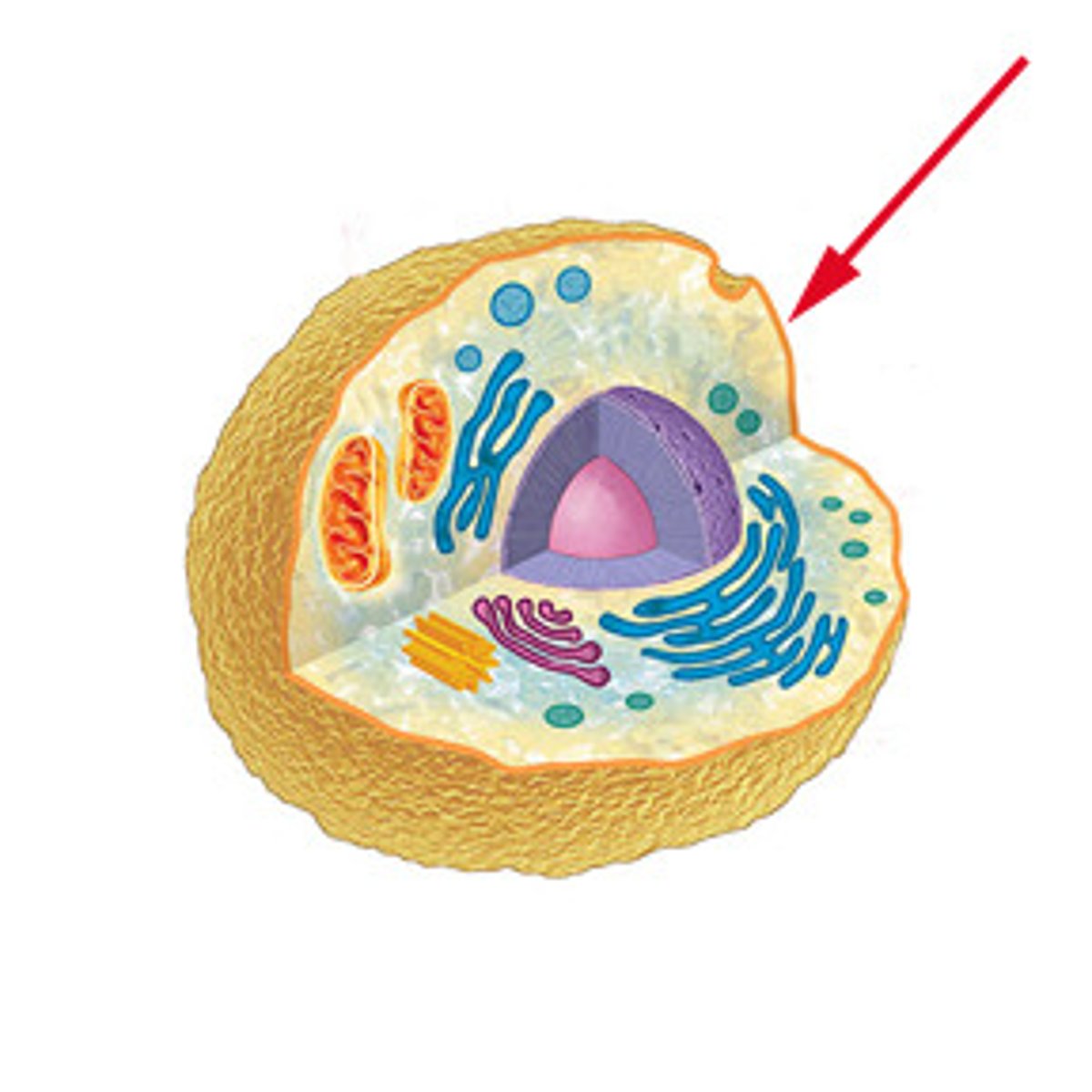
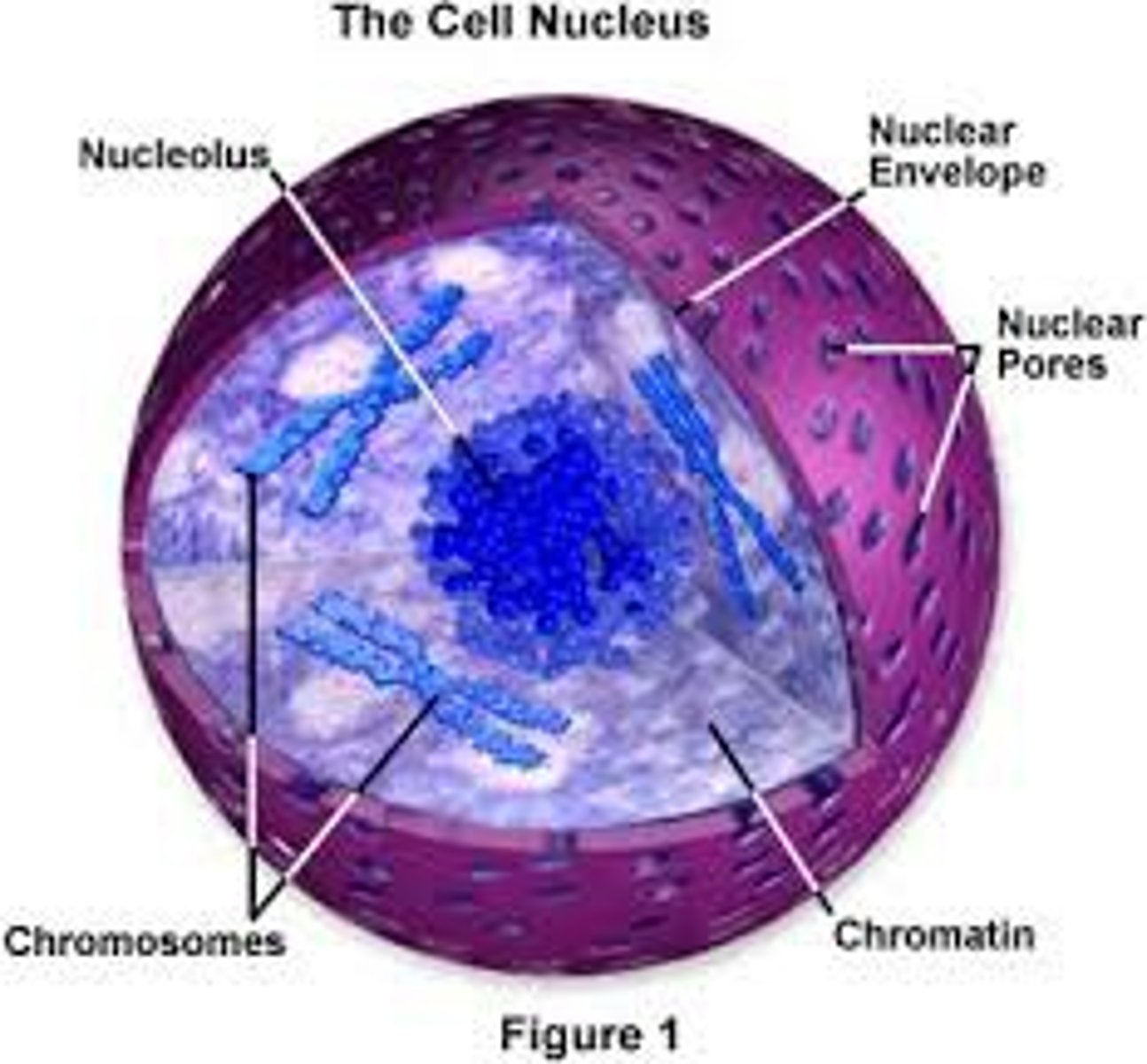
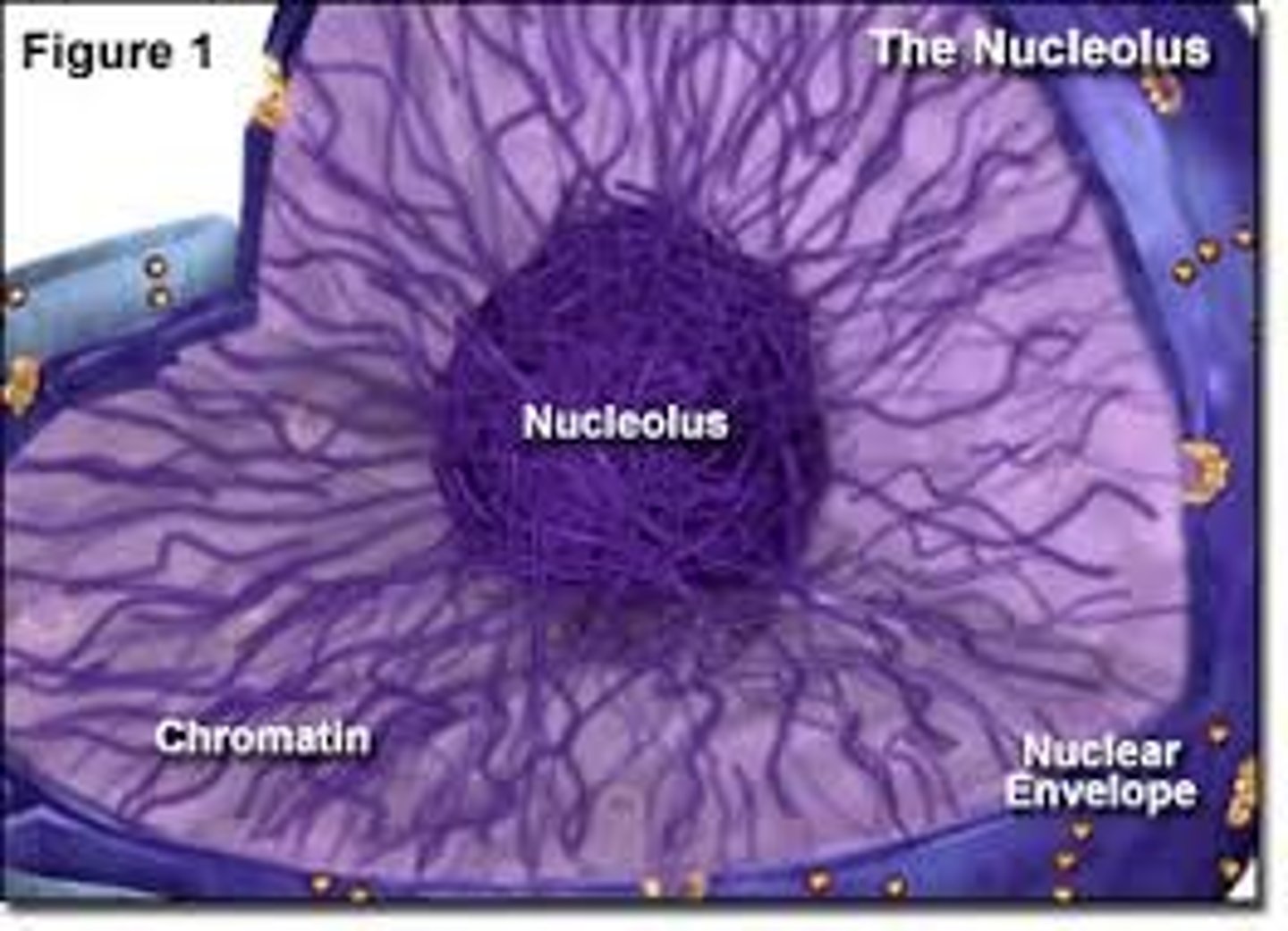
Nucleus contains:
nuclear envelope (pores), nucleolus, chromatin, DNA, nucleoplasm, chromosomes
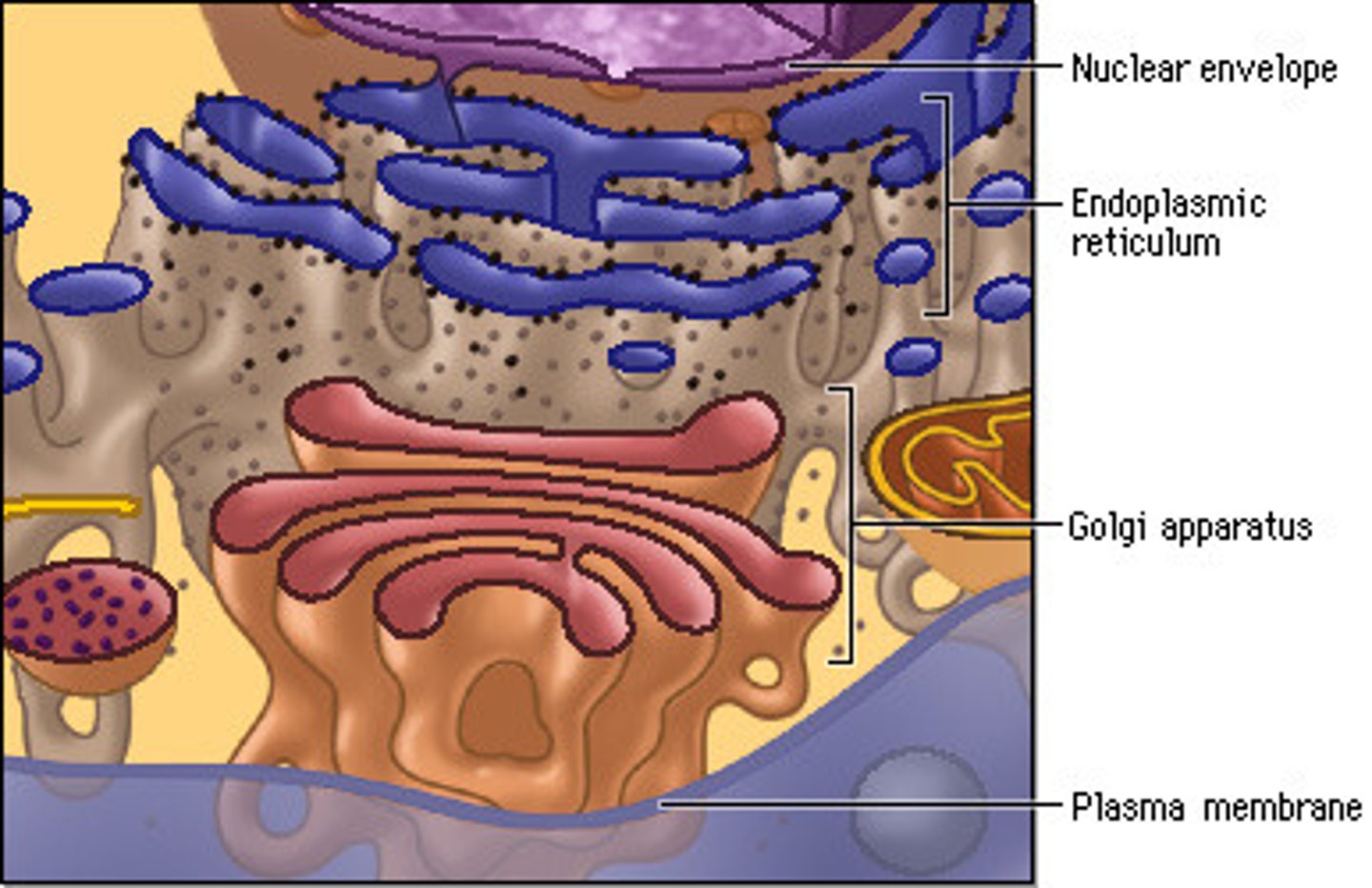
Nuclear envelope consists of:
-Rough endoplastic reticulum (ribosomes)
-Smooth endoplastic reticulum (makes membrane-phospholipid metabolism)
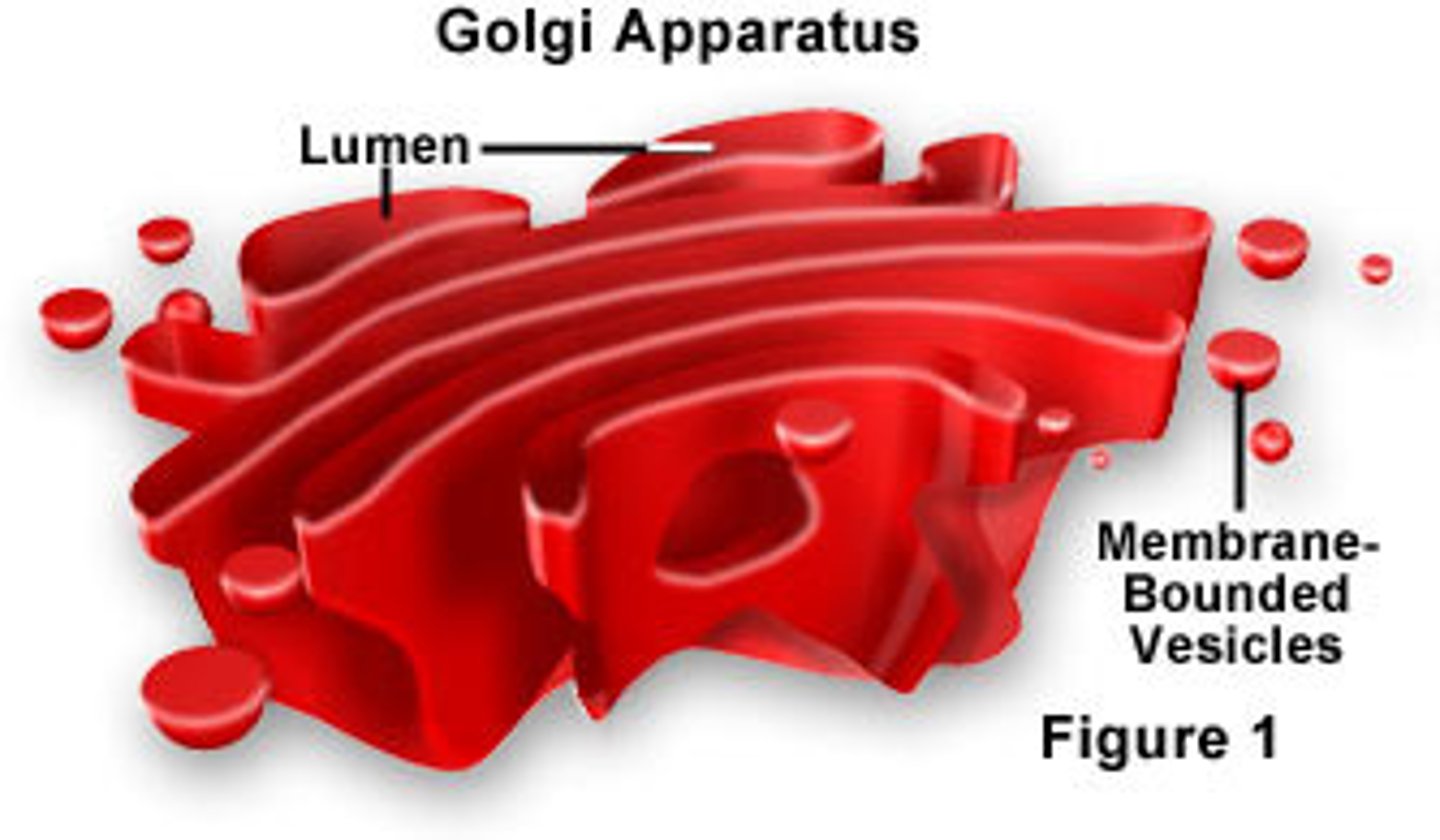
Golgi Apparatus
Collects, sorts, packages, and distributes materials (processes proteins and packages them into lysosomes).
SHIPPING CENTER.
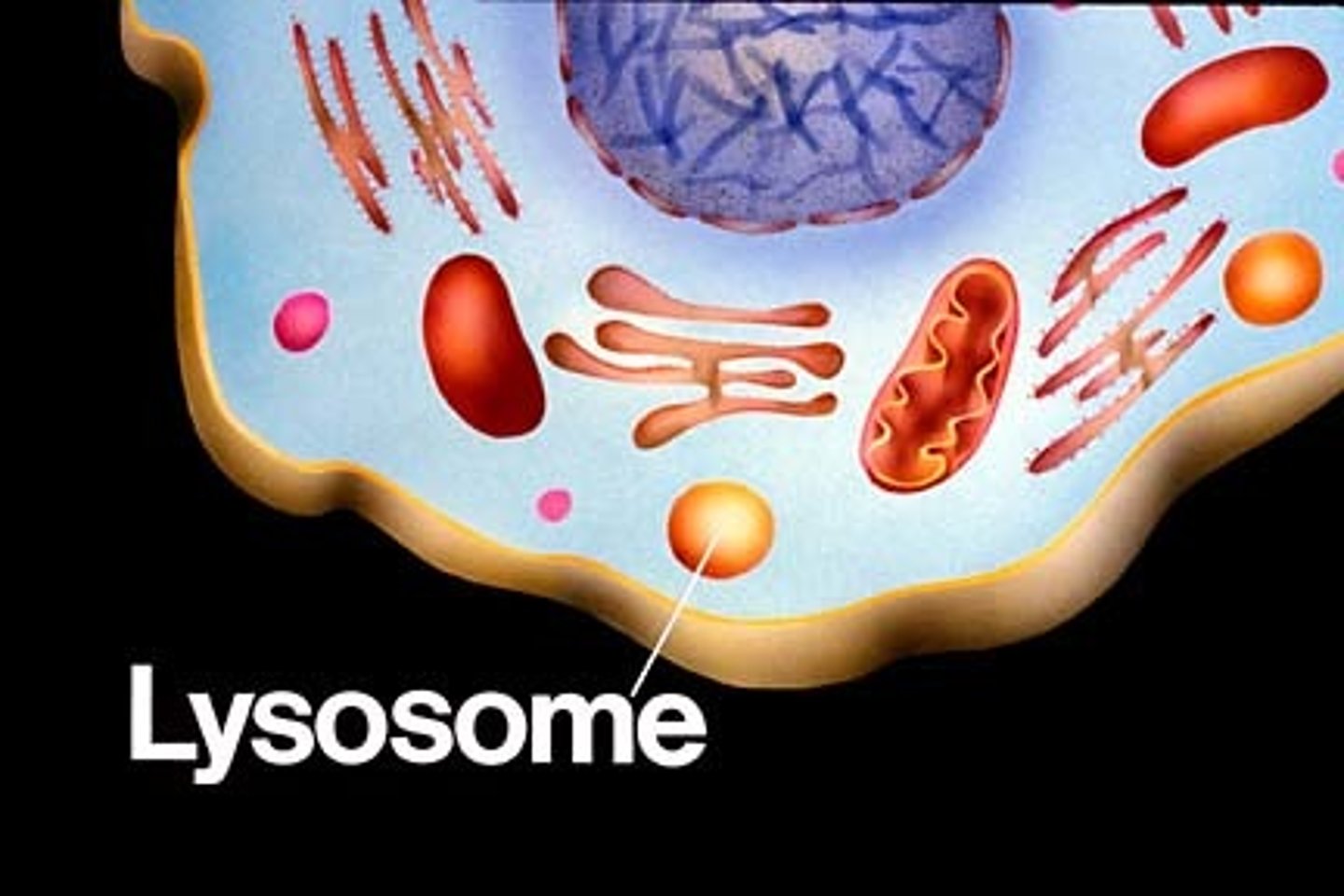
Lysosomes have to bond with ________ to digest. Enzymes are produced in these...
vesicles
Vacuole and Vesicles
Membrane bound sacks
-vesicle: smaller
Lysosomes
has enzyme to DIGEST food or damaged organelles. GARBAGE DISPOSAL
-made by golgi apparatus
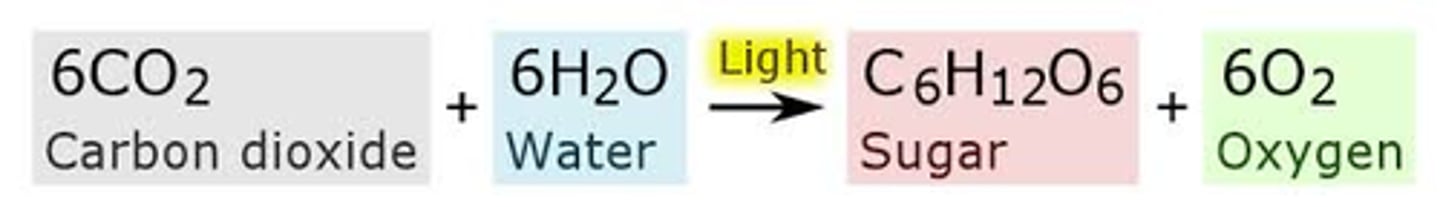
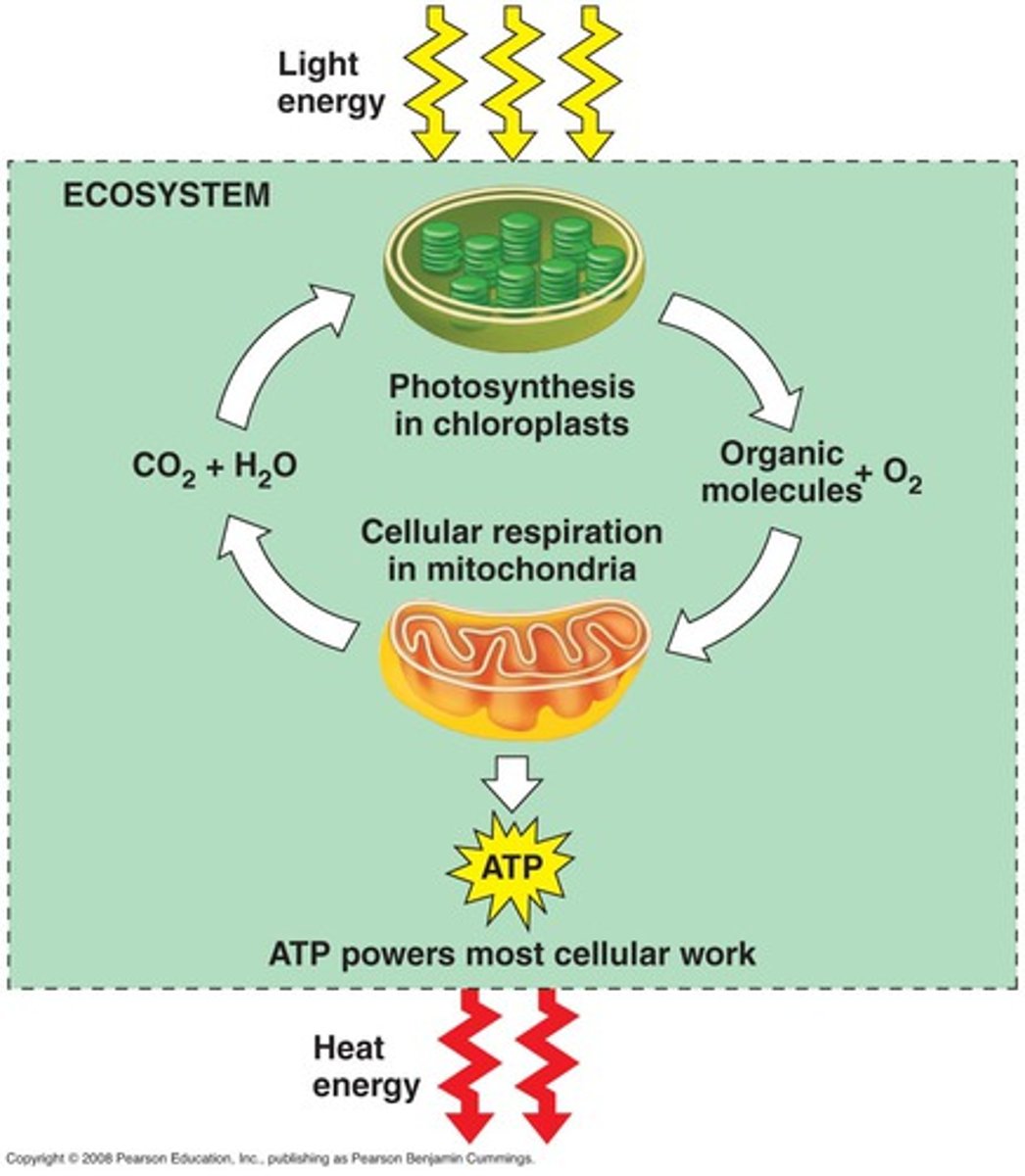
Photosynthesis
Plants, algae, and cyanobacteria.
Solar energy needed
Cellular Respiration
all organisms convert chemical energy to ATP
Carb+O ---> CO2 + H2O + energy

Chemical reactions happen in this space
Thylakoid space
Photosynthesis happens in the ___________.
Cellular respiration happens in the ____________.
Chloroplast; Mitochondria
Cytoskeleton
protein fibers that hold together cells.
-can be stained with fluorescent dye
Actin Filaments
2 long thin, flexible actin chains twisted in helix
-Microfilaments
-looks like web.
-projections in intestinal cells as microvilli
-formation of pseudopods in amoebid movement
-muscle contraction movement
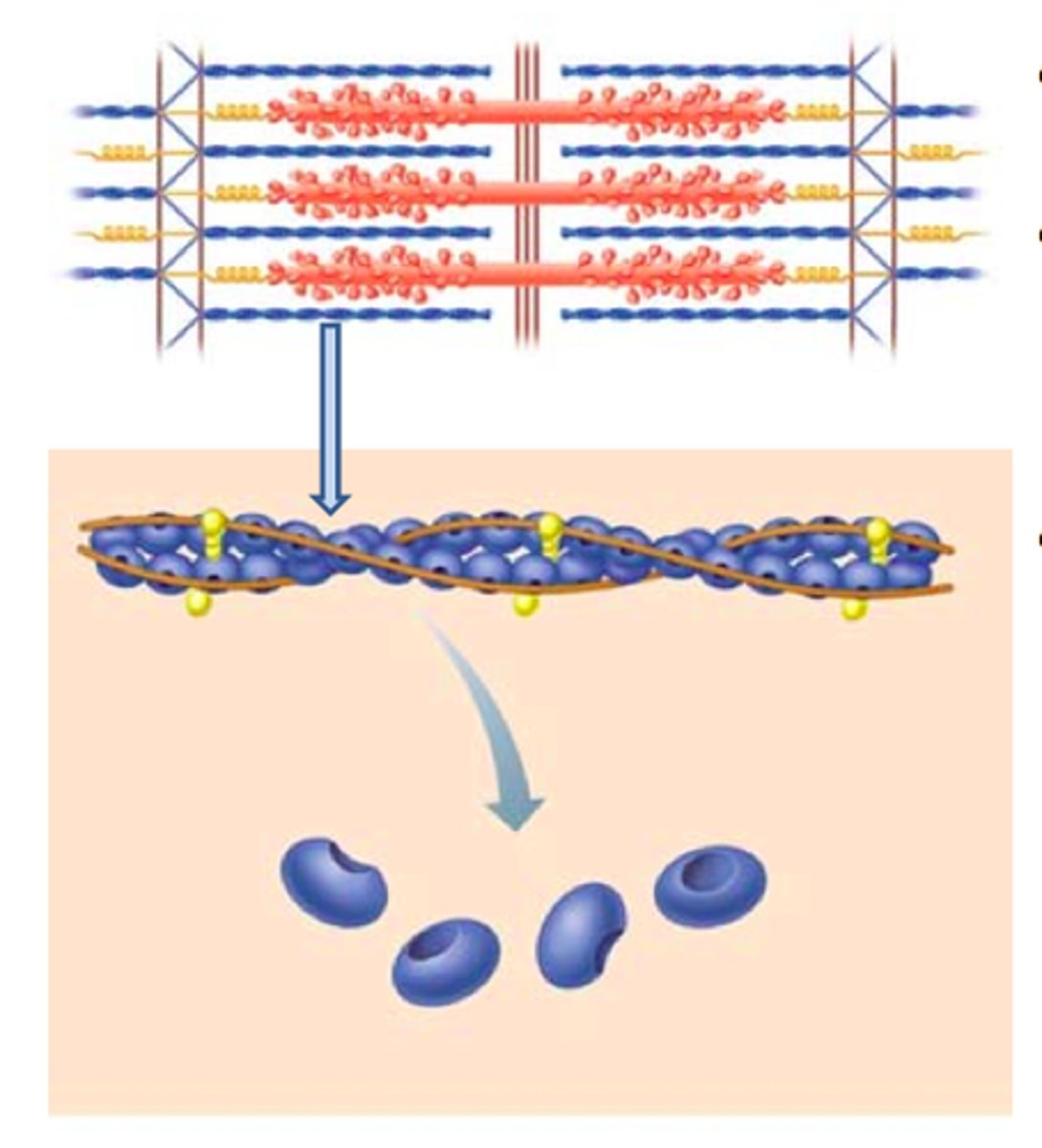
Myosin can pull actin along with _______.
ATP
Plasma membrane is composed of
Proteins and Lipids
Cytoplasm
semifluid in cells
has water, salts, dissolved organic molecules.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
synthesizes phospholipids, produces testosterone, and detoxifies drugs.
-makes vesicles
Centriole
formation of basal bodies
Nucleolus
produces subunits of ribosomes
Polysacharrides
-starch, glycogen, chitin, and cellulose.
-"star-gly-cel-chi"
A nucleotide has:
phosphate, sugar, and a nitrogenous base
Triglyceride
3 fatty acids
1 glycerol backbone
Lipids are organic compounds composed mainly of __________ and _______ atoms linked together by ________covalent bonds.
carbon, hydrogen, covalent
Hypertonic solution
water leaves the cell, shrivels (crenation)
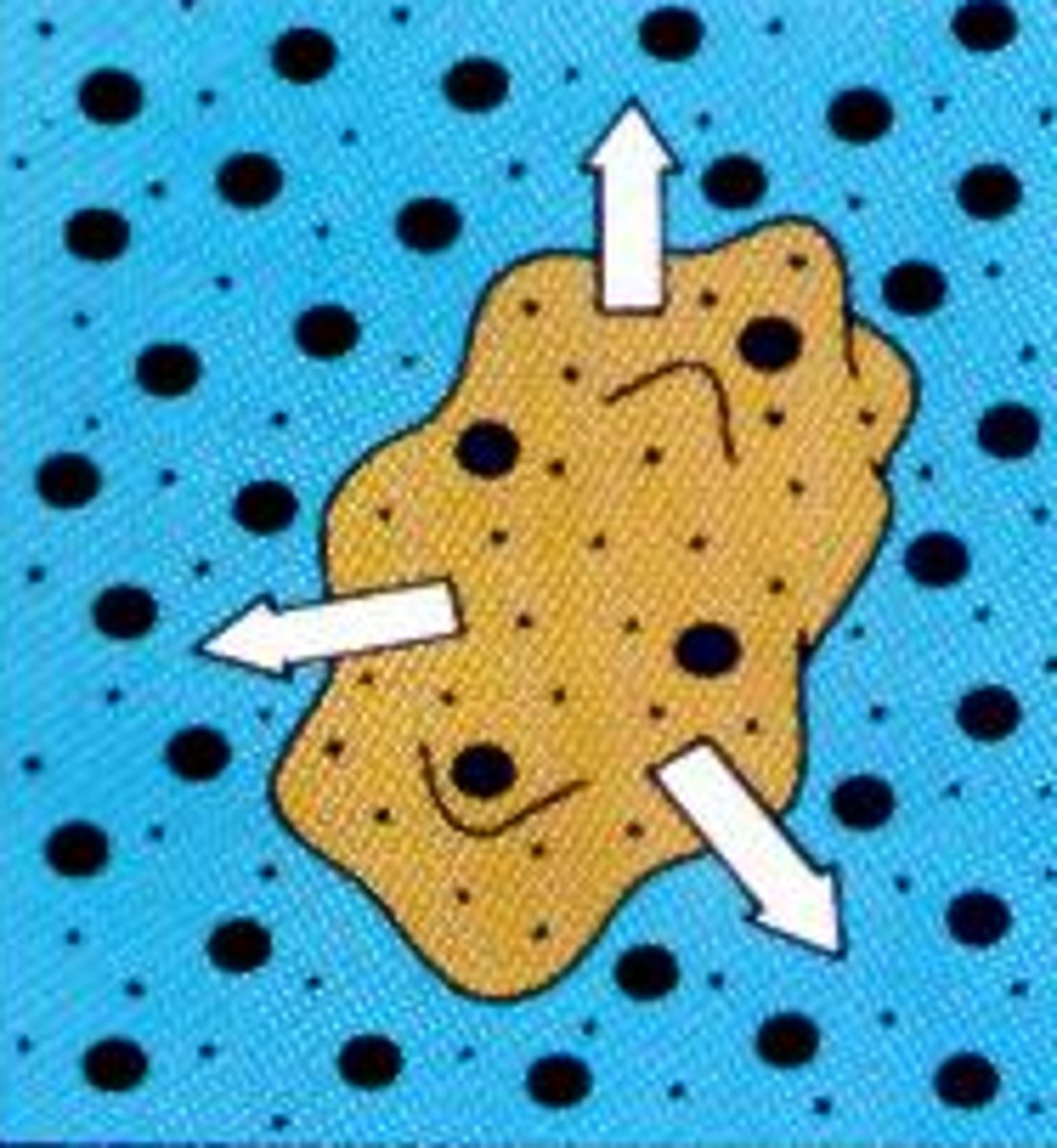

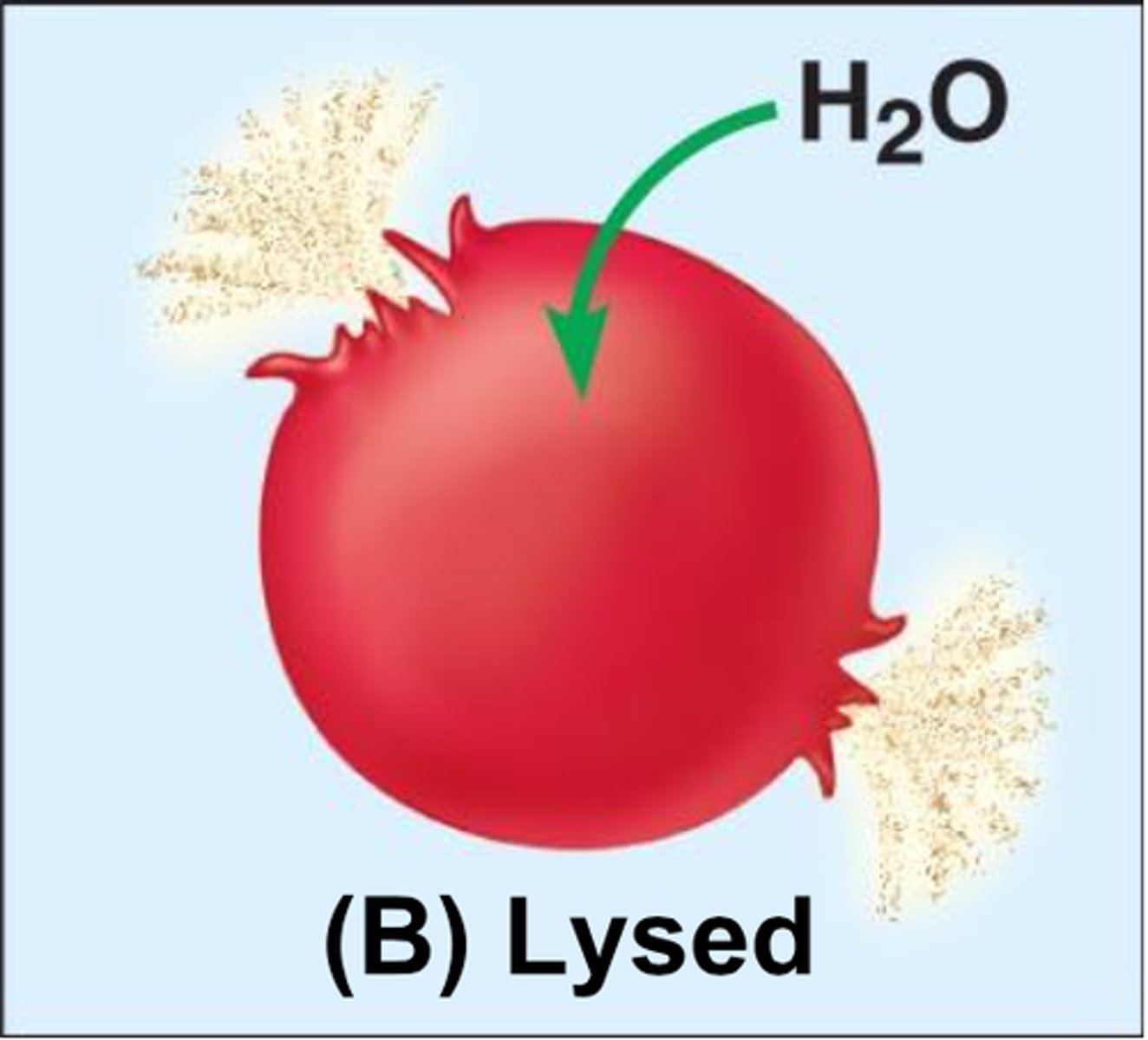
Hypotonic solution
water enters cell and bursts (lysis)
Intermediate Filaments
medium sized
-Supports nuclear envelope
-helps CELL TO CELL junction (strengthen hair and join skin)
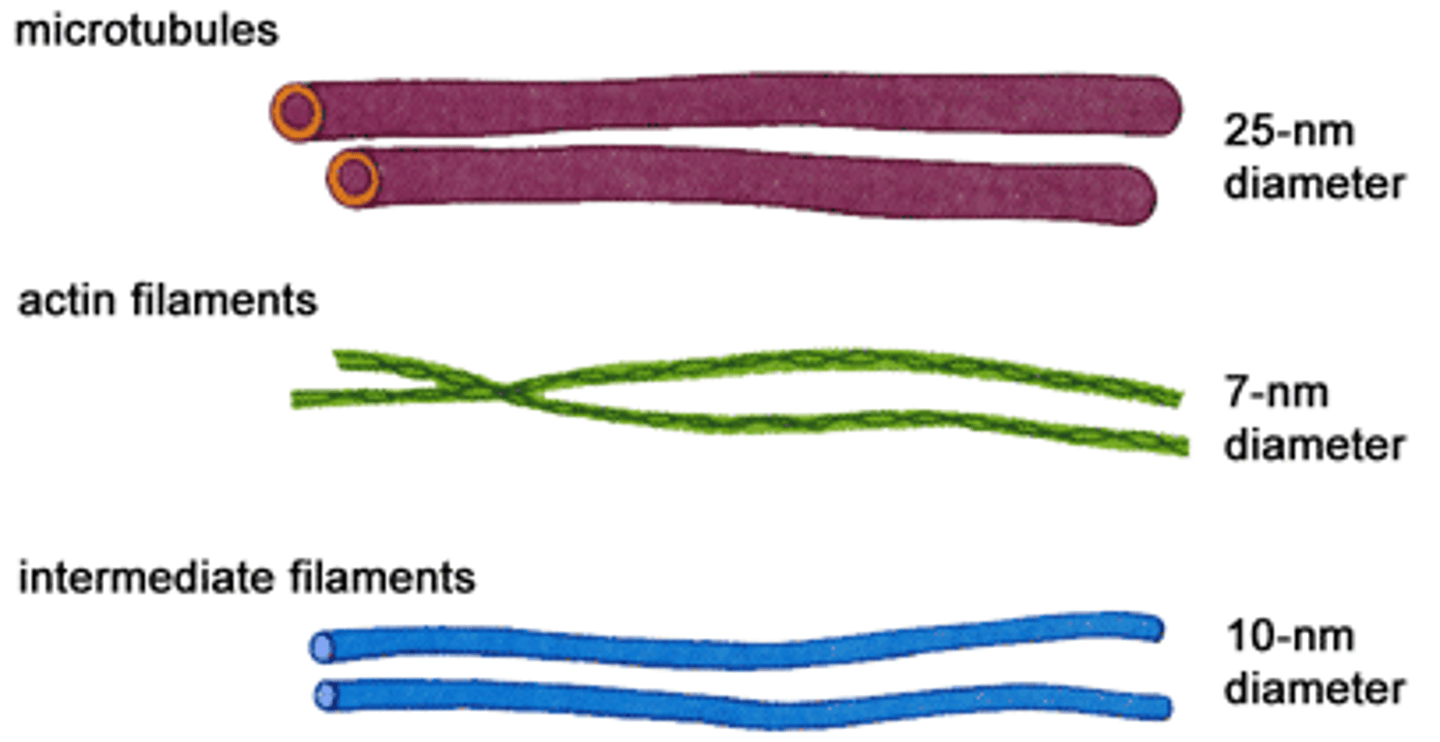
Microtubules
hollow cylinders of tubulin protein
-controlled by microtubule organization center
maintains cell shape, interacts with motor molecules - kenesin and dynein to move organelles and forms spindle apparatus (cell division)
ex: chameleons changing color
Cillia and Flagella
hair like projections - aid in movement
Only in Eurkaryotes
Cillia much shorter that flagella and more numerous
Both membrane bound cylinders. 9+2 patter of microtubules.
Endosymbiotic theory
Mitochondria and chloroplasts derived from prokaryotes that were taken up by a larger cell. Mitochondria- orginially heterotrphic bacteria. Chloroplasts- originally cyanobacteria. After in host cell, bacteria and host begin to live together cooperatively.
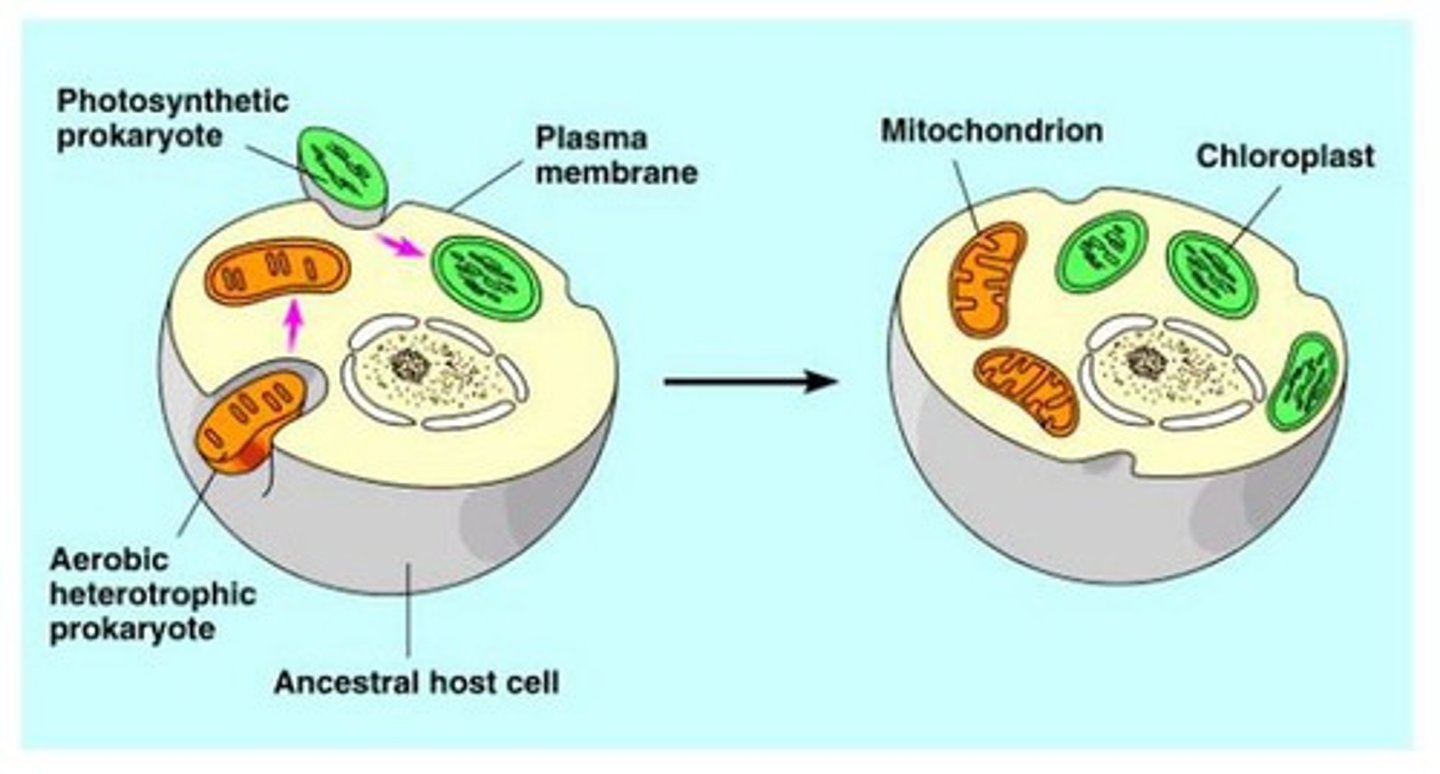
Similarities in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells according to Endosymbiotic Theory
Both: similar structure and size, double membrane, genetic information and divide by splitting. DNA is a circular loop. Have ribosomes that make proteins
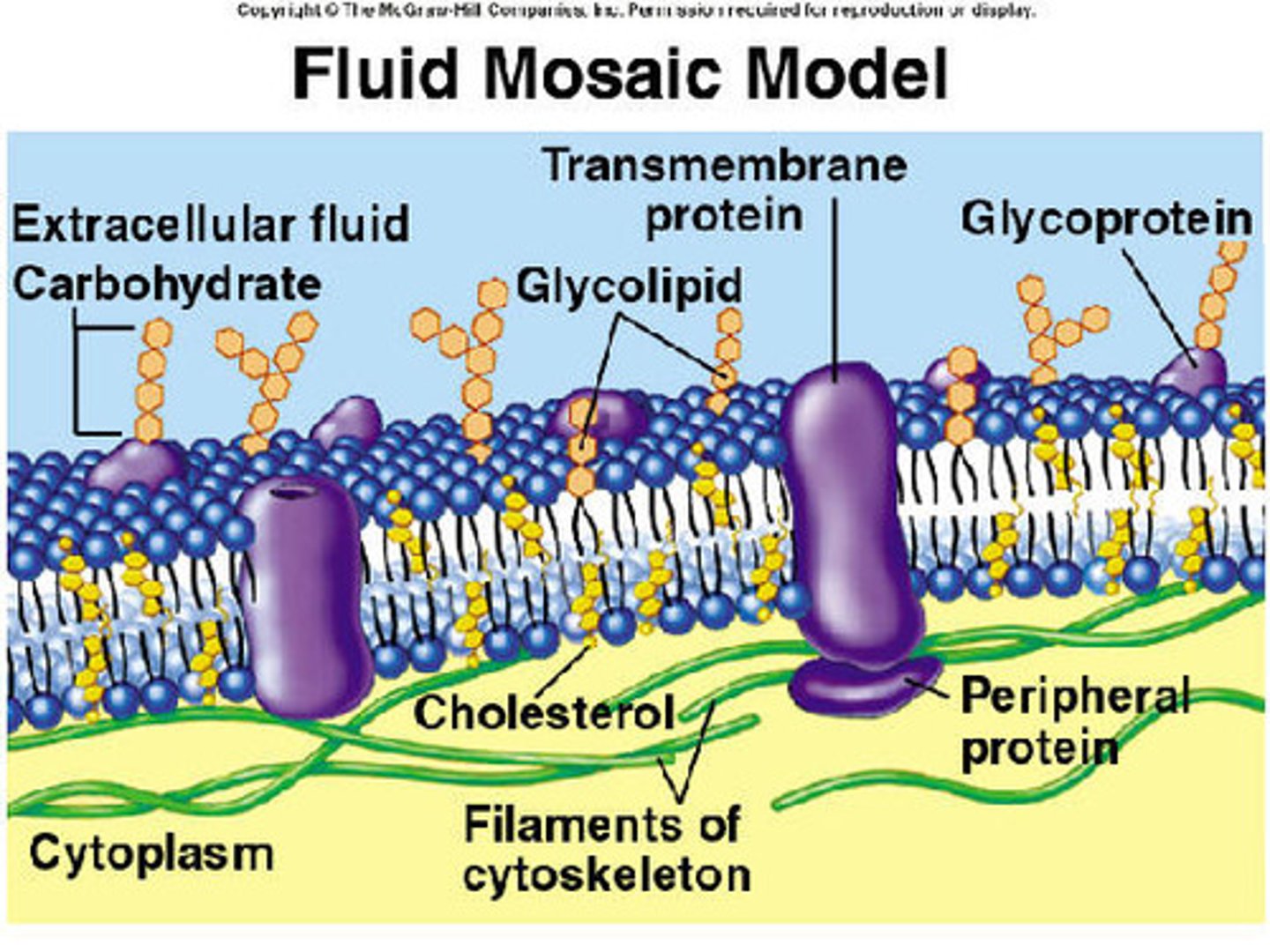
Fluid Mosaic Model
selectively permeable, maintains homeostasis, and has proteins and phospholipids.
ONLY SMALL NON POLAR (HYDROPHOBIC) can PASS!
Characteristic of Glucose that makes it unable to diffuse across membrane?
Large polar molecule. Hydroxyl
Channel proteins
allow certain molecules through, has aquaporins specialized for water.
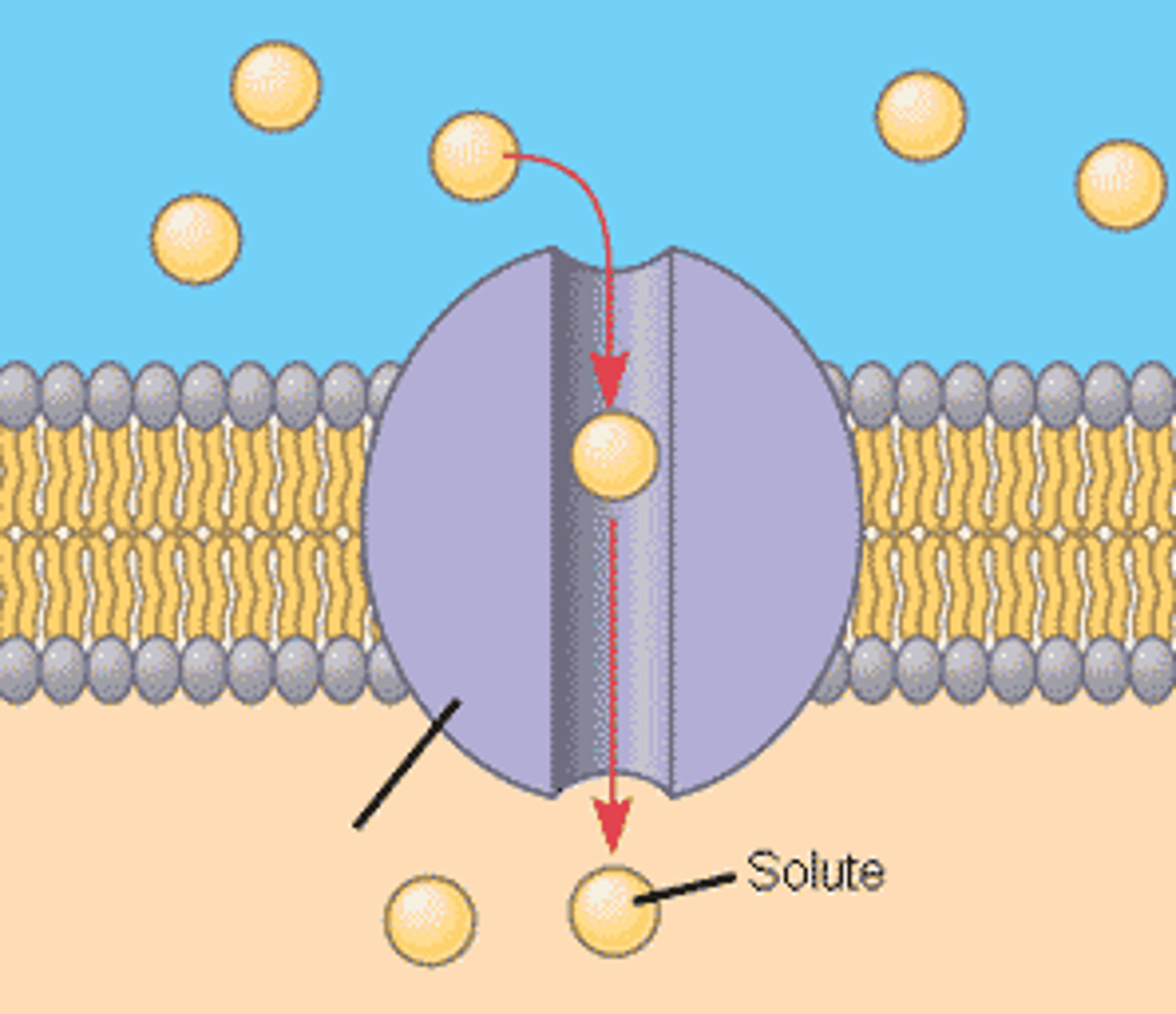
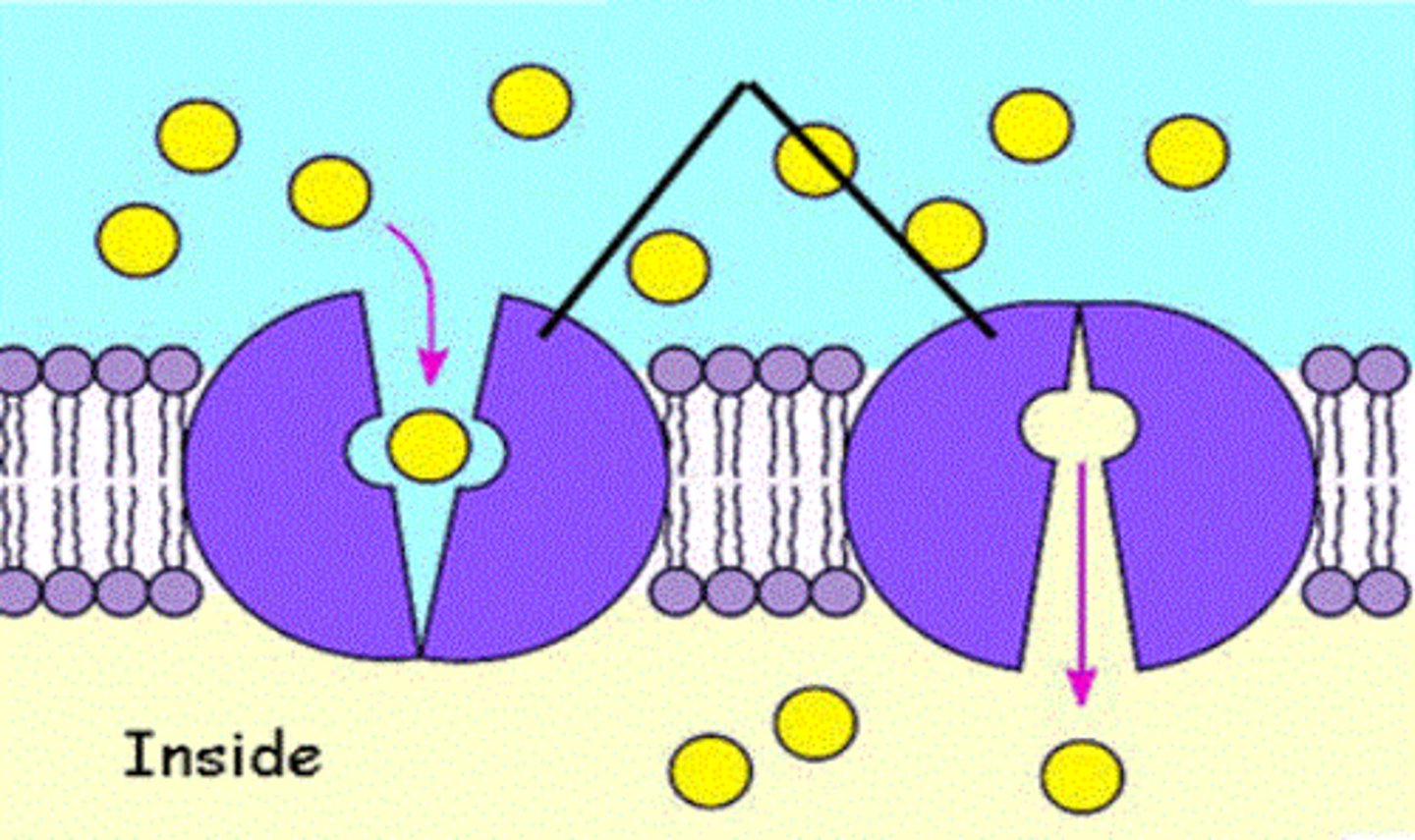
Carrier proteins
carry sugar across plasma membrane. GLUT PROTEINS
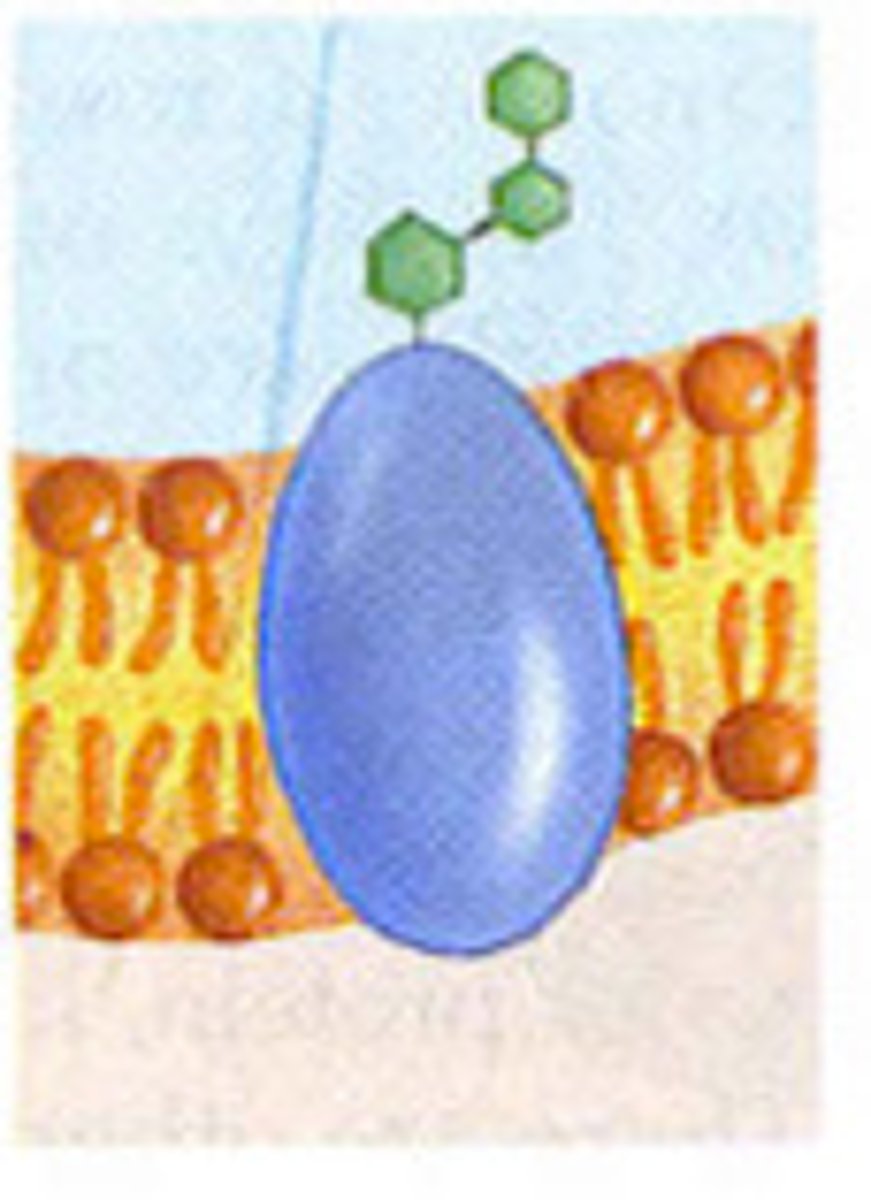
Cell recognition protein
glycoprotein different for everyone. Blood types. White blood cell ATTACK FOREIGN CELLS
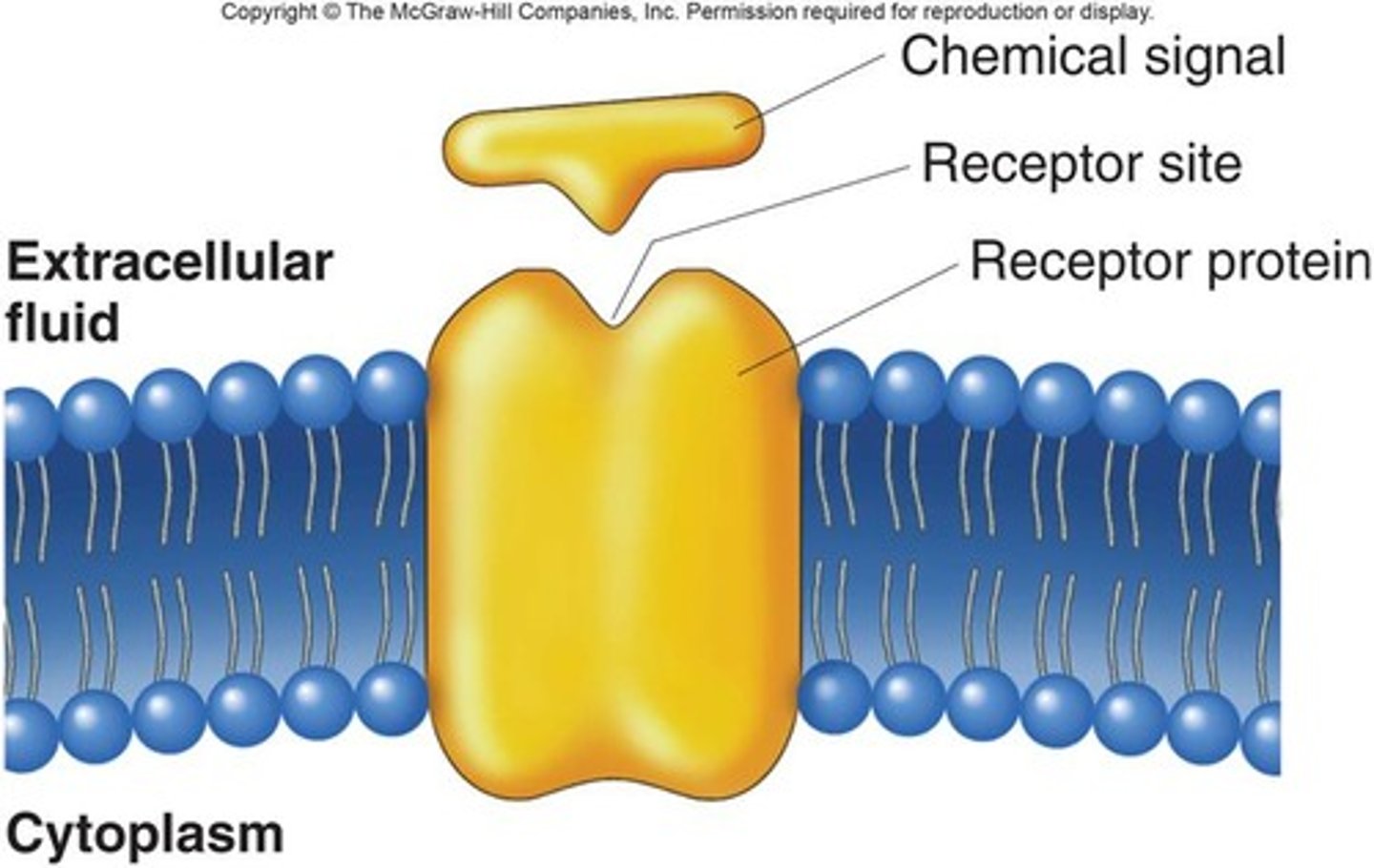
Receptor proteins
hormones! binds to specific molecule
INSULIN
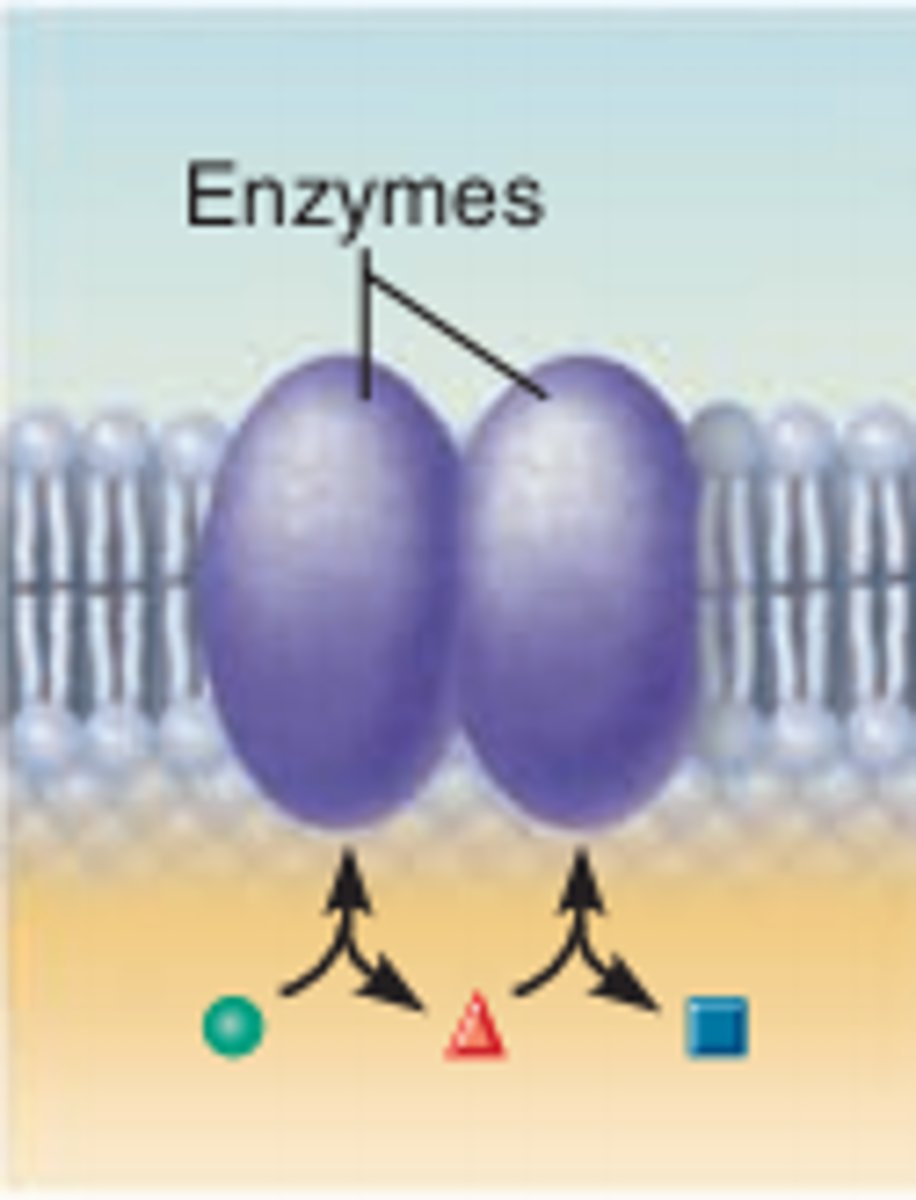
Enzymatic Protein
catalyze and speed up reactions.
-cholera, diarrhea