module 4: nucleus
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
the _ membrane of the nuclear envelope runs continuously with the membrane of the _ _.
outer, rough er
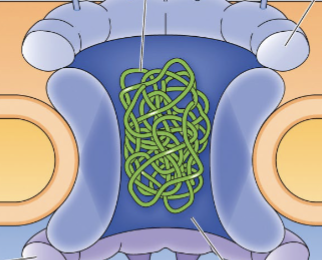
Which structural component of the nuclear pore acts as a barrier to prevent the passage of large molecules?
fg-nups
Which molecule is known as a molecule switch, driving the import/export of proteins across the nuclear pore?
Ran
Which enzyme is responsible for remodeling mRNA transcripts as they exit to the cytoplasmic side of the nuclear pore?
helicase
In a nondividing cell, sequences of DNA that don't contain a lot of genes or contain genes that aren't used in the cell become highly condensed into _
heterochromatin
Heterochromatin is condensed by histone _
methylation
Histone methylation promotes _ _
gene silencing
For DNA that contains genes that will be highly utilized in the cell, histones are _
acetylated
Acetylated histones form _
euchromatin
Euchromatin allows for _ _
gene expression
Where would you expect to find replication factories and transcription factories in the nucleus?
interior associated with euchromatin
Which nuclear body is the most prominent in the nucleus?
nucleolus
Polycomb bodies house clusters of proteins that __ transcription by __ lysine residues on histone 3. These nuclear bodies are associated with __
repress, methylating, heterochromatin
Cajal bodies and nuclear speckles mediate the assembly and storage of _ which play an important role in pre-mRNA processing.
snRNPs
_ _ prevents large molecules from passing and permits small, water-soluble molecules.
nuclear pores
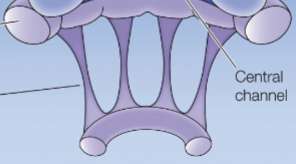
nuclear _ form a _ _ with chromatin and transcriptional machinery.
nup, nuclear basket
proteins needing to be imported must need _ _ _
nuclear localization signal
proteins that have nls bind to nuclear transport receptors called _
importins
protein trafficking pathway
proteins with nls bind to importins, prc interacts with cytoplasmic filaments, prc goes thru pore by fg-nups, proteins dissociates from importin by ran gpt
what only functions in the nucleus that regulates import/exports for gene expression?
transcription factors
explain how gene expression is regulated by transport
transcript factors mask nuclear local signal with cytoplasmic proteins, phosphorylation can alter nuclear
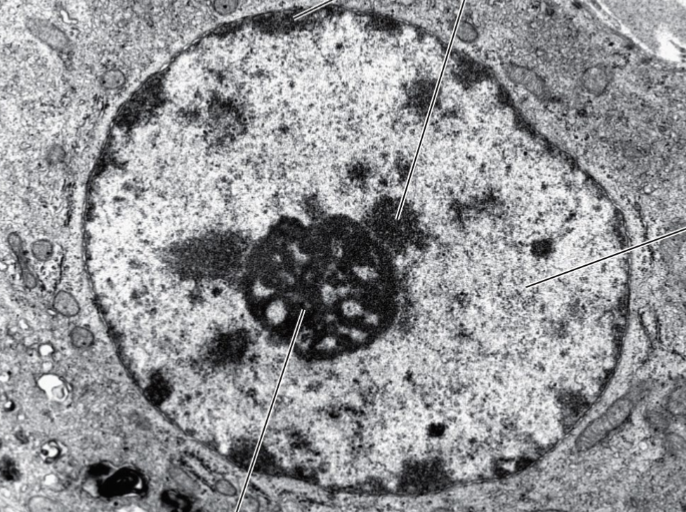
where does heterochromatin located?
edge of the cell, around nucleolus
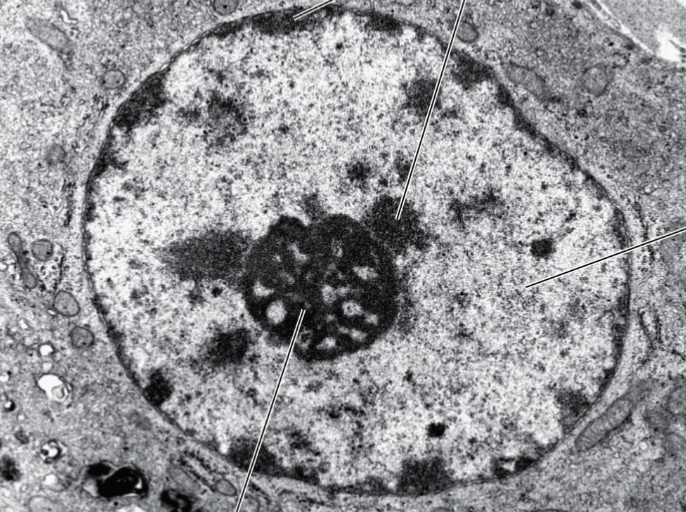
where does euchromatin located?
central of cell
euchromatin is transcriptionally _.
active
heterochromatin is transcriptionally _.
repressed
euchromatin is ? packed chromatin that is transcriptionally ? and gene ?, allowing access for rna ? and ? ?.
loosely, active, rich, polymerase, transcription factors
heterochromatin is ? condensed chromatin that is gene ? and is transcriptionally ? because the ? structure blocks access to the ? ?.
tightly, poor, repressed, compact, transcriptional machinery
what have distinct volume-occupying regions in the nucleus where individual chromosomes are located?
chromatin territories
what has precise, large, 3-d positioning of specific positioning of specific chromatin segments in the nuclear space?
chromatin localization
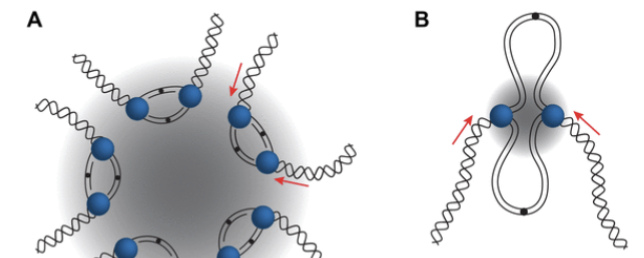
what factory is concentrated in the heart of the nucleus where euchromatin is located?
replication
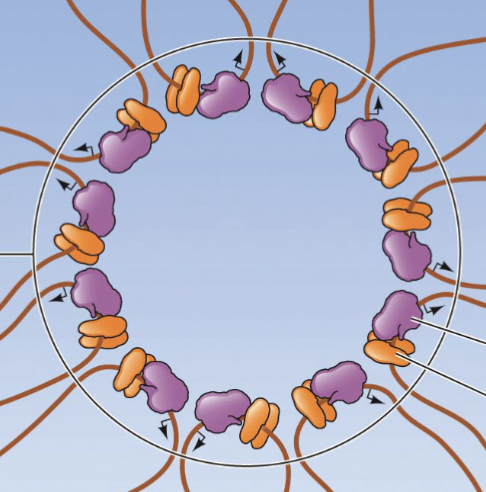
what factory occurs in the sites with. clustered rna polymerase?
transcription
nuclear bodies are ? which promotes chemical reaction by concentrating molecules.
membraneless
cytoplasmic organelles are ? in the cytoplasm with distinct structures and specialized functions.
membranous