BIO 344 Exam 4
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/129
Earn XP
Last updated 10:10 PM on 4/16/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
130 Terms
1
New cards
What controls blood platelet aggregation?
a signaling pathway that includes g-proteins and IP3
2
New cards
Describe the polymerization of Actin filament.
1. Actin subunit binds to ATP
2. it attaches to a growing filament
3. ATP is hydrolyzed to ADP
3
New cards
Describe the polymerization of microtubules.
1. tubulin heterodimer subunit binds to GTP
2. it attaches to a growing filament
3. GTP hydrolyzed to GDP
4
New cards
What is the difference between the plus and minus end of actin?
Plus end: rapid elongation, grows rapidly
Minus end: ARP complex nucleates actin filament growth, more stable
Minus end: ARP complex nucleates actin filament growth, more stable
5
New cards
What are the plus and minus ends of filaments?
Plus end: the growing and shrinking end
Minus end: site of nucleation
Minus end: site of nucleation
6
New cards
What is the difference between the plus and minus end of microtubules?
Plus end: grows and shrinks rapidly
Minus end: no growth, nucleation site
\+beta tubulin and -alpha tubulin
Minus end: no growth, nucleation site
\+beta tubulin and -alpha tubulin
7
New cards
What happens when the GTP cap is lost?
microtubule shrinks
8
New cards
What happens when end unit binds GTP cap?
microtubule grows
9
New cards
What are GTP caps?
an area where several tubulin heterodimers, on the positive end of a filament, still have GTP bound to them and have not yet hydrolyzed to GDP
* microtubule filaments
* GTP cap = microtubule grows
* no GTP cap = microtubule shrinks
* microtubule filaments
* GTP cap = microtubule grows
* no GTP cap = microtubule shrinks
10
New cards
What type of filaments have GTP caps?
microtubules
11
New cards
What is an example of an intermediate filament?
keratin
12
New cards
How can a mutation in a keratin gene lead to blistering?
keratin (intermediate filament) provide strength to skin cells
when mutation occurs, strength is lost, skin cells are torn apart with minor amount of force, causes blistering
when mutation occurs, strength is lost, skin cells are torn apart with minor amount of force, causes blistering
13
New cards
How are microtubules nucleated? What is the protein involved?
Protein Complex Containing y-tubulin at the minus end
14
New cards
How are actin filaments nucleated? What is the protein involved?
* Cells direct ARP complex where it wants actin to grow
* ARP acts as a scaffold upon which singular acting subunits join together to make filament
* ARP acts as a scaffold upon which singular acting subunits join together to make filament
15
New cards
What is a centrosome?
microtubule organizing center
* contain y-tubulin ring complexes
* contain y-tubulin ring complexes
16
New cards
What is a mitotic spindle?
structure made of microtubules that controls chromosome movement (segregate chromosomes into two daughter cells) during mitosis
17
New cards
How does profilin affect actin polymerization rates?
makes it more likely that actin subunit will be added to filament
* is a recruiter and will cause rapid plus end growth
* is a recruiter and will cause rapid plus end growth
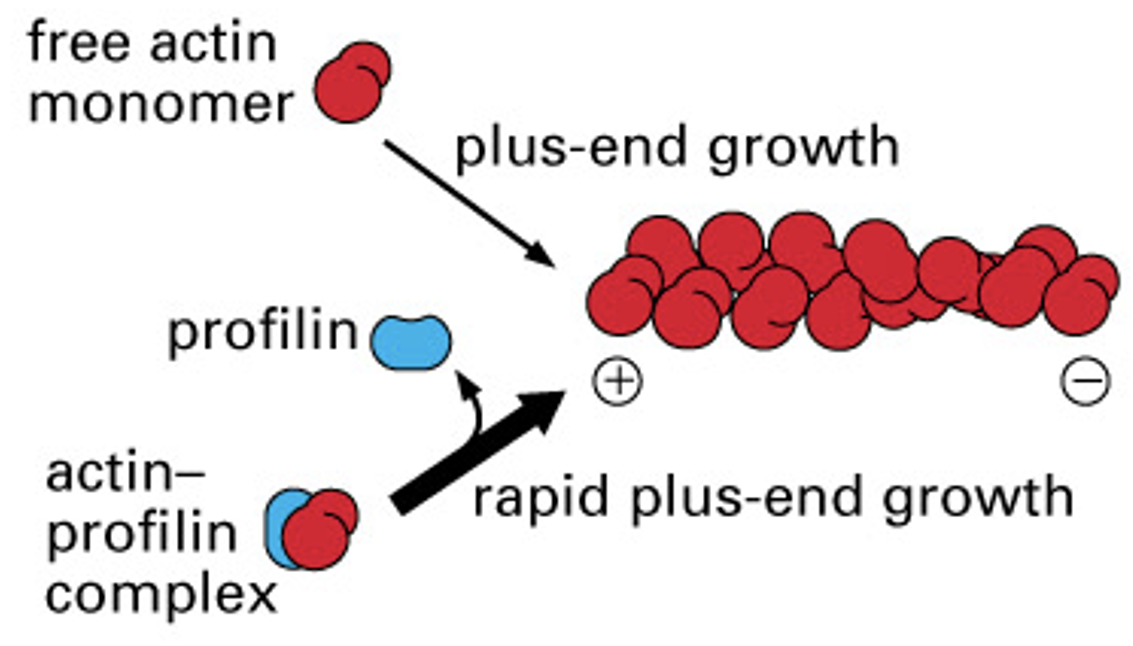
18
New cards
How does thymosin affect actin polymerization rates?
binds actin filaments making them unavailable to be added to plus end of filaments
* causes inhibition of growth
* causes inhibition of growth
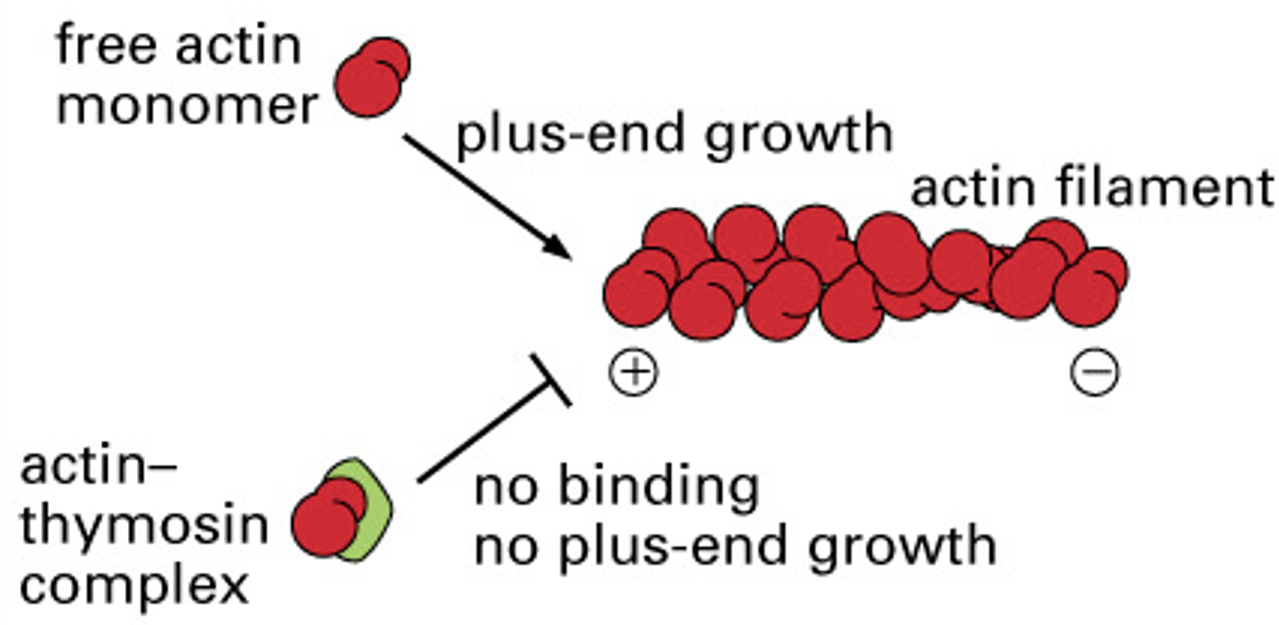
19
New cards
How does stathmin affect the polymerization rate of microtubules?
binds tubulin heterodimers and makes them unavailable to be incorporated into filaments
results in fewer subunits added
GTP hydrolyzed and shrinks losing GTP cap
results in fewer subunits added
GTP hydrolyzed and shrinks losing GTP cap
20
New cards
How does capping of filaments affect their polymerization rates?
GTP cap:
* refers to the end subunits of a microtubule that have GTP bound, this allows the microtubule to continue to grow
Protein cap:
* gelsolin will stabilize actin filaments and prevent them from growing
* refers to the end subunits of a microtubule that have GTP bound, this allows the microtubule to continue to grow
Protein cap:
* gelsolin will stabilize actin filaments and prevent them from growing
21
New cards
How do cross-linking proteins organize different assemblies of actin filaments?
* actin binds to many other proteins inside cell
* often cross linked by other proteins
* Cross linking protein length determine how far apart/close together subunits will be
* Different assemblies of actin filaments are regulated by actin binding proteins
* ex: fimbrin
* often cross linked by other proteins
* Cross linking protein length determine how far apart/close together subunits will be
* Different assemblies of actin filaments are regulated by actin binding proteins
* ex: fimbrin
22
New cards
What impact would fimbrin have on the properties of actin bundles?
creates strong, rigid bundles of actin filaments
* actin cross linking protein
* ex: microvilli in intestinal epithelium cells
* short
* actin cross linking protein
* ex: microvilli in intestinal epithelium cells
* short
23
New cards
What impact would filamin have on the properties of actin bundles?
cross links actin filaments to make a 3D network with gel-like properties
* important for movement
* ex: melanoma crawls poorly, does not metastasize, actin not cross linked
* long
* important for movement
* ex: melanoma crawls poorly, does not metastasize, actin not cross linked
* long
24
New cards
Why are there fimbrin cross-linking proteins in microvilli?
fimbrin cross-linking is tightly packed and ordered, which makes it great for forming 3D networks such as microvilli
holds shape
parallel bundle, tight packing, prevents myosin II from entering bundle
holds shape
parallel bundle, tight packing, prevents myosin II from entering bundle
25
New cards
What is a platelet and what cell is it derived from?
cell fragments released by megakaryocytes
26
New cards
What happens to GTP when filament needs to grow? When it needs to shrink?
* apha tubulins have GTP bound
* GTP cap is lost, GTP hydrolyzed into GDP
* GTP cap is lost, GTP hydrolyzed into GDP
27
New cards
How does the cytoskeleton change when a platelet is activated?
1. inactive platelets full of long actin filaments
2. gelsolin cuts up actin, creates uncapped actin fragments
3. profilin causes rapid filament growth
4. new filaments cross-linked by fimbrin
5. creates spikes in platelet to form a clot by attaching to other platelets
28
New cards
What is the first activation pathway in blood coagulation?
* Un-activated platelet full of capped actin filament
* platelet binds to signal-mediated Ca2+ influx and gelsolin activated
* gelsolin cuts capped actin
* actin fragments bind profilin causing growth
* new actin crosslinked by fimbrin and filamin
* actin changes shape into platelet
* platelet binds to signal-mediated Ca2+ influx and gelsolin activated
* gelsolin cuts capped actin
* actin fragments bind profilin causing growth
* new actin crosslinked by fimbrin and filamin
* actin changes shape into platelet
29
New cards
What is the second activation pathway in blood coagulation?
activation of protein kinase C by Ca2+ and diacylglycerol (DAG)
1. signal molecule binds to G-protein linked receptor, activated
2. GDP to GTP divides into subunits
3. Activated alpha g-protein moves laterally through membrane to active phospholipase C
4. Active phospholipase C cleaves PIP2 into DAG and IP3
5. DAG covalently attaches to membrane while IP3 travels to ER and acts as signaling molecule to open IP3-gated Ca2+-release channel
6. Ca2+ influx out of ER into cytosol
7. Ca2+ and DAG attaches to protein kinase C to activate it
1. signal molecule binds to G-protein linked receptor, activated
2. GDP to GTP divides into subunits
3. Activated alpha g-protein moves laterally through membrane to active phospholipase C
4. Active phospholipase C cleaves PIP2 into DAG and IP3
5. DAG covalently attaches to membrane while IP3 travels to ER and acts as signaling molecule to open IP3-gated Ca2+-release channel
6. Ca2+ influx out of ER into cytosol
7. Ca2+ and DAG attaches to protein kinase C to activate it
30
New cards
What is fibrin and how is it made?
emerges from clump of platelets during blood coagulation
* helps to hold platelets together
* proteins that bind blood clots
* made from platelets form plug facilitating production
* helps to hold platelets together
* proteins that bind blood clots
* made from platelets form plug facilitating production
31
New cards
What are myosins?
* is the thick filament of a sarcomere (dark band)
* myosin heads are on outside of thick filament
* has motor heads that attach to actin
* myosin head binds and hydrolyzes ATP
* C-terminus to N-terminus
* coiled-coil of two alpha helices
* neck/hinge region and light chains connect head and tail
* myosin heads are on outside of thick filament
* has motor heads that attach to actin
* myosin head binds and hydrolyzes ATP
* C-terminus to N-terminus
* coiled-coil of two alpha helices
* neck/hinge region and light chains connect head and tail
32
New cards
What filament are myosins associated with?
actin filaments
* they work together to pull the z-discs of the sarcomeres together
* they work together to pull the z-discs of the sarcomeres together
33
New cards
In what part of the myosin protein is the motor activity located?
at the motor head of the filament
* N-terminus side
* connected by a neck/hinge region which allows head to perform “power stroke” and slide the filaments across each other
* N-terminus side
* connected by a neck/hinge region which allows head to perform “power stroke” and slide the filaments across each other
34
New cards
How are organelles moved around a cell?
microtubules
35
New cards
What is a skeletal muscle cell?
* many nuclei
* fusion of myoblasts
* striated
* large
* filled with myofibrils
* myofibrils are made up of sarcomeres
* fusion of myoblasts
* striated
* large
* filled with myofibrils
* myofibrils are made up of sarcomeres
36
New cards
How is a skeletal muscle cell formed?
fusion of myoblasts
37
New cards
What is a myofibril?
long contractile fibers in skeletal muscles
* multiple sarcomeres attached together
* are apart of a skeletal muscle cell
* multiple sarcomeres attached together
* are apart of a skeletal muscle cell
38
New cards
Describe the structure of myofibrils in detail.
basic rod like structure of a muscle cell that has multiple nuclei and is striated
* sarcomeres attached together
* light band = actin filaments
* dark band = myosin proteins
* sarcomeres attached together
* light band = actin filaments
* dark band = myosin proteins
39
New cards
What is a Z-disc?
Plate-like structure in sarcomeres to which the plus ends of actin filaments are localized
* think dark line in a sarcomere
* pulled together results in a muscle contraction
* think dark line in a sarcomere
* pulled together results in a muscle contraction
40
New cards
What is a sarcomere?
Structural (repeat) unit of myofibrils in a striated muscle that is responsible for contraction
* It consists of a dark thick band of myosin and a thin light band of actin with z-discs at the end
* It consists of a dark thick band of myosin and a thin light band of actin with z-discs at the end
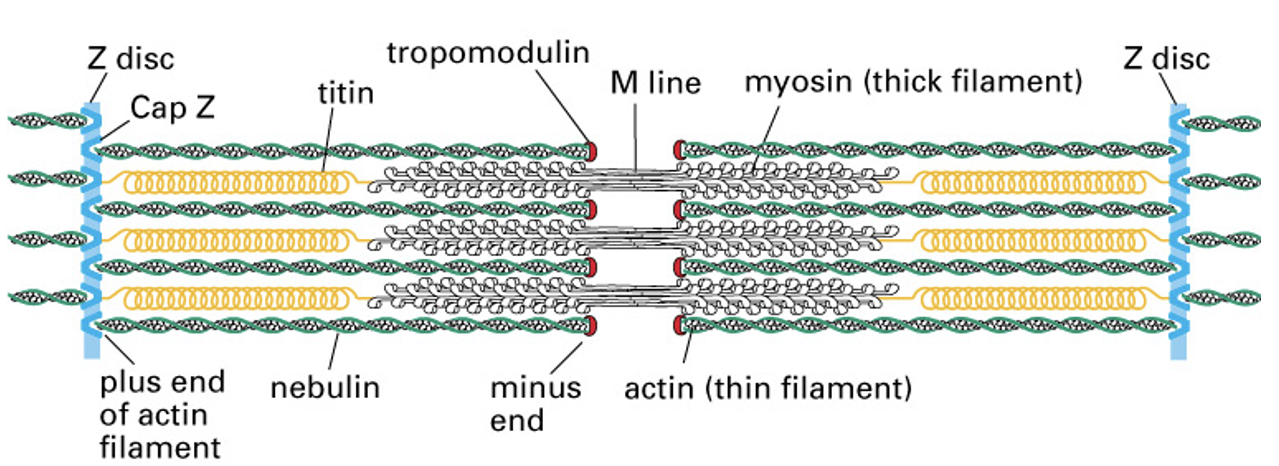
41
New cards
How do your muscles move?
the actin filaments (thin) are pulled by the myosin filaments (dark) to bring the z-discs closer together, resulting in muscle contraction
42
New cards
Describe how a muscle cell recieves a signal for contraction in detail.
43
New cards
What are transverse tubules? Why are transverse tubules necessary?
a deep invagination of the sarcolemma (considered to be outside of cell)
* increase the contact of the plasma membrane and the sarcoplasmic reticulum which allows depolarization of the membrane to quickly penetrate the interior of the cell
* allow space for myofibrils and myosin proteins to attach to actin
* increase the contact of the plasma membrane and the sarcoplasmic reticulum which allows depolarization of the membrane to quickly penetrate the interior of the cell
* allow space for myofibrils and myosin proteins to attach to actin
44
New cards
What is the sarcoplasmic reticulum?
Ca2+ reservoir
45
New cards
Describe how Ca2+ causes myofibrils to contract in detail.
Ca2+ binds troponin to move tropomyosin → muscle cell contraction
* influx of Ca2+ through channels triggers a major release of Ca2+ into the cytoplasm through the SR calcium release channels
* This stimulates myofibril contraction
* Ca influx will cause troponin to become activated which will remove tropomyosin from actin
* Actins binding sites are now available for myosin to bind and begin pulling the actin essentially bringing the z-discs together and causing a muscle contraction
* influx of Ca2+ through channels triggers a major release of Ca2+ into the cytoplasm through the SR calcium release channels
* This stimulates myofibril contraction
* Ca influx will cause troponin to become activated which will remove tropomyosin from actin
* Actins binding sites are now available for myosin to bind and begin pulling the actin essentially bringing the z-discs together and causing a muscle contraction
46
New cards
What is tropomyosin?
covers actin filament denying myosin motorhead to bind
prevents muscle cell contraction
prevents muscle cell contraction
47
New cards
What is troponin?
* controls muscle contraction
* can move tropomyosin allowing myosin to bind, causes muscle cell contraction
* activated by Ca2+
* can move tropomyosin allowing myosin to bind, causes muscle cell contraction
* activated by Ca2+
48
New cards
What is the role of tight junctions in intestinal epithelial cells?
prevent passive glucose transporters from moving into the lumen
49
New cards
What proteins are present in tight junctions?
claudin and occludin
50
New cards
What are claudins?
main component of sealing strands
\
\
51
New cards
How can integrins signal back?
if cell is attached to ECM
* unattached cells undergo apoptosis
* unattached cells undergo apoptosis
52
New cards
What are proteases?
* can cut through basal lamina
* cancer medication target these to prevent movement of cell
* those bound to surface receptors are needed to crawl through basal lamina
* cancer medication target these to prevent movement of cell
* those bound to surface receptors are needed to crawl through basal lamina
53
New cards
What do integrins do?
link extracellular matrix to cytoskeleton
54
New cards
What do cadherins do?
* connect actin filaments of different cells
* bind intermediate filaments together
* bind intermediate filaments together
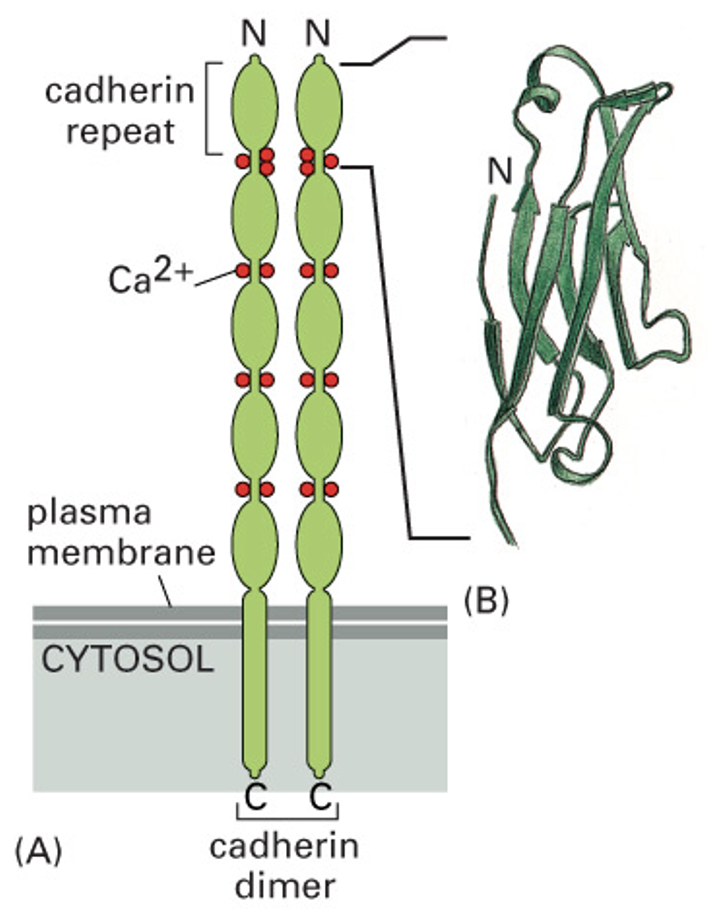
55
New cards
How does Ca2+ affect cadherin structure?
Ca2+ required for rigid shape to form junctions and to establish cell to cell connection
56
New cards
What kind of molecules can pass through gap junctions?
molecules smaller than 1000 Daltons
57
New cards
What are connexins?
transmembrane subunits that make up connexons
6 make up one connexon in gap junctions
6 make up one connexon in gap junctions
58
New cards
What does the extracellular matrix consist of?
Proteoglycans (glycosaminoglycan)
fibrous proteins (collagen)
fibrous proteins (collagen)
59
New cards
What is a proteoglycan?
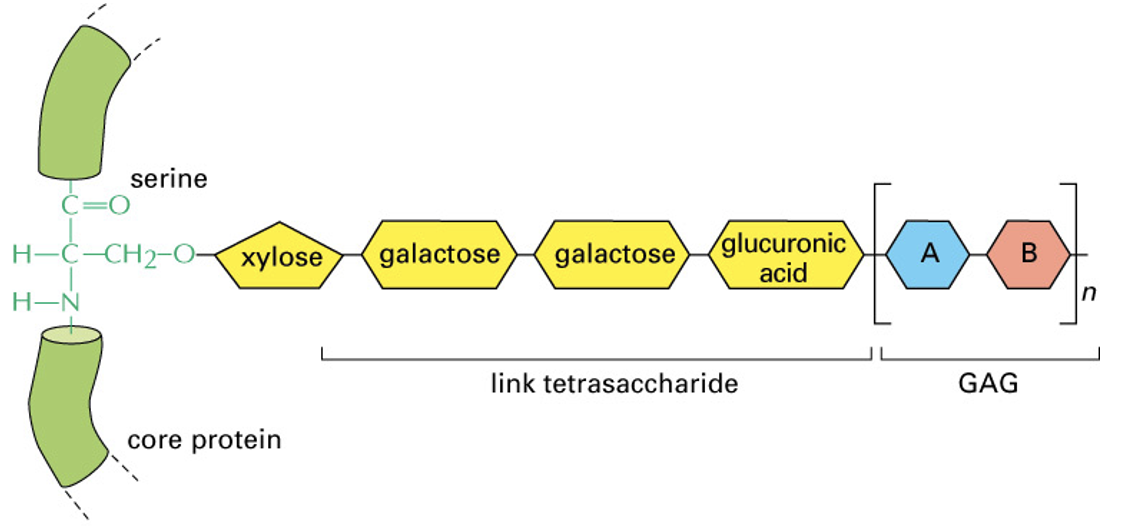
formed from glycosaminoglycan (GAG) linked to its core protein via tetrasaccharide linker
60
New cards
Describe the different parts of a proteoglycan.
structure:
core protein - linker tetrasaccharides - GAG
core protein - linker tetrasaccharides - GAG
61
New cards
What are glycosaminoglycans?
these chains occupy large amounts of space and form hydrated gels
chains - proteins and carbohydrates
chains - proteins and carbohydrates
62
New cards
Describe the structure of glycosaminoglycans.
long chain of repeating disaccharides in connective tissue
attach to its core protein by tetrasaccharide linker
attach to its core protein by tetrasaccharide linker
63
New cards
What do fibroblasts do?
produce and secrete extracellular matrix compounds
\- Excrete large amounts of extracellular components
\- Excrete large amounts of extracellular components
64
New cards
Where would you find fibroblasts?
connective tissue
65
New cards
What is collagen?
* main structural protein of extracellular matrix in connective tissue
* fibrous protein
* provides tensile strength
* regulate cell adhesion
* support chematoxis and migration
* direct tissue development
* fibrous protein
* provides tensile strength
* regulate cell adhesion
* support chematoxis and migration
* direct tissue development
66
New cards
Describe the structure of collagen?
* long protein
* 3 amino acid chains wrapped around each other
* each chain has a repeating amino acid pattern
* glycine - amino acid X - amino acid Y
* 3 amino acid chains wrapped around each other
* each chain has a repeating amino acid pattern
* glycine - amino acid X - amino acid Y
67
New cards
What is the basal lamina?
proteins woven together to make a 2D sheet
* basement membrane
* sheer layer of proteins
* surrounds skeletal cells
* basement membrane
* sheer layer of proteins
* surrounds skeletal cells
68
New cards
What is the basal lamina made of?
* collagen
* integrin
* laminin
* nidogen
* perlecan
* integrin
* laminin
* nidogen
* perlecan
69
New cards
What are the functions of the basal lamina?
\- Separates epithelial cells from connective tissue
\- Acts as filter to remove nitrogen/toxins from kidneys
\- Re-establish neuromuscular junctions after muscle injury
\- Acts as filter to remove nitrogen/toxins from kidneys
\- Re-establish neuromuscular junctions after muscle injury
70
New cards
Which filament makes up the mitotic spindle?
microtubule
71
New cards
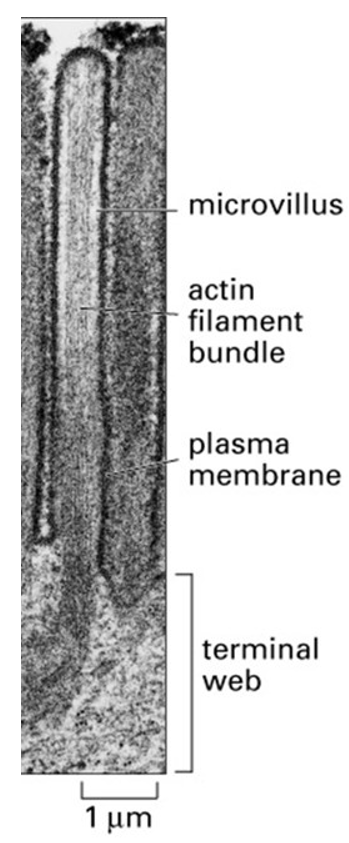
\
The image above shows a microvillus in an intestinal epithelial cell. What protein is cross-linking the actin filaments in the microvillus?
The image above shows a microvillus in an intestinal epithelial cell. What protein is cross-linking the actin filaments in the microvillus?
fimbrin
72
New cards
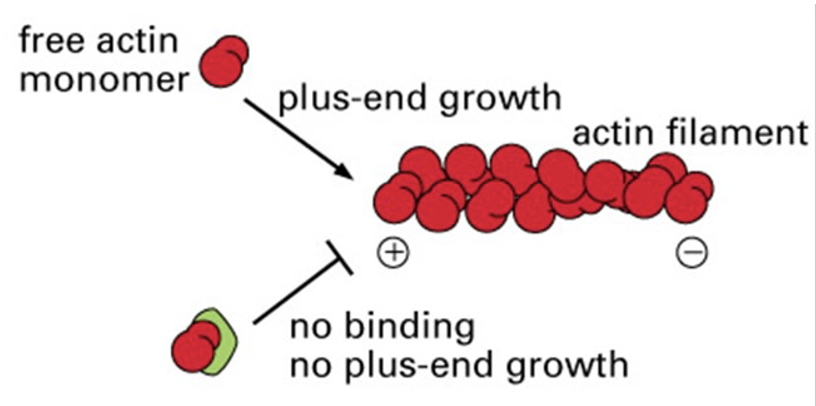
What is the green protein in the image?
thymosin
73
New cards
What radiates out from centrosomes?
microtubules
* located outside of nucleus
* located outside of nucleus
74
New cards
Which actin subunit complex would be incorporated into a new actin filament the fastest?
an actin-profilin complex
75
New cards
What do microtubules need in order to grow?
A GTP cap
76
New cards
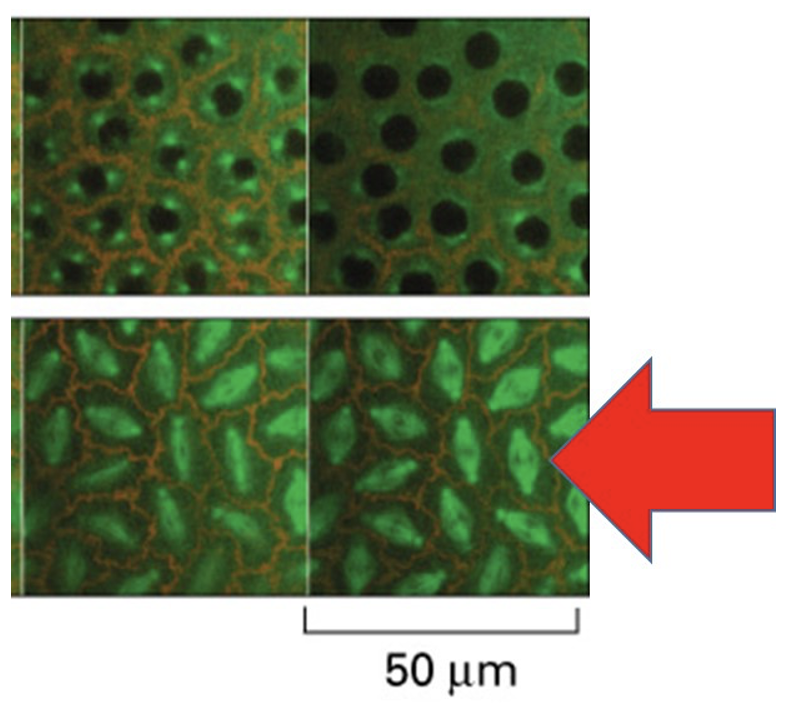
The image above shows rapidly dividing cells in fruit fly embryo. What filament makes up the fluorescent green structures that red arrow is pointing at?
microtubules
77
New cards
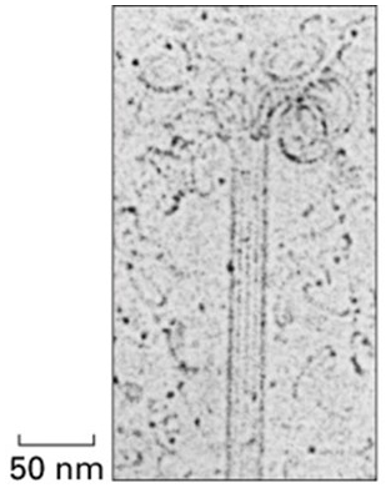
What is shown in the electron microscope image above?
a microtubule shrinking
78
New cards
What motor protein can bind microtubules?
* kenesin
* kinetochore
* dynein
* ( pull cargo along microtubules)
* kinetochore
* dynein
* ( pull cargo along microtubules)
79
New cards
Dynein
from + end to - end
80
New cards
Kenesin
from - end to + end
81
New cards
Kinetochore
pulls chromosomes along mitotic spindle (made of microtubules)
82
New cards
What are gamma-tubulin rings?
are scaffolding upon which microtubules are built
83
New cards
What do protein control?
how many subunits are available to build filaments
84
New cards
What is nucleation?
the rate limiting step
85
New cards
What takes longest when starting a new actin filament?
adding the first few subunits together (nucleus)
* actin is also dynamic
* actin is also dynamic
86
New cards
What is the ARP complex?
a scaffold upon which a new actin filament can start
* Arp3 and Arp2 and other proteins make up complex
* complex + actin monomers = nucleated actin filament
* Arp3 and Arp2 and other proteins make up complex
* complex + actin monomers = nucleated actin filament
87
New cards
Where in cells would gamma-tubulin proteins be found?
in centrosomes
88
New cards
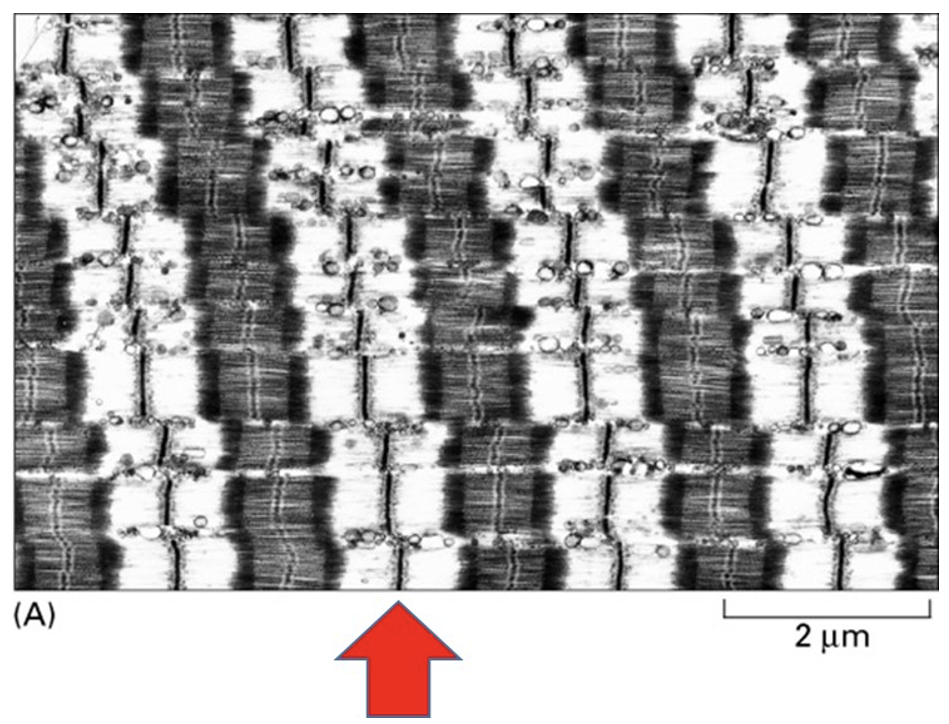
What does the red arrow in the image above point to?
a Z-disc
89
New cards
What causes the power stroke in muscle cell contraction, where the hinge region of the myosin motor protein changes shape while the myosin motor head is attached to the actin filament?
the release of ADP from myosin
90
New cards
What proteins do Ca2+ ions, that rush out of a sarcoplasmic reticulum, bind?
the troponin complex
91
New cards
How do your muscles move?
Z-discs in sarcomeres are brought closer together when myosin pulls on actin filaments
92
New cards
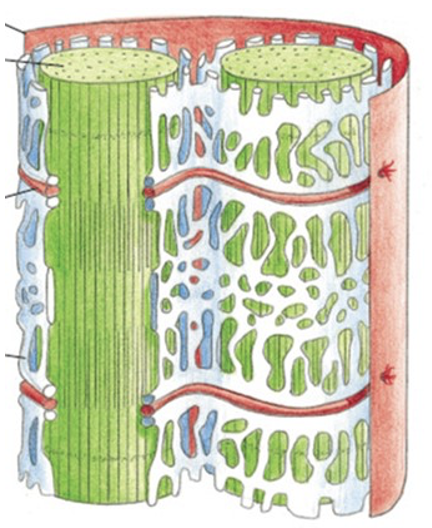
What is the function of the white organelle in the image?
it stores the Ca2+ needed for muscle cell contraction
93
New cards
Describe the structure of gap junctions?
made of connexons which are made up of 6 transmembrane connexin subunits
94
New cards
Why sever actin filaments during platelet activation?
* Severing actin filaments with gelsolin will create more actin fragments in the area which means more (+) ends for rapid actin growth to occur
* Actin in the cytoskeleton allow the platelets to change shape rapidly and form a primary plug at the site of injury
* Actin in the cytoskeleton allow the platelets to change shape rapidly and form a primary plug at the site of injury
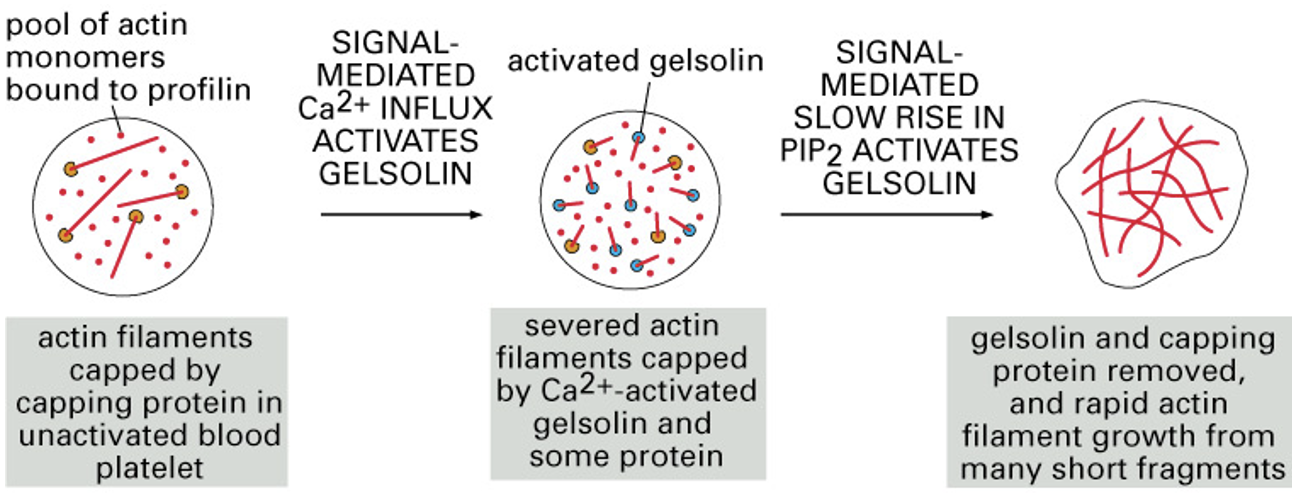
95
New cards
What does Gelsolin do?
severs actin filaments
* activated by signal mediated Ca2+ influx
* acts as cap once it severs filaments, can’t be removed until signal mediated PIP2 comes
* once removed, actin cross-linking may begin
* activated by signal mediated Ca2+ influx
* acts as cap once it severs filaments, can’t be removed until signal mediated PIP2 comes
* once removed, actin cross-linking may begin
96
New cards
What is the difference between the T and D forms of filament subunits?
\- T form = ATP for actin and GTP for tubulin
\- D form = ADP for actin and GDP for tubulin
\- If the heterodimer binds GTP it can form a GTP cap which allows the microtubule to grow
\- If the GTP is hydrolyzed to GDP and the heterodimer binds this GDP, then the microtubule loses its GTP cap, and this causes the microtubule to shrink
\- D form = ADP for actin and GDP for tubulin
\- If the heterodimer binds GTP it can form a GTP cap which allows the microtubule to grow
\- If the GTP is hydrolyzed to GDP and the heterodimer binds this GDP, then the microtubule loses its GTP cap, and this causes the microtubule to shrink
97
New cards
What is Filamin?
crosslinks actin into 3D networks with gel like properties which is important for movement
98
New cards
Describe the shape of microtubules that are growing and shrinking.
growing = flat
shrinking = spirals
shrinking = spirals
99
New cards
What do platelets do?
initiates blood coagulation
100
New cards
What are occluding junctions?
\- Seal cells together in an epithelium in a way that prevents even small molecules form leaking from one side of the sheet to the other
\- Tight junctions
\- Tight junctions